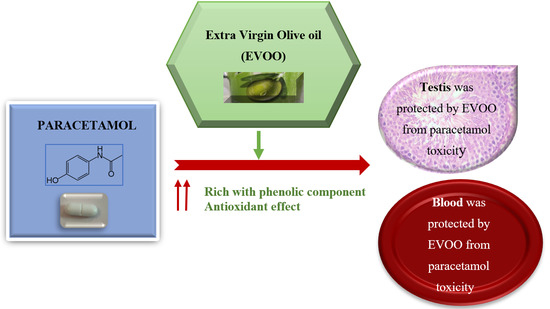
Extra Virgin Olive Oil Protects the Testis and Blood from the Toxicity of Paracetamol (Overdose) in Adult Male Rats
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
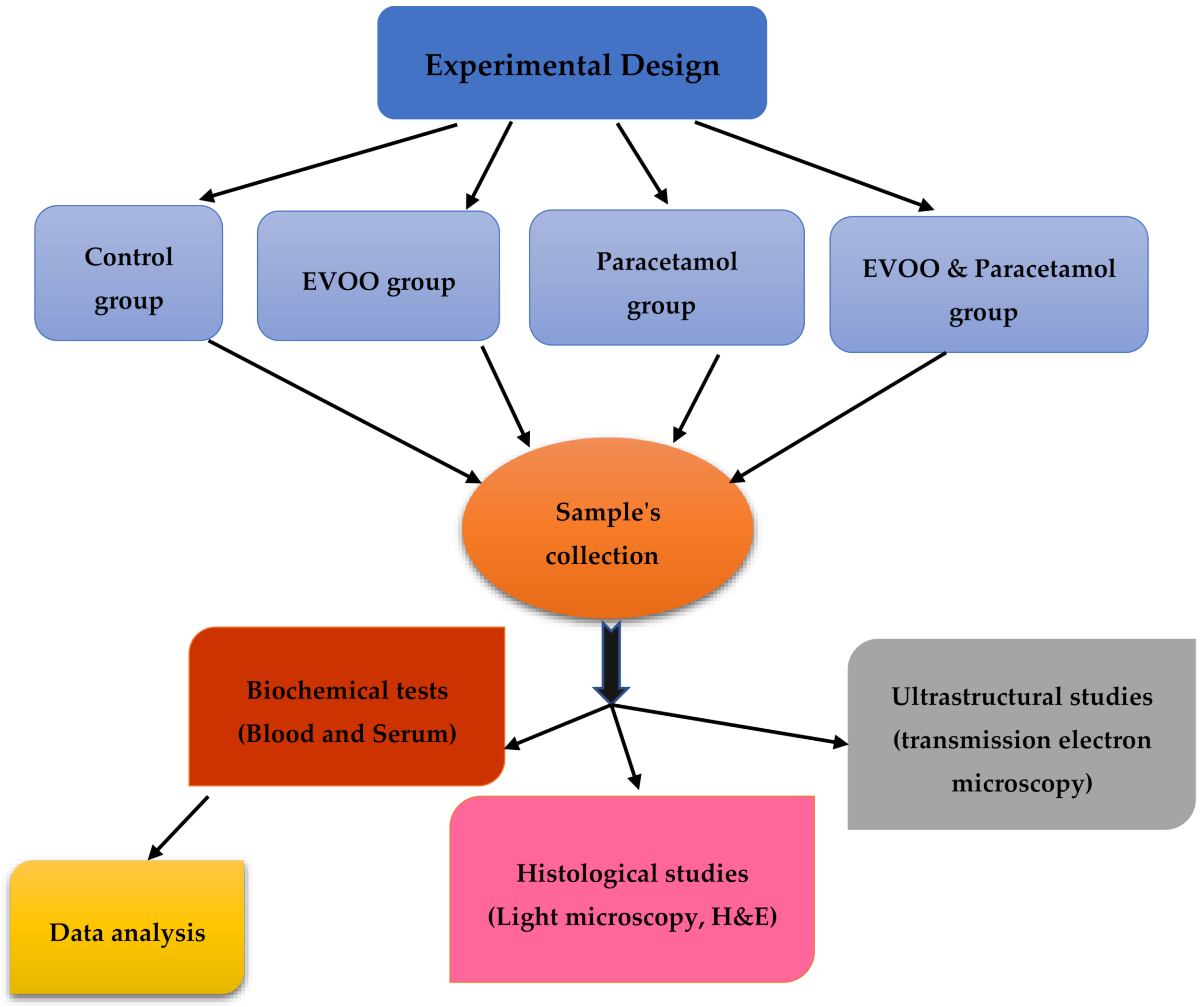
