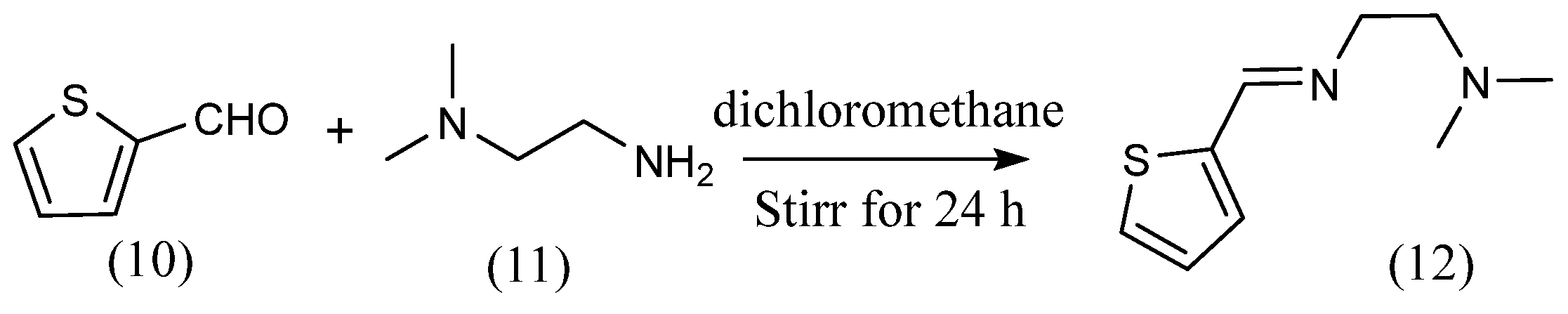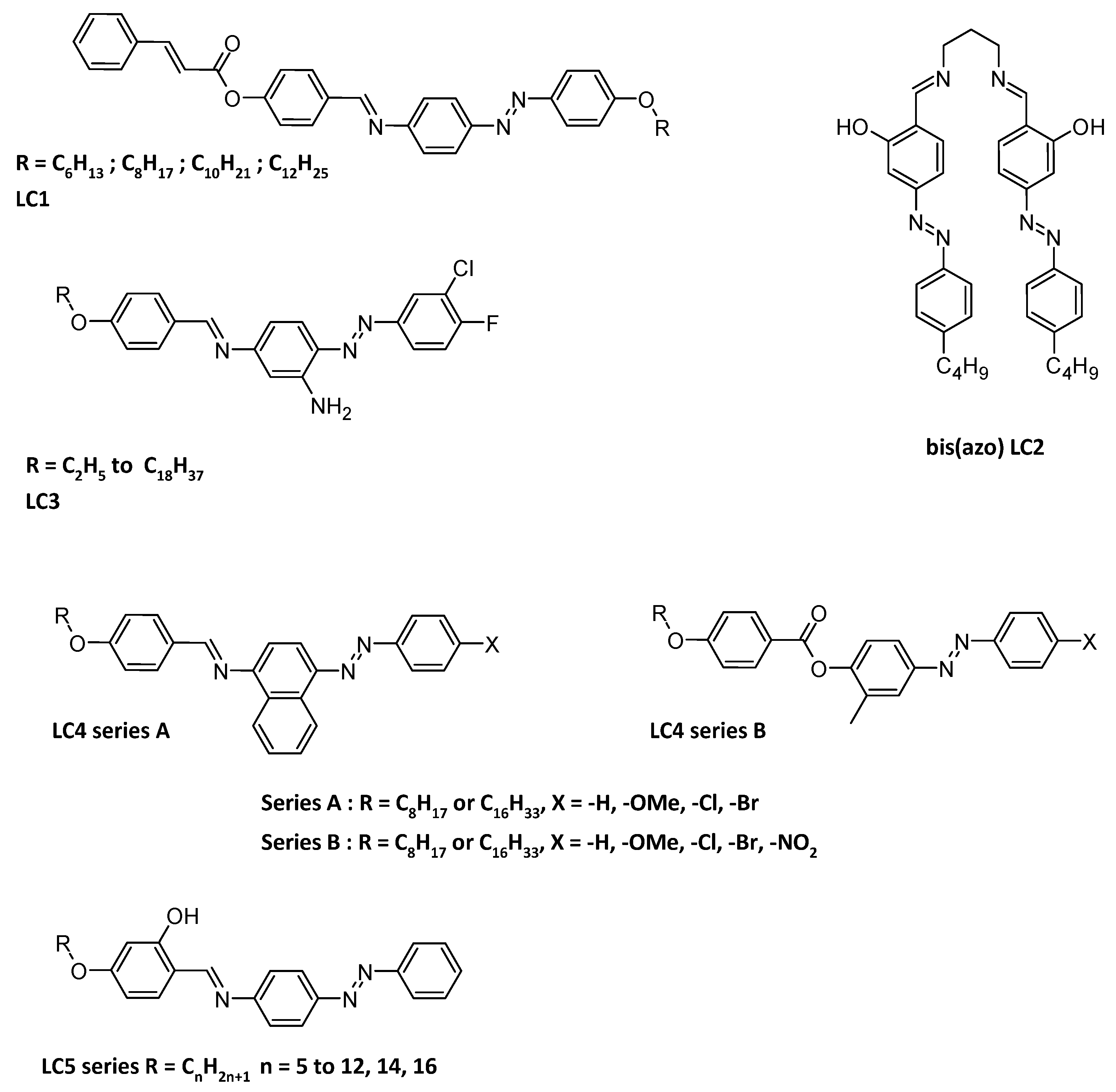Abstract
Azo-Schiff bases contain an azo photochrome showing isomerization accompanying with color change, and an imine moiety (which can contribute to the metal complexation capability). The syntheses of these molecules will be described, and their dyes applications will be discussed, such as for fuel cells, as photometric or colorimetric sensors. In addition, liquid crystals and their antibacterial efficiencies will also be discussed.
1. Introduction
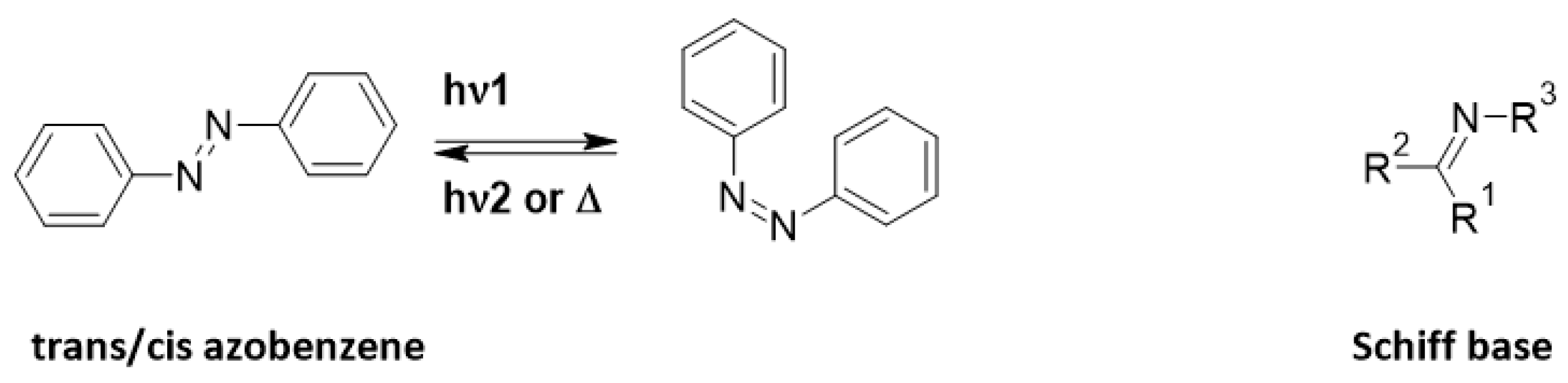
Azo-Schiff bases are molecules composed of azo systems coupled to Schiff bases (Figure 1). The rich database of azo molecules gives numerous opportunities for synthetic pathways [1,2]. Also, the complex possibilities of Schiff bases have made them molecules of choice for various applications [3]. Indeed, azo dyes are a large family of photochromic compounds which can reversibly switch from trans to cis form due to light or heat [4,5,6] and have numerous applications including catalysis, antimicrobial and photopharmacological, in food or as textile colorants [7,8,9,10,11]. Liquid crystals can be also modified by the trans/cis isomerization of azo molecules [12,13,14]. Schiff bases are a sub-class of imines, being either secondary ketimines/aldimines depending on their structure [15]. They were discovered by Hugo Schiff [16]. They were enlarged to salen ligands (which also sometimes exhibit photochromic and thermochitomic behavior) to complex cations [17,18,19].
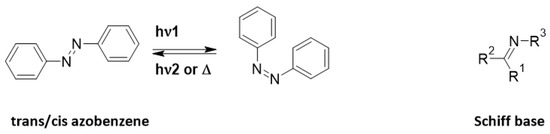
Figure 1.
General representation of azobenzene and Schiff base.
2. Syntheses and Structures of Azobenzene-Containing Schiff-Bases
2.1. Schiff Base Synthesis
2.1.1. Main Imine Syntheses
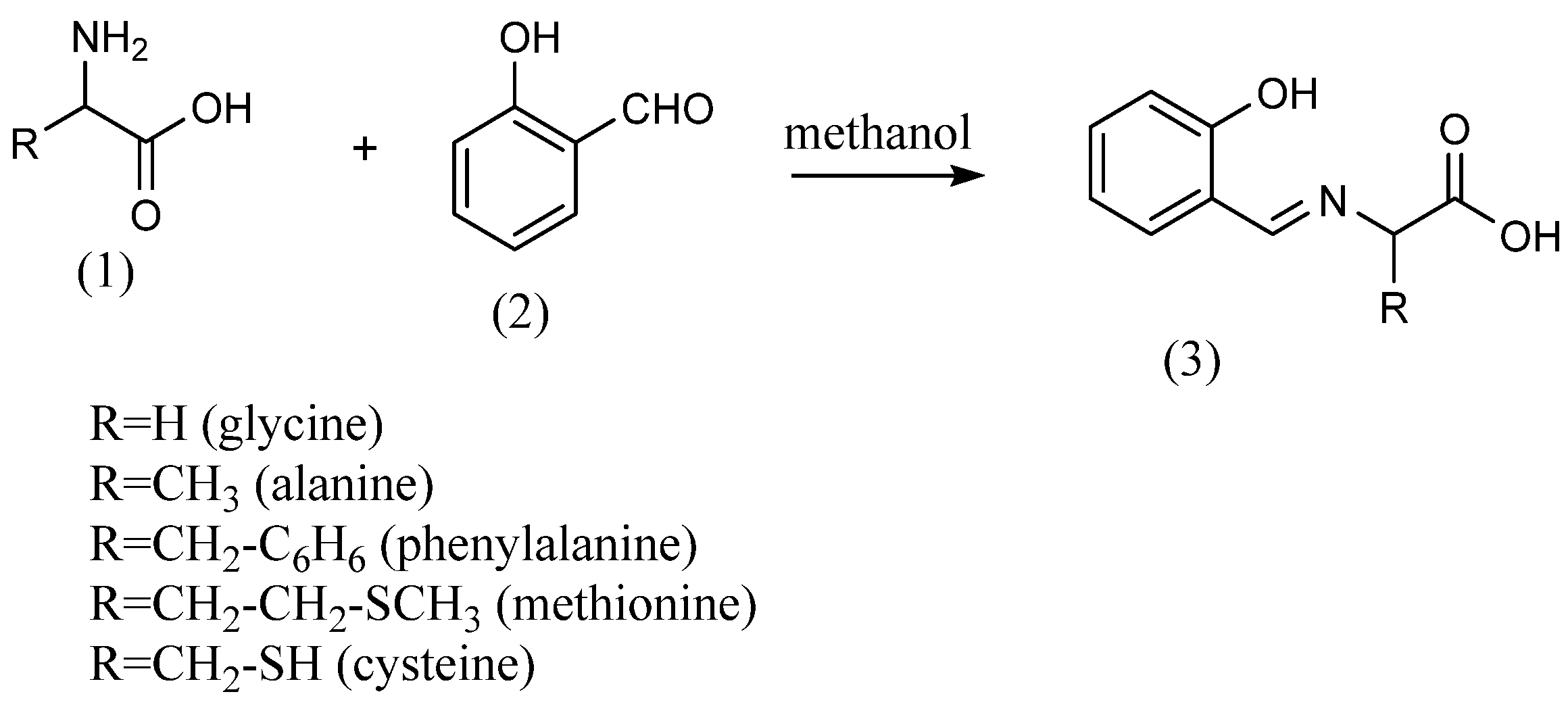
M. A. Neelakantan et al. [20] synthesized Schiff bases from o-vanillin and primary amines. The 2-amino-N-(2-pyridyl)-benzene sulfonamide and equal amounts of o-vanillin were refluxed in ethanol for 8 h to produce imines. R. Ramesh et al. [21] synthesized Schiff bases using the condensation reaction of salicylaldehyde with the primary amines methylamine, cyclohexylamine and 2-aminopyridine. Eren Keskioglu et al. [22] synthesized two Schiff bases using primary amines. The first one was obtained by mixing 1,4-bis(3-aminopropyl) piperazine dissolved in methanol at 40 °C with 2-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde solution at 40 °C and refluxing for 2 h. Then, imines were obtained by refluxing 2-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde with 1,8-diamino-p-menthane dissolved in methanol at 40 °C for 1 day. Zahid H. Chohan et al. The authors of [23] synthesized amino acid Schiff bases using five different amino acids (Scheme 1). The amino acids (1) employed were glycine, alanine, phenylalanine, methionine and cysteine. The amino acid Schiff bases (3) were obtained by dissolving each amino acid in methanol and adding equal molar amounts of salicylaldehyde (2) to the amino acids.
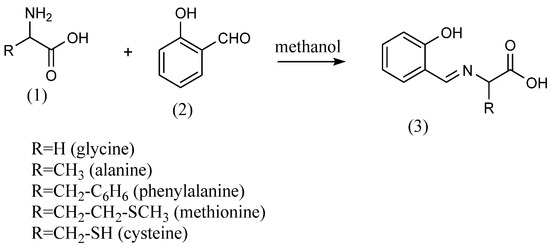
Scheme 1.
Schiff bases from amino acids [23].
2.1.2. Aniline to Arylamines
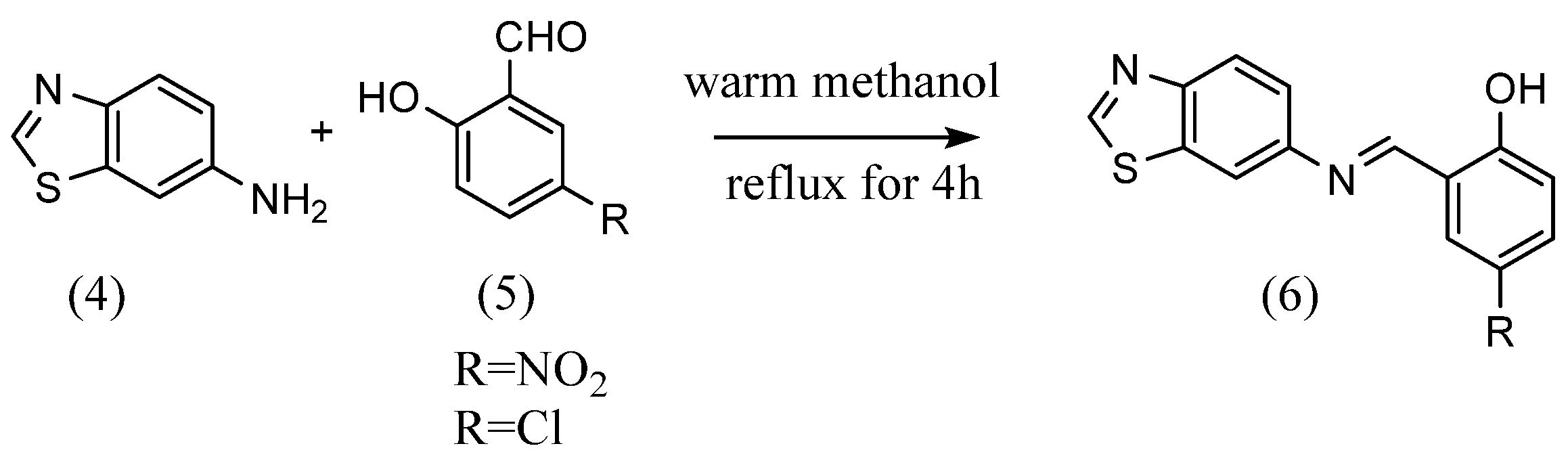
Zahid H. Chohan et al. [24] synthesized four Schiff bases with different substituents. 2-Amino-5-hydroxypyridine dissolved in ethanol was mixed with an equivalent mole of salicylaldehyde dissolved in ethanol. Then, several drops of sulfuric acid were added, and the Schiff base was obtained by refluxing for 2 h. Schiff bases with different substituents were obtained using the same reaction method as above with 2-aminopyridine having nitro, methoxy and bromo groups. Narendrula Vamsikrishna et al. The authors of [25] synthesized two Schiff bases with different substituents (Scheme 2). 6-Aminobenzothiazole (4) and equal amounts of 5-nitrosalicylaldehyde or 5-chlorosalicylaldehyde (5) were mixed in a warm methanol solution. The mixture was then refluxed for 4 hours, resulting in the formation of a Schiff base with benzothiazoline (6). Rua Alnoman et al. [26] synthesized Schiff bases with alkyl chains by refluxing equal molar amounts of 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde and 4-hexyloxyaniline in ethanol solution.
