Abstract
The study evaluates five types of commercial textiles with different cotton and polyester contents widely used in the garment industry. These textile samples have been subjected to treatment by the exhaustion method using zinc oxide nanoparticles (NP ZnO) (textile functionalization) with the aim of improving their efficiency in blocking UV radiation. The ZnO nanoparticles have been obtained by two methods: The green or also called biosynthesis (using the extract of Coriandrum sativum as an organic reducing agent), and the chemical method (using NaOH as an inorganic reducing agent). The results related to the green method show having achieved a defined geometric configuration with an average size of 97.77 nm (SD: 9.53). On the contrary, the nanostructures obtained by the chemical method show pentagonal configurations with average sizes of 113 nm (SD: 6.72). The textiles functionalized with NP ZnO obtained by biosynthesis showed a better efficiency in blocking ultraviolet radiation (UV).
1. Introduction
In recent decades, nanotechnology has deepened the level of research, in such a way that it has come to control various properties that atoms and molecules possess, even handling individual atoms with high precision, generating functional materials and devices on the nanometric scale. The properties of nanomaterials are also of research interest to scientists and researchers related to the textile industry, which has led to the use of nanotechnology being studied with greater emphasis because textiles are considered one of the best areas to apply nanotechnology. In this sense, it is known that fibers provide optimal substrates based on the type of thread (material) or grammage. This is how nanotechnology takes advantage of the mentioned textile properties [1].
Functionalized textiles have been the subject of several studies in which all are aimed at producing fabrics with different functional performances. For example, silver nanoparticles (NP Ag) have been used to impart antimicrobial applications [2,3], titanium dioxide to block UV rays, and self-cleaning properties in textiles [4,5,6]. We have semiconductor nanoparticles like ZnO for antimicrobial and UV blocking properties [7,8,9]. It should be noted that metal oxide nanoparticles are more preferred by researchers than silver nanoparticles, mostly due to cost issues. In addition, zinc and titanium oxides have zero toxicity and are chemically stable when subjected to high temperatures, in addition to having photocatalytic characteristics due to their degree of oxidation. This type of nanomaterial has an excellent surface-volume ratio as a result of a significant increase in the effectiveness of catalytic processes (due to their oxidation) compared to bulk materials [10].
At present, there are conventional methods of textile treatment where they tend to provide characteristics such as water repellency, stains, and UV blocking. However, they often do not produce permanent effects, losing their functions after washing or use. Nanoparticles can provide high durability for treated textiles since they have a high surface energy that guarantees a better affinity for fabrics, thus, increasing durability for treated textiles [11,12], since the nanoscale material is bonded to the surface of the fabric by Van de Waals forces, which provides fastness to washing. It is known that reducing the size of the particles to nanometric dimensions greatly changes the properties of the material.
Focusing on ZnO, currently, it is widely used due to its electrical, electronic, photocatalytic, optical, dermatological, and antimicrobial properties [13,14,15,16,17,18,19], research is focused on preventing nanoparticle agglomeration and increasing dispersion stability [20,21,22]. The applicative potential of NP ZnO is thanks to the fact that it has three advantages. First, it is a semiconductor with a bandwidth of 3.37 eV with excitation binding energy of 60 meV. Second, it is also a functional oxide that presents excellent photocatalytic activity. Lastly, this is a piezoelectric whose applications are linked to the manufacture of sensors and transducers. Furthermore, ZnO is biocompatible and comes with high biosafety, which broadens the spectrum of biomedical applications. This is how NP ZnO are presented as nanomaterials of high importance for future research and applications.
This is how, in recent years, research has been intensified aimed at obtaining products that protect the skin against UV radiation, ranging from sunscreen to functionalized textiles. However, very little is known about the true potential, and, in turn, the ignorance of this type of material by the population and the textile industry still exists.
In the textile field, and especially in garments, there is a lack of knowledge about the degree of sun protection, since most of them do not offer sufficient blocking action of ultraviolet radiation, leading to the skin not being sufficiently protected despite being covered with a garment [23]. UV protection in textiles depends on a series of variables, ranging from the type and origin of the fiber [24], the weft, porosity, color, among others [25].
The effects of skin exposure to UV radiation range from simple cases such as low-grade burns to erythema, pruritus, blisters, and pigmentation [26].
The main objective of this research is to provide an improvement to textiles in what corresponds to UV protection. For this, five types of textiles are evaluated, coating them with ZnO nanoparticles obtained by two methods, wet chemistry and green. In the latter case, we use Coriandrum sativum extract as a reducer. Both syntheses were made from the precursor zinc acetate.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Leaf Extract
Fresh leaves of Coriandrum sativum were collected from the surroundings of the province of Trujillo, Peru. The leaves were subjected to washing once with tap water and subsequently three times with ultrapure water to eliminate any dust particles from the surface that it might contain, which is followed by oven drying at 35 °C for 10 h. The dried leaves of C. sativum were subjected to mechanical grinding and sieving to obtain a fine powder. For the preparation of the extract, 5 g of dry powder were dissolved in 83.33 mL of ultrapure water. The mixture was heated to a hotplate with stirring for 4 h at 70 °C. Finally, the mixture was cooled to room temperature and filtered using Whatman filter paper (No. 3). The remaining extract was brought to refrigeration (12 °C) for use in future syntheses. The extract was used as a reducer in the synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles without adding other chemical compounds.
2.2. Preparation of ZnO Nanoparticles by the Green Chemistry Method
A total of 30 mL of the ACS Merck zinc acetate precursor (CAS No. 5970-45-6) 0.21 M was prepared, which is the same that was brought to a hotplate until reaching a temperature of 70 °C and magnetic stirring at 450 rpm. This was followed by adding dropwise 20 mL of aqueous extract of C. sativum under constant stirring (600 rpm). The mixture was kept for 4 h at a constant temperature. Finally, the sample was calcined in a muffle oven for 2 h at 500 °C.
2.3. Preparation of ZnO Nanoparticles by the Wet Chemistry Method
The protocol used was based on that described by Aquino and Col. [27] with a minimal change. A total of 15 mL of ACS Merck zinc acetate precursor solution (CAS No. 5970-45-6) 0.6 M was prepared, which was kept at 60 °C and stirred at 600 rpm for 5 min. In another beaker, the Merck ACS NaOH solution (CAS No. 1310-73-2) 0.01 M was prepared, followed by the NaOH solution, which was added dropwise to the precursor solution in a burette of zinc acetate. This process was done with constant stirring (600 rpm) and at 60 °C. Once this first process was completed, 100 mL of ACS Merck absolute ethanol (CAS No. 64-17-5) was added by slowly dripping for 3 h. Finally, the sample was calcined in a muffle furnace at 500 °C for 2 h.
2.4. Characterization of ZnO
The colloidal samples were initially characterized by UV-Vis spectrophotometry (Hewlett Packard, 8452, CA, USA) in the range of 340–800 nm, to evaluate the presence of optical absorbance and surface plasmon resonance peak (RPS), in addition to the evaluation of optical transmittance in treated textiles.
The size, shape, and elemental composition analysis of the ZnO nanoparticles were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (Tescan Vega 3 with Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy, STEM and Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy, EDS detectors, 4.0 uL drop on coated cooper grid evaporated to dryness). Special emphasis has been given to the characterization of the ZnO nanoparticles made by the green chemistry method. This is due to the better efficiency in the results obtained from the synthesis and its influence on the textile treatment. This is how it has also been evaluated by FTIR (Thermo Scientific, Nicolet iS50, Germany) for this type of nanostructure.
The resistance to UV radiation of the various treated textiles was through the use of a sensor (PCE-UV34, Germany) to evaluate the intensity of blocked UV radiation (in mW/cm2). This evaluation was both under conditions of direct solar radiation, and simulated UV-A radiation. For this last case, an experimental design was used based on a closed cabin, which contained the source of UV-A radiation in the upper part (400–315 nm) (Ultraviolet focus/365 nm).
It is worth mentioning that there are more energetic wavelengths in the UV range, which are UV-B (315–280 nm) and UV-C (280–100 nm). However, NP ZnO do not usually cause changes in their physical properties around these wavelengths.
2.5. Nanocomposite Coating on Cotton Fabrics
The methodology adopted for the textile treatment was the same for both the chemical and green NP ZnO synthesis protocols. For this, the dry powder of the nanomaterial was diluted in ultrapure water and taken to ultrasound for 30 min at room temperature. Then it was contained in a beaker and brought to magnetic stirring (400 rpm) where the textile samples were immersed for 1 h and kept at 70 °C. Finally, the textile sample was placed in an oven at 100 °C for 15 min. It is worth mentioning that each textile sample was treated under the same initial nanomaterial concentrations.
