Biomarker Gene Signature Discovery Integrating Network Knowledge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Techniques
2.1. Overview
2.2. Network Centric Approaches
2.2.1. Network Features
2.2.2. Pathway Activity
2.2.3. Differential Sub-Networks
2.3. Data Centric Approaches
2.3.1. Mathematical Embedding
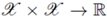 can be thought of as a special similarity measure between arbitrary objects x ∈
can be thought of as a special similarity measure between arbitrary objects x ∈ 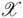 , which fulfills additional mathematical requirements, namely symmetry (i.e., k(x,y) = k(y,x) for all x,y ∈
, which fulfills additional mathematical requirements, namely symmetry (i.e., k(x,y) = k(y,x) for all x,y ∈ 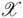 ) and positive semi-definiteness (i.e., k(x,y) =
) and positive semi-definiteness (i.e., k(x,y) = 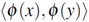 for all x,y, where (·) denotes the dot product in Hilbert space
for all x,y, where (·) denotes the dot product in Hilbert space 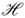 and
and 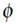 :
: 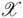 →
→ 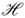 is some arbitrary map) [21,48]. Among many other applications kernel functions have been proposed for nodes in a graph or network based on the notion of random walks. A random walk is a stochastic process that consists of a sequence of moves that are taken along the graph structure according to some defined probability distribution. The diffusion kernels [49] is a specific similarity measure for nodes in a graph that considers all random walk paths connecting nodes x and y, but weights each path in dependency on the path length. This is done in an exponentially decreasing way. Diffusion kernels are mathematically equivalent to the fundamental solution of the heat equation in physics, which describes the evolution of heat in a region under certain boundary conditions. If instead of exponentially decreasing weights for path lengths a linear weighting scheme is preferred, one arrives at the pseudo-inverse of the graph Laplacian [50]. In the same paper also a random walk kernel is proposed, which simply bounds the number of random walk steps to p.
is some arbitrary map) [21,48]. Among many other applications kernel functions have been proposed for nodes in a graph or network based on the notion of random walks. A random walk is a stochastic process that consists of a sequence of moves that are taken along the graph structure according to some defined probability distribution. The diffusion kernels [49] is a specific similarity measure for nodes in a graph that considers all random walk paths connecting nodes x and y, but weights each path in dependency on the path length. This is done in an exponentially decreasing way. Diffusion kernels are mathematically equivalent to the fundamental solution of the heat equation in physics, which describes the evolution of heat in a region under certain boundary conditions. If instead of exponentially decreasing weights for path lengths a linear weighting scheme is preferred, one arrives at the pseudo-inverse of the graph Laplacian [50]. In the same paper also a random walk kernel is proposed, which simply bounds the number of random walk steps to p. 2.3.2. Biased Feature Selection
3. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Sorlie, T.; Perou, C.M.; Tibshirani, R.; Aas, T.; Geisler, S.; Johnsen, H.; Hastie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Thorsen, T.; Quist, H.; Matese, J.C.; Brown, P.O.; Botstein, D.; Lonning, P.E.; Borresen-Dale, A.L. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10869–10874. [Google Scholar]
- van ’t Veer, L.J.; Dai, H.; van de Vijver, M.J.; He, Y.D.; Hart, A.A.M.; Mao, M.; Peterse, H.L.; van der Kooy, K.; Marton, M.J.; Witteveen, A.T.; Schreiber, G.J.; Kerkhoven, R.M.; Roberts, C.; Linsley, P.S.; Bernards, R.; Friend, S.H. Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature 2002, 415, 530–536. [Google Scholar]
- Duda, R.; Hart, P.; Stork, D. Pattern Classification; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Tibshirani, R.; Hastie, T.; Narasimhan, B.; Chu, G. Diagnosis of multiple cancer types by shrunken centroids of gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 6567–6572. [Google Scholar]
- Guyon, I.; Weston, J.; Barnhill, S.; Vapnik, V. Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines. Mach. Learn. 2002, 46, 389–422. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Uriarte, R.; de Andres, S.A. Gene selection and classification of microarray data using random forest. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusher, V.G.; Tibshirani, R.; Chu, G. Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing radiation response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5116–5121. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, J.; Zou, H. Hybrid huberized support vector machines for microarray classification and gene selection. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 412–419. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.H.; Ahn, J.; Lin, X.; Park, C. Gene selection using support vector machines with non-convex penalty. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, N.; Toedt, G.; Lichter, P.; Benner, A. Elastic SCAD as a novel penalization method for SVM classification tasks in high-dimensional data. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeman, J. L-1 penalized estimation in the cox proportional hazards model. Biom. J. 2010, 52, 70–84. [Google Scholar]
- Binder, H.; Schumacher, M. Incorporating pathway information into boosting estimation of high-dimensional risk prediction models. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gönen, M. Statistical aspects of gene signatures and molecular targets. Gastrointest. Cancer Res. 2009, 3, S19–S21. [Google Scholar]
- Blazadonakis, M.E.; Zervakis, M.E.; Kafetzopoulos, D. Integration of gene signatures using biological knowledge. Artif. Intell. Med. 2011, 53, 57–71. [Google Scholar]
- Kanehisa, M.; Araki, M.; Goto, S.; Hattori, M.; Hirakawa, M.; Itoh, M.; Katayama, T.; Kawashima, S.; Okuda, S.; Tokimatsu, T.; Yamanishi, Y. KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D480–D484. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, T.S.K.; Kandasamy, K.; Pandey, A. Human protein reference database and human proteinpedia as discovery tools for systems biology. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 577, 67–79. [Google Scholar]
- Cerami, E.G.; Gross, B.E.; Demir, E.; Rodchenkov, I.; Babur, O.; Anwar, N.; Schultz, N.; Bader, G.D.; Sander, C. Pathway commons, a web resource for biological pathway data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D685–D690. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, S.R.; Kemmeren, P.; Zhao, X.C.; Greenblatt, J.F.; Spencer, F.; Holstege, F.C.P.; Weissman, J.S.; Krogan, N.J. Toward a comprehensive atlas of the physical interactome of Saccharomycescerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2007, 6, 439–450. [Google Scholar]
- Gade, S.; Porzelius, C.; Faelth, M.; Brase, J.; Wuttig, D.; Kuner, R.; Binder, H.; Sueltmann, H.; Beissbarth, T. Graph based fusion of miRNA and mRNA expression data improves clinical outcome prediction in prostate cancer. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schölkopf, B.; Smola, A.J. Learning with Kernels; Schölkopf, B., Mika, S., Burges, C.J., Knirsch, K.-R.M., Rätsch, G., Smola, A.J., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tikhonov, A.; Arsenin, V. Solutions of Ill-Posed Problems; W.H. Winston & Sons: Washington, DC, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, I.W.; Linding, R.; Warde-Farley, D.; Liu, Y.; Pesquita, C.; Faria, D.; Bull, S.; Pawson, T.; Morris, Q.; Wrana, J.L. Dynamic modularity in protein interaction networks predicts breast cancer outcome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, T.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Xu, J.; Yu, H.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Topol, E.J.; Wang, Q.; Rao, S. Towards precise classification of cancers based on robust gene functional expression profiles. BMC Bioinform. 2005, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Gene Ontology Consortium. The Gene Ontology (GO) database and informatics resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D258–D261.
- Vaske, C.J.; Benz, S.C.; Sanborn, J.Z.; Earl, D.; Szeto, C.; Zhu, J.; Haussler, D.; Stuart, J.M. Inference of patient-specific pathway activities from multi-dimensional cancer genomics data using PARADIGM. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, i237–i245. [Google Scholar]
- Teschendorff, A.E.; Gomez, S.; Arenas, A.; El-Ashry, D.; Schmidt, M.; Gehrmann, M.; Caldas, C. Improved prognostic classification of breast cancer defined by antagonistic activation patterns of immune response pathway modules. BMC Cancer 2010, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Chuang, H.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Ideker, T.; Lee, D. Inferring pathway activity toward precise disease classification. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2008, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Daigle, B.J.; Petzold, L.R.; Doyle, F.J. Core module biomarker identification with network exploration for breast cancer metastasis. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bild, A.H.; Yao, G.; Chang, J.T.; Wang, Q.; Potti, A.; Chasse, D.; Joshi, M.B.; Harpole, D.; Lancaster, J.M.; Berchuck, A.; Olson, J.A.; Marks, J.R.; Dressman, H.K.; West, M.; Nevins, J.R. Oncogenic pathway signatures in human cancers as a guide to targeted therapies. Nature 2006, 439, 353–357. [Google Scholar]
- Bentink, S.; Wessendorf, S.; Schwaenen, C.; Rosolowski, M.; Klapper, W.; Rosenwald, A.; Ott, G.; Banham, A.H.; Berger, H.; Feller, A.C.; Hansmann, M.L.; Hasenclever, D.; Hummel, M.; Lenze, D.; Mller, P.; Stuerzenhofecker, B.; Loeffler, M.; Truemper, L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Spang, R. in Malignant Lymphomas Network Project of the, M.M. Pathway activation patterns in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Leukemia 2008, 22, 1746–1754. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.X.; Sieuwerts, A.M.; Zhang, Y.; Martens, J.W.M.; Smid, M.; Klijn, J.G.M.; Wang, Y.; Foekens, J.a. Pathway analysis of gene signatures predicting metastasis of node-negative primary breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2007, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeman, J.; van de Geer, S.; de Kort, F.; van Houwelingen, H. A global test for groups of genes: Testing association with a clinical outcome. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Kammers, K.; Lang, M.; Hengstler, J.G.; Schmidt, M.; Rahnenfuhrer, J. Survival models with preclustered gene groups as covariates. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, L.; Rousseeuw, P. Finding Groups in Data: An Introduction to Cluster Analysis; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, H.Y.; Lee, E.; Liu, Y.T.; Lee, D.; Ideker, T. Network-based classification of breast cancer metastasis. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2007, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.A.; Koyutürk, M. Identification of coordinately dysregulatedsubnetworks in complex phenotypes. Pac. Symp.Biocomput. 2010, 2010, 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Fortney, K.; Kotlyar, M.; Jurisica, I. Inferring the functions of longevity genes with modular subnetwork biomarkers of Caenorhabditis elegans aging. Genome Biol. 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Yoon, B.J.; Dougherty, E.R. Identification of diagnostic subnetwork markers for cancer in human protein-protein interaction network. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Yoon, Y.; Park, C.; Shin, E.; Park, S. Integrative gene network construction for predicting a set of complementary prostate cancer genes. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1846–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutkowski, J.; Ideker, T. Protein networks as logic functions in development and cancer. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.A.; Nibbe, R.K.; Chance, M.R.; Koyutürk, M. Subnetwork state functions define dysregulatedsubnetworks in cancer. J. Comput. Biol. 2011, 18, 263–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, P.; Colak, R.; Salari, R.; Moser, F.; Davicioni, E.; Schönhuth, A.; Ester, M. Inferring cancer subnetwork markers using density-constrained biclustering. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, i625–i631. [Google Scholar]
- Dittrich, M.T.; Klau, G.W.; Rosenwald, A.; Dandekar, T.; Müller, T. Identifying functional modules in protein-protein interaction networks: An integrated exact approach. Bioinformatics (Oxford, UK) 2008, 24, i223–i231. [Google Scholar]
- Dao, P.; Wang, K.; Collins, C.; Ester, M.; Lapuk, A.; Sahinalp, S.C. Optimally discriminative subnetwork markers predict response to chemotherapy. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, i205–i213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alon, N.; Dao, P.; Hajirasouliha, I.; Hormozdiari, F.; Sahinalp, S.C. Biomolecular network motif counting and discovery by color coding. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, i241–i249. [Google Scholar]
- Shawe-Taylor, J.; Cristianini, N. Kernel Methods for Pattern Analysis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kondor, R.; Lafferty, J. Diffusion Kernels on Graphs and Other Discrete Input Spaces. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML ’02), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 8-12 July 2002.
- Gao, C.; Dang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wilkins, D. Graph ranking for exploratory gene data analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapaport, F.; Zinovyev, A.; Dutreix, M.; Barillot, E.; Vert, J.P. Classification of microarray data using gene networks. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsch, D.; Tranchevent, L.C.; Thienpont, B.; Thorrez, L.; Esch, H.V.; Devriendt, K.; Moreau, Y. Network analysis of differential expression for the identification of disease-causing genes. PLoS One 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.S.; Chen, L. Detecting disease associated modules and prioritizing active genes based on high throughput data. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xuan, J.; Riggins, R.; Clarke, R.; Wang, Y. Identifying cancer biomarkers by network-constrained support vector machines. BMC Syst. Biol. 2011, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Shen, X.; Pan, W. Network-based support vector machine for classification of microarray samples. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannes, M.; Brase, J.; Fröhlich, H.; Sültmann, H.; Beissbarth, T. Integration of pathway knowledge into a reweighted recursive feature elimination approach for risk stratification of cancer patients. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2136–2144. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, J.L.; Breitling, R.; Higham, D.J.; Gilbert, D.R. GeneRank: Using search engine technology for the analysis of microarray experiments. BMC Bioinform. 2005, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Page, L.; Brin, S.; Motwani, R.; Winograd, T. The PageRank Citation Ranking: Bringing Order to the Web; Technical Report 1999-66; Stanford InfoLab: Stanford, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, H. Network-constrained regularization and variable selection for analysis of genomic data. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cun, Y.; Fröhlich, H. Prognostic signatures patient in gene for stratification breast cancer—Accuracy, stability and interpretability of gene selection approaches using prior knowledge on protein-protein interactions. BMC Bioinform. 2012. revised. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Cun, Y.; Fröhlich, H. Biomarker Gene Signature Discovery Integrating Network Knowledge. Biology 2012, 1, 5-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology1010005
Cun Y, Fröhlich H. Biomarker Gene Signature Discovery Integrating Network Knowledge. Biology. 2012; 1(1):5-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology1010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleCun, Yupeng, and Holger Fröhlich. 2012. "Biomarker Gene Signature Discovery Integrating Network Knowledge" Biology 1, no. 1: 5-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology1010005
APA StyleCun, Y., & Fröhlich, H. (2012). Biomarker Gene Signature Discovery Integrating Network Knowledge. Biology, 1(1), 5-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology1010005