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Biochemical Tests
2.4. Histological and Ultrastructural Studies
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
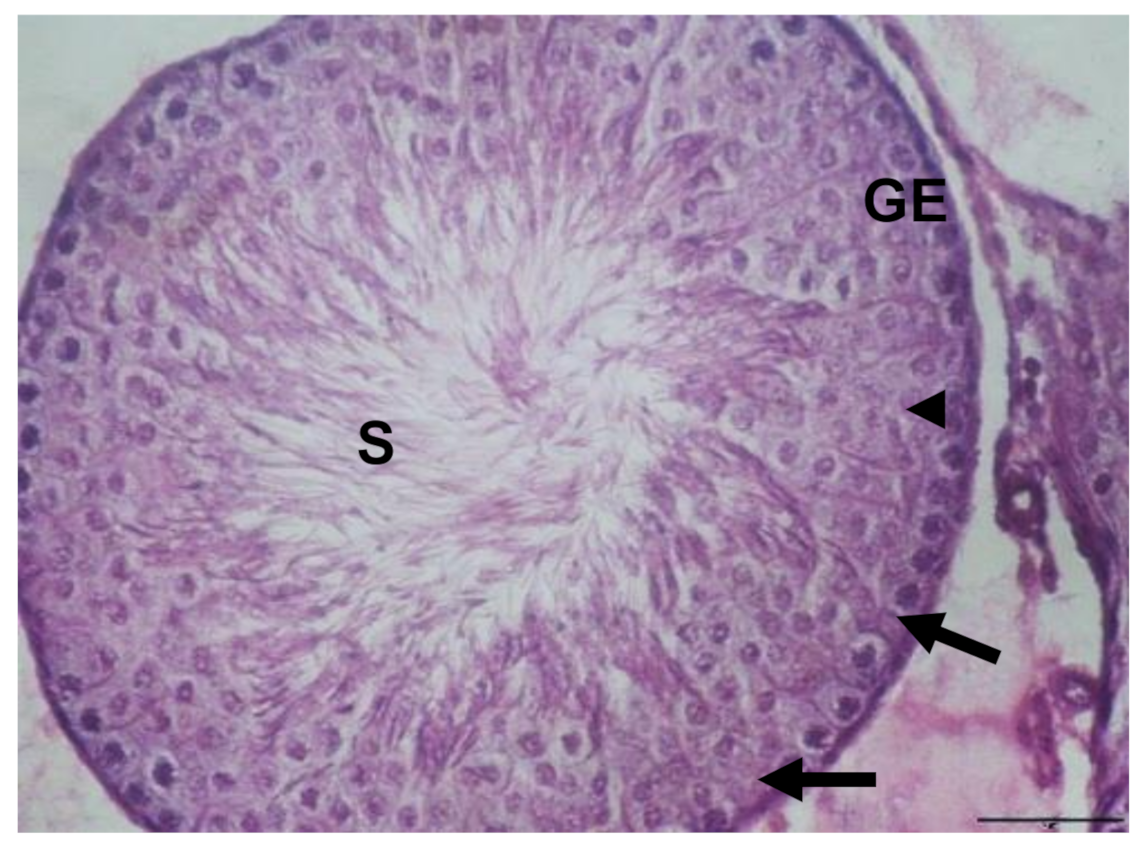
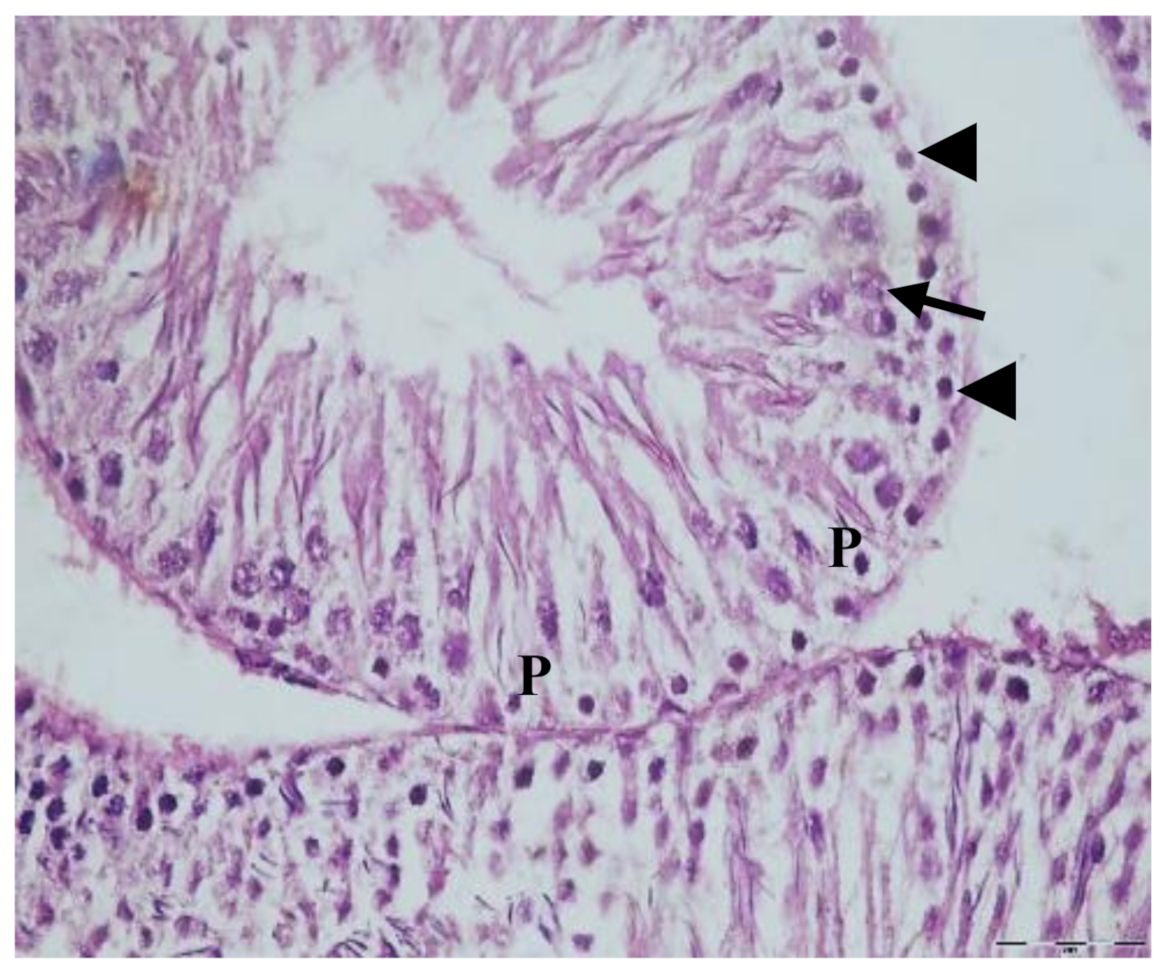
