Novel Algicides against Bloom-Forming Cyanobacteria from Allelochemicals: Design, Synthesis, Bioassay, and 3D-QSAR Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
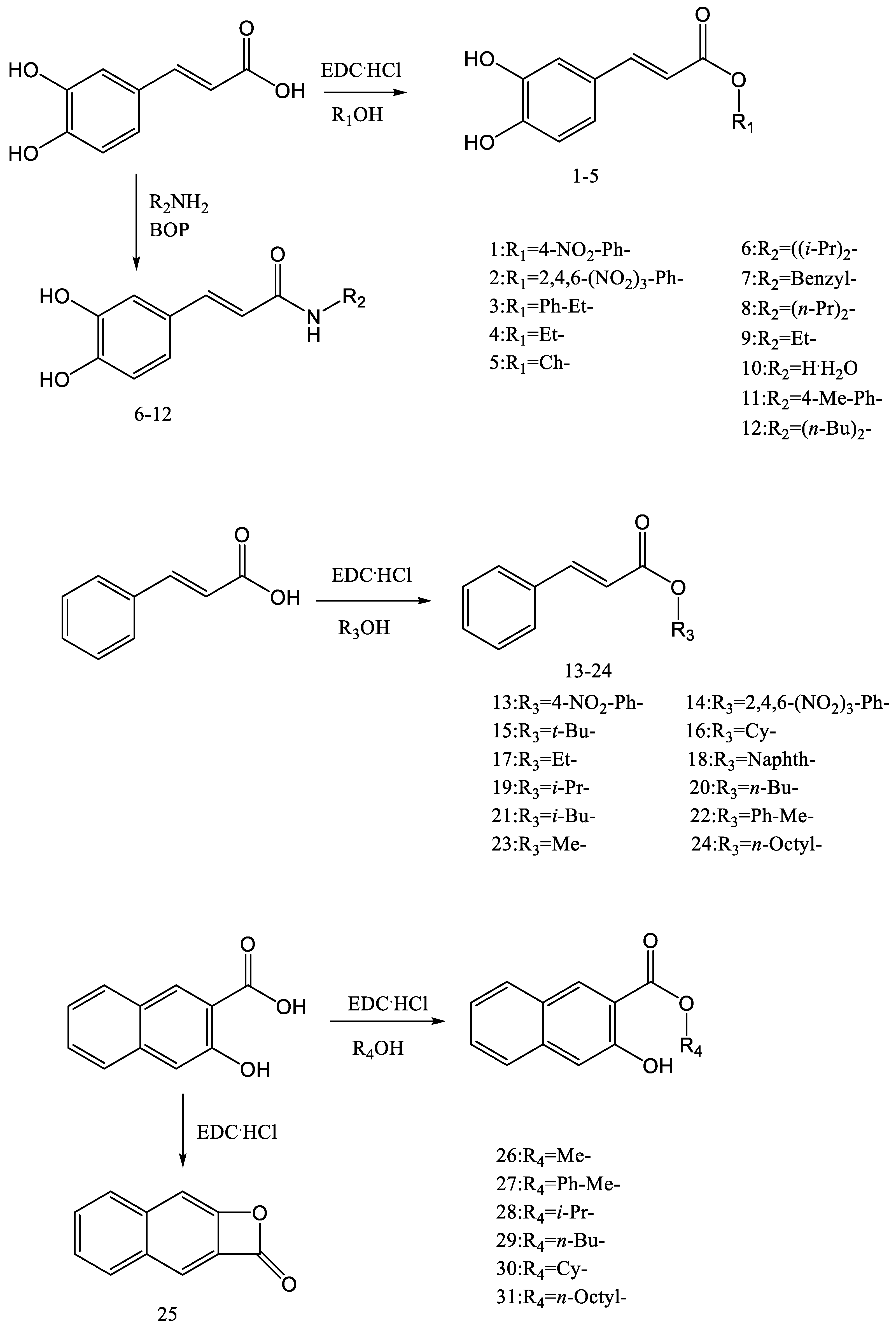
2.1. Chemistry General
2.2. Synthesis of Caffeic Acid Esters
2.3. Synthesis of Caffeic Acid Amides
2.4. Synthesis of Cinnamic Acid Esters
2.5. Synthesis of 2-Hydroxy-3-Naphthoic Acid Esters
2.6. Algicidal Activity Assay
2.7. Physiological Assays
2.8. 3D-QSAR Model Study
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Algicidal Activity of Synthesized Compounds
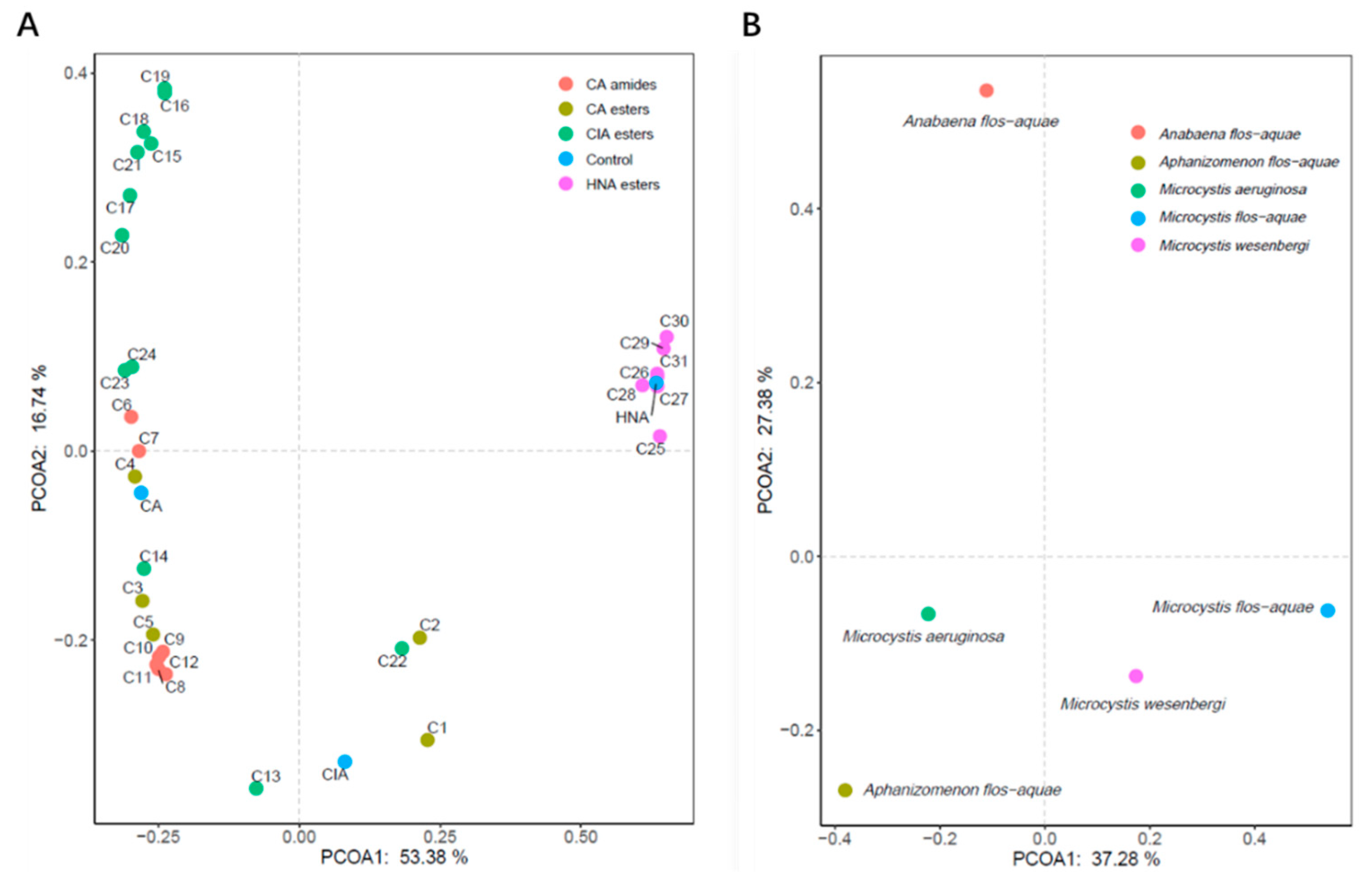
3.2. Structure–Activity Relationship Analysis
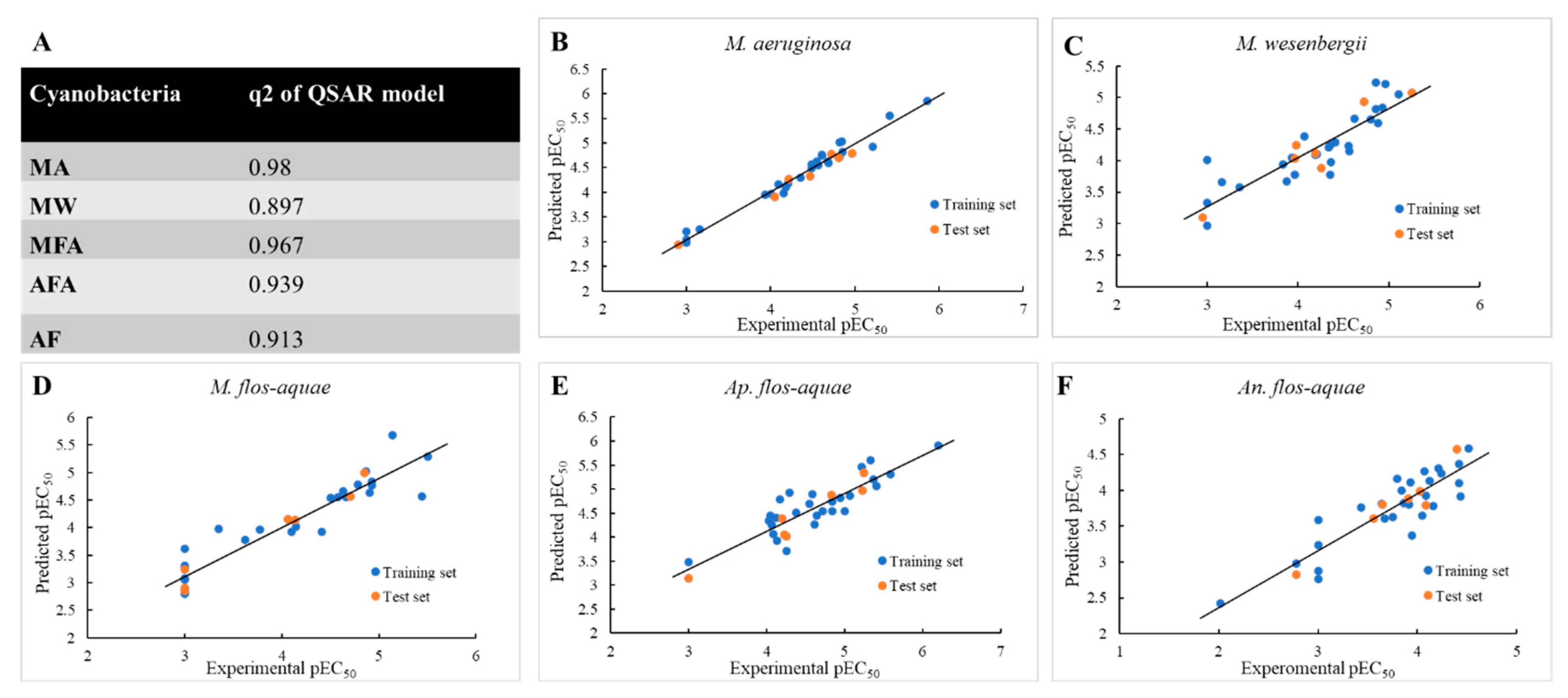
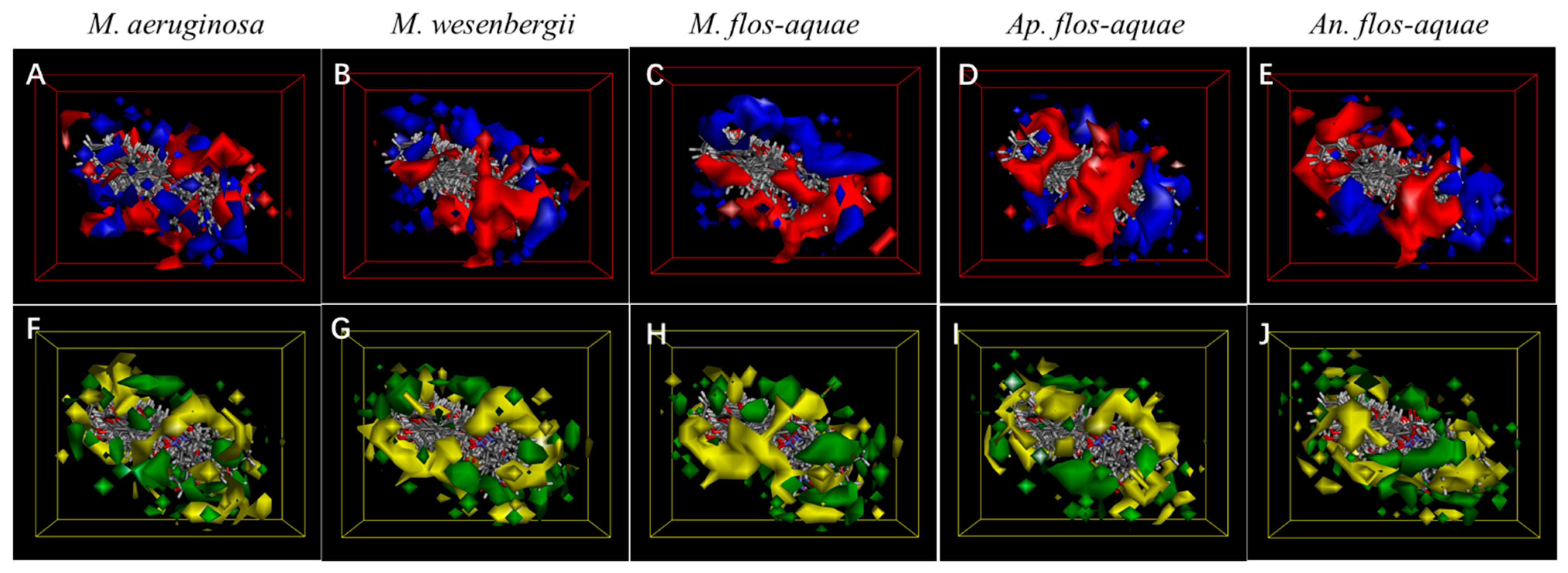
3.3. 3D-QSAR Analysis
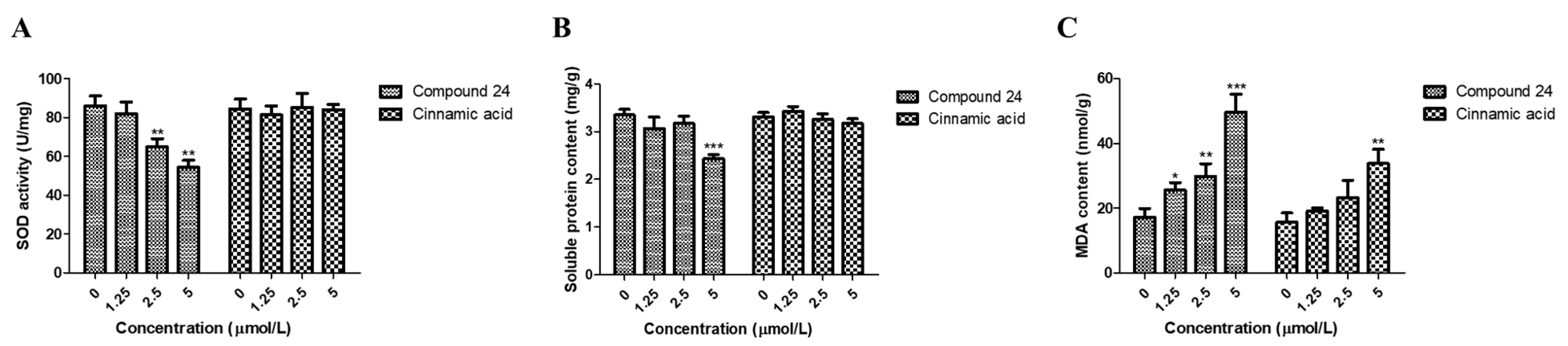
3.4. Physiological Assays
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, W.-J.; Hu, X.; Huang, W.-J.; Murrell, M.; Lehrter, J.C.; Lohrenz, S.; Chou, W.-C.; Zhai, W.-D.; Hollibaugh, J.T.; Wang, Y.; et al. Acidification of subsurface coastal waters enhanced by eutrophication. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ling, J.; Li, L.; Guan, X. The effectiveness of bisulfite-activated permanganate technology to enhance the coagulation efficiency of Microcystis aeruginosa. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 1545–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J. Issue of Cyanobacteria Blooms in Taihu Lake, China. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2016, 19, 99–109. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, B.Y.; Zhu, X.; Sotto, P.; Paulino, Y. Oral exposure to environmental cyanobacteria toxins: Implications for cancer risk. Environ. Int. 2021, 148, 106381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Xie, R.