3. Results and Discussion
There is a diversity of applications that are given to organic matter in general. In this case, the use of a vegetable with the aim of obtaining an extract rich in metabolites that play a role as a chemical agent reducer, is considered a challenge because, from the phytochemical and metabolomic point of view, it involves evaluating a series of agents that generate a chemical reaction and aim to obtain nanostructures with new properties and phenomena that are governed by some physical laws. The handling of matter at the nanoscale from a purely chemical procedure implies greater precision and guarantee to obtain nanostructures of homogeneous sizes with high stability and with a defined geometric shape, which would simplify the processes. The mechanisms of reducing conventional chemical synthesis are defined using chemical agents such as ascorbates, sodium citrate, sodium borohydride, among others, whose mechanism allows us to have a rigorous control of the size and shape of the NP ZnO, generating chemical processes of nucleation and growth.
However, this research has developed a methodology for the green synthesis of NP ZnO with the aim of evaluating its efficiency in the functionalization of textiles in order to improve the neutralization of UV radiation. This case of textile treatment is also evaluated with NP ZnO made by the chemical method.
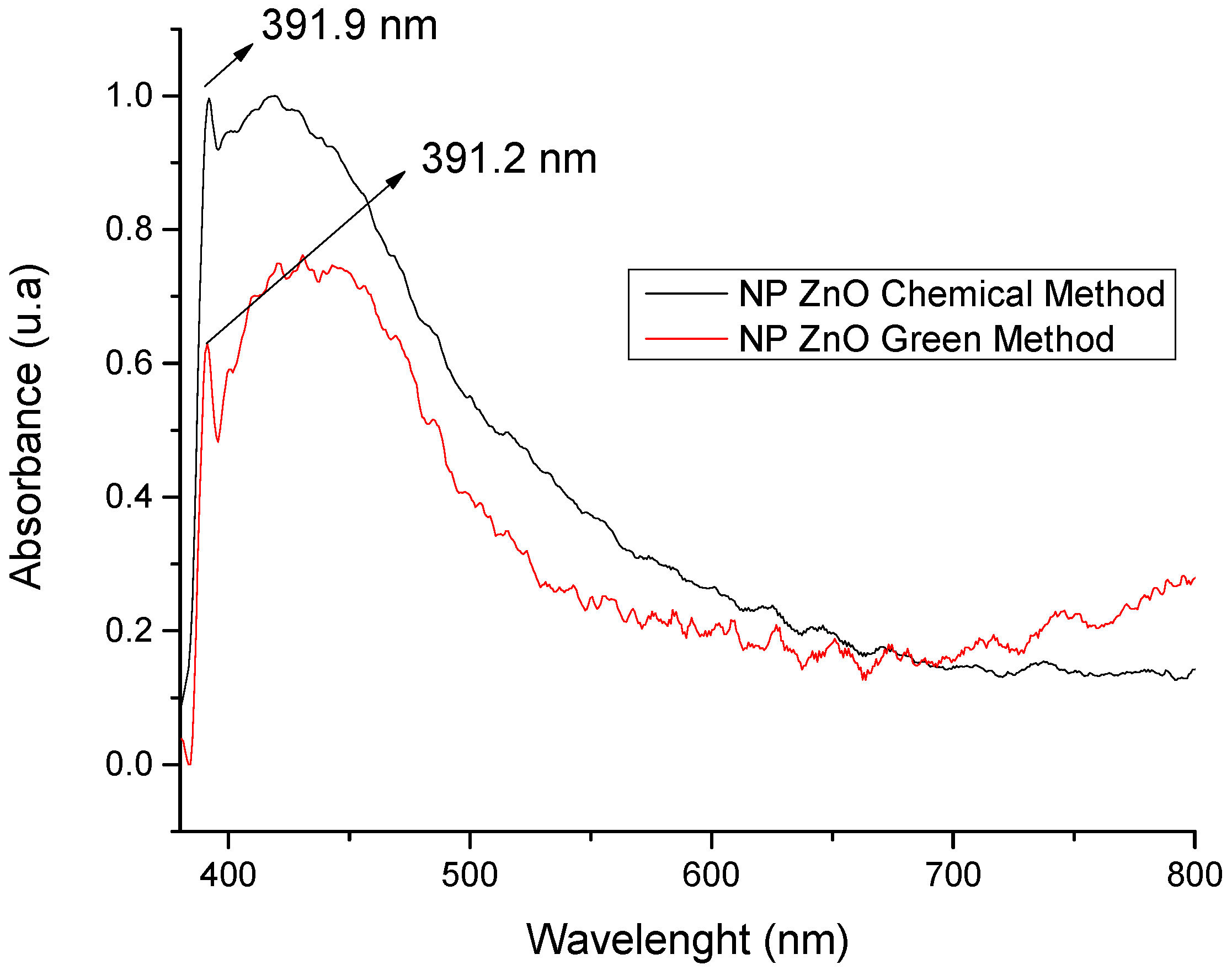
In Figure 1, the optical absorbance peaks for the NP ZnO obtained by both methods are shown. For the case of the chemical method, the typical peak of ZnO is located at 391.9 nm/0.9962 u.a, and, for the case of the green method, it is located at 391.2 nm/0.6294 u.a. The difference is minimal in what corresponds to its projection with respect to the wavelength, which justifies the efficiency in obtaining the ZnO nanostructure. However, the variation is in absorbance, which is translated as the efficiency of nanoparticle production because, based on these results, by spectrophotometry, it allows us to partially infer that the chemical method has a better efficiency in nanoparticle production compared to the green method where its production is reduced almost by half (based on absorbance, since this value is closely related to production). However, this is not a limiting and/or determining factor because the geometry achieved is of vital importance, in addition to its size and the homogeneity of the nanostructured material.
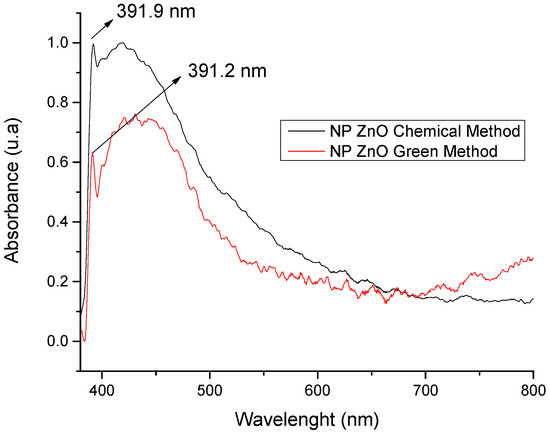
Figure 1.
Spectrophotometry of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by the chemical and green methods.
Thus, the research has obtained images by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (for the case of NP ZnO obtained by the green method), and images by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (for NP ZnO obtained by the chemical method), which show the shape and average size of the achieved nanostructure.
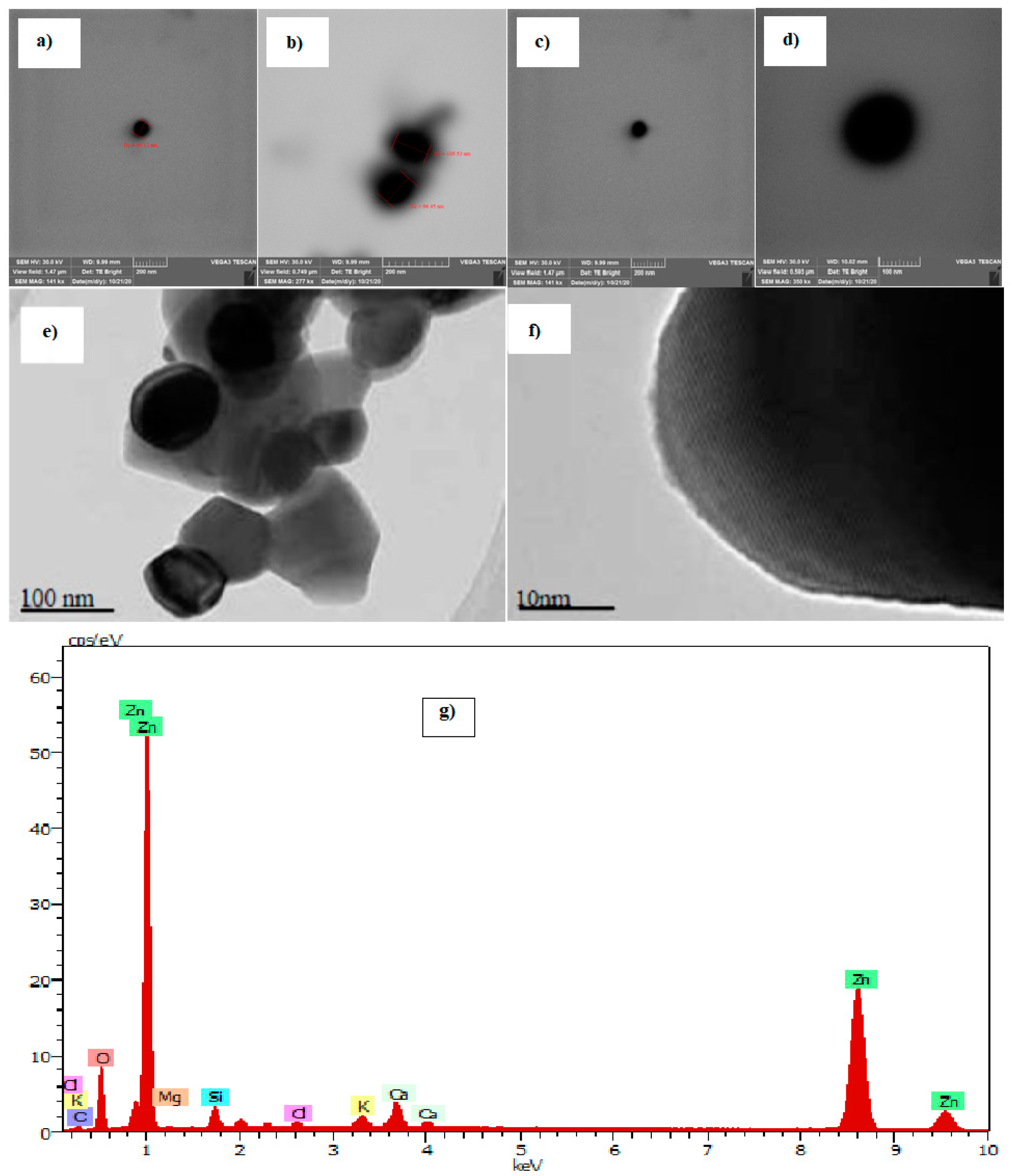
It is clear that the size of the nanoparticles obtained by the green method has an average value of 97.77 nm, (SD = 9.53), and they have a highly defined spherical geometry that improves their physical properties at the nanoscale. However, the nanostructures obtained by the chemical method do not have a defined geometry, prevailing pentagonal shapes with an irregular side with an average size of approximately 113 nm, (SD = 6.72) (Figure 2).
