Decolorization and Detoxification of Industrial Wastewater Containing Indigo Carmine by Aspergillus niger AN400 in Sequential Reactors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cultivation, Production, and Counting of Fungal Spores
2.2. Immobilization of the Biomass
2.3. Industrial Effluent
2.4. Experimental Setup
2.5. Determination of A. niger Mycelium-Adsorbed Dye
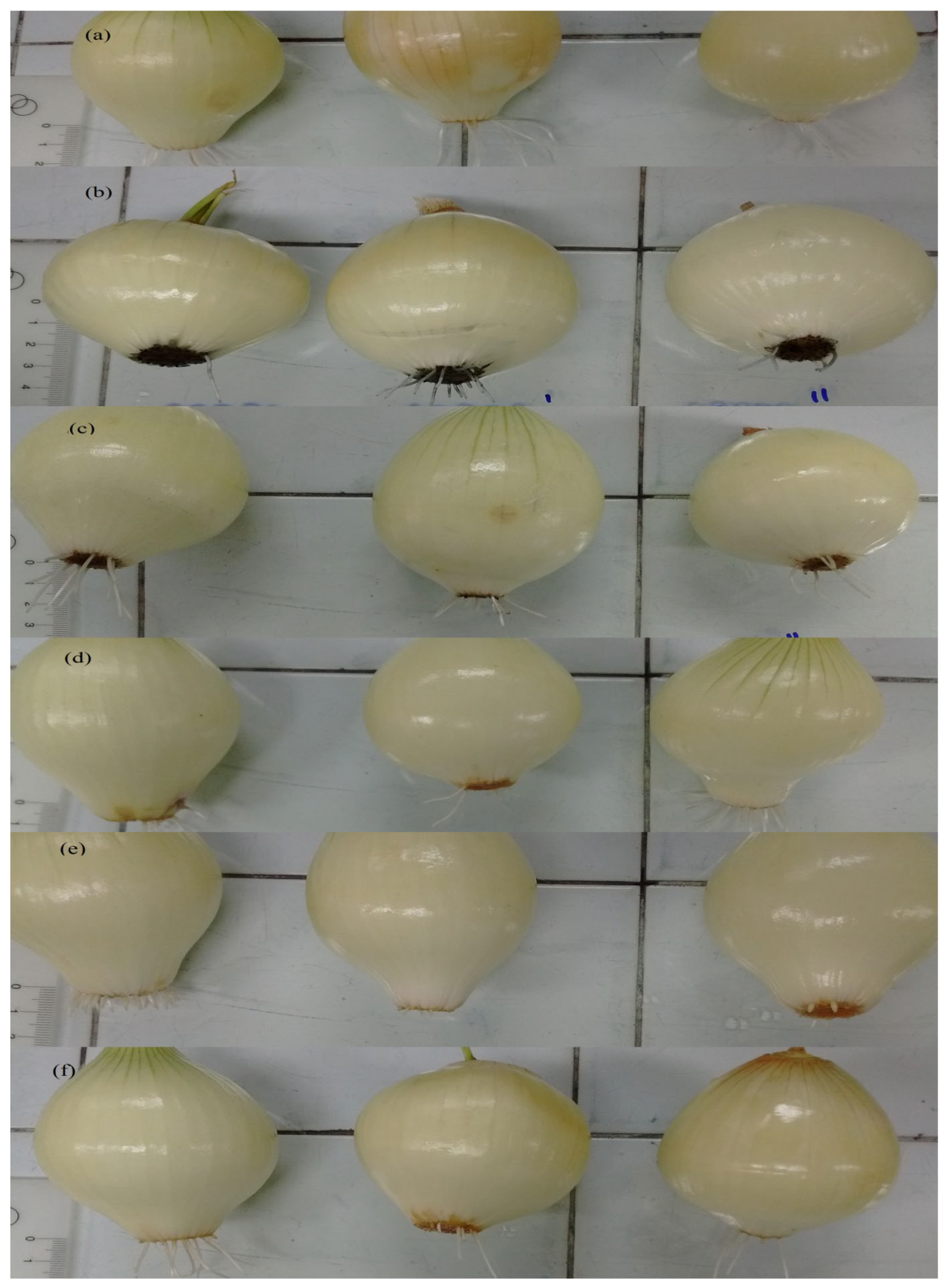
2.6. Toxicity Bioassay
2.7. Colony-Forming Unit Count
3. Results and Discussion
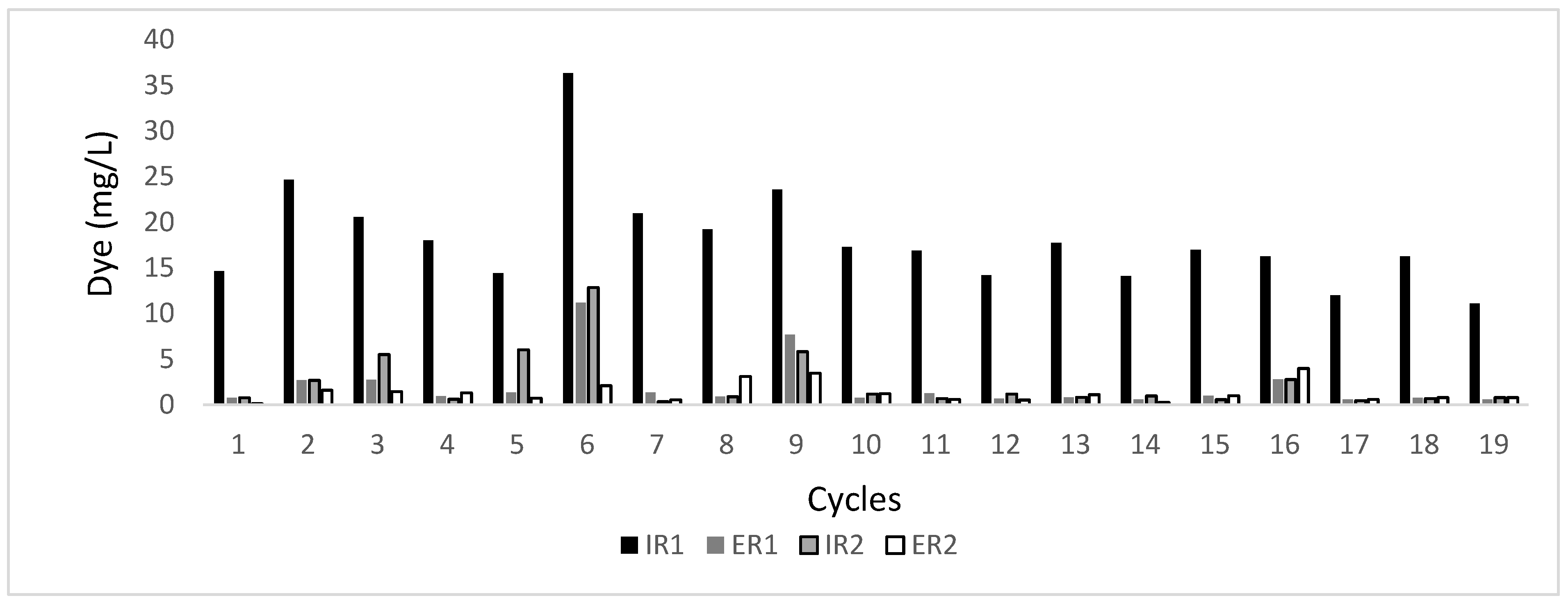
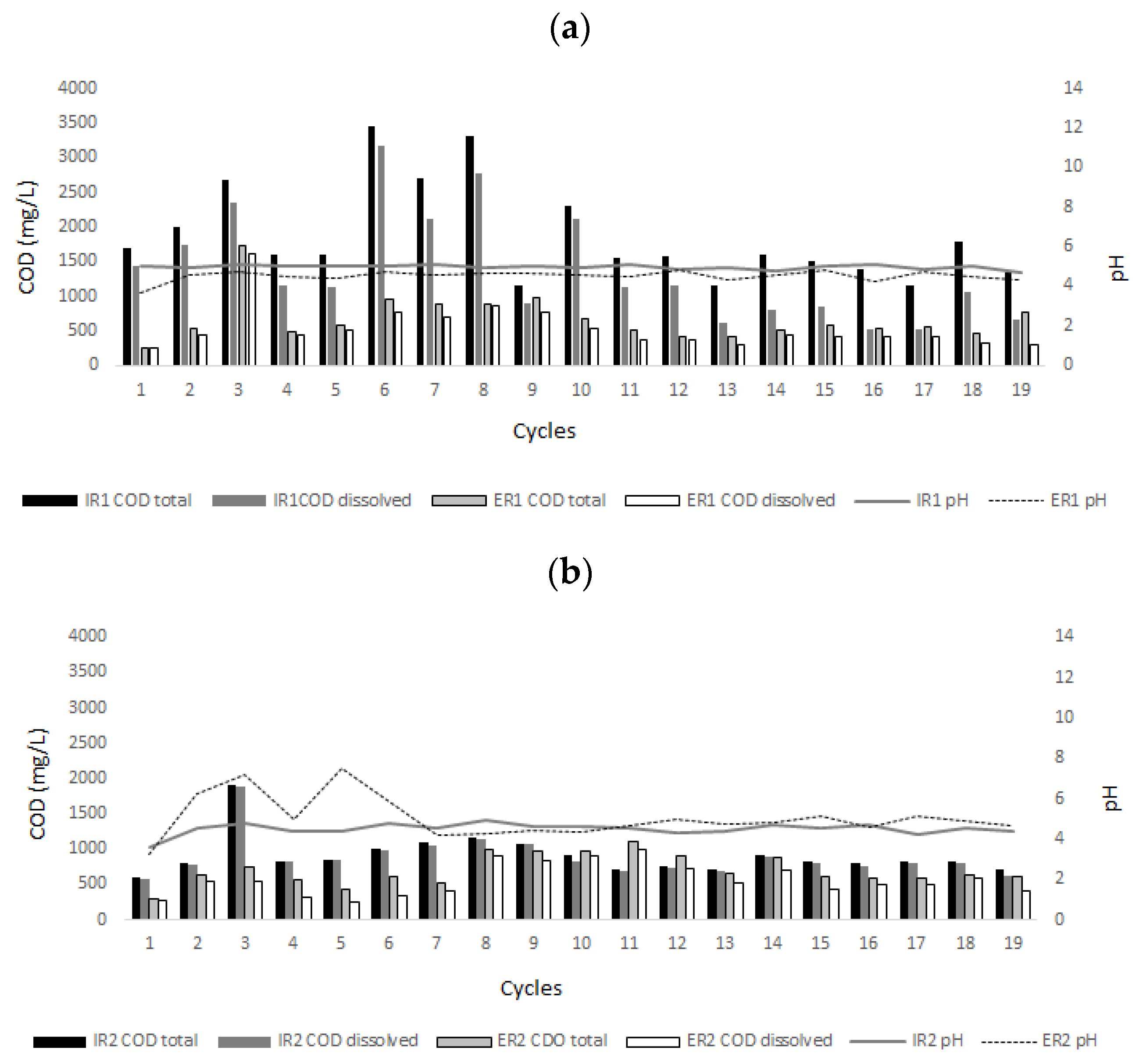
3.1. Decolorization of Textile Industrial Wastewater
3.2. Dye Removal through Adsorption
3.3. Toxicity Assessment
3.4. Microorganisms’ Viability after Treatment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moreira, L.; Galvão, A.R.; Braga, V.; Braga, A.; Teixeira, J. Sustainability as a Gateway to Textile International Markets: The Portuguese Case. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Suárez, L.A.; Sierra-Sánchez, A.G.; Linares-Hernández, I.; Martínez-Miranda, V.; Teutli-Sequeira, E.A. A Critical Review of Textile Industry Wastewater: Green Technologies for the Removal of Indigo Dyes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 10553–10590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ristea, M.-E.; Zarnescu, O. Indigo Carmine: Between Necessity and Concern. J. Xenobiotics 2023, 13, 509–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattanaik, L.; Duraivadivel, P.; Hariprasad, P.; Naik, S.N. Utilization and Re-Use of Solid and Liquid Waste Generated from the Natural Indigo Dye Production Process–A Zero Waste Approach. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Cherwoo, L.; Singh, R. Decoding Dye Degradation: Microbial Remediation of Textile Industry Effluents. Biotechnol. Notes 2023, 4, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linke, J.A.; Rayat, A.; Ward, J.M. Production of Indigo by Recombinant Bacteria. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2023, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Z.; Dai, X.; Xian, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhong, H.; Li, Y. Novel Ternary Heterogeneous Reduction Graphene Oxide (RGO)/BiOCl/TiO2 Nanocomposites for Enhanced Adsorption and Visible-Light Induced Photocatalytic Activity toward Organic Contaminants. Materials 2020, 13, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishor, R.; Purchase, D.; Saratale, G.D.; Saratale, R.G.; Ferreira, L.F.R.; Bilal, M.; Chandra, R.; Bharagava, R.N. Ecotoxicological and Health Concerns of Persistent Coloring Pollutants of Textile Industry Wastewater and Treatment Approaches for Environmental Safety. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishor, R.; Purchase, D.; Ferreira, L.F.R.; Mulla, S.I.; Bilal, M.; Bharagava, R.N. Environmental and Health Hazards of Textile Industry Wastewater Pollutants and Its Treatment Approaches. In Handbook of Environmental Materials Management; Hussain, C.M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–24. ISBN 978-3-319-58538-3. [Google Scholar]
- Alderete, B.L.; da Silva, J.; Godoi, R.; da Silva, F.R.; Taffarel, S.R.; da Silva, L.P.; Garcia, A.L.H.; Júnior, H.M.; de Amorim, H.L.N.; Picada, J.N. Evaluation of Toxicity and Mutagenicity of a Synthetic Effluent Containing Azo Dye after Advanced Oxidation Process Treatment. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, V.; Swarna Karthika, T.; Mansiya, C.; Alagar, M. An over Review on Recently Developed Techniques, Mechanisms and Intermediate Involved in the Advanced Azo Dye Degradation for Industrial Applications. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1224, 129195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendón-Castrillón, L.; Ramírez-Carmona, M.; Ocampo-López, C.; González-López, F.; Cuartas-Uribe, B.; Mendoza-Roca, J.A. Treatment of Water from the Textile Industry Contaminated with Indigo Dye: A Hybrid Approach Combining Bioremediation and Nanofiltration for Sustainable Reuse. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 8, 100498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paździor, K.; Bilińska, L. Microscopic Analysis of Activated Sludge in Industrial Textile Wastewater Treatment Plant. Autex Res. J. 2022, 22, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindhal, T.; Rakholiya, P.; Varjani, S.; Pandey, A.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Ng, H.Y.; Taherzadeh, M.J. A Critical Review on Advances in the Practices and Perspectives for the Treatment of Dye Industry Wastewater. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samsami, S.; Mohamadizaniani, M.; Sarrafzadeh, M.-H.; Rene, E.R.; Firoozbahr, M. Recent Advances in the Treatment of Dye-Containing Wastewater from Textile Industries: Overview and Perspectives. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 143, 138–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zee, F.P.; Villaverde, S. Combined Anaerobic–Aerobic Treatment of Azo Dyes—A Short Review of Bioreactor Studies. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1425–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Alves, M. Dyes-Environmental Impact and Remediation. In Environmental Protection Strategies for Sustainable Development; Malik, A., Grohmann, E., Eds.; Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 111–162. ISBN 978-94-007-1591-2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, D.; Huang, W.; Yang, Y.; Ji, M.; Nghiem, L.D.; Trinh, Q.T.; Tran, N.H. Insights into Biofilm Carriers for Biological Wastewater Treatment Processes: Current State-of-the-Art, Challenges, and Opportunities. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tohamy, R.; Ali, S.S.; Li, F.; Okasha, K.M.; Mahmoud, Y.A.-G.; Elsamahy, T.; Jiao, H.; Fu, Y.; Sun, J. A Critical Review on the Treatment of Dye-Containing Wastewater: Ecotoxicological and Health Concerns of Textile Dyes and Possible Remediation Approaches for Environmental Safety. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iscen, C.F.; Gül, Ü.D.; Yavuz, A.A.; İlhan, S. Decolorization of Dye Solution Containing Remazol Black B by Aspergillus Niger Isolated from Hypersaline Environment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 12497–12504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kövilein, A.; Aschmann, V.; Hohmann, S.; Ochsenreither, K. Immobilization of Aspergillus Oryzae DSM 1863 for L-Malic Acid Production. Fermentation 2022, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizato, E.; Lopes, A.C.; Rocha, R.D.C.; Barbosa, A.M.; Cunha, M.A.A. Textile Effluent Characterization and Evaluation of Capacity Color Removal Using the Fungus Lasiodiplodia Theobromae MMPI. Eng. Sanit. e Ambient. 2017, 22, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia-Hernández, L.J.; Wong-Paz, J.E.; Ascacio-Valdés, J.A.; Contreras-Esquivel, J.C.; Chávez-González, M.L.; Martínez-Pérez, A.; Castillo-Olvera, G.; Aguilar, C.N. Kinetic Study of Fungal Growth of Several Tanninolytic Strains Using Coffee Pulp Procyanidins. Fermentation 2022, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceretta, M.B.; Nercessian, D.; Wolski, E.A. Current Trends on Role of Biological Treatment in Integrated Treatment Technologies of Textile Wastewater. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 651025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-A.; Grace Liu, P.-W.; Whang, L.-M.; Wu, Y.-J.; Cheng, S.-S. Effect of Soil Organic Matter on Petroleum Hydrocarbon Degradation in Diesel/Fuel Oil-Contaminated Soil. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2020, 129, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, E.J.R.; Corso, C.R. Comparative Study of Toxicity of Azo Dye Procion Red MX-5B Following Biosorption and Biodegradation Treatments with the Fungi Aspergillus Niger and Aspergillus Terreus. Chemosphere 2014, 112, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, M.S.; Mostafa, M.K.; Mohamed, S.A.; Sobhy, N.A.; Nasr, M. Bioremediation of Red Azo Dye from Aqueous Solutions by Aspergillus Niger Strain Isolated from Textile Wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, G.; Barbosa, B.C.A.; Rodrigues, K.; Aquino, M.; Pereira, L. Potential of the Filamentous Fungus Aspergillus Niger AN 400 to Degrade Atrazine in Wastewaters. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 9, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, G.; Cavalcante, F.R.; Silveira, R.B.; Pereira, L.; Barbosa, B.; Rodrigues, K. Surfactant Biodegradation in Batch Reactors with Aspergillus Niger AN400. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2019, 24, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheswaran, B.; Al-Ansari, M.; Al-Humaid, L.; Sebastin Raj, J.; Kim, W.; Karmegam, N.; Mohamed Rafi, K. In Vivo Degradation of Polyethylene Terephthalate Using Microbial Isolates from Plastic Polluted Environment. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdana, A.T.; Arianata, M.; Retno, T.; Larasati, D. Optimization of Benzene and Toluene Biodegradation by Aspergillus Niger and Phanerochaete Chrysosporium. J. AL-AZHAR Indones. SERI SAINS DAN Teknol. 2019, 5, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyanka, U.; Lens, P.N.L. Enhanced Removal of Hydrocarbons BTX by Light-Driven Aspergillus Niger ZnS Nanobiohybrids. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2022, 157, 110020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; ISBN 9780875530130. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, P.R.; Cantú, A.M. Ensayos Toxicológicos Para La Evaluación de Sustancias Químicas En Agua y Suelo: La Experiencia En México; Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales: Oaxaca, Mexico, 2008; ISBN 9789688178829. [Google Scholar]
- Brasil Conselho Nacional de Meio Ambiente–CONAMA. Resolução N° 430 de 13 de Maio de 2011. 2011. Available online: https://www.ibama.gov.br/component/legislacao/?view=legislacao&legislacao=118583 (accessed on 29 November 2023).
- CEARÁ Conselho Estadual de Meio Ambiente. COEMA. Resolução 02 de Fevereiro de 2017. 2017. Available online: https://www.semace.ce.gov.br/wp-content/uploads/sites/46/2019/09/COEMA-02-2017.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2023).