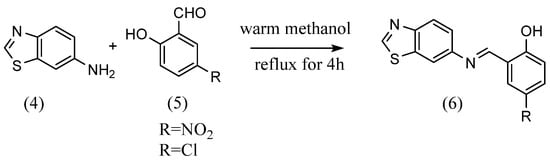
Scheme 2.
Benzothiozolic Schiff bases [25].
2.1.3. Two Aldehydes and Aniline
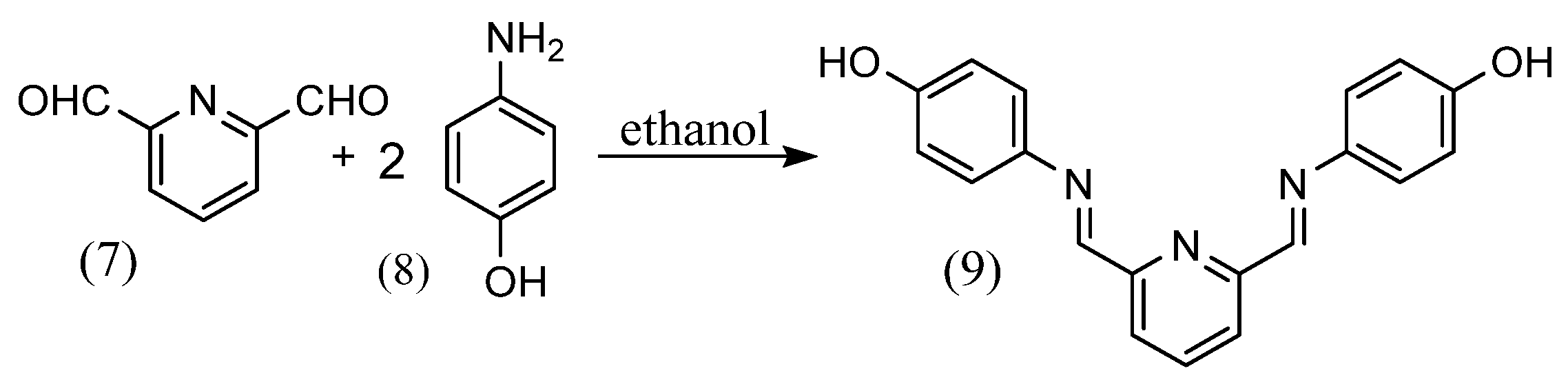
Santiago Zolezzi et al. [27] synthesized a salen-type of alkyl diamine structure by adding a small amount of a methanol solution of 2 equivalents of salicylaldehyde to a methanol solution of ethylene diamine or 1R,2R-(+)-,1S,2S-(−)-1,2-diphenylethylene diamine and stirring. Gehad G. Mohamed [28] synthesized Schiff bases (9) by stirring 2,6-pyridinedicarboxaldehyde (7) and two equivalents of 2-aminophenol (8) in ethanol solution (Scheme 3). Rachid Souane et al. [29] synthesized four tridentate ligand complexes with different substituents. The Schiff-base ligands were obtained by adding 2,6-diacetylpyridine, an excess amount of 2,6-dimethylaniline and a few drops of formic acid to methanol and stirring at 50 °C. Ligands of other substituents were also synthesized with each reagent. The ligand and metal chloride were then added to THF and stirred at room temperature to obtain the tridentate ligand complex.
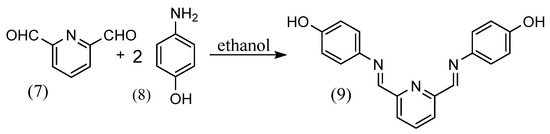
Scheme 3.
Synthesis by Gehad G. Mohamed [28].
2.1.4. Unusual Imine Synthesis
This section describes synthetic methods for imine that are different from the methods described so far. Paola Vicini et al. [30] reported a method for the synthesis of imines using arylaldehydes and hetero 5-membered ring aromatic amines. Benzo[d]isothiazol-3-ylamine or 5-methyl-benzo[d]isothiazol-3-ylamine and arylaldehyde and acetic acid were added to ethanol and stirred to yield the imine. Jaegyeong Lee et al. [31] reported a method for the synthesis of imines from five-membered ring aldehydes and amines (Scheme 4). Imines with five-membered rings (12) were obtained by stirring 2-thiophene carboxaldehyde (10) and N,N-dimethylethylenediamine (11) in dichloromethane solution for 24 h. There are other syntheses of imines using thiophene carboxaldehyde. Hakan Kizilkaya et al. [32] also synthesized imines with five-membered rings using 2-thiophenecarboxyaldehyde: a methanol solution of 2-thiophenecarboxyaldehyde was added every 4 min to a methanol solution of an equal volume of 4-aminopyridine. After addition, the imine was obtained by refluxing for 12 h. Raafat M. Issa et al. [33] synthesized imines using 5-membered ring amines and aldehydes, whereby 4-aminoantipyrine and equal amounts of aldehydes were dissolved in ethanol and refluxed for several hours to give imines. Abdullah M. Asiri et al. [34] similarly synthesized six imines with different substituents from five-membered ring amines and various aldehydes. A. Xavier et al. [35] synthesized imines from diketones and anilines. By stirring equal amounts of benzyl and aniline in ethanol for several hours, they synthesized imines in which the two carbon–oxygen double bonds of benzyl were converted to carbon–nitrogen double bonds. Aliasghar Jarrahpour et al. [36] synthesized imines from cyclic ketones and amines. The imine was obtained by dissolving aromatic diamines, two equivalents of Isatin and glacial acetic acid in ethanol and refluxing for several hours.

Scheme 4.
Synthetic pathway by Jaegyeong Lee et al. [31].
2.1.5. Complex Synthesis: Aldehyde Coordination First, Imine Synthesis on Metal
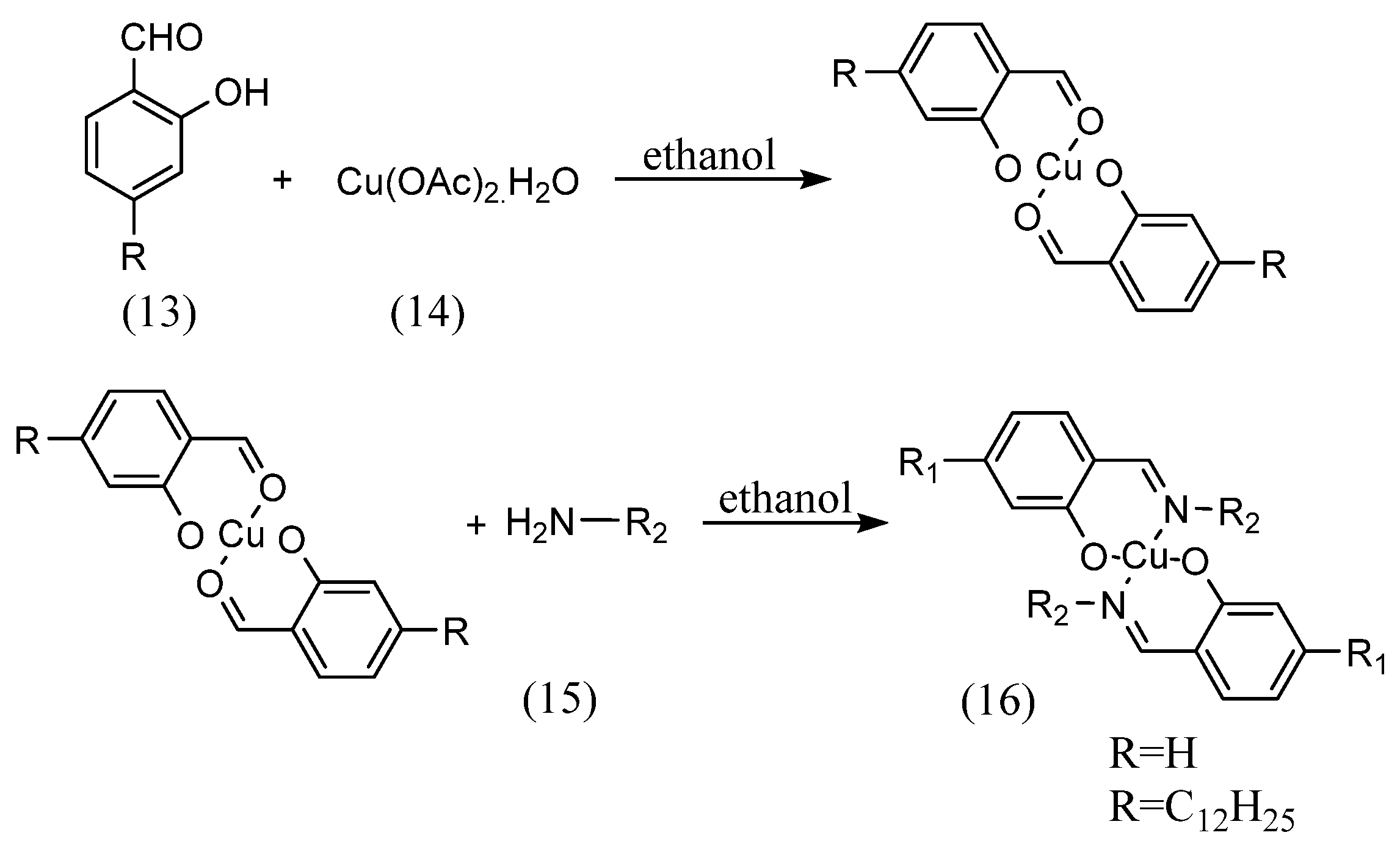
This is so-called ‘template’ synthesis associated with preparation of metal complexes. Reinhard Paschke et al. [37] synthesized complexes by coordinating aldehydes to metals and then imines (Scheme 5). The 4-n-alkyloxy-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde (13) and copper(II) acetate monohydrate (14) were mixed in ethanol solution. The copper complex with imine (16) was then synthesized by adding an equal volume of amine (15) diluted in ethanol solution and stirring.
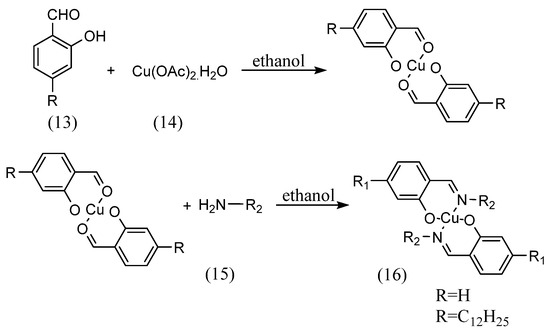
Scheme 5.
Strategy of Reinhard Paschke et al. [37].
2.2. Main Azo Schiff Base Synthetic Method
2.2.1. Azobenzene Synthesis by Mills Reaction
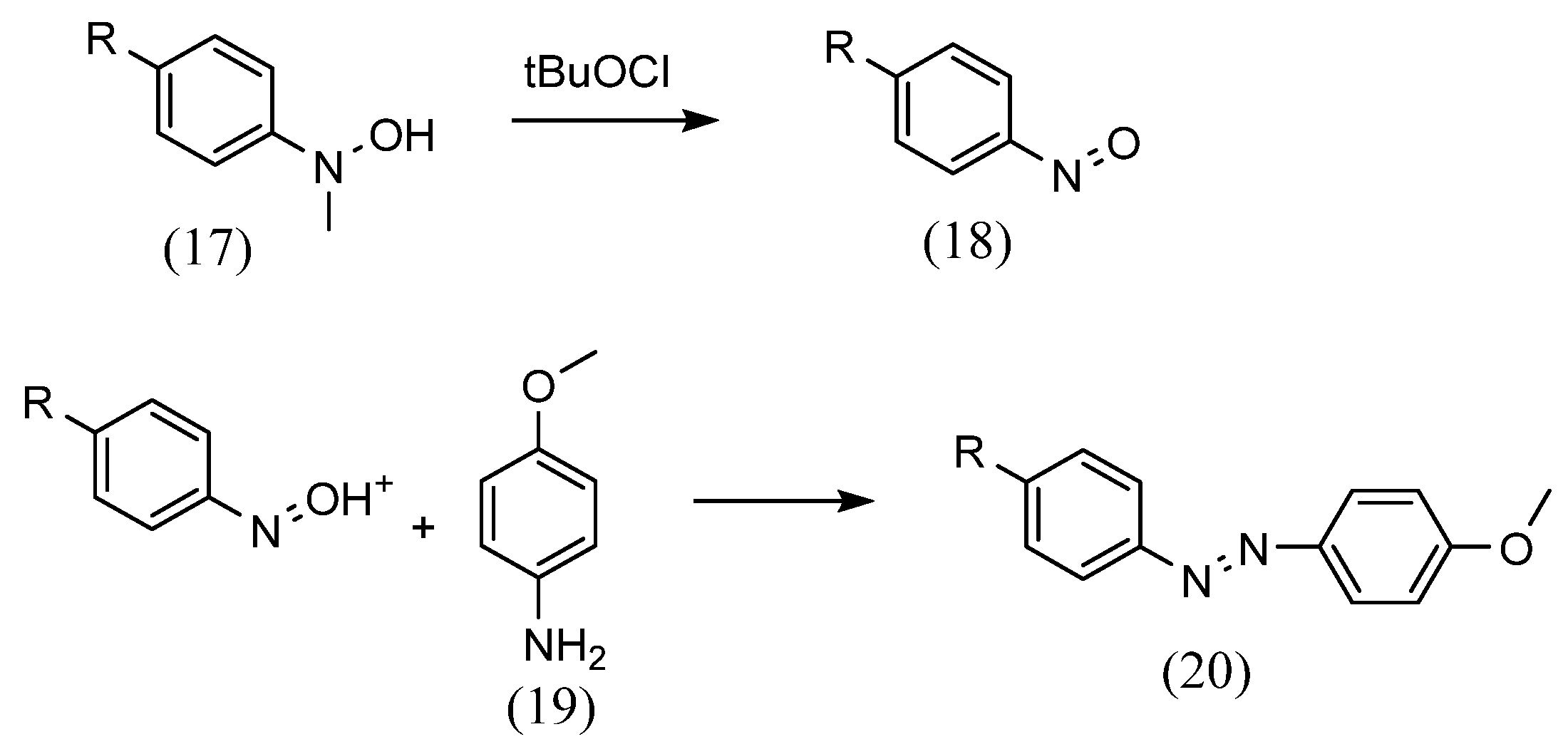
Numerous methods are used to synthesize azobenzene compounds for Schiff-base complex formation. First, as for azo group formation, Mills reactions can be performed. Estíbaliz Merino [38] synthesized azo compounds using the Mills reaction, in which aniline reacts with aromatic nitroso derivatives in glacial acetic acid (Scheme 6). The aromatic nitroso derivatives (18) were obtained by oxidation of aromatic methylhydroxylamine (17) with tBuOCl at −78 °C. This was mixed with aniline (19) and stirred at room temperature to yield azobenzene (20).
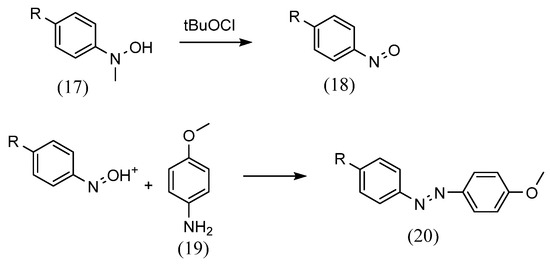
Scheme 6.
Estíbaliz Merino [38] method.
