Comparative Pathogenicity of Aeromonas spp. in Cultured Red Hybrid Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × O. mossambicus)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Aeromonas spp.
2.2. Screening for Myo-Inositol Utilizing Strains and Blood Agar Characteristics
2.3. Acclimatization of Red Hybrid Tilapia
2.4. Preparation of Different Concentrations of Aeromonas spp.
2.5. Pathogenicity Study
2.6. Histopathological Assessment
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
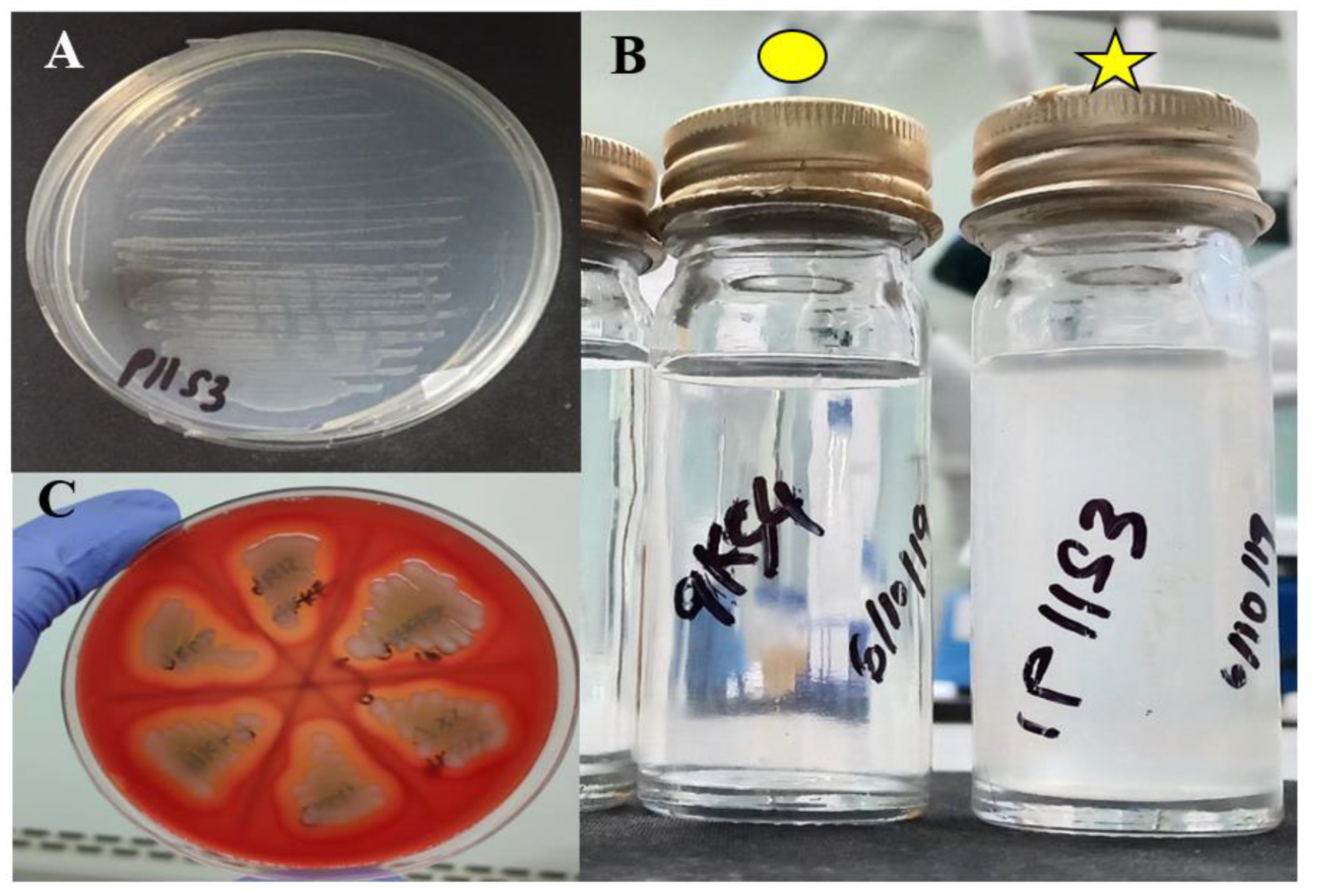
3.1. Characterization of Aeromonas spp.
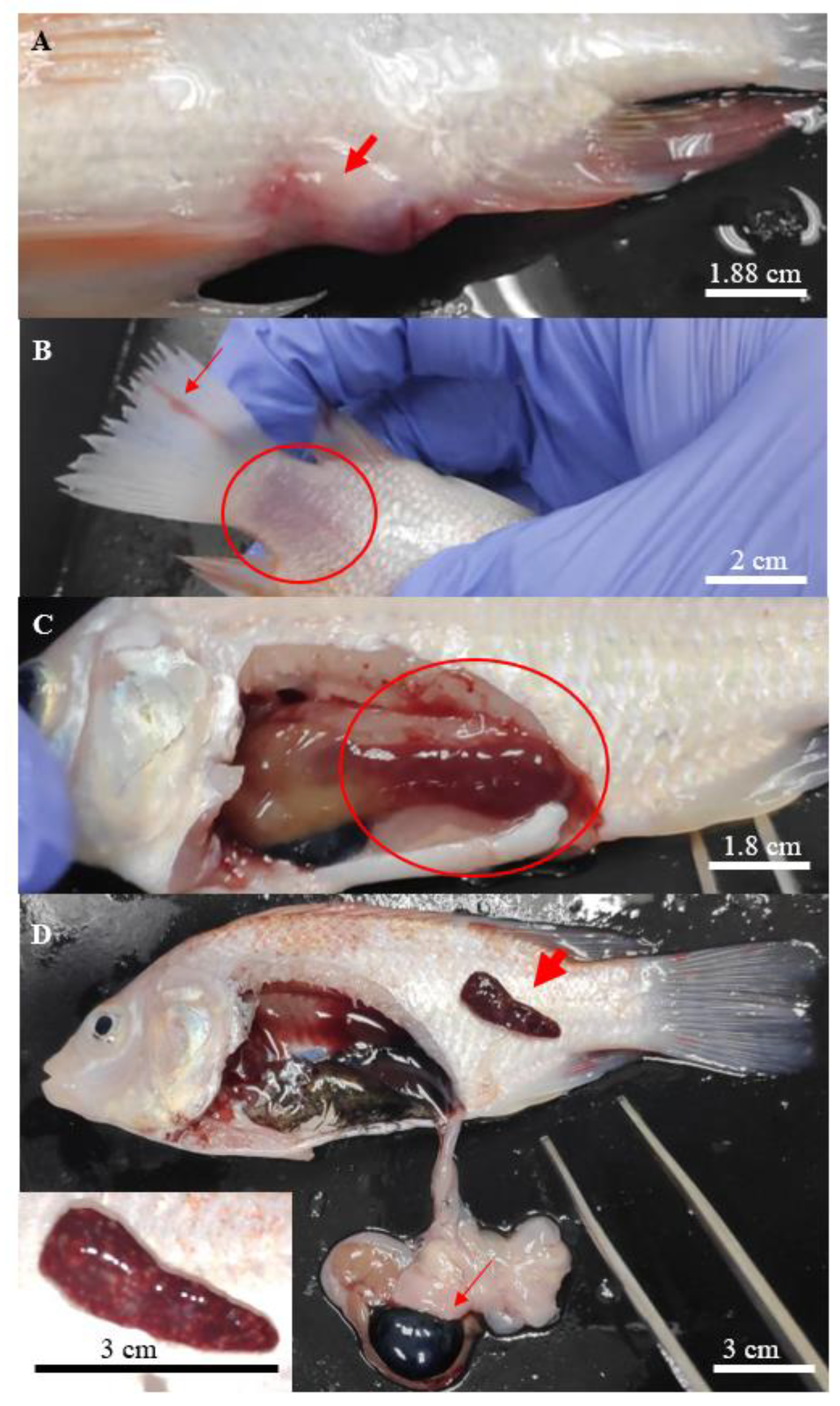
3.2. Clinicopathological Changes of Infected Fish
3.3. Lethal Dose of Aeromonas spp. in Red Hybrid Tilapia
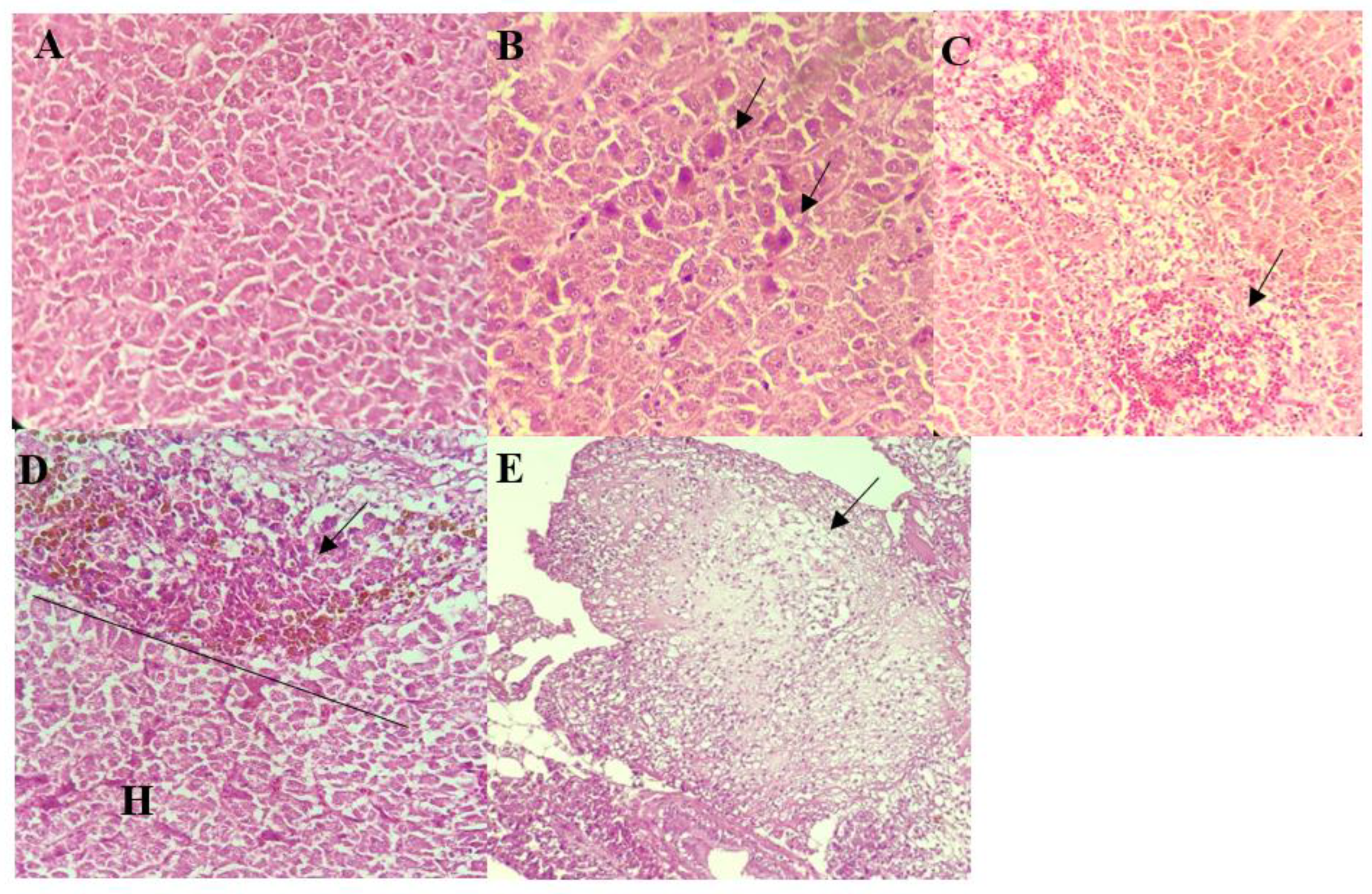
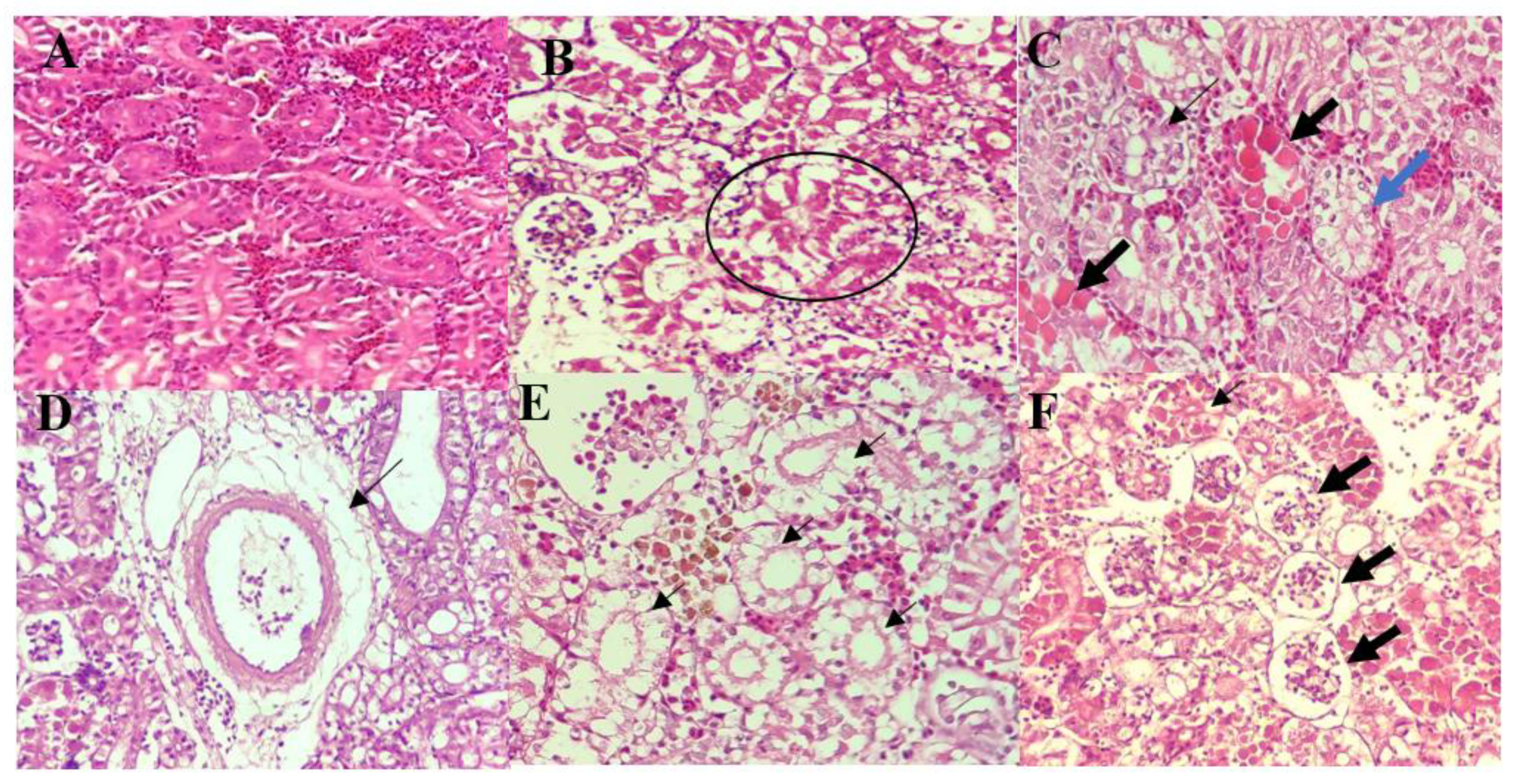
3.4. Histopathological Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Species | Strain | Virulence Genes | NCBI Accession Number | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ahp | fla | act | ela | hly | alt | lip | aer | |||
| A. dhakensis | 1P11S3 * | + | + | + | + | + | MT371976 | |||
| A. dhakensis | 4PS2 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | MT372009 |
| A. hydrophila | 8TK3 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | MT372063 |
| A. veronii | 6TS5 | + | + | + | + | MT372033 | ||||
| A. caviae | 7X11 | + | + | + | + | + | MT372047 | |||
| A. jandaei | 7KL3 | + | + | + | MT372043 | |||||

References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020. Sustainability in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020; Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/ca9229en/ca9229en.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2021).
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2010; p. 197. Available online: http://www.fao.org/documents/card/en/c/f9f071ce-7bee-5107-a343-097685d0d683/ (accessed on 26 June 2021).