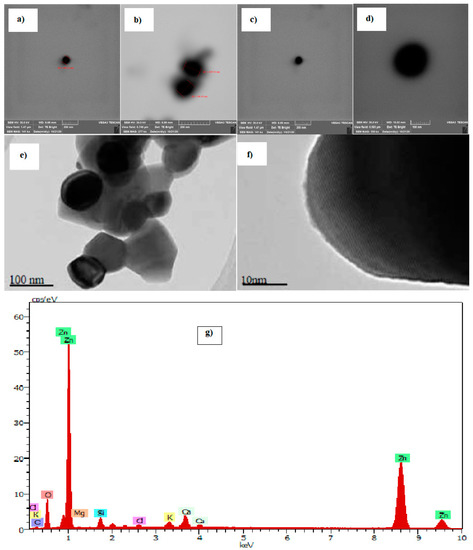
Figure 2.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of ZnO nanoparticles (NP). NP ZnO obtained by the green method (a–d), NP ZnO obtained by the chemical method (e,f) [25], and EDS spectrum of the ZnO nanoparticles obtained by the green method (g).
The defined homogeneous shape of the nanoparticles obtained by the green method, consolidate their physical properties, which would advance to better properties and efficiency for their various applications. This is how we highlight a more in-depth study of the nanomaterial obtained by the green method. For this, it is important to check by means of an elemental analysis if the material obtained has the molecules of the compound zinc oxide (ZnO), of which the result is shown in Figure 2g, thus, denoting the existence of the element under study.
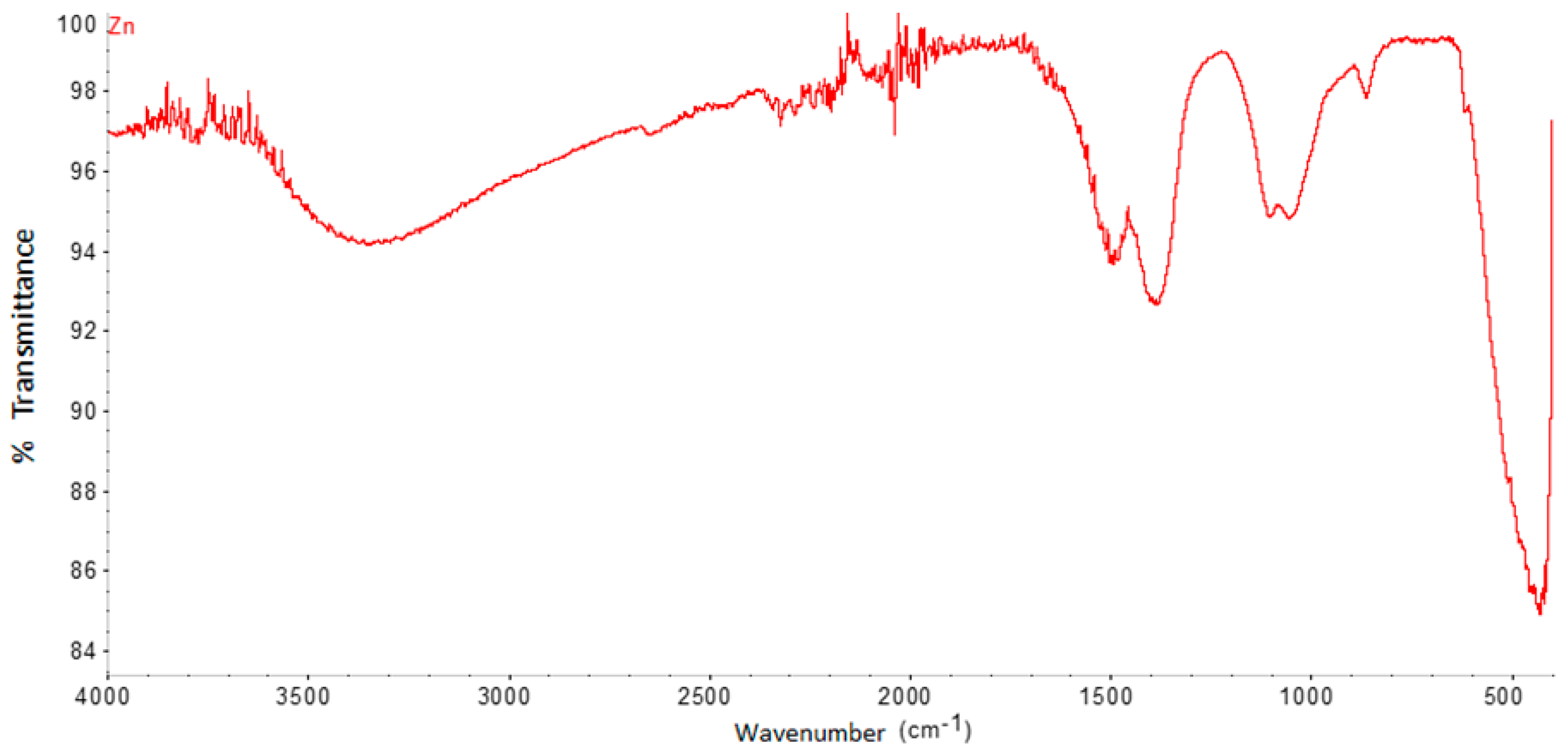
The FTIR spectrum of ZnO nanoparticles (Figure 3) shows significant absorption peaks at 3387.8 cm−1, 1389.9 cm−1, 1074.1 cm−1, and 429.08 cm−1. The band close to 429.08 cm−1 is assigned to ZnO, while, that of 1389.9, is assigned to H-O-H.
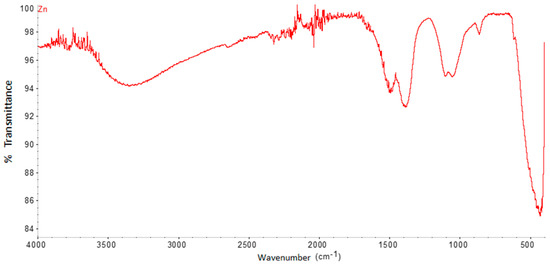
Figure 3.
FTIR spectrum of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by the green method.
This research is linked to functionalizing five types of textiles with ZnO nanoparticles elaborated by the previously mentioned methods, with the aim of evaluating their efficiency in blocking UV radiation, since various investigations already comment on the potential of zinc oxide in UV blocking and even its potential antimicrobial properties [28,29,30,31,32].
