Abstract
This study investigates the mechanical properties of bamboo fiber-reinforced polydimethylsiloxane (BF-PDMS) foams with up to 3.4% (by mass) fiber during compression. Pristine PDMS foams and BF-PDMS composite foams were fabricated using a sugar leaching method. Compression test results of pristine PDMS and BF-PDMS composite foams display plateau and densification regions. Predictions of a modified phenomenological foam (PF) model based on Maxwell and Kelvin–Voight models are in good agreement with compression test results. Stiffness coefficients were extracted by fitting results of compression tests to the modified PF model. Spring and densification coefficients of BF-PDMS composite foams are 2.5- and 15-fold greater than those of pristine PDMS foams, respectively. Strains corresponding to onset of densification computed using extracted coefficients were 35% and 25% for pristine PDMS foams and BF-PDMS composite foams, respectively. Compressing foams at 6.0 and 0.5 mm/min results in highest and lowest compressive stress, respectively. Insights from this study are useful in many areas such as environmental protection, pressure sensing, and energy where PDMS composite foams will find applications.
1. Introduction
Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) foams are a class of porous material comprising of pristine and PDMS sponge and those with fillers. PDMS foams have attracted tremendous attention as they promise a range of potential applications from sound absorbers to wearable sensors [1,2]. A recent review described numerous applications that arise from the unique combination of facile fabrication process, ease of controlling pore morphology, and chemical properties of PDMS [3]. PDMS foams have outstanding superhydrophobic and superoleophilic properties that make them immensely suitable as a sorbent for oil in water [4,5]. PDMS foam is a robust sorbent to remove various types of vegetables oils as well as alkanes, chloroalkanes, toluene, methanol, gasoline, and crude oils [6,7]. Adding graphene to PDMS foams further improved oil sorption for toluene, gasoline and vegetable oil at high capacity [8]. Furthermore, PDMS foams can be used repeatedly and not affected significantly by soaking in solvents [9].
While numerous studies have focused on development of processes and demonstrating applications of PDMS foams, fewer studies have investigated mechanical behavior of PDMS foams and even its dense counterpart [10,11,12]. Understanding mechanical behavior of PDMS foams is important in pressure sensors where high sensitivity and consistent mechanical behaviors are desired. A recent study revealed that porosity of PDMS foam has a significant effect on the elastic modulus and Poisson’s ratio, for porosities less than 50%, while pore size has no effect [13]. When ratio of resin to curing agent was changed from 10:1 to 20:1, elastic modulus of PDMS foams decreased 1.69-fold; densification occurred at higher strains and hysteresis increased 2-fold [14].