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Wang, J.; Liang, Q. Nitrite-responsive hydrogel for long-term and smart control of cyanobacteria bloom. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 125150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leao, P.N.; Pereira, A.R.; Liu, W.-T.; Ng, J.; Pevzner, P.A.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Konig, G.M.; Vasconcelos, V.M.; Gerwick, W.H. Synergistic allelochemicals from a freshwater cyanobacterium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11183–11188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.-W.; Fu, J.; Song, S.; Zhang, P.; Yang, X.-H.; Zhang, L.-R.; Luo, Y.; Liu, C.-H.; Zhu, H.-L. Interspecific Competition between Microcystis aeruginosa and Anabaena flos-aquae from Taihu Lake, China. Z. Naturforsch. C 2014, 69, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, S.; Inoue, Y.; Hosomi, M. Algal growth inhibition effects and inducement modes by plant-producing phenols. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1855–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Acharya, K.; Hao, X.; Li, S. Isolation and identification of an anti-algal compound from Artemisia annua and mechanisms of inhibitory effect on algae. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.N.; Liu, B.Y.; Ge, F.J.; He, Y.; Lu, Z.Y.; Zhou, Q.H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wu, Z.B.; Gao, Y.N.; Liu, B.Y. Joint effects of allelochemical nonanoic acid, N-phenyl-1-naphtylamine and caffeic acid on the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. Allelopath. J. 2015, 35, 249–257. [Google Scholar]