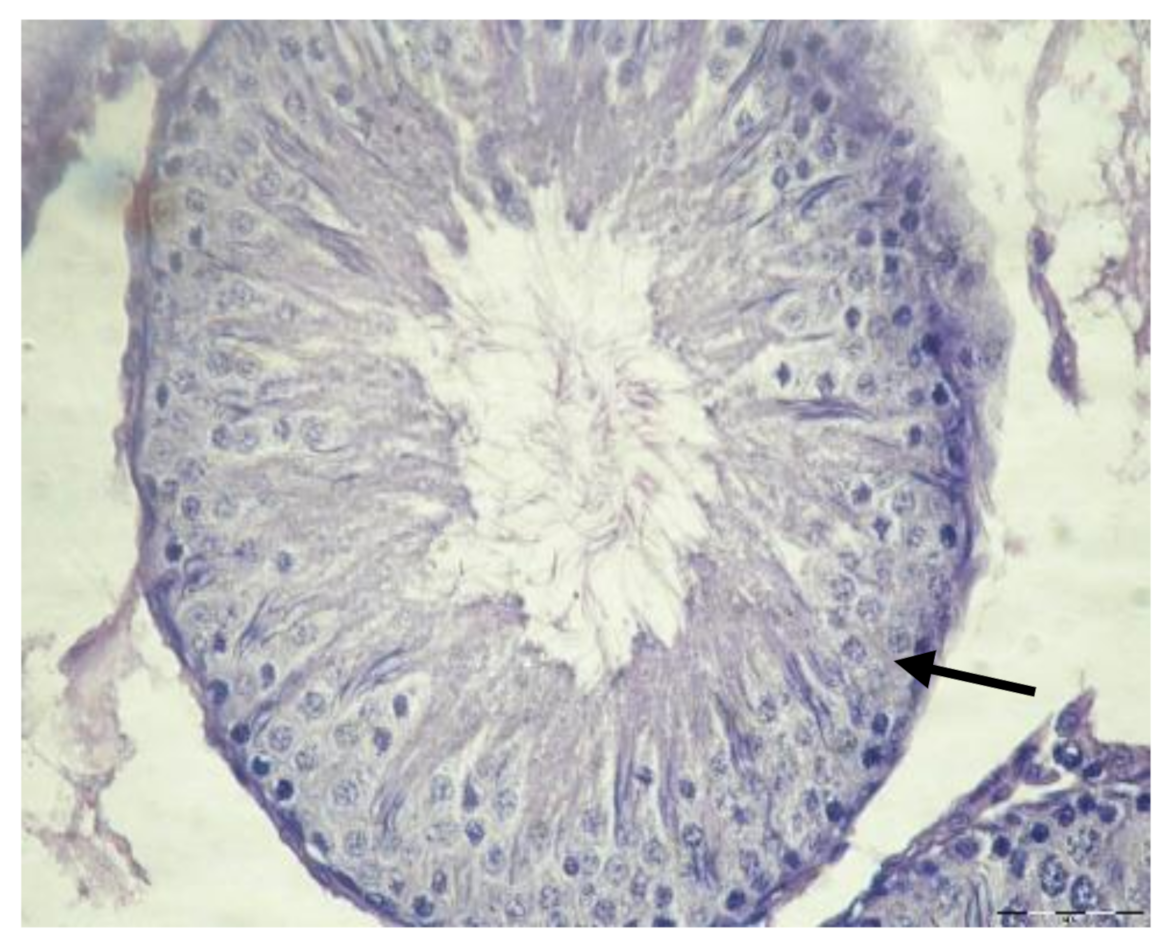
3.1. Histological Results
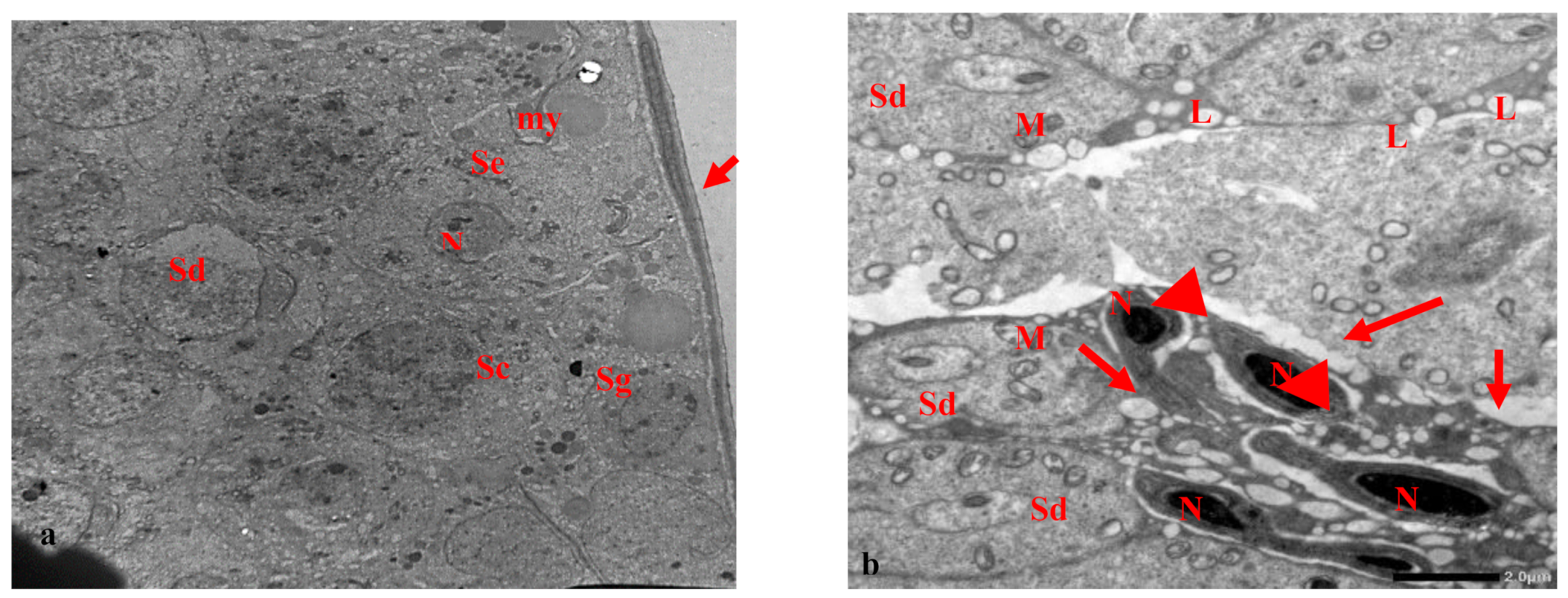
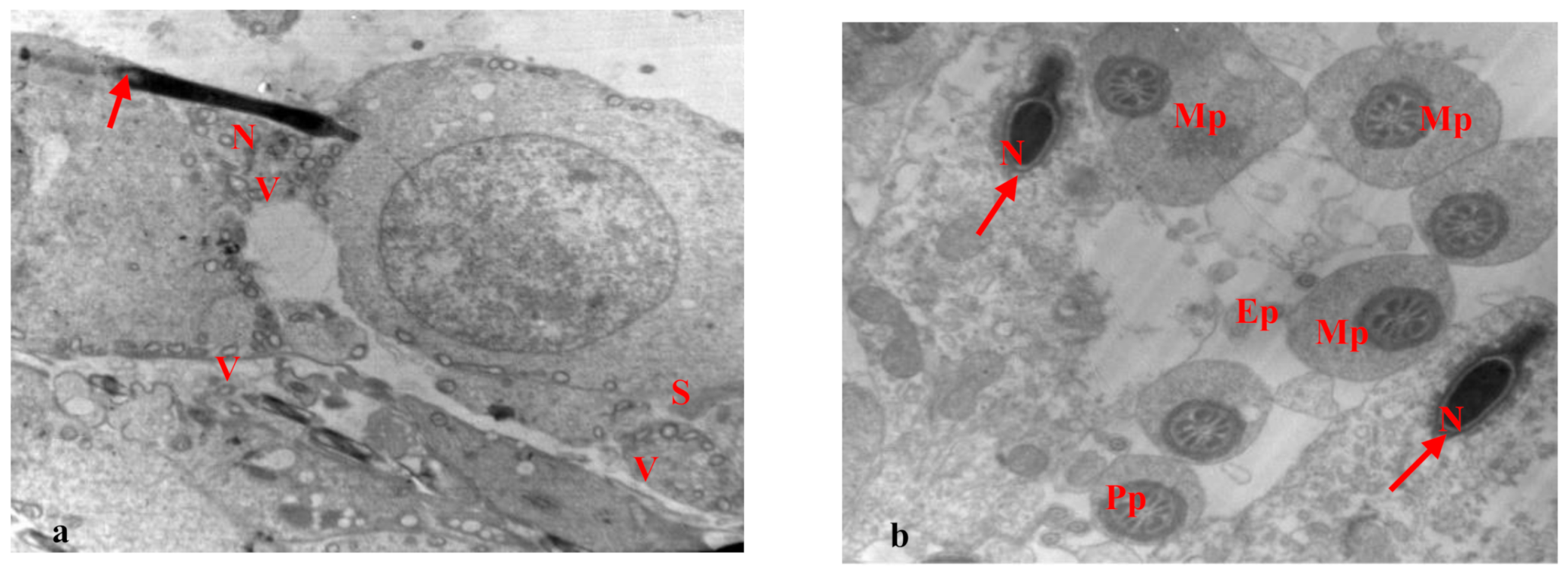
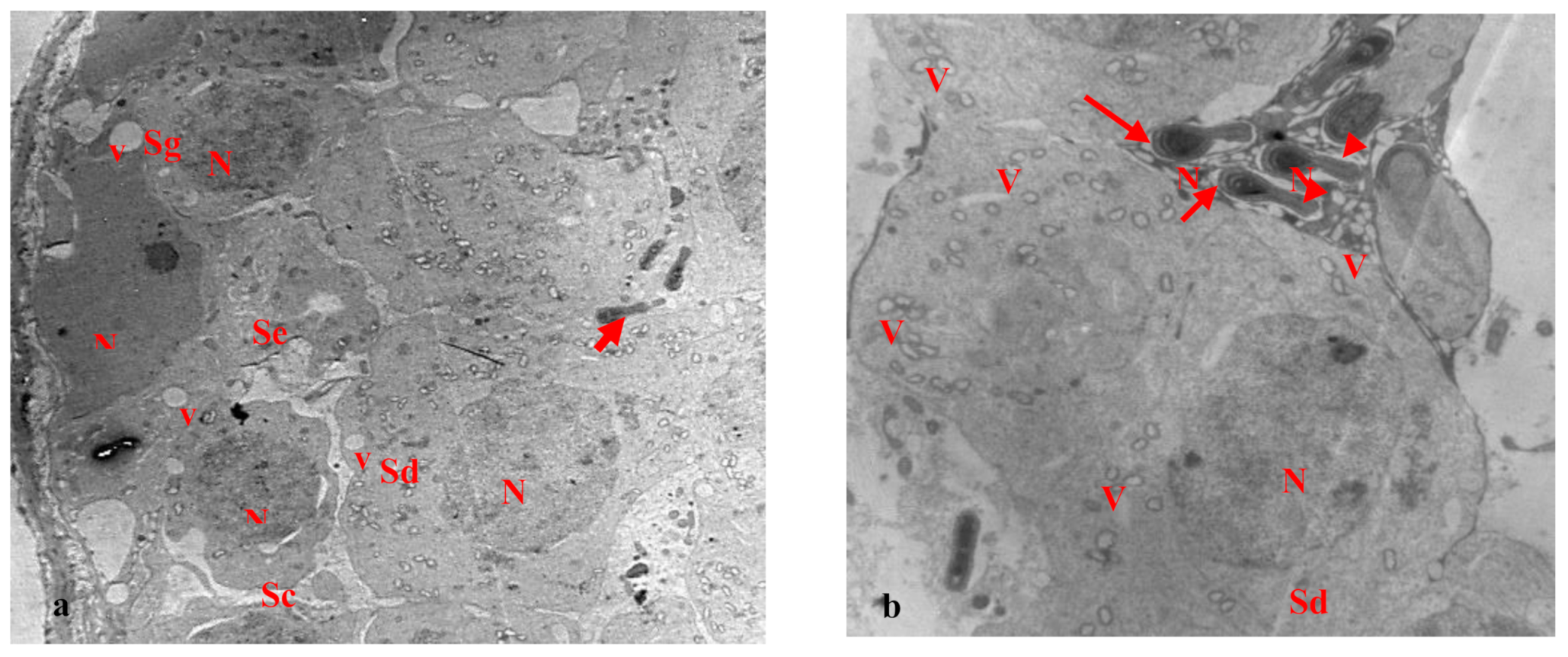
3.2. Electron Microscopy Results
3.3. Hematological Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benista, M.J.-B.; Nowak, J.Z. Paracetamol: Mechanism of action, applications and safety concern. Acta Pol. Pharm. Drug. Res. 2014, 71, 11–23. Available online: https://europepmc.org/article/med/24779190/ (accessed on 15 February 2020).