- Ribeiro, I.A. Teste Com Raízes de Cebola Para Avaliação de Toxicidade de Efluentes Industriais. Ph.D. Thesis, São Paulo University, São Paulo, Brazil, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Anastasi, A.; Spina, F.; Romagnolo, A.; Tigini, V.; Prigione, V.; Varese, G.C. Integrated Fungal Biomass and Activated Sludge Treatment for Textile Wastewaters Bioremediation. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 123, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Pan, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Salah zene, A.; Tian, Y. Biosorption of Congo Red from Aqueous Solutions Based on Self-Immobilized Mycelial Pellets: Kinetics, Isotherms, and Thermodynamic Studies. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 24601–24612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, R.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Robra, K.-H.; Schneider, M.; Gübitz, G. Indigo Degradation with Laccases from Polyporus sp. and Sclerotium Rolfsii. Text. Res. J. 2001, 71, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellamatrice, P.M. Biodegradação e Toxicidade de Corantes Têxteis e Efluentes Da Estação de Tratamento de Águas Residuárias de Americana. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, S.; Cui, D.; Sun, H.; Liu, C.; Li, L.; Zhao, M. The Biodegradation of Indigo Carmine by Bacillus Safensis HL3 Spore and Toxicity Analysis of the Degradation Products. Molecules 2022, 27, 8539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybczyńska-Tkaczyk, K.; Korniłłowicz-Kowalska, T.; Szychowski, K.A.; Gmiński, J. Biotransformation and Toxicity Effect of Monoanthraquinone Dyes during Bjerkandera Adusta CCBAS 930 Cultures. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.H.; Cheow, Y.L.; Ng, S.L.; Ting, A.S.Y. Biodegradation of Triphenylmethane Dyes by Non-White Rot Fungus Penicillium Simplicissimum: Enzymatic and Toxicity Studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2019, 13, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Martínez, J.D.; Balagurusamy, N.; Montañez, J.; Peralta, R.A.; de Fátima Peralta Muniz Moreira, R.; Bracht, A.; Peralta, R.M.; Morales-Oyervides, L. Synthetic Dyes Biodegradation by Fungal Ligninolytic Enzymes: Process Optimization, Metabolites Evaluation and Toxicity Assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, R.; Khardenavis, A.A.; Purohit, H.J. Diverse Metabolic Capacities of Fungi for Bioremediation. Indian J. Microbiol. 2016, 56, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Effluent Characterization | Concentration (mg/L) |
|---|---|
| COD total | 7046 ± 1586 |
| COD dissolved | 6220 ± 1475 |
| Dye | 100 ± 4 |
| Ammonia | 45.87 ± 12 |
| Nitrite | 9.73 ± 3 |
