The Role and Expression of Angiogenesis-Related miRNAs in Gastric Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Angiogenesis and Cancer
1.2. Angiogenesis and Gastric Cancer
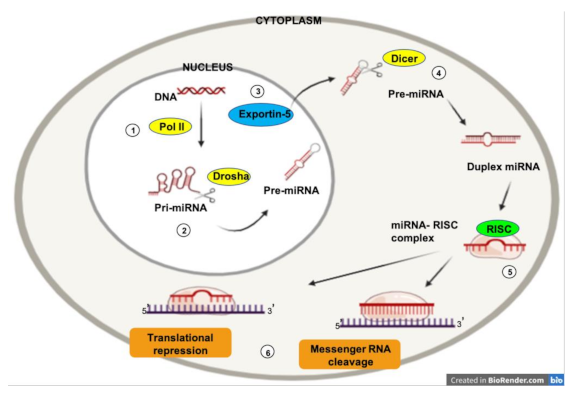
1.3. MicroRNAs and Cancer
1.4. MicroRNAs and Angiogenesis
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. MicroRNAs Involved in the VEGF Pathway
3.2. MicroRNAs Involved in the HIF Pathway
3.3. MicroRNAs Involved in HGF/c-MET Signaling
3.4. MicroRNAs Involved in the PI3K Pathway
3.4.1. MicroRNAs Targeting PTEN
3.4.2. MicroRNAs Targeting FOXO
3.4.3. MicroRNAs Targeting mTOR
3.4.4. MicroRNAs Targeting NF-κB
3.5. MicroRNAs Involved in STAT-3 Signaling
| miRNA | Target Genes | Classification | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-1 | VEGF-A EDN1 MET | VEGF pathway | Azarbarzin et al., 2020 [23] |
| miR-29a/c | VEGF | VEGF pathway | Zhang et al., 2016 [64] |
| miR-27b | VEGF-C | VEGF pathway | Liu et al., 2015 [65] |
| miR-101 | |||
| miR-128 | |||
| miR-126 | VEGF-A | VEGF pathway | Cuzziol et al., 2020 [62] Yang et al., 2015 [63] |
| miR-590 | VEGFR1/2 NRP1 | VEGF pathway | Mei et al., 2020 [66] |
| miR-210 | HIF | HIF pathway | Seo et al., 2019 [68] |
| miR-574-5p | PTPN3 | HIF pathway | Azarbarzin et al., 2020 [23] Zhang et al., 2020 [67] |
| miR-616-3p | PTEN | PI3K pathway VEGF pathway | Wu et al., 2018 [60] |
| miR-26a/b | HGF | HGF/c-MET signaling | Si et al., 2017 [69] |
| miR-18a | mTOR | PI3K pathway | Yang et al., 2015 [63] |
| miR-23a | PTEN | PI3K pathway | Azarbarzin et al., 2020 [23] Du et al., 2020 [70] |
| miR-101-2 | mTOR/PIK3CB/TSC1 | PI3K pathway | Riquelme et al., 2016 [76] |
| miR-125b-2 | PI3K pathway | ||
| miR-451a | PI3K pathway | ||
| miR-135b | FOXO1 | PI3K pathway | Bai et al., 2019 [74] |
| miR-382 | PTEN | PI3K pathway | Du et al., 2020 [70] Seo et al., 2019 [68] |
| miR-532-5p | NCF2 | PI3K pathway | Zhang et al., 2018 [75] |
| miR-718 | PTEN | PI3K pathway | Du et al., 2020 [70] |
| miR-155 | c-MYB/VEGF FOXO3a | Other—c-MYB PI3K pathway | Azarbarzin et al., 2020 [23] Deng et al., 2020 [72] Zhou et al., 2019 [73] |
| miR-874 | STAT-3/VEGF-A | STAT-3 signaling | Cuzziol et al., 2020 [62] Zhang et al., 2015 [78] |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.L.; Rouhi, P.; Dahl Jensen, L.; Zhang, D.; Ji, H.; Hauptmann, G.; Ingham, P.; Cao, Y. Hypoxia-induced pathological angiogenesis mediates tumor cell dissemination, invasion, and metastasis in a zebrafish tumor model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19485–19490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dabrosin, C.; Yin, X.; Fuster, M.M.; Arreola, A.; Rathmell, W.K.; Generali, D.; Nagaraju, G.P.; El-Rayes, B.; Ribatti, D.; et al. Broad targeting of angiogenesis for cancer prevention and therapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 35, S224–S243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, C.; Poppleton, H.; Kocak, M.; Hogg, T.L.; Fuller, C.; Hamner, B.; Oh, E.Y.; Gaber, M.W.; Finklestein, D.; Allen, M.; et al. A perivascular niche for brain tumor stem cells. Cancer Cell 2007, 11, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathia, J.D.; Heddleston, J.M.; Venere, M.; Rich, J.N. Deadly teamwork: Neural cancer stem cells and the tumor microenvironment. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 8, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, S.P.; Stainier, D.Y. Molecular control of endothelial cell behaviour during blood vessel morphogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Folkman, J. Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell 1996, 86, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeriswyl, V.; Christofori, G. The angiogenic switch in carcinogenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2009, 19, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergers, G.; Benjamin, L.E. Tumorigenesis and the angiogenic switch. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, C.; Chu, X. New insights into the regulatory role of microRNA in tumor angiogenesis and clinical implications. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieto, E.; Ferraraccio, F.; Orditura, M.; Castellano, P.; Mura, A.L.; Pinto, M.; Zamboli, A.; De Vita, F.; Galizia, G. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is an independent prognostic indicator of worse outcome in gastric cancer patients. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 15, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, D.I.; Zachary, I. The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family: Angiogenic factors in health and disease. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Forma, A.; Tyczynska, M.; Kedzierawski, P.; Gietka, K.; Sitarz, M. Gastric carcinogenesis: A comprehensive review of the angiogenic pathways. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Zhan, P.; Zhou, Y.; Fang, W.; Zhao, P.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, N. Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial growth factor immunohistochemical expression in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 9473–9484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziello, J.E.; Jovin, I.S.; Huang, Y. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF)-1 regulatory pathway and its potential for therapeutic intervention in malignancy and ischemia. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2007, 80, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Basilico, C.; Arnesano, A.; Galluzzo, M.; Comoglio, P.M.; Michieli, P. A high affinity hepatocyte growth factor-binding site in the immunoglobulin-like region of Met. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 21267–21277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organ, S.L.; Tsao, M.S. An overview of the c-MET signaling pathway. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2011, 3, S7–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birchmeier, C.; Birchmeier, W.; Gherardi, E.; Vande Woude, G.F. Met, metastasis, motility and more. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trusolino, L.; Comoglio, P.M. Scatter-factor and semaphorin receptors: Cell signalling for invasive growth. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalhoub, N.; Baker, S.J. PTEN and the PI3-kinase pathway in cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2009, 4, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelman, J.A.; Luo, J.; Cantley, L.C. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Meng, L.H. Emerging roles of class I PI3K inhibitors in modulating tumor microenvironment and immunity. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarbarzin, S.; Safaralizadeh, R.; Khojasteh, M.B.; Baghbanzadeh, A.; Baradaran, B. Current perspectives on the dysregulated microRNAs in gastric cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 7253–7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 2008, 132, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, P.A.; Grandis, J.R. STAT3 signaling: Anticancer strategies and challenges. Mol. Interv. 2011, 11, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, M.; Platt, D.; Lemtalsi, T.; Gu, X.; Brooks, S.E.; Marrero, M.B.; Caldwell, R.B. VEGF differentially activates STAT3 in microvascular endothelial cells. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1562–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Han, Z.C. STAT3: A critical transcription activator in angiogenesis. Med. Res. Rev. 2008, 28, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, N.; Hillan, K.J.; Gerber, H.P.; Novotny, W. Discovery and development of bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF antibody for treating cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, N.; Kerbel, R.S. Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature 2005, 438, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerbel, R.S. Tumor angiogenesis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2039–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, C.S.; Tomasek, J.; Yong, C.J.; Dumitru, F.; Passalacqua, R.; Goswami, C.; Safran, H.; Dos Santos, L.V.; Aprile, G.; Ferry, D.R.; et al. Ramucirumab monotherapy for previously treated advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (REGARD): An international, randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2014, 383, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, H.; Muro, K.; Van Cutsem, E.; Oh, S.C.; Bodoky, G.; Shimada, Y.; Hironaka, S.; Sugimoto, N.; Lipatov, O.; Kim, T.Y.; et al. Ramucirumab plus paclitaxel versus placebo plus paclitaxel in patients with previously treated advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (RAINBOW): A double-blind, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1224–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qin, S.; Xu, J.; Xiong, J.; Wu, C.; Bai, Y.; Liu, W.; Tong, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, R.; et al. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase III Trial of Apatinib in Patients With Chemotherapy-Refractory Advanced or Metastatic Adenocarcinoma of the Stomach or Gastroesophageal Junction. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1448–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Kang, W.K.; Di Bartolomeo, M.; Chau, H.H.; Yoon, S.; Cascinu, S.; Ryu, M.; Kim, J.C.; Lee, K.; Oh, S.C.; et al. Randomized phase III ANGEL study of rivoceranib (apatinib) + best supportive care (BSC) vs placebo + BSC in patients with advanced/metastatic gastric cancer who failed ≥2 prior chemotherapy regimens. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30 (Suppl. 5), v851–v934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Leung, L.H.; Liu, L.; Yang, F.; Yao, X. Efficacy and safety of angiogenesis inhibitors in advanced gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, J.; Diederichs, S. MicroRNA biogenesis and cancer. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 676, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.H.; Reimers, M.; Maher, B.; Williamson, V.; McMichael, O.; McClay, J.L.; van den Oord, E.J.; Riley, B.P.; Kendler, K.S.; Vladimirov, V.I. MicroRNA expression profiling in the prefrontal cortex of individuals affected with schizophrenia and bipolar disorders. Schizophr. Res. 2010, 124, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, V.P.; Ngo, T.A.; Pernestig, A.K.; Tilevik, D.; Kant, K.; Nguyen, T.; Wolff, A.; Bang, D.D. MicroRNA amplification and detection technologies: Opportunities and challenges for point of care diagnostics. Lab. Investig. 2019, 99, 452–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, J.D.; Ludlow, A.T.; LaRanger, R.; Wright, W.E.; Shay, J.W. Comparison of DNA Quantification Methods for Next Generation Sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Jiang, T.; Liu, Y.; Huai, G.; Lan, C.; Li, G.; Jia, G.; Wang, K.; Yang, M. Droplet digital PCR-based circulating microRNA detection serve as a promising diagnostic method for gastric cancer. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miotto, E.; Saccenti, E.; Lupini, L.; Callegari, E.; Negrini, M.; Ferracin, M. Quantification of circulating miRNAs by droplet digital PCR: Comparison of EvaGreen- and TaqMan-based chemistries. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 2638–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Ingolia, N.T.; Weissman, J.S.; Bartel, D.P. Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA levels. Nature 2010, 466, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lages, E.; Ipas, H.; Guttin, A.; Nesr, H.; Berger, F.; Issartel, J.P. MicroRNAs: Molecular features and role in cancer. Front. Biosci. 2012, 17, 2508–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Li, B.; Yang, Z.; Fang, H.; Zhang, G.M.; Feng, Z.H.; Huang, B. Regulation of HIF-1alpha and VEGF by miR-20b tunes tumor cells to adapt to the alteration of oxygen concentration. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, J.; Lin, J.H.; Brenot, A.; Kim, J.W.; Provot, S.; Werb, Z. GATA3 suppresses metastasis and modulates the tumour microenvironment by regulating microRNA-29b expression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Chang, B.H.; Danesh, F.R. Identification of microRNA-93 as a novel regulator of vascular endothelial growth factor in hyperglycemic conditions. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 23457–23465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Peng, X.C.; Zheng, X.L.; Wang, J.; Qin, Y.W. MiR-126 restoration down-regulate VEGF and inhibit the growth of lung cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Lung Cancer 2009, 66, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Yang, J.; Yin, S.; Zhang, H.; Fan, Y.; Sun, C.; Gu, J.; Xi, J.J. The synergistic regulation of VEGF-mediated angiogenesis through miR-190 and target genes. RNA 2014, 20, 1328–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhao, N.; Li, S.; Fang, J.H.; Chen, M.X.; Yang, J.; Jia, W.H.; Yuan, Y.; Zhuang, S.M. MicroRNA-195 suppresses angiogenesis and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting the expression of VEGF, VAV2, and CDC42. Hepatology 2013, 58, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Xu, L.Y.; Li, E.M. A family of pleiotropically acting microRNAs in cancer progression, miR-200: Potential cancer therapeutic targets. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 1896–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Er, K.; Mao, C.; Yan, Q.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Cui, F.; Zhao, W.; Shi, H. miR-203 suppresses tumor growth and angiogenesis by targeting VEGFA in cervical cancer. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 32, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.J.; Zhang, Y.N.; Liao, J.Z.; Ke, K.P.; Chang, Y.; Li, P.Y.; Wang, M.; Lin, J.S.; He, X.X. MiR-497 suppresses angiogenesis and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting VEGFA and AEG-1. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 29527–29542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Ma, R.; Si, W.; Li, S.; Xu, Y.; Tu, X.; Wang, Q. MicroRNA-503 targets FGF2 and VEGFA and inhibits tumor angiogenesis and growth. Cancer Lett. 2013, 333, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, P.; Liu, X.; Dong, J.; Li, J.; Huang, C.; Wu, R.; Lv, Y. Downregulation of miRNA-638 promotes angiogenesis and growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting VEGF. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 30702–30711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakuchi, M.; Yagi, S.; Ito, T.; Lowenstein, C.J. MicroRNA-22 regulates hypoxia signaling in colon cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakuchi, M.; Lotterman, C.D.; Bao, C.; Hruban, R.H.; Karim, B.; Mendell, J.T.; Huso, D.; Lowenstein, C.J. P53-induced microRNA-107 inhibits HIF-1 and tumor angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6334–6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.T.; Chen, P.S.; Johansson, G.; Chu, C.Y.; Wang, M.Y.; Jeng, Y.M.; Yu, S.L.; Chen, J.S.; Chang, K.J.; Jee, S.H.; et al. MicroRNA-519c suppresses hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression and tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 2675–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Pu, J.; Qi, T.; Qi, M.; Yang, C.; Li, S.; Huang, K.; Zheng, L.; Tong, Q. MicroRNA-145 inhibits the growth, invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis of neuroblastoma cells through targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 2 alpha. Oncogene 2014, 33, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.H.; Lin, C.; Liu, C.C.; Jiang, W.W.; Huang, M.Z.; Liu, X.; Guo, W.J. MiR-616-3p promotes angiogenesis and EMT in gastric cancer via the PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 501, 1068–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Lei, Y.; Ge, Q.; Lv, N.; Zhou, X.; Chen, C. Reduced miR-126 expression facilitates angiogenesis of gastric cancer through its regulation on VEGF-A. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 11873–11885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuzziol, C.I.; Castanhole-Nunes, M.M.U.; Pavarino, E.C.; Goloni-Bertollo, E.M. MicroRNAs as regulators of VEGFA and NFE2L2 in cancer. Gene 2020, 759, 144994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, R.W.; Sui, P.C.; He, H.T.; Ding, L. Dysregulation of non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 10956–10981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Bai, M.; Deng, T.; Liu, R.; Wang, X.; Qu, Y.; Duan, J.; Zhang, L.; Ning, T.; Ge, S.; et al. Cell-derived microvesicles mediate the delivery of miR-29a/c to suppress angiogenesis in gastric carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2016, 375, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.T.; Xing, A.Y.; Chen, X.; Ma, R.R.; Wang, Y.W.; Shi, D.B.; Zhang, H.; Li, P.; Chen, H.F.; Li, Y.H.; et al. MicroRNA-27b, microRNA-101 and microRNA-128 inhibit angiogenesis by down-regulating vascular endothelial growth factor C expression in gastric cancers. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 37458–37470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, B.; Chen, J.; Yang, N.; Peng, Y. The regulatory mechanism and biological significance of the Snail-miR590-VEGFR-NRP1 axis in the angiogenesis, growth and metastasis of gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, R.; Xu, R.; Shang, J.; He, H.; Yang, Q. MicroRNA-574-5p in gastric cancer cells promotes angiogenesis by targeting protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 3 (PTPN3). Gene 2020, 733, 144383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, A.N.; Jung, Y.; Jang, H.; Lee, E.; Bae, H.I.; Son, T.; Kwon, O.; Chung, H.Y.; Yu, W.; Lee, Y.M. Clinical significance and prognostic role of hypoxia-induced microRNA 382 in gastric adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ning, T.; Bai, M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Ying, G.; Ba, Y. miR-26a/b Inhibit Tumor Growth and Angiogenesis by Targeting the HGF-VEGF Axis in Gastric Carcinoma. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 1670–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Liang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.M.; Wang, Z.N.; Lin, X.Y. Gastric Cancer Cell-Derived Exosomal microRNA-23a Promotes Angiogenesis by Targeting PTEN. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, C.; Yang, X.; Sun, Q. High miR-718 Suppresses Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog (PTEN) Expression and Correlates to Unfavorable Prognosis in Gastric Cancer. Med. Sci. Monit 2018, 24, 5840–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, T.; Zhang, H.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Bai, M.; Sun, W.; Wang, X.; Si, Y.; Ning, T.; Zhang, L.; et al. Exosome miR-155 Derived from Gastric Carcinoma Promotes Angiogenesis by Targeting the c-MYB/VEGF Axis of Endothelial Cells. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Deng, T.; Ning, T.; Liu, R.; Liu, D.; Bai, M.; Ying, G.; Ba, Y. Exosomes Carrying MicroRNA-155 Target Forkhead Box O3 of Endothelial Cells and Promote Angiogenesis in Gastric Cancer. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2019, 15, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Deng, T.; Zhu, K.; Ning, T.; Fan, Q.; Ying, G.; et al. miR-135b Delivered by Gastric Tumor Exosomes Inhibits FOXO1 Expression in Endothelial Cells and Promotes Angiogenesis. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1772–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, B.; Shen, C.; Wu, M.; Zhao, J.; Guo, Q.; Luo, Y. miR-17-92 cluster is connected with disease progression and oxaliplatin/capecitabine chemotherapy efficacy in advanced gastric cancer patients: A preliminary study. Medicine 2018, 97, e12007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riquelme, I.; Tapia, O.; Leal, P.; Sandoval, A.; Varga, M.G.; Letelier, P.; Buchegger, K.; Bizama, C.; Espinoza, J.A.; Peek, R.M.; et al. miR-101-2, miR-125b-2 and miR-451a act as potential tumor suppressors in gastric cancer through regulation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Cell Oncol. 2016, 39, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Chen, Z.H.; Chen, D.L.; Tian, X.P.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhou, Z.W.; Gao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, C.; Zheng, Z.S.; et al. LINC01410-miR-532-NCF2-NF-kB feedback loop promotes gastric cancer angiogenesis and metastasis. Oncogene 2018, 37, 2660–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, J.; Zhi, X.; Xie, K.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, L.; Xu, H.; Xu, Z. miR-874 functions as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting angiogenesis through STAT3/VEGF-A pathway in gastric cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 1605–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aoyagi, K.; Kouhuji, K.; Yano, S.; Miyagi, M.; Imaizumi, T.; Takeda, J.; Shirouzu, K. VEGF significance in peritoneal recurrence from gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 2005, 8, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fondevila, C.; Metges, J.P.; Fuster, J.; Grau, J.J.; Palacin, A.; Castells, A.; Volant, A.; Pera, M. p53 and VEGF expression are independent predictors of tumour recurrence and survival following curative resection of gastric cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Fang, J.; Yang, C. Overexpression of both VEGF-A and VEGF-C in gastric cancer correlates with prognosis, and silencing of both is effective to inhibit cancer growth. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2013, 6, 586–597. [Google Scholar]
- Alessandrini, L.; Manchi, M.; De Re, V.; Dolcetti, R.; Canzonieri, V. Proposed Molecular and miRNA Classification of Gastric Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, C.S.; Tabernero, J.; Tomasek, J.; Chau, I.; Melichar, B.; Safran, H.; Tehfe, M.A.; Filip, D.; Topuzov, E.; Schlittler, L.; et al. Biomarker analyses in REGARD gastric/GEJ carcinoma patients treated with VEGFR2-targeted antibody ramucirumab. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Muro, K.; Cunningham, D.; Bodoky, G.; Sobrero, A.; Cascinu, S.; Ajani, J.; Oh, S.C.; Al-Batran, S.E.; Wainberg, Z.A.; et al. Biomarker analyses of second-line ramucirumab in patients with advanced gastric cancer from RAINBOW, a global, randomized, double-blind, phase 3 study. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 127, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refolo, M.G.; Lotesoriere, C.; Lolli, I.R.; Messa, C.; D’Alessandro, R. Molecular mechanisms of synergistic action of Ramucirumab and Paclitaxel in Gastric Cancers cell lines. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masood, N.; Basharat, Z.; Khan, T.; Yasmin, A. Entangling Relation of Micro RNA-let7, miRNA-200 and miRNA-125 with Various Cancers. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2017, 23, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.I.; Faheem, A. miRNA: A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Tool for Pancreatic Cancer. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2017, 27, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, G.; Tian, W.; Deng, Y.; Xu, Y. MiRNA-based Therapeutics for Lung Cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 23, 5989–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, A.; Kupcinskas, J. MicroRNAs as non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers for gastric cancer: Current insights and future perspectives. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3313–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, V.Y.; Chu, K.M. MiRNA as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 10432–10439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Pan, R.