- Olaleye, M.T.; Rocha, B.T.J. Acetaminophen induced liver damage in mice: Effect of some medicinal plants on the oxidative defense system. Exp. Toxicol. Phathol. 2008, 59, 319–327. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18054472/ (accessed on 15 February 2020). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luangpirom, A.; Kourchampa, W.; Junaimuang, T. Attenuating effect of Allium ascalonicum L. on paracetamol induced seminal quality impairment in mice. J. Med. Plan. Res. 2012, 6, 2655–2659. Available online: http://www.academicjournals.org/app/webroot/article/article1380786182_Lu/ (accessed on 15 February 2020). [CrossRef]
- Oyedeji, K.O.; Bolarinwa, A.F.; Ojeniran, S.S. Effect of Paracetamol (Acetaminophen) On Haematological and Reproductive Parameters in Male Albino Rats. IOSR J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2013, 4, 65–70. Available online: http://www.iosrjournals.org/iosr-jpbs/papers/Vol4-issue6/O0466570/ (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- Khayyat, L.I. Protective effects of extra virgin olive oil against paracetamol-induced liver toxicity in Wistar albino rats. Eurasia J. Biosci. 2016, 10, 30–40. Available online: http://ejobios.org/article/ (accessed on 15 February 2020).
- Khayyat, L.I. Evaluate of the efficacy of Extra Virgin Olive Oil against Paracetamol overdose induced renal toxicity in albino rats. Umm. Al-Qura Univ. J. App. Sci. 2018, 5, 1–13. Available online: https://uqu.edu.sa/en/jas/ (accessed on 15 February 2020).
- Banihani, S.A. Effect of paracetamol on semen quality. Andrologia 2018, 50, e12874. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28752572/ (accessed on 15 February 2020). [CrossRef]
- Stark, A.H.; Mader, Z. Olive oil as a functional food: Epidemiology and nutritional approaches. Nutr. Rev. 2002, 60, 170–176. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12078915/ (accessed on 15 March 2020). [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Gonzalez, R.; Estruch, M.A. Mediterranean diet, antioxidants and cancer: The need for randomized trials. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2004, 13, 327–333. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15554561/ (accessed on 15 February 2020). [CrossRef]
- Miles, E.A.; Zoubouli, P.; Calder, P.C. Differential anti-inflammatory effects of phenolic compounds from extra virgin olive oil identified in human whole blood cultures. Nutrients 2005, 21, 389–394. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15797683/ (accessed on 15 February 2020). [CrossRef]
- Panagiotakos, D.B.; Pitsavos, C.; Stefanadis, C. Dietary patters: A Mediterranean diet score and its relation to clinical and biological markers of cardiovascular disease risk. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2006, 16, 559–568. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17126772/ (accessed on 15 February 2020). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, S.; Awad, A.; Elewa, Y. Antidotal impact of extra virgin olive oil against genotoxicity, cytotoxicity and immunotoxicity induced by hexavalent chromium in rat. Int. J. Veter. Sci. Med. 2013, 1, 65–73. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2314459913000276/ (accessed on 15 March 2020). [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Paiva-Martins, F.; Rodrigues, V.; Calheiros, R.; Marques, M.P.J. Characterization of antioxidant olive oil biophenols by spectroscopic methods. J. Sci. Food Agri. 2011, 2, 309–314. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/jsfa.4186 (accessed on 15 February 2020). [CrossRef]
- Rafehi, H.; Ververis, K.; Karagiannis, T.C. Mechanisms of action of phenolic compounds in olive. J. Diet Suppl. 2012, 9, 96–109. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22607645/ (accessed on 15 February 2020). [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Jiménez, F.; Cienfuegos, A.; Badimon, L.; Barja, G. International conference on the health effect of olive oil. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 35, 421–424. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16008542/ (accessed on 15 February 2020).
- Oliveras-López, M.-J.O.; Berná, G.; Carneiro, E.M.; Serrana, H.L.-G.; Franz Martín, F.; Carmen López, M. An Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Rich in Polyphenolic Compounds Has Antioxidant Effects in Of1 Mice. J. Nutr. 2008, 1704–1708. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/jn/article/138/6/1074/4670254/ (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- AL-Ani, N.K.H. Protective influence of olive oil on reproductive parameters in male rat treated with cadmium. Glob. J. Bio-Sci. Biot. 2013, 2, 500–505. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/ (accessed on 15 February 2020).
