Analysis of Codon Usage of Speech Gene FoxP2 among Animals
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Codon Usage Bias and Codon Usage Indices
2.2. Relative Synonymous Codon Usage
2.3. PR2 Plot
2.4. Correspondence Analysis
2.5. Neutrality Plot
2.6. Software Used
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Indices of Codon Usage
3.2. Codon Usage Pattern
3.3. Analysis of PR2 Plot
3.4. Analysis of Neutrality Plot
3.5. Correspondence Analysis
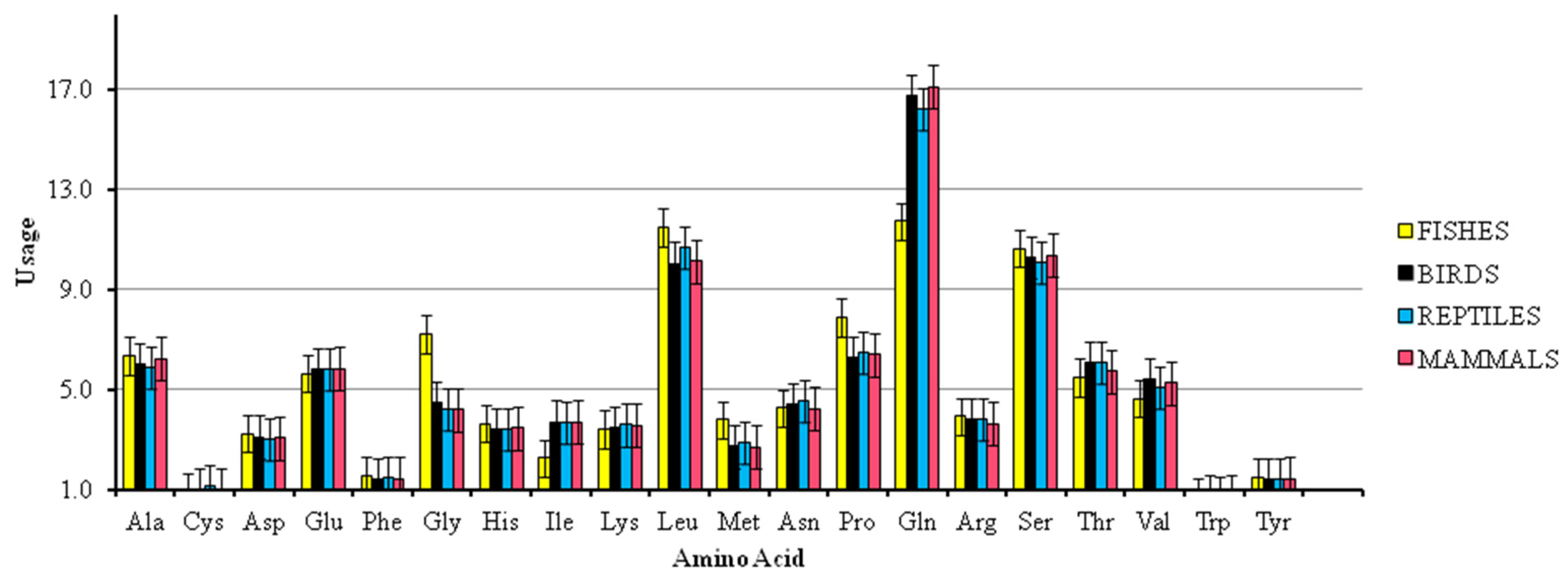
3.6. Analysis of Amino Acid Composition and Protein Properties
3.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grantham, R.; Gautier, C.; Gouy, M. Codon frequencies in 119 individual genes confirm corsistent choices of degenerate bases according to genome type. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980, 8, 1893–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouy, M.; Gautier, C. Codon usage in bacteria: Correlation with gene expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982, 10, 7055–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, P.M.; Tuohy, T.M.F.; Mosurski, K.R. Codon usage in yeast: Cluster analysis clearly differentiates highly and lowly expressed genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986, 14, 5125–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, P.; Li, W.-H. The codon adaptation index-a measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987, 15, 1281–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Campbell, A.; Karlin, S. Correlations between Shine-Dalgarno sequences and gene features such as predicted expression levels and operon structures. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 5733–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osawa, S.; Ohama, T.; Yamao, F.; Muto, A.; Jukes, T.H.; Ozeki, H.; Umesono, K. Directional mutation pressure and transfer RNA in choice of the third nucleotide of synonymous two-codon sets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Onofrio, G.; Mouchiroud, D.; Aïssani, B.; Gautier, C.; Bernardi, G. Correlations between the compositional properties of human genes, codon usage, and amino acid composition of proteins. J. Mol. Evol. 1991, 32, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobry, J.; Gautier, C. Hydrophobicity, expressivity