Bamboo plant is fast growing and hence is a sustainable source of fibers compared to other plants. Furthermore, bamboo fibers have excellent mechanical properties and have been added to polymers to improve strength [15]. Polypropylene reinforced with bamboo fibers primed with maleic anhydride-grafted polypropylene has a tensile strength of between 32 and 36 MPa; three times that of wood pulp board for packaging [16]. Bamboo fibers have been reported to be a viable replacement for glass and carbon fibers as reinforcement in polymer composites for automotive and aerospace applications [17].
Biomass and PDMS foams, separately, have been widely investigated as sorbents for oil. However, hybrid foams comprising of both biomass and PDMS foam are much less studied. Adding biomass to PDMS foams will reduce costs and improve environmental sustainability. Here, we prepared hybrid bamboo fiber reinforced-PDMS foams with various bamboo fiber loadings and investigated the mechanical property at various displacement rates during compression. Addition of bamboo to PDMS foam may contribute to pore recovery when incorporated for use in reusable sorbent for oil. Compressions results will be discussed in the context of the behavior of other polymeric foams and analyzed using a modified phenomenological foam model to extract stiffness coefficients. These results will be useful towards development of energy efficient BF-PDMS foam sorbents that will not require excessive energy to squeeze oil out.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fiber Preparation
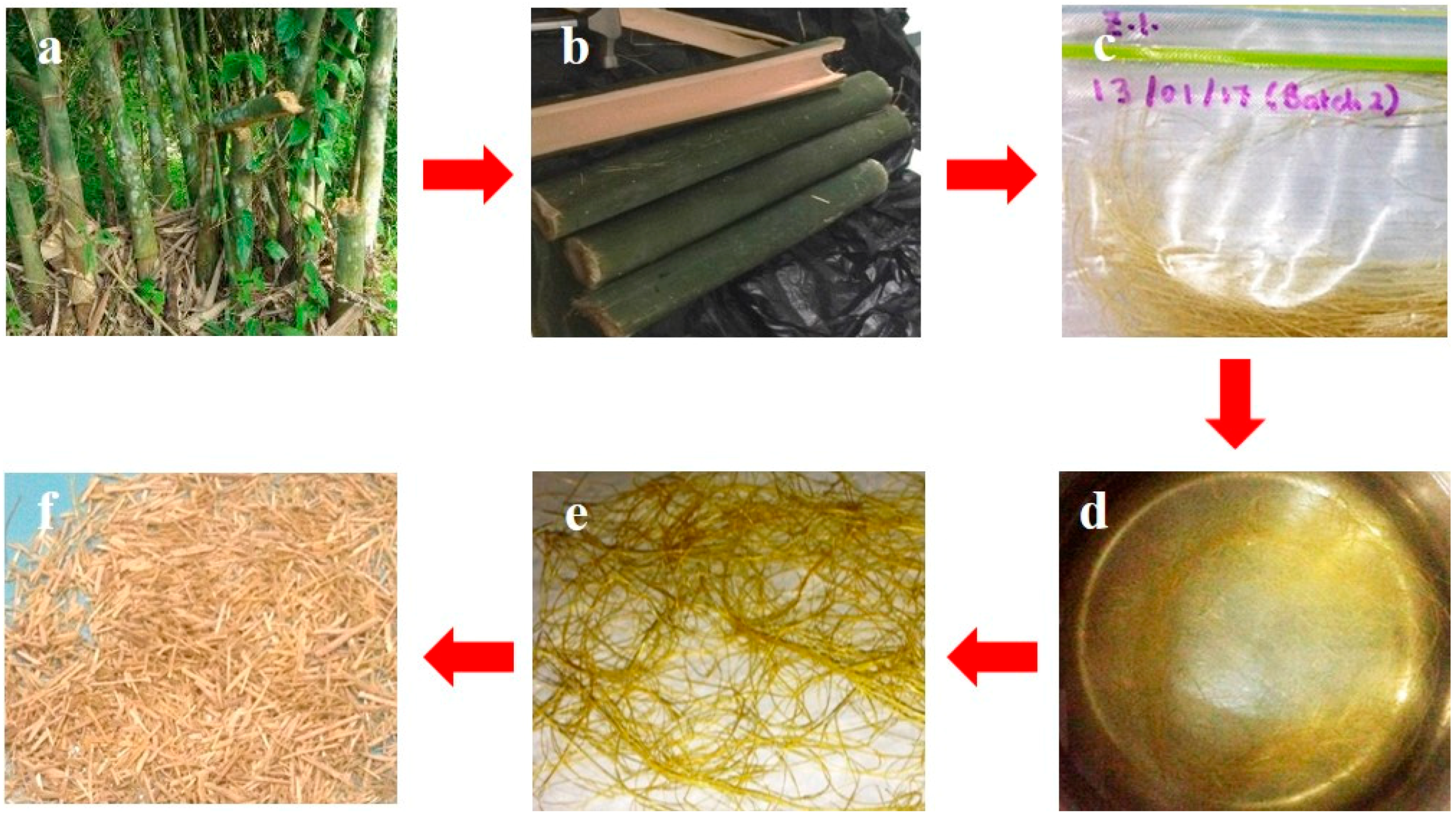
Bamboo fibers were harvested from Dendrocalamus asper species that are native and ubiquitous in Southeast Asia. Bamboo fibers were collected from plants growing in Masin, Brunei-Muara District, Brunei Darussalam (4°50′14.5″ N 114°50′41.1″ E). Figure 1 shows typical bamboo plant and detailed process flow to extract fibers.

Figure 1.
Fiber preparation starts with (a) selecting suitable bamboo plant, (b) followed by cutting, and (c) manually separating fibers. Fibers are sequentially (d) boiled, (e) dried, and (f) cut to size.