Simona Fazekašová et al. [39] conducted the synthesis of azo compounds using the Mills reaction. This involved the oxidation of ethyl 4-aminobenzoate, resulting in the conversion of amino groups to nitroso groups. The azo compound was synthesized by condensation of an amine to the nitroso group. Andreas Aemissegger et al. [40] also synthesized azo compounds using the Mills reaction by utilizing a protecting group. 3-Nitrophenylacetic acid was stirred with tert-butanol, Boc2O and DMAP to desorb the proton of acetic acid to afford a compound with a tert-butyl attached and the nitro group was reduced to a nitroso group. Next, 3-nitrobenzylamine hydrochloride, Fmoc-Cl and DIPEA were stirred in a dichloromethane solution to produce a compound with Fmoc attached to the hydrogen of the amino group. The nitro group in this compound was reduced to an amino group. Using the compound containing the nitroso group and the amino group, the azo compound was obtained using the Mills reaction. Finally, the tert-butyl protection was removed and the azo compound containing a carboxylic acid was obtained by carboxylic acid. In addition, Hidenori Nishioka et al. [41] synthesized azo compounds using the Mills reaction with aniline after reducing the nitro group of the aromatic ring to a nitroso group. Juliane Sørensen et al. [42] reduced the nitro group of the aromatic ring to an amino group and synthesized azo compounds by azo coupling with aniline. Furthermore, etherification at the para-position of the azo compound gave azo compounds containing ether bonds. Beate Priewisch et al. [43] oxidized the amino group of an aromatic ring with oxone to a nitroso group. By reacting the nitroso group with the amino group before oxidation, they synthesized azo compounds. Furthermore, Byung-Chan Yu et al. [44] synthesized azo compounds by oxidizing the amino group of aniline to a nitroso group with oxone, followed by azo coupling with p-iodoaniline. Click chemistry occurred at the para position of the azo compound, and azo compounds with carbon–carbon triple bonds and aromatic rings were synthesized. Ege Hosgor et al. [45] reduced the nitro group of the aromatic ring to an amino group by Pd/C catalytic reduction followed by CuBr-catalyzed azo coupling to synthesize azo compounds. Suju Fan et al. [46] synthesized azobenzene compounds from aromatic compounds with amino groups by NaClO, while Subhas Samanta et al. [47] used AgO as catalyst. Alford Antoine John et al. [48] synthesized azo compounds in dichloromethane solution. They synthesized azo compounds in a new way by using 2 equivalents of NCS/DBU as catalyst.
2.2.2. Azo Schiff Base Synthesis by Diazotization Method
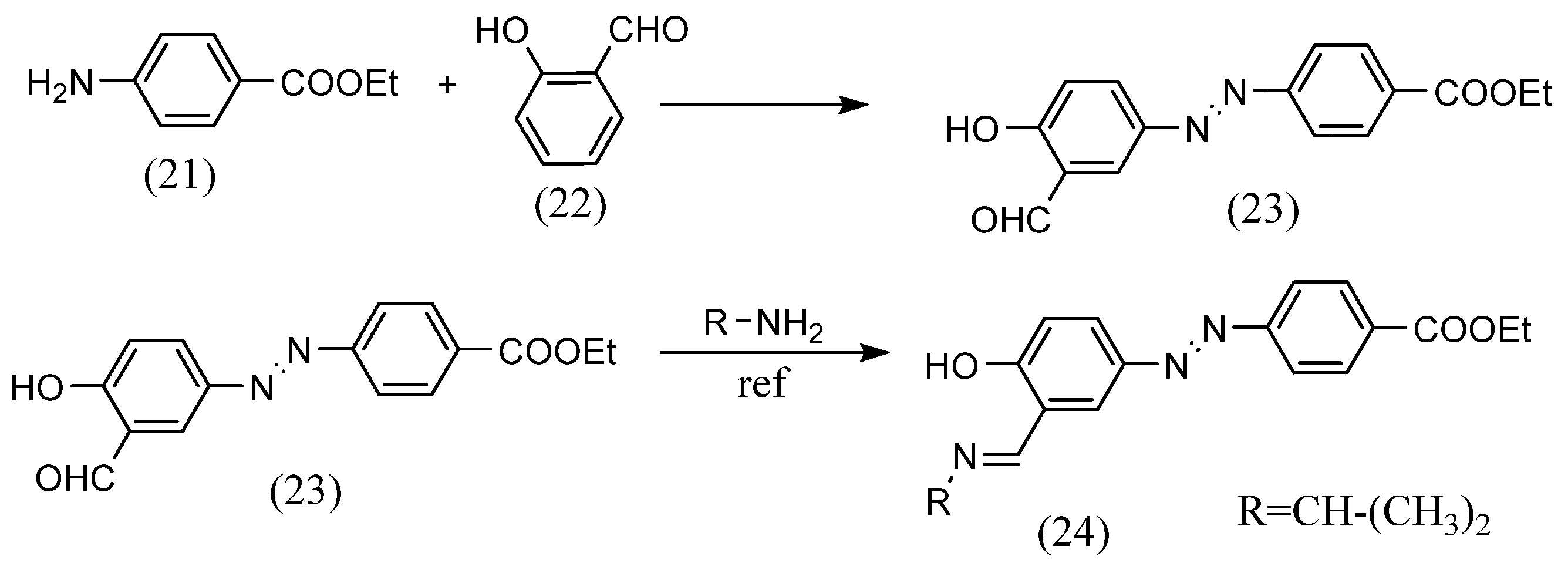
The diazo coupling can also lead to azo-containing Schiff-base ligands for metal complexes. For example, Octavia A. Blackburn et al. [49] synthesized azobenzene Schiff bases by azo coupling of diazonium salts derived from anilines with aldehydes and the reaction of the aldehydes with amines (Scheme 7). Hydrochloric acid and ethyl 4-aminobenzoate (21), cooled in an ice bath, were stirred while being added to an aqueous sodium nitrite solution. The solution was then added to an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution of salicylaldehyde (22) and stirred, and crystals (23) were obtained by filtration. In this compound, equal amounts of i-propylamine and glacial acetic acid were dissolved in ethanol and refluxed. As a result, an azobenzene Schiff base (24) was obtained.
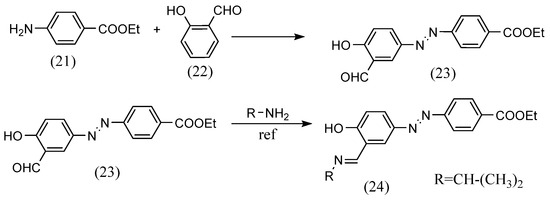
Scheme 7.
Synthetic part reported by Octavia A. Blackburn et al. [49].
Harmeet Kaur et al. [50] similarly synthesized azobenzene Schiff bases by diazotizing aniline derivatives with hydrochloric acid and sodium nitrite, followed by reaction with salicylic aldehyde. In a similar way, Siham Slassi et al. [51] synthesized azobenzene compounds from amines by sodium nitrite and azobenzene Schiff bases by reaction of aldehydes in azobenzene compounds with amines. o-Toluidine dissolved in hydrochloric acid and water was cooled to 0 °C and sodium nitrite solution was added dropwise. This solution was added dropwise to an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution of salicylaldehyde and stirred to give the compound. This compound and benzaldehyde were dissolved in methanol, propylamine was added, and refluxing for 2 h gave the azobenzene Schiff base. Mehmet Gulcan et al. [52] also synthesized azobenzene Schiff bases and metal complexes with azobenzene Schiff bases as ligands by reacting very large amines with aldehydes in azo compounds obtained by azo coupling. Azo aldehydes were obtained by azo coupling with salicylaldehyde and aniline. It was dissolved in ethanol and added to an equal volume of N-aminopyrimidin-2-one dissolved in ethanol. The solution was refluxed for 4 h, resulting in an azobenzene Schiff base ligand. Further, the various metals and ligands were dissolved in a mixture of methanol and chloroform and refluxed for 1 h to yield the metal complexes.
2.2.3. Structural Variations Due to Orientation When the Azo and Imine Groups Are in the Same Benzene Ring
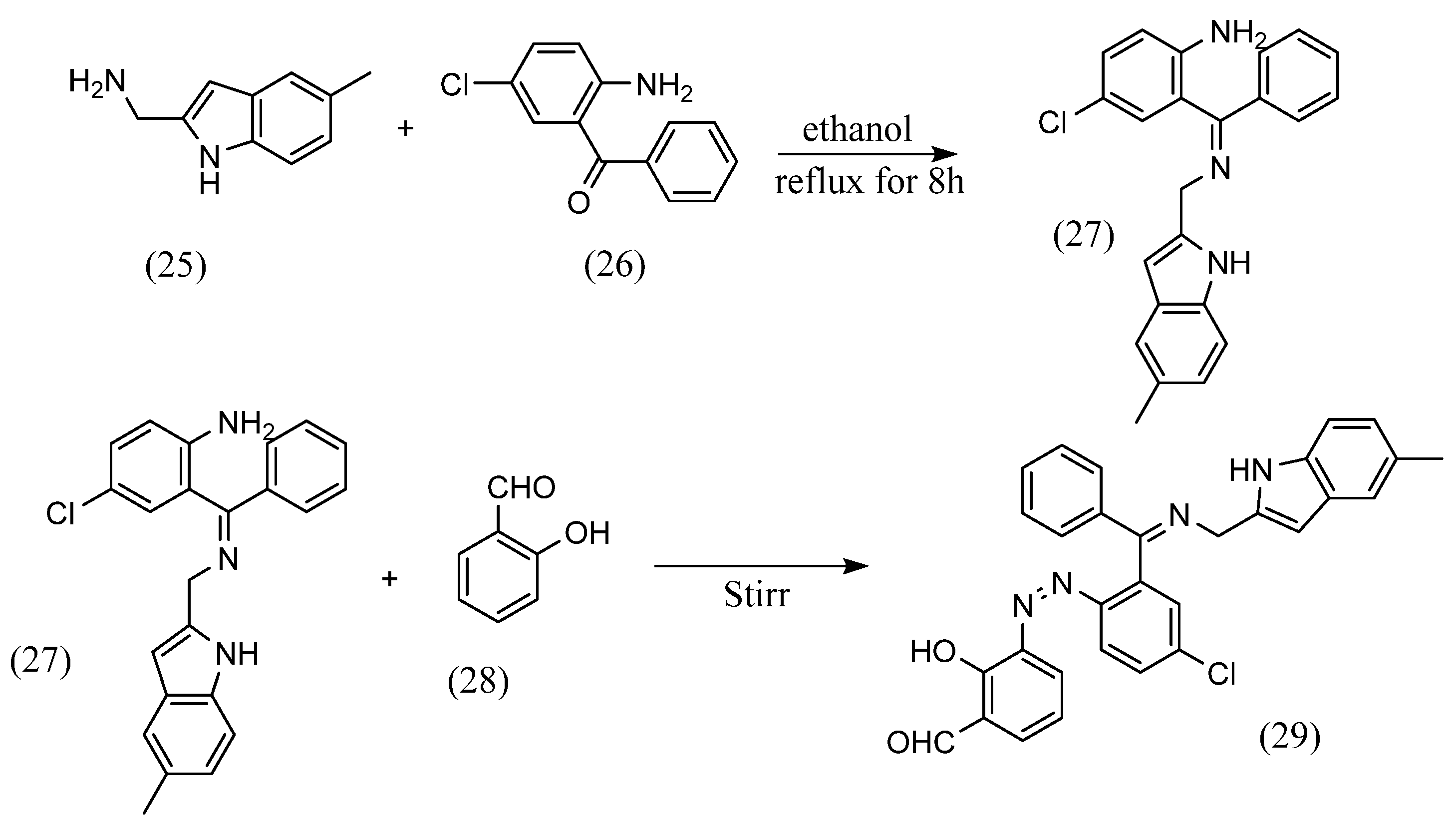
As for structural variations, this section states orientation where the azo and imine groups are in the same benzene ring, azobenzene Schiff bases were synthesized at the para, meta and ortho positions of the benzene ring. For example, Ti feng Jiao et al. [53] synthesized azobenzene Schiff bases, which are an azobenzene and Schiff base bonded to the para position of the benzene ring. Chao Gao et al. [54] also synthesized azobenzene Schiff base with azobenzene and Schiff base bonded to the meta-position of the benzene ring. Furthermore, Hiyam Hadi Alkam et al. [55] synthesized an azobenzene Schiff base with azobenzene and the Schiff base bonded at the ortho position (Scheme 8). (5-methyl-1H-indol-2- yl)methanamine (25) and equal amounts of 2-amino-5-chlorobenzophenone (26) were dissolved in ethanol and mixed. Ethanol solution of K2CO3 was added to the solution and then it was refluxed for 8 h. The resulting precipitate (27) was dissolved in a mixture of water and ethanol containing sulfuric acid, to which was added aqueous sodium nitrite solution. The resulting diazonium and sodium hydroxide solution were then added to an ethanol solution of salicylaldehyde (28) and stirred at low temperature. As a result, an azobenzene Schiff base (29) was obtained, in which the azobenzene and Schiff base were bonded to the ortho position of the benzene ring.
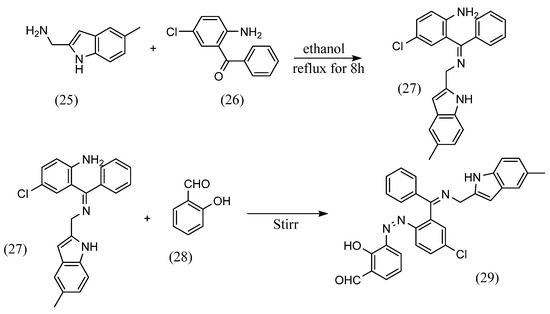
Scheme 8.
Synthetic method by Hiyam Hadi Alkam et al. [55].
2.2.4. Azoaldehyde, Schiff Base and Complex Synthesis
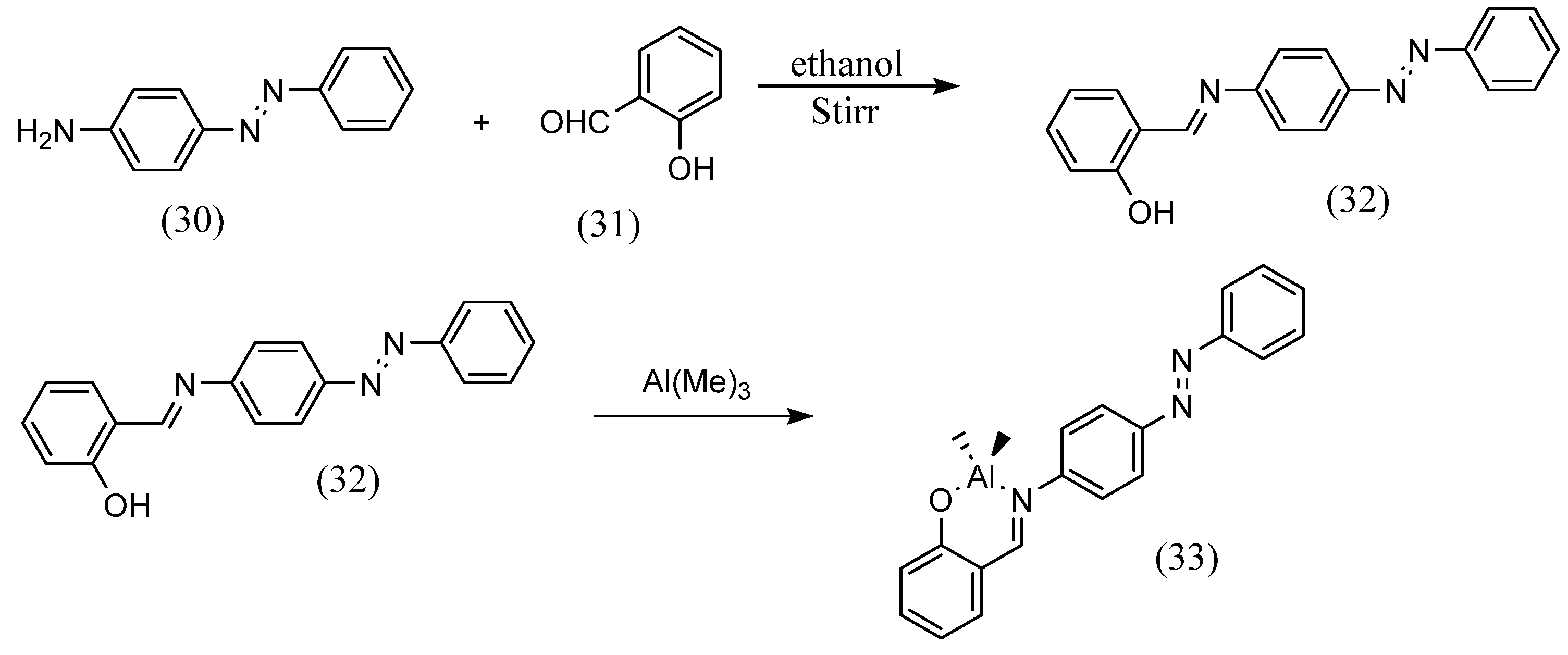
Siham Slassi et al. [56] synthesized azobenzene Schiff bases using a pre-existing azo. 2-hydroxy-5-(o-tolyldiazenyl)benzaldehyde was dissolved in methanol and added to an equal volume of N-(3-Aminopropyl)imidazole. These were refluxed to afford the azobenzene Schiff base. Sandeep Kaler et al. [57] synthesized azobenzene Schiff bases with different substituents by using various salicylaldehydes with existing azobenzene compounds (Scheme 9). They also synthesized metal complexes with these ligands. Azobenzene Schiff bases were obtained by dissolving 4-phenyl(diazenyl)aniline (30) and salicylic aldehyde (31) in ethanol and stirring. Azobenzene Schiff-base complexes (33) were obtained by stirring the ligand (32) with Al(Me)3 or Zn(Et)2 in toluene at 1:2 or 1:1.
