A Novel Approach to Design and Evaluate BNCT Neutron Beams Combining Physical, Radiobiological, and Dosimetric Figures of Merit
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
- minimum epithermal neutron flux, > 10 (cm s).
- minimum degree of collimation as neutron current over epithermal neutron flux > 0.7
- maximum gamma dose rate epithermal neutron flux < 2 · 10 (cm Gy)
- maximum thermal neutron and epithermal neutron flux ratio < 0.05
- maximum fast neutron dose rate over epithermal neutron flux < 2 · 10 (cm Gy)
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. BSA Material and Geometrical Composition
2.2. Evaluation of Physical in-Air Parameters
2.3. Evaluation of the Therapeutic Potential of Beams Using Radiobiological FOMs
2.4. Evaluation of the Beams Suitability by Out-of-Beam Dosimetry
Treatment Planning Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
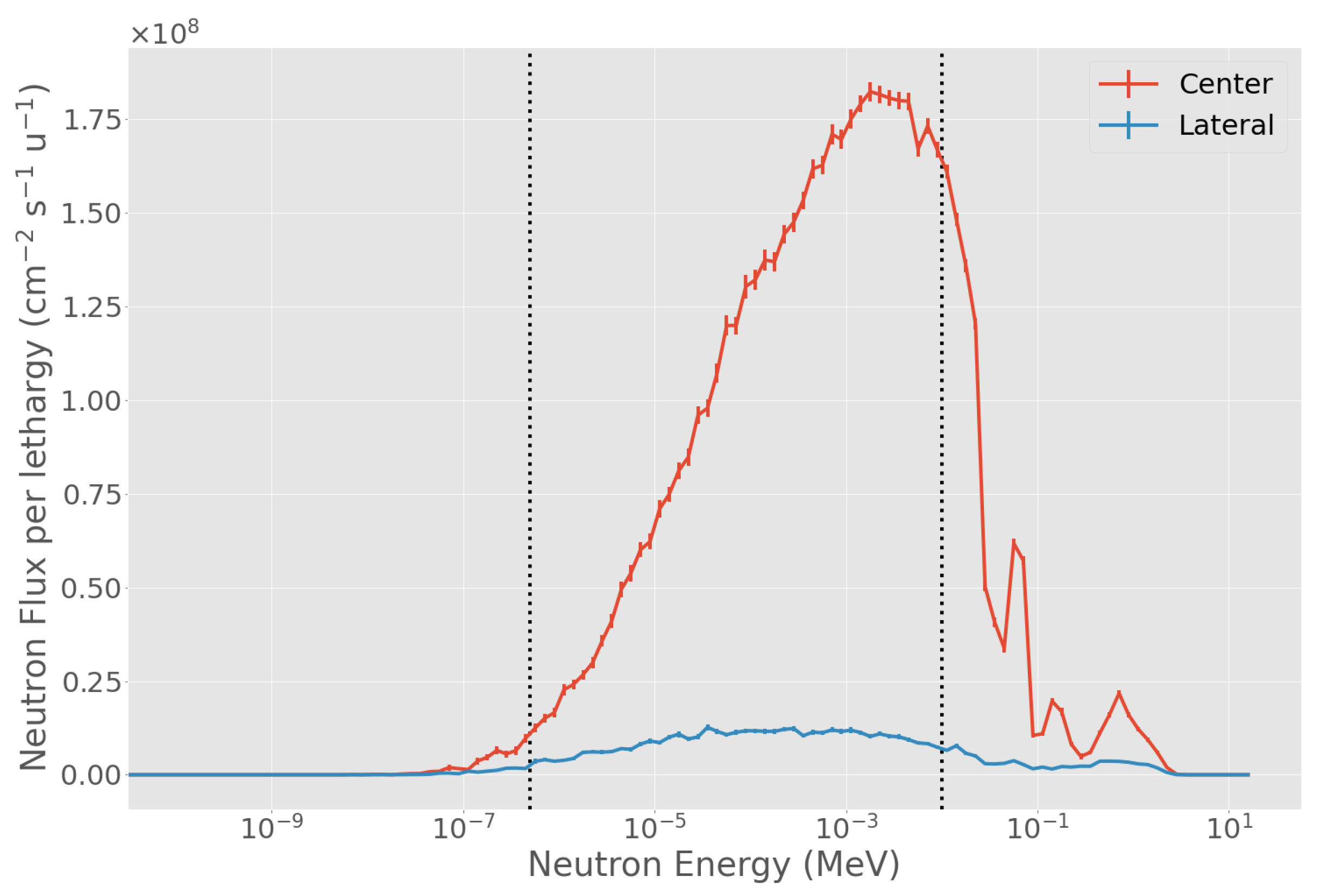
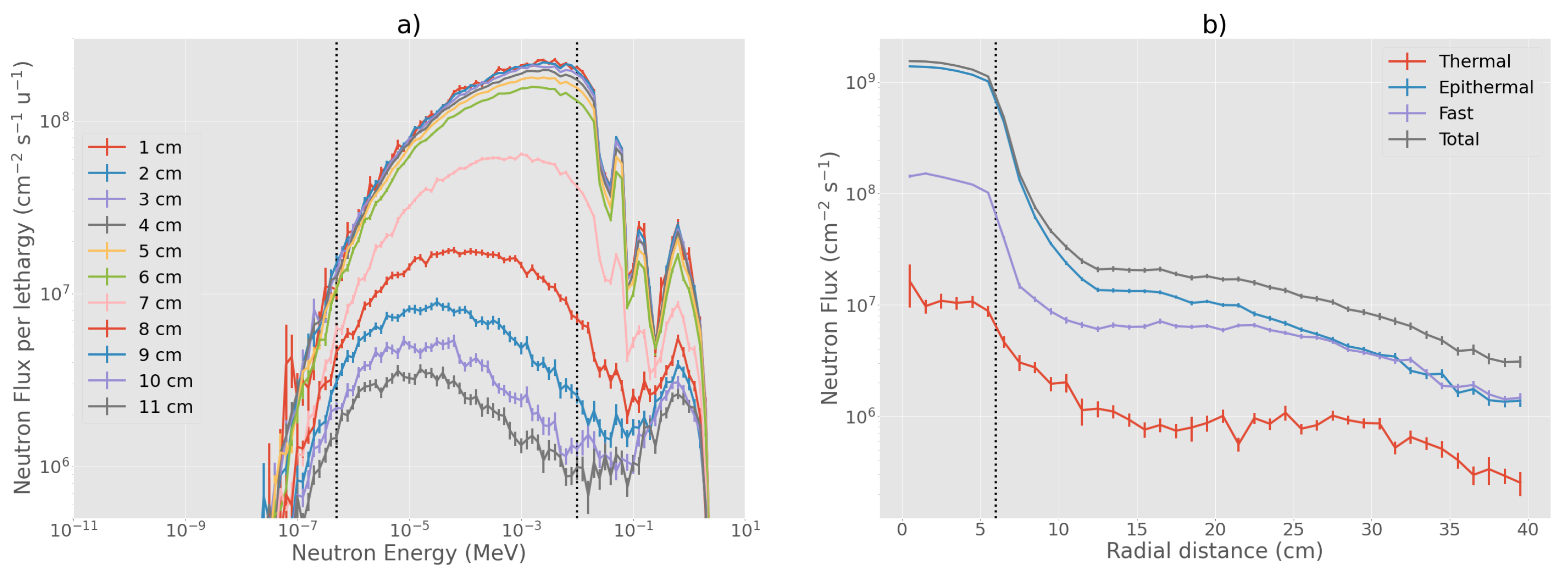
3.1. Evaluation of Physical in-Air Parameters
3.2. Radiobiological FOM
3.3. Out-of-Beam Dosimetry
Comparison with Other Beams
3.4. Characteristics of the Selected Beam
3.5. Treatment Planning
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BNCT | Boron Neutron Capture Therapy |
| BSA | Beam Shaping Assembly |
| INFN | Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare |
| IAEA | International Atomic Energy Agency |
| TCP | Tumor Control Probability |
| NTCP | Normal Tissue Complication Probability |
| UTCP | Uncomplicated Tumor Control Probability |
| FOM | Figure of Merit |
| RFQ | Radio Frequency Quadrupole |
| H&N | Head and Neck |
References
- Koivunoro, H.; Kankaanranta, L.; Seppälä, T.; Haapaniemi, A.; Mäkitie, A.; Joensuu, H. Boron neutron capture therapy for locally recurrent head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: An analysis of dose response and survival. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 137, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez, P.; Pereira, M.; Casal, M.; González, S.; Feld, D.; Santa Cruz, G.; Kessler, J.; Longhino, J.; Blaumann, H.; Rebagliati, R.J.; et al. BNCT for skin melanoma in extremities: Updated Argentine clinical results. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2009, 67, S50–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.L.; Chou, F.I.; Lin, K.H.; Pan, P.S.; Lee, J.C.; Huang, W.S.; Liu, Y.M.; Chao, Y.; Chen, Y.W. Using salvage Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) for recurrent malignant brain tumors in Taiwan. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2020, 160, 109105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreiner, A.J.; Bergueiro, J.; Cartelli, D.; Baldo, M.; Castell, W.; Asoia, J.G.; Padulo, J.; Sandín, J.C.S.; Igarzabal, M.; Erhardt, J.; et al. Present status of accelerator-based BNCT. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2016, 21, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyanagi, Y.; Sakurai, Y.; Kumada, H.; Tanaka, H. Status of accelerator-based BNCT projects worldwide. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2160, 050012. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, M. Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT): A unique role in radiotherapy with a view to entering the accelerator-based BNCT era. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreiner, A.; Vento, V.T.; Levinas, P.; Bergueiro, J.; Di Paolo, H.; Burlon, A.; Kesque, J.; Valda, A.; Debray, M.; Somacal, H.; et al. Development of a tandem-electrostatic-quadrupole accelerator facility for BNCT. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2009, 67, S266–S269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumada, H.; Matsumura, A.; Sakurai, H. New challenge for advanced BNCT in University of Tsukuba. In the front edge of BNCT development. In Proceedings of the Sixth Young Researchers BNCT Meeting, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 5–8 December 2011; pp. 132–136. [Google Scholar]