The fiber extraction process starts with identifying bamboo plants free from mildew, discoloration, and dried portions. Internode sections, each 35 cm long, were cut from bamboo plants. Bamboo fibers were extracted manually and boiled in water for 5 h. The fibers were placed in an oven and dried at 100 °C in air. After drying, fibers were cut into lengths of between 2 to 4 mm. Fibers were stored in a sealed vacuum bag between process steps and prior to use.
2.2. Bamboo Fiber-Reinforced PDMS Foam
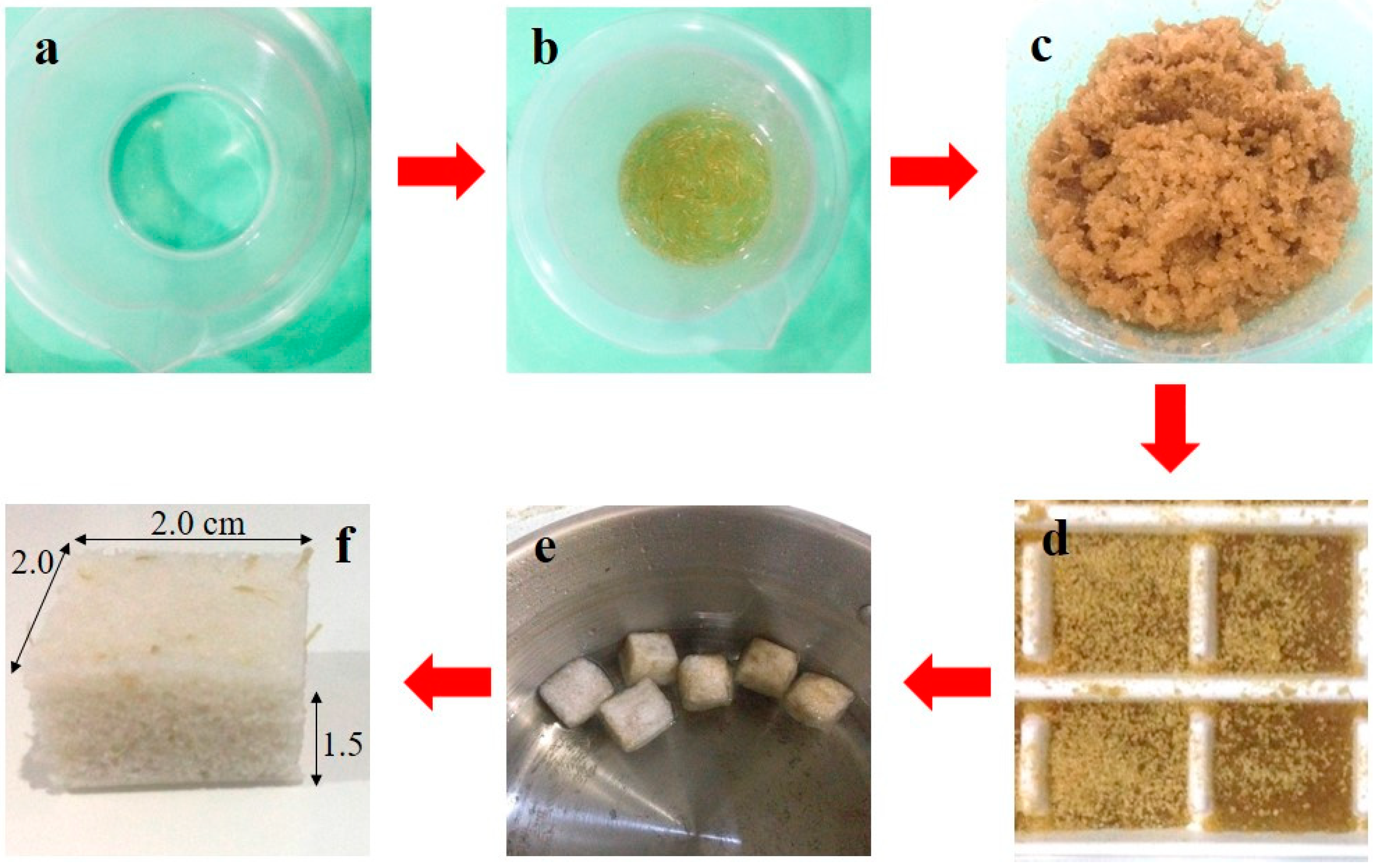
Figure 2 shows the steps used to prepare BF-PDMS. PDMS (Sylgard 184 silicone elastomer) was purchased from Dow Corning (Midland, MI, USA) and used without any modification. The elastomer kit received from Dow Corning comprised of two fluids. Part A is the resin consisting of vinyl-terminated siloxane oligomers and Part B is the curing agent consisting of tetra (trimethylsiloxy) silane, in the presence of a catalyst such as Karsted’s catalyst or H2PtCl6 through a hydrosilylation mechanism [18].
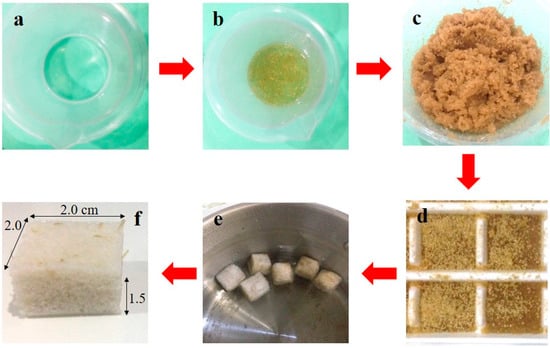
Figure 2.
Preparation of bamboo fiber-reinforced polydimethylsiloxane (BF-PDMS) foam involves (a) mixing resin and curing agent, (b) adding sugar, (c) followed by adding bamboo fibers. The mixture was stirred and (d) poured into molds, (e) followed by boiling, and (f) then cut to cuboids of dimensions 2.0 × 2.0 × 1.5 cm3.
Appropriate amounts of bamboo fibers and sugar were added to the PDMS resin/curing agent mixture as stated in Table 1. The resulting mixture was stirred vigorously until a uniform dispersion was obtained. The mixture was poured into molds and left to cure at room temperature over 24 h. The solidified mixture was then boiled in water for 5 h to dissolve the sugar and form a porous structure. After sugar particles were dissolved, the porous composite were cut into cuboids of dimensions 2.0 × 2.0 × 1.5 cm3. Amounts of PDMS resin, curing agent, and brown sugar were kept constant to ensure that mechanical property of PDMS matrix and porosity of the BF-PDMS are due to the bamboo fiber loading.

Table 1.
Mass of components for bamboo fiber-polydimethylsiloxane (BF-PDMS) of various fiber loadings.
2.3. Mechanical, Thermal and Morphological Characterization
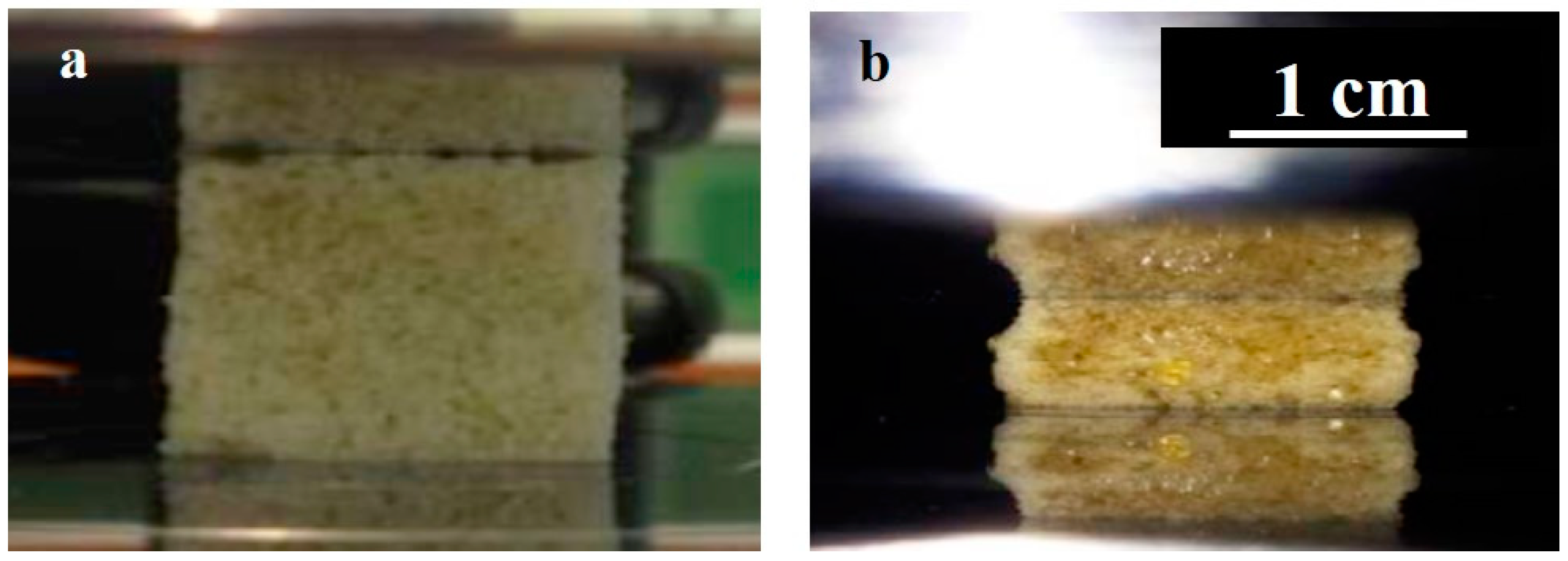
Uniaxial compression tests were carried out using an Instron 5565 universal testing machine (Norwood, MA, USA) with a 5 kN load cell. The machine was controlled using a Bluehill software. Figure 3 shows optical images of the experimental setup in which a BF-PDMS foam was placed between compression platens. Foams were compressed at a constant displacement rate of 0.5, 2.0, and 6.0 mm/min. Samples were compressed up to at least 60% strain for all different bamboo fiber loadings. Data were collected in the loading cycle only. Three compression tests were carried out for each type of fiber loading.