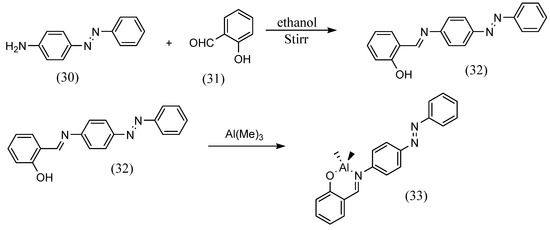
Scheme 9.
Synthesis by Sandeep Kaler et al. [57].
Ali M. Hassan et al. [58] similarly synthesized azobenzene Schiff bases through the condensation of a preexisting azobenzene compound with aldehydes. They also synthesized metal complexes with these ligands. o-Vanillin and 4-aminoazobenzene were dissolved in methanol, and the mixed solution was refluxed to produce the precipitate, i.e., the ligands. The azobenzene Schiff-base complex was obtained by dissolving the ligand and hydrated metal acetate in methanol and refluxing the mixture.
2.2.5. If There Are More than One Amino Group, Can a Schiff Base Ligand Be Formed First?
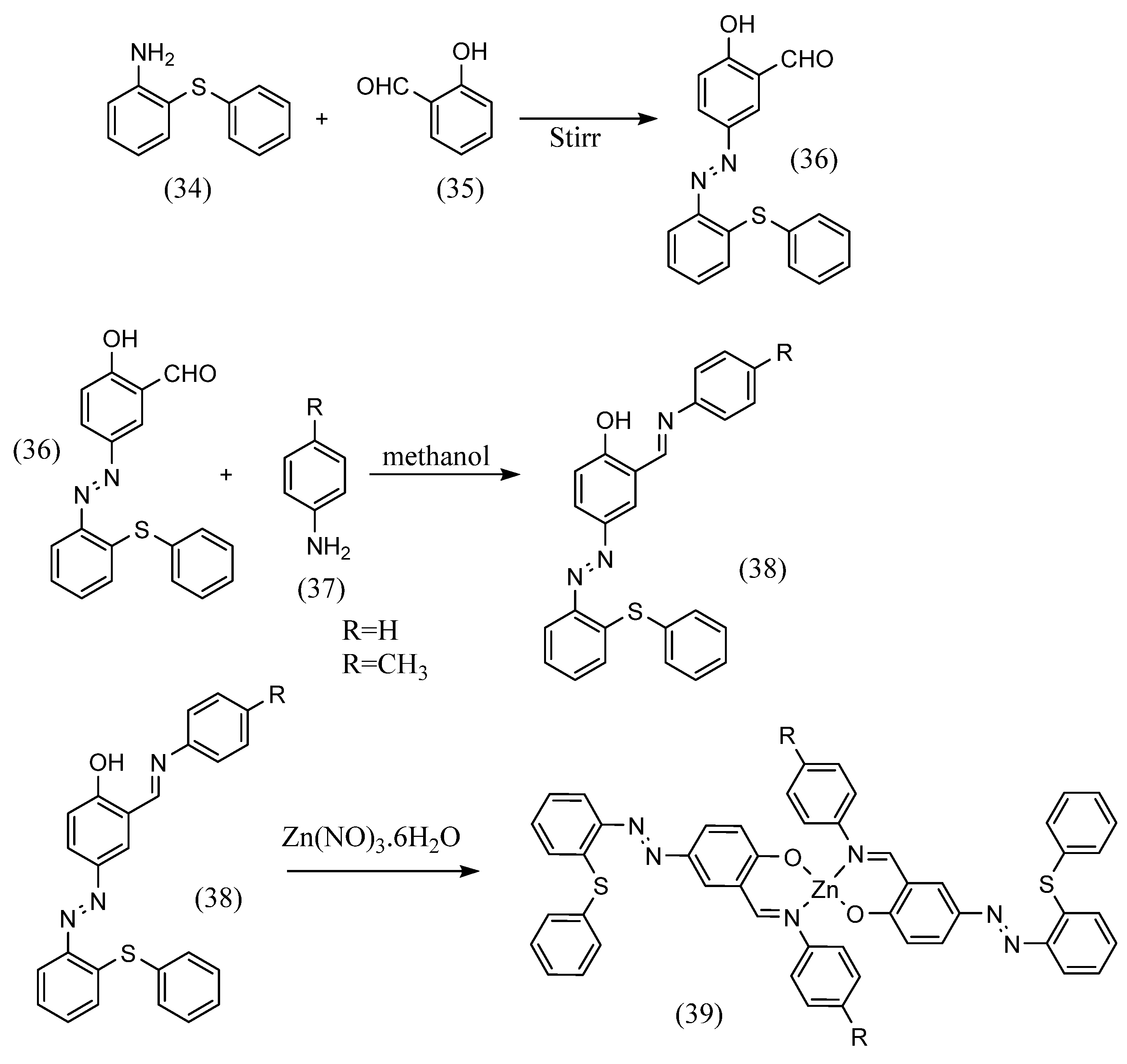
Yogesh Kumar et al. [59] formed a Schiff base with an aldehyde on one side with aniline after the first step of azo coupling (Scheme 10). They synthesized a trans Schiff-base complex with two bidentate chelates. 2-(Phenylthio)aniline (34) was stirred with hydrochloric acid and sodium nitrite solution. Next, this was mixed with an aqueous alkaline solution in which salicylic aldehyde (35) was dissolved and stirred to obtain an azo compound with an aldehyde moiety (36). Furthermore, a methanol solution of the azo compound, aniline (37), and acetic acid in equal volumes was refluxed to yield the azobenzene Schiff base (38). Using this as a ligand, a trans form of bis(didentate)-type Schiff-base complex (39) was obtained by dropping Zn(NO3)2-6H2O into the ligand solution.
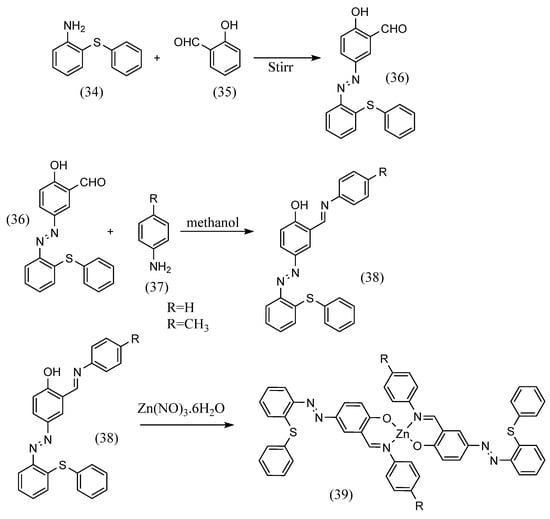
Scheme 10.
Synthetic pathway by Yogesh Kumar et al. [59].
Nidhi Nigam et al. [60] introduce aniline and aldehyde simultaneously, but only azo coupling occurs first. They synthesized azo-Schiff bases in which the remaining aldehyde and a large glycosyl amine form a Schiff base.
2.2.6. Adjustment of the Number of Imines
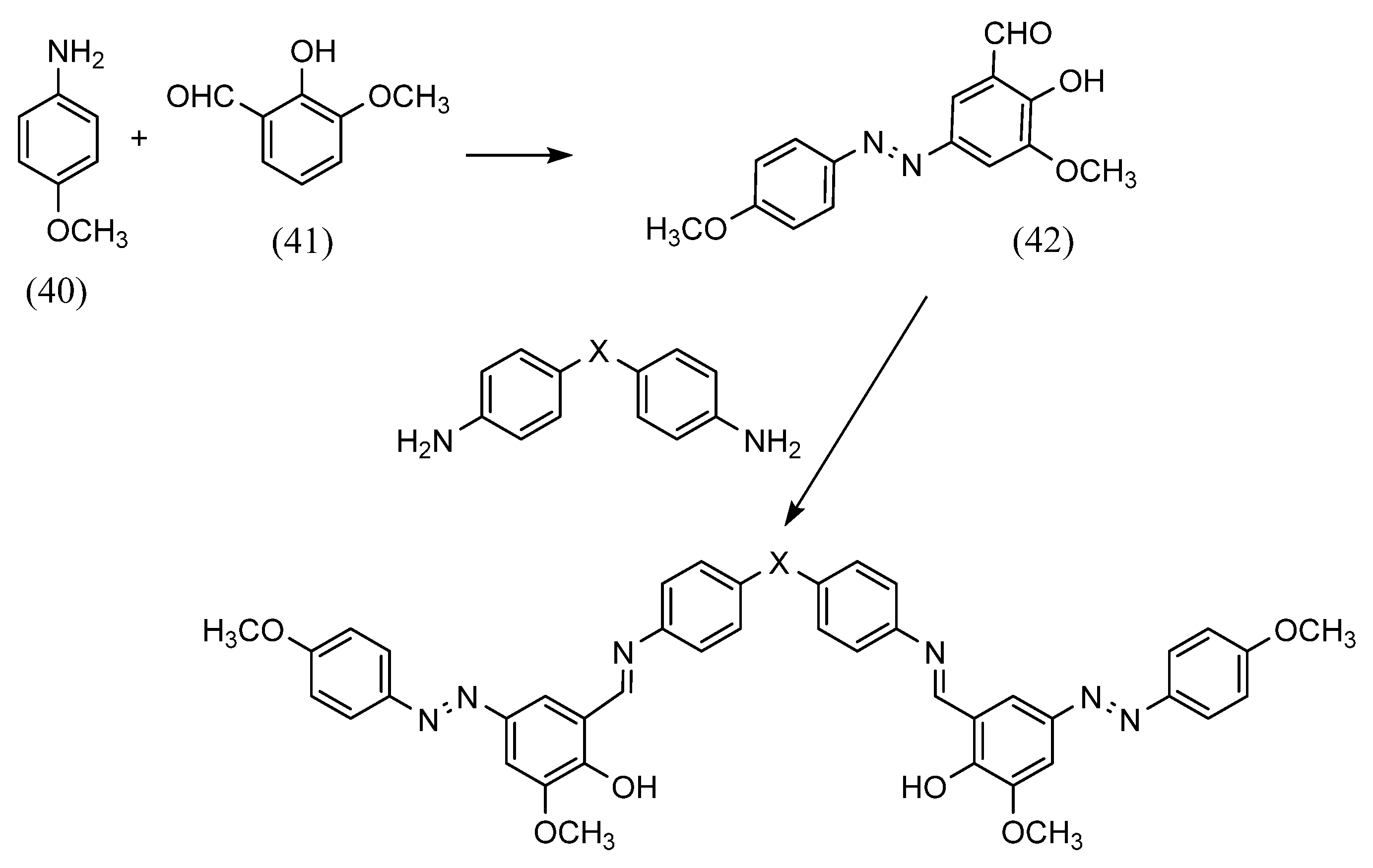
Azobenzene Schiff bases with various structures can be synthesized by adjusting the amino group. A. A. Jarrahpour et al. [61] synthesized azobenzene Schiff bases using different aromatic amines (Scheme 11). First, azo compounds were obtained by azo coupling (40) (41). They further obtained the azobenzene Schiff base by reacting the azo compound with an aldehyde (42). In this process, azobenzene Schiff-base ligands were synthesized that can form one-sided and two-sided Schiff bases by changing the amino and diamino.
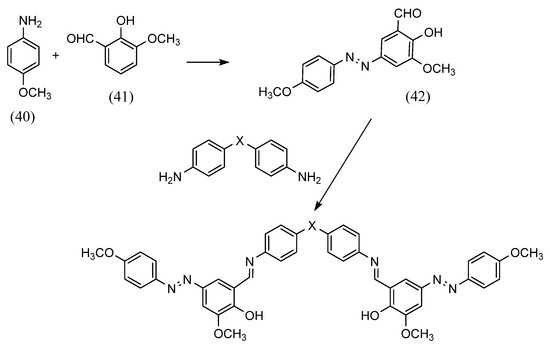
Scheme 11.
Synthesis of A. A. Jarrahpour et al. [61].
Khalil K. Abid et al. [62] also synthesized azobenzene Schiff bases using pre-existing azo compounds. In that case, the diamines formed Schiff bases with aldehydes on both sides. On the other hand, S. El-Sayed Saeed et al. [63] used diamine, but only one side reacted with aldehyde to form Schiff base.
2.2.7. Unusual Reactions
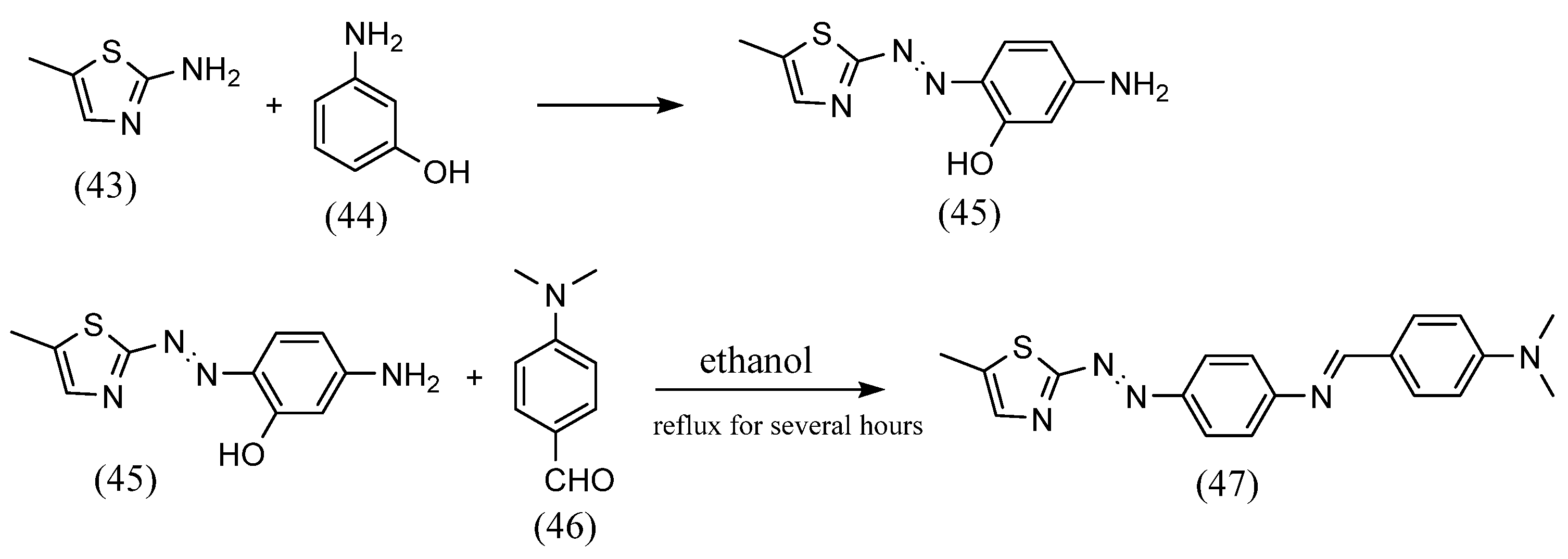
An unusual method for the synthesis of azobenzene Schiff bases, which is different from the previously described methods, was reported. Koichi Tanaka et al. [64] synthesized azobenzene Schiff bases, which are closed cyclic molecules with alternating azo and imine, by using azo and diamine with a preformed dialdehyde. Azobenzene-4,4′-dicarbaldehyde and (1R,2R)-1,2-diaminocyclohexane were dissolved in dichloromethane, resulting in the formation of macrocyclic Schiff bases. Khalid Jawad Al-Adilee et al. [65] synthesized azobenzene Schiff base containing a five-membered ring (Scheme 12). 2-Amino-5-methylthiazole (43) was dissolved in concentrated hydrochloric acid and a solution of sodium nitrite was added. This solution was mixed with 3-amino phenol (44) in the presence of sodium hydroxide solution to give an azo compound with an amine group (45). This was dissolved in ethanol, and 4-(dimethylamino)benzaldehyde (46) and glacial acetic acid were added and refluxed at 80 °C for several hours. As a result, an azobenzene Schiff base with an amine (47) at the phenyl on the azo group side and an aldehyde bound from the outside was obtained.
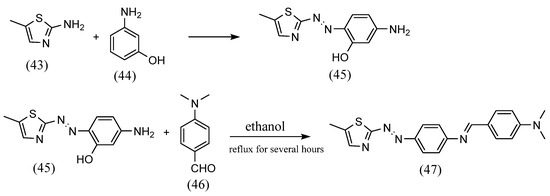
Scheme 12.