- He, M.; Zhang, T.; Wu, A.; Nie, L. Inhibition of Cinnamic acid on Microcystis aeruginosa K. and Scenedesmus arcuatus L. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2008, 14, 774–778. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.N.; Liu, B.Y.; Xu, D.; Zhou, Q.H.; Hu, C.Y.; Ge, F.J.; Zhang, L.P.; Wu, Z.B. Phenolic Compounds Exuded from Two Submerged Freshwater Macrophytes and Their Allelopathic Effects on Microcystis aeruginosa. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2011, 20, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, B.; Jun, H.; Ting, S.; Wei, W.; Junyi, Z. Study on the species and succession of cyanobacteria bloom in Taihu Lake. In Proceedings of the 2014 Annual Conference of the Chinese Society for Environmental Science (Chapter 5), Chengdu, China, 22–23 October 2014; pp. 4435–4440. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X.; Kong, F.; Zeng, Q.; Cao, H.; Qian, S.; Zhang, M. Seasonal variation of Microcystis in Lake Taihu and its relationships with environmental factors. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Nakahara, H. The formation and degradation of cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon flos-aquae blooms: The importance of pH, water temperature, and day length. Limnology 2005, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yu, B.; Peng, X.; Yu, G.; Wei, Z.; Wang, G.; Li, R. Non-microcystin producing Microcystis wesenbergii (Komárek) Komárek (Cyanobacteria) representing a main waterbloom-forming species in Chinese waters. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Guo, P.; Zhang, S. Response of the cyanobacterium Microcystis flos-aquae to levofloxacin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 3858–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Shi, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Kong, Y. Inactivation of harmful Anabaena flos-aquae by ultrasound irradiation: Cell disruption mechanism and enhanced coagulation. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2020, 69, 105254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, J.; Suelter, C. An evaluation of the Coomassie brilliant blue G-250 dye-binding method for quantitative protein determination. Anal. Biochem. 