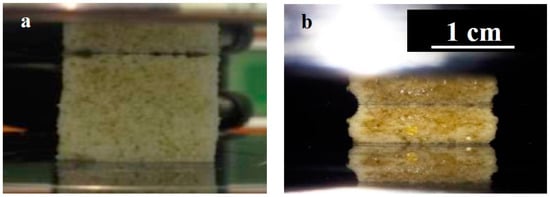
Figure 3.
Optical images of BF-PDMS foams between platens: (a) before and (b) during compression.
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was carried out using a Labsys TGA-ATD (Calluire, Lyon, France) system from 50 °C to 600 °C at 10 °C/min constant heating rate. Analysis was done in nitrogen at a constant flow rate of 30 mL/min. Samples between 17 to 21 mg each were placed on alumina crucibles. TGA was carried out for bamboo fiber, PDMS foam, and BF-PDMS composite. For the BF-PDMS foam, the sample used for TGA analysis was taken from the 3.4% BF-PDMS. However, the actual amount of fiber in the sample may be more than 3.4% due the discrete size of fibers. Structure of bamboo fibers, PDMS foams, and BF-PDMS composite foam were characterized by a Nikon Optiphot light microscope (Minato, Tokyo, Japan). Average pore size in foams was determined by using an open source image processing tool (Image J, National Institute of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA) from at least 100 data points.
3. Mathematical Model
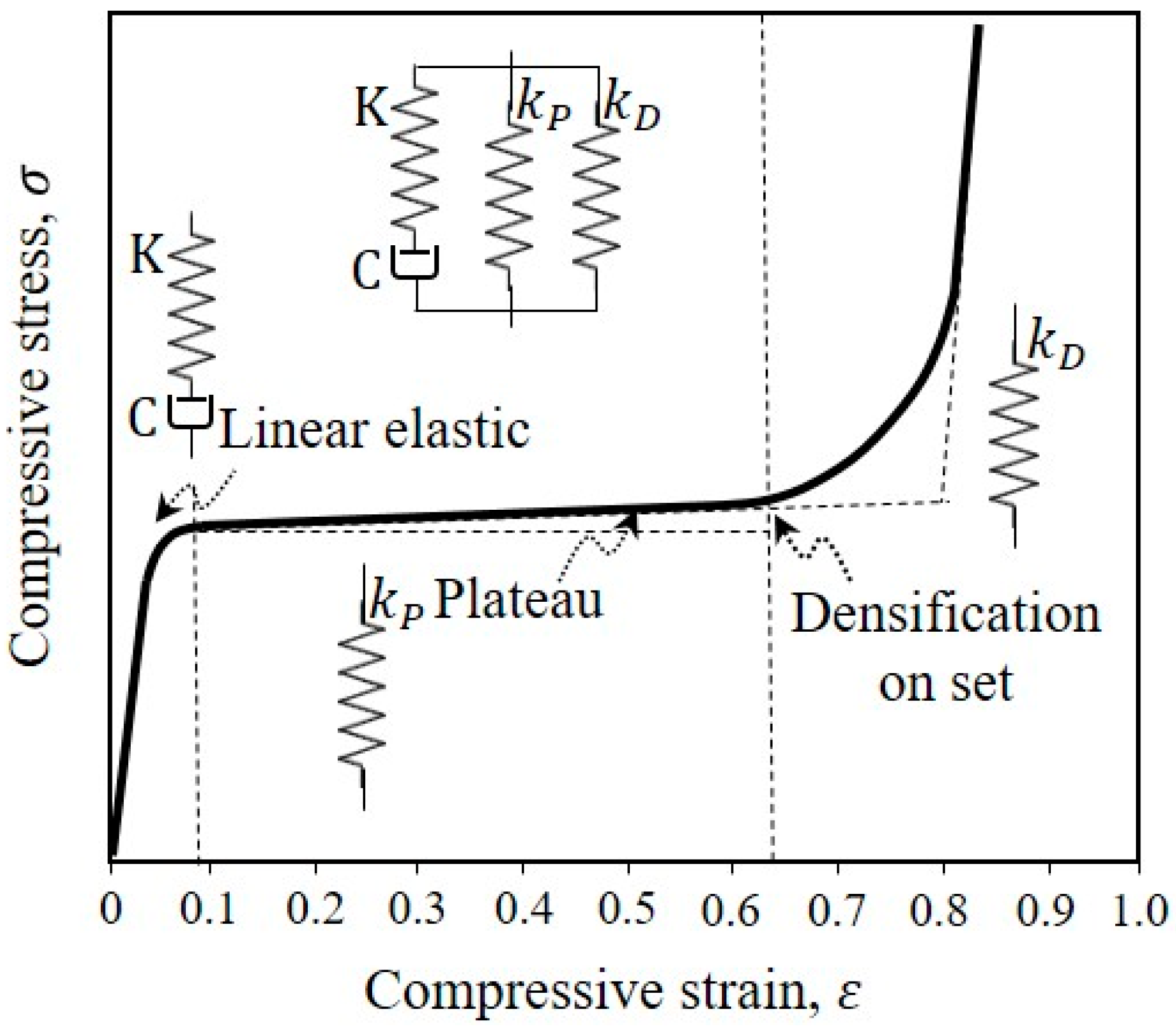
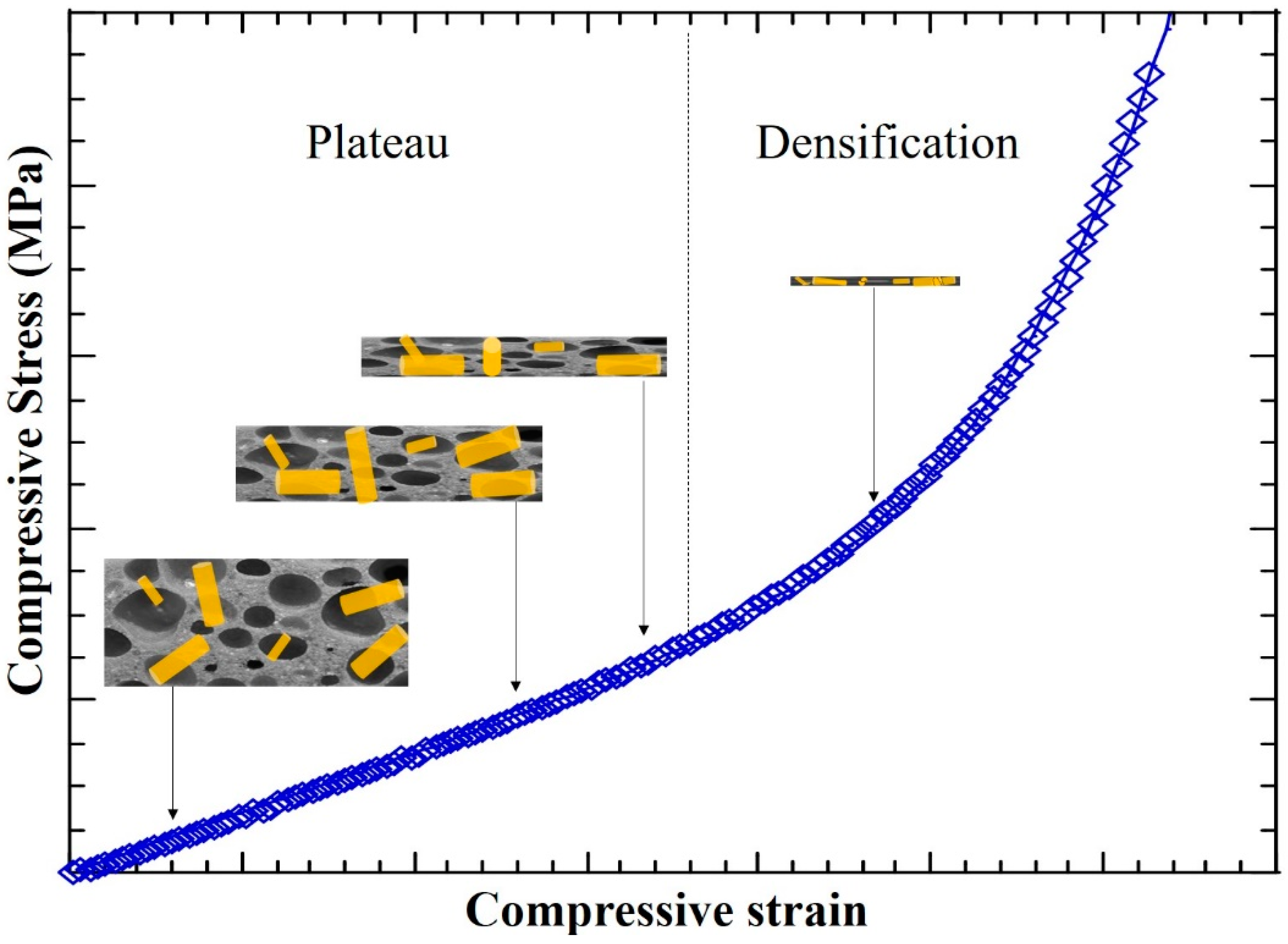
Compression test data of PDMS and BF-PDMS composite foams was analyzed using a modified phenomenological foam model. The original phenomenological model was developed to predict experimental compression curves of polyurethane foams of different densities and able to treat any variable strain rates [19]. The original model combined dashpot and spring elements as in Kelvin–Voight and Maxwell models to develop the elastic, plateau, and densification regions observed in compression curves of polyurethane foams (Figure 4).