- Aleynik, V.; Burdakov, A.; Davydenko, V.; Ivanov, A.; Kanygin, V.; Kuznetsov, A.; Makarov, A.; Sorokin, I.; Taskaev, S. BINP accelerator based epithermal neutron source. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2011, 69, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savolainen, S.; Kortesniemi, M.; Timonen, M.; Reijonen, V.; Kuusela, L.; Uusi-Simola, J.; Salli, E.; Koivunoro, H.; Seppälä, T.; Lönnroth, N.; et al. Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) in Finland: Technological and physical prospects after 20 years of experiences. Phys. Med. 2013, 29, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, J.; Anderson, O.; Reginato, L.; Vella, M.; Yu, S. A 2.5 MeV electrostatic quadrupole DC accelerator for BNCT application. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms. 1995, 99, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.A.; Beynon, T.D.; Green, S.; James, N.D. Toward a final design for the Birmingham boron neutron capture therapy neutron beam. Med. Phys. 1999, 26, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfon, S.; Paul, M.; Arenshtam, A.; Berkovits, D.; Bisyakoev, M.; Eliyahu, I.; Feinberg, G.; Hazenshprung, N.; Kijel, D.; Nagler, A.; et al. High-power liquid-lithium target prototype for accelerator-based boron neutron capture therapy. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2011, 69, 1654–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathot, S. The Trasco-Spes RFQ. In Proceedings of the LINAC 2004 Conference, Lübeck, Germany, 16–20 August 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, J.; Colautti, P.; Fabritsiev, S.; Gervash, A.; Giniyatulin, R.; Lomasov, V.; Makhankov, A.; Mazul, I.; Pisent, A.; Pokrovsky, A.; et al. Be target development for the accelerator-based SPES-BNCT facility at INFN Legnaro. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2009, 67, S270–S273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farías, R.O.; Bortolussi, S.; Menéndez, P.R.; González, S.J. Exploring Boron Neutron Capture Therapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Phys. Med. 2014, 30, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanch, J.C.; Zhou, X.L.; Brownell, G.L. A Monte Carlo Investigation of the Dosimetric Properties of Monoenergetic Neutron Beams for Neutron Capture Therapy. Radiat. Res. 1991, 126, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisceglie, E.; Colangelo, P.; Colonna, N.; Santorelli, P.; Variale, V. On the optimal energy of epithermal neutron beams for BNCT. Phys. Med. Biol. 2000, 45, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.K.C.; Moore, B.R. Thick beryllium target as an epithermal neutron source for neutron capture therapy. Med. Phys. 1994, 21, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, D.; Beynon, T. A design study for an accelerator-based epithermal neutron beam for BNCT. Phys. Med. Biol. 1995, 40, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, B.W.; Yanch, J.C.; Klinkowstein, R.E. Development of a high-power water cooled beryllium target for use in accelerator-based boron neutron capture therapy. Med. Phys. 1998, 25, 1967–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Zhou, X.L. Thick target neutron yields for the 7 Li (p, n) 7 Be reaction near threshold. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 1999, 152, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, W.; Grimes, S.; Massey, T.; Al-Quraishi, S.; Jacobs, D.; Brient, C.; Yanch, J. Measurement of the thick-target 9 Be (p, n) neutron energy spectra. Nucl. Sci. Eng. 2001, 138, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlon, A.; Kreiner, A.; Valda, A.; Minsky, D.; Somacal, H.; Debray, M.; Stoliar, P. Optimization of a neutron production target and a beam shaping assembly based on the 7 Li (p, n) 7 Be reaction for BNCT. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms. 2005, 229, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Bengua, G.; Tanaka, K.; Nakagawa, Y. Variations in lithium target thickness and proton energy stability for the near-threshold 7Li (p, n) 7Be accelerator-based BNCT. Phys. Med. Biol. 2007, 52, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceballos, C.; Esposito, J.; Agosteo, S.; Colautti, P.; Conte, V.; Moro, D.; Pola, A. Towards the final BSA modeling for the accelerator-driven BNCT facility at INFN LNL. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2011, 69, 1660–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorer, D.; Wambersie, G.; Whitmore, G.; Zamenhof, R.; Levin, V.; Andreo, P.; Dodd, D. Current Status of neutron capture therapy. IAEA 2001, 8, 75–77. [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto, S.; Kiger, W., III; Harling, O. Sensitivity studies of beam directionality, beam size, and neutron spectrum for a fission converter-based epithermal neutron beam for boron neutron capture therapy. Med. Phys. 1999, 26, 1979–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, M.; González, S.; Minsky, D.; Kreiner, A. Evaluation of performance of an accelerator-based BNCT facility for the treatment of different tumor targets. Phys. Med. 2013, 29, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capoulat, M.; Kreiner, A. A 13 C (d, n)-based epithermal neutron source for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Phys. Med. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agosteo, S.; Colautti, P.; Esposito, J.; Fazzi, A.; Introini, M.; Pola, A. Characterization of the energy distribution of neutrons generated by 5MeV protons on a thick beryllium target at different emission angles. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2011, 69, 1664–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postuma, I. Clinical Application of Accelerator-Based Boron Neutron Capture Therapy: Optimisation of Procedures, Tailoring of a Neutron Beam and Evaluation of Its Dosimetric Performance. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pavia, Pavia, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goorley, T.; James, M.; Booth, T.; Brown, F.; Bull, J.; Cox, L.J.; Durkee, J.; Elson, J.; Fensin, M.; Forster, R.A.; et al. Initial MCNP6 Release Overview. Nucl. Technol. 2012, 180, 298–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankaanranta, L.; Seppälä, T.; Koivunoro, H.; Saarilahti, K.; Atula, T.; Collan, J.; Salli, E.; Kortesniemi, M.; Uusi-Simola, J.; Välimäki, P.; et al. Boron Neutron Capture Therapy in the Treatment of Locally Recurred Head-and-Neck Cancer: Final Analysis of a Phase I/II Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 82, e67–e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provenzano, L.; Koivunoro, H.; Postuma, I.; Longhino, J.; Boggio, E.; Farías, R.; Bortolussi, S.; González, S. The essential role of radiobiological figures of merit for the assessment and comparison of beam performances in boron neutron capture therapy. Phys. Med. 2019, 67, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, S.J.; Pozzi, E.C.C.; Hughes, A.M.; Provenzano, L.; Koivunoro, H.; Carando, D.G.; Thorp, S.I.; Casal, M.R.; Bortolussi, S.; Trivillin, V.A.; et al. Photon iso-effective dose for cancer treatment with mixed field radiation based on dose–response assessment from human and an animal model: Clinical application to boron neutron capture therapy for head and neck cancer. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 7938–7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckerman, K.; Cristy, M.; Ryman, J. The ORNL Mathematical Phantom Series; Oak Ridge National Laboratory: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 1996.