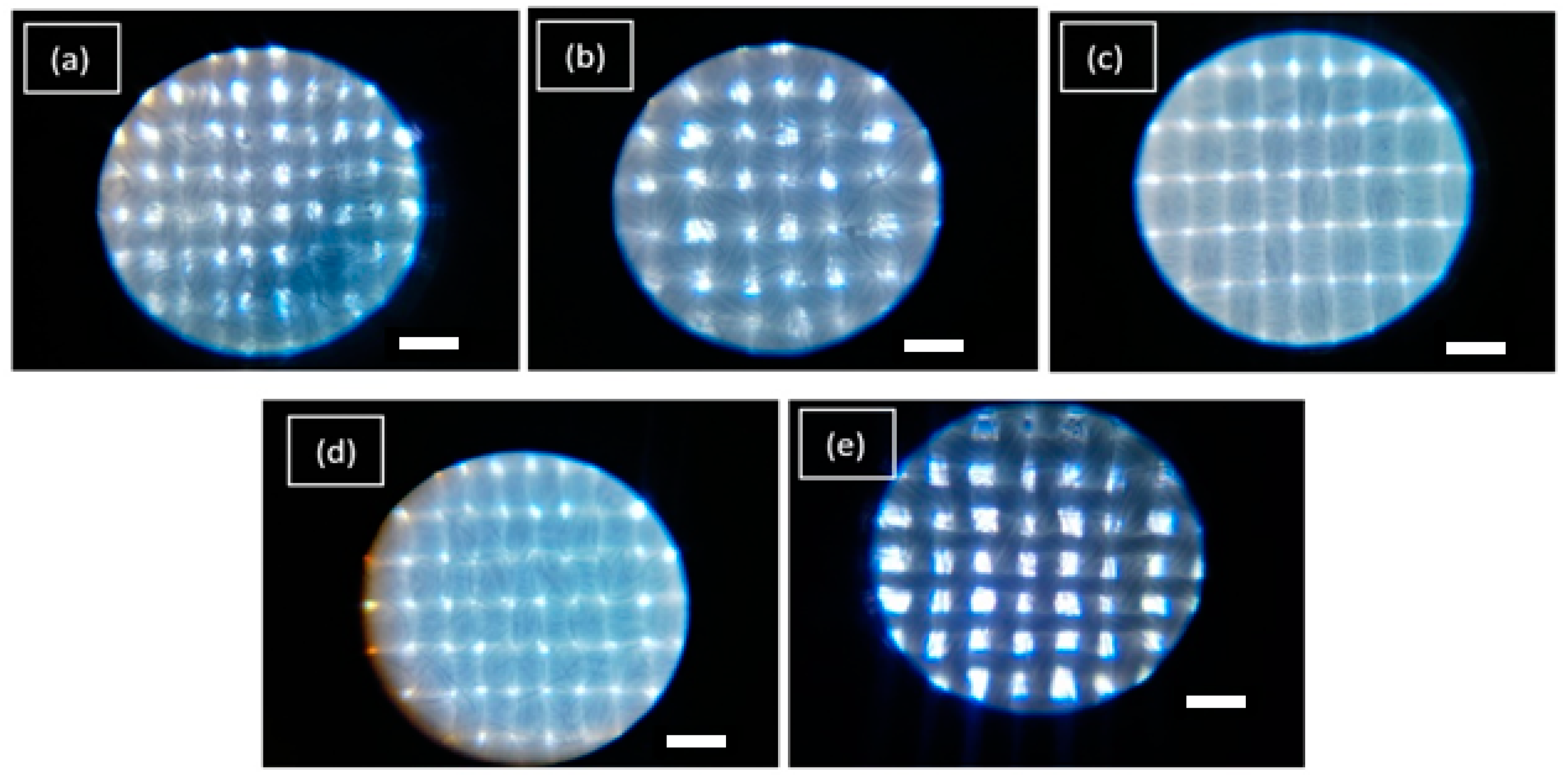
The evaluation was based on control samples of the evaluated textiles (without treatment), and with NP ZnO treatments obtained by the green and chemical methods. In this case, textiles of greater demand and applications at the level of basic clothing are being evaluated. Even at a medical level, the following occurs: textile 30/70 which corresponds to 30% cotton and 70% polyester, which is the type of fabric that is weft and warp with taffeta construction, 70/30 textile that corresponds to a higher content of cotton (70%) and polyester (30%), which is the type of fabric and construction similar to the first case. The anti-fluid textile is 100% polyester (filament) with a taffeta construction and a grammage of 114 g/m2. It is for purely medical use. Regarding the antimicrobial textile, it has a general composition of 100% polyester with chemical treatment (not shown) with a plain weave and under tests of its antimicrobial properties by the AATCC 100 standard. The rayon textile is similar to fibers such as silk, wool, or cotton. Its composition is to be an artificial cellulosic fiber of low grammage density (Figure 4).
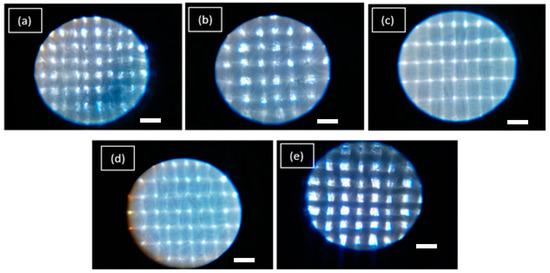
Figure 4.
Micrographs of the textiles under study without treatment with NP ZnO. 30/70 (a), 70/30 (b), Anti-fluid (c). Antimicrobial (d). Rayon (e). Scale bar = 20 µm.
In the micrographs shown in Figure 4, you can see the different configurations of each textile, where its grammage is totally different in each case. The anti-fluid and anti-microbial textiles are the most saturated. In turn, the fibers have a better fabric homogeneity. The 30/70 and 70/30 textile samples, the grammage is intermediate, they do not have a good alignment in their fibers, and it is also the case of rayon textile, where it is possible to observe empty spaces between weft and warp, which makes this textile in one of the least UV blocking. The configuration of the grammage is important in blocking UV radiation. However, factors such as the content of polyester intervene, being a synthetic material, which generates internal reflections and, therefore, its ability to neutralize UV radiation makes it minimal [33].
The optical transmittance of the textiles was performed using a UV-vis spectrophotometer (Hewlett Packard, 8452, CA, USA) with the aim of calculating the ultraviolet protection factor (UPF), using the equations provided by the test method of America AATCC 183-2004 [34].
where E(λ) is relative erythemal spectral effectiveness, S(λ) is a solar spectral irradiance in Wm−2 nm−1, T(λ) is the average spectral transmittance of the fabric, and Δλ is the bandwidth in nm.
The blocking percentage for UV-A radiation (which is the case of the lamp that has been used) (315–400 nm), is calculated using the equation below [35].
The UPF calculation (Equation (1)) aims to indicate the amount of material that reduces exposure to UV rays, in addition to being a term applied to textiles for the previously mentioned purposes. In the case of this research, a UV-A lamp and solar radiation are being used. In the first case, it is adjusted to quantify it by means of Equation (2). It is worth mentioning that, according to the ASTM standard for solar protection, only textiles with a UPF value greater than 15 are considered to be UV radiation blocking materials.
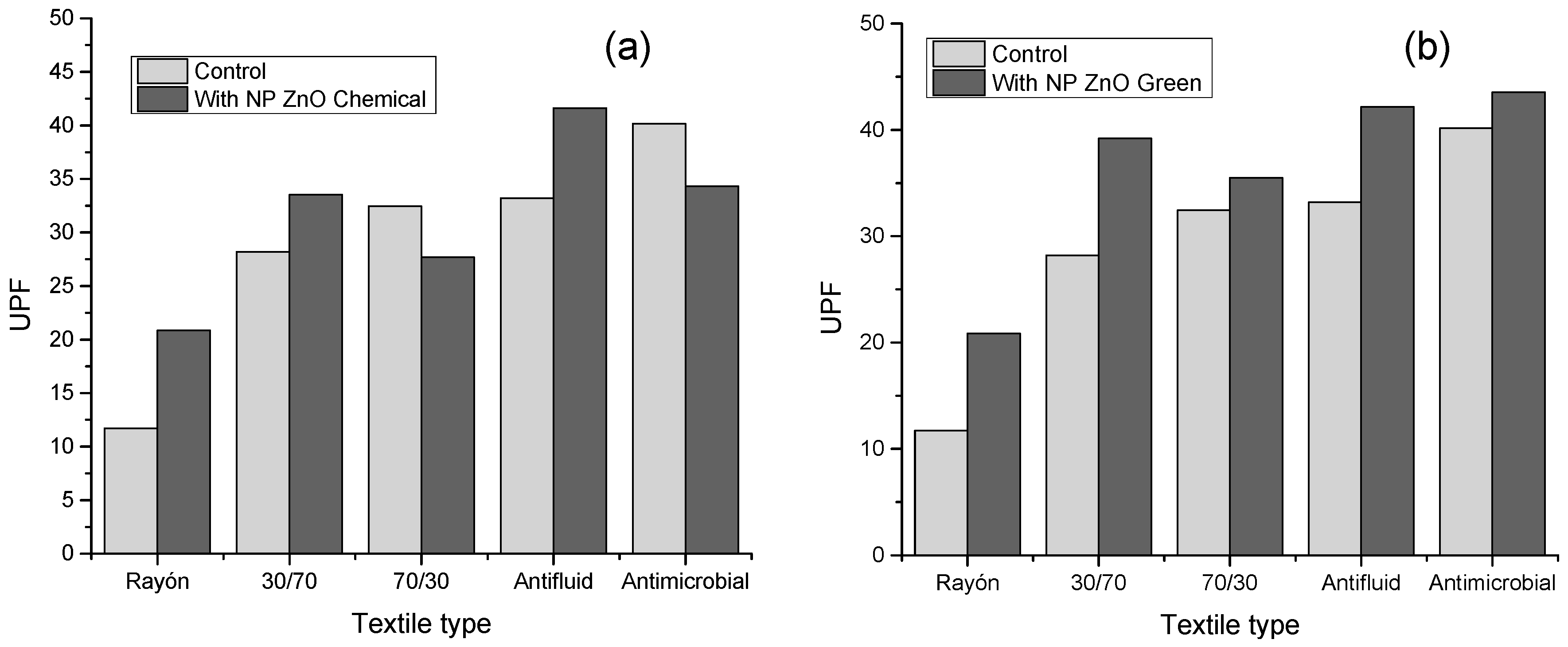
Figure 5 shows the UPF values calculated for the different textiles evaluated based on their respective treatments with NP ZnO by the chemical and green methods, and their comparison based on the control sample (textile without treatment), according to the AATCC standard 183-2004. Based on Table 1, UPF values greater than 15 have the category of “good protection.” This is how the control sample of the rayon textile is the only one that has a UPF value of 11.73, which implies a terrible UPF protection value. The other control textiles have values above the minimum necessary to have a “good” category, textile 30/70 with UPF 28.21, 70/30 with UPF 32.47, anti-fluid UPF 33.21, and anti-microbial UPF 40.17.