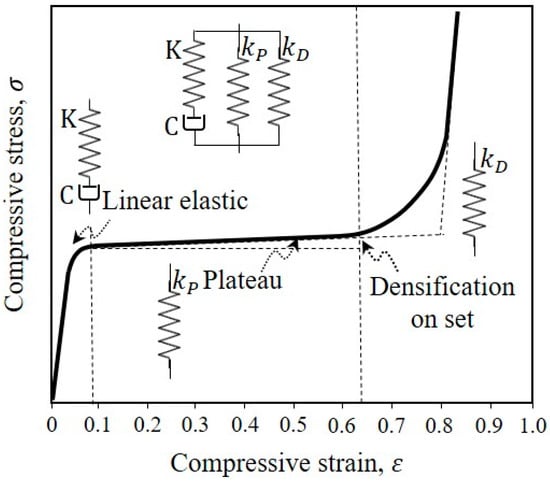
Figure 4.
Schematic stress–strain curve showing elastic, plateau, and densification regions during compression of a polymeric foam and the phenomenological foam (PF) model proposed by Alzoubi et al. [19].
The equation for compression stress for three regions of the foam that includes the linear elastic, the plateau and densification regions is given by [19]
where:
= Compression stress
= Strain and strain rate, respectively
= Spring constant and dashpot damping coefficient in linear region, respectively
= Spring constant in plateau region
= Densification coefficient and polynomial exponent of nonlinear spring element in densification region, respectively.
On the right hand side of Equation (2), the first, second and third terms are stress components from the linear elastic region, plateau, and densification regions, respectively.
4. Results and Discussion
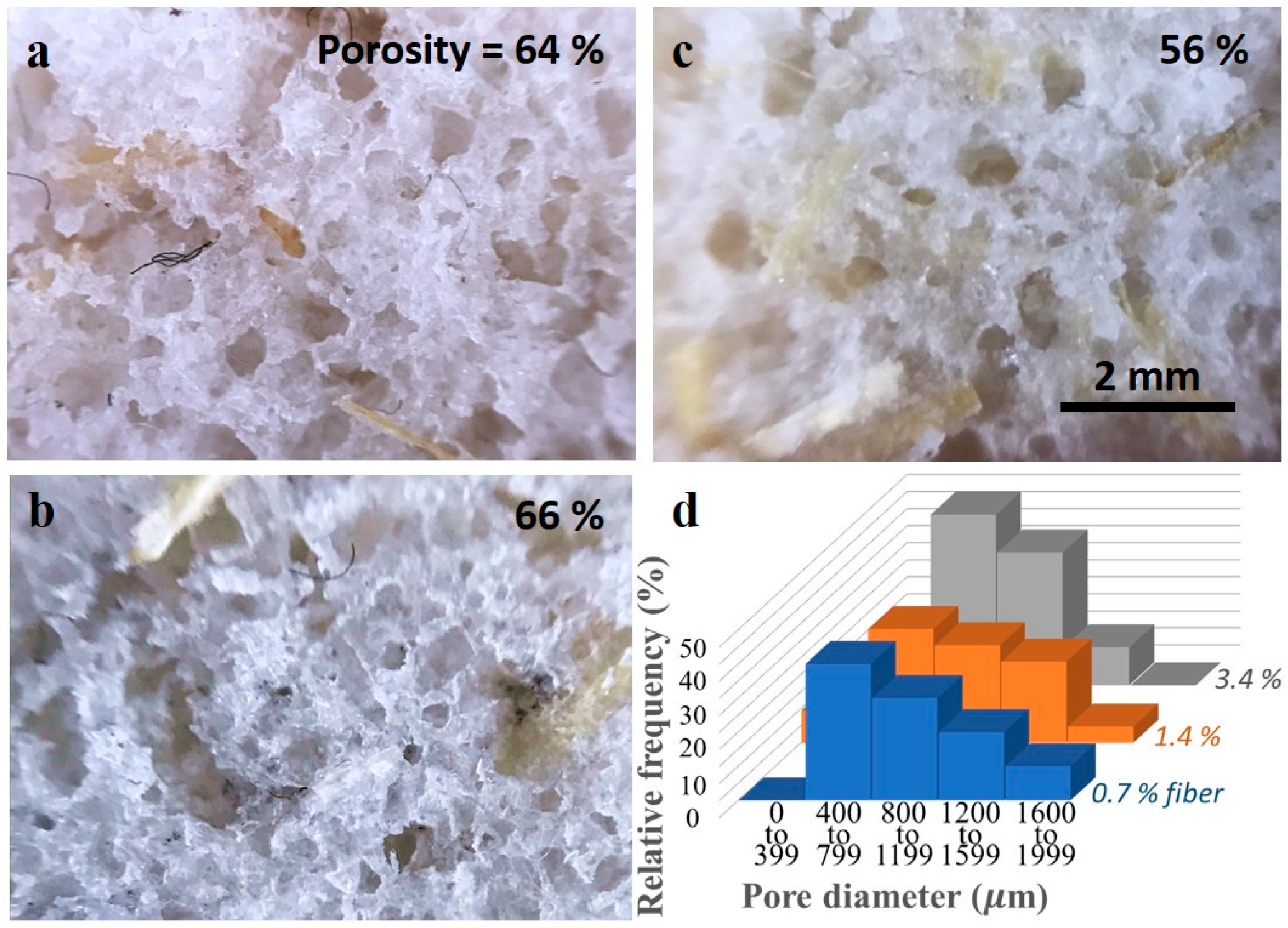
Porous morphology of bamboo fiber-reinforced PDMS (BF-PDMS) foams can be observed in Figure 5. BF-PDMS foams have an open cell structure in which pores are interconnected throughout the foam: such an interconnected pore structure is important for oil/absorption. Bamboo fibers are embedded in the PDMS cell walls and traverse across a few pores. Distribution of pore size is shown in Figure 5d. The largest percentage of pores in the three loadings lie between 400 to 799 micrometers with the maximum pore size observed at about 2000 micrometers.