and aromaticity are the major trends of amino-acid usage in 999 Escherichia coli chromosome-encoded genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 3174–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Dafu, D. The relationship between synonymous codon usage and protein structure. FEBS Lett. 1998, 434, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio, G.; Ghosh, T.C.; Bernardi, G. The base composition of the genes is correlated with the secondary structures of the encoded proteins. Gene 2002, 300, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikemura, T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes: A proposal for a synonymous codon choice that is optimal for the E. coli translational system. J. Mol. Biol. 1981, 151, 389–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikemura, T. Correlation between the abundance of yeast transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in protein genes: Differences in synonymous codon choice patterns of yeast and Escherichia coli with reference to the abundance of isoaccepting transfer RNAs. J. Mol. Biol. 1982, 158, 573–597. [Google Scholar]
- Bulmer, M. Coevolution of codon usage and transfer RNA abundance. Nat. Cell Biol. 1987, 325, 728–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaya, S.; Yamada, Y.; Kudo, Y.; Ikemura, T. Studies of codon usage and tRNA genes of 18 unicellular organisms and quantification of Bacillus subtilis tRNAs: Gene expression level and species-specific diversity of codon usage based on multivariate analysis. Gene 1999, 238, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueoka, N. Directional mutation pressure, selective constraints, and genetic equilibria. J. Mol. Evol. 1992, 34, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sueoka, N. Two Aspects of DNA Base Composition: G+C Content and Translation-Coupled Deviation from Intra-Strand Rule of A=T and G=C. J. Mol. Evol. 1999, 49, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sau, K.; Deb, A. Temperature Influences Synonymous Codon and Amino Acid Usage Biases in the Phages Infecting Extremely Thermophilic Prokaryotes. Silico Biol. 2009, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, G.; Bernardi, G. Compositional constraints and genome evolution. J. Mol. Evol. 1986, 24, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlin, S.; Mrázek, J. What Drives Codon Choices in Human Genes? J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 262, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antezana, M.A.; Kreitman, M. The Nonrandom Location of Synonymous Codons Suggests That Reading Frame-Independent Forces Have Patterned Codon Preferences. J. Mol. Evol. 1999, 49, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sueoka, N.; Kawanishi, Y. DNA G+C content of the third codon position and codon usage biases of human genes. Gene 2000, 261, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, B.R. The Role of Context-Dependent Mutations in Generating Compositional and Codon Usage Bias in Grass Chloroplast DNA. J. Mol. Evol. 2003, 56, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.S.L.; Fisher, S.; Hurst, J.A.; Vargha-Khadem, F.; Monaco, A. A forkhead-domain gene is mutated in a severe speech and language disorder. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 413, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pengra, I.G.; Marchaterre, M.A.; Bass, A.H. FoxP2 Expression in a Highly Vocal Teleost Fish with Comparisons to Tetrapods. Brain Behav. Evol. 2018, 91, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Liu, F.-C.; Oishi, T.; Mori, T.; Higo, N.; Hayashi, M.; Hirokawa, K.; Takahashi, H. Expression ofFOXP2in the developing monkey forebrain: Comparison with the expression of the genesFOXP1,PBX3, andMEIS2. J. Comp. Neurol. 2008, 509, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, P.; Reep, R.L.; Stoll, M.L.; Ophir, A.G.; Phelps, S.M. Conservation and diversity of Foxp2 expression in muroid rodents: Functional implications. J. Comp. Neurol. 2009, 512, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, E.; Tokarev, K.; Düring, D.N.; Retamosa, E.C.; Weiss, M.; Arpenik, N.; Scharff, C. Differential coexpression of FoxP1, FoxP2, and FoxP4 in the Zebra Finch (Taeniopygia guttata) song system. J. Comp. Neurol. 2015, 523, 1318–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopka, G.; Roberts, T.F. Insights into the Neural and Genetic Basis of Vocal Communication. Cell 2016, 164, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haesler, S.; Rochefort, C.; Georgi, B.; Licznerski, P.; Osten, P.; Scharff, C. Incomplete and Inaccurate Vocal Imitation after Knockdown of FoxP2 in Songbird Basal Ganglia Nucleus Area X. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramitsu, I.; Kudo, L.C.; London, S.E.; Geschwind, D.H.; White, S.A. Parallel FoxP1 and FoxP2 Expression in Songbird and Human Brain Predicts Functional Interaction. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 3152–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haesler, S.; Wada, K.; Nshdejan, A.; Morrisey, E.E.; Lints, T.; Jarvis, E.D.; Scharff, C. FoxP2 Expression in Avian Vocal Learners and Non-Learners. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 3164–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.S.L.; Gerrelli, D.; Monaco, A.P.; Fisher, S.E.; Copp, A.J. FOXP2 expression during brain development coincides with adult sites of pathology in a severe speech and language disorder. Brain 2003, 126, 2455–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itakura, T.; Chandra, A.; Yang, Z.; Xue, X.; Wang, B.; Kimura, W.; Hikosaka, K.; Inohaya, K.; Kudo, A.; Uezato, T.; et al. The Medaka FoxP2, a Homologue of Human Language Gene FOXP2, has a Diverged Structure and Function. J. Biochem. 2007, 143, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Medina-Martínez, O.; Chu, L.-F.; Samaco, R.C.; Jamrich, M. Expression of FoxP2 during zebrafish development and in the adult brain. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2006, 50, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Gu, W.; Ma, J.; Sun, X.; Lu, Z. Analysis of synonymous codon usage in H5N1 virus and other influenza A viruses. Biosystems 2005, 81, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, F. The ‘effective number of codons’ used in a gene. Gene 1990, 87, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.H.; Smith, D.K.; Rabadan, R.; Peiris, M.; Poon, L.L.M. Codon usage bias and the evolution of influenza A viruses. Codon Usage Biases of Influenza Virus. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 253. [Google Scholar]