Synthesis by Khalid Jawad Al-Adilee et al. [65].
Manish Kumar et al. [66] synthesized Schiff bases by azo coupling followed by formation of a five-membered ring, deprotection of the amino group and aldehyde. p-Aminoacetanilide was used as raw material for azo coupling of the amino group. This was added to a solution of methylhydrazine and Na2CO3 and stirred. Azo compounds with five-membered rings were obtained. Furthermore, an azobenzene Schiff base was obtained by stirring the azo compound and salicylic aldehyde in ethanol. Nagwa H. S. Ahmed et al. [67] synthesized Schiff bases after azo coupling. The azo moiety is separated from the Schiff base moiety by an ester bond that is then formed. Azo compounds were synthesized from ethyl aminobenzoate and phenol. Various reactions with azo compounds yielded compounds containing benzoic acid and azo moieties. Schiff bases were also obtained from 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde and aniline. The benzoic acid-azo compound and Schiff base were dissolved in dichloromethane, N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide and 4-(dimethylamino) pyridine were added, and the mixture was stirred for 72 h. The result was a compound in which the azo moiety and the Schiff base moiety were separated by an ester bond.
3. Azobenzene-Containing Schiff-Bases Applications
Colorants can have a positive impact on the study of chemical or biological interest, such as metals posing an issue for health or pathogenic bacteria. But they can also play a great role in the formation of liquid crystals [68,69,70]. In the case of ions sensors in water, which may be dangerous for health, advanced research was made for easy tools for sensing them, including colorants [71,72,73,74]. But azo moieties, known for their coloring properties and coupled to Schiff bases known to complex ions, can give excellent results.
3.1. Sensors
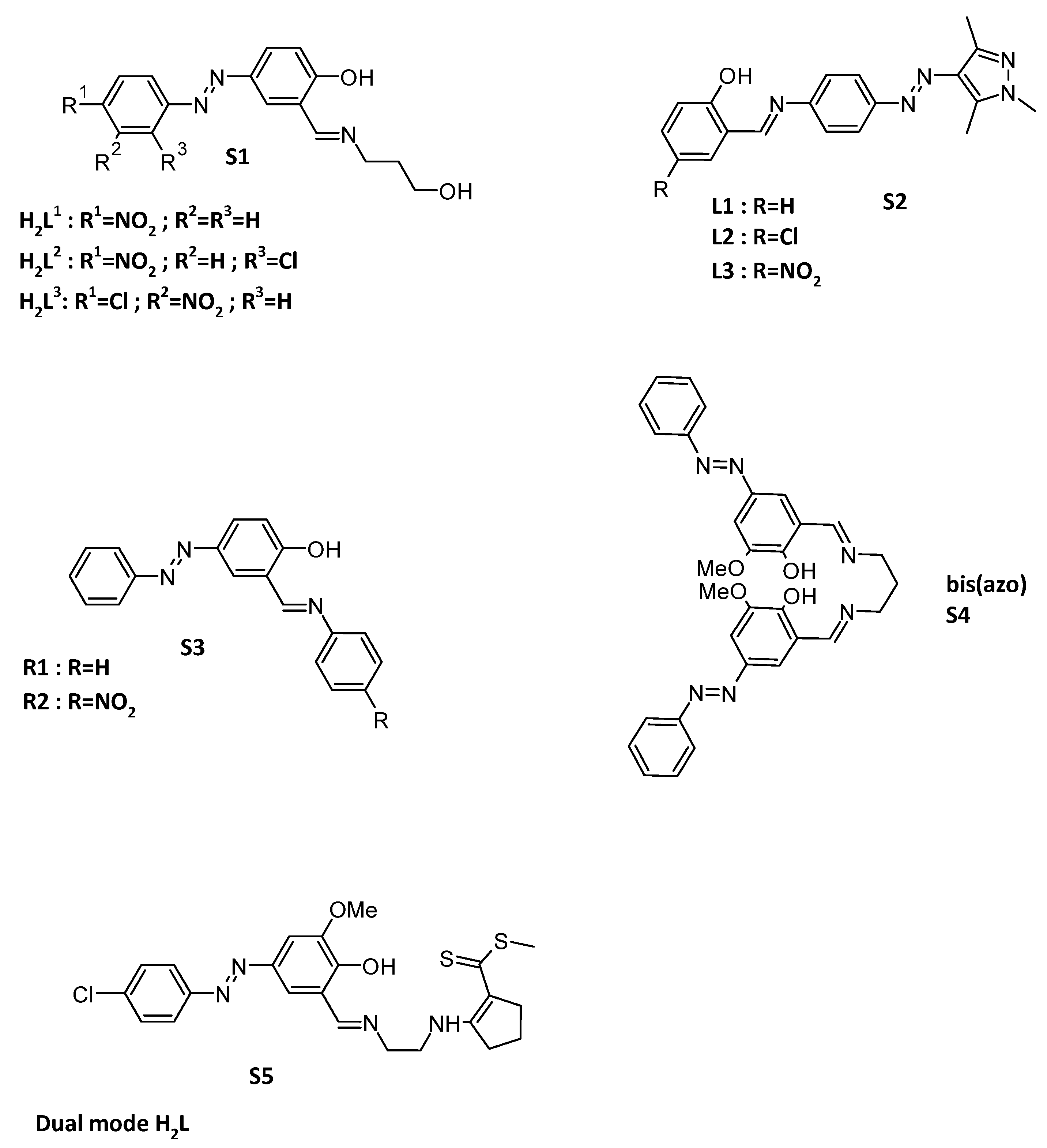
Optical and colorimetric sensing of ions are of great interest, particularly when the sensors demonstrate specificity towards certain ions over others. For example, H2L1–H2L3 (S1) ligands were synthesized (Figure 2) and showed changes upon the addition of F−, Hg2+ and Cd2+, but no changes on the addition of Cl−, Br−, NO3−, OAc−, HSO4−, H2PO4−, CN−, or Mn2+, Fe2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ [75]. While functionalized with two chlorines, these ligands can be selective for naked-eye detection of F− and Al3+ [76]. For the detection of F−, Schiff base-linked arylazopyrazoles, S2 (Figure 2) shows a specific photometric detection of fluoride ions. The chelation can be reversible upon the addition of H+, but the spectrometric data at 488 nm showed a fatigue phenomenon [66]. Very simple molecules can also lead to a selective colorimetric assessment of fluoride and acetate ions in solution. This kind of sensor can be synthesized in only two steps to get what was called by the authors receptors R1 and R2 (S3, Figure 2) [77]. In contrary, bis(azo) Schiff bases (S4, Figure 2) can selectively complex aluminum ions [78]. A 1:1 stoichiometry binding between the chemosensor and Al3+ ions has been confirmed from Job’s plot. This 1:1/Al3+:ligand complexation stoichiometry was also found when the azo moiety beard a naphthalene fluorophore [79]. An inhibition molecular logic gate has been constructed using the ligand bis(azo) where Al3+ and EDTA act as inputs and fluorescence emission is the output. When a tetradentate Schiff base based on a bis(azo) moiety is included in the preparation of a PVC membrane, this leads to a Al3+ selective electrode [80]. Selectivity can also depend on detection methods. Indeed, when two cations can selectively be detected by two different optical methods, this dual mode is of great interest. This is the case for example for the dual mode H2L ligand (S5, Figure 2) which showed a selective fluorescence recognition of Al3+ with a noticeable fluorescence enhancement and a colorimetric detection of Co2+ [81].
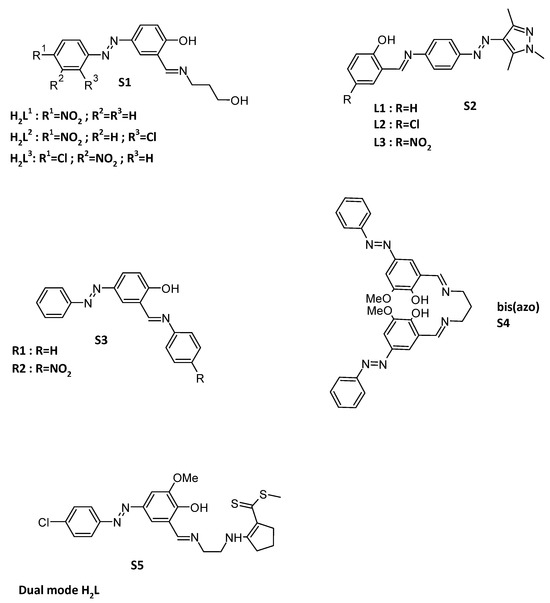
Figure 2.
Structures of ligands H2Ln S1 [75]; Schiff base-linked arylazopyrazoles Ln S2 [66]; receptors Rn S3 [77]; bis(azo) ligand S4 [78]; dual mode H2L S5 [81].
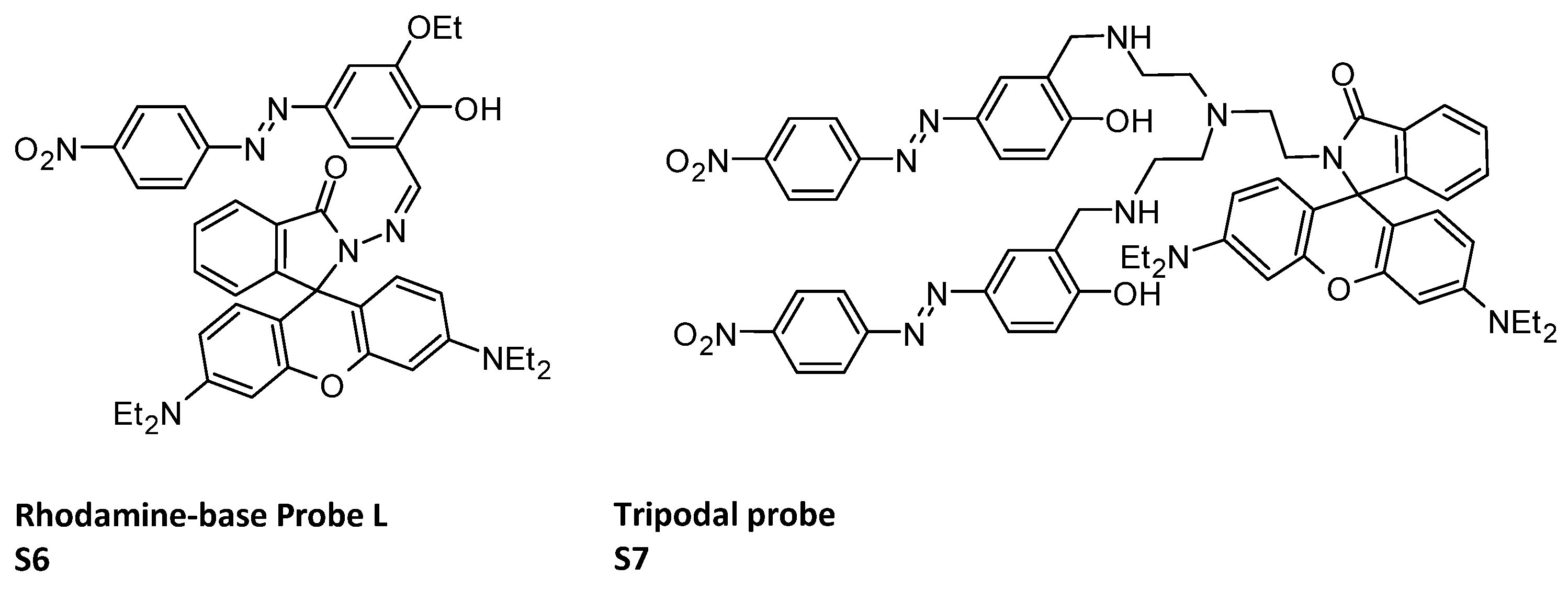
The incorporation of Rhodamine into the sensor structure can result in the development of probes capable of sensing multiple ions and facilitate imaging within human lymphocyte cells (HLCs). Indeed, ligands can map the intracellular concentration of Al3+ and Cr3+ in HLCs. This holds true for the rhodamine–azobenzene-based single molecular probe LS6 (Figure 3), which encompasses a Schiff base moiety capable of complexing with cations [82]. It is noteworthy that the onset of photo-induced electron transfer (PET) process is mainly responsible for ‘Turn-Off’ emissive behavior of the sensor. Again, the inhibition of isomerization and appropriate complexation in presence of specific guest and functional group attached to the fluorophore makes the PET process invalid and initiates the chelation-enhanced fluorescence process (CHEF), arresting the previous electron transfer. This strong ‘Turn-On’ selectivity of sensor L was also observed when sensor solution was treated with Al3+ or Cr3+ under UV lamp at 366 nm. Rhodamine can also be part of a tripodal probe (S7, Figure 3) [83] which can recognize or discriminate F−, AcO− and H2PO4− anions over a wide range of pH (3 to 12).
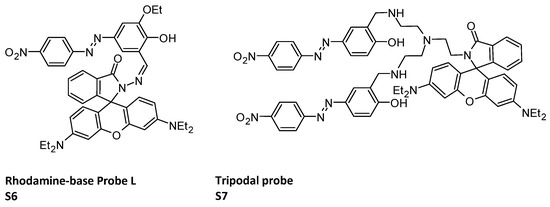
Figure 3.
Structures of rhodamine-base Probe L S6 [82]; tripodal probe S7 [83].
3.2. Liquid Crystals
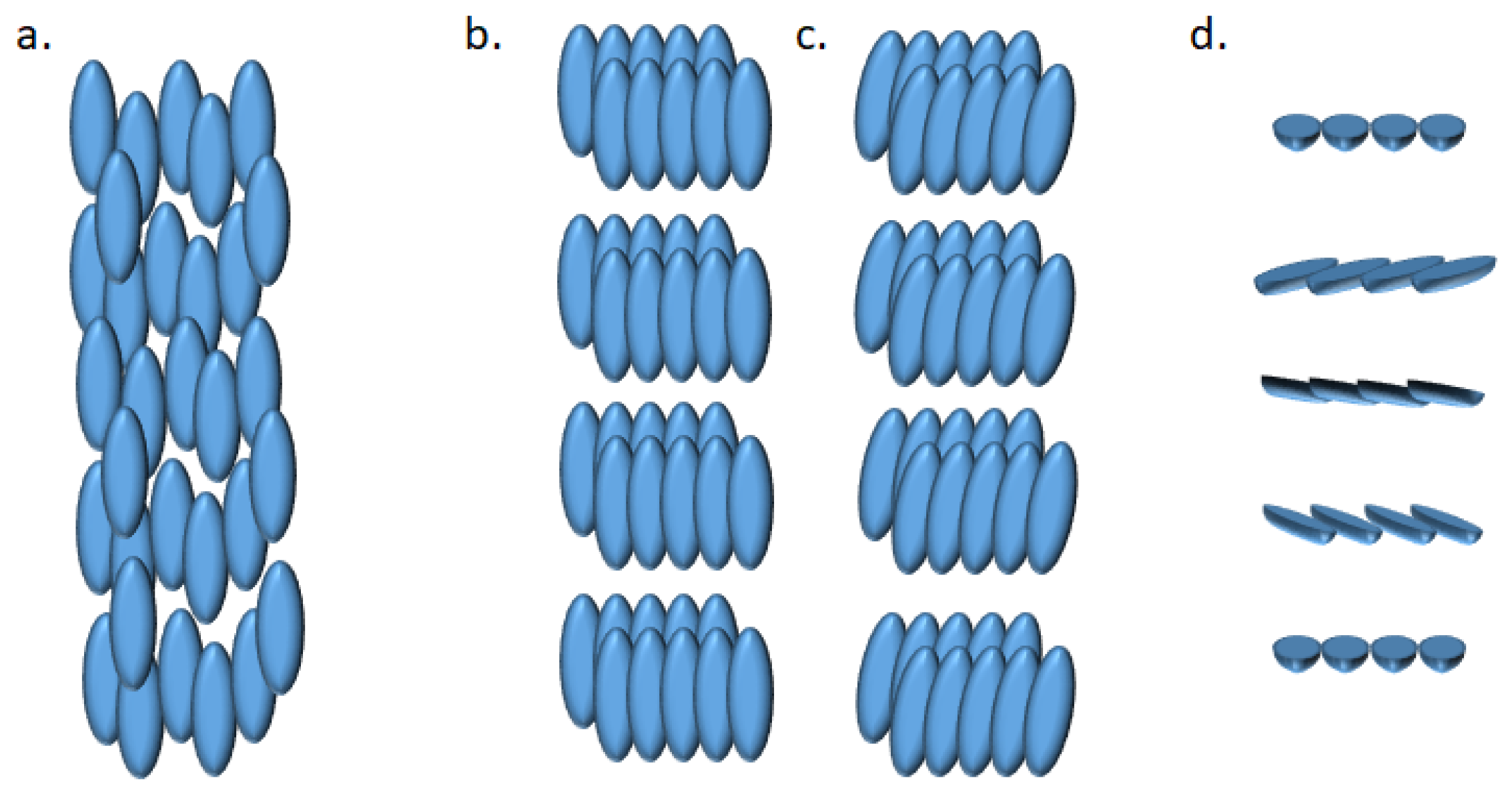
Liquid crystal state [84] is a phase of matter observed between the liquid and crystal phases. Amongst the various types of mesophase (which are phases specific to liquid crystals and intermediate between the isotropic liquid and crystalline solid states,) the nematic phase can be found. In this phase, molecules have no positional order but tend to point in the same direction. Another type of mesophase is the smectic phase, where molecules maintain a general direction such as in nematic phase, but also tend to align in layers or planes (Figure 4).