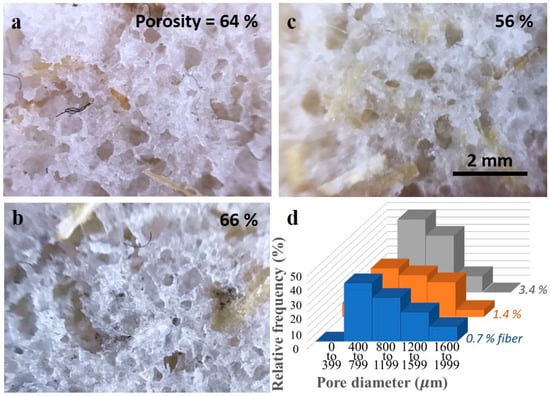
Figure 5.
Optical microscopy images of BF-PDMS with (a) 0.7%, (b) 1.4%, and (c) 3.4% fiber loadings. Distribution of pore size is given in (d).
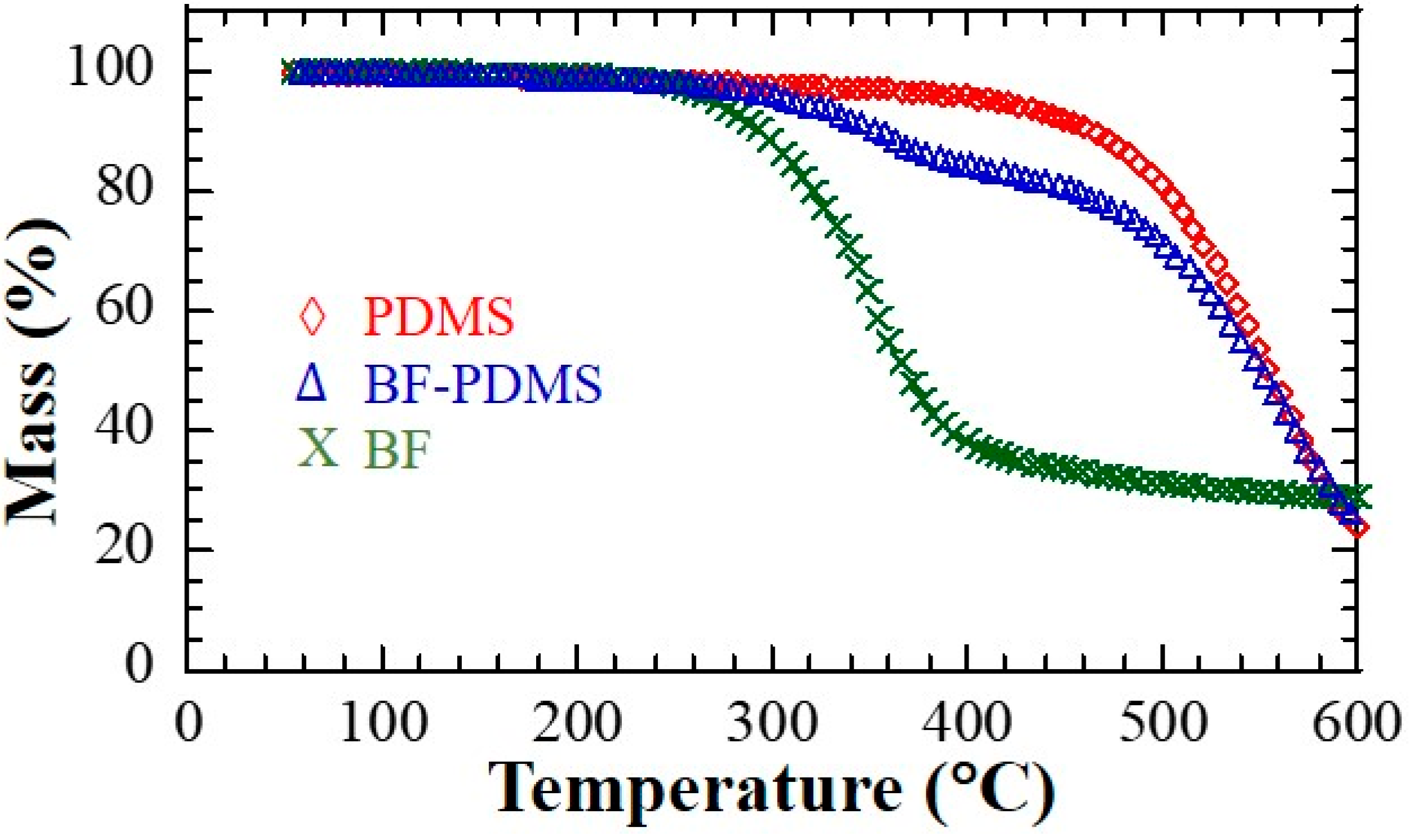
Thermogravimetric results are shown in Figure 6. The temperature corresponding to 5% mass loss (Td5%) for PDMS, BF-PDMS and treated bamboo fibers are 354.84, 307.49, and 265.82 °C, respectively. A recent study using similar conditions reported Td5% of 360 °C for pristine PDMS [20]. The 5 °C difference could possibly be due to the porous nature of the PDMS in the current study. A recent study reported a Td5% 236 °C of for bamboo fiber treated with NaOH solution although species of the bamboo used were not stated [21]. Mass loss in natural fibers starts with decomposition of hemicellulose which takes place between 220 and 315 °C with maximum mass loss at 268 °C which is very close to the Td5% value observed in this study [22,23]. It must be noted that onset for mass loss in BF-PDMS starts at around 270 °C which is most likely due to hemicullelose degradation in the bamboo fiber.