1977, 81, 478–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Z.; Tang, H.R.; Luo, Y. Variation in Antioxidant Enzyme Activities of Two Strawberry Cultivars with Short-term Low Temperature Stress. World J. Agric. Sci. 2008, 4, 458–462. [Google Scholar]
- Heath, R. Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys 1968, 125, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, J.; Zhu, H.-L. 4,5-Dihydropyrazole derivatives containing oxygen-bearing heterocycles as potential telomerase inhibitors with anticancer activity. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 23904–23913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Luo, Y.; Fu, J.; Zhou, J.; Kyzas, G. Molecular docking and 3D-QSAR studies on the glucocorticoid receptor antagonistic activity of hydroxylated polychlorinated biphenyls. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2016, 27, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Song, Y.; Chen, G.; Wang, Y.-X.; Tian, Y.; Fan, W.-W.; Yang, Y.-S.; Cheng, T.; Zhu, H.-L. Optimization of substituted cinnamic acyl sulfonamide derivatives as tubulin polymerization inhibitors with anticancer activity. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 3634–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, K.; Baba, A. Therapeutic potential of superoxide dismutase (SOD) for resolution of inflammation. Inflamm. Res. 2006, 55, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, P.I.; Krishnaswamy, M. The effect of zinc stress combined with high irradiance stress on membrane damage and antioxidative response in bean seedlings. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2011, 74, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.H.; Wang, P.; Zhang, C.X.; Zhang, M.X.; Hu, F. Herbicidal potential of allelochemicals from Lantana camara against Eichhornia crassipes and the alga Microcystis aeruginosa. Weed Res. 2006, 46, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.-H.; Han, M.-S.; Ahn, C.-Y.; Kim, H.-S.; Yoon, B.-D.; Oh, H.-M. Growth inhibition of bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa by rice straw extract. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Roger, S.-F.; Luo, X. Allelopathically inhibitory effects of eucalyptus extracts on the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Hu, H.-Y.; Xie, X.; Sakoda, A.; Sagehashi, M.; Li, F.-M. Gramine-induced growth inhibition, oxidative damage and antioxidant responses in freshwater cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 91, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Huang, J.; Tang, J.; Wang, N.; Zhang, L.; Gu, L.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Z.; Huang, Y. Allelopathic inhibition of juglone (5-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone) on the growth and physiological performance in Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.-L.; Yu, X.-B.; Zhang, C.; Wang, G.-X. Growth inhibition and microcystin degradation effects of Acinetobacter guillouiae A2 on Microcystis aeruginosa. Res. Microbiol. 2015, 166, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowling, L.; Baker, P. Major cyanobacterial bloom in the Barwon-Darling River, Australia, in 1991, and underlying limnological conditions. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1996, 47, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xiao, M. Environmental factors related to the dominance of Microcystis wesenbergii and Microcystis aeruginosa in a eutrophic lake. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Huang, W.-M.; Liu, Y.-D.; Li, D.; Shen, Y.