Discovery and Validation of a Novel Step Catalyzed by OsF3H in the Flavonoid Biosynthesis Pathway
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cloning and Construction of Plasmids
2.2. Strain and Media
2.3. Transformation to Yeast
2.4. Colony PCR
2.5. Protein Isolation and Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Extraction and Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) of Kaempferol and Quercetin
2.7. Kaempferol and Quercetin Identification via LCMS-MS and NMR
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
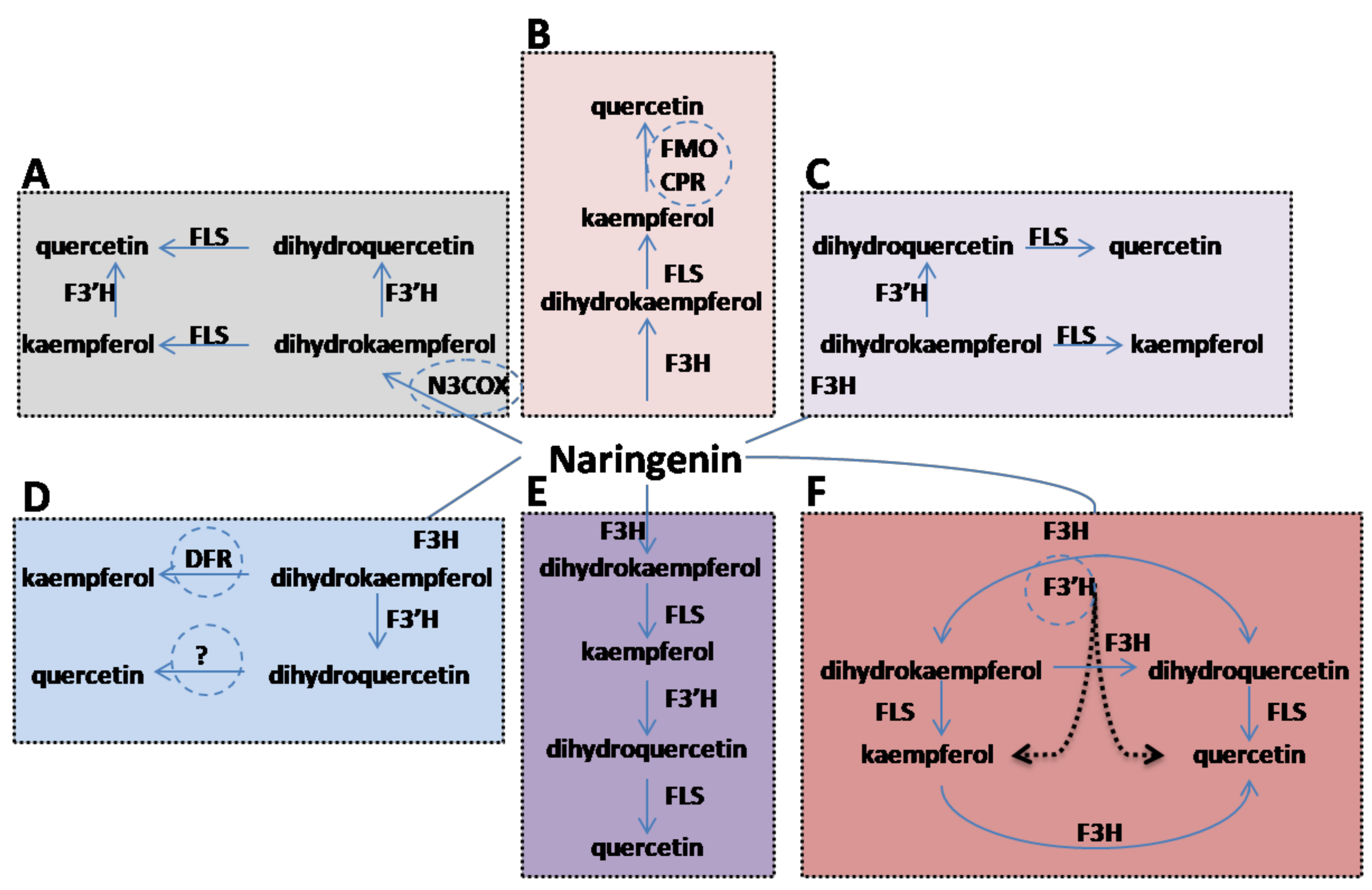
3.1. Cloning Of F3H and Designing of Kaempferol and Quercetin Pathway
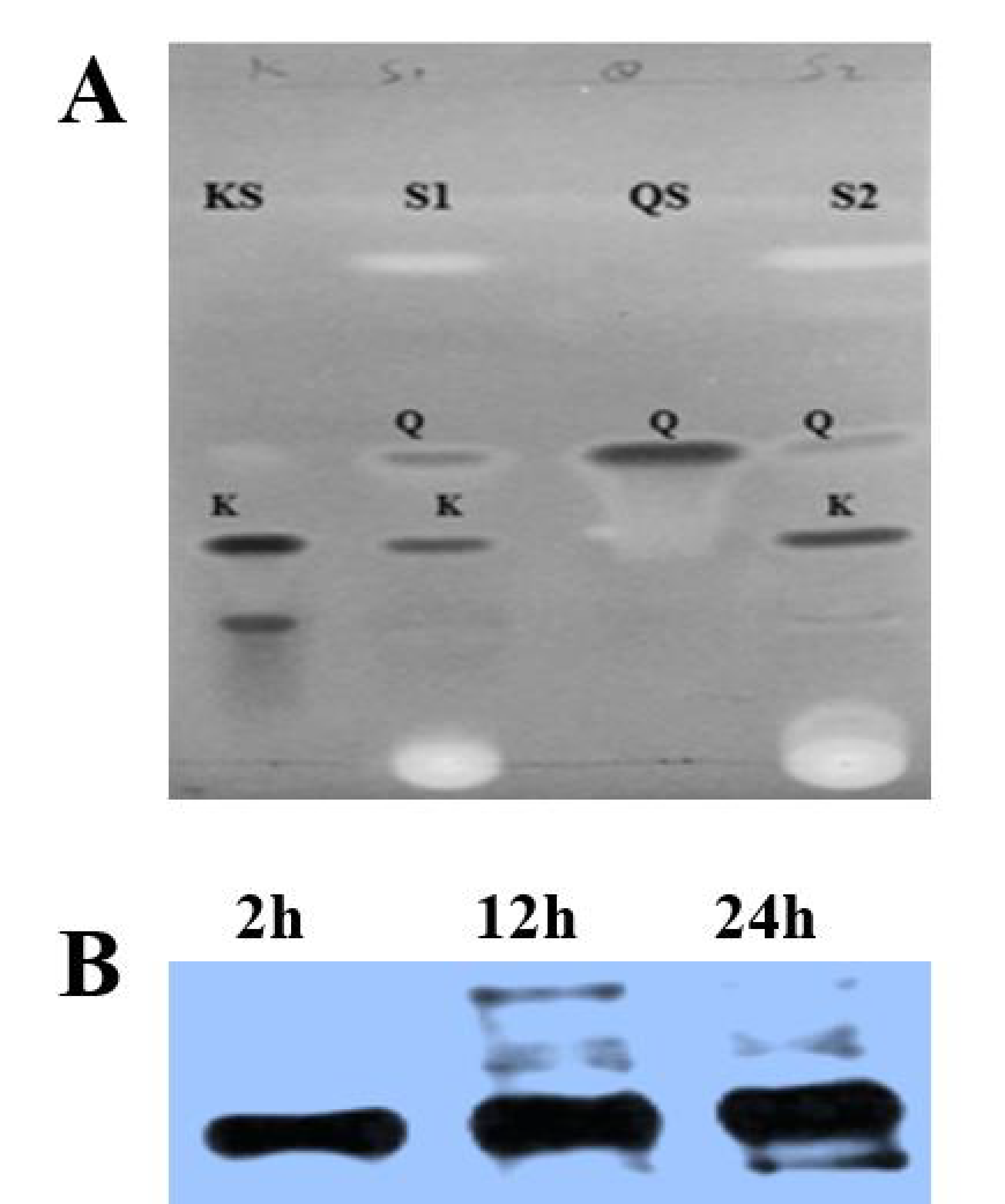
3.2. TLC Analysis
3.3. OsF3H Expression in Yeast
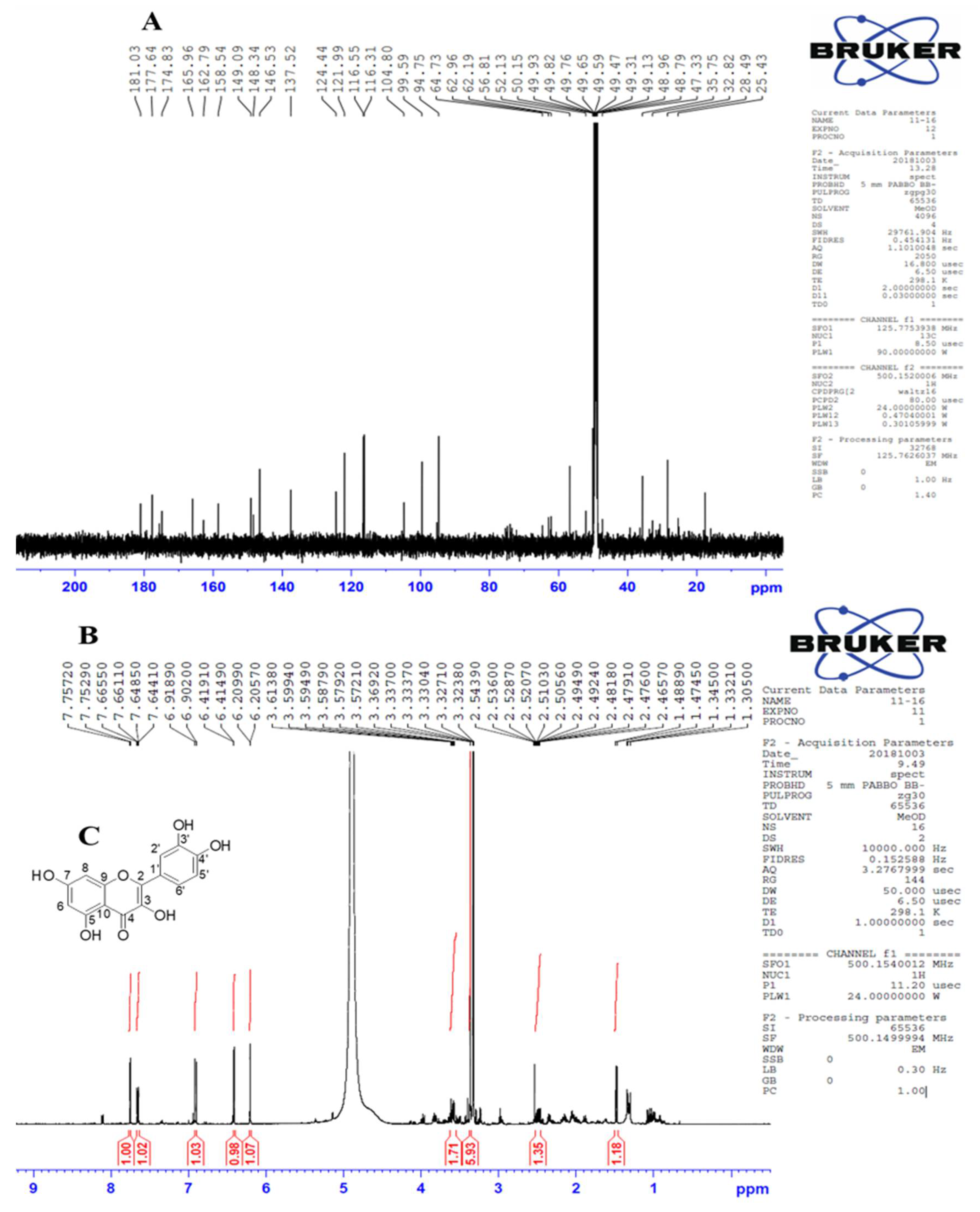
3.4. Identification of Kaempferol and Quercetin via Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
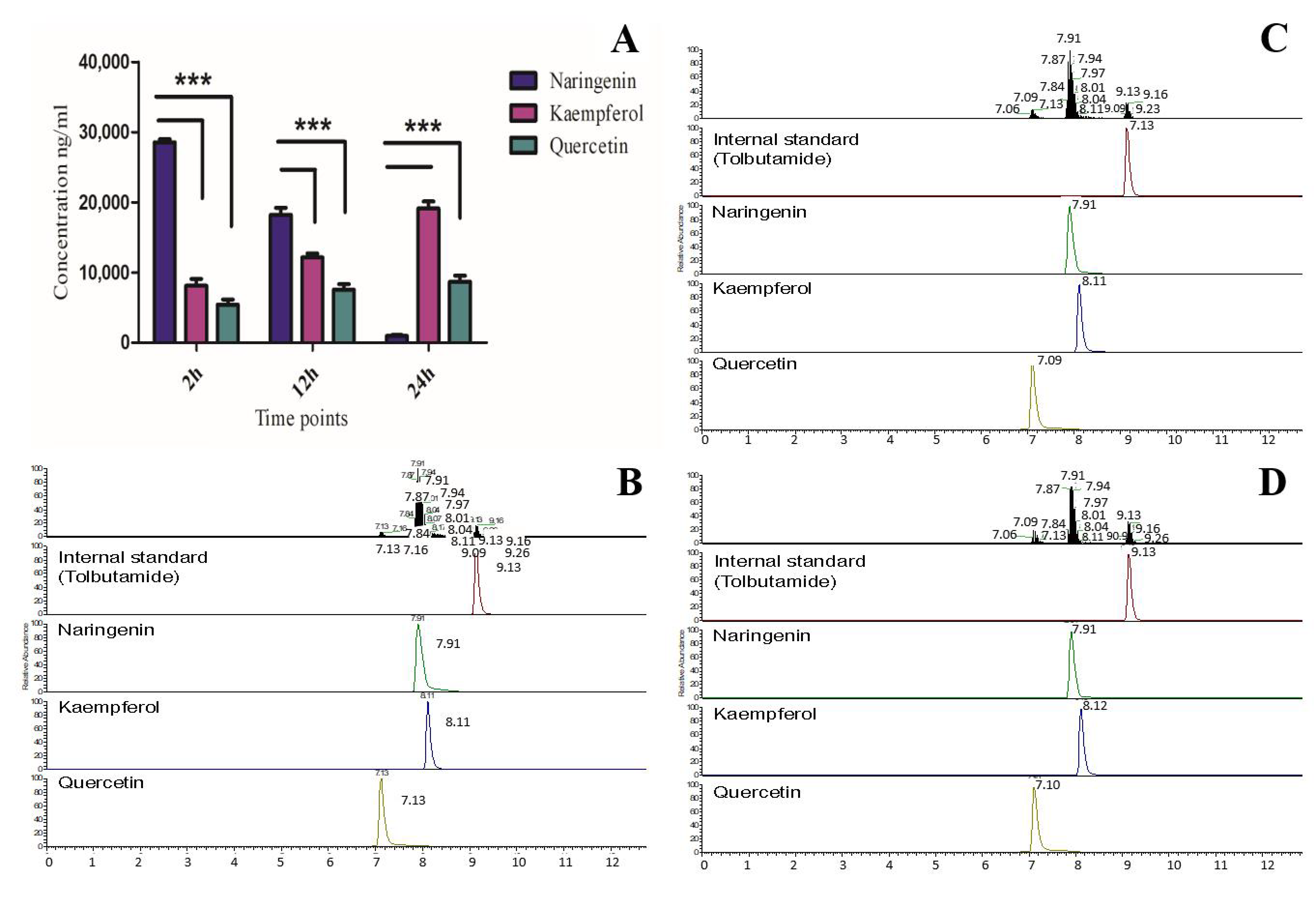
3.5. In Vivo Activity of OsF3H in Yeast and Quantification of Kaempferol and Quercetin via LCMS-MS
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tahara, S. A Journey of Twenty-Five Years through the Ecological Biochemistry of Flavonoids. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 1387–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grotewold, E. Plant metabolic diversity: A regulatory perspective. Trends Plant. Sci. 2005, 10, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepiniec, L.; Debeaujon, I.; Routaboul, J.-M.; Baudry, A.; Pourcel, L.; Nesi, N.; Caboche, M. Genetics and biochemistry of seed flavonoids. Annu. Rev. Plant. Biol. 2006, 57, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, S.; Stacey, G.; Yu, O. Distinct, crucial roles of flavonoids during legume nodulation. Trends Plant. Sci. 2007, 12, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, R.A.; Steele, C.L. Flavonoids and isoflavonoids—A gold mine for metabolic engineering. Trends Plant. Sci. 1999, 4, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, S.; Mithofer, A. Flavones and flavone synthases. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 2399–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buer, C.S.; Imin, N.; Djordjevic, M.A. Flavonoids: New Roles for Old Molecules. J. Integr. Plant. Biol. 2010, 52, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, R.H.; Hsieh, S.C.; Yu, Y.L.; Huang, M.H.; Huang, Y.C.; Hsieh, Y.H. Fisetin inhibits migration and invasion of human cervical cancer cells by down-regulating urokinase plasminogen activator expression through suppressing the p38 MAPK-dependent NF-kappaB signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.Y.; Chen, Y.C. A review of the dietary flavonoid, kaempferol on human health and cancer chemoprevention. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcelik, B.; Orhan, I.; Toker, G. Antiviral and antimicrobial assessment of some selected flavonoids. Z. Fur Nat. C J. Biosci. 2006, 61, 632–638. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, Y.; Sato, H.; Igarashi, K. Anti-diabetic effects of a kaempferol glycoside-rich fraction from unripe soybean (Edamame, Glycine max L. Merrill. ‘Jindai’) leaves on KK-A(y) mice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 1677–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthukrishnan, S.D.; Kaliyaperumal, A.; Subramaniyan, A. Identification and determination of flavonoids, carotenoids and chlorophyll concentration in Cynodon dactylon (L.) by HPLC analysis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, L.; Ding, W.; Liu, X.; Cheng, X.; Cai, J.; Hua, E.; Jiang, H. Biosynthesis and engineering of kaempferol in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Cell Fact 2017, 16, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deboo, G.B.; Albertsen, M.C.; Taylor, L.P. Flavanone 3-hydroxylase transcripts and flavonol accumulation are temporally coordinate in maize anthers. Plant. J. Cell Mol. Biol. 1995, 7, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.B.; Kim, K.; Kim, Y.; Tuan, P.A.; Kim, H.H.; Cho, J.W.; Park, S.U. Cloning and Characterization of a Flavonol Synthase Gene from Scutellaria baicalensis. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, L.; Gutiérrez-del-Río, I.; Entrialgo-Cadierno, R.; Villar, C.J.; Lombó, F. De novo biosynthesis of myricetin, kaempferol and quercetin in Streptomyces albus and Streptomyces coelicolor. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Strucko, T.; Stahlhut, S.G.; Kristensen, M.; Svenssen, D.K.; Forster, J.; Nielsen, J.; Borodina, I. Metabolic engineering of yeast for fermentative production of flavonoids. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Messner, B.; Faus-Kessler, T.; Hoffmann, T.; Schwab, W.; Hajirezaei, M.-R.; von Saint Paul, V.; Heller, W.; Schäffner, A.R. Feedback inhibition of the general phenylpropanoid and flavonol biosynthetic pathways upon a compromised flavonol-3-O-glycosylation. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 2465–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xiang, Y.; Deng, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, S. Simultaneous Analysis of Anthocyanin and Non-Anthocyanin Flavonoid in Various Tissues of Different Lotus (Nelumbo) Cultivars by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, A.; Velasco, A.G.-V.; Lucas, J.A.; Gutierrez-Mañero, F.J.; Ramos-Solano, B. The Flavonol-Anthocyanin Pathway in Blackberry and Arabidopsis: State of the Art; InTech: London, UK, 2017; pp. 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Leonard, E.; Yan, Y.; Koffas, M.A. Functional expression of a P450 flavonoid hydroxylase for the biosynthesis of plant-specific hydroxylated flavonols in Escherichia coli. Metab. Eng. 2006, 8, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyahisa, I.; Funa, N.; Ohnishi, Y.; Martens, S.; Moriguchi, T.; Horinouchi, S. Combinatorial biosynthesis of flavones and flavonols in Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 71, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, F. Getting started with yeast. In Methods in Enzymology; Guthrie, C., Fink, G.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002; Volume 350, pp. 3–41. [Google Scholar]