- Krstić, D.; Nikezić, D. Input files with ORNL—Mathematical phantoms of the human body for MCNP-4B. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2007, 176, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petoussi-Henss, N.; Bolch, W.E.; Eckerman, K.F.; Endo, A.; Hertel, N.; Hunt, J.; Pelliccioni, M.; Schlattl, H.; Zankl, M. Conversion Coefficients for Radiological Protection Quantities for External Radiation Exposures. Ann. ICRP 2020, 40, 1–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Masunaga, S.I.; Kinashi, Y.; Takagaki, M.; Sakurai, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Ono, K. The effects of boron neutron capture therapy on liver tumors and normal hepatocytes in mice. Cancer Sci. 2000, 91, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coderre, J.A.; Turcotte, J.C.; Riley, K.J.; Binns, P.J.; Harling, O.K.; Kiger, W. Boron neutron capture therapy: Cellular targeting of high linear energy transfer radiation. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2003, 2, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiger, J.L.; Kiger, W.S., III; Riley, K.J.; Binns, P.J.; Patel, H.; Hopewell, J.W.; Harling, O.K.; Busse, P.M.; Coderre, J.A. Functional and histological changes in rat lung after boron neutron capture therapy. Radiat. Res. 2008, 170, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farías, R.; Garabalino, M.; Ferraris, S.; Santa María, J.; Rovati, O.; Lange, F.; Trivillin, V.; Monti Hughes, A.; Pozzi, E.; Thorp, S.; et al. Toward a clinical application of ex situ boron neutron capture therapy for lung tumors at the RA-3 reactor in Argentina. Med. Phys. 2015, 42, 4161–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanaoka, K.; Watabe, T.; Naka, S.; Kanai, Y.; Ikeda, H.; Horitsugi, G.; Kato, H.; Isohashi, K.; Shimosegawa, E. FBPA PET in boron neutron capture therapy for cancer: Prediction of (10)B concentration in the tumor and normal tissue in a rat xenograft model. EJNMMI Res. 2014, 4, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimosegawa, E.; Isohashi, K.; Naka, S.; Horitsugi, G. Assessment of 10B concentration in boron neutron capture therapy: Potential of image-guided therapy using 18FBPA PET. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2016, 30, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kono, Y.; Kurihara, H.; Kawamoto, H.; Yasui, N.; Honda, N.; Igaki, H.; Itami, J. Radiation absorbed dose estimates for 18F-BPA PET. Acta Radiol. 2017, 58, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farias, R.O.; González, S.J. MultiCell model as an optimized strategy for BNCT treatment planning. In Proceedings of the 15th International Congress on Neutron Capture Therapy, Tsukuba, Japan, 10–14 September 2012; pp. 148–150. [Google Scholar]
- Farias, R.O. Dosimetría y modelado computacional para irradiaciones extracorpóreas en humanos en el marco de la Terapia por Captura Neutrónica en Boro. Ph.D. Thesis, Comision Nacional de Energia Atomica, Istituto de Tecnologia, Universidad Nacional de General San Martin, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Koivunoro, H. Dosimetry and Dose Planning in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy: Monte Carlo Studies. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera, M. Simulación computacional de la producción de flujos neutrónicos y planificación de tratamiento para la Terapia por Captura Neutrónica en Boro con aceleradores. Ph.D. Thesis, Nacional de Energia Atomica, Istituto de Tecnologia, Universidad Nacional de General San Martin, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Nigg, D.; Wemple, C.; Seren, T.; Seppälä, T.; Auterinen, I. Improved evaluation of the free-beam spectrum of the FiR 1 clinical epithermal-neutron beam facility for BNCT. In INEEL BNCT Research Program Annual Report; CY-2000; Idaho National Laboratory (INL): Idaho Falls, ID, USA, 2001; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- González, S.J.; Cruz, G.A.S. The photon-isoeffective dose in boron neutron capture therapy. Radiat. Res. 2012, 178, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