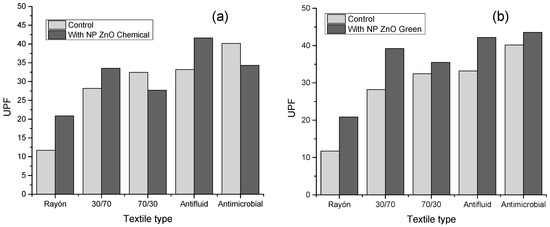
Figure 5.
Ultraviolet protection factors (UPF) values of the textiles evaluated as a function of the control sample (without treatment). (a) Textile samples with NP ZnO treatment by a chemical route. (b) Textile samples with NP ZnO treatment by a green route.

Table 1.
Ultraviolet protection factors (UPF) rating and protection grades [30].
However, it is noteworthy that the rayon sample has an improvement when subjected to treatment with NP ZnO both by the chemical and green methods, reaching UPF values of 20.87 and 20.88, respectively, becoming considered to be “good protection.”
It is also observed that, when the textile treatment is with NP ZnO obtained by the green method, in all cases, there is an increase in the UPF value. This is possibly due to the spherical geometry defined and observed in the SEM images. Otherwise, it happens with textiles treated with NP ZnO by a chemical route, where, for the 70/30 and antimicrobial cases, the UPF values decrease when compared to the control.
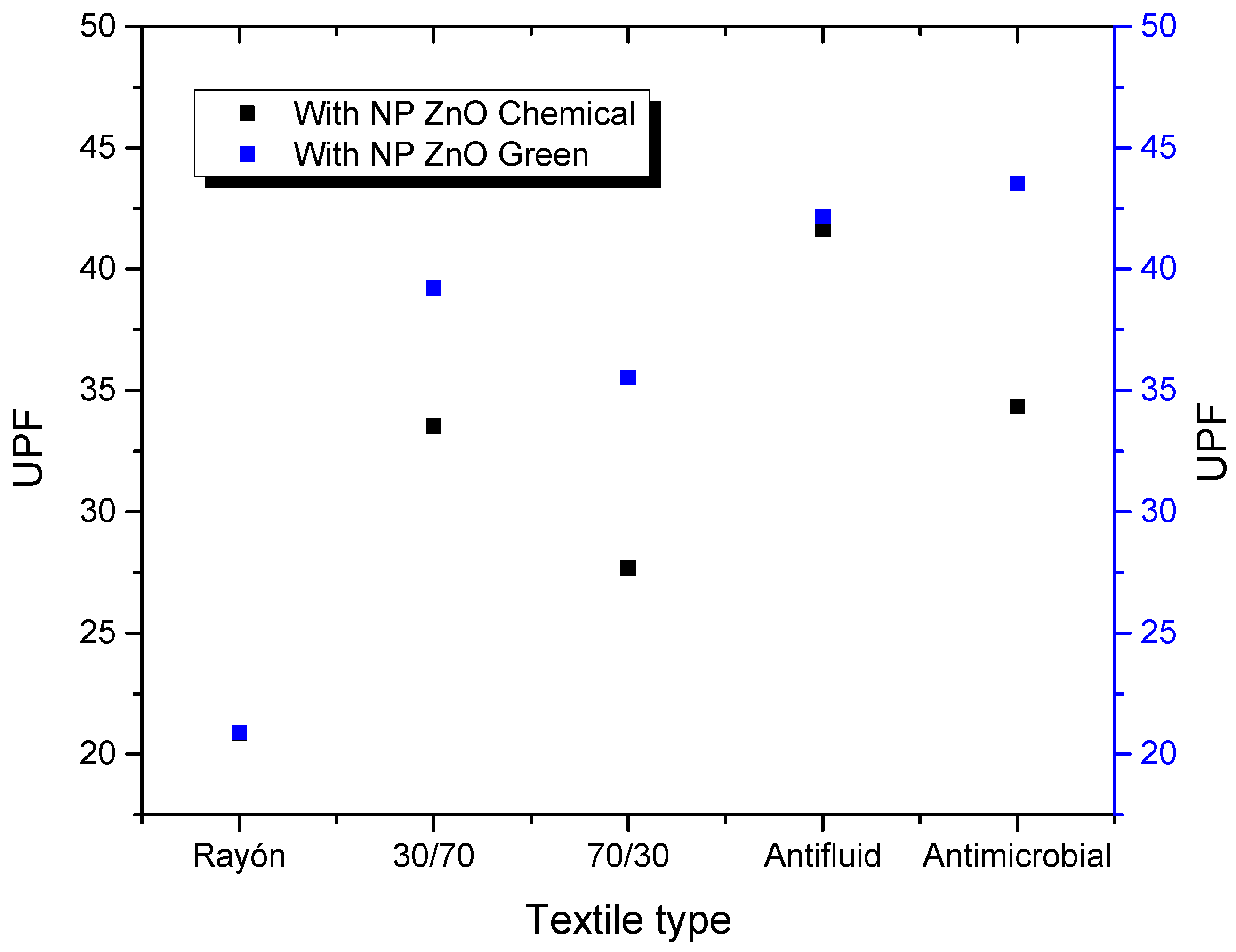
Figure 6 shows a comparative graph of UPF values corresponding to textiles treated with NP ZnO by the chemical and green methods. It is observed that, in most cases, there is an increase in protection by the textiles treated with NP obtained by a green route. These results will be corroborated by other techniques described in the following paragraphs.
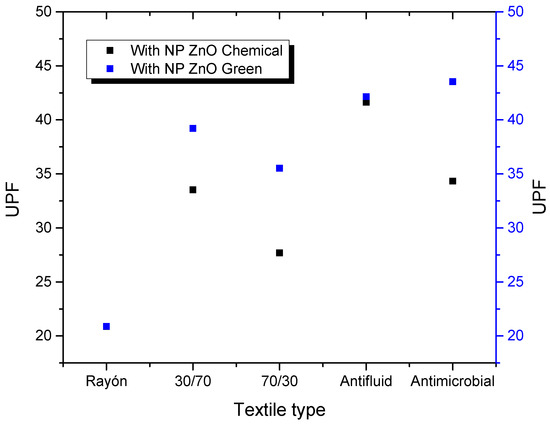
Figure 6.
UPF values of the different textiles evaluated and treated with NP ZnO by chemical and green methods.