| Nitrate | 2 ± 1 |
| pH | 10 ± 1 |
| Sample | Root Length (cm) | Growth Inhibition (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Tap water | 4.9 ± 1.70 | 0 |
| IR1 | 0.53 ± 0.68 | 89.2 ± 15 |
| ER1 | 0.76 ± 0.75 | 84.5 ± 7 |
| ER2 | 1.03 ± 0.65 | 79.1 ± 10 |
| Reference | Fungal Species | C0 * (mg/L) | Dye | Dye Class | Toxicity Test | Inhibition (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This work | Aspergillus niger AN400 | 18 ± 6 | Indigo Carmine | Indigoid | Onion bulbs (Allium cepa) | 79.1 ± 10 |
| Pizato et al. [22] | Lasiodiplodia theobromae MMPI | NM | NM | NM | Artemia salina | 100 |
| Rybczyńska-Tkaczyk et al. [43] | Bjerkandera adusta CCBAS 930 | 10 | Alizarin Blue Black B | Anthraquinone | Lepidium sativum L. | 39 |
| Chen et al. [44] | Penicillium simplicissimum | 50 | Violet Metil | Triphenylmethane | Vigna radiata | 21.06 |
| 50 | Malachite Green | Triphenylmethane | Vigna radiata | 29.05 | ||
| 50 | Cotton Blue | Triphenylmethane | Vigna radiata | 0 | ||
| Sosa-Martínez et al. [45] | Phanerochaete chrysosporium | 50 | Malachite Green | Triphenylmethane | Vibrio fischeri | 0 |
| 50 | Congo Red | Azo | Vibrio fischeri | 18.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodrigues, K.; de Sousa, A.M.X.; dos Santos, A.D.O.; Barbosa, B.C.A.; Silva, A.R.; Pereira, L.; Silva, G.M.M. Decolorization and Detoxification of Industrial Wastewater Containing Indigo Carmine by Aspergillus niger AN400 in Sequential Reactors. Colorants 2024, 3, 73-85. https://doi.org/10.3390/colorants3010005
Rodrigues K, de Sousa AMX, dos Santos ADO, Barbosa BCA, Silva AR, Pereira L, Silva GMM. Decolorization and Detoxification of Industrial Wastewater Containing Indigo Carmine by Aspergillus niger AN400 in Sequential Reactors. Colorants. 2024; 3(1):73-85. https://doi.org/10.3390/colorants3010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodrigues, Kelly, Alana M. X. de Sousa, Andreza D. O. dos Santos, Bárbara C. A. Barbosa, A. Rita Silva, Luciana Pereira, and Glória M. M. Silva. 2024. "Decolorization and Detoxification of Industrial Wastewater Containing Indigo Carmine by Aspergillus niger AN400 in Sequential Reactors" Colorants 3, no. 1: 73-85. https://doi.org/10.3390/colorants3010005
APA StyleRodrigues, K., de Sousa, A. M. X., dos Santos, A. D. O., Barbosa, B. C. A., Silva, A. R., Pereira, L., & Silva, G. M. M. (2024). Decolorization and Detoxification of Industrial Wastewater Containing Indigo Carmine by Aspergillus niger AN400 in Sequential Reactors. Colorants, 3(1), 73-85. https://doi.org/10.3390/colorants3010005