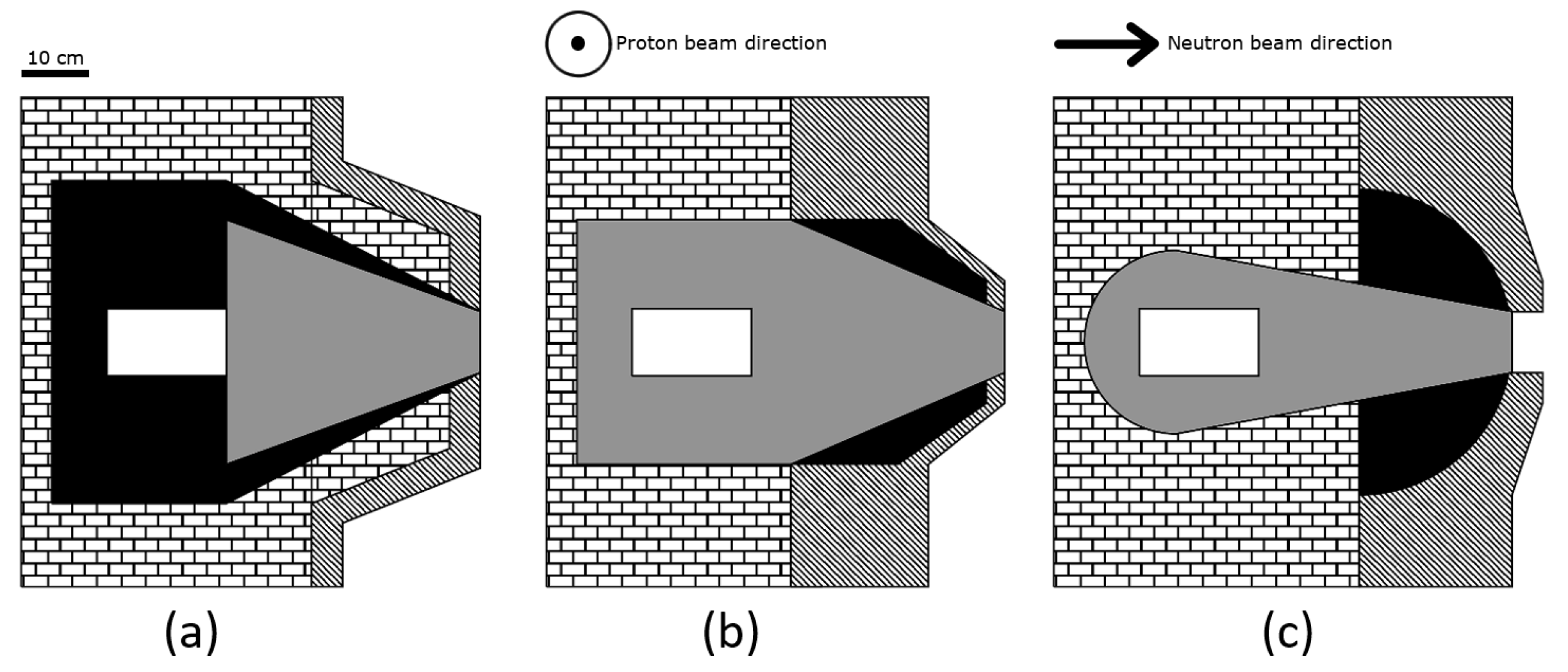

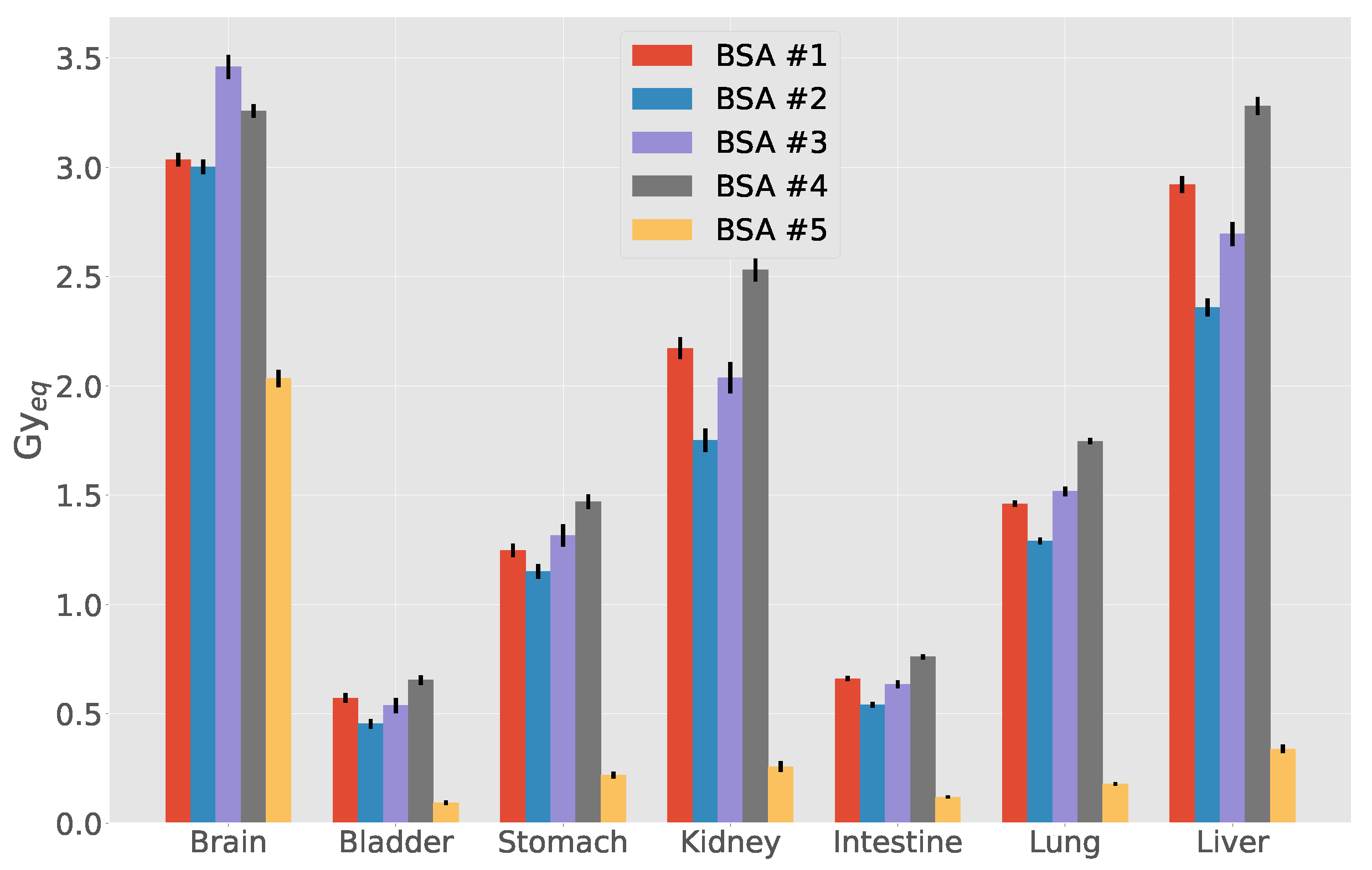
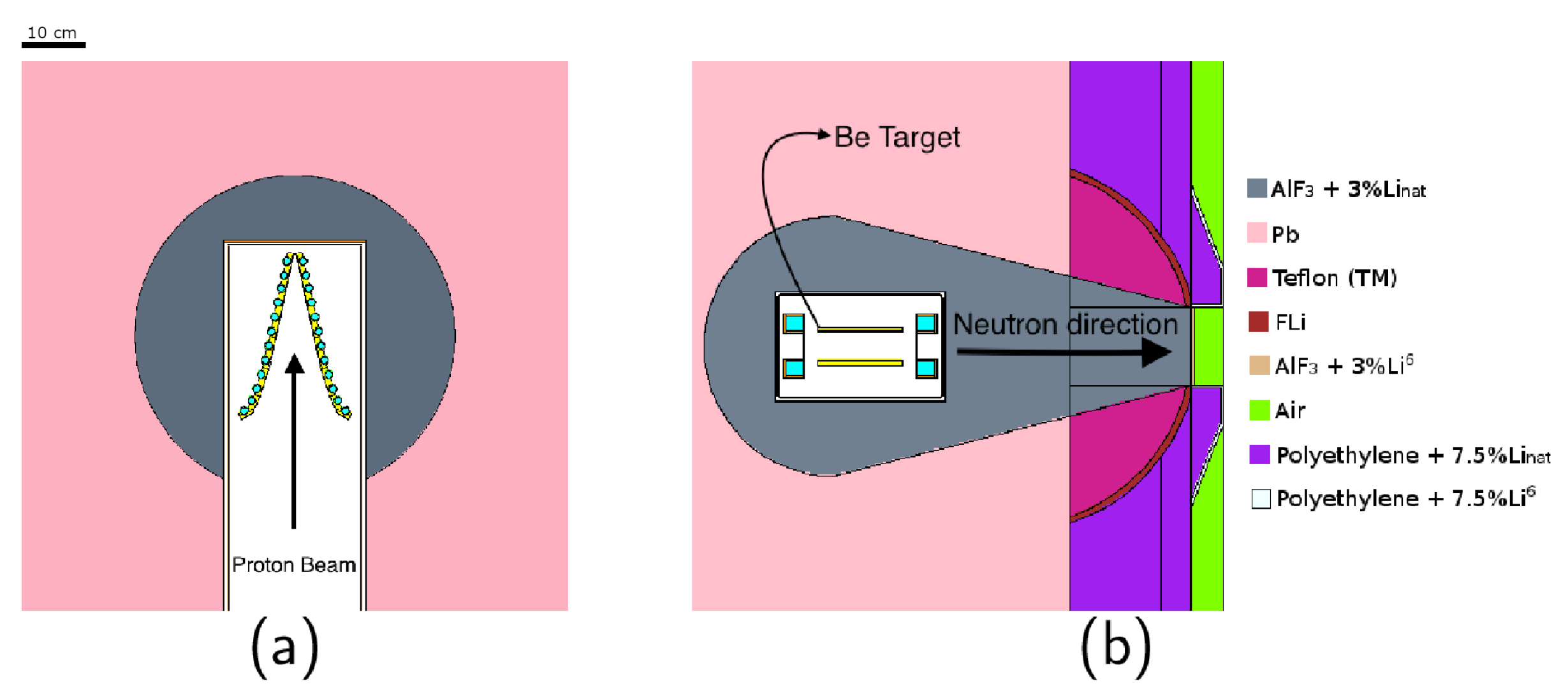


| BSA | Shield 1 | Shield 2 | Reflector | Bulk Material Composition (Thickness [cm]) | Design |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | Pb | HW + CLi | Pb | AlF (35.5) + LiF (1) + Bi (0.5) + Ti (1) | Figure 1b |
| #2 | Pb | C + CHLi | Pb | AlF (35.5) + LiF (1) + Bi (0.5) + Ti (1) | Figure 1a |
| #3 | Pb | C + CLi + CHLi + LiF | Pb + LiF | AlF (35.75) + LiF (1.5) + Bi (0.5) + Ti (1) | Figure 1b |
| #4 | Pb | C + CLi | Pb | AlF (35.5) + LiF (1) + Bi (0.5) + Ti (1) | Figure 1b |
| #5 | Pb | LiF + Teflon | CHLi | AlF with 3% mass of LiF (37) | Figure 1c |
| 10 (cm s) | - | 10 (cm Gy) | 10 (cm Gy) | - |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| >1 | <0.05 | <2.0 | <2.0 | >0.7 |
| Tissue | RBE | RBE | CBE | B Concentration (μg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brain | 1 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 15 |
| Skin | 1 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 22.5 |
| Liver | 1 | 3.2 | 4.2 | 15 |
| Lung | 1 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 15 |
| Kidney | 1 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 75 |
| Bladder | 1 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 15 |
| Tumor | 1 | 2.2 | 5.3 | 52.5 |
| 10 (cm s) | - | 10 (cm Gy) | 10 (cm Gy) | - | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recommended | >1 | <0.05 | <2.0 | <2.0 | >0.7 |
| BSA #1 | 2.58 | 0.019 | 9.16 | 3.96 | 0.59 |
| BSA #2 | 2.56 | 0.054 | 6.70 | 6.66 | 0.60 |
| BSA #3 | 1.73 | 0.004 | 7.71 | 2.70 | 0.62 |
| BSA #4 | 2.79 | 0.018 | 9.09 | 3.78 | 0.59 |