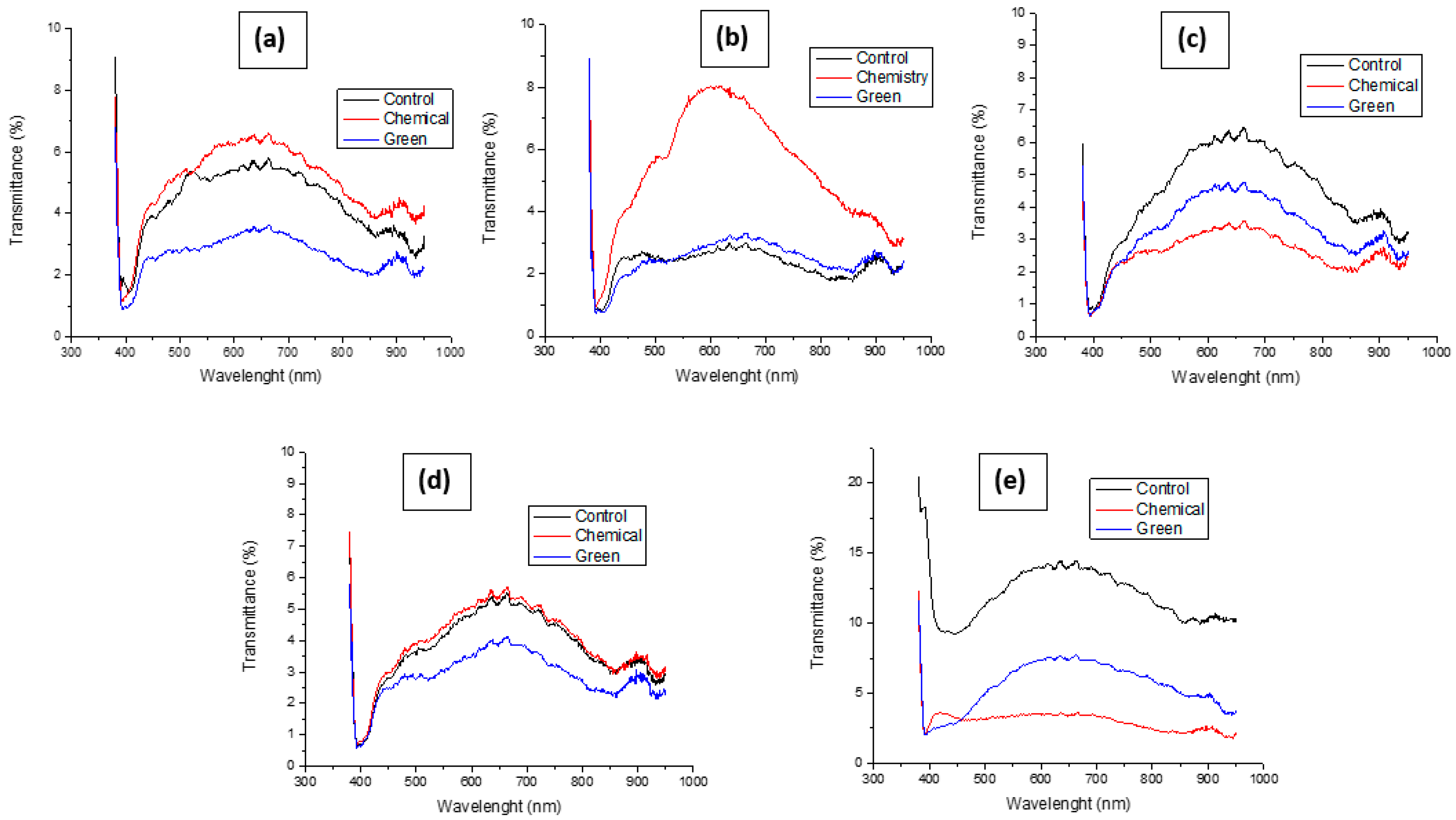
In Figure 7, it is possible to observe the transmittances for each batch of textiles, which ranges from the control textile (without treatment) to those with the previously mentioned treatments. its variation is clearly notorious. The results have been arranged in Table 2 and Figure 8. Based on these results, it is possible to obtain percentage values regarding the variation in transmittance after treatment, obtaining that, in the case of the 30/70 textile, it has an initial transmittance value, which decreases by 18.88% when a treatment is carried out with NP ZnO obtained by the chemical method. However, this value decreases much more when the treatment is with nanoparticles obtained by the green method, reaching 39.02%. For the 70/30 textile sample, the context is a little different, since an opposite change has been seen due to the fact that the transmittance of the textile containing chemical treatment increased by +14.73% when compared to the control textile. This is possibly due to the fact that containing more cotton has absorbed in greater quantity ZnO nanostructures with a larger diameter (approximately 113 nm) and with an undefined geometry (polygonal) (Figure 2). However, for the sample treated by the green method, there is a reduction in transmittance by 9.42%, which would be in line with the relationship that the nanostructure achieved by this method is smaller in diameter and with defined spherical geometry, helping its incorporation into cotton fibers.
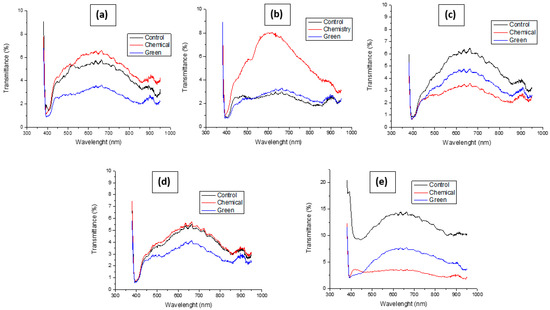
Figure 7.
Optical transmittances of different textiles treated with NP ZnO by chemical and green methods. 30/70 (a), 70/30 (b). Anti-fluid (c). Anti-microbial (d). Rayon (e) based on your control sample (no treatment).

Table 2.
Evaluation of transmittance (%T) in textiles functionalized with NP ZnO by the chemical and green methods.
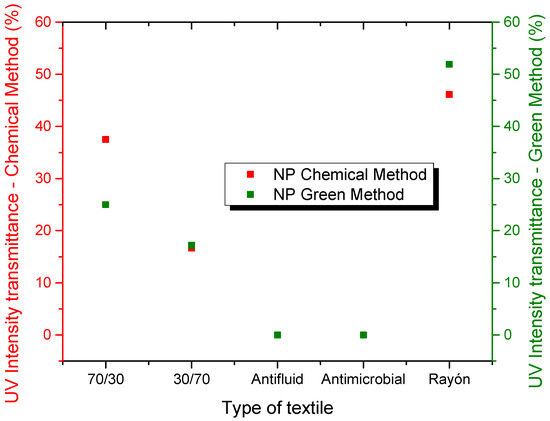
Figure 8.
Comparison of the transmittance (%T) of the different textiles based on the type of functionalization treatment with NP ZnO by the chemical and green methods.
For the anti-fluid textile, we observe in the micrographs that its framework is more orderly and denser. Despite this, the nanoparticles found spaces for their location, implying variations in their transmittance. Thus, for the sample treated by the chemical method, their reduction in transmittance is 25.39% and, for the green method, the reduction is 26.97%. The antimicrobial textile in its chemical treatment had a similar behavior to the 70/30 sample where the value increased by 14.53%, while, for the sample treated by the green method, it decreased by 7.65%, possibly due to what was stated in the previous case. Furthermore, it is notable that, among all the samples under study, this is the one that contributed little to reducing transmittance, possibly due to the high content of polyester, which meant that few nanoparticles could be incorporated into cotton fibers. In the case of the rayon textile sample, the results are quite promising because, according to the micrographs, its textile density is low, observing spaces that help to achieve high levels of transmittance. However, it favors the high cotton content since it is the place where nanostructures can easily be incorporated. This is how, for the sample with chemical treatment, a reduction of 78.01% was obtained, whose value is identical to that achieved by the sample treated by the green method.
The textile samples were also analyzed under the influence of UV lamp (UV 365 nm) and solar radiation, tested with a UV light intensity sensor (mW/cm2) (PCE-UV34, GmbH, Germany) (±0.01%) and an experimental arrangement planned for the occasion with the objective of obtaining congruent data.