- Sueoka, N. Intrastrand parity rules of DNA base composition and usage biases of synonymous codons. J. Mol. Evol. 1996, 42, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrière, G.; Thioulouse, J. Use and misuse of correspondence analysis in codon usage studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 4548–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.C.; Hickey, D.A. Rapid divergence of codon usage patterns within the rice genome. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueoka, N. Directional mutation pressure and neutral molecular evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 2653–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satapathy, S.S.; Sahoo, A.K.; Ray, S.K.; Ghosh, T.C. Codon degeneracy and amino acid abundance influence the measures of codon usage bias: Improved Nc () and ENCprime () measures. Genes Cells 2017, 22, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babicki, S.; Arndt, D.; Marcu, A.; Liang, Y.; Grant, J.R.; Maciejewski, A.; Wishart, D.S. Heatmapper: Web-enabled heat mapping for all. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W147–W153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Afgan, E.; Baker, D.; Batut, B.; van den Beek, M.; Bouvier, D.; Čech, M.; Chilton, J.; Clements, D.; Coraor, N.; Grüning, B.A.; et al. The Galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W537–W544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Du, H.; Qu, Z.; Li, X.-Q.; Xiang, H. Differences in Codon Usage Bias between Photosynthesis-Related Genes and Genetic System-Related Genes of Chloroplast Genomes in Cultivated and Wild Solanum Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; He, J.; Jia, X.; Qi, Q.; Liang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Ping, Y.; Liu, S.; Sun, J. Analysis of codon usage bias of mitochondrial genome in Bombyx mori and its relation to evolution. BMC Evol. Biol. 2014, 14, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabe, A.; Miyashita, N.T. Patterns of codon usage bias in three dicot and four monocot plant species. Genes Genet. Syst. 2003, 78, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Song, H.; Kuang, Y.; Chen, S.; Tian, P.; Li, C.; Nan, Z. Genome-Wide Analysis of Codon Usage Bias in Epichloë festucae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mandal, S.; Mazumder, T.H.; Panda, A.K.; Kumar, N.S.; Jin, F. Analysis of synonymous codon usage patterns of HPRT1 gene across twelve mammalian species. Genetics 2020, 112, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, T.H.; Chakraborty, S. Gaining insights into the codon usage patterns of TP53 gene across eight mammalian species. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Romero, H.; Zavala, A.; Musto, H. Codon usage in Chlamydia trachomatis is the result of strand-specific mutational biases and a complex pattern of selective forces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 2084–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, A.; Mazumder, T.H.; Chakraborty, S. Understanding molecular biology of codon usage in mitochondrial complex IV genes of electron transport system: Relevance to mitochondrial diseases. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 6397–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulmer, M. The selection-mutation-drift theory of synonymous codon usage. Genetics 1991, 129, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalucki, Y.M.; Power, P.M.; Jennings, M.P. Selection for efficient translation initiation biases codon usage at second amino acid position in secretory proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 5748–5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Guan, D.; Ma, L.; Xie, J.; Xu, S. Analysis of synonymous codon usage pattern of genes in unique non–blood-sucking leech Whitmania pigra. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 9850–9858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supek, F.; Vlahoviček, K. Comparison of codon usage measures and their applicability in prediction of microbial gene expressivity. BMC Bioinform. 2005, 6, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behura, S.K.; Severson, D.W. Comparative Analysis of Codon Usage Bias and Codon Context Patterns between Dipteran and Hymenopteran Sequenced Genomes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43111. [Google Scholar]
- Salinas, J.; Matassi, G.; Montero, L.M.; Bernardi, G. Compositional compartmentalization and compositional patterns in the nuclear genomes of plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 4269–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šmarda, P.; Bureš, P.; Horová, L.; Leitch, I.J.; Mucina, L.; Pacini, E.; Tichý, L.; Grulich, V.; Rotreklová, O. Ecological and evolutionary significance of genomic GC content diversity in