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, D. Circ_DCAF6 potentiates cell stemness and growth in breast cancer through GLI1-Hedgehog pathway. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2020, 116, 104492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Xie, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Li, B.; Li, F.; Li, F.; Cheng, Y.; Mei, H.; Meng, H.; et al. Use of lung-specific exosomes for miRNA-126 delivery in non-small cell lung cancer. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabry, D.; El-Deek, S.E.M.; Maher, M.; El-Baz, M.A.H.; El-Bader, H.M.; Amer, E.; Hassan, E.A.; Fathy, W.; El-Deek, H.E.M. Role of miRNA-210, miRNA-21 and miRNA-126 as diagnostic biomarkers in colorectal carcinoma: Impact of HIF-1alpha-VEGF signaling pathway. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2019, 454, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhasan, L. MiR-126 Modulates Angiogenesis in Breast Cancer by Targeting VEGF-A -mRNA. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 20, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Lu, H.P.; Chen, G.; Yang, J.; Huang, W.Y.; Wang, X.M.; Huang, S.P.; Gao, L.; Liu, J.; Fu, Z.W.; et al. Downregulation of miRNA-126-3p is associated with progression of and poor prognosis for lung squamous cell carcinoma. FEBS Open Bio 2020, 10, 1624–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.F.; Carlsen, A.L.; Heegaard, N.H.; Sorensen, F.B.; Jakobsen, A. Changes in circulating microRNA-126 during treatment with chemotherapy and bevacizumab predicts treatment response in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Switlik, W.Z.; Karbownik, M.S.; Suwalski, M.; Kozak, J.; Szemraj, J. Serum miR-210-3p as a Potential Noninvasive Biomarker of Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Preliminary Study. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2019, 23, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Chen, C.; Wu, Z.; Bai, P.; Li, S.; Chen, B.; Liu, R.; Zhang, K.; Li, W.; et al. Serum exosomal miR-210 as a potential biomarker for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 120, 1492–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Lin, L.; Cai, H.; Tang, M.; Wang, Z. Prognostic evaluation of microRNA-210 expression in pediatric osteosarcoma. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhu, S.; Tao, Z.; Ye, S. High circulating miR-18a, miR-20a, and miR-92a expression correlates with poor prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet Vega, A.; Pericay, C.; Moya, I.; Ferrer, A.; Dotor, E.; Pisa, A.; Casalots, A.; Serra-Aracil, X.; Oliva, J.C.; Ruiz, A.; et al. microRNA expression profile in stage III colorectal cancer: Circulating miR-18a and miR-29a as promising biomarkers. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kral, J.; Korenkova, V.; Novosadova, V.; Langerova, L.; Schneiderova, M.; Liska, V.; Levy, M.; Veskrnova, V.; Spicak, J.; Opattova, A.; et al. Expression profile of miR-17/92 cluster is predictive of treatment response in rectal cancer. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, P.P.; Huang, J.J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Yuan, J.Z.; Ma, E.M.; Liu, X.; Bai, J. Reduced serum exosomal miR-874 expression predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesanakurti, D.; Maddirela, D.R.; Chittivelu, S.; Rao, J.S.; Chetty, C. Suppression of tumor cell invasiveness and in vivo tumor growth by microRNA-874 in non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 434, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, J.; Su, X.; Cao, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y. MicroRNA874 inhibits proliferation and invasion of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells by directly targeting paired box 6. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giuppi, M.; La Salvia, A.; Evangelista, J.; Ghidini, M. The Role and Expression of Angiogenesis-Related miRNAs in Gastric Cancer. Biology 2021, 10, 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10020146
Giuppi M, La Salvia A, Evangelista J, Ghidini M. The Role and Expression of Angiogenesis-Related miRNAs in Gastric Cancer. Biology. 2021; 10(2):146. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10020146
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiuppi, Martina, Anna La Salvia, Jessica Evangelista, and Michele Ghidini. 2021. "The Role and Expression of Angiogenesis-Related miRNAs in Gastric Cancer" Biology 10, no. 2: 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10020146
APA StyleGiuppi, M., La Salvia, A., Evangelista, J., & Ghidini, M. (2021). The Role and Expression of Angiogenesis-Related miRNAs in Gastric Cancer. Biology, 10(2), 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10020146







