Multi-Class Parrot Image Classification Including Subspecies with Similar Appearance
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. CNN-Based Biological Image Recognition
2.2. Framework for Object Detection
3. Materials and Methods
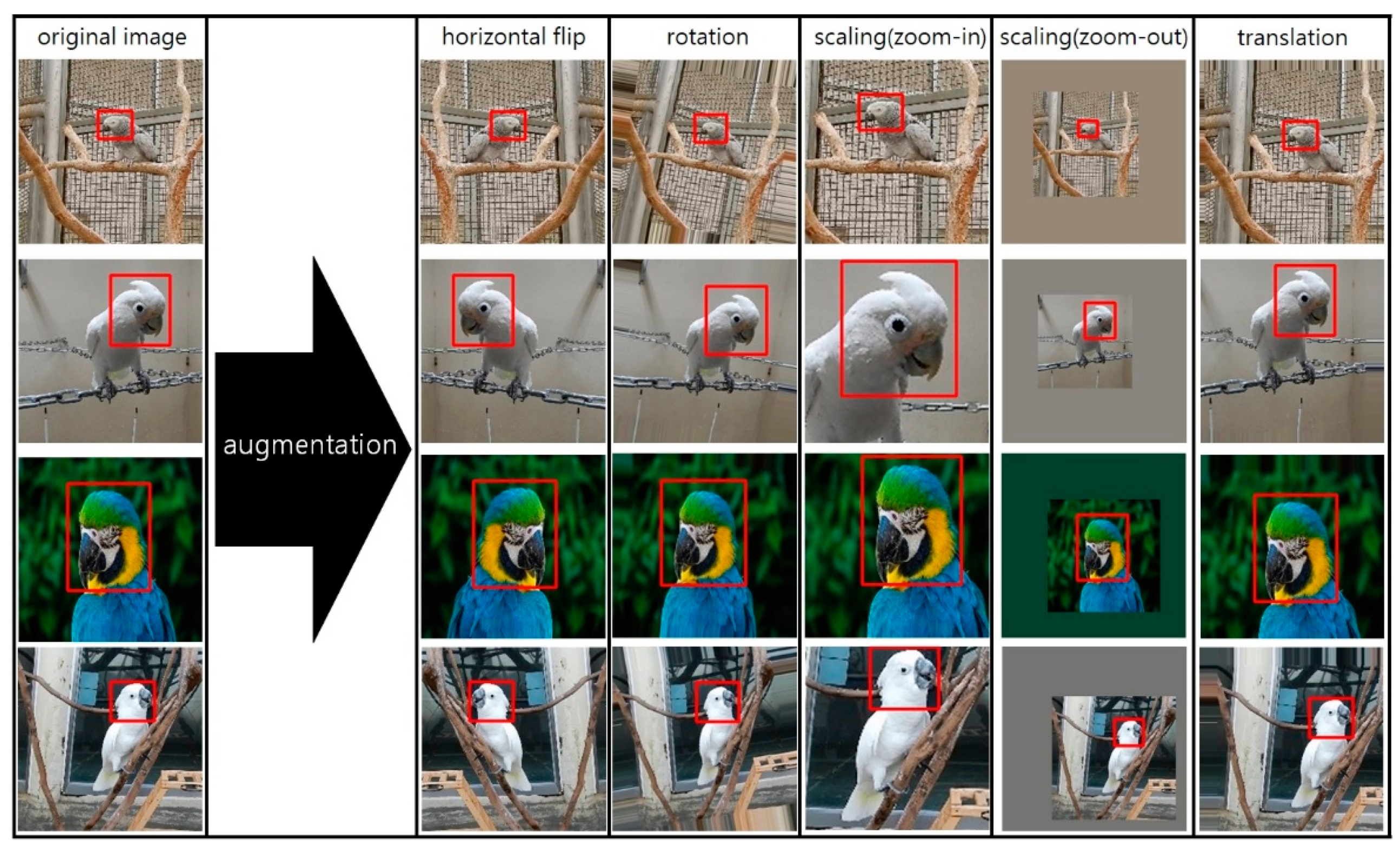