-W.; Li, G.-B. Environmental mechanism of change in cyanobacterial species composition in the northeastern part of Lake Dianchi (China). Fresen. Env. Bull. 2007, 16, 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, G.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, X.; Chen, W. Growth Inhibition of Microcystis aeruginosa by Copper-based MOFs: Performance and Physiological Effect on Algal Cells. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, R.; Prasath, B.B.; Nandakumar, R.; Santhanam, P.; Shivashangari, K.S.; Ravikumar, V. Growth inhibition of bloom forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa by green route fabricated copper oxide nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 14232–14240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compounds | EC50 (µmol/L) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. aeruginosa | M. wesenbergii | M. flos-aquae | Ap. flos-aquae | An. flos-aquae | ||
| CA esters | 1 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 2 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | |
| 3 | 61.52 | 65.00 | 73.40 | 55.01 | >100 | |
| 4 | 32.50 | 24.10 | 23.20 | 75.15 | >100 | |
| 5 | 27.40 | 64.90 | 31.50 | 24.10 | >100 | |
| CA amides | 6 | 27.54 | 10.82 | 7.27 | 54.80 | >150 |
| 7 | 70.38 | 27.24 | 3.59 | 85.30 | 69.59 | |
| 8 | >100 | >100 | 80.00 | 28.00 | >150 | |
| 9 | >100 | >100 | >100 | 50.56 | 75.63 | |
| 10 | 89.30 | >100 | 87.00 | 58.80 | 93.88 | |
| 11 | >100 | 62.50 | >100 | 42.10 | >150 | |
| 12 | 115.40 | 109.60 | >100 | 19.10 | 121.4 | |
| CIA esters | 13 | 65.54 | >100 | >100 | 92.78 | 88.81 |
| 14 | 99.60 | 43.42 | 38.60 | 14.49 | >100 | |
| 15 | 20.55 | 7.73 | 13.70 | 22.72 | 36.89 | |
| 16 | 10.72 | 5.56 | 19.61 | 5.59 | 39.9 | |
| 17 | 15.26 | 11.69 | 16.47 | 3.94 | 81.57 | |
| 18 | 13.93 | 13.17 | 12.56 | 0.63 | 61.15 | |
