Structural and Predicted Functional Diversities of Bacterial Microbiome in Response to Sewage Sludge Amendment in Coastal Mudflat Soil
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Sewage Sludge
2.2. Experimental Design, and Soil Sampling
2.3. Soil Physicochemical Assays
2.4. DNA Extraction and 16S rDNA Amplicon Sequencing
2.5. Data Processing of Bioinformatics
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Influences of Sewage Sludge on Soil Physicochemical Properties
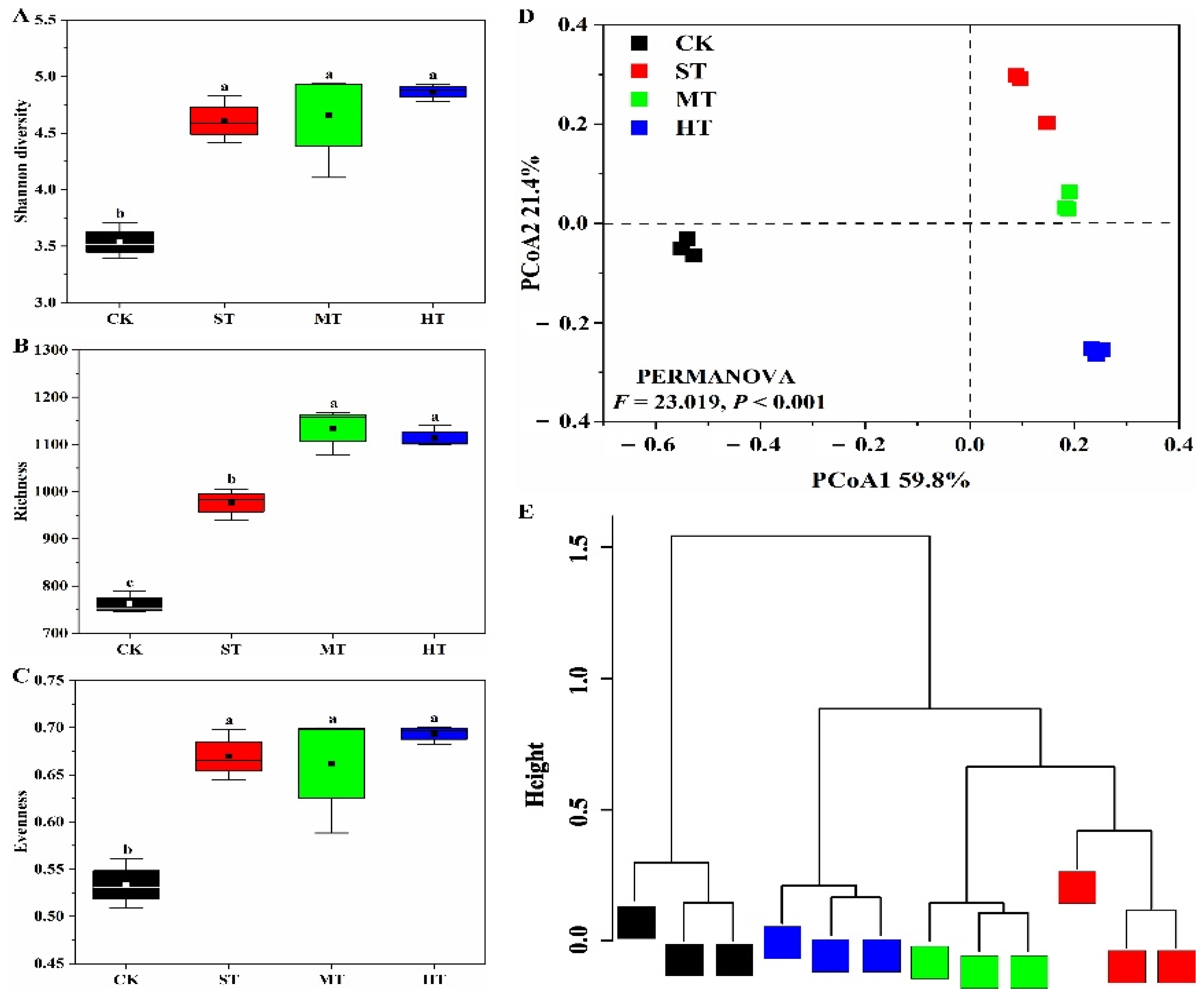
3.2. α- and β-Diversity Analysis of Bacterial Community
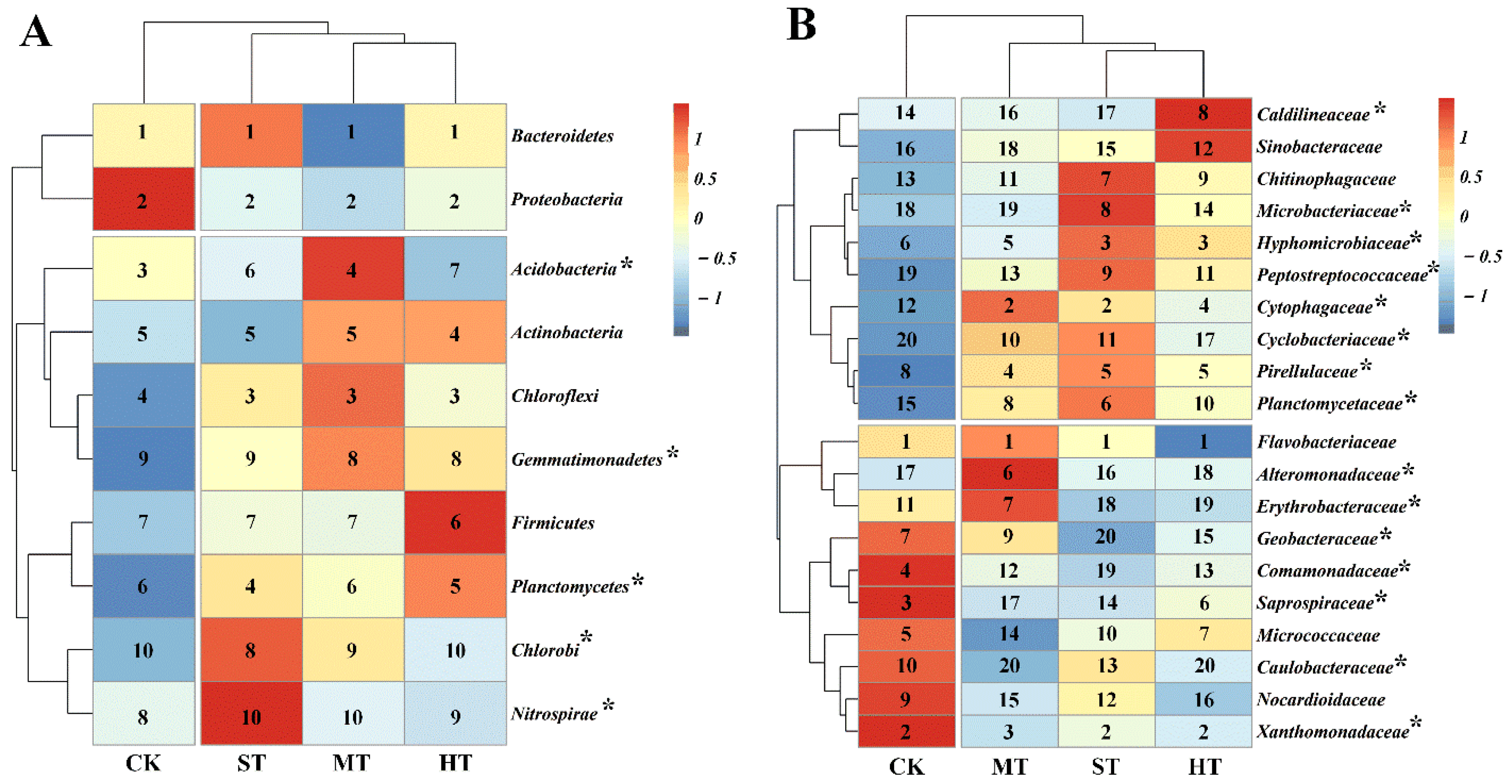
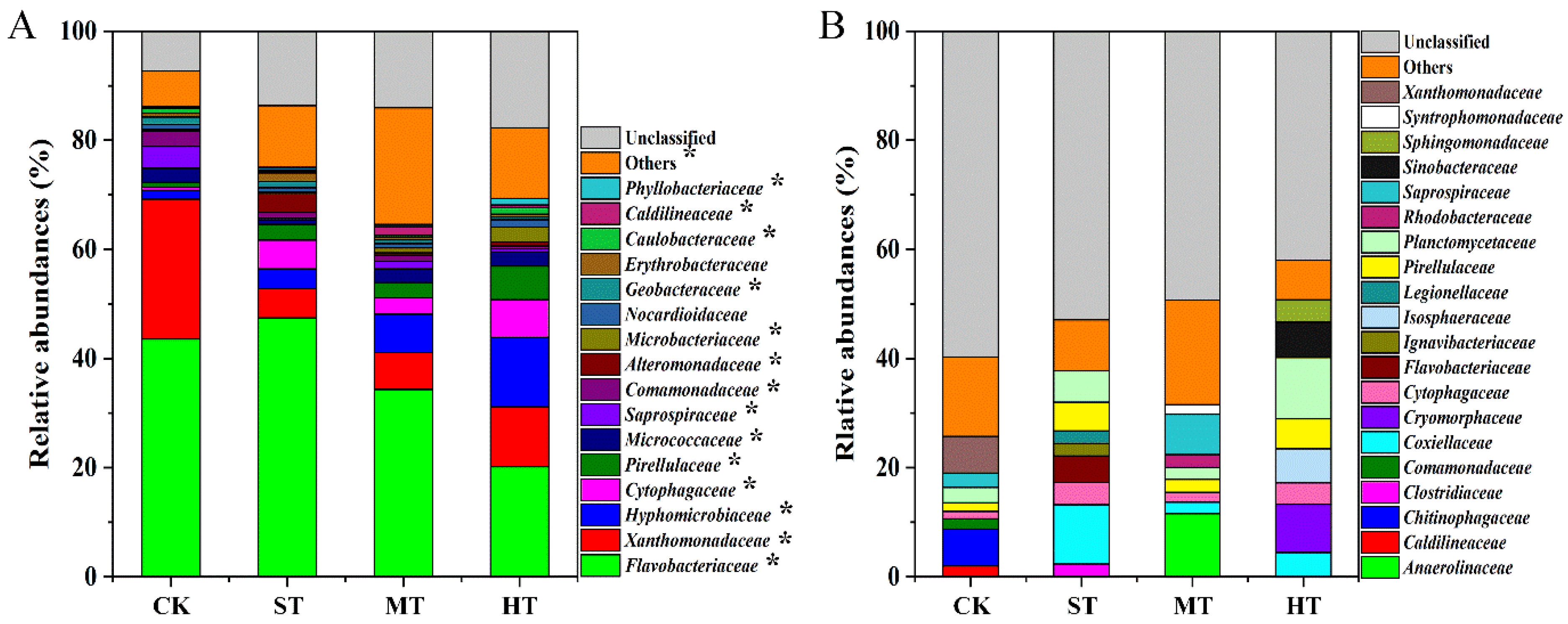
3.3. Soil Bacterial Community Composition
3.4. Core and Unique Bacterial Microbiomes
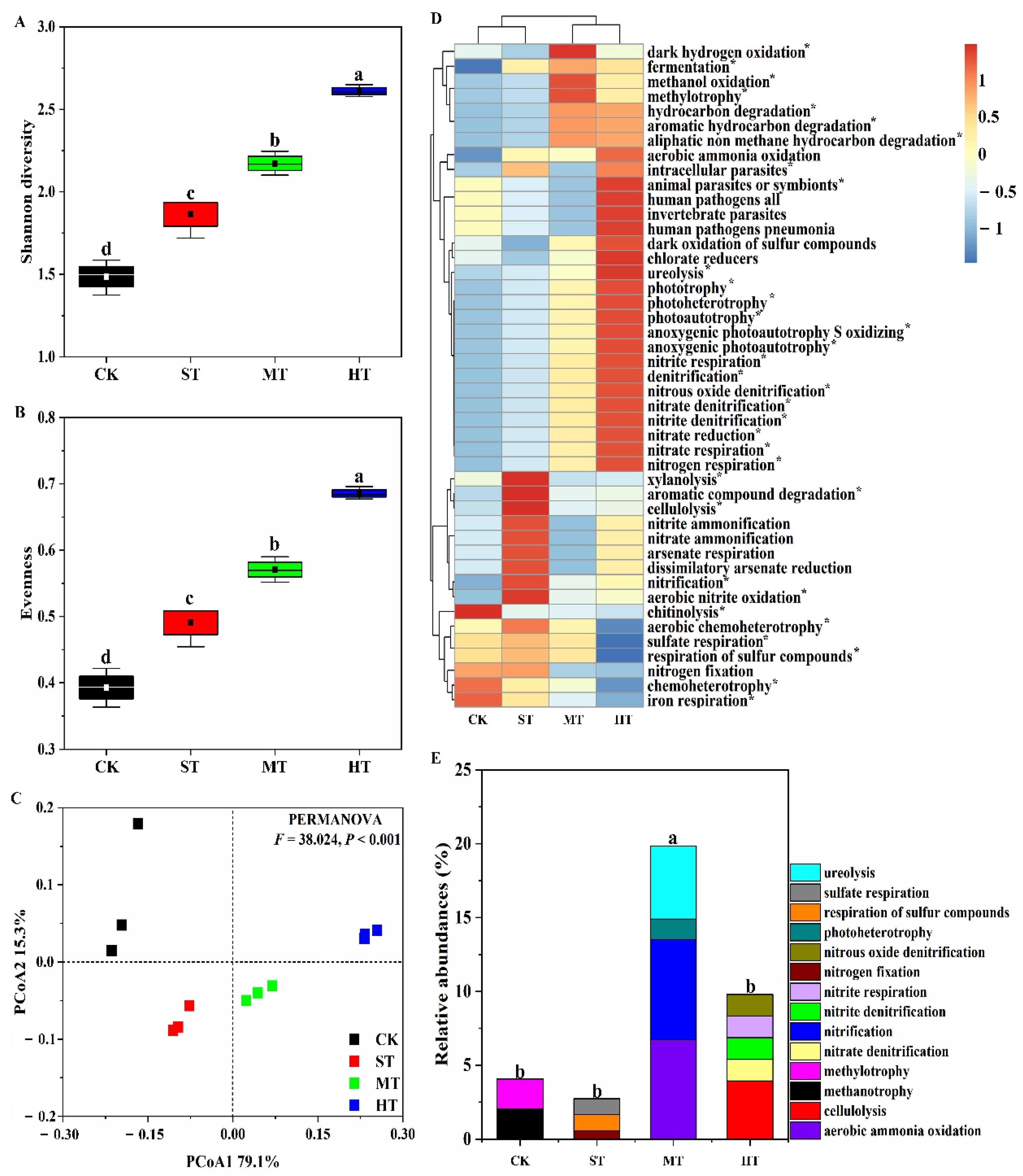
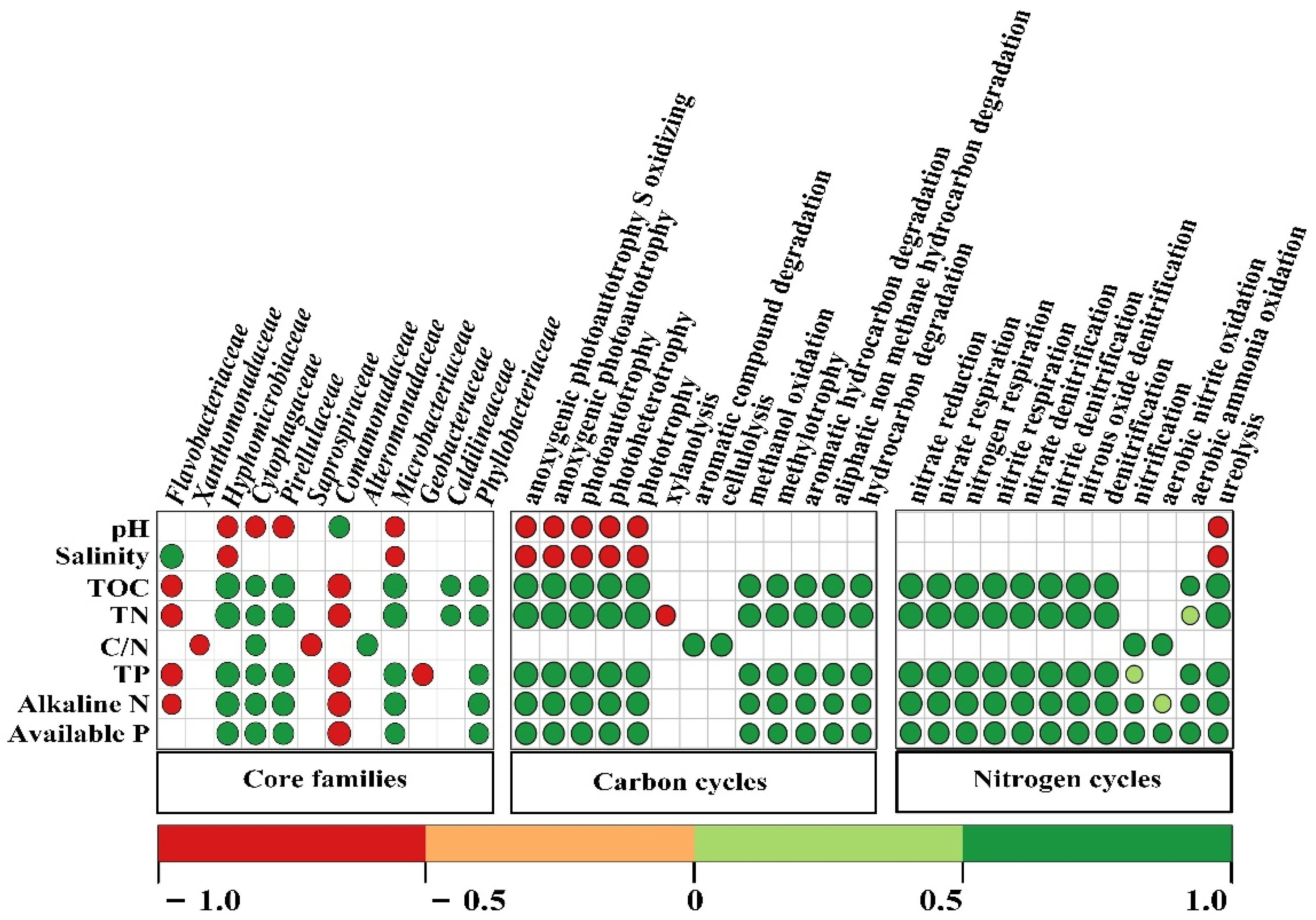
3.5. Functional Prediction of Core and Unique OTUs
3.6. Correlations of Soil Bacterial Community and Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Sewage Sludge Significantly Alleviated Saline–Alkali Stresses and Elevated Nutrient Availability in Coastal Mudflat Soil
4.2. Sewage Sludge-Amended Coastal Mudflat Soil Harboring Diverse Bacterial Community Structure and Diversity
4.3. Sewage Sludge Application Potentially Contributed to the Predicted Functional Diversity Improvement in Mudflat Soil
4.4. Bacterial Community and Predicted Functional Diversities Promotion in Coastal Mudflat Soil Might Be Driven by the Microhabitat Modification Induced by Sewage Sludge Application
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shao, H.B.; Chu, L.Y.; Lu, H.Y.; Qi, W.C.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Kuang, S.P.; Tang, B.P.; Wong, V. Towards sustainable agriculture for the salt-affected soil. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.C.; Zuo, W.G.; Shao, H.B.; Msei, L.J.; Tang, B.P.; Gu, C.H.; Wang, X.K.; Guan, Y.X. Eastern China coastal mudflats: Salt-soil amendment with sewage sludge. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3803–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.F.; Pu, L.J.; Zhu, M.; Meadows, M.; Sun, L.C.; Wu, T.; Bu, X.G.; Xu, Y. Differential effects of various reclamation treatments on soil characteristics: An experimental study of newly reclaimed tidal mudflats on the east China coast. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wall, G. Mudflat development in Jiangsu Province, China: Practices and experiences. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2010, 53, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.Z.; Wong, M.H. Current status of coastal zone issues and management in China: A review. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.C.; Zuo, W.G.; Yan, Y.Y.; Gu, C.H.; Guan, Y.X.; Mei, L.J.; Xue, W.J.; Shan, Y.H.; Feng, K. Sewage sludge amendment combined with green manuring to a coastal mudflat salt-soil in eastern China: Effects on soil physicochemical properties and maize yield. Int. J. Agron. 2017, 2017, 8526598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.H.; Wan, X.H.; Zhu, X.M.; Bao, X.W. Modeling studies of the far-field effects of tidal flat reclamation on tidal dynamics in the East China Seas. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 133, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Cai, Y.L.; Ran, W.R.; Zhao, X.L.; Jiang, H. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of soil salinity after the establishment of vegetation on a coastal saline field. Catena 2015, 127, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.F.; Pu, L.J.; Zhu, M.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.H. Linkage between soil salinization indicators and physicochemical properties in a long-term intensive agricultural coastal reclamation area, Eastern China. J. Soil Sediment. 2019, 19, 3699–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.C.; Xue, W.J.; Yan, Y.Y.; Zuo, W.G.; Shan, Y.H.; Feng, K. The challenge of improving coastal mudflat soil: Formation and stability of organo-mineral complexes. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorenush, M.H.; Sepaskhah, A.R. Modelling capillary rise and soil salinity for shallow saline water table under irrigated and non-irrigated conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 61, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.H.; Liu, L.P.; Shao, T.Y.; Shao, H.B.; Liu, Z.P. Developing and sustainably utilize the coastal mudflat areas in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qadir, M.; Schubert, S.; Ghafoor, A.; Murtaza, G. Amelioration strategies for sodic soils: A review. Land Degrad. Dev. 2001, 12, 357–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.C.; Tao, T.Y.; Gu, C.H.; Wang, L.; Feng, K.; Shan, Y.H. Mudflat soil amendment by sewage sludge: Soil physicochemical properties, perennial ryegrass growth, and metal uptake. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2013, 59, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.Q.; Yu, Y.N.; Gao, R.W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, R.; Long, X.H.; Shen, Q.R.; Chen, W.; Cai, F. High-throughput absolute quantification sequencing reveals the effect of different fertilizer applications on bacterial community in a tomato cultivated coastal saline soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Shao, H.B.; Shao, C.Y.; Chen, P.; Zhao, S.J.; Brestic, M.; Chen, X.B. Physiological adaptive mechanisms of plants grown in saline soil and implications for sustainable saline agriculture in coastal zone. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2013, 35, 2867–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; He, W.J.; Bian, L.X.; Zhang, Z.S.; Tang, X.L.; An, M.X.; Li, L.X.; Han, G.X. Salt adaptability in a halophytic soybean (Glycine soja) involves photosystems coordination. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.P.; Long, X.H.; Shao, H.B.; Liu, Z.P.; Tao, Y.; Zhou, Q.S.; Zong, J.Q. Ameliorants improve saline–alkaline soils on a large scale in northern Jiangsu Province; China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.N.L.; Dalal, R.C.; Greene, R.S.B. Carbon dynamics of sodic and saline soils following gypsum and organic material additions: A laboratory incubation. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2009, 41, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.G.; Xu, K.D.; Zhang, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Gu, C.H.; Bai, Y.C.; Shan, Y.H.; Dai, Q.G. Heavy metal distribution and uptake by maize in a mudflat soil amended by vermicompost derived from sewage sludge. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 30154–30166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, H.; Clarke, B.O.; Pritchard, D.L.; Meehan, B.; Beshah, F.; Smith, S.R.; Porter, N.A. A critical review of nitrogen mineralization in biosolids-amended soil, the associated fertilizer value for crop production and potential for emissions to the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 1310–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agamuthu, P.; Tan, Y.S.; Fauziah, S.H. Bioremediation of hydrocarbon contaminated soil using selected organic wastes. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 18, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.G.; Gu, C.H.; Zhang, W.J.; Xu, K.D.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.C.; Shan, Y.H.; Dai, Q.G. Sewage sludge amendment improved soil properties and sweet sorghum yield and quality in a newly reclaimed mudflat land. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.G.; Bai, Y.C.; Lv, M.; Tang, Z.H.; Ding, C.; Gu, C.H.; Shan, Y.H.; Dai, Q.G.; Li, M. Sustained effects of one-time sewage sludge addition on rice yield and heavy metals accumulation in salt-affected mudflat soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 7476–7490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.A.; Zedler, J.B.; Falk, D.A. Ecological Theory and Restoration Ecology; Foundations of Restoration Ecology; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; pp. 