3.1. Dataset and Preprocessing
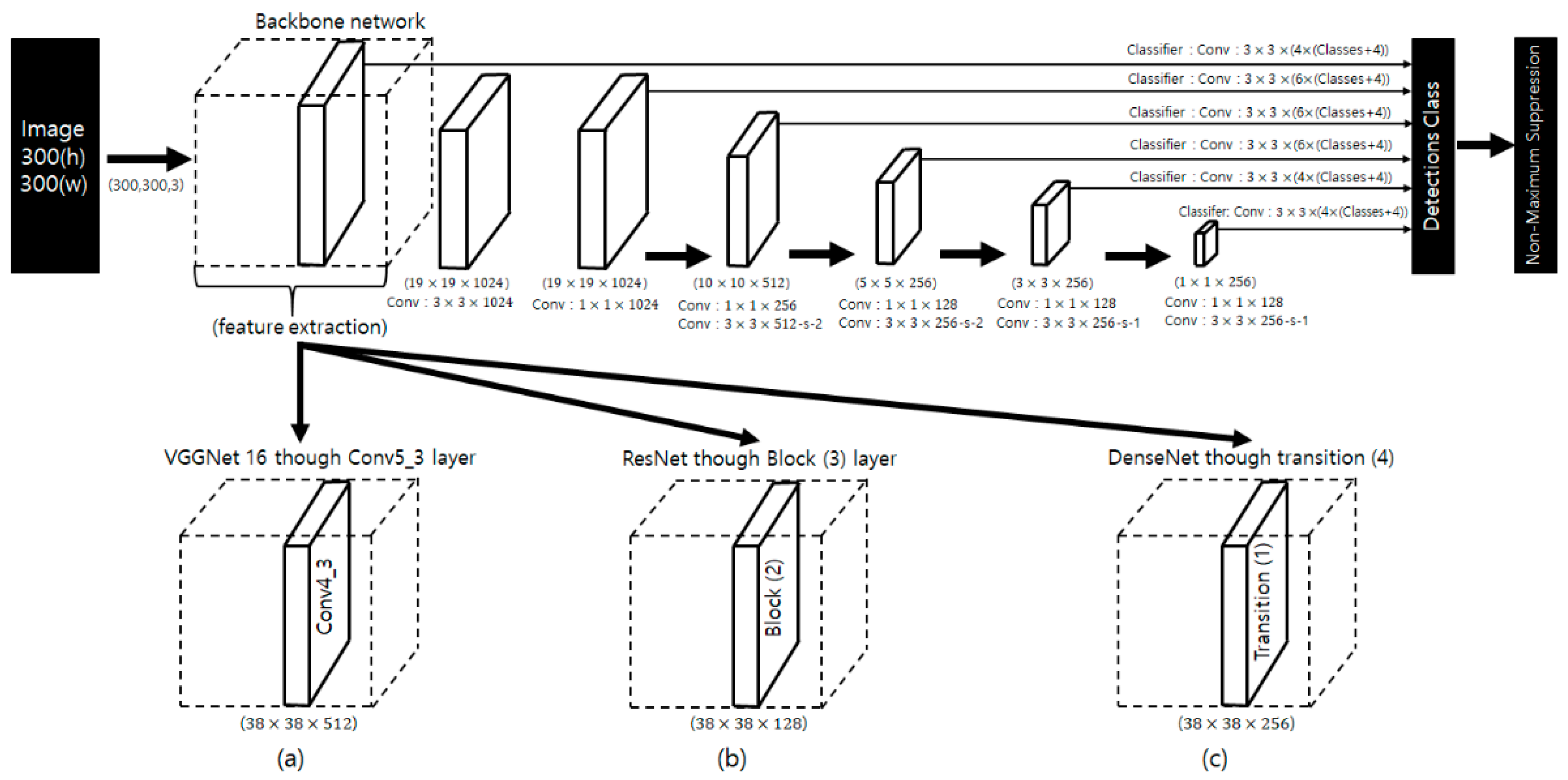
3.2. Deep Neural Networks
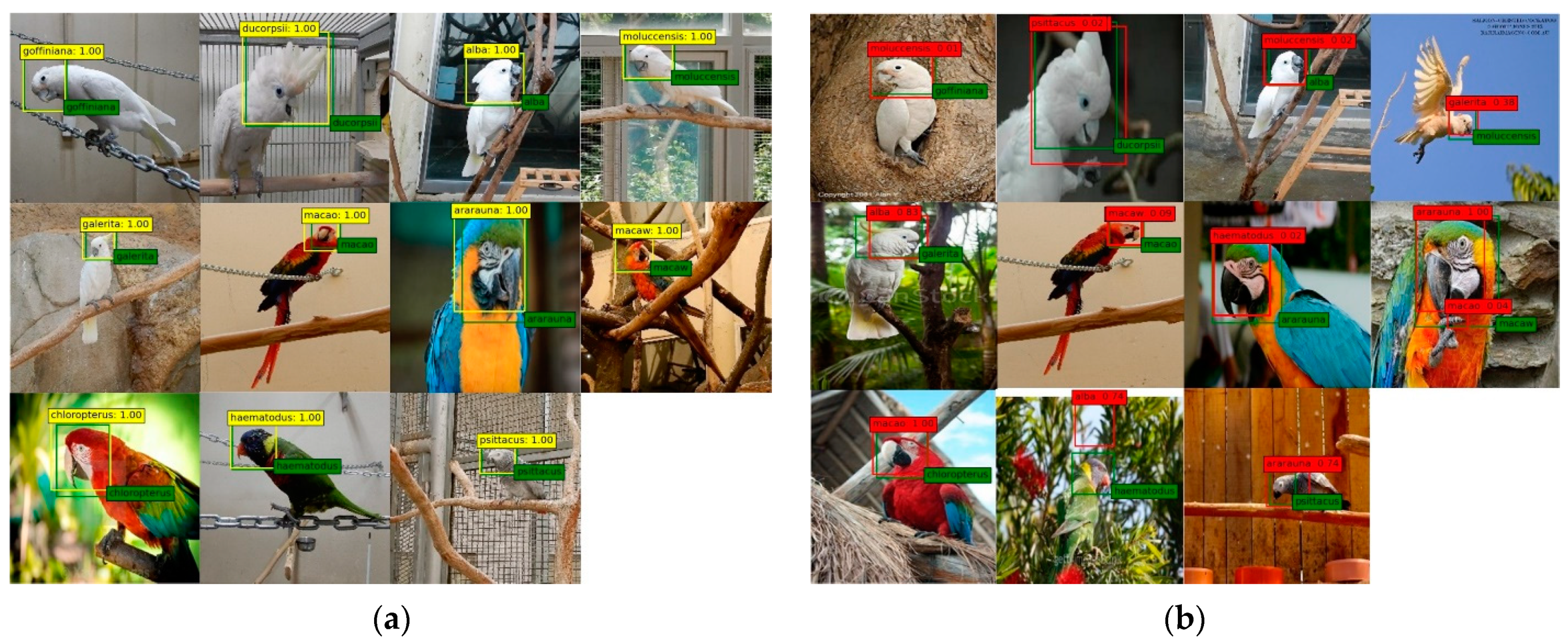
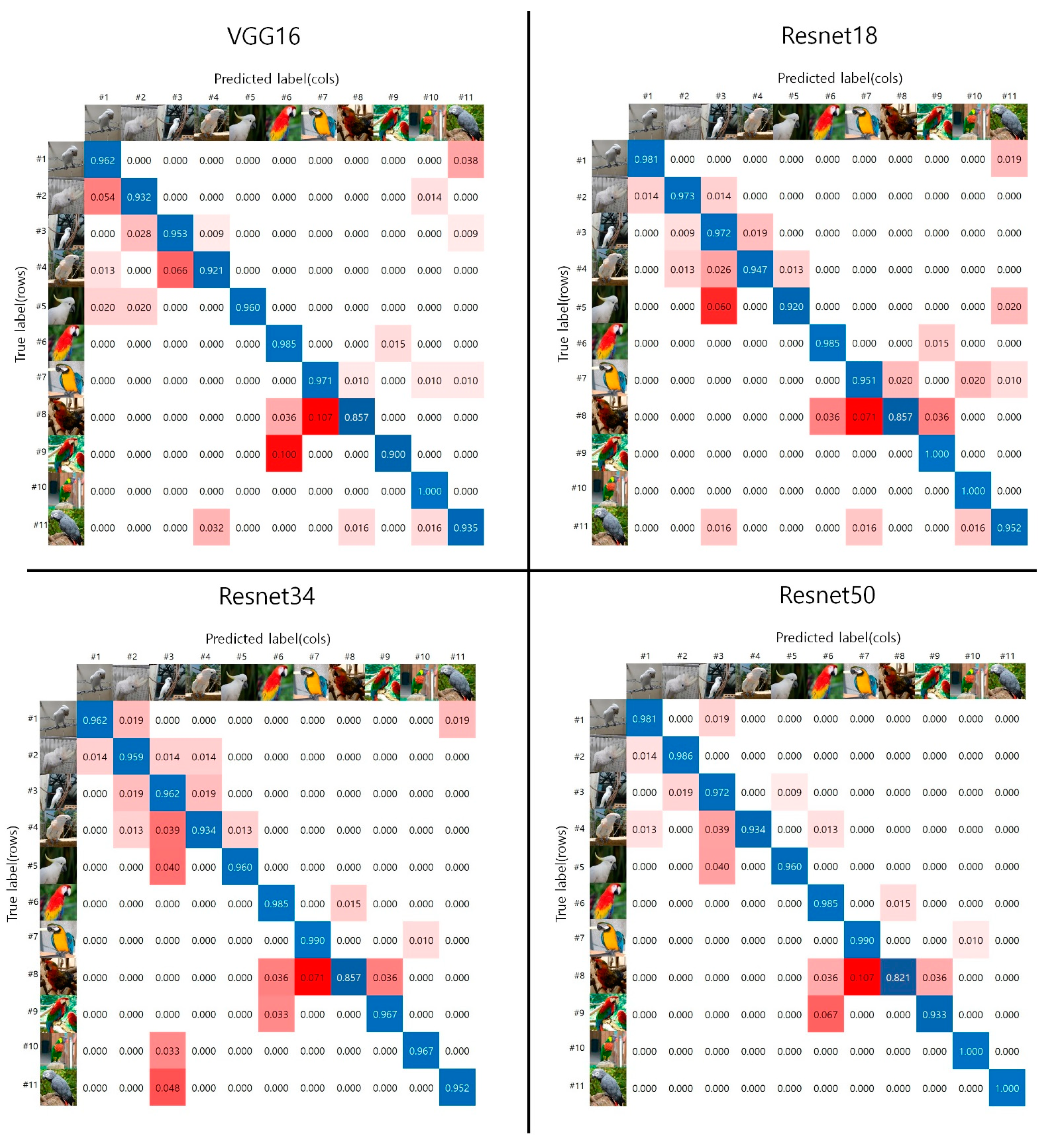
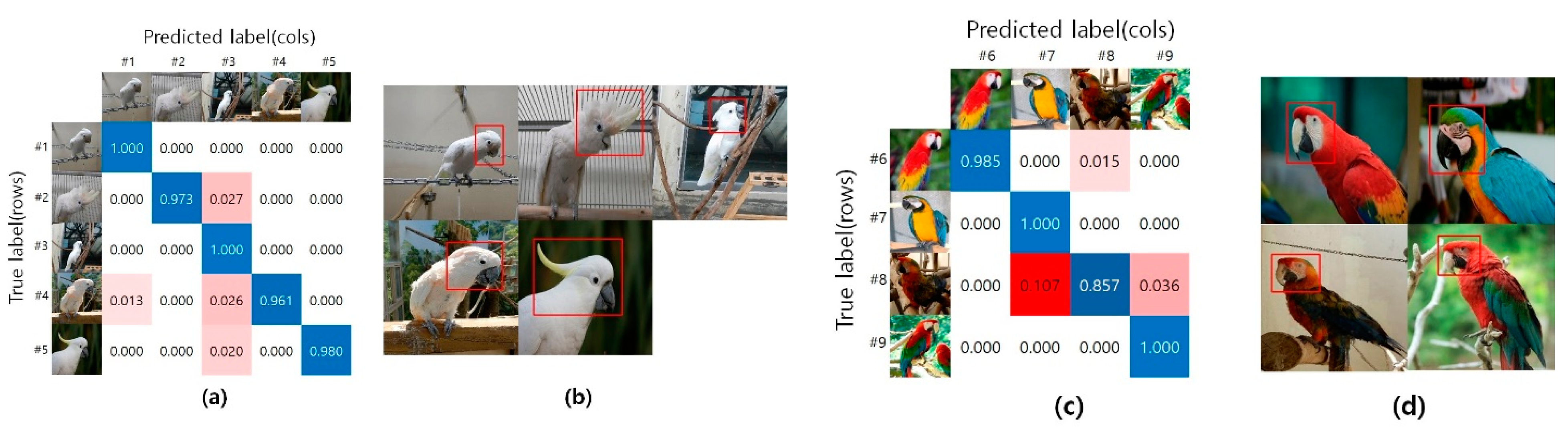
4. Experimental Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pires, S.F. The illegal parrot trade: A literature review. Glob. Crime 2012, 13, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, E.R.; Baker, S.E.; Macdonald, D.W. Global trade in exotic pets 2006–2012. Conserv. Biol. 2014, 28, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, C. Transnational crime and the developing world. Wash. Glob. Financ. Integr. 2017. Available online: https://gfintegrity.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Transnational_Crime-final.pdf (accessed on 5 February 2018).