| BSA #5 | 1.08 | 0.009 | 9.50 | 4.17 | 0.74 |
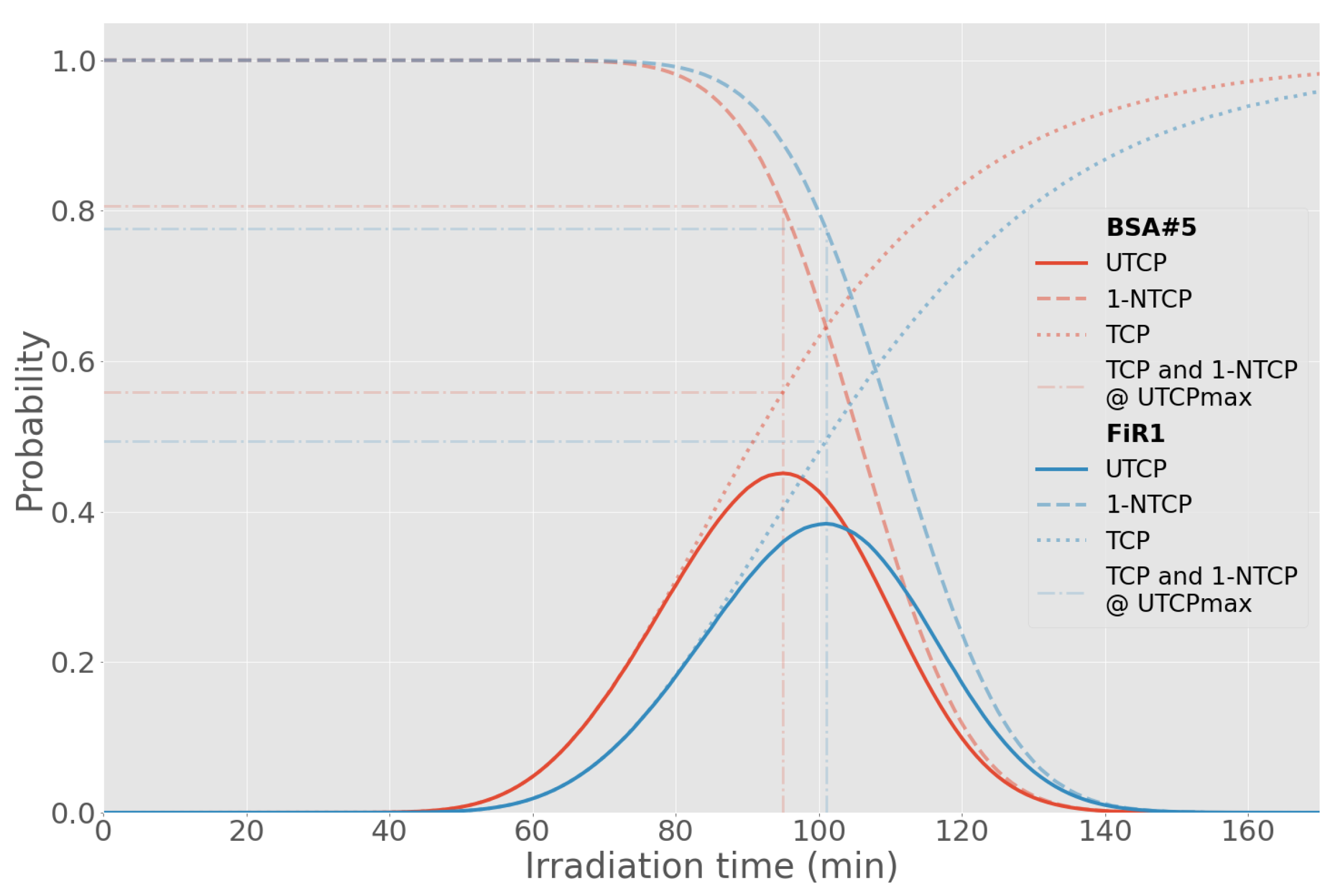
| BSA | T (min) | UTCP | TCP | NTCP | D (Gy) | % Dose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n,) | (n,p) | (n,n’) | |||||||
| #1 | 10 | 0.41 ± 0.06 | 0.50 ± 0.04 | 0.19 ± 0.11 | 5.79 | 61 | 6 | 6 | 27 |
| #2 | 12.5 | 0.40 ± 0.07 | 0.52 ± 0.04 | 0.23 ± 0.13 | 6.15 | 59 | 5 | 6 | 30 |
| #3 | 20 | 0.44 ± 0.07 | 0.57 ± 0.05 | 0.23 ± 0.10 | 5.81 | 62 | 7 | 6 | 25 |
| #4 | 9.5 | 0.40 ± 0.07 | 0.54 ± 0.05 | 0.26 ± 0.11 | 5.98 | 61 | 6 | 6 | 27 |
| #5 | 24.5 | 0.47 ± 0.07 | 0.58 ± 0.05 | 0.18 ± 0.09 | 5.59 | 62 | 9 | 6 | 23 |
| Fir 1 | 33 | 0.45 ± 0.07 | 0.54 ± 0.05 | 0.17 ± 0.08 | 4.80 | 78 | 2 | 8 | 12 |
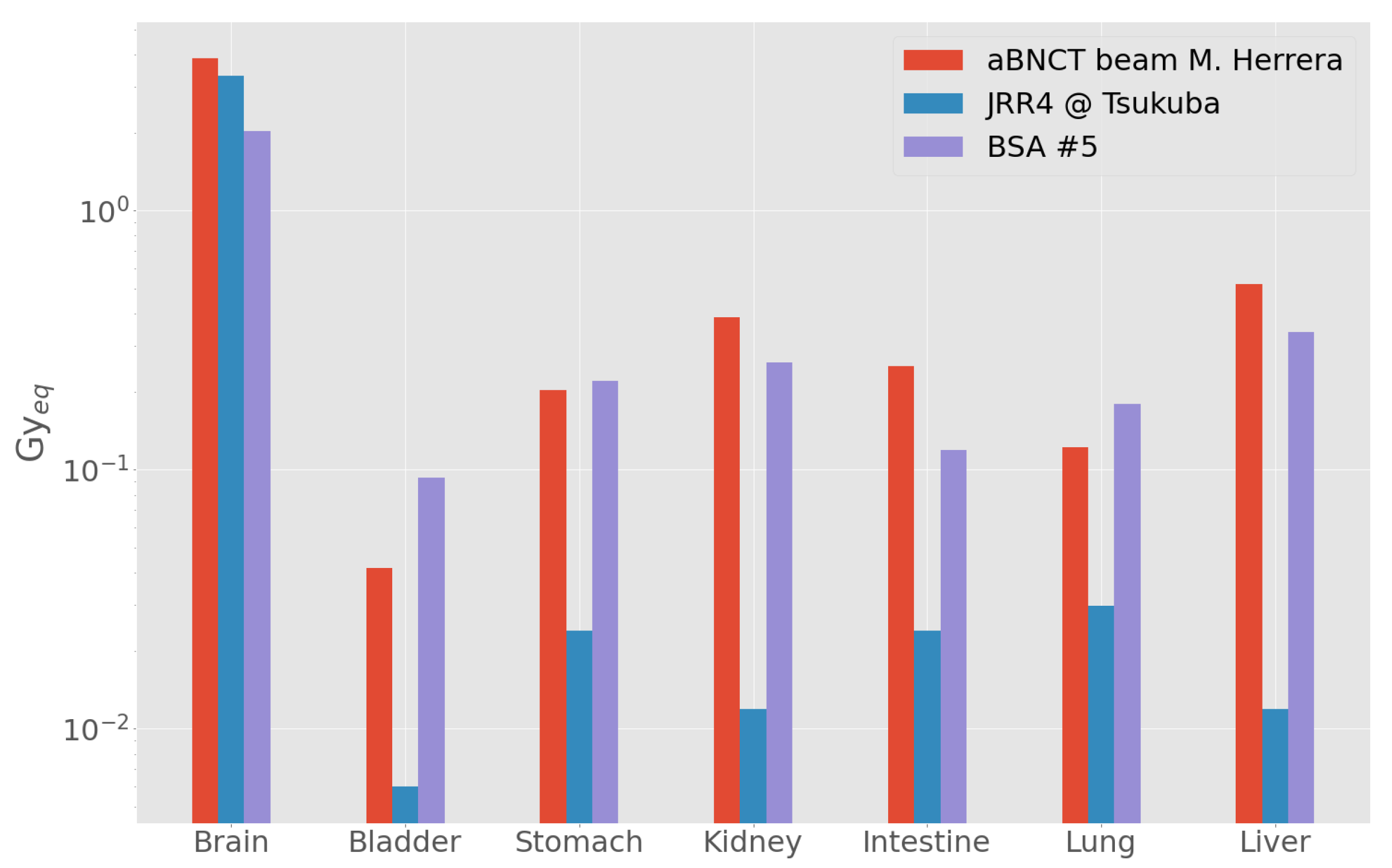
| Organ | D (cGy) | D (cGy) | D (cGy) | D (cGy) | D (cSv) | D (cGy_Eq) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brain | 1.060 | 1.210 | 41.4 | 43.8 | 511.0 | 203 ± 4 |
| Bladder | 0.106 | 0.122 | 0.1 | 6.3 | 48.0 | 9 ± 1 |
| Stomach | 0.151 | 0.174 | 1.0 | 14.9 | 77.0 | 22 ± 2 |
| Kidneys | 0.121 | 0.139 | 0.3 | 11.0 | 226.0 | 26 ± 2 |
| Intestine | 0.105 | 0.120 | 0.3 | 8.3 | 51.0 | 12 ± 1 |
| Lungs | 0.188 | 0.216 | 2.9 | 0.6 | 80.0 | 18 ± 1 |
| Liver | 0.133 | 0.153 | 0.8 | 11.5 | 112.0 | 34 ± 2 |
| Heart | 0.187 | 0.215 | 2.2 | 16.6 | 95.0 | 28 ± 2 |
| Spleen | 0.121 | 0.140 | 1.0 | 14.5 | 65.0 | 21 ± 2 |
| Head | 0.551 | 0.631 | 19.9 | 37.2 | 282.0 | 115 ± 2 |
| Thyroid | 0.483 | 0.554 | 9.1 | 26.8 | 232.0 | 68 ± 7 |
| Testicles | 0.078 | 0.090 | 0.1 | 7.1 | 38.0 | 9 ± 1 |
| Pancreas | 0.107 | 0.124 | 0.3 | 9.1 | 53.0 | 13 ± 1 |
| Pharynx | 0.712 | 0.818 | 14.5 | 33.6 | 337.0 | 98 ± 8 |
| Marrow | 0.145 | 0.166 | 4.9 | 16.0 | 80.0 | 35 ± 1 |
| Adrenal | 0.091 | 0.105 | 1.0 | 10.1 | 48.0 | 16 ± 4 |
| Thymus | 0.249 | 0.287 | 1.6 | 17.7 | 120.0 | 29 ± 4 |
| Skin | 0.173 | 0.198 | 6.8 | 20.6 | 128.0 | 54 ± 1 |
| Trunk | 0.143 | 0.165 | 1.8 | 14.6 | 74.0 | 24 ± 1 |