- Mohamad, S.N.; Noordin, W.N.M.; Ismail, N.F.; Hamzah, A. Red hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis spp.) broodstock development programme in Malaysia: Status, challenges and prospects for future development. Asian Fish. Sci. 2021, 34, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Huicab-Pech, Z.; Landeros-Sánchez, C.; Castañeda-Chávez, M.; Lango-Reynoso, F.; López-Collado, C.; Platas Rosado, D. Current state of bacteria pathogenicity and their relationship with host and environment in tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2016, 7, 428. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Lu, M. Tilapia polyculture: A global review. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 2363–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monir, M.S.; Yusoff, S.M.; Mohamad, A.; Ina-Salwany, M.Y. Vaccination of tilapia against motile Aeromonas septicemia: A review. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2020, 32, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Rathore, G.; Kapoor, D.; Mishra, B.N.; Lakra, W.S. Detection of aerolysin gene in Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from fish and pond water. Indian J. Microbiol. 2008, 48, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kozińska, A.; Pkala, A. Characteristics of disease spectrum in relation to species, serogroups, and adhesion ability of motile aeromonads in fish. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 949358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jagoda, S.S.d.S.; Wijewardana, T.G.; Arulkanthan, A.; Igarashi, Y.; Tan, E.; Kinoshita, S.; Watabe, S.; Asakawa, S. Characterization and antimicrobial susceptibility of motile aeromonads isolated from freshwater ornamental fish showing signs of septicaemia. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2014, 109, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, H.T.; Techatanakitarnan, C.; Jindakittikul, P.; Thaiprayoon, A.; Taengphu, S.; Charoensapsri, W.; Khunrae, P.; Rattanarojpong, T.; Senapin, S. Aeromonas jandaei and Aeromonas veronii caused disease and mortality in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amal, M.N.A.; Koh, C.B.; Nurliyana, M.; Suhaiba, M.; Nor-Amalina, Z.; Santha, S.; Diyana-Nadhirah, K.P.; Yusof, M.T.; Ina-Salwany, M.Y.; Zamri-Saad, M. A case of natural co-infection of Tilapia Lake Virus and Aeromonas veronii in a Malaysian red hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × O. mossambicus) farm experiencing high mortality. Aquaculture 2018, 485, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basri, L.; Nor, R.M.; Salleh, A.; Yasin, I.S.M.; Saad, M.Z.; Rahaman, N.Y.A.; Barkham, T.; Amal, M.N.A. Co-Infections of Tilapia Lake Virus, Aeromonas hydrophila and Streptococcus agalactiae in farmed red hybrid tilapia. Animals 2020, 10, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratev, D.; Odeyemi, O.A. Antimicrobial resistance of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from different food sources: A mini-review. J. Infect. Public Health 2016, 9, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Emeish, W.F.; Mohamed, H.M.; Elkamel, A.A. Aeromonas infections in African sharptooth catfish. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2018, 9, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharia, P.; Pokhrel, H.; Kalita, B.; Hussain, I.A. Histopathological changes in Indian major carp, Labeo rohita (Hamilton), experimentally infected with Aeromonas hydrophila associated with hemorrhagic septicemia of Central Brahmaputra valley of Assam, India. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2018, 6, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- AlYahya, S.A.; Ameen, F.; Al-Niaeem, K.S.; Al-Sa’adi, B.A.; Hadi, S.; Mostafa, A.A. Histopathological studies of experimental Aeromonas hydrophila infection in blue tilapia, Oreochromis aureus. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musthafa, M.S.; Asgari, S.M.; Elumalai, P.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Doan, H.V. Protective efficacy of Shilajit enriched diet on growth performance and immune resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila in Oreochromis mossambicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 82, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoel, S.; Vadstein, O.; Jakobsen, A.N. Species distribution and prevalence of putative virulence factors in mesophilic Aeromonas spp. isolated from fresh retail sushi. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Rodriguez, S.A.; Lozano-Olvera, R.; Garcia-Gasca, M.T.; Abad-Rosales, S.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Ayalla-Arellano, J. Virulence of the fish pathogen Aeromonas dhakensis: Genes involved, characterization and histopathology of experimentally infected hybrid tilapia. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2018, 129, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popovic, N.T.; Teskeredzic, E.; Strunjak-Perovic, I.; Coz-Rakovac, R. Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from wild freshwater fish in Croatia. Vet. Res. Commun. 2000, 24, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen-Ivey, C.R.; Hossain, M.J.; Odom, S.E.; Terhune, J.S.; Hemstreet, W.G.; Shoemaker, C.A.; Zhang, D.; Xu, D.-H.; Griffin, M.J.; Liu, Y.-J.; et al. Classification of a hypervirulent Aeromonas hydrophila pathotype responsible for epidemic outbreaks in warm-water fishes. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awan, F.; Dong, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, N.; Mushtaq, M.H.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y. Comparative genome analysis provides deep insights into Aeromonas hydrophila taxonomy and virulence-related factors. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bebak, J.; Wagner, B.; Burnes, B.; Hanson, T. Farm size, seining practices, and salt use: Risk factors for Aeromonas hydrophila outbreaks in farm-raised catfish, Alabama, USA. Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 118, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.J.; Sun, D.; McGarey, D.J.; Wrenn, S.; Alexander, L.M.; Martino, M.E.; Xing, Y.; Terhune, J.S.; Liles, M.R. An Asian origin of virulent Aeromonas hydrophila responsible for disease epidemics in United States-farmed catfish. Am. Soc. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peatman, E.; Mohammed, H.; Kirby, A.; Shoemaker, C.A.; Yildirim-Aksoy, M.; Beck, B.H. Mechanisms of pathogen virulence and host susceptibility in virulent Aeromonas hydrophila infections of channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Aquaculture 2018, 482, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.J.; Waldbieser, G.C.; Sun, D.; Capps, N.K.; Hemstreet, W.B.; Carlisle, K.; Griffin, M.J.; Khoo, L.; Goodwin, A.E.; Sonstegard, T.S.; et al. Implication of lateral genetic transfer in the emergence of Aeromonas hydrophila isolates of epidemic outbreaks in channel catfish. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baumgartner, W.A.; Ford, L.; Hanson, L. Lesions caused by virulent Aeromonas hydrophila in farmed catfish (Ictalurus punctatus and I. punctatus × I. furcatus) in Mississippi. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2017, 29, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, M.; Jiang, J.; Xie, X.; Wu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Kwok, A.H.Y.; Zhang, W.; Yao, H.; Lu, C.; Leung, F.C.; et al. Novel insights into the pathogenicity of epidemic Aeromonas hydrophila ST251 clones from comparative genomics. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. The genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, pathogenicity, and infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 35–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pu, W.; Guo, G.; Yang, N.; Li, Q.; Yin, F.; Wang, P.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, J. Three species of Aeromonas (A. dhakensis, A. hydrophila and A. jandaei) isolated from freshwater crocodiles (Crocodylus siamensis) with pneumonia and septicemia. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Tong, S.; Zhang, S.M.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Wei, W.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, X. Aeromonas veronii associated with red gill disease and its induced immune response in Macrobrachium nipponense. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 5163–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam-Sayuti, M.; Ina-Salwany, M.Y.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Yusof, M.T.; Annas, S.; Najihah, M.Y.; Liles, M.R.; Monir, M.S.; Zaidi, Z.; Amal, M.N.A. The prevalence, putative virulence genes, and antibiotic resistance profiles of Aeromonas spp. isolated from cultivated freshwater fish in peninsular Malaysia. Aquaculture 2021, 540, 736719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez, M.A.; Catalán, V.; Apráiz, D.; Figueras, M.J.; Martínez-Murcia, A.J. Phylogenetic analysis of members of the genus Aeromonas based on gyrB gene sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanson, L.A.; Liles, M.R.; Hossain, M.J.; Griffin, M.J.; William, G. Motile Aeromonas septicemia. In Fish Health Section Blue Book, 2nd ed.; Bethesda, M.D., Ed.; American Fisheries Society—Fish Health Section: Bethesda, Maryland, 2014; Available online: https://units.fisheries.org/fhs/wp-content/uploads/sites/30/2017/08/1.2.9-Motile-Aeromonas-Septicemia-2014.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2021).
