RAB11-Mediated Trafficking and Human Cancers: An Updated Review
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
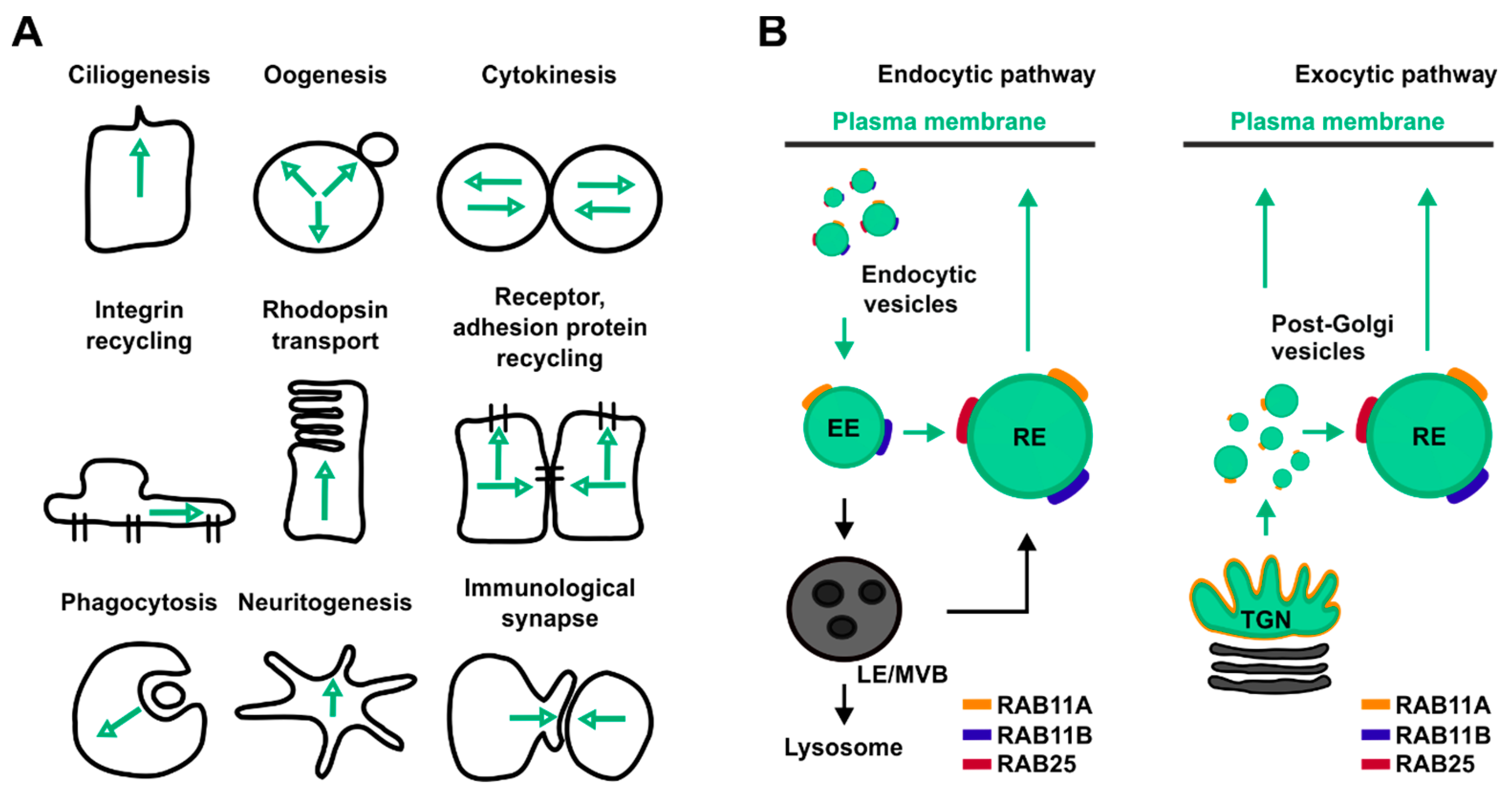
2. Different RAB11 Isoforms for Distinct Cellular Functions
3. RAB11-Mediated Trafficking Sustains Proliferative Signaling
4. RAB11-Mediated Sorting Controls Intracellular Accumulation of Surface Proteins
5. RAB11 Balances Distinct Trafficking Routes with Opposing Functions
6. RAB11 Sets the Time for PtdIns Conversion on Endosomal Membrane Microdomain
7. RAB11 Targeting for Human Cancer Treatment
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mellman, I.; Yarden, Y. Endocytosis and cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a016949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, S.L. Reciprocal regulation of signaling and endocytosis: Implications for the evolving cancer cell. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 2623–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal Krishnan, P.D.; Golden, E.; Woodward, E.A.; Pavlos, N.J.; Blancafort, P. Rab GTPases: Emerging Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressive Regulators for the Editing of Survival Pathways in Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goitre, L.; Trapani, E.; Trabalzini, L.; Retta, S.F. The Ras superfamily of small GTPases: The unlocked secrets. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1120, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenmark, H. Rab GTPases as coordinators of vesicle traffic. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutagalung, A.H.; Novick, P.J. Role of Rab GTPases in membrane traffic and cell physiology. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 119–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzeng, H.T.; Wang, Y.C. Rab-mediated vesicle trafficking in cancer. J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 23, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yao, H.; Li, C.; Fang, J.Y.; Xu, J. Regulation of PD-L1: Emerging Routes for Targeting Tumor Immune Evasion. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welz, T.; Wellbourne-Wood, J.; Kerkhoff, E. Orchestration of cell surface proteins by Rab11. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.P.; Lukman, S. Allosteric binding sites in Rab11 for potential drug candidates. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scapin, S.M.; Carneiro, F.R.; Alves, A.C.; Medrano, F.J.; Guimaraes, B.G.; Zanchin, N.I. The crystal structure of the small GTPase Rab11b reveals critical differences relative to the Rab11a isoform. J. Struct. Biol. 2006, 154, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, E.E.; Horgan, C.P.; McCaffrey, M.W. Rab11 proteins in health and disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2012, 40, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobajima, T.; Yoshimura, S.; Iwano, T.; Kunii, M.; Watanabe, M.; Atik, N.; Mushiake, S.; Morii, E.; Koyama, Y.; Miyoshi, E.; et al. Rab11a is required for apical protein localisation in the intestine. Biol. Open 2014, 4, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Yehia, G.; Wang, J.; Stypulkowski, E.; Sakamori, R.; Jiang, P.; Hernandez-Enriquez, B.; Tran, T.S.; Bonder, E.M.; Guo, W.; et al. Global ablation of the mouse Rab11a gene impairs early embryogenesis and matrix metalloproteinase secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 32030–32043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxfield, F.R.; McGraw, T.E. Endocytic recycling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullrich, O.; Reinsch, S.; Urbe, S.; Zerial, M.; Parton, R.G. Rab11 regulates recycling through the pericentriolar recycling endosome. J. Cell Biol. 1996, 135, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campa, C.C.; Margaria, J.P.; Derle, A.; Del Giudice, M.; De Santis, M.C.; Gozzelino, L.; Copperi, F.; Bosia, C.; Hirsch, E. Rab11 activity and PtdIns(3)P turnover removes recycling cargo from endosomes. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018, 14, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kumar, R.; Navarre, J.; Casanova, J.E.; Goldenring, J.R. Regulation of vesicle trafficking in madin-darby canine kidney cells by Rab11a and Rab25. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 29138–29146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redpath, G.M.I.; Ecker, M.; Kapoor-Kaushik, N.; Vartoukian, H.; Carnell, M.; Kempe, D.; Biro, M.; Ariotti, N.; Rossy, J. Flotillins promote T cell receptor sorting through a fast Rab5-Rab11 endocytic recycling axis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, C.; Vicinanza, M.; Ashkenazi, A.; Gratian, M.J.; Zhang, Q.; Bento, C.F.; Renna, M.; Menzies, F.M.; Rubinsztein, D.C. The RAB11A-Positive Compartment Is a Primary Platform for Autophagosome Assembly Mediated by WIPI2 Recognition of PI3P-RAB11A. Dev. Cell 2018, 45, 114–131.e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walia, V.; Cuenca, A.; Vetter, M.; Insinna, C.; Perera, S.; Lu, Q.; Ritt, D.A.; Semler, E.; Specht, S.; Stauffer, J.; et al. Akt Regulates a Rab11-Effector Switch Required for Ciliogenesis. Dev. Cell 2019, 50, 229–246.e227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, J.C.; Wall, A.A.; Luo, L.; Stow, J.L. Sequential recruitment of Rab GTPases during early stages of phagocytosis. Cell. Logist. 2016, 6, e1140615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Liu, Z.; Hu, R.; Bo, L.; Minshall, R.D.; Malik, A.B.; Hu, G. Inactivation of Rab11a GTPase in Macrophages Facilitates Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Neutrophils. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 1660–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, F.; Sun, K.; Wei, W.; Yu, C.; Wei, Z. F-actin disassembly factor MICAL1 binding to Myosin Va mediates cargo unloading during cytokinesis. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assaker, G.; Ramel, D.; Wculek, S.K.; Gonzalez-Gaitan, M.; Emery, G. Spatial restriction of receptor tyrosine kinase activity through a polarized endocytic cycle controls border cell migration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 22558–22563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, S.; Kubo, K.; Waguri, S.; Yabashi, A.; Shin, H.W.; Katoh, Y.; Nakayama, K. Rab11 regulates exocytosis of recycling vesicles at the plasma membrane. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 4049–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugsten, E.M.; Brech, A.; Liestol, K.; Norman, J.C.; Wesche, J. Photoactivation approaches reveal a role for Rab11 in FGFR4 recycling and signalling. Traffic 2014, 15, 665–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapierre, L.A.; Dorn, M.C.; Zimmerman, C.F.; Navarre, J.; Burnette, J.O.; Goldenring, J.R. Rab11b resides in a vesicular compartment distinct from Rab11a in parietal cells and other epithelial cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 290, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimsey, N.J.; Coronel, L.J.; Cordova, I.C.; Trejo, J. Recycling and Endosomal Sorting of Protease-activated Receptor-1 Is Distinctly Regulated by Rab11A and Rab11B Proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 2223–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvis, M.R.; Bertrand, C.A.; Ameen, N.; Golin-Bisello, F.; Butterworth, M.B.; Frizzell, R.A.; Bradbury, N.A. Rab11b regulates the apical recycling of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in polarized intestinal epithelial cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 2337–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khvotchev, M.V.; Ren, M.; Takamori, S.; Jahn, R.; Sudhof, T.C. Divergent functions of neuronal Rab11b in Ca2+-regulated versus constitutive exocytosis. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 10531–10539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, K.T.; Lee, H.J.; Smith, J.J.; Lapierre, L.A.; Kamath, V.P.; Chen, X.; Aronow, B.J.; Yeatman, T.J.; Bhartur, S.G.; Calhoun, B.C.; et al. Loss of Rab25 promotes the development of intestinal neoplasia in mice and is associated with human colorectal adenocarcinomas. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dozynkiewicz, M.A.; Jamieson, N.B.; Macpherson, I.; Grindlay, J.; van den Berghe, P.V.; von Thun, A.; Morton, J.P.; Gourley, C.; Timpson, P.; Nixon, C.; et al. Rab25 and CLIC3 collaborate to promote integrin recycling from late endosomes/lysosomes and drive cancer progression. Dev. Cell 2012, 22, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.W.; Agarwal, R.; Mitra, S.; Lee, J.S.; Carey, M.; Gray, J.W.; Mills, G.B. Rab25 increases cellular ATP and glycogen stores protecting cancer cells from bioenergetic stress. Embo Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porther, N.; Barbieri, M.A. The role of endocytic Rab GTPases in regulation of growth factor signaling and the migration and invasion of tumor cells. Small Gtpases 2015, 6, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wandinger-Ness, A.; Zerial, M. Rab proteins and the compartmentalization of the endosomal system. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a022616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, D.; Bouadis, A.; Ronchetti, R.; Merino, M.J.; Steeg, P.S. Rab11a differentially modulates epidermal growth factor-induced proliferation and motility in immortal breast cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2006, 100, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Q.; Fu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Du, Y.; Li, Q.; Qiu, X.; Wang, E. Rab11a promotes proliferation and invasion through regulation of YAP in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 27800–27811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Lu, M.; Liu, Z.K.; Li, H.; Yong, Y.L.; Zhang, R.Y.; Chen, Z.N.; Bian, H. Rab11a regulates MMP2 expression by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 153046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Chen, H.; Liu, H. Rab11a sustains GSK3beta/Wnt/beta-catenin signaling to enhance cancer progression in pancreatic cancer. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2016, 37, 13821–13829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agostino, L.; Nie, Y.; Goswami, S.; Tong, K.; Yu, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Flores, J.; Zhang, X.; Balasubramanian, I.; Joseph, I.; et al. Recycling Endosomes in Mature Epithelia Restrain Tumorigenic Signaling. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4099–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, E.N.; Burnette, M.D.; Justice, M.E.; Schnepp, P.M.; Hedrick, V.; Clancy, J.W.; Guldner, I.H.; Lamere, A.T.; Li, J.; Aryal, U.K.; et al. Rab11b-mediated integrin recycling promotes brain metastatic adaptation and outgrowth. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.H.; Lee, H.Y. Rab25 and RCP in cancer progression. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2019, 42, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mor, O.; Nativ, O.; Stein, A.; Novak, L.; Lehavi, D.; Shiboleth, Y.; Rozen, A.; Berent, E.; Brodsky, L.; Feinstein, E.; et al. Molecular analysis of transitional cell carcinoma using cDNA microarray. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7702–7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Wei, J.; Lu, J.; Tong, Z.; Liao, B.; Yu, B.; Zheng, F.; Huang, X.; Chen, Z.; Fang, Y.; et al. Overexpression of Rab25 contributes to metastasis of bladder cancer through induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and activation of Akt/GSK-3beta/Snail signaling. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 2401–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Lu, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, M. Expression of Rab25 correlates with the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer. Chin. J. Cancer Res. Chung Kuo Yen Cheng Yen Chiu 2013, 25, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.Y.; Cho, K.H.; Jeong, K.J.; Park, Y.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Rha, S.Y.; Park, C.G.; Mills, G.B.; Cheong, J.H.; Lee, H.Y. Rab25 augments cancer cell invasiveness through a beta1 integrin/EGFR/VEGF-A/Snail signaling axis and expression of fascin. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, e435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Cui, B.; Gao, M.; Li, Z.; Xu, C.; Fan, S.; He, W. Knockdown of Ras-Related Protein 25 (Rab25) Inhibits the In Vitro Cytotoxicity and In Vivo Antitumor Activity of Human Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells. Oncol. Res. 2017, 25, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, D.; Zhao, W.; Feng, Y.; Liu, J. Overexpression of Rab25 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and invasion. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2016, 37, 7713–7718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.W.; Lahad, J.P.; Kuo, W.L.; Lapuk, A.; Yamada, K.; Auersperg, N.; Liu, J.; Smith-McCune, K.; Lu, K.H.; Fishman, D.; et al. The RAB25 small GTPase determines aggressiveness of ovarian and breast cancers. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.F.; Yang, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, T.; Guo, J.T.; Chen, L.; Li, M.; Chu, J.; Liang, C.Y.; Liu, Y. Expression of Ras-related protein 25 predicts chemotherapy resistance and prognosis in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 13998–14008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, U.; Park, K.H.; Whang, Y.M.; Sung, J.S.; Won, N.H.; Park, J.K.; Kim, Y.H. EGFR endocytosis is a novel therapeutic target in lung cancer with wild-type EGFR. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 1265–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, D.; Gruen, G.C.; Heider, D.; Morgner, J.; Reis, H.; Schmid, K.W.; Jendrossek, V. The action of small GTPases Rab11 and Rab25 in vesicle trafficking during cell migration. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 29, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Chen, B.; Zhou, Y.; Shan, Y. High expression of Rab25 contributes to malignant phenotypes and biochemical recurrence in patients with prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy. Cancer Cell Int. 2017, 17, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natrajan, R.; Williams, R.D.; Hing, S.N.; Mackay, A.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Fenwick, K.; Iravani, M.; Valgeirsson, H.; Grigoriadis, A.; Langford, C.F.; et al. Array CGH profiling of favourable histology Wilms tumours reveals novel gains and losses associated with relapse. J. Pathol. 2006, 210, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Chan, K.W.; Bao, J.Y.; Wong, K.Y.; Chen, J.N.; Kwan, P.S.; Tang, K.H.; Fu, L.; Qin, Y.R.; Lok, S.; et al. Rab25 is a tumor suppressor gene with antiangiogenic and anti-invasive activities in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 6024–6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amornphimoltham, P.; Rechache, K.; Thompson, J.; Masedunskas, A.; Leelahavanichkul, K.; Patel, V.; Molinolo, A.; Gutkind, J.S.; Weigert, R. Rab25 regulates invasion and metastasis in head and neck cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 1375–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.M.; Ding, M.; Aribi, A.; Shah, P.; Rao, K. Loss of RAB25 expression in breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 2957–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Nie, Y.; Knowles, B.; Sakamori, R.; Stypulkowski, E.; Patel, C.; Das, S.; Douard, V.; Ferraris, R.P.; Bonder, E.M.; et al. TLR sorting by Rab11 endosomes maintains intestinal epithelial-microbial homeostasis. Embo J. 2014, 33, 1882–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xie, B.; Qiu, Y.; Jing, D.; Zhang, J.; Duan, Y.; Li, Z.; Fan, M.; He, J.; Qiu, Y.; et al. Rab25-Mediated EGFR Recycling Causes Tumor Acquired Radioresistance. iScience 2020, 23, 100997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, S.; Montgomery, J.E.; Kolar, M.J.; Li, G.; Jeong, K.J.; Peng, B.; Verdine, G.L.; Mills, G.B.; Moellering, R.E. Stapled peptide inhibitors of RAB25 target context-specific phenotypes in cancer. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, S.; Federico, L.; Zhao, W.; Dennison, J.; Sarkar, T.R.; Zhang, F.; Takiar, V.; Cheng, K.W.; Mani, S.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Rab25 acts as an oncogene in luminal B breast cancer and is causally associated with Snail driven EMT. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 40252–40265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cheng, J.M.; Volk, L.; Janaki, D.K.; Vyakaranam, S.; Ran, S.; Rao, K.A. Tumor suppressor function of Rab25 in triple-negative breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 2799–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caswell, P.T.; Chan, M.; Lindsay, A.J.; McCaffrey, M.W.; Boettiger, D.; Norman, J.C. Rab-coupling protein coordinates recycling of alpha5beta1 integrin and EGFR1 to promote cell migration in 3D microenvironments. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 183, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, P.A.; Caswell, P.T.; Doyle, B.; Iwanicki, M.P.; Tan, E.H.; Karim, S.; Lukashchuk, N.; Gillespie, D.A.; Ludwig, R.L.; Gosselin, P.; et al. Mutant p53 drives invasion by promoting integrin recycling. Cell 2009, 139, 1327–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caswell, P.T.; Spence, H.J.; Parsons, M.; White, D.P.; Clark, K.; Cheng, K.W.; Mills, G.B.; Humphries, M.J.; Messent, A.J.; Anderson, K.I.; et al. Rab25 associates with alpha5beta1 integrin to promote invasive migration in 3D microenvironments. Dev. Cell 2007, 13, 496–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.C.; Wei, W.C.; Hung, C.N.; Kuo, J.F.; Hsu, C.P.; Chang, K.J.; Chao, W.T. Rab11 collaborates E-cadherin to promote collective cell migration and indicates a poor prognosis in colorectal carcinoma. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 46, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koseska, A.; Bastiaens, P.I.H. Processing Temporal Growth Factor Patterns by an Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Network Dynamically Established in Space. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 36, 359–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, H.M.; Coyle, J.; Arumugam, S. To be more precise: The role of intracellular trafficking in development and pattern formation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2020, 48, 2051–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fedoseienko, A.; Chen, B.; Burstein, E.; Jia, D.; Billadeau, D.D. Endosomal receptor trafficking: Retromer and beyond. Traffic 2018, 19, 578–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergés, M.; Luton, F.; Gruber, C.; Tiemann, F.; Reinders, L.G.; Huang, L.; Burlingame, A.L.; Haft, C.R.; Mostov, K.E. The mammalian retromer regulates transcytosis of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harterink, M.; Port, F.; Lorenowicz, M.J.; McGough, I.J.; Silhankova, M.; Betist, M.C.; van Weering, J.R.T.; van Heesbeen, R.; Middelkoop, T.C.; Basler, K.; et al. A SNX3-dependent retromer pathway mediates retrograde transport of the Wnt sorting receptor Wntless and is required for Wnt secretion. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, F.; Gallon, M.; Winfield, M.; Thomas, E.C.; Bell, A.J.; Heesom, K.J.; Tavaré, J.M.; Cullen, P.J. A global analysis of SNX27-retromer assembly and cargo specificity reveals a function in glucose and metal ion transport. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNally, K.E.; Faulkner, R.; Steinberg, F.; Gallon, M.; Ghai, R.; Pim, D.; Langton, P.; Pearson, N.; Danson, C.M.; Nagele, H.; et al. Retriever is a multiprotein complex for retromer-independent endosomal cargo recycling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 1214–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zech, T.; Calaminus, S.D.; Caswell, P.; Spence, H.J.; Carnell, M.; Insall, R.H.; Norman, J.; Machesky, L.M. The Arp2/3 activator WASH regulates α5β1-integrin-mediated invasive migration. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 3753–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, T.S.; Billadeau, D.D. A FAM21-containing WASH complex regulates retromer-dependent sorting. Dev. Cell 2009, 17, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derivery, E.; Sousa, C.; Gautier, J.J.; Lombard, B.; Loew, D.; Gautreau, A. The Arp2/3 activator WASH controls the fission of endosomes through a large multiprotein complex. Dev. Cell 2009, 17, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Gomez, T.S.; Metlagel, Z.; Umetani, J.; Otwinowski, Z.; Rosen, M.K.; Billadeau, D.D. WASH and WAVE actin regulators of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) family are controlled by analogous structurally related complexes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 10442–10447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.H.; Doyle, J.M.; Ramanathan, S.; Gomez, T.S.; Jia, D.; Xu, M.; Chen, Z.J.; Billadeau, D.D.; Rosen, M.K.; Potts, P.R. Regulation of WASH-dependent actin polymerization and protein trafficking by ubiquitination. Cell 2013, 152, 1051–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solinger, J.A.; Rashid, H.O.; Prescianotto-Baschong, C.; Spang, A. FERARI is required for Rab11-dependent endocytic recycling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, H.A.; Dionne, H.; Rusten, T.E.; Brech, A.; Fisher, W.W.; Pfeiffer, B.D.; Celniker, S.E.; Stenmark, H.; Bilder, D. Regulation of early endosomal entry by the Drosophila tumor suppressors Rabenosyn and Vps45. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 4167–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, M.H.; Cho, K.H.; Jeong, K.J.; Park, Y.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Yu, S.L.; Park, C.G.; Mills, G.B.; Lee, H.Y. RCP induces Slug expression and cancer cell invasion by stabilizing β1 integrin. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Datta, A.; Govindarajan, K.; Tam, W.L.; Han, J.; George, J.; Wong, C.; Ramnarayanan, K.; Phua, T.Y.; et al. RCP is a human breast cancer-promoting gene with Ras-activating function. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2171–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundry, C.; Marco, S.; Rainero, E.; Miller, B.; Dornier, E.; Mitchell, L.; Caswell, P.T. Phosphorylation of Rab-coupling protein by LMTK3 controls Rab14-dependent EphA2 trafficking to promote cell:cell repulsion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.; Liang, Y.N.; Stepanova, A.A.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, F.; Vasilyeva, N.V. Increased Eps15 homology domain 1 and RAB11FIP3 expression regulate breast cancer progression via promoting epithelial growth factor receptor recycling. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2017, 39, 1010428317691010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, H.N.; Rust, A.G.; Wright, N.A.; ten Hoeve, J.; de Ridder, J.; Eldridge, M.; van der Weyden, L.; Berns, A.; Gadiot, J.; Uren, A.; et al. Insertional mutagenesis identifies multiple networks of cooperating genes driving intestinal tumorigenesis. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, H.; Rust, A.G.; Ward, J.M.; Yew, C.C.; Jenkins, N.A.; Copeland, N.G. Sleeping Beauty transposon mutagenesis identifies genes that cooperate with mutant Smad4 in gastric cancer development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E2057–E2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, L.; Gard, J.M.C.; Prekeris, R.; Nagle, R.B.; Morrissey, C.; Knudsen, B.S.; Miranti, C.K.; Cress, A.E. Novel Regulation of Integrin Trafficking by Rab11-FIP5 in Aggressive Prostate Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Deng, X.; Yang, X.; Jin, H.; Gu, D.; Lv, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Huo, X.; Shen, Q.; et al. Hypoxia upregulates Rab11-family interacting protein 4 through HIF-1α to promote the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2015, 34, 6007–6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, P.A.; Trinidad, A.G.; Timpson, P.; Morton, J.P.; Zanivan, S.; van den Berghe, P.V.; Nixon, C.; Karim, S.A.; Caswell, P.T.; Noll, J.E.; et al. Mutant p53 enhances MET trafficking and signalling to drive cell scattering and invasion. Oncogene 2013, 32, 1252–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worby, C.A.; Dixon, J.E. Sorting out the cellular functions of sorting nexins. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozier, G.E.; Carlton, J.; McGregor, A.H.; Gleeson, P.A.; Teasdale, R.D.; Mellor, H.; Cullen, P.J. The phox homology (PX) domain-dependent, 3-phosphoinositide-mediated association of sorting nexin-1 with an early sorting endosomal compartment is required for its ability to regulate epidermal growth factor receptor degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 48730–48736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonetti, B.; Paul, B.; Chaudhari, K.; Weeratunga, S.; Steinberg, F.; Gorla, M.; Heesom, K.J.; Bashaw, G.J.; Collins, B.M.; Cullen, P.J. Molecular identification of a BAR domain-containing coat complex for endosomal recycling of transmembrane proteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 1219–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlton, J.; Bujny, M.; Peter, B.J.; Oorschot, V.M.; Rutherford, A.; Mellor, H.; Klumperman, J.; McMahon, H.T.; Cullen, P.J. Sorting nexin-1 mediates tubular endosome-to-TGN transport through coincidence sensing of high- curvature membranes and 3-phosphoinositides. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurten, R.C.; Cadena, D.L.; Gill, G.N. Enhanced degradation of EGF receptors by a sorting nexin, SNX1. Science 1996, 272, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.N.; Holdren, M.S.; Nguyen, A.P.; Furuya, M.H.; Bianchini, M.; Levy, E.; Mordoh, J.; Liu, A.; Guncay, G.D.; Campbell, J.S.; et al. Sorting nexin 1 down-regulation promotes colon tumorigenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 6952–6959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, A.; Tammineni, P.; Wang, S.; Gerdes, J.; Murr, A.; Kwan, K.Y.; Cai, Q.; Grant, B.D. SNX-1 and RME-8 oppose the assembly of HGRS-1/ESCRT-0 degradative microdomains on endosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E307–E316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, A.; Grant, B.D. Endosomal microdomains: Formation and function. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2020, 65, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sönnichsen, B.; De Renzis, S.; Nielsen, E.; Rietdorf, J.; Zerial, M. Distinct membrane domains on endosomes in the recycling pathway visualized by multicolor imaging of Rab4, Rab5, and Rab11. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 149, 901–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, C.; Repnik, U.; Segeletz, S.; Brouilly, N.; Kalaidzidis, Y.; Verbavatz, J.M.; Zerial, M. Correlative single-molecule localization microscopy and electron tomography reveals endosome nanoscale domains. Traffic 2019, 20, 601–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campa, C.C.; Franco, I.; Hirsch, E. PI3K-C2α: One enzyme for two products coupling vesicle trafficking and signal transduction. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 1552–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, I.; Gulluni, F.; Campa, C.C.; Costa, C.; Margaria, J.P.; Ciraolo, E.; Martini, M.; Monteyne, D.; De Luca, E.; Germena, G.; et al. PI3K class II α controls spatially restricted endosomal PtdIns3P and Rab11 activation to promote primary cilium function. Dev. Cell 2014, 28, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, I.; Margaria, J.P.; De Santis, M.C.; Ranghino, A.; Monteyne, D.; Chiaravalli, M.; Pema, M.; Campa, C.C.; Ratto, E.; Gulluni, F.; et al. Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase-C2α Regulates Polycystin-2 Ciliary Entry and Protects against Kidney Cyst Formation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2016, 27, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketel, K.; Krauss, M.; Nicot, A.S.; Puchkov, D.; Wieffer, M.; Müller, R.; Subramanian, D.; Schultz, C.; Laporte, J.; Haucke, V. A phosphoinositide conversion mechanism for exit from endosomes. Nature 2016, 529, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fili, N.; Calleja, V.; Woscholski, R.; Parker, P.J.; Larijani, B. Compartmental signal modulation: Endosomal phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate controls endosome morphology and selective cargo sorting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15473–15478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips-Krawczak, C.A.; Singla, A.; Starokadomskyy, P.; Deng, Z.; Osborne, D.G.; Li, H.; Dick, C.J.; Gomez, T.S.; Koenecke, M.; Zhang, J.S.; et al. COMMD1 is linked to the WASH complex and regulates endosomal trafficking of the copper transporter ATP7A. Mol. Biol. Cell 2015, 26, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starokadomskyy, P.; Gluck, N.; Li, H.; Chen, B.; Wallis, M.; Maine, G.N.; Mao, X.; Zaidi, I.W.; Hein, M.Y.; McDonald, F.J.; et al. CCDC22 deficiency in humans blunts activation of proinflammatory NF-κB signaling. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 2244–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartuzi, P.; Billadeau, D.D.; Favier, R.; Rong, S.; Dekker, D.; Fedoseienko, A.; Fieten, H.; Wijers, M.; Levels, J.H.; Huijkman, N.; et al. CCC- and WASH-mediated endosomal sorting of LDLR is required for normal clearance of circulating LDL. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedoseienko, A.; Wijers, M.; Wolters, J.C.; Dekker, D.; Smit, M.; Huijkman, N.; Kloosterhuis, N.; Klug, H.; Schepers, A.; Willems van Dijk, K.; et al. The COMMD Family Regulates Plasma LDL Levels and Attenuates Atherosclerosis Through Stabilizing the CCC Complex in Endosomal LDLR Trafficking. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 1648–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, A.; Fedoseienko, A.; Giridharan, S.S.P.; Overlee, B.L.; Lopez, A.; Jia, D.; Song, J.; Huff-Hardy, K.; Weisman, L.; Burstein, E.; et al. Endosomal PI(3)P regulation by the COMMD/CCDC22/CCDC93 (CCC) complex controls membrane protein recycling. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronzier, E.; Parks, X.X.; Qudsi, H.; Lopes, C.M. Statin-specific inhibition of Rab-GTPase regulates cPKC-mediated IKs internalization. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorvina, A.; Shandala, T.; Wang, S.; Sharkey, D.J.; Parkinson-Lawrence, E.; Selemidis, S.; Brooks, D.A. CDKI-73 is a Novel Pharmacological Inhibitor of Rab11 Cargo Delivery and Innate Immune Secretion. Cells 2020, 9, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgquist, S.; Broberg, P.; Tojjar, J.; Olsson, H. Statin use and breast cancer survival—A Swedish nationwide study. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.F.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Bojesen, S.E. Statin use and reduced cancer-related mortality. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1792–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene Name | Chromosome Position | Number of Coding Exon | Number of Amino Acids | Percentage of Identity | Tissue Expression |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAB11A | 15q22.31 | 5 | 216 | 100% (with RAB11A) | Ubiquitous |