- Alacs, E.A.; Georges, A.; FitzSimmons, N.N.; Robertson, J. DNA detective: A review of molecular approaches to wildlife forensic. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2010, 6, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mridula, B.; Bonde, P. Harnessing the power of deep learning to save animals. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2017, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Ni, Q. IoT-driven automated object detection algorithm for urban surveillance systems in smart cities. IEEE Int. Things J. 2017, 5, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mhalla, A.; Chateau, T.; Gazzah, S.; Amara, N.E.B. An embedded computer-vision system for multi-object detection in traffic surveillance. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 20, 4006–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Z. Colonic polyp detection in endoscopic videos with single shot detection based deep convolutional neural network. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 75058–75066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, E.; Han, Y.; Oh, I.S. Mushroom Image Recognition using Convolutional Neural Network and Transfer Learning. KIISE Trans. Comput. Pract. 2018, 24, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.; Maclagan, S.J.; Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, T.; Flemons, P.; Andrews, K.; Phung, D. Animal recognition and identification with deep convolutional neural networks for automated wildlife monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Data Science and Advanced Analytics (DSAA), Tokyo, Japan, 19–21 October 2017; pp. 40–49. [Google Scholar]
- Norouzzadeh, M.S.; Nguyen, A.; Kosmala, M.; Swanson, A.; Palmer, M.S.; Packer, C.; Clune, J. Automatically identifying, counting, and describing wild animals in camera-trap images with deep learning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5716–E5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Yu, B.H. Automatic Identification of Wild Animals using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the Korean Society of Environment and Ecology Conference Korean Society of Environment and Ecology Annual, Busan, Korea, 4 April 2018; pp. 34–35. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, P.; Xing, L.; Liu, Y.; Guo, S.; Qiao, Y. Marine Animal Detection and Recognition with Advanced Deep Learning Models. In Proceedings of the CLEF (Working Notes), Dublin, Ireland, 11–14 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Labao, A.B.; Naval, P.C., Jr. Cascaded deep network systems with linked ensemble components for underwater fish detection in the wild. Ecol. Inform. 2019, 52, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.; Kim, T.; Nam, U.; Lee, E.C. Image segmentation and identification of parrot by using Faster R-CNN. In Proceedings of the ICNCT 2019, Okinawa, Japan, 12–14 January 2019; pp. 91–92. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armi, L.; Fekri-Ershad, S. Texture image analysis and texture classification methods-A review. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.06554. [Google Scholar]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–26 June 2005; pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Everingham, M.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The pascal visual object classes (voc) challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2010, 88, 303–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- DarkLabel. Available online: https://darkpgmr.tistory.com/16 (accessed on 18 July 2017).