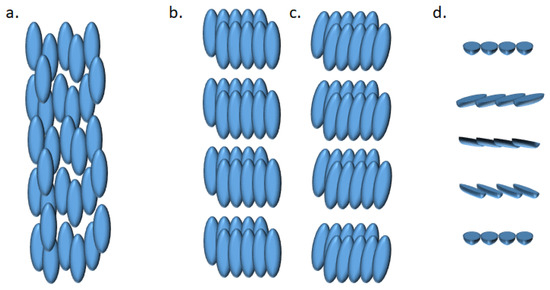
Figure 4.
Representation of (a) nematic, (b) smectic A, (c) smectic C and (d) cholesteric phases of liquid crystals.
The cholesteric phase and columnar phase are other possible types. Normally, calamitic liquid crystals (calamitic liquid crystals, characterized by their elongated, rod-like shape consisting of a rigid ring system, a connective linkage group, and a flexible terminal group [85]) of low alkyl chain length are nematic, the medium length are nematic / smectic and high members are entirely smectic. Upon heating and cooling, all the synthesized azo Schiff-based LC1 series (Figure 5) exhibited two phase transitions, from crystal to nematic and from nematic to isotropic while heating to 285 °C and reversely on cooling to 169 °C [86]. When two azobenzene Schiff base are linked by a propylenediamine moiety (LC2, Figure 5), and are complexing lanthanides, smectic A phases are observed while heating to 80 °C (Ligand alone), 90 °C (La(III) and Ce(III) complexes), 91 °C (Sm(III) complex) and 75 °C (Gd(III) complex) [62]. When cholesteryl mono-, bis- or tripodal molecules were performed with branched azobenzenes, it was shown that the liquid crystal phase behavior was closely related to the number of mesogenic units and the rigidity and flexibility of the structure. Indeed, the mesophase ranges were widened as the chain length increased in the same series, or when de degree of branching increased [87]. Halogenated (and especially fluorinated) compounds (LC3 series, Figure 5) can exhibit smectic A phase, even with high chain length [88]. Terminal substituents can also play an important role in the mesomorphism. That is how, for example, two series of alkyl-, methoxy- or halide-azobenzenes possessing links ester or imine to aryl moieties functionalized by C8 or C16 ethers were evaluated for their mesomorphic properties (LC4 series, Figure 5). It was found that A1, A3, B1-B9 exhibited a nematic phase, while A2, A4-A10, B10, B11 organized into smectic/nematic phases. Additionally, B12 exclusively exhibited a smectic phase [89]. Finally, Cu(II) or Ni(II) complexes with a M:L/1:2 stoichiometry were discussed. But this time, it was shown that the mesophoric or phase transition was not only due to the ligand, but also to the metal used. Indeed, for ligands from n = 5 to n = 11, upon heating, the phases went from crystal to smectic A and then to nematic and then to isotropic. For ligands having a longer chain length (n = 12, 14, 16), the phase went from crystal to smectic A and then to isotropic. For the copper complexes (n = 5 to 11, 12, 14, 16) it was found that the mesophoric phases went from crystal to smectic A and then to isotropic. And finally for nickel complexes, only a transition phase from crystal to isotropic was found upon heating [90].
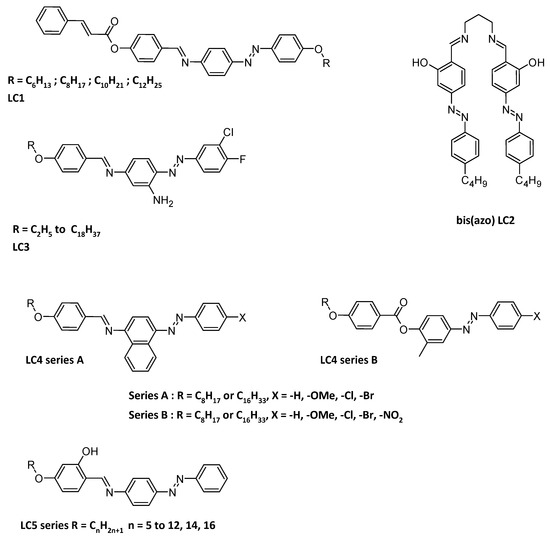
Figure 5.
Structures of LC1 [86]; of bis(azo) LC2 [62], of halogenated LC3 [88]; of series A and B LC4 [89]; LC5 series [90].
3.3. Enzymatic Fuel Cells and Electrode Mediators
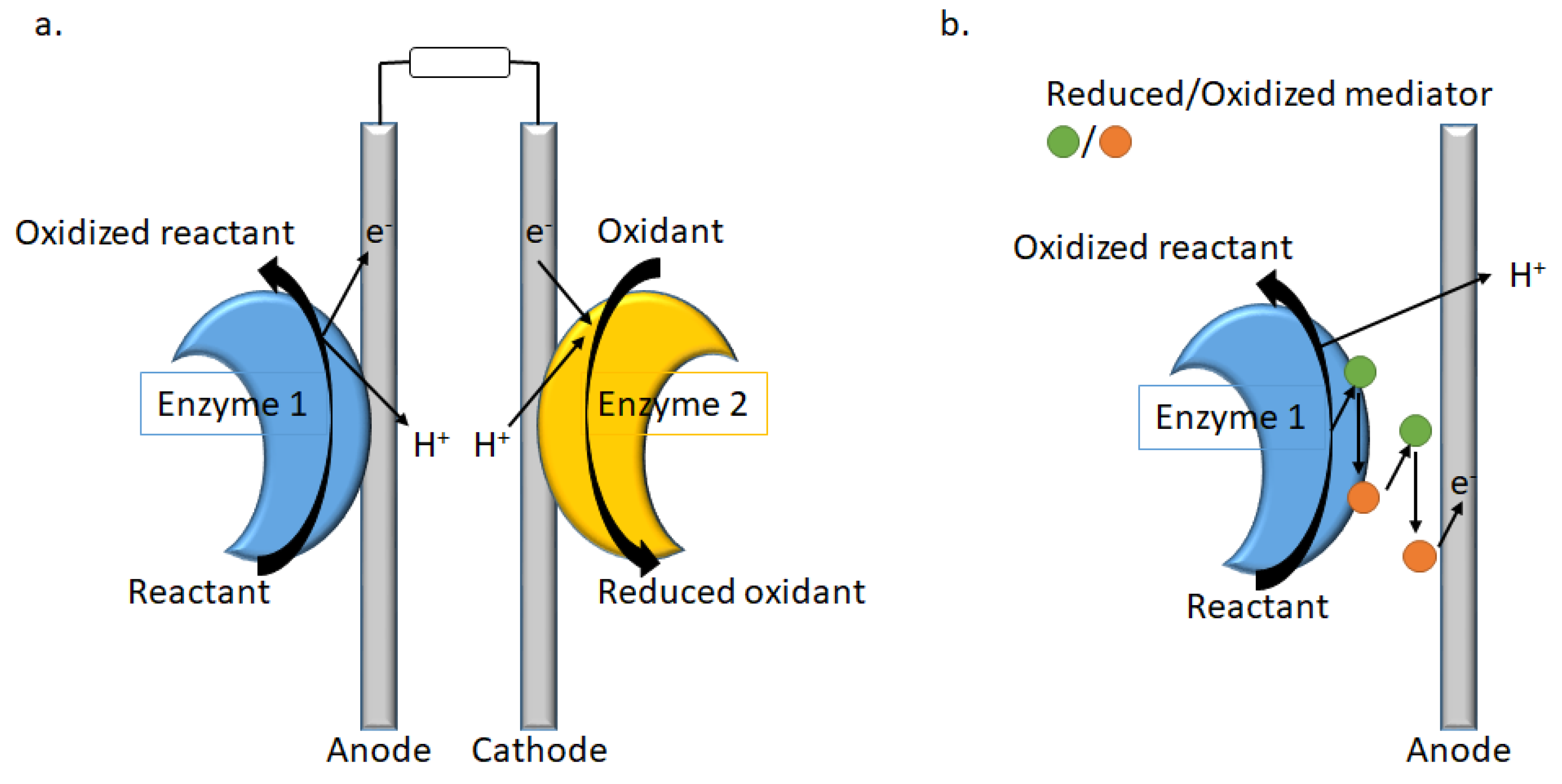
Enzymatic fuel cells (EFC) play an important role in replacing non-selective metal catalysts, currently used in low-temperature fuel cells, with enzymes as catalysts. The process consists in the fuel oxidation by enzyme 1 (Figure 6), providing electrons and protons, coupled to oxidant reduction by enzyme 2, consuming electrons and protons [91].
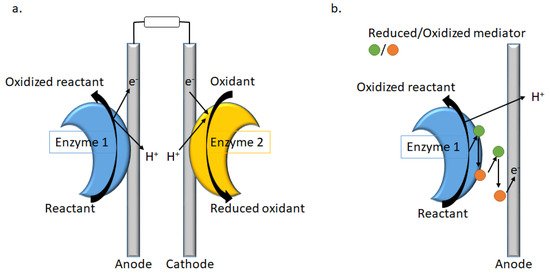
Figure 6.
Representation of (a) an EFC with direct electron transfer (DET), and (b) mediated electron transfer (MET) at the anode.
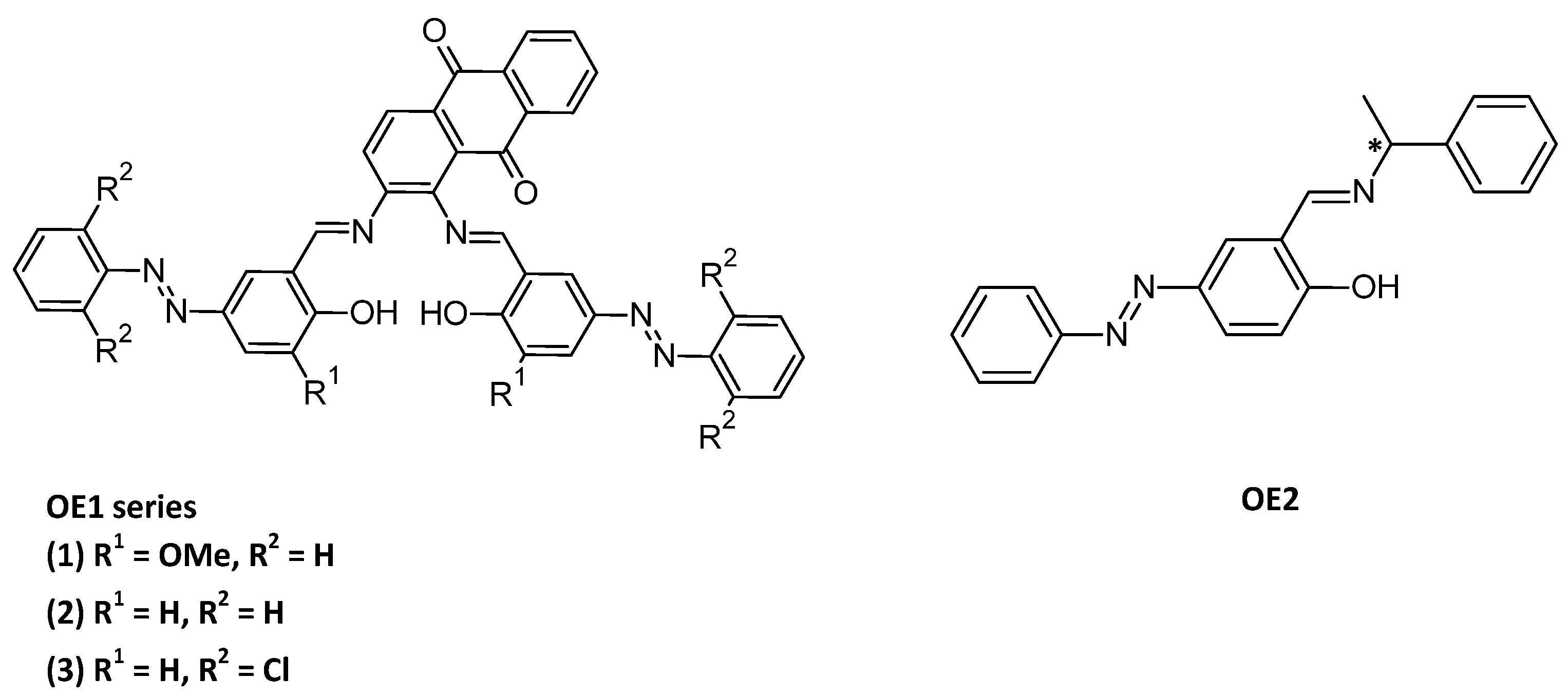
As an alternative to DET, synthetic redox substrates (mediators) can be used to shuttle electrons between the enzyme and the electrode for a mediated electron transfer (MET, Figure 6). For example, if laccase, a multi-copper oxidase [92], can be used in the cathodic compartment of the enzymatic biofuel cells because of its low redox potential, new Cu(II) complexes OE1 were designed and investigated as mediators [93]. The Schiff-base ligands consisted of both a redox-active (anthraquinone) and a photochromic (azobenzene) moiety (Figure 7). But the main point is the incorporation of the complexes in the hydrophobic pocket site of the laccase surface, as well as the oligopeptide linker used to bind the enzyme to the surface. As the azobenzene moiety can switch from trans to cis reversibly within short time without degradation, a docking simulation in laccase is of great interest (OE2, Figure 7) [94] as well as the chirality of the oligopeptide linker, while the electron-transfer between the cathode and the enzyme is improved by using Schiff base copper complexes with or without azobenzene moiety [95].
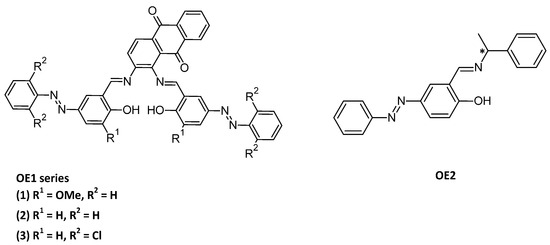
Figure 7.
Structures of OE1 series [93]; OE2 [94].
3.4. UV-Protection and Anti-Corrosive Effect
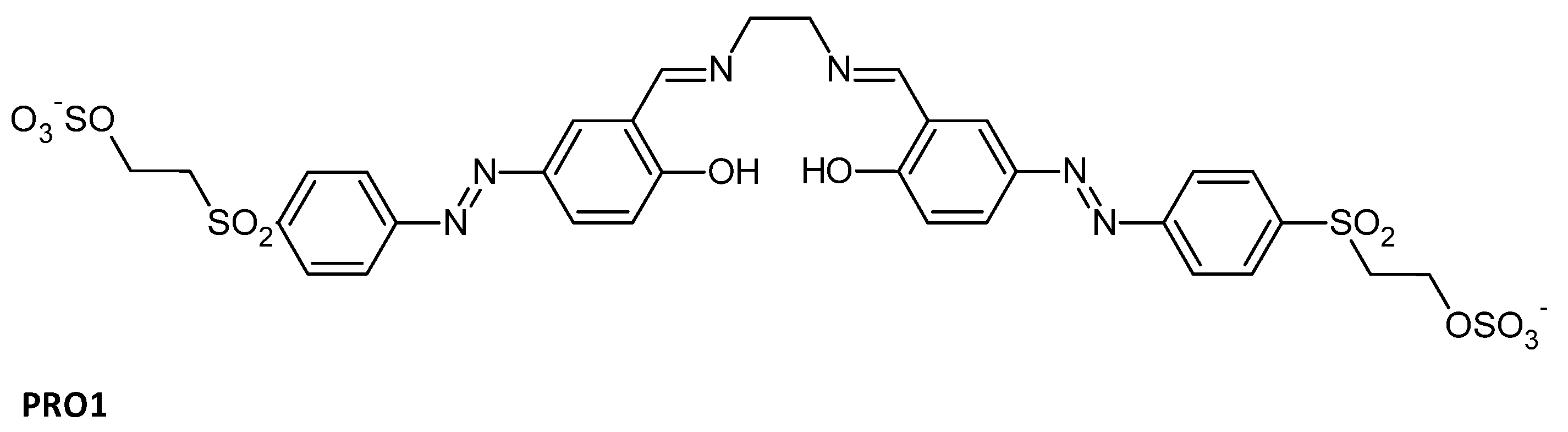
Azobenzene Schiff base possesses excellent photochromic or thermochromic properties based on intermolecular proton transfer or cis-trans isomerization. When applied to a modified cellulosic fabric, it can not only protect the fibers or skin against UVs, but also maintain the properties of the matter. For example, an azobenzene Schiff base containing two reactive groups was synthesized (PRO1, Figure 8) and the functional cellulose fabrics had UV-protection properties with (UPF = 31.7) [96]. When applied on polyester clothing, pyrazole–vanillin Schiff base disperse azo-dyed fabrics tested in an ultraviolet-protection-factor test provided superior UV protection [97].