- Domínguez-Vías, G.; Segarra, A.B.; Martínez-Cañamero, M.; Ramírez-Sánchez, M.; Prieto, I. Influence of a Virgin Olive Oil versus Butter Plus Cholesterol-Enriched Diet on Testicular Enzymatic Activities in Adult Male Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, M.J.; Naveed, A.K.; Ahmed, T.; Khan, S.; Azeem, Z. Hypolipidemic Effect of Extra Virgin Olive Oil in Diabetic Rats. J. Rawalpindi Med. Coll. 2012, 16, 70–72. Available online: http://www.journalrmc.com/volumes/1394782471/ (accessed on 15 February 2020).
- Farràs, M.; Canyelles, M.; Fitó, M.; Escolà-Gil, J.C. Effects of Virgin Olive Oil and Phenol-Enriched Virgin Olive Oils on Lipoprotein Atherogenicity. Nutrients 2020, 12, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammi, C.; Bellumori, M.; Cecchi, L.; Bartolomei, M.; Bollati, C.; Clodoveo, M.L.; Corbo, F.; Arnoldi, A.; Mulinacci, A. Extra Virgin Olive Oil Phenol Extracts Exert Hypocholesterolemic Effects through the Modulation of the LDLR Pathway: In Vitro and Cellular Mechanism of Action Elucidation. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelino, G.; Hiane, P.A.; Freitas, K.D.C.; Santana, L.F.; Pott, A.; Donadon, J.R.; Guimarães, R.D.C.A. Effects of Olive Oil and Its Minor Components on Cardiovascular Diseases, Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellumori, M.; Cecchi, L.; Innocenti, M.; Clodoveo, M.L.; Corbo, F.; Mulinacci, N. The EFSA Health Claim on Olive Oil Polyphenols: Acid Hydrolysis Validation and Total Hydroxytyrosol and Tyrosol Determination in Italian Virgin Olive Oils. Molecules 2019, 24, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Haldar, N.; Bhattacharya, S.; Biswas, S.; Biswas, M. Hepatoprotective activity of Litchi chiesas leaf against paracetamol-induced liver damage in rats. Middle-East J. Sci. Res. 2014, 20, 292–296. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/ (accessed on 15 February 2020).
- Henry, R. Clinical Chemistry; Principles and Technics, 2nd ed.; Medical Dept., Harper & Row: Hagerstown, MD, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Patton, C.; Crouch, S. Spectrophotometric and kinetics investigation of the Berthelot reaction for the determination of ammonia. Anal. Chem 1977, 49, 464–468. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/ac50011a034/ (accessed on 15 February 2020). [CrossRef]
- Caraway, W. Determination of uric acid in serum by carbonate method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1955, 25, 840–845. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14387986/ (accessed on 15 March 2020). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, C.L.; Dolder, H. Rat testicular structure and ultrastructure after paracetamol treatment. Contraception 2002, 66, 463–467. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12499042/ (accessed on 15 March 2020). [CrossRef]