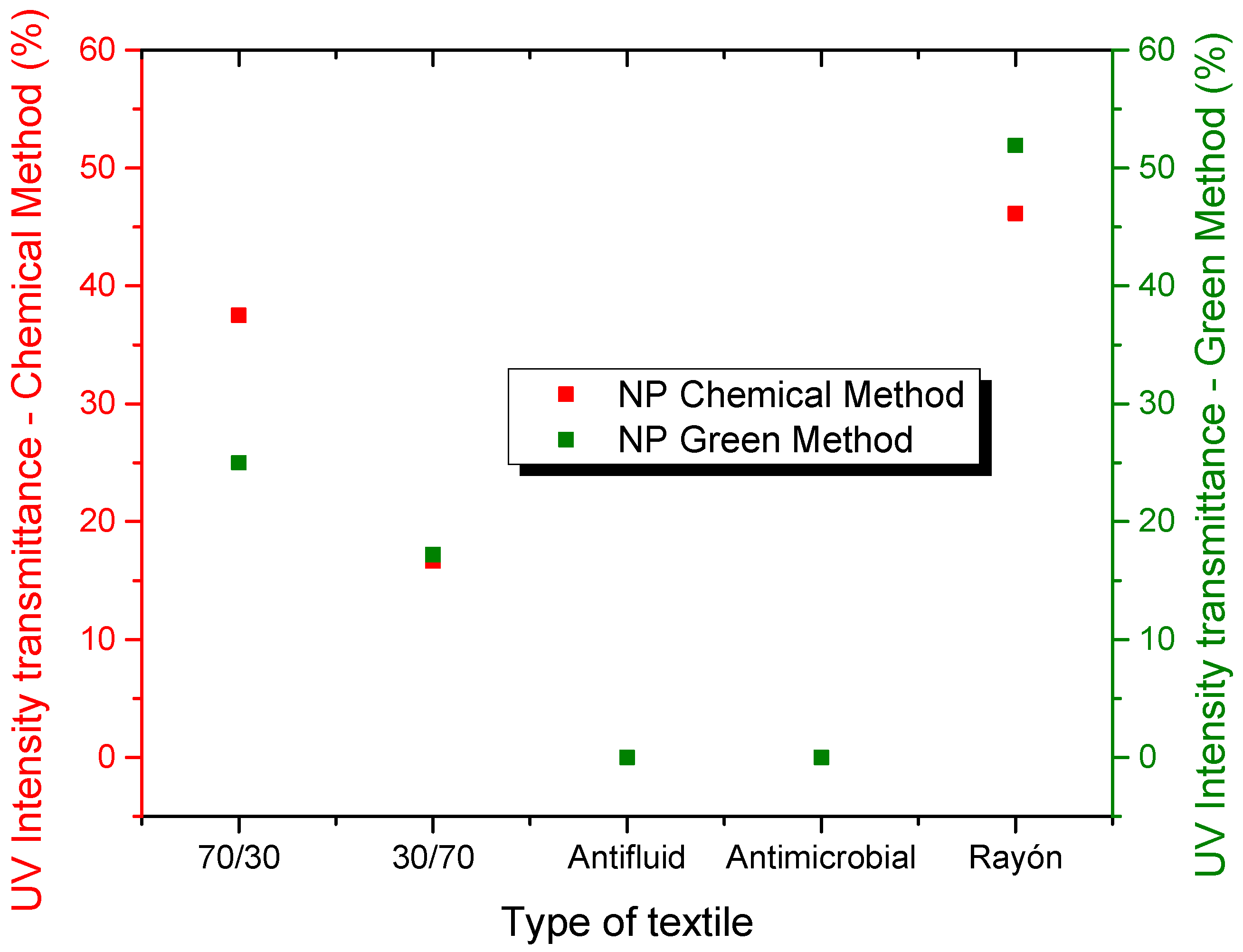
In Table 3 and Table 4, the textiles treated with the chemical and green methods are evaluated, respectively, with the influence of the UV lamp, considering the control sample (without treatment) as an experimental basis. In the case of textile samples with chemical treatment, it can be concluded that the textile that has best blocked UV radiation is rayon (46.15% better than the control), followed by the 70/30 textile. Once again, it is due to its high cotton content, which allows a better incorporation of nanostructures. However, anti-fluid and anti-microbial textiles did not generate change. The samples treated with NP ZnO by the green method (Table 4) achieved a better UV blocking efficiency in the rayon textile sample (51.92% better than the control), and, in turn, more efficient than the textile treated by the chemical method. These results are related to those obtained by transmittance.

Table 3.
Evaluation of textiles treated by the chemical method, based on blocking the intensity of UV radiation, provided with a UV-A lamp system, and its comparison with the control textile.

Table 4.
Evaluation of textiles treated by the green method, based on blocking the intensity of UV radiation, provided with a UV-A lamp system, and its comparison with the control textile.
Similarly, the samples were evaluated under the influence of solar radiation, where it was possible to obtain the intensity of UV solar radiation (mW/cm2) and its comparison with the control sample. Table 5 shows the specimens treated with the chemical method, with the rayon textile being the one that obtained the best reduction efficiency (59.73% better than the control). Table 6 shows the same evaluation but for the textiles treated by the green method, where the rayon textile also managed to be among the textiles that obtained the best UV blocking efficiency (56.19% better than the control).

Table 5.
Evaluation of textiles treated by the chemical method, based on blocking the intensity of UV radiation emitted by the sun, and its comparison with the control textile.

Table 6.
Evaluation of textiles treated by the green method, based on blocking the intensity of UV radiation emitted by the sun, and its comparison with the control textile.
In the garment manufacturing industry, most textiles used for this purpose provide some protection against UV radiation, since the effectiveness of a textile against UV blocking is determined by several factors, such as thickness, porosity, color, and density [36,37,38]. Thus, to improve the UV protection properties in textiles, various researchers have been applying nanoparticles of silicon dioxide, titanium dioxide, zinc dioxide, copper oxide, silver, and zinc oxide. Nanomaterials that are gaining considerable attention in the industrial sector, with the aim of satisfying the growing demand for textile products with innovative functionalities [39,40,41,42,43].
Research on the functionalization of textiles with NP ZnO is based on the treatment of pure cotton fabrics, which contributes to a better performance in UV blocking [44,45,46] achieving maximum values of up to UPF 161.74, considering high concentrations of the nanomaterial in question. However, other works with identical treatments report maximum UPF 20 values using lower concentrations of ZnO [47], and all of them using 100% cotton textiles.
In the case of this research, using the same textile material is avoided in typical research work because they are materials being used more in the garment manufacturing industry due to their low cost. However, there is little information at the research level with the textiles we are using, contributing that, despite the high content of synthetic material such as polyester, low grammage density materials can improve their UV protection properties using ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by a sustainable method and low cost. As seen in the results presented, in all cases, there is an improvement in the UPF protection factor with values between “good” and “very good” in their categorization.
The UV blocking mechanism consists of ZnO having a direct band gap of 3.37 eV and, therefore, an improved light absorption capacity with an energy hv that coincides with the band gap of the UV band [48]. This is how the treated textile sample remains in contact with the ambient atmosphere. The oxygen molecules absorb the electrons from the conduction band and generate superoxide radicals. Samples irradiated by UV light have a mechanism where pairs of electron holes are generated from textile surfaces modified with ZnO nanostructures. In this sense, the oxygen ions in the depletion layer absorb the holes and release oxygen molecules because of the exposure of the textile to the atmosphere.
4. Conclusions
The study allowed evaluating the functionalization of various textiles with zinc oxide nanoparticles obtained by chemical and green protocols (using Coriandrum sativum extract). The green synthesis methodology achieved nanostructures with defined spherical geometry and an average size of 97.77 nm, which allowed better adherence in those textiles with a high cotton content. The transmittance results indicate a decrease of 78.01% for the rayon textile treated by the green method, with this result being the best in what corresponds to this optical property, with respect to blocking UV radiation in a similar way. The rayon textile functionalized with the NP ZnO with chemical treatment managed to improve this property by 59.73% for the chemical method, and by 56.19% for the green method. The other textiles under study showed a better performance than those indicated, showing a minimal and intermediate improvement compared to the control sample. These functionalized textiles can be used in the manufacture of garments with efficient UV blocking.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.A.-C. Methodology, D.A.-C., D.D.-N., and L.J.-C. Validation, D.A.-C., D.D.-N., and L.J.-C. Formal analysis, D.A.-C. Investigation, D.A.-C., D.D.-N., and L.J.-C. Resources, D.A.-C. and D.D.-N. Data curation, D.A.-C. Writing—original draft preparation, D.A.-C. Writing—review and editing, D.A.-C., D.D.-N., and L.J.-C. Visualization, L.J.-C. Supervision, D.A.-C. Project administration, D.A.-C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was developed with the funding of the UPN-20201002 research project from the la Universidad Privada del Norte, Perú.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Rocío Quiliano, Head of Research of the Dirección de Investigación y Desarrollo (DID)-Universidad Privada del Norte for your support and constant management.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Mehta, M.D. Nanotechnology and the Developing World Lab-on-Chip Technology for Health and Environmental Applications. Bull. Sci. Technol. Soc. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumala Rao, G.; Babu, B.; Joyce Stella, R.; Pushpa Manjari, V.; Venkata Reddy, C.; Shim, J.; Ravikumar, R.V.S.S.N. Synthesis and characterization of VO2+ doped ZnO-CdS composite nanopowder. J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 1081, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simončič, B.; Klemenčič, D. Preparation and performance of silver as an antimicrobial agent for textiles: A review. Text. Res. J. 2016, 86, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- User, G.; Durán, N.; Marcato, P.D.; De Souza, G.I.H.; Alves, O.L.; Esposito, E. Delivered by Ingenta to: Antibacterial Effect of Silver Nanoparticles Produced by Fungal Process on Textile Fabrics and Their Effluent Treatment. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2007, 3, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneshwaran, N.; Kumar, S.; Kathe, A.A.; Varadarajan, P.V.; Prasad, V. Functional finishing of cotton fabrics using zinc oxide-soluble starch nanocomposites. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 5087–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, B.; Deng, Z.; Xin, J.H.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, G. Room temperature synthesis of rutile nanorods and their applications on cloth. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 1927–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassabo, A.G.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Mohamed, A.L.; Hebeish, A.A. Development of multifunctional modified cotton fabric with tri-component nanoparticles of silver, copper and zinc oxide. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 210, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Sun, G.; Xu, F.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Fu, S. Facile synthesis of SiO2 @TiO2 hybrid NPs with improved photocatalytic performance. Micro Nano Lett. 2018, 13, 666–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglioni, P.; Dei, L.; Fratoni, L.; Lo Nostro, P.; Moroni, M. Process for the Preparation of Nano- and Micro-Particles of Group II and Transition Metals Oxides and Hydroxides, the Nano- and Micro-Particles Thus Obtained and Their Use in the Ceramic, Textile and Paper Industries. 2003. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/CA2480303A1/en11 (accessed on 8 October 2020).