monocots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4096–E4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, A.; Mazumder, T.H.; Choudhury, M.N.; Chakraborty, S. Codon bias and gene expression of mitochondrial ND2 gene in chordates. Bioinformation 2015, 11, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jenkins, G.M.; Holmes, E.C. The extent of codon usage bias in human RNA viruses and its evolutionary origin. Virus Res. 2003, 92, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, A.; Mazumder, T.H.; Barbhuiya, P.A.; Chakraborty, S. Similarities and dissimilarities of codon usage in mitochondrial ATP genes among fishes, aves, and mammals. IUBMB Life 2020, 72, 899–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
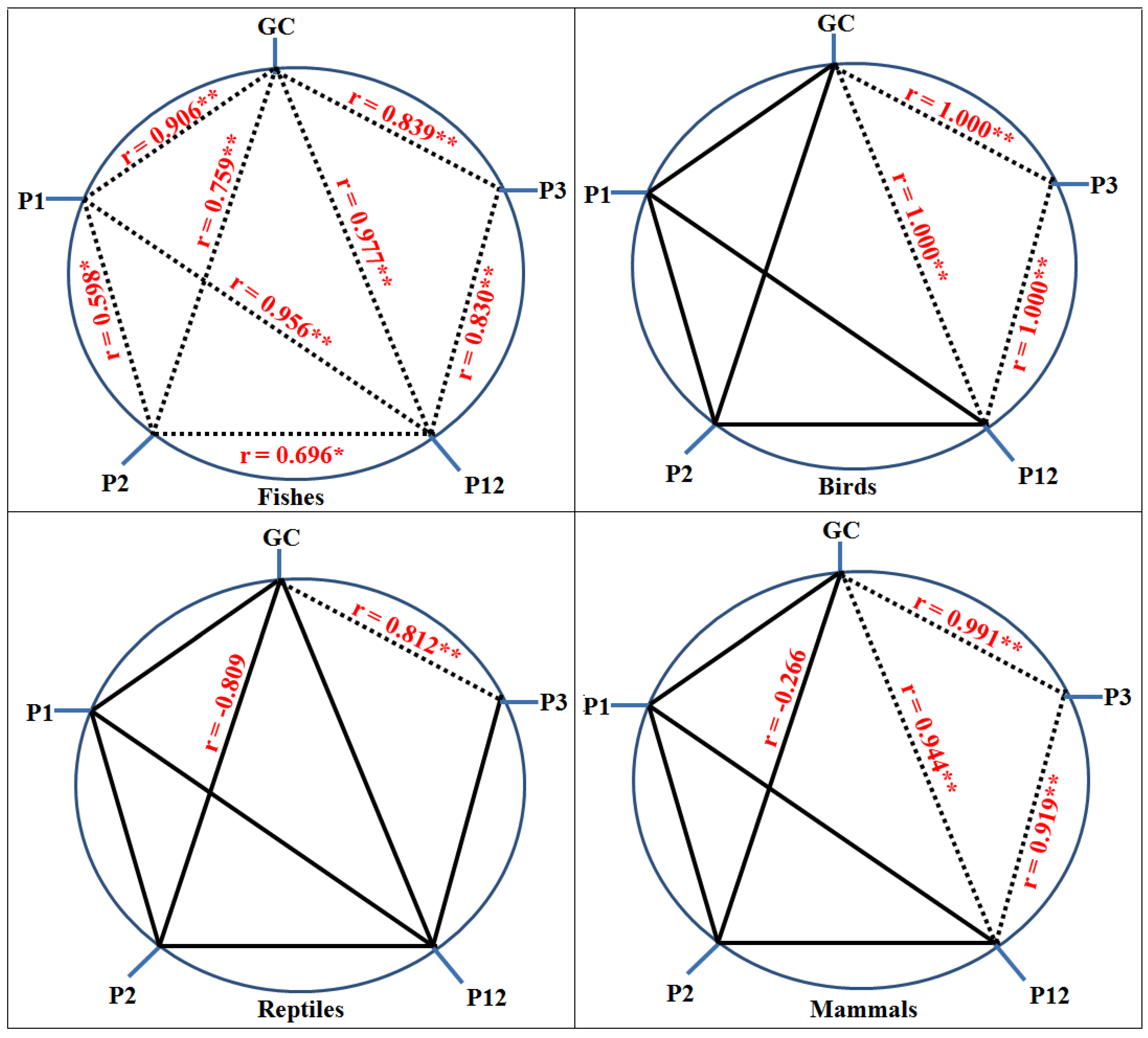

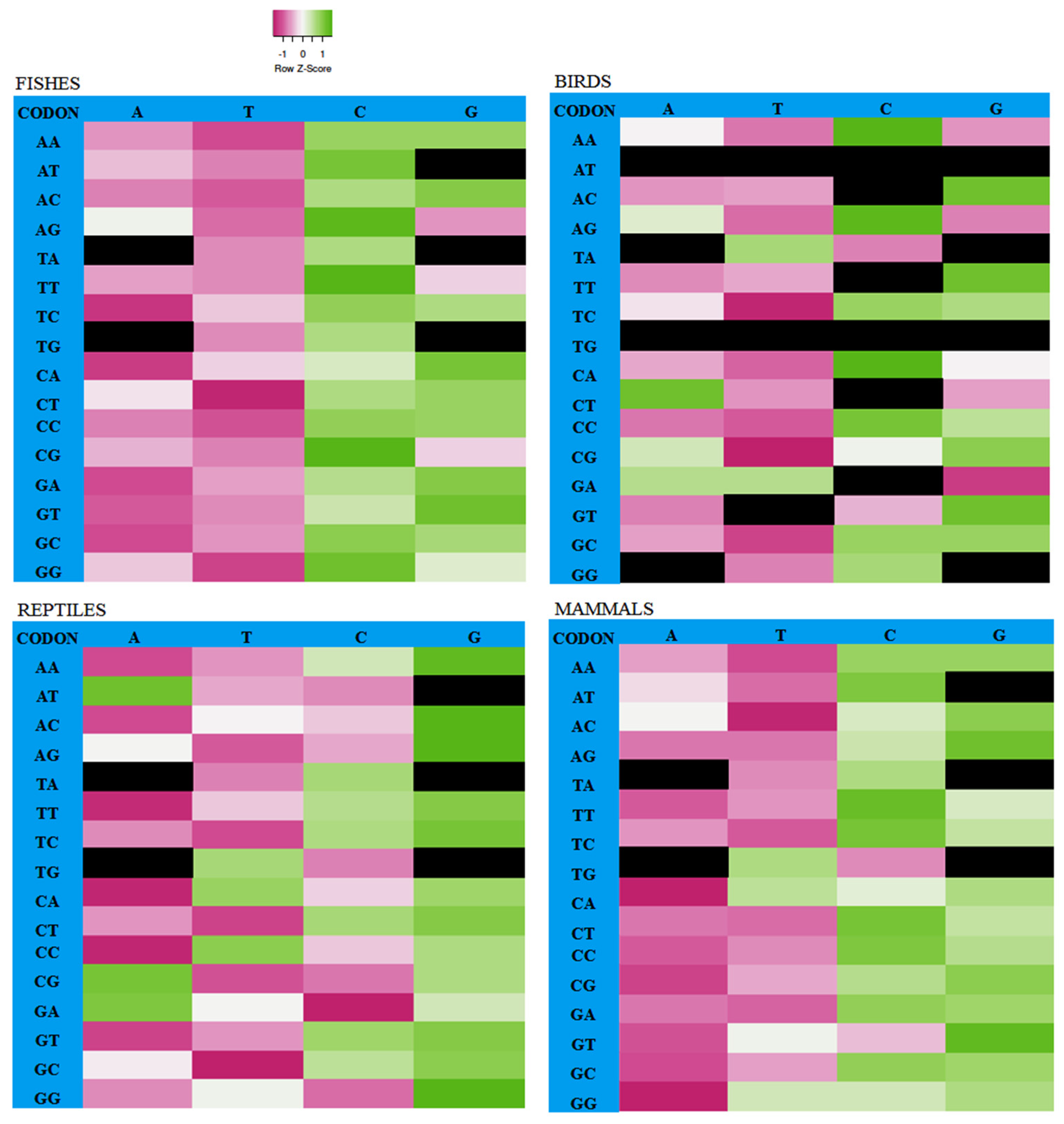

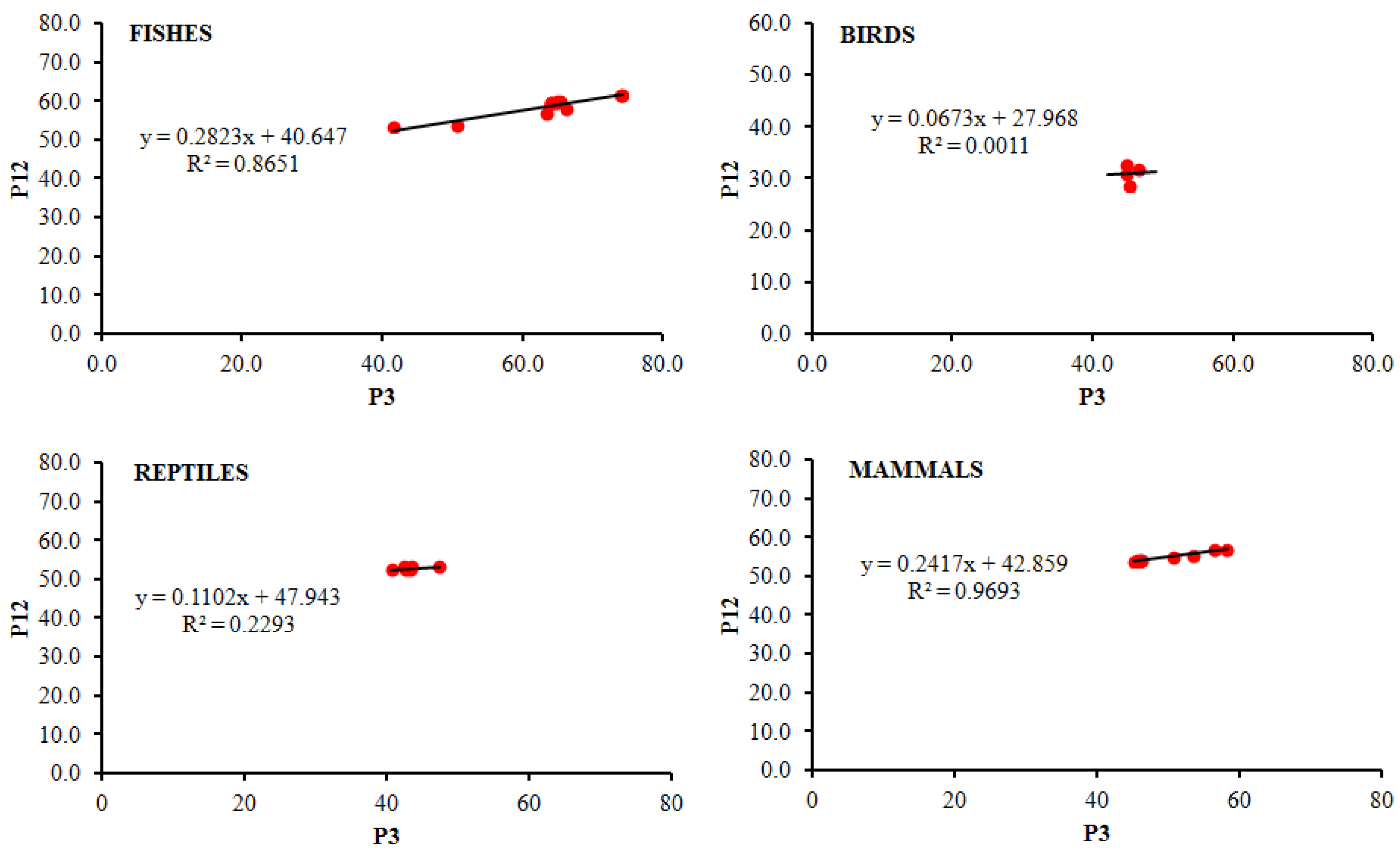
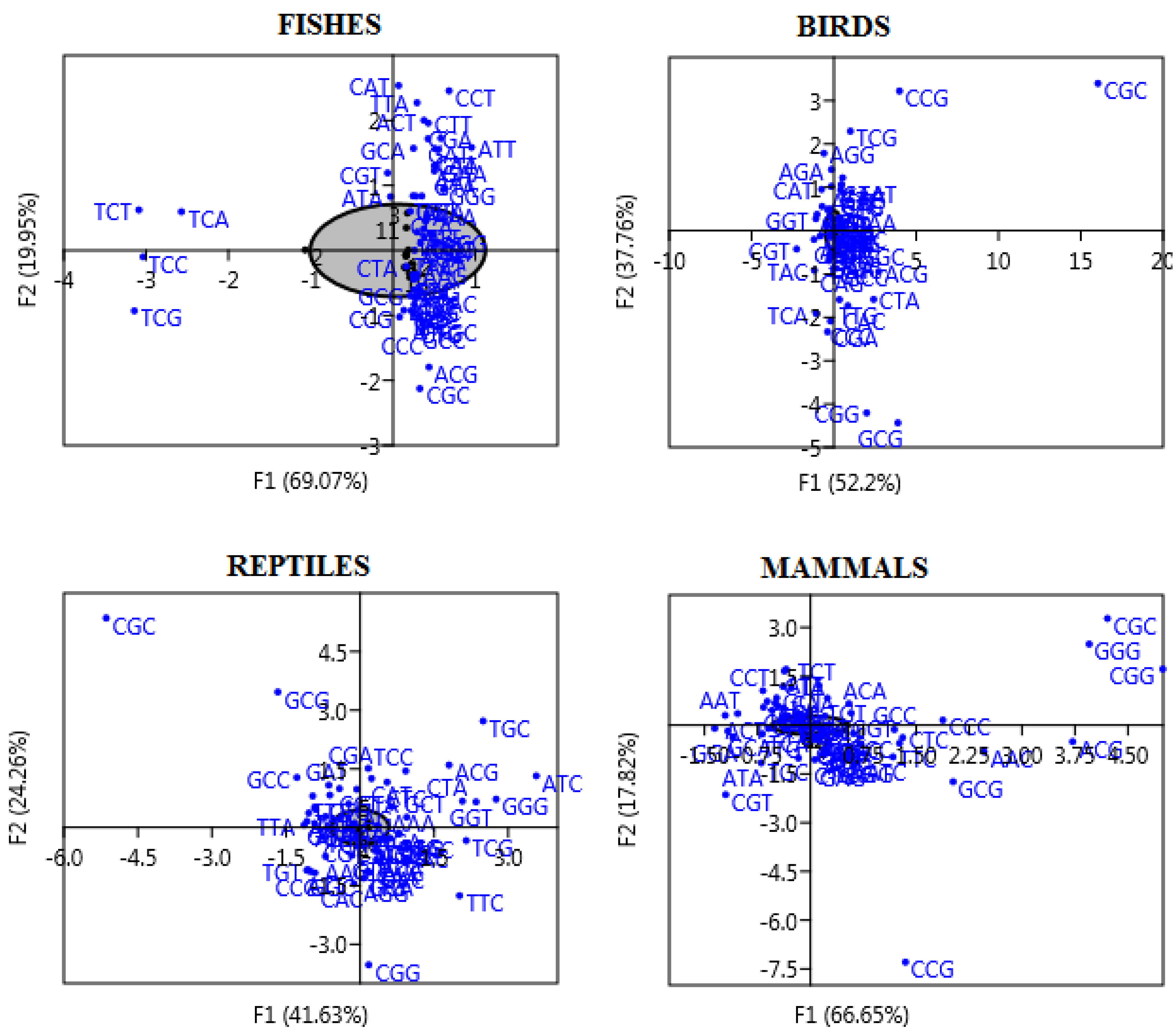

| Fish | Birds | Reptiles | Mammals | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lengthcds | 2228 ± 101.57 | 2118 ± 28.14 | 2153 ± 42.20 | 2134 ± 36.45 |
| GCcds | 55.8 ± 4.05 | 47.7 ± 0.48 | 46.8 ± 0.70 | 49.2 ± 1.98 |
| P1 | 61.2 ± 1.64 | 59.2 ± 0.14 | 58.7 ± 0.67 | 60.2 ± 0.45 |
| P2 | 43.0 ± 2.33 | 38.4 ± 0.68 | 38.2 ± 0.20 | 38.3 ± 0.72 |
| P3 | 63.2 ± 8.99 | 45.3 ± 0.86 | 43.4 ± 2.05 | 49.0 ± 4.86 |
| P12 | 52.1 ± 1.92 | 31.6 ± 0.07 | 48.4 ± 0.28 | 49.3 ± 0.57 |
| ENC | 52.22 ± 3.47 | 53.05 ± 1.95 | 54.65 ± 1.23 | 54.63 ± 1.24 |
| GRAVY | −0.62 ± 0.04 | −0.74 ± 0.01 | −0.72 ± 0.04 | −0.74 ± 0.04 |
| AROMATICITY | 0.04 ± 0.001 | 0.01 ± 0.001 | 0.04 ± 0.001 | 0.04 ± 0.002 |
| FISH | A3% | T3% | G3% | C3% | GC3% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A% | r = 0.966 ** | r = 0.912 ** | r = −0.931 ** | r = −0.946 ** | r = −0.945 ** |
| T% | r = 0.979 ** | r = 0.989 ** | r = −0.971 ** | r = −0.993 ** | r = −0.990 ** |
| G% | r = −0.952 ** | r = −0.892 ** | r = 0.915 ** | r = 0.929 ** | r = 0.928 ** |
| C% | r = −0.984 ** | r = −0.988 ** | r = 0.974 ** | r = 0.993 ** | r = 0.992 ** |
| GC% | r = −0.986 ** | r = −0.958 ** | r = 0.962 ** | r = 0.980 ** | r = 0.978 ** |
| BIRDS | A3% | T3% | G3% | C3% | GC3% |
| A% | r = 0.980 * | r = 0.898 | r = −0.893 | r = −0.983 * | r = −0.983 * |
| T% | r = 0.649 | r = 0.967 * | r = −0.816 | r = −0.887 | r = −0.887 |
| G% | r = −0.835 | r = −0.865 | r = 0.700 * | r = 0.941 | r = 0.929 |