| RAB11B | 19p13.2 | 5 | 218 | 89% (with RAB11A) | Wide, enriched in brain testis, heart |
| RAB25 | 1q22 | 5 | 213 | 61% and 66% (with RAB11A and RAB11B) | Wide, enriched in lung kidney, gastric tract |
| Roles | Expression Status | Cancer Type | Mechanism of Action | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oncogenic | Over expression | Breast cancer | Increased signaling (ERK) Increased expression (EGFR) | Proliferation | [38] |
| Non-small cell lung cancer | Decreased signaling (Hippo) | Tumorigenesis invasion | [39] | ||
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | Increased signaling (PI3K/AKT) Increased expression (MMP2) | Tumorigenesis invasion | [40] | ||
| Pancreatic cancer | Increased signaling (GSK3β/Wnt/β-catenin) | Proliferation invasion | [41] | ||
| Tumor suppressive | Under expression | Colon cancer | Decreased signaling (Hippo/YAP/IL6) | Tumorigenesis | [42] |
| Roles | Expression Status | Cancer Type | Mechanism of Action | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oncogenic | Over expression | Breast cancer | Increased expression (β1-Integrin) | Metastasis | [43] |
| Tumor suppressive | Not yet defined | Not yet defined | Not yet defined | Not yet defined | Not yet defined |
| Roles | Expression Status | Cancer Type | Mechanism of Action | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oncogenic | Over expression | Bladder cancer | Increased signaling (AKT/GSK3β /SNAIL) | Tumorigenesis metastasis | [45,46] |
| Gastric cancer | Increased signaling (β1-Integrin/EGFR/SNAIL) | Invasion metastasis | [47,48] | ||
| Glioblastoma | Increased signaling (AKT) | Tumorigenesis | [49] | ||
| Liver cancer | Increased signaling (AKT/WNT) | Invasion | [50] | ||
| Luminal Breast cancer | Increased signaling (β1-Integrin/EGFR/SNAIL) | Tumorigenesis metastasis | [48,51] | ||
| Lung Cancer | Increased signaling (EGFR) | Tumorigenesis invasion | [52,53] | ||
| Ovarian cancer | Increased signaling (β1-Integrin/EGFR/SNAIL) | Tumorigenesis metastasis | [48,51] | ||
| Prostate cancer | Not yet defined | Tumorigenesis invasion | [54,55] | ||
| Wilms | Not yet defined | Tumorigenesis | [56] | ||
| Tumor suppressive | Under expression | Colon cancer | Increased expression (EGFR) | Tumorigenesis | [32] |
| Oesophageal cancer | Reduced signaling (ERK/FAK) | Tumorigenesis invasion | [57] | ||
| Head and Neck cancer | Reduced cytoskeleton (F-actin) | Metastasis | [58] | ||
| Triple negative breast cancer | Reduced expression (VEGF/VEGFR) | Tumorigenesis | [34,59] |
| Molecule Name | Mechanism of Action | Specificity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pitavastatin | HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor | Not yet determined | [43] |
| Simvastatin | HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor | Not yet determined | [43,112] |
| Fluvastatin | HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor | Not yet determined | [112] |
| CDKI-73 | Not yet determined | Not yet determined | [113] |
| RFP14 | RAB11:FIP interaction inhibitor | RAB25 | [62] |
| RFP24 | RAB11:FIP interaction inhibitor | RAB25 | [62] |
| RFP26 | RAB11:FIP interaction inhibitor | RAB11A, RAB25 | [62] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferro, E.; Bosia, C.; Campa, C.C. RAB11-Mediated Trafficking and Human Cancers: An Updated Review. Biology 2021, 10, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10010026
Ferro E, Bosia C, Campa CC. RAB11-Mediated Trafficking and Human Cancers: An Updated Review. Biology. 2021; 10(1):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10010026
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerro, Elsi, Carla Bosia, and Carlo C. Campa. 2021. "RAB11-Mediated Trafficking and Human Cancers: An Updated Review" Biology 10, no. 1: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10010026
APA StyleFerro, E., Bosia, C., & Campa, C. C. (2021). RAB11-Mediated Trafficking and Human Cancers: An Updated Review. Biology, 10(1), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10010026