- Subash, A.A.; Chandramouli, K.V.; Ramachandran, T.; Rajendran, R.; Muthusamy, M. Preparation, characterization, and functional analysis of zinc oxide nanoparticle-coated cotton fabric for antibacterial efficacy. J. Text. Inst. 2012, 103, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.W.H.; Yuen, C.W.M.; Leung, M.Y.S.; Ku, S.K.A.; Lam, H.L.I. Selected applications of nanotechnology in textiles. AUTEX Res. J. 2006, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Adraider, Y.; Pang, Y.X.; Nabhani, F.; Hodgson, S.N.; Sharp, M.C.; Al-Waidh, A. Photocatalytic activity of titania coatings synthesised by a combined laser/sol-gel technique. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 54, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.W.; Dai, Z.R.; Wang, Z.L. Nanobelts of semiconducting oxides. Science 2001, 291, 1947–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.S.; Avouris, P.; Pan, Z.W.; Wang, Z.L. Field-effect transistors based on single semiconducting oxide nanobelts. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H.; Yamasaki, O.; Kanzaki, H.; Tada, J.; Arata, J. Effects of zinc oxide on the attachment of Staphylococcus aureus strains. J. Dermatol. Sci. 1998, 17, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Sun, Z.; Huang, P.; Li, Y.; Hu, N. Some basic aspects of polymer nanocomposites: A critical review. Nano Mater. Sci. 2019, 1, 2–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.S.M.; Azab, W.I.M.E.; Ali, H.R.; Mansour, M.S.M. Green synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of anthracene. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 45012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cierech, M.; Kolenda, A.; Grudniak, A.M.; Wojnarowicz, J.; Woźniak, B.; Gołaś, M.; Swoboda-Kopeć, E.; Łojkowski, W.; Mierzwińska-Nastalska, E. Significance of polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) modification by zinc oxide nanoparticles for fungal biofilm formation. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 510, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, E.; Cheng, G.; Ma, X.; Pang, X.; Zhao, Q. Surface modification of zinc oxide nanoparticle by PMAA and its dispersion in aqueous system. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 5227–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan Parra, M.; Haque, F.Z. Structural and optical properties of poly-vinylpyrrolidone modified ZnO nanorods synthesized through simple hydrothermal process. Optik (Stuttgart) 2014, 125, 4629–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, A.; Ahmed, F.; Arshi, N.; Chaman, M.; Naqvi, A.H. Formation and characterization of ZnO nanopowder synthesized by sol-gel method. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 496, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xin, J.H.; Tao, X.M.; Daoud, W.A. ZnO nanorods grown on cotton fabrics at low temperature. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 398, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, A. Que es el UPF en un tejido. Rev. Química Text. 1999, 144, 72–80. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzáles-Púmariega, M.; Vernhes Tamayo, M.S.-L.A. La radiación ultravioleta, su efecto dañino y consecuencias para la salud humana. Rev. Fac. Nac. Salud. Pública 2002, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Cabrera Morales, C.M.; López-Nevot, M.A. Efectos de la radiación ultravioleta (UV) en la inducción de mutaciones de p53 en tumores de piel. Oncology 2006, 29, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilabertea, Y.; Coscojuelaa, C.; Ma Carmen Sáenz de Santamaríab, S.G. Fotoprotección. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2003, 94, 271–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, P.; Osorio, A.M.; Ninán, E.; Torres, F. Caracterización de nanopartículas de ZnO sintetizadas por el método de precipitación y su evaluación en la incorporación en pinturas esmalte. Rev. Soc. Química Perú 2018, 84, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, S.; Siva, P.; Balu, K.S.; Suriyaprabha, R.; Rajendran, V.; Maaza, M. Acalypha indica–mediated green synthesis of ZnO nanostructures under differential thermal treatment: Effect on textile coating, hydrophobicity, UV resistance, and antibacterial activity. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 3184–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakir, B.A.; Budama, L.; Topel, Ö.; Hoda, N. Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using PS-b-PAA reverse micelle cores for UV protective, self-cleaning and antibacterial textile applications. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 414, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, D.K.; Mani, G.K.; Babu, K.J.; Das, A.; Balaguru Rayappan, J.B. Nanostructured ZnO on cotton fabrics—A novel flexible gas sensor & UV filter. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 194, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, L.E.; Huachani, J.; Uribe, C.; Solís, J.; Gómez, M.; Costa, S.; Costa, S. Blocking erythemally weighted UV radiation using cotton fabrics functionalized with ZnO nanoparticles in situ. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 469, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran Thi, V.H.; Lee, B.K. Development of multifunctional self-cleaning and UV blocking cotton fabric with modification of photoactive ZnO coating via microwave method. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2017, 338, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association of Textile, Apparel and Material Professionals, Transmittance or Blocking of Erythemally Weighted Ultraviolet through Fabric AATCC Test Method. Available online: https://members.aatcc.org/store/tm183/579/ (accessed on 6 December 2020).
- Qu, M.; He, J.; Zhang, J. Superhydrophobicity, Learn from the Lotus Leaf. In Biomimetics Learning from Nature; InTech: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- International, A. ASTM D6603-12 Especificación Estándar para el Etiquetado de Textiles con Protección UV. Available online: https://www.astm.org/DATABASE.CART/HISTORICAL/D6603-12.htm (accessed on 6 December 2020).
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Sun, P.; Yang, J.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y. Superhydrophobic and ultraviolet-blocking cotton textiles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 1277–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumdar, A.; Das, A.; Hatua, P. Effects of fabric thickness and inter-yarn pore size on ultraviolet radiation protection by polyester woven fabrics. Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutawa, F.; Buabbas, H. Photoprotection: Clothing and glass. Dermatol. Clin. 2014, 32, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandimurugan, R.; Thambidurai, S. UV protection and antibacterial properties of seaweed capped ZnO nanoparticles coated cotton fabrics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoičić, M.B.; Milošević, M.V.; Miličević, D.S.; Suljovrujić, E.H.; Ćirić-Marjanović, G.N.; Radetić, M.M.; Šaponjić, Z.V. Influence of TiO2 nanoparticles on formation mechanism of PANI/TiO2 nanocomposite coating on PET fabric and its structural and electrical properties. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 278, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetisen, A.K.; Qu, H.; Manbachi, A.; Butt, H.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Hinestroza, J.P.; Skorobogatiy, M.; Khademhosseini, A.; Yun, S.H. Nanotechnology in Textiles. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 3042–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Guo, Z. Versatile superamphiphobic cotton fabrics fabricated by coating with SiO2/FOTS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 426, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouadil, B.; Cherkaoui, O.; Safi, M.; Zahouily, M. Surface modification of knit polyester fabric for mechanical, electrical and UV protection properties by coating with graphene oxide, graphene and graphene/silver nanocomposites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 414, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shateri-Khalilabad, M.; Yazdanshenas, M.E. Bifunctionalization of cotton textiles by ZnO nanostructures: Antimicrobial activity and ultraviolet protection. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belay, A.; Mekuria, M.; Adam, G. Incorporation of zinc oxide nanoparticles in cotton textiles for ultraviolet light protection and antibacterial activities. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2020, 10, 184798042097005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, L.; Fang, D.; Toh, G.W.; Yue, X.; Chen, Y.; Lin, H. In situ generation and deposition of nano-ZnO on cotton fabric by hyperbranched polymer for its functional finishing. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 1625–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, T.R.; Samanta, A.K.; Sajid, M.; Kaware, R. UV protection and antimicrobial finish on cotton khadi fabric using a mixture of nanoparticles of zinc oxide and poly-hydroxy-amino methyl silicone. Text. Res. J. 2019, 89, 2260–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazer, M.; Maali Amiri, M. ZnO nano reactor on textiles and polymers: Ex situ and in situ synthesis, application, and characterization. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 1453–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).