| 19 | 20.81 | 13.81 | 11.78 | 4.59 | 30.27 | |
| 20 | 18.98 | 18.82 | 14.15 | 14.84 | 82.09 | |
| 21 | 24.51 | 13.88 | 11.77 | 6.06 | 57.33 | |
| 22 | 80.72 | >100 | 71.31 | 89.85 | >100 | |
| 23 | 15.29 | 27.81 | 21.66 | 14.36 | >100 | |
| 24 | 1.38 | 38.62 | 26.58 | 5.29 | >100 | |
| HNA esters | 25 | 33.84 | 105.60 | >100 | 62.45 | >100 |
| 26 | 32.34 | 46.26 | >100 | 11.39 | >100 | |
| 27 | 24.47 | 134.68 | >100 | 8.48 | >100 | |
| 28 | 61.62 | >100 | >100 | 81.31 | >100 | |
| 29 | 28.35 | 44.44 | >100 | 9.93 | 37.99 | |
| 30 | 14.34 | 15.88 | >100 | 2.56 | 38.23 | |
| 31 | 35.50 | 55.10 | >100 | 5.94 | 224.24 | |
| Controls | CA | 6.18 | 44.00 | 3.13 | 74.00 | 138.00 |
| CIA | 3.87 | 85.88 | 169.92 | 26.10 | >200 | |
| HNA | 43.84 | 117.18 | >100 | 66.58 | 84.64 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hou, W.; Fu, J. Novel Algicides against Bloom-Forming Cyanobacteria from Allelochemicals: Design, Synthesis, Bioassay, and 3D-QSAR Study. Biology 2021, 10, 1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111145
Luo Y, Yang Y, Hou W, Fu J. Novel Algicides against Bloom-Forming Cyanobacteria from Allelochemicals: Design, Synthesis, Bioassay, and 3D-QSAR Study. Biology. 2021; 10(11):1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111145
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Yin, Yushun Yang, Wenguang Hou, and Jie Fu. 2021. "Novel Algicides against Bloom-Forming Cyanobacteria from Allelochemicals: Design, Synthesis, Bioassay, and 3D-QSAR Study" Biology 10, no. 11: 1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111145
APA StyleLuo, Y., Yang, Y., Hou, W., & Fu, J. (2021). Novel Algicides against Bloom-Forming Cyanobacteria from Allelochemicals: Design, Synthesis, Bioassay, and 3D-QSAR Study. Biology, 10(11), 1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111145