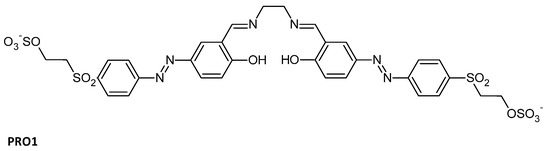
Figure 8.
Structures of PRO1 UV-protecting Azo-Schiff bases [96].
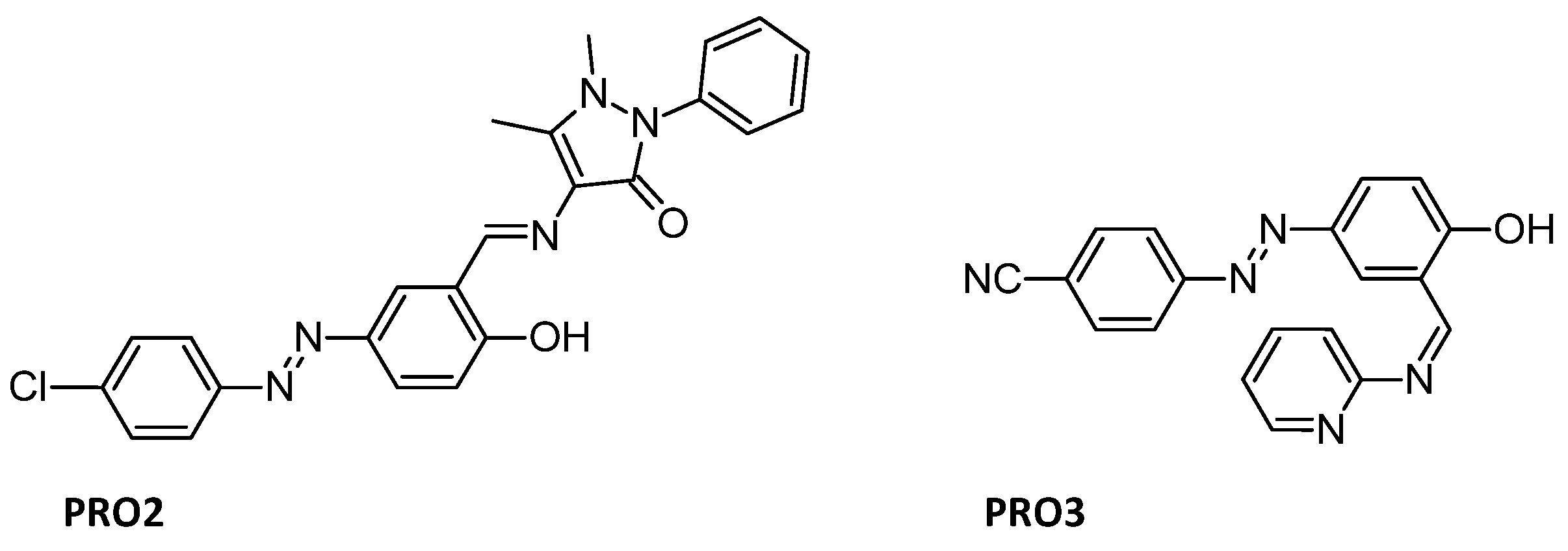
Anticorrosive behavior of Azo-Schiff bases is also well known. For example, Azo Schiff-base ligand PRO2 (Figure 9) on mild steel in HCl solution was investigated and showed that the anticorrosive effect increased with concentration, but decreased with increasing temperature [98]. It was also found that carbon steel can be protected from corrosion in 1 M H2SO4, including at low concentration [99], by an azo Schiff base with the surfactant Tween 80 was used to solubilize the inhibitor PRO3 (Figure 9) [100].
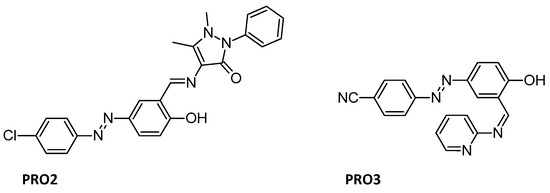
Figure 9.
Structures of anticorrosive PRO2 [98]; PRO3 [100].
3.5. Anticancer and Antibacterials
Azo-Schiff bases can exhibit good anticancer properties. For example, when Co-, Cu-, Mn-, Ni- and pd-complexes were tested for their DNA-cleavage capabilities, all the compounds showed two strand DNA cleaving properties [101]. Another results showed significant augmentation of apoptosis in tumor cells treated with zinc–azo Schiff-base complexes, showing their anti-tumor activity [102]. When agents are based of o-vanillin and azo moieties, Schiff-base ligand and its Cu(II), Zr(IV) and Mn(II) complexes exhibited the highest cytotoxic activity against HepG-2 and HCT compared to cisplatin as a reference drug [58]. Whereas, when molecules are imidazole-based, Co(II) complex was the most potent anticancer agent and exhibited high DNA Topo-II inhibitory activity [103].
But this kind of molecules can also, when complexing metals, inhibit the growth in Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria (see comparisons in Table 1).

Table 1.
Bacterial growth inhibition. a disc inhibition zone (mm). b MICs values (µg/mL). c MICs values (µMol/mL)—not tested on these bacteria.
Indeed, by various ways of analyses, such as disc diffusion, or liquid-mediated turbidity/optical densities, products were described to be effective against many bacteria such as Klebsiella pneumonia, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterococcus faecalis, Bacillus subtilis or even Salmonella typhi. It is noticeable that not only the metal used is important as it can act on the antibacterial activity (for example between copper and zinc on B. subtilis with UV7, or between copper and nickel on E. coli with UV9a), but also by using one metal, the variation of ligand can lower the antibacterial activity (for example, using zinc with UV5a, UV5b and UV5c on E. coli, or S. aureus…). This shows that all these parameters have to be taken into account for the antibacterial activity of Azo-Schiff bases.
4. Conclusions
Azo-Schiff bases are molecules containing an azo photochrome (which can be responsible for the isomerization of the molecule, but also its color), and an imine moiety (which can contribute to the metal complexation capability). For their syntheses, the chemoselectivity was described, as when a salicylaldehyde compound and an aniline are introduced simultaneously, the azobenzene is formed first, and then the remaining aldehyde can lead to the imine formation. Another crucial aspect is the targeted number of imine bonds. Indeed, depending on the experimental procedures, multiple imines or a single one can be formed. Finally, the reaction demonstrates versatility that is considered uncommon. The formation of Azo-Schiff bases opens up possibilities for a broad range of compounds, and the diverse applications stemming from these compounds are very interesting. For example, these molecules can lead to liquid crystals, fuel cells or even antibacterials, paving the way to innovative, everyday-use devices for a better future.
Author Contributions
E.L. writing and editing; C.T. writing; T.A. Editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the University of Technology of Compiègne, ESCOM and the University of Tokyo.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hamon, F.; Djedaini-Pilard, F.; Barbot, F.; Len, C. Azobenzenes—Synthesis and Carbohydrate Applications. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 10105–10123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.V.; Kipp, W.H. Mechanism of the Base-Catalyzed Synthesis of Azobenzenes. J. Org. Chem. 1971, 36, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinn, E.; Harris, C.M. Schiff Base Metal Complexes as Ligands1. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1969, 4, 391–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, I.C.; Jacquemin, D.; Vacher, M. Cis→ Trans Photoisomerisation of Azobenzene: A Fresh Theoretical Look. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 19155–19165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandara, H.M.D.; Friss, T.R.; Enriquez, M.M.; Isley, W.; Incarvito, C.; Frank, H.A.; Gascon, J.; Burdette, S.C. Proof for the Concerted Inversion Mechanism in the Trans→cis Isomerization of Azobenzene Using Hydrogen Bonding To Induce Isomer Locking. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 4817–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crecca, C.R.; Roitberg, A.E. Theoretical Study of the Isomerization Mechanism of Azobenzene and Disubstituted Azobenzene Derivatives. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 8188–8203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bafana, A.; Devi, S.S.; Chakrabarti, T. Azo Dyes: Past, Present and the Future. Environ. Rev. 2011, 19, 350–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drillaud, N.; Banaszak-Léonard, E.; Pezron, I.; Len, C. Synthesis and Evaluation of a Photochromic Surfactant for Organic Reactions in Aqueous Media. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 9553–9561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léonard, E.; Mangin, F.; Villette, C.; Billamboz, M.; Len, C. Azobenzenes and Catalysis. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 379–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomare, A.; Ciardelli, F.; Marchini, M.; Solaro, R. Polymeric Dispersions of Model Azobenzene Dyes. Polymer 2005, 46, 2086–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, A.; Fayeulle, A.; Vayssade, M.; Billamboz, M.; Lénard, E. New Trends on Photoswitchable Antibiotics: From Syntheses to Applications. Photocatal. Res. Potential 2023, 1, 10007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Lv, J.; Zhu, C.; Qin, L.; Yu, Y. Photodeformable Azobenzene-containing Liquid Crystal Polymers and Soft Actuators. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1904224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skačej, G.; Querciagrossa, L.; Zannoni, C. On the Effects of Different Trans and Cis Populations in Azobenzene Liquid Crystal Elastomers: A Monte Carlo Investigation. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 5805–5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, H.; Chen, S. New Azobenzene Liquid Crystal with Dihydropyrazole Heterocycle and Photoisomerization Studies. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 200474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, G.P.; Smith, P.A.S.; Tavernier, D. Glossary of Class Names of Organic Compounds and Reactivity Intermediates Based on Structure (IUPAC Recommendations 1995). Pure Appl. Chem. 1995, 67, 1307–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiff, H. Mittheilungen Aus Dem Universitätslaboratorium in Pisa: Eine Neue Reihe Organischer Basen. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1864, 131, 118–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrow, J.F.; Jacobsen, E.N. Asymmetric Processes Catalyzed by Chiral (Salen) Metal Complexes. In Organometallics in Process Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 123–152. [Google Scholar]
- Breinbauer, R.; Jacobsen, E.N. Cooperative Asymmetric Catalysis with Dendrimeric [Co (Salen)] Complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 3604–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wantulok, J.; Szala, M.; Quinto, A.; Nycz, J.E.; Giannarelli, S.; Sokolová, R.; Książek, M.; Kusz, J. Synthesis, Electrochemical and Spectroscopic Characterization of Selected Quinolinecarbaldehydes and Their Schiff Base Derivatives. Molecules 2020, 25, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelakantan, M.A.; Esakkiammal, M.; Mariappan, S.S.; Dharmaraja, J.; Jeyakumar, T. Synthesis, Characterization and Biocidal Activities of Some Schiff Base Metal Complexes. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 72, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, R.; Maheswaran, S. Synthesis, spectra, dioxygen affinity and antifungal activity of Ru (III) Schiff base complexes. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2003, 96, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskioğlu, E.; Gündüzalp, A.B.; Hamurcu, F.; Erk, B.C. Fe(III) and Co(III) Complexes of Tetradentate (ONNO) Schiff Base Ligands: Synthesis, Characterization, Properties and Biological Activity. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2008, 70, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chohan, Z.H.; Arif, M.; Sarfraz, M. Metal-based antibacterial and antifungal amino acid derived Schiff bases: Their synthesis, characterization and in vitro biological activity. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 2007, 21, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chohan, Z.H.; Munawar, A.; Supuran, C.T. Transition Metal Ion Complexes of Schiff-Bases. Synthesis, Characterization and Antibacterial Properties. Met.-Based Drugs 2001, 8, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamsikrishna, N.; Kumar, M.P.; Ramesh, G.; Ganji, N.; Daravath, S.; Shivaraj. DNA Interactions and Biocidal Activity of Metal Complexes of Benzothiazole Schiff Bases: Synthesis, Characterization and Validation. J. Chem. Sci. 2017, 5, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnoman, R.; Al-Nazawi, F.K.; Ahmed, H.A.; Hagar, M.S. Optical, and Geometrical Approaches of New Natural Fatty Acids’ Esters/Schiff Base Liquid Crystals. Molecules 2019, 24, 4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolezzi, S.; Spodine, E.; Decinti, A.; Mohamed, G.G. Electrochemical Studies of Copper(II) Complexes with Schiff-Base Ligands. Polyhedron 2022, 21, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, G.G. Synthesis, Characterization and Biological Activity of Bis(Phenylimine) Schiff Base Ligands and Their Metal Complexes. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2006, 64, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souane, R.; Isel, F.; Peruch, F.; Lutz, P.J. Pyridine Bis(Imine) Cobalt or Iron Complexes for Ethylene and 1-Hexene (Co)Polymerisation. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2002, 5, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicini, P.; Geronikaki, A.; Incerti, M.; Busonera, B.; Poni, G.; Cabras, C.A.; La Colla, P. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Benzo[d]Isothiazole, Benzothiazole and Thiazole Schiff Bases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 4785–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Melchakova, I.; Nayab, S.; Kim, K.; Ko, Y.H.; Yoon, M.; Avramov, P.; Lee, H. Synthesis and Characterization of Zinc (II), Cadmium (II), and Palladium (II) Complexes with the Thiophene-Derived Schiff Base Ligand. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 6016–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizilkaya, H.; Dag, B.; Aral, T.; Genc, N.; Erenler, R. Synthesis, Characterization, and Antioxidant Activity of Heterocyclic Schiff Bases. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2020, 67, 1696–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, R.M.; Khedr, A.M.; Rizk, H.F. UV–vis, IR and 1H NMR spectroscopic studies of some Schiff bases derivatives of 4-aminoantipyrine. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2005, 62, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiri, A.M.; Khan, S. Synthesis and Anti-Bacterial Activities of Some Novel Schiff Bases Derived from Aminophenazone. Molecules 2010, 15, 6850–6858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, A.; Srividhya, N. Synthesis and Study of Schiff Base Ligands. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. 2014, 7, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrahpour, A.; Khalili, D.; Clercq, E.D.; Salmi, C.; Brunel, J.M. Synthesis, Antibacterial Antifungal and Antiviral Activity Evaluation of Some New Bis-Schiff Bases of Isatin and Their Derivatives. Molecules 2007, 12, 1720–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschke, R.; Liebsch, S.; Tschierske, C.; Oakley, M.A.; Sinn, E. Synthesis and Mesogenic Properties of Binuclear Copper(II) Complexes Derived from Salicylaldimine Schiff Bases. Inorg. Chem 2003, 42, 8230–8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, E. Synthesis of Azobenzenes: The Coloured Pieces of Molecular Materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3835–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazekašová, S.; Gonda, J.; Martinková, M.; Pilátová, M.B.; Majirská, M.; Turčanová, V.; Jáger, D.T. Synthesis and anticancer profile of novel FTY720 analogues with azobenzene frameworks. Tetrahedron 2023, 137, 133391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aemissegger, A.; Hilvert, D. Synthesis and Application of an Azobenzene Amino Acid as a Light-Switchable Turn Element in Polypeptides. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, H.; Liang, X.; Asanuma, H. Effect of the Ortho Modification of Azobenzene on the Photoregulatory Efficiency of DNA Hybridization and the Thermal Stability of Its Cis Form. Chem.–A Eur. J. 2010, 16, 2054–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, J.; Hansen, E.J.; Larsen, D.; Elmquist, M.A.; Buchleithner, A.; Florean, L.; Beeren, S.R. Light-controlled enzymatic synthesis of γ-CD using a recyclable azobenzene template. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 7725–7732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priewisch, B.; Ruck-Braun, K. Efficient Preparation of Nitrosoarenes for the Synthesis of Azobenzenes. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 2350–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.-C.; Shirai, Y.; Tour, J.M. Syntheses of New Functionalized Azobenzenes for Potential Molecular Electronic Devices. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 10303–10310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosgor, E.; Akdag, A. Synthesis of Azobenzene Containing Macrocycles Exhibiting Unexpected Fluorescence. Chem. Pap. 2022, 76, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Lam, Y.; He, L.; Xin, J.H. Synthesis and Photochromism of Catechol-Containing Symmetrical Azobenzene Compounds. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2022, 9, 211894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Beharry, A.A.; Sadovski, O.; McCormick, T.M.; Babalhavaeji, A.; Tropepe, V.; Woolley, G.A. Photoswitching Azo Compounds In Vivo with Red Light. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 9777–9784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine John, A.; Lin, Q. Synthesis of Azobenzenes Using N-Chlorosuccinimide and 1,8-Diazabicyclo[5.4.0]Undec-7-Ene (DBU). J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 9873–9876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, O.A.; Coe, B.J.; Fielden, J.; Helliwell, M.; McDouall, J.J.W.; Hutchings, M.G. Nickel(II) and Palladium(II) Complexes of Azobenzene-Containing Ligands as Dichroic Dyes. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 9136–9150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Lim, S.M.; Ramasamy, K.; Vasudevan, M.; Shah, S.A.A.; Narasimhan, B. Diazenyl Schiff Bases: Synthesis, Spectral Analysis, Antimicrobial Studies and Cytotoxic Activity on Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cell Line (HCT-116). Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slassi, S.; El-Ghayoury, A.; Aarjane, M.; Yamni, K.; Amine, A. New Copper(II) and Zinc(II) Complexes Based on Azo Schiffbase Ligand: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Photoisomerization Study and Antibacterial Activity. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, 5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulcan, M.; Özdemir, S.; Dündar, A.; İspir, E.; Kurtoğlu, M. Mononuclear Complexes Based on Pyrimidine Ring Azo Schiff-Base Ligand: Synthesis, Characterization, Antioxidant, Antibacterial, and Thermal Investigations. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2014, 640, 1754–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, T.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Zhou, J. Optical Property and Photoisomerization of Some Functional Azobenzene Derivatives with Aromatic Substituted Groups. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2011, 121–126, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Qu, D.; Tian, H. A Light-Powered Stretch–Contraction Supramolecular System Based on Cobalt Coordinated [1]Rotaxane. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 1126–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkam, H.; Alwan, A.W.; Al Shemary, R.K.R. Complexes of Co (II), Cu (II), Ni (II), Pt (II) And Pd (II) with N3O-Chelating Ligand Incorporating Azo and Schiff Base Moieties: Synthesis, Spectroscopic, Thermal Decomposition, Theoretical Studies, and Thermodynamic Parameters. Int. J. Pharm. Res. 2021, 13, 3370–3378. [Google Scholar]