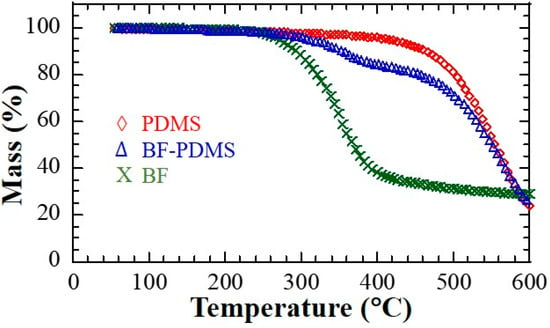
Figure 6.
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) curves of bamboo fiber (BF), bamboo fiber-reinforced polydimethylsiloxane (BF-PDMS), and polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) under N2 atmosphere at the heating rate of 10 °C/min.
Analysis of the compression response was carried out by modifying the model proposed by Alzoubi et al. [19]. Since responses of PDMS foams and BF-PDMS composite foams lack a linear elastic region, the corresponding elastic stress component in Equation (1) was removed to obtain the relationship below.
A fitting of Equation (2) was made to stress–strain curves to extract and which are the spring constant in plateau region and densification coefficient, respectively. The polynomial exponent, , of nonlinear spring element in densification region for many foam materials, for example, the polynomial exponent for families of latexes and polyurethanes is 4, and this value is assumed for PDMS [15]. Nonlinear curve fitting of Equation (2) to responses were done using the Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm in which a chi square value representing the sum of squared error between the original data and calculated fit were computed. The algorithm varies parameter values slightly and re-evaluates chi square repeatedly until the best fit is obtained.
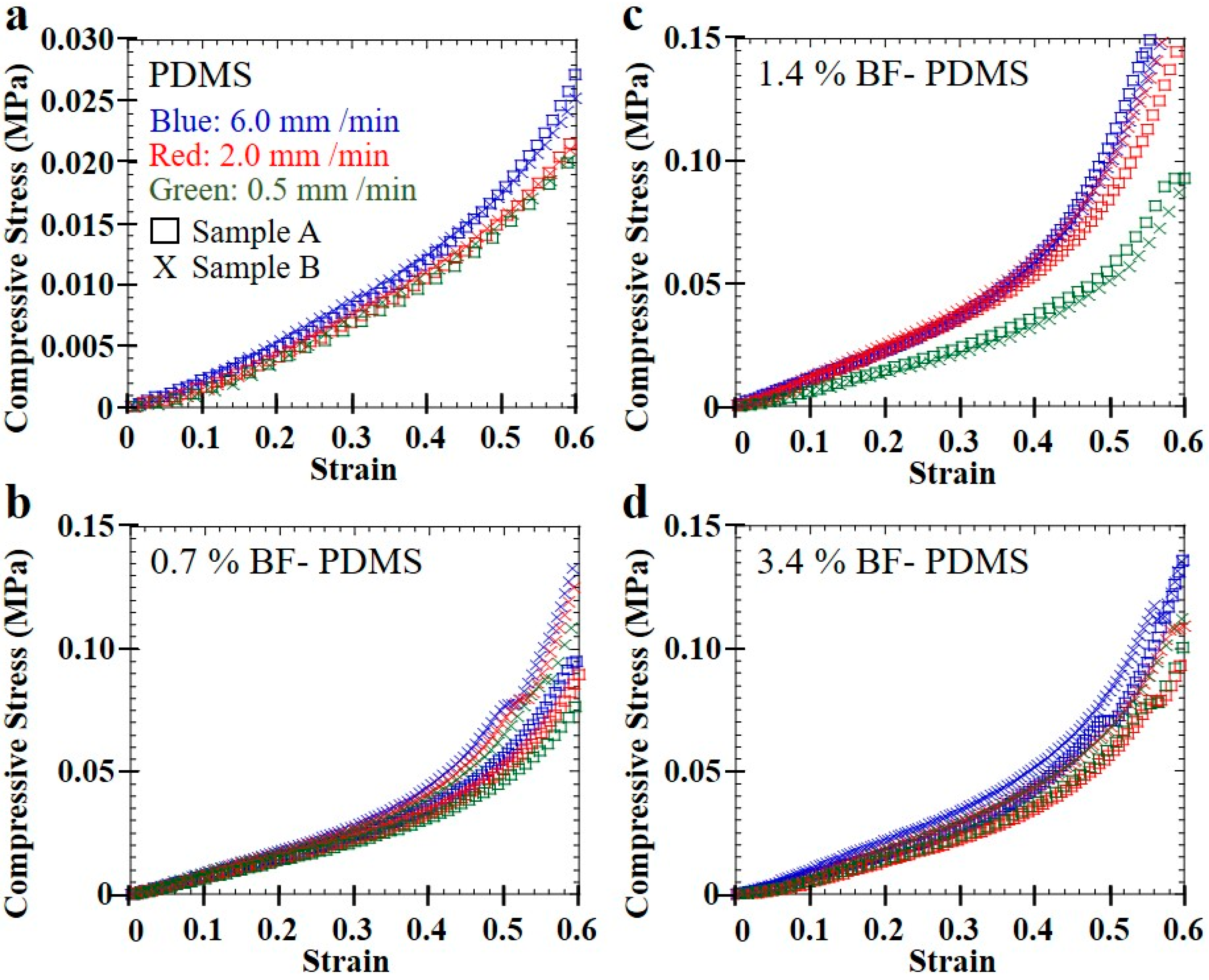