- El-Maddawy, Z.K.; El-Sayed, Y.S. Comparative analysis of the protective effects of curcumin and N-acetyl cysteine against paracetamol-induced hepatic, renal, and testicular toxicity in Wistar rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 3468–3479. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29152699/ (accessed on 15 March 2020). [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.A.M. Toxic effect of paracetamol on male reproductive system of adult rabbits. Int. J. Pharm. Bio. Sci. 2013, 4, 806–821. Available online: https://ijpbs.net/counter.php?aid=2068/ (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- Samuel, S.A.; Francis, A.O.; Ayomide, O.; Onyinyechi, U.-O. Effect of paracetamol-induced liver damage on some hematological parameters: Red blood cell (RBC) count, white blood cell (WBC) count, and packed cell volume (PCV) in wister rats of either sex. Indo Am. J. Pharm. Res. 2015, 5, 2231–6876. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/ (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- Visioli, F.; Galli, C.; Grande, S.; Colonnelli, K.; Patelli, C.; Galli, G.; Caruso, D. Hydroxytyrosol excretion differs between rats and humans and depends on the vehicle of administration. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 2612–2615. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12888646// (accessed on 15 March 2020). [CrossRef]
- Nakbi, A.; Tayeb, W.; Hammami, M. Effects of olive oil and its fractions on oxidative stress and the liver’s fatty acid composition in 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-treated rats. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 7, 80. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2987329/ (accessed on 15 March 2020). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabiani, R.; Rosignoli, P.; Bartolomeo, A.; Fuccelli, R.; Servili, M.; Montedoro, G.F.; Morozzi, G. Oxidative DNA Damage Is Prevented by Extracts of Olive Oil, Hydroxytyrosol, and Other Olive Phenolic Compounds in Human Blood Mononuclear Cells and HL60 Cells. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1411–1416. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18641183/ (accessed on 15 March 2020). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- María-Isabel, C. Olive oil and the cardiovascular system. Pharm. Res. 2007, 55, 175–186. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17321749/ (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- Santis, S.D.; Liso, M.; Verna, G.; Curci, F.; Milani, G.; Faienza, M.F.; Franchini, C.; Moschetta, A.; Chieppa, M.; Clodoveo, M.L.; et al. Extra Virgin Olive Oil Extracts Modulate the Inflammatory Ability of Murine Dendritic Cells Based on Their Polyphenols Pattern: Correlation between Chemical Composition and Biological Function. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Cell Part | Morphological Parameters |
|---|---|
| Nucleus | Shape, Chromatin, Number of nucleoli |
| Cytoplasm | Morphology of organelles, Vacuoles, Lipid droplets |
| Plasma membrane | Shape, Basement membrane |
| Flagella | Shape |
| Control | Paracetamol | EVOO | Paracetamol + EVOO | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