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imageNet classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1026–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Duda, R.O.; Hart, P.E.; Stork, D.G. Pattern Classification and Scene Analysis; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1973; Volume 3, pp. 731–739. [Google Scholar]
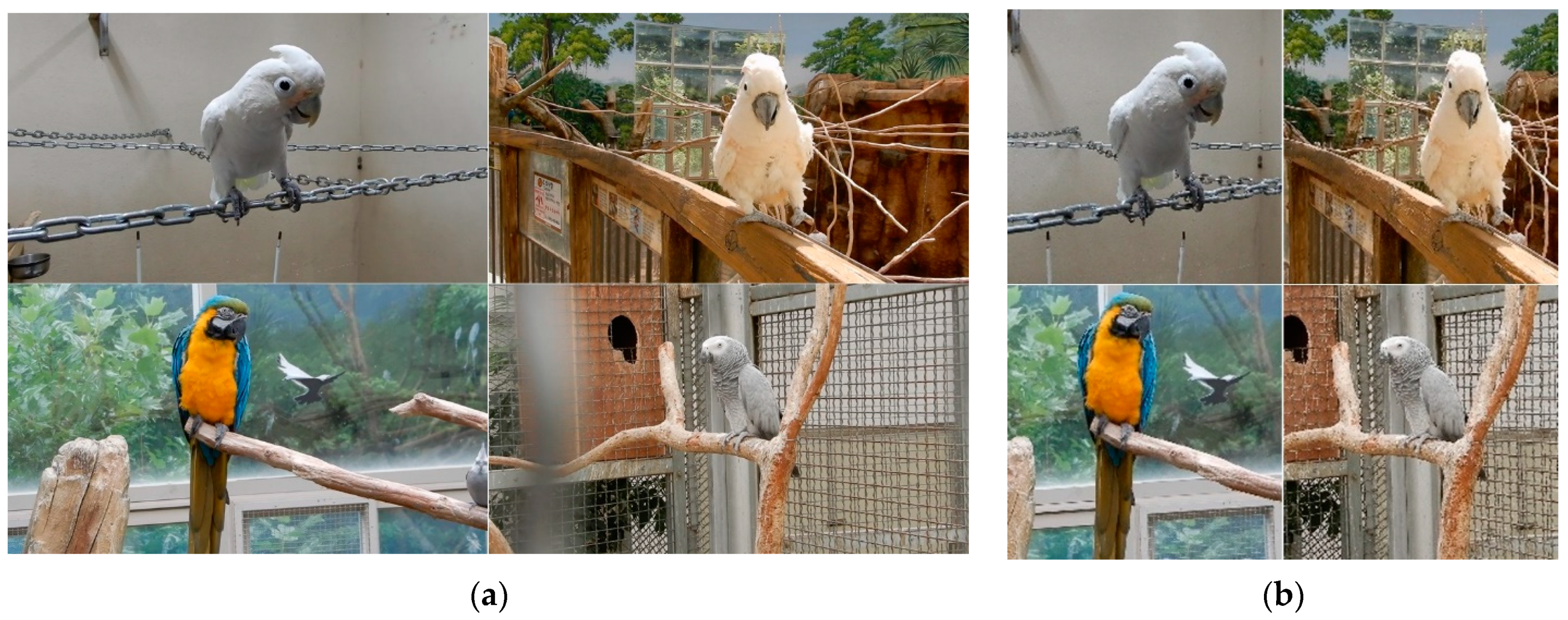



| Scientific Name | Train Set | Validation Set | Test Set |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cacatua goffiniana | 3248 | 50 | 52 |
| Cacatua ducorpsii | 3300 | 70 | 74 |
| Cacatua alba | 2880 | 102 | 106 |
| Cacatua moluccensis | 3460 | 74 | 76 |
| Cacatua galerita | 3136 | 48 | 50 |
| Ara macao | 3080 | 66 | 68 |
| Ara ararauna | 2808 | 100 | 102 |
| Camelot macaw | 3224 | 26 | 28 |
| Ara chloroptera | 3224 | 26 | 30 |
| Trichoglossus Haematodus | 3380 | 28 | 30 |
| Psittacus erithacus | 2740 | 58 | 62 |
| Total | 34,480 | 648 | 678 |
| Picture |  |  |  |  |
| Common name | Goffin’s cockatoo | Solomons cockatoo | The white cockatoo | Moluccan cockatoo |
| Scientific name | Cacatua goffiniana | Cacatua ducorpsii | Cacatua alba | Cacatua moluccensis |
| CITES listing | Appendix I | Appendix II | Appendix II | Appendix I |
| Picture |  |  |  |  |
| Common name | The sulphur-crested cockatoo | Red and yellow macaw | Blue and gold macaw | Camelot macaw |
| Scientific name | Cacatua galerita | Ara macao | Ara ararauna | (Ara ararauna × Ara macao) × Ara cholroptera |
| CITES listing | Appendix II | Appendix I | Appendix II | |
| Picture |  |  |  | |
| Common name | Red and green macaw | Rainbow lorikeet | Gray parrot | |
| Scientific name | Ara chloroptera | Trichoglossus haematodus | Psittacus erithacus | |
| CITES listing | Appendix II | Appendix II | Appendix I |
| Layers | Specification | |
|---|---|---|
| Conv 2 | 300 300 64 | 3 3 Conv, stride 1, name: conv1_1 |
| 300 300 64 | 3 3 Conv, stride 1, name: conv1_2 | |
| Pooling | 150 150 64 | 2 2 Max Pool, stride 2 |
| Conv 2 | 150 150 128 | 3 3 Conv, stride 1, name: conv2_1 |
| 150 150 128 | 3 3 Conv, stride 1, name: conv2_2 | |
| Pooling | 75 75 128 | 2 2 Max Pool, stride 2 |
| Conv 3 | 75 75 256 | 3 3 Conv, stride 1, name: conv3_1 |
| 75 75 256 | 3 3 Conv, stride 1, name: conv3_2 | |
| 75 75 256 | 3 3 Conv, stride 1, name: conv3_3 | |
| Pooling | 38 38 256 | 2 2 Max Pool, stride 2 |
| Conv 3 | 38 38 512 | 3 3 Conv, stride 1, name: conv4_1 |
| 38 38 512 | 3 3 Conv, stride 1, name: conv4_2 | |
| 38 38 512 | 3 3 Conv, stride 1, name: conv4_3 | |
| Pooling | 19 19 512 | 2 2 Max Pool, stride 2 |