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldford, J.E.; Lu, N.; Bajić, D.; Estrela, S.; Tikhonov, M.; Sanchez-Gorostiaga, A.; Segrè, D.; Mehta, P.; Sanchez, A. Emergent simplicity in microbial community assembly. Science 2018, 361, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Qi, L.L.; Li, W.M.; Hu, B.X.; Dai, Z.X. Bacterial community variations with salinity in the saltwater-intruded estuarine aquifer. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollister, E.B.; Engledow, A.S.; Hammett, A.J.M.; Provin, T.L.; Wilkinson, H.H.; Gentry, T.J. Shifts in microbial community structure along an ecological gradient of hypersaline soils and sediments. ISME J. 2010, 4, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Druzhinina, I.S.; Pan, X.Y.; Yuan, Z.L. Microbially mediated plant salt tolerance and microbiome-based solutions for saline agriculture. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1245–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kindi, S.; Abed, R.M. Effect of biostimulation using sewage sludge; soybean meal; and wheat straw on oil degradation and bacterial community composition in a contaminated desert soil. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curci, M.; Lavecchia, A.; Cucci, G.; Lacolla, G.; Corato, U.D.; Crecchio, C. Short-term effects of sewage sludge compost amendment on semiarid soil. Soil Syst. 2020, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarick, K.A.; Doxtader, K.G.; Redente, E.F.; Brobst, R.B. Biosolids effects on microbial activity in shrubland and grassland soils. Soil Sci. 2004, 169, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S.A.P.; Bettiol, W.; Cerri, C.C. Effect of sewage sludge on microbial biomass, basal respiration, metabolic quotient and soil enzymatic activity. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2005, 30, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Azhari, N.; Lainé, S.; Sappin-Didier, V.; Beguet, J.; Rouard, N.; Philippot, L.; Martin-Laurent, F. Long-term impact of 19 years’ farmyard manure or sewage sludge application on the structure; diversity and density of the protocatechuate-degrading bacterial community. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 158, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guo, K.L.; Huang, L.; Ji, Z.Y.; Jiang, H.M.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.F. Responses of absolute and specific enzyme activity to consecutive application of composted sewage sludge in a Fluventic Ustochrept. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, B.C.; Figueiredo, R.S.; Araújo, J.C.; Matos, A.T. Bacterial community dynamics in tropical soil after sewage sludge amendment. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 82, 2937–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattana, S.; Petrovičová, B.; Landi, L.; Gelsomino, A.; Cortés, P.; Ortiz, O.; Renella, G. Sewage sludge processing determines its impact on soil microbial community structure and function. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 75, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.J.; Yang, J.S.; Wang, X.P.; Xie, W.P.; Zheng, F.L.; Li, H.Q.; Tang, C.; Zhu, H. Response of soil characteristics and bacterial communities to nitrogen fertilization gradients in a coastal salt-affected agroecosystem. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.F.; Wu, T.; Zhu, M.; Jiang, G.J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.H.; Pu, L.J. Comparison of random forest and multiple linear regression models for estimation of soil extracellular enzyme activities in agricultural reclaimed coastal saline land. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.K. Soil Agricultural Chemical Analysis Method; China Agricultural Science Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Ni, T.; Li, Y.; Xiong, W.; Ran, W.; Shen, B.; Shen, Q.R.; Zhang, R.F. Responses of bacterial communities in arable soils in a rice-wheat cropping system to different fertilizer regimes and sampling times. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ni, T.; Li, J.; Lu, Q.; Fang, Z.Y.; Huang, Q.W.; Zhang, R.F.; Li, R.; Shen, B.; Shen, Q.R. Effects of organic–inorganic compound fertilizer with reduced chemical fertilizer application on crop yields, soil biological activity and bacterial community structure in a rice–wheat cropping system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 99, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, D.; Price, M.N.; Goodrich, J.; Nawrocki, E.P.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Probst, A.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R.; Hugenholtz, P. An improved Greengenes taxonomy with explicit ranks for ecological and evolutionary analyses of bacteria and archaea. ISME J. 2012, 6, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2007, 73, 5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louca, S.; Parfrey, L.W.; Doebeli, M. Decoupling function and taxonomy in the global ocean microbiome. Science 2016, 353, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.J. Permutational multivariate analysis of variance. Dep. Stat. Univ. Auckl. Auckl. 2005, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldro, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.C.; Zang, C.Y.; Gu, M.J.; Gu, C.H.; Shao, H.B.; Guan, Y.X.; Wang, X.K.; Zhou, X.J.; Shan, Y.H.; Feng, K. Sewage sludge as an initial fertility driver for rapid improvement of mudflat salt-soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, I.; Murtaza, G.; Zahir, Z.A.; Farooq, M. Effect of humic and fulvic acid transformation on cadmium availability to wheat cultivars in sewage sludge amended soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 16071–16079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.L.; Bai, J.H.; Jia, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Q.Q.; Lu, Q.Q. Shifts of soil microbial community composition along a short-term invasion chronosequence of Spartina alterniflora in a Chinese estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, M.J.; Athamneh, B.M. Changes in soil fertility and plant uptake of nutrients and heavy metals in response to sewage sludge application to calcareous soils. J. Agric. 2004, 3, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ludibeth, S.M.; Marina, I.E.; Vicenta, E.M. Vermicomposting of sewage sludge: Earthworm population and agronomic advantages. Compost Sci. Util. 2012, 20, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latare, A.M.; Kumar, O.; Singh, S.K.; Gupta, A. Direct and residual effect of sewage sludge on yield; heavy metals content and soil fertility under rice–wheat system. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 69, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacprzak, M.; Neczaj, E.; Fijakowski, K.; Grobelak, A.; Grosser, A.; Worwag, M.; Rorat, A.; Brattebo, H.; Almås, Å.; Singh, B.R. Sewage sludge disposal strategies for sustainable development. Environ. Res. 2017, 156, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, E.M.; Alrumman, S.A.; El-Bebany, A.F.; Hesham, A.E.L.; Taher, M.A.; Fawy, K.F. The effects of different sewage sludge amendment rates on the heavy metal bioaccumulation; growth and biomass of cucumbers (Cucumis sativus L.). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 16371–16382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florentino, A.L.; Ferraz, A.V.; Gonçalves, J.L.M.; Asensiod, V.; Muraoka, T.; Dias, C.T.S.; Nogueira, T.A.R.; Capra, G.F.; Abreu-Junior, C.H. Long-term effects of residual sewage sludge application in tropical soils under Eucalyptus plantations. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellier, A.; Gauquelin, T.; Baldy, V.; Ballini, C. Effect of organic amendment on soil fertility and plant nutrients in a post-fire Mediterranean ecosystem. Plant Soil. 2014, 376, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marando, G.; Jiménez, P.; Hereter, A.; Julià, M.; Ginovart, M.; Bonmatí, M. Effects of thermally dried and composted sewage sludges on the fertility of residual soils from limestone quarries. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2011, 49, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.S.; Riaz, M.; Shahzad, S.M.; Yasmeen, T.; Ashraf, M.; Siddique, M.; Mubarik, M.S.; Bragazza, L.; Buttler, A. Fresh and composted industrial sludge restore soil functions in surface soil of degraded agricultural land. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.F.; Li, P.F.; Zhong, J.X.; Shen, Z.J.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.T.; Isabwe, A.; Zhu, X.Y.; Ding, Q.S.; Zhang, S.; et al. Spartina alterniflora invasion alters soil bacterial communities and enhances soil N2O emissions by stimulating soil denitrification in mangrove wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlemann, D.P.; Labrenz, M.; Jürgens, K.; Bertilsson, S.; Waniek, J.J.; Andersson, A.F. Transitions in bacterial communities along the 2000 km salinity gradient of the Baltic Sea. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calleja-Cervantes, M.E.; Aparicio-Tejo, P.M.; Villadas, P.J.; Irigoyen, I.; Irañeta, J.; Fernández-González, A.J.; Fernández-López, M.; Menéndez, S. Rational application of treated sewage sludge with urea increases GHG mitigation opportunities in Mediterranean soils. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 238, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shade, A.; Handelsman, J. Beyond the Venn diagram: The hunt for a core microbiome. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aagaard, K.; Ma, J.; Antony, K.M.; Ganu, R.; Petrosino, J.; Versalovic, J. The placenta harbors a unique microbiome. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 237ra65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Oliverio, A.M.; Brewer, T.E.; Benavent-González, A.; Eldridge, D.J.; Bardgett, R.D.; Maestre, F.T.; Singh, B.K.; Fierer, N. A global atlas of the dominant bacteria found in soil. Science 2018, 359, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, G.; Tang, X.M.; Shao, K.Q.; Gong, Y. Pyrosequencing analysis of bacterial communities in Lake Bosten; a large brackish inland lake in the arid northwest of China. Can. J. Microbiol. 2016, 62, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, P.; Mahapatra, S.; Mohapatra, M.; Kim, J.Y.; Adhya, T.K.; Raina, V.; Suar, M.; Pattnaik, A.K.; Rastogi, G. Salinity and macrophyte drive the biogeography of the sedimentary bacterial communities in a brackish water tropical coastal lagoon. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, W.S.; Zhang, X.C.; Zhu, F.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.F.; Shi, Y.; Hartley, W.; Xue, S.G. Appropriate human intervention stimulates the development of microbial communities and soil formation at a long-term weathered bauxite residue disposal area. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usharani, B. Metagenomics study of the microbes in constructed wetland system treating sewage. Int. Lett. Nat. Sci. 2019, 74, 26–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraishi, A.; Imhoff, J.F. Bacteria Rhodoplanes. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Academic: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.; Condron, L.M.; Clough, T.J.; Fiers, M.; Stewart, A.; Hill, R.A.; Sherlock, R.R. Biochar induced soil microbial community change: Implications for biogeochemical cycling of carbon; nitrogen and phosphorus. Pedobiologia 2011, 54, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernat, K.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Zielińska, M.; Wojnowska-Baryła, I.; Wersocka, J. Valorisation of the selectively collected organic fractions of municipal solid waste in anaerobic digestion. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 148, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Feng, L.J.; Yang, G.F.; Mu, J. The carbon source separation from fermented sewage sludge for stimulation of denitrification and bisphenol A removal. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 3595–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolińska, A.; Kuźniar, A.; Zielenkiewicz, U.; Banach, A.; Błaszczyk, M. Indicators of arable soils fatigue–bacterial families and genera: A metagenomic approach. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, S.; Lavorel, S.; Chapin, F.S.; Tecco, P.A.; Gurvich, D.E.; Grigulis, K. Functional diversity-at the crossroads between ecosystem functioning and environmental filters. In Terrestrial Ecosystems in a Changing World; Global Change—The IGBP Series; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston-Mafham, J.; Boddy, L.; Randerson, P.F. Analysis of microbial community functional diversity using sole-carbon-source utilisation profiles—A critique. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2002, 42, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, I.; Avilés, M.; Aguirreolea, J.; Sánchez-Díaz, M. Effect of sanitized and non-sanitized sewage sludge on soil microbial community and the physiology of pepper plants. Plant Soil. 2008, 310, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frac, M.; Oszust, K.; Lipiec, J. Community level physiological profiles (CLPP), characterization and microbial activity of soil amended with dairy sewage sludge. Sensors 2012, 12, 3253–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Dai, J.L.; Wang, R.Q.; Zhang, J. Effects of long-term sewage irrigation on agricultural soil microbial structural and functional characterizations in Shandong; China. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2008, 44, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, R.F.; Pazianotto, R.A.A. Microbial activities in soil cultivated with corn and amended with sewage sludge. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanomi, G.; Lorito, M.; Vinale, F.; Woo, S.L. Organic amendments; beneficial microbes; and soil microbiota: Toward a unified framework for disease suppression. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2018, 56, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.B.; Cai, Z.C. Differential responses of soil bacterial community and functional diversity to reductive soil disinfestation and chemical soil disinfestation. Geoderma 2019, 348, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, J.R.; Viger, M.; Arnold, E.C.; Harris, Z.M.; Ventura, M.; Miglietta, F.; Girardin, C.; Edwards, R.J.; Rumpel, C.; Fornasier, F.; et al. Biochar alters the soil microbiome and soil function: Results of next-generation amplicon sequencing across Europe. GCB Bioenergy 2017, 9, 591–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Peng, C.H.; Yang, B.; Song, H.X.; Li, Q.; Jiang, L.; Wei, G.; Wang, K.F.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.R.; et al. Contrasting soil bacterial community; diversity; and function in two forests in China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.T.; Rochelle-Newall, E.; Ribolzi, O.; Janeau, J.L.; Huon, S.; Latsachack, K.; Pommier, T. Land use strongly influences soil organic carbon and bacterial community export in runoff in tropical uplands-. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Valdez, F.; Fernández-Luqueño, F.; Luna-Guido, M.L.; Marsch, R.; Olalde-Portugal, V.; Dendooven, L. Microorganisms in sewage sludge added to an extreme alkaline saline soil affect carbon and nitrogen dynamics. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 45, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatt, C.G.; Liu, Z.F.; Ludwig, M.; Kühl, M.; Jensen, S.I.; Bryant, D.A.; Ward, D.M. Temporal metatranscriptomic patterning in phototrophic Chloroflexi inhabiting a microbial mat in a geothermal spring. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frąc, M.; Oszust, K.; Lipiec, J.; Jezierska-Tys, S.; Nwaichi, E.O. Soil microbial functional and fungal diversity as influenced by municipal sewage sludge accumulation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 8891–8908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, J.I.; Nicol, G.W. Archaeal and bacterial ammonia-oxidisers in soil: The quest for niche specialisation and differentiation. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Hu, B.X.; Ren, H.J.; Zhang, J. Composition and functional diversity of microbial community across a mangrove-inhabited mudflat as revealed by 16S rDNA gene sequences. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timonen, S.; Sinkko, H.; Sun, H.; Sietio, O.M.; Rinta-Kanto, J.M.; Kiheri, H.; Heinonsalo, J. Ericoid roots and mycospheres govern plant-specific bacterial communities in boreal forest humus. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 73, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuerst, J.A.; Sagulenko, E. Beyond the bacterium: Planctomycetes challenge our concepts of microbial structure and function. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara, R.; Ikenaga, M.; Dean, A.L.; Pisani, C.; Boyer, J.N. Changes in sediment bacterial community in response to long-term nutrient enrichment in a subtropical seagrass-dominated estuary. Microb. Ecol. 2014, 68, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Chen, X.P.; Nie, M.; Fang, S.B.; Tang, B.P.; Quan, Z.X.; Li, B.; Fang, C.M. Effects of Spartina alterniflora invasion on the abundance; diversity; and community structure of sulfate reducing bacteria along a successional gradient of coastal salt marshes in China. Wetlands 2017, 37, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Huang, H.; Biber, P.; Bethel, M. Litter decomposition of Spartina alterniflora and Juncus roemerianus: Implications of climate change in salt marshes. J. Coast. Res. 2017, 33, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.B.; Liu, Y.Q.; Lin, X.G.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zeng, J.; Hou, J.Z.; Yang, Y.P.; Yao, T.D.; Knight, R.; Chu, H.Y. Geographic distance and pH drive bacterial distribution in alkaline lake sediments across Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 2457–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Deng, Y.C.; Che, R.X.; Han, C.; Zhong, W.H. Bacterial community composition in soils covered by different vegetation types in the Yancheng tidal marsh. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 21517–21532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousk, J.; Bååth, E.; Brookes, P.C.; Lauber, C.L.; Lozupone, C.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rath, K.M.; Fierer, N.; Murphy, D.V.; Rousk, J. Linking bacterial community composition to soil salinity along environmental gradients. ISME J. 2019, 13, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xie, W.X.; Cui, Y.Q.; Fan, Q.C. Distribution characteristics of available sulfur content in soils of Spartina alterniflora tidal flat and mudflat in Jiaozhou Bay. Wetland Sci. 2017, 15, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neina, D. The role of soil pH in plant nutrition and soil remediation. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2019, 2019, 5794869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, Z.R.; Feng, X.; Liu, H.Y.; Jiang, Y. Variations in soil bacterial taxonomic profiles and putative functions in response to straw incorporation combined with N fertilization during the maize growing season. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 283, 106578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Reich, P.B.; Khachane, A.N.; Campbell, C.D.; Thomas, N.; Freitag, T.E.; Abu Al-Soud, W.; Sørensen, S.; Bardgett, R.D.; Singh, B.K. It is elemental: Soil nutrient stoichiometry drives bacterial diversity. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1176–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, S.M. Microbial community ecology: Function over phylogeny. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 0032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, S.; Whalen, J.K. Biochemical cycling of nitrogen and phosphorus in biochar-amended soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Ladau, J.; Clemente, J.C.; Leff, J.W.; Owens, S.M.; Pollard, K.S.; Knight, R.; Gilbert, J.A.; McCulley, R.L. Reconstructing the microbial diversity and function of pre-agricultural tallgrass prairie soils in the United States. Science 2013, 342, 621–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldrop, M.P.; Firestone, M.K. Response of microbial community composition and function to soil climate change. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 52, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Y.; Zhou, X.; Guo, D.; Zhao, J.H.; Yan, L.; Feng, G.Z.; Gao, Q.; Yu, H.; Zhao, L.P. Soil pH is the primary factor driving the distribution and function of microorganisms in farmland soils in northeastern China. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Sun, Q.; Ji, L.D.; Zhang, J.X. Influence of fertilizers and soil conditioners on soil bacterial diversity and the quality of wine grape (Cabernet Sauvignon). Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 4277–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muwawa, E.M.; Obieze, C.C.; Makonde, H.M.; Jefwa, J.M.; Kahindi, J.H.; Khasa, D.P. 16S rRNA gene amplicon-based metagenomic analysis of bacterial communities in the rhizospheres of selected mangrove species from Mida Creek and Gazi Bay, Kenya. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.X.; Qiu, X.W.; Zhang, J.B.; Tao, C.Y. Effects of seaweed fertilizer on enzyme activities; metabolic characteristics; and bacterial communities during maize straw composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 286, 121375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.P.; Ai, C.; Zhou, W.; Liang, G.Q.; He, P. Structure and assembly cues for rhizospheric nirK-and nirS-type denitrifier communities in long-term fertilized soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 119, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatments § | pH | Salinity (g·kg−1) | TOC (g·kg−1) | TN (g·kg−1) | TP (g·kg−1) | AN (mg·kg−1) | AP (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 8.91 ± 0.18 a | 6.33 ± 1.23 a | 3.96 ± 0.98 c | 0.47 ± 0.01 c | 0.81 ± 0.02 c | 32.5 ± 1.0 c | 27.2 ± 3.1 c |
| ST | 8.59 ± 0.04 ab | 4.65 ± 0.36 ab | 8.80 ± 1.52 b | 0.56 ± 0.04 c | 1.32 ± 0.14 b | 100.7 ± 10.8 b | 77.5 ± 4.4 b |
| MT | 8.53 ± 0.10 ab | 4.44 ± 0.04 ab | 12.11 ± 0.64 b | 1.08 ± 0.02 b | 1.39 ± 0.06 b | 98.6 ± 14.1 b | 78.8 ± 2.9 ab |
| HT | 8.28 ± 0.10 b | 3.50 ± 0.38 b | 17.64 ± 1.67 a | 1.38 ± 0.09 a | 2.69 ± 0.13 a | 163.4 ± 2.1 a | 92.3 ± 6.0 a |
| Treatments § | CK | ST | MT | HT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 106 * | |||
| ST | 116 | 136 | ||
| MT | 137 | 285 | 112 | |
| HT | 38 | 213 | 272 | 95 |
| Core OTUs | 215 | 215 | 215 | 215 |
| Total OTUs | 514 | 718 | 764 | 634 |
| Environmental Factors | Community Composition # | Community Structure $ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon Diversity | Richness | Evenness | PCoA1 | |
| pH | −0.76 ** | |||
| Salinity | −0.64 * | −0.70 * | −0.71 ** | |
| TOC | 0.71 ** | 0.81 ** | 0.70 * | 0.93 ** |
| TN | 0.83 ** | 0.87 ** | 0.80 ** | 0.94 ** |
| TP | 0.82 ** | 0.76 ** | 0.83 ** | 0.86 ** |
| AN | 0.62 * | 0.85 ** | ||
| AP | 0.58 * | 0.61 * | 0.64 * | 0.77 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shen, C.; Xu, L.; Yi, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zuo, W.; Gu, C.; Shan, Y.; Bai, Y. Structural and Predicted Functional Diversities of Bacterial Microbiome in Response to Sewage Sludge Amendment in Coastal Mudflat Soil. Biology 2021, 10, 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121302
Li Y, Wang Y, Shen C, Xu L, Yi S, Zhao Y, Zuo W, Gu C, Shan Y, Bai Y. Structural and Predicted Functional Diversities of Bacterial Microbiome in Response to Sewage Sludge Amendment in Coastal Mudflat Soil. Biology. 2021; 10(12):1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121302
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yunlong, Yimin Wang, Chao Shen, Lu Xu, Siqiang Yi, Yilin Zhao, Wengang Zuo, Chuanhui Gu, Yuhua Shan, and Yanchao Bai. 2021. "Structural and Predicted Functional Diversities of Bacterial Microbiome in Response to Sewage Sludge Amendment in Coastal Mudflat Soil" Biology 10, no. 12: 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121302
APA StyleLi, Y., Wang, Y., Shen, C., Xu, L., Yi, S., Zhao, Y., Zuo, W., Gu, C., Shan, Y., & Bai, Y. (2021). Structural and Predicted Functional Diversities of Bacterial Microbiome in Response to Sewage Sludge Amendment in Coastal Mudflat Soil. Biology, 10(12), 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121302