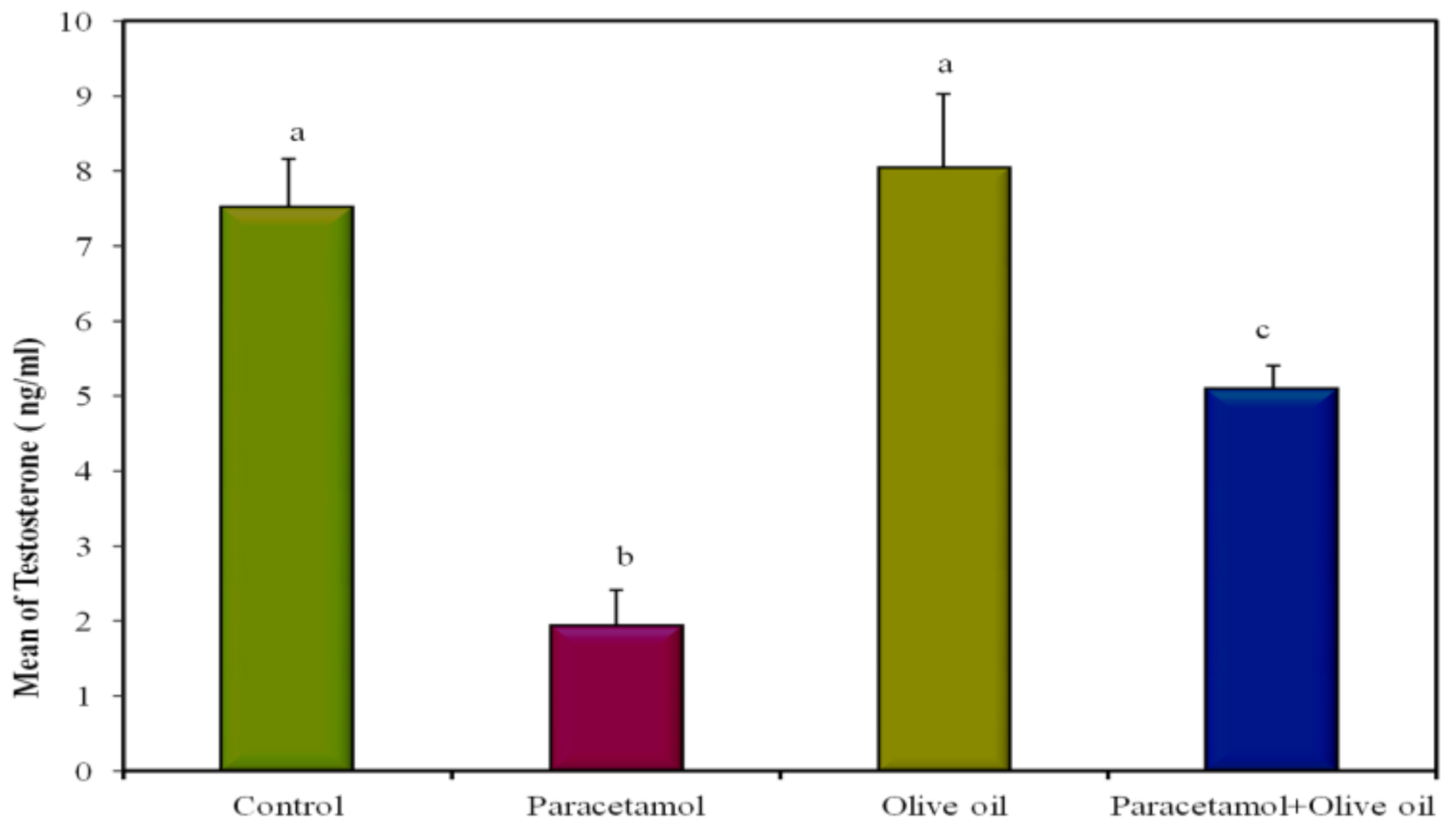
| Testosterone (ng/mL) | 7.52 a ± 0.64 | 1.94 b ± 0.47 | 8.04 a ± 0.98 | 5.10 c ± 0.30 | <0.001 * |
| Control | Paracetamol | EVOO | Paracetamol + EVOO | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
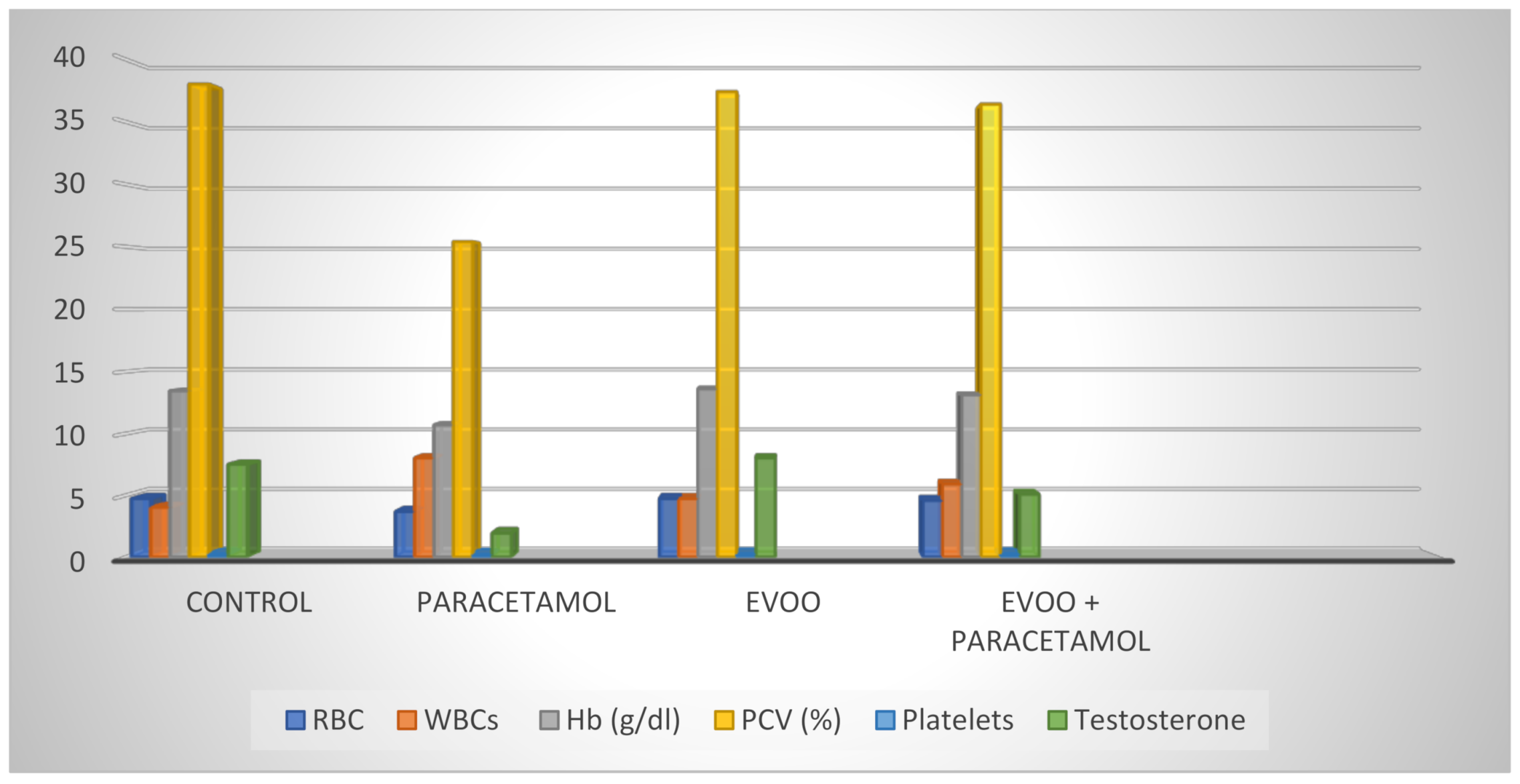
| RBC (106/mL) | 4.75 a ± 0.13 | 3.69 b ± 0.20 | 4.75 a ± 0.24 | 4.59 a ± 0.24 | 0.006 * |
| Hb (g/dl) | 13.46 a ± 0.42 | 10.70 b ± 0.80 | 13.62 a ± 0.76 | 13.14 a ± 0.89 | 0.043 * |
| PCV (%) | 38.00 a ± 1.64 | 25.40 b ± 2.06 | 37.40 a ± 2.29 | 36.40 a ± 2.25 | 0.002 * |
| Platelets (103/mL) | 262.60 a ± 16.23 | 213.20 b ± 17.78 | 258.20 a ± 15.23 | 259.80 a ± 16.04 | 0.103 * |
| Control | Paracetamol | EVOO | Paracetamol + EVOO | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBCs (103/mm3) | 4040.0 a ± 166.13 | 8040.0 b ± 370.94 | 4740.0 a ± 297.66 | 5920.0 c ± 278.21 | <0.001 * |
| Differential WBC count % Neutrophils | 59.00 ± 1.70 | 58.60 ± 2.11 | 56.60 ± 2.27 | 58.40 ± 2.16 | 0.851 |
| Stab forms | 2.80 a ± 0.37 | 6.20 b ± 0.86 | 3.0 a ± 0.32 | 2.60 a ± 0.51 | 0.001 * |
| Lymphocytes | 33.40 ab ± 1.91 | 28.40 a ± 2.09 | 36.0 b ± 1.90 | 33.80 ab ± 2.13 | 0.092 |
| Monocytes | 3.60 ± 0.51 | 5.20 ± 0.58 | 3.40 ± 0.51 | 4.00 ± 0.84 | 0.214 |
| Eosinophils | 1.20 ± 0.37 | 1.60 ± 0.40 | 1.00 ± 0.32 | 1.20 ± 0.49 | 0.758 |
| Basophils | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | - |
| EVOO + Paracetamol | EVOO | Paracetamol | Control | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBC (106/mL) | 4.59 a ± 0.24 | 4.75 a ± 0.24 | 3.69 b ± 0.20 | 4.75 a ± 0.13 |
| WBCs (103/mm3) | 5920.0 c ± 278.21 | 4740.0 a ± 297.66 | 8040.0 b ± 370.94 | 4040.0 a ± 166.13 |
| Hb (g/dL) | 13.14 a ± 0.89 | 13.62 a ± 0.76 | 10.70 b ± 0.80 | 13.46 a ± 0.42 |
| PCV (%) | 36.40 a ± 2.25 | 37.40 a ± 2.29 | 25.40 b ± 2.06 | 38.00 a ± 1.64 |
| Platelets (103/mL) | 259.80 a ± 16.04 | 258.20 a ± 15.23 | 213.20 b ± 17.78 | 262.60 a ± 16.23 |
| Testosterone (ng/mL) | 5.10 c ± 0.30 | 8.04 a ± 0.98 | 1.94 b ± 0.47 | 7.52 a ± 0.64 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khayyat, L.I. Extra Virgin Olive Oil Protects the Testis and Blood from the Toxicity of Paracetamol (Overdose) in Adult Male Rats. Biology 2021, 10, 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10101042
Khayyat LI. Extra Virgin Olive Oil Protects the Testis and Blood from the Toxicity of Paracetamol (Overdose) in Adult Male Rats. Biology. 2021; 10(10):1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10101042
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhayyat, Latifa Ishaq. 2021. "Extra Virgin Olive Oil Protects the Testis and Blood from the Toxicity of Paracetamol (Overdose) in Adult Male Rats" Biology 10, no. 10: 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10101042
APA StyleKhayyat, L. I. (2021). Extra Virgin Olive Oil Protects the Testis and Blood from the Toxicity of Paracetamol (Overdose) in Adult Male Rats. Biology, 10(10), 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10101042