- Gietz, R.D.; Schiestl, R.H. Quick and easy yeast transformation using the LiAc/SS carrier DNA/PEG method. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, M.; Merante, F.; Robinson, B.H. A rapid and reliable DNA preparation method for screening a large number of yeast clones by polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23, 4924–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-Y.; Wen, P.-F.; Kong, W.-F.; Pan, Q.-H.; Zhan, J.-C.; Li, J.-M.; Wan, S.-B.; Huang, W.-D. Effect of salicylic acid on phenylpropanoids and phenylalanine ammonia-lyase in harvested grape berries. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2006, 40, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isla, M.I.; Vattuone, M.A.; Sampietro, A.R. Essential group at the active site of Frapaeoluminvertase. Phytochemistry 1998, 47, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harborne, A.J. Phytochemical Methods, A Guide to Modern Techniques of Plant Analysis; Springer Pvt. Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, R.A.; Howles, P.A.; Lamb, C.; He, X.-Z.; Reddy, J.T. Prospects for the Metabolic Engineering of Bioactive Flavonoids and Related Phenylpropanoid Compounds. In Flavonoids in the Living System; Manthey, J.A., Buslig, B.S., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trantas, E.; Panopoulos, N.; Ververidis, F. Metabolic engineering of the complete pathway leading to heterologous biosynthesis of various flavonoids and stilbenoids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab. Eng. 2009, 11, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumberg, D.; Muller, R.; Funk, M. Yeast vectors for the controlled expression of heterologous proteins in different genetic backgrounds. Gene 1995, 156, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Salmon, K.; Shen, M.W.; Aeling, K.A.; Ito, E.; Irwin, B.; Tran, U.P.; Hatfield, G.W.; Da Silva, N.A.; Sandmeyer, S. A vector set for systematic metabolic engineering in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 2011, 28, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Lou, F.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, S. Coumaroyl flavonol glycosides from the leaves of Ginkgo biloba. Phytochemistry 2001, 58, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.M.; Alper, H.S. Synthetic biology and molecular genetics in non-conventional yeasts: Current tools and future advances. Fungal Genet. Biol. Fg B 2016, 89, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.-M.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Y.-P. Phenolic Derivatives with Free-Radical-Scavenging Activities from Ixeridium gracile (DC.) Shih. Chem. Biodivers. 2007, 4, 2172–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahlhut, S.G.; Siedler, S.; Malla, S.; Harrison, S.J.; Maury, J.; Neves, A.R.; Forster, J. Assembly of a novel biosynthetic pathway for production of the plant flavonoid fisetin in Escherichia coli. Metab. Eng. 2015, 31, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crozier, A.; Jaganath, I.B.; Clifford, M.N. Dietary phenolics: Chemistry, bioavailability and effects on health. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 1001–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, M.; Ahuja, P.S.; Yadav, S.K. Post-transcriptional silencing of flavonol synthase mRNA in tobacco leads to fruits with arrested seed set. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajeeth, C. Quantitative estimation of gallic acid, rutin and quercetin in certain herbal plants by HPTLC method. Der Chem. Sin. 2010, 1, 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, S.; Kumar, P. Production, isolation and identification of flavonoids from aerial parts of Hiptage benghalensis. Int. J. Life Sci. Pharma Res. 2012, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.; Srivastava, A.; Srivastava, S.; Rawat, A.K.S.; Khan, A.R. Simultaneous quantification of syringic acid and kaempferol in extracts of Bergenia species using validated high-performance thin-layer chromatographic-densitometric method. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2016, 54, 460–465. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, N.; Gupta, R.C. Simultaneous determination of kaempferol and quercetin in Heteropogon Contortus (L.) Beauv. by validated high-performance thin layer chromatography. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant. Anal. 2018, 49, 2247–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Chromatographic System | Solvent | Ratio | Rf Value of Kaempferol | Rf Value of Quercetin | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ethyl acetate: glacial acetic acid: formic acid: water | 100:11:11:25 | 0.49 | 0.35 | [41] |
| 2 | Benzene: acetic Acid: water | 125:72:3 | 0.35 | 0.24 | [42] |
| 3 | N-butanol: acetic acid: water | 4:01:05 | 0.45 | 0.31 | [42] |
| 4 | Toluene: ethyl acetate: formic acid | 5:04:01 | 0.36 | 0.24 | [43] |
| 5 | N-hexane: ethylacetate: acetic acid | 31:14:5 | 0.28 | 0.18 | [43] |
| 6 | Toluene: ethyl acetate: formic acid | 7: 3: 0.5 | 0.44 | 0.32 | [44] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jan, R.; Asaf, S.; Paudel, S.; Lubna; Lee, S.; Kim, K.-M. Discovery and Validation of a Novel Step Catalyzed by OsF3H in the Flavonoid Biosynthesis Pathway. Biology 2021, 10, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10010032
Jan R, Asaf S, Paudel S, Lubna, Lee S, Kim K-M. Discovery and Validation of a Novel Step Catalyzed by OsF3H in the Flavonoid Biosynthesis Pathway. Biology. 2021; 10(1):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10010032
Chicago/Turabian StyleJan, Rahmatullah, Sajjad Asaf, Sanjita Paudel, Lubna, Sangkyu Lee, and Kyung-Min Kim. 2021. "Discovery and Validation of a Novel Step Catalyzed by OsF3H in the Flavonoid Biosynthesis Pathway" Biology 10, no. 1: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10010032
APA StyleJan, R., Asaf, S., Paudel, S., Lubna, Lee, S., & Kim, K.-M. (2021). Discovery and Validation of a Novel Step Catalyzed by OsF3H in the Flavonoid Biosynthesis Pathway. Biology, 10(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10010032