| Conv 3 | 19 19 512 | 3 3 Conv, stride 1, name: conv5_1 |
| 19 19 512 | 3 3 Conv, stride 1, name: conv5_2 | |
| 19 19 512 | 3 3 Conv, stride 1, name: conv5_3 | |
| Pooling | 19 19 512 | 3 3 Max Pool, stride 1 |
| Weight parameters (unit: million) | 25 | |
| Layers | 18-Layer | 34-Layer | 50-Layer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conv | 75 75 64 | 7 7 Conv, stride 2 3 3 Max Pool, stride 2 | ||
| Block (1) | 75 75 64 | |||
| Block (2) | 38 38 128 | |||
| Block (3) | 19 19 256 | |||
| Weight parameters (unit: million) | 10 | 16 | 23 | |
| Layers | 18-Layer | 30-Layer | 50-Layer | 121-Layer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conv | 75 75 64 | 7 7 Conv, stride 2 3 3 max pooling, stride 2 | |||
| Dense block (1) | 75 75 256 | ||||
| Transition (1) | 75 75 256 | 1 1 Conv | |||
| 38 38 256 | 2 2 average pooling, stride 2 | ||||
| Dense block (2) | 38 38 384 | ||||
| Transition (2) | 38 38 384 | 1 1 Conv | |||
| 19 19 384 | 2 2 average pooling, stride 2 | ||||
| Dense block (3) | 19 19 512 | ||||
| Transition (3) without pooling | 19 19 512 | 1 1 Conv | |||
| Dense block (4) | 19 19 640 | ||||
| Transition (4) without pooling | 19 19 640 | 1 1 Conv | |||
| Weight parameters (unit: million) | 13 | 20 | 32 | 39 | |
| Predicted Class | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | ||
| Actual class | Positive | TP | FN |
| Negative | FP | TN | |
| Network Model | Mean Average Precision (Unit: %) | Inference Time (Unit: s) |
|---|---|---|
| VGG 16 | 95.7 | 0.29 |
| ResNet18 | 96.4 | 0.25 |
| ResNet34 | 96 | 0.28 |
| ResNet50 | 96 | 0.33 |
| DenseNet18 | 96.6 | 0.38 |
| DenseNet30 | 96.3 | 0.47 |
| DenseNet50 | 95.6 | 0.64 |
| DenseNet121 | 96.2 | 0.69 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, W.; Lee, E.C. Multi-Class Parrot Image Classification Including Subspecies with Similar Appearance. Biology 2021, 10, 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111140
Jang W, Lee EC. Multi-Class Parrot Image Classification Including Subspecies with Similar Appearance. Biology. 2021; 10(11):1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111140
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Woohyuk, and Eui Chul Lee. 2021. "Multi-Class Parrot Image Classification Including Subspecies with Similar Appearance" Biology 10, no. 11: 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111140
APA StyleJang, W., & Lee, E. C. (2021). Multi-Class Parrot Image Classification Including Subspecies with Similar Appearance. Biology, 10(11), 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111140