| Beam | T (min) | UTCP | TCP | NTCP | D (Gy) | % Dose | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n,) | (n,p) and (n,n’) | |||||||
| BSA #5 | 95 | 0.45 ± 0.07 | 0.56 ± 0.05 | 0.19 ± 0.11 | 6.0 | 62 | 8 | 30 |
| FiR 1 | 101 | 0.38 ± 0.07 | 0.49 ± 0.05 | 0.22 ± 0.12 | 5.4 | 74 | 6 | 20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Postuma, I.; González, S.; Herrera, M.S.; Provenzano, L.; Ferrarini, M.; Magni, C.; Protti, N.; Fatemi, S.; Vercesi, V.; Battistoni, G.; et al. A Novel Approach to Design and Evaluate BNCT Neutron Beams Combining Physical, Radiobiological, and Dosimetric Figures of Merit. Biology 2021, 10, 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030174
Postuma I, González S, Herrera MS, Provenzano L, Ferrarini M, Magni C, Protti N, Fatemi S, Vercesi V, Battistoni G, et al. A Novel Approach to Design and Evaluate BNCT Neutron Beams Combining Physical, Radiobiological, and Dosimetric Figures of Merit. Biology. 2021; 10(3):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030174
Chicago/Turabian StylePostuma, Ian, Sara González, Maria S Herrera, Lucas Provenzano, Michele Ferrarini, Chiara Magni, Nicoletta Protti, Setareh Fatemi, Valerio Vercesi, Giuseppe Battistoni, and et al. 2021. "A Novel Approach to Design and Evaluate BNCT Neutron Beams Combining Physical, Radiobiological, and Dosimetric Figures of Merit" Biology 10, no. 3: 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030174
APA StylePostuma, I., González, S., Herrera, M. S., Provenzano, L., Ferrarini, M., Magni, C., Protti, N., Fatemi, S., Vercesi, V., Battistoni, G., Anselmi Tamburini, U., Hao Liu, Y., Kankaanranta, L., Koivunoro, H., Altieri, S., & Bortolussi, S. (2021). A Novel Approach to Design and Evaluate BNCT Neutron Beams Combining Physical, Radiobiological, and Dosimetric Figures of Merit. Biology, 10(3), 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030174