| C% | r = −0.881 | r = −0.981 | r = 0.908 | r = 0.994 ** | r = 0.994 ** |
| GC% | r = −0.915 | r = −0.963 * | r = 0.902 | r = 1.000 ** | r = 0.999 ** |
| REPTILES | A3% | T3% | G3% | C3% | GC3% |
| A% | r = 0.967 ** | r = 0.299 | r = −0.879 | r = −0.452 | r = −0.957 ** |
| T% | r = −0.389 ** | r = 0.553 | r = 0.290 | r = −0.285 | r = 0.056 |
| G% | r = −0.944 ** | r = 0.222 | r = 0.958 ** | r = −0.111 ** | r = 0.684 |
| C% | r = 0.081 | r = −0.931 ** | r = −0.166 | r = 0.865 * | r = 0.384 |
| GC% | r = −0.827 * | r = −0.549 | r = 0.767 | r = 0.605 | r = 0.961 ** |
| MAMMALS | A3% | T3% | G3% | C3% | GC3% |
| A% | r = 0.987 ** | r = 0.956 ** | r = −0.812 ** | r = −0.968 ** | r = −0.983 ** |
| T% | r = 0.954 ** | r = 0.998 ** | r = −0.913 ** | r = −0.893 ** | r = −0.983 ** |
| G% | r = −0.968 ** | r = −0.984 ** | r = 0.950 ** | r = 0.870 ** | r = 0.985 |
| C% | r = −0.972 ** | r = −0.931 ** | r = 0.739 ** | r = 0.990 ** | r = 0.964 ** |
| GC% | r = −0.989 ** | r = −0.980 ** | r = 0.858 ** | r = 0.953 ** | r = 0.995 ** |
| ENC | P1 | P2 | P3 | P12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIRDS | −0.200 | 0.800 | 1.000 ** | 0.949 |
| FISH | −0.742 ** | −0.505 | −0.938 ** | −0.754 ** |
| REPTILES | 0.290 | −0.493 | 0.543 | 0.638 |
| MAMMALS | 0.251 | −0.257 | 0.305 | −0.046 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mazumder, T.H.; Alqahtani, A.M.; Alqahtani, T.; Emran, T.B.; A. Aldahish, A.; Uddin, A. Analysis of Codon Usage of Speech Gene FoxP2 among Animals. Biology 2021, 10, 1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111078
Mazumder TH, Alqahtani AM, Alqahtani T, Emran TB, A. Aldahish A, Uddin A. Analysis of Codon Usage of Speech Gene FoxP2 among Animals. Biology. 2021; 10(11):1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111078
Chicago/Turabian StyleMazumder, Tarikul Huda, Ali M. Alqahtani, Taha Alqahtani, Talha Bin Emran, Afaf A. Aldahish, and Arif Uddin. 2021. "Analysis of Codon Usage of Speech Gene FoxP2 among Animals" Biology 10, no. 11: 1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111078
APA StyleMazumder, T. H., Alqahtani, A. M., Alqahtani, T., Emran, T. B., A. Aldahish, A., & Uddin, A. (2021). Analysis of Codon Usage of Speech Gene FoxP2 among Animals. Biology, 10(11), 1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111078