- Raj, N.S.; Swaminathan, T.R.; Dharmaratnam, A.; Raja, S.A.; Ramraj, D.; Lal, K.K. Aeromonas veronii caused bilateral exophthalmia and mass mortality in cultured Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.) in India. Aquaculture 2019, 512, 734278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyatha, C.V.; Chitra, K.C. Acute toxicity of triclosan on the native freshwater fish, Anabas testudineus (Bloch, 1792): Behavioural alterations and histopathological lesions. Int. J. Life Sci. 2018, 6, 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, S.; Omar, N.; Yusoff, S.M.; Obukwho, E.B.; Nwunuji, T.P.; Hanan, L.; Samad, J. Clinicopathological features and immunohistochemical detection of antigens in acute experimental Streptococcus agalactiae infection in red tilapia (Oreochromis spp.). SpringerPlus 2013, 2, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soto-Rodriguez, S.A.; Cabanillas-Ramos, J.; Alcaraz, U.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Romalde, J.L. Identification and virulence of Aeromonas dhakensis, Pseudomonas mosselii and Microbacterium paraoxydans isolated from Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, cultivated in Mexico. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 115, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Jiang, J.; Gao, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, H.; Bing, X.; Zjamg, X. Histopathological analysis and the immune related gene expression profiles of mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi) infected with Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 83, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhamed, H.; Ibrahim, I.; Baumgartner, W.; Lawrence, M.L.; Karsi, A. Characterization of histopathological and ultrastructural changes in channel catfish experimentally infected with virulent Aeromonas hydrophila. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratev, D.; Stoev, S.; Vashin, I.; Daskalov, H. Some varieties of pathological changes in experimental infection of carps (Cyprinus carpio) with Aeromonas hydrophila. J. Aquac. Eng. Fish. Res. 2015, 1, 191–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xu, D.; Shoemaker, C. Experimental induction of motile Aeromonas septicemia in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) by waterborne challenge with virulent Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquac. Rep. 2016, 3, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orozova, P.; Barker, M.; Austin, D.A.; Austin, B. Identification and pathogenicity to rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), of some aeromonads. J. Fish Dis. 2009, 32, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriero, M.M.; Maia, A.A.M.; Sousa, R.L.M.; Henrique-Silva, F. Characterization of a new strain of Aeromonas dhakensis isolated from diseased pacu fish (Piaractus mesopotamicus) in Brazil. J. Fish Dis. 2016, 39, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Wang, N.; Pan, Z.H.; Lu, C.P.; Liu, Y.J. Identity and virulence properties of Aeromonas isolates from diseased fish, healthy controls and water environment in China. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 55, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahi, N.; Mallik, S.K.; Sahoo, M.; Das, P. Biological characteristics and pathogenicity of a virulent Aeromonas hydrophila associated with ulcerative syndrome in farmed rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), in India. Isr. J. Aquac. 2013, 65, 926–936. [Google Scholar]
- Pauzi, N.A.; Mohamad, N.; Azzam-Sayuti, M.; Yasin, I.S.M.; Saad, M.Z.; Nasruddin, N.S.; Azmai, M.N.A. Antibiotic susceptibility and pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from red hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × Oreochromis mossambicus) in Malaysia. Vet. World 2020, 13, 2166–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Pridgeon, J.W.; Klesius, P.H. Expression and activity of recombinant proaerolysin derived from Aeromonas hydrophila cultured from diseased channel catfish. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 165, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Sinha, A.K.; Makkar, H.P.S.; Boeck, G.D.; Becker, K. Phytate and phytase in fish nutrition. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2012, 96, 335–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krings, E.; Krumbach, K.; Bathe, B.; Keller, R.; Wendisch, V.; Sahm, H.; Eggeling, L. Characterization of myo-inositol utilization by Corynebacterium glutamicum: The stimulon, identification of transporters, and influence on L-Lysine formation. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 8054–8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boutte, C.C.; Srinivasan, B.S.; Flannick, J.A.; Novak, A.F.; Martesans, A.T.; Batzoglou, S.; Viollier, P.H.; Crosson, S. Genetic and computational identification of a conserved bacterial metabolic module. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, P.L.; Lamy, B.; Ko, W.C. Aeromonas dhakensis, an increasingly recognized human pathogen. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 0793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen-Ivey, C.R.; Figueras, M.J.; McGarey, D.; Liles, M.R. Virulence factors of Aeromonas hydrophila: In the wake of reclassification. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 01337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Bacterial Concentration | Number of Deaths at Specific Time (Hour Post Infection) | Sample Number | Cumulative Mortality (%) | LD50–240h (CFU/mL) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (CFU/mL) | 24 | 48 | 72 | 96 | 120 | 144 | 168 | 192 | 216 | 240 | ||||
| A. dhakensis 1P11S3 * | 103 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 2 (10) | 1 × 107 |
| 105 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 4 (20) | ||
| 107 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 11 (55) | ||
| A. dhakensis 4PS2 | 103 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 1 (5) | 1 × 105 |
| 105 | 1 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 8 (40) | ||
| 107 | 11 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 19 (95) | ||
| A. hydrophila 8TK3 | 103 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 3 (15) | 1 × 105 |
| 105 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 12 (60) | ||
| 107 | 7 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 18 (90) | ||
| A. veronii 6TS5 | 103 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 2 (10) | 1 × 107 |
| 105 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 6 (30) | ||
| 107 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 20 | 9 (45) | ||
| A. caviae 7X11 | 103 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 0 (0) | 1 × 107 |
| 105 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 6 (30) | ||
| 107 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 10 (50) | ||
| A. jandaei 7KL3 | 103 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 4 (20) | 1 × 1011 |
| 105 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 5 (25) | ||
| 107 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 7 (35) | ||
| Control (sterile TSB) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 0 (0) | |
| Species | Organ | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Liver | Spleen | Kidney | |
| A. dhakensis 1P11S3 (107 CFU/mL) * | 1.0 ± 0.0 a | 2.0 ± 0.1 a | 1.0 ± 0.0 a |
| A. dhakensis 4PS2 (107 CFU/mL) | 2.0 ± 0.1 c | 2.0 ± 0.0 a | 3.0 ± 0.0 c |
| A. hydrophila 8TK3 (107 CFU/mL) | 3.0 ± 0.0 b | 3.0 ± 0.0 b | 3.0 ± 0.0 b |
| A. veronii 6TS5 (107 CFU/mL) | 1.0 ± 0.0 a | 2.0 ± 0.0 a | 1.0 ± 0.1 a |
| A. caviae 7X11 (107 CFU/mL) | 1.0 ± 0.0 a | 2.0 ± 0.0 a | 1.0 ± 0.0 a |
| A. jandaei 7KL3 (107 CFU/mL) | 1.0 ± 0.0 a | 1.1 ± 0.1 c | 2.1 ± 0.1 d |
| Control (sterile TSB) | 0.0 ± 0.0 d | 0.0 ± 0.0 d | 0.0 ± 0.0 e |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azzam-Sayuti, M.; Ina-Salwany, M.Y.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Annas, S.; Yusof, M.T.; Monir, M.S.; Mohamad, A.; Muhamad-Sofie, M.H.N.; Lee, J.Y.; Chin, Y.K.; et al. Comparative Pathogenicity of Aeromonas spp. in Cultured Red Hybrid Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × O. mossambicus). Biology 2021, 10, 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111192
Azzam-Sayuti M, Ina-Salwany MY, Zamri-Saad M, Annas S, Yusof MT, Monir MS, Mohamad A, Muhamad-Sofie MHN, Lee JY, Chin YK, et al. Comparative Pathogenicity of Aeromonas spp. in Cultured Red Hybrid Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × O. mossambicus). Biology. 2021; 10(11):1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111192
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzzam-Sayuti, Mohamad, Md Yasin Ina-Salwany, Mohd Zamri-Saad, Salleh Annas, Mohd Termizi Yusof, Md Shirajum Monir, Aslah Mohamad, Mohd Hafiz Ngoo Muhamad-Sofie, Jing Yie Lee, Yong Kit Chin, and et al. 2021. "Comparative Pathogenicity of Aeromonas spp. in Cultured Red Hybrid Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × O. mossambicus)" Biology 10, no. 11: 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111192
APA StyleAzzam-Sayuti, M., Ina-Salwany, M. Y., Zamri-Saad, M., Annas, S., Yusof, M. T., Monir, M. S., Mohamad, A., Muhamad-Sofie, M. H. N., Lee, J. Y., Chin, Y. K., Amir-Danial, Z., Asyiqin, A., Lukman, B., Liles, M. R., & Amal, M. N. A. (2021). Comparative Pathogenicity of Aeromonas spp. in Cultured Red Hybrid Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × O. mossambicus). Biology, 10(11), 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111192