- Slassi, S.; Aarjane, M.; Amine, A. Synthesis, molecular geometry, Hirshfeld surface analysis, spectroscopic (NMR, UV–visible), DFT and TD-DFT calculations of an azoimidazole-based Schiff base. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2022, 19, 4789–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaler, S.; McKeown, P.; Ward, B.D.; Jones, M.D. Aluminium(III) and Zinc(II) Complexes of Azobenzene-Containing Ligands for Ring-Opening Polymerisation of ε-Caprolactone and Rac-Lactide. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.M.; Said, A.O.; Heakal, B.H.; Younis, A.; Aboulthana, W.M.; Mady, M.F. Green Synthesis, Characterization, Antimicrobial and Anticancer Screening of New Metal Complexes Incorporating Schiff Base. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 32418–32431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.; Singh, V.D.; Dwivedi, B.K.; Singh, N.K.; Pandey, D.S. Solid State Emissive Azo-Schiff Base Ligands and Their Zn(II) Complexes: Acidochromism and Photoswitching Behaviour. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, N.; Kumar, S.; Dutta, P.K.; Pei, S.; Ghosh, T. Chitosan Containing Azo-Based Schiff Bases: Thermal, Antibacterial and Birefringence Properties for Bio-Optical Devices. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 5575–5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrahpour, A.A.; Motamedifar, M.; Pakshir, K.; Hadi, N.; Zarei, M. Synthesis of Novel Azo Schiff Bases and Their Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities. Molecules 2004, 9, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, K.K.; Al-barody, S.M. Synthesis, Characterisation and Liquid Crystalline Behaviour of Some Lanthanides Complexes Containing Two Azobenzene Schiff Base. Liq. Cryst. 2014, 41, 1303–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, S.E.; Al-Harbi, T.M.; Alhakimi, A.N.; El-Hady, M.M.A. Synthesis and Characterization of Metal Complexes Based on Aniline Derivative Schiff Base for Antimicrobial Applications and UV Protection of a Modified Cotton Fabric. Coatings 2022, 12, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Fukuoka, S.; Miyanishi, H.; Takahashi, H. Novel chiral Schiff base macrocycles containing azobenzene chromophore: Gelation and guest inclusion. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 2693–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Adilee, K.J.; Hasan, S.R. Synthesis, Characterization and Biological Activity of Heterocyclic Azo-Schiff Base Ligand Derived from 2-Amino-5-Methyl Thiazol and Some Transition Metal Ions. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 790, 012031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Agarkar, H.; Degani, M.S. New Schiff Base-Linked Arylazopyrazoles as Reagents for the Photometric Detection of Fluoride Ions. J. Anal. Chem. 2023, 78, 866–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.H.S.; Saad, G.R.; Ahmed, H.A.; Hagar, M. New Wide-Stability Four-Ring Azo/Ester/Schiff Base Liquid Crystals: Synthesis, Mesomorphic, Photophysical, and DFT Approaches. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 9643–9656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Shang, L. Cholesteric Cellulose Liquid Crystal Ink for Three-Dimensional Structural Coloration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2204113119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A. Adaptive Camouflage Textiles with Thermochromic Colorant and Liquid Crystal for Multidimensional Combat Background, a Technical Approach for Advancement in Defence Protection. Am. J. Mater. Eng. Technol. 2021, 9, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, C.; Choi, J.-H.; Kim, J.P. Improving the Contrast Ratio of Red Pixels in Liquid-Crystal Displays by Synthesizing Synergists from an Anthraquinone Colorant. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2010, 533, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Alam, R. Recent Developments in the Creation of a Single Molecular Sensing Tool for Ternary Iron (III), Chromium (III), Aluminium (III) Ionic Species: A Review. Luminescence 2023, 38, 1026–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, B.; Choe, D.; Kim, C. An Effective Colorimetric Sensor for Detecting Cu2+ Based on Benzothiazole Moiety. Color. Technol. 2021, 137, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdemir, S.; Malkondu, S.; Alici, O. A Highly Selective and Sensitive Benzothiazole-based ‘Turn-on’ Fluorescent Sensor for Hg2+ Ion. Color. Technol. 2015, 131, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szala, M.; Nycz, J.E.; Malecki, G.J.; Sokolova, R.; Ramesova, S.; Switlicka-Olszewska, A.; Strzelczyk, R.; Podsiadly, R.; Machura, B. Synthesis of 5-Azo-8-Hydroxy-2-Methylquinoline Dyes and Relevant Spectroscopic, Electrochemical and Computational Studies. Dyes Pigment. 2017, 142, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabahmadi, R.; Orojloo, M.; Amani, S. Azo Schiff Bases as Colorimetric and Fluorescent Sensors for Recognition of F−, Cd2+ and Hg2+ Ions. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 7384–7393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orojloo, M.; Amani, S. A Highly Selective Chemosensor for Naked-Eye Detection of Fluoride and Aluminium(iii) Ions Based on a New Schiff Base Derivative. Aust. J. Chem. 2016, 69, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reena, V.; Suganya, S.; Velmathi, S. Synthesis and Anion Binding Studies of Azo-Schiff Bases: Selective Colorimetric Fluoride and Acetate Ion Sensors. J. Fluor. Chem. 2013, 153, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Brandão, P.; Saha, A. A Robust Fluorescent Chemosensor for Aluminium Ion Detection Based on a Schiff Base Ligand with an Azo Arm and Application in a Molecular Logic Gate. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 101924–101936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabhai, S.; Dolai, M.; Dey, S.K.; Choudhury, S.M.; Das, B.; Dey, S.; Jana, A.; Banerjee, D.R. A Naphthalene-Based Azo Armed Molecular Framework for Selective Sensing of Al3+. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 6885–6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, A.; Esmaeilbeig, A.R.; Jarrahpour, A.A.; Khajeh, B.; Kia, R. Aluminium(III)-Selective Electrode Based on a Newly Synthesized Tetradentate Schiff Base. Talanta 2002, 58, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadbakht, R.; Chidan, N.; Menati, S.; Koolivand, M. A New Azo-Schiff Base Dual-Mode Chemosensor: Colorimetric Detection of Cobalt Ions and Fluorometric Detection of Aluminum Ions in Aqueous Ethanol Solution. J. Fluoresc. 2023, 33, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabhai, S.; Dolai, M.; Dey, S.K.; Dhara, A.; Choudhury, S.M.; Das, B.; Dey, S.; Jana, A. Rhodamine-Azobenzene Based Single Molecular Probe for Multiple Ions Sensing: Cu2+, Al3+, Cr3+ and Its Imaging in Human Lymphocyte Cells. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 219, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Fang, J.-A.; Zhao, J.-L.; Ruan, Q.; Zeng, X.; Luo, Q.-Y.; Redshaw, C. An Efficient ICT-Based Ratio/Colorimetric Tripodal Azobenzene Probe for the Recognition/Discrimination of F−, AcO− and H2PO4− Anions. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 221, 117174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisoyi, H.K.; Li, Q. Liquid Crystals: Versatile Self-Organized Smart Soft Materials. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 4887–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaddoura, M.; Belfield, K. Synthesis, Characterization and Texture Observations of Calamitic Liquid Crystalline Compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 4772–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvarasu, C.; Kannan, P. Effect of Azo and Ester Linkages on Rod Shaped Schiff Base Liquid Crystals and Their Photophysical Investigations. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1125, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ge, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Tian, M.; Yao, D. Novel Branched Liquid Crystal Oligomers Containing Azo and Schiff Base Groups. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1273, 134322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katariya, K.D.; Nakum, K.J.; Hagar, M. New Fluorinated Azo/Schiff Base Liquid Crystals: Synthesis, Characterisation, Mesomorphic Study and DFT Calculations. Liq. Cryst. 2022, 49, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaker, B.T.; Kanojiya, J.B.; Tandel, R.S. Effects of Different Terminal Substituents on the Mesomorphic Behavior of Some Azo-Schiff Base and Azo-Ester-Based Liquid Crystals. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2010, 528, 120–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeap, G.-Y.; Heng, B.-T.; Kakeya, M.; Takeuchi, D.; Gorecka, E.; Ito, M.M. Synthesis, 2D NMR and X-Ray Diffraction Studies on Cu(II) and Ni(II) Complexes with Ligands Derived from Azobenzene-Cored Schiff Base: Mesomorphic Behaviors of Cu(II)–Phenolates and Crystal Structure of Bis[4-(4-Alkoxy-2-Hydroxybenzylideneamino)Azobenzene]Copper(II). J. Mol. Struct. 2011, 999, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leech, D.; Kavanagh, P.; Schuhmann, W. Enzymatic Fuel Cells: Recent Progress. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 84, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Yuan, L.; Jia, L.; Xue, P.; Yao, H. Recent Developments of a Co-Immobilized Laccase–Mediator System: A Review. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 29498–29506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajiwara, K.; Pradhan, S.; Haraguchi, T.; Sinha, C.; Parida, R.; Giri, S.; Roymahaptra, G.; Akitsu, T. Photo-Tunable Azobenzene-Anthraquinone Schiff Base Copper Complexes as Mediators for Laccase in Biofuel Cell Cathode. Symmetry 2020, 12, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunitake, F.; Kim, J.-Y.; Yagi, S.; Yamzaki, S.; Haraguchi, T.; Akitsu, T. Chiral Recognition of Azo-Schiff Base Ligands, Their Cu(II) Complexes, and Their Docking to Laccase as Mediators. Symmetry 2019, 11, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwagi, K.; Tassinari, F.; Haraguchi, T.; Banerjee-Gosh, K.; Akitsu, T.; Naaman, R. Electron Transfer via Helical Oligopeptide to Laccase Including Chiral Schiff Base Copper Mediators. Symmetry 2020, 12, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y. Preparation and UV-Protective Properties of Functional Cellulose Fabrics Based on Reactive Azobenzene Schiff Base Derivative. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noser, A.A.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Abd El Salam, H.A.; El-Ebiary, N.M.A.; Mandour, H.S.A. Pyrazole-Vaniline Schiff Base Disperse Azo Dyes for UV Protective Clothing: Synthesis, Characterization, Comparative Study of UPF, Dyeing Properties and Potent Antimicrobial Activity. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2023, 20, 2963–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukrishnan, P.; Prakash, P.; Shankar, K.; Kathiresan, A. Azo Schiff Base as Antiscaling Agent for Mild Steel in Hydrochloric Acid: Electrochemical, Non-Electrochemical, and DFT Studies. J. Bio-Tribo-Corros. 2019, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albo Hay Allah, M.A.; Balakit, A.A.; Salman, H.I.; Abdulridha, A.A.; Sert, Y. New Heterocyclic Compound as Carbon Steel Corrosion Inhibitor in 1 M H2SO4, High Efficiency at Low Concentration: Experimental and Theoretical Studies. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2023, 37, 525–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulridha, A.A.; Albo Hay Allah, M.A.; Makki, S.Q.; Sert, Y.; Salman, H.E.; Balakit, A.A. Corrosion Inhibition of Carbon Steel in 1 M H2SO4 Using New Azo Schiff Compound: Electrochemical, Gravimetric, Adsorption, Surface and DFT Studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 315, 113690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeğiner, G.; Gülcan, M.; Işık, S.; Ürüt, G.Ö.; Özdemir, S.; Kurtoğlu, M. Transition Metal (II) Complexes with a Novel Azo-Azomethine Schiff Base Ligand: Synthesis, Structural and Spectroscopic Characterization, Thermal Properties and Biological Applications. J. Fluoresc. 2017, 27, 2239–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.; Singh, N.K.; Singh, V.D.; Ali, I.; Tiwari, R.K.; Kumar, A.; Pandey, D.S. DNA/Protein Binding and Anticancer Activity of Zn(II) Complexes Based on Azo-Schiff Base Ligands. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2022, 538, 120963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdy, A.R.E.; Abu Ali, O.A.; Serag, W.M.; Fayad, E.; Elshaarawy, R.F.M.; Gad, E.M. Synthesis, Characterization, and Biological Activity of Co(II) and Zn(II) Complexes of Imidazoles-Based Azo-Functionalized Schiff Bases. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1259, 132726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İspir, E. The Synthesis, Characterization, Electrochemical Character, Catalytic and Antimicrobial Activity of Novel, Azo-Containing Schiff Bases and Their Metal Complexes. Dyes Pigment. 2009, 82, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarigul, M.; Deveci, P.; Kose, M.; Arslan, U.; Türk Dagi, H.; Kurtoglu, M. New Tridentate Azo–Azomethines and Their Copper(II) Complexes: Synthesis, Solvent Effect on Tautomerism, Electrochemical and Biological Studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 1096, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasare, M.S.; Dhavan, P.P.; Jadhav, B.L.; Pawar, S.D. Synthesis of Azo Schiff Base Ligands and Their Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) Metal Complexes as Highly-Active Antibacterial Agents. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 10792–10797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, C.; Sumathi, S.; Tharmaraj, P.; Sheela, C.D. Synthesis, Characterization, and Biological Activity of Some Transition Metal Complexes Derived from Novel Hydrazone Azo Schiff Base Ligand. Int. J. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 2011, 493942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hamdani, A.A.S.; Balkhi, A.M.; Falah, A.; Shaker, S.A. Synthesis and Investigation of Thermal Properties of Vanadyl Complexes with Azo-Containing Schiff-Base Dyes. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2016, 20, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, J.; Paidesetty, S.K. Biological Investigation of Novel Metal Complexes of 2-Amino-4-Substituted Phenylthiazole Schiff Bases. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 2018, 13, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Atbi, H.S.; Al-Salami, B.K.; Al-Assadi, I.J. New Azo-Azomethine Derivative of Sulfanilamide: Synthesis, Characterization, Spectroscopic, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activity Study. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1294, 052033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karem, L.; Ganim, F.; Al-Shemary, R. Synthesis, characterization, structural, thermal, pom studies, antimicrobial and DNA cleavage activity of a new schiff base-azo ligand and ITS complexation with selected metal ions. Biochem. Cell. Arch. 2018, 18, 1437–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Al Radi, K.A.; Fahad, T.A.; Ali, A.A. Synthesis and Spectral Characterization of Some Transition Metal Complexes of Azo-Schiff Base Derivative of Metoclopramide. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Al Zoubi, W.; Al-Hamdani, A.A.S.; Ahmed, S.D.; Ko, Y.G. A New Azo-Schiff Base: Synthesis, Characterization, Biological Activity and Theoretical Studies of Its Complexes. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selma, B. A Novel Azo-Schiff Base Ligand and Its Cobalt, Copper, Nickel Complexes: Synthesis, Characterization, Antimicrobial, Catalytic and Electrochemical Features. Anadolu Univ. J. Sci. Technol. A-Appl. Sci. Eng. 2016, 17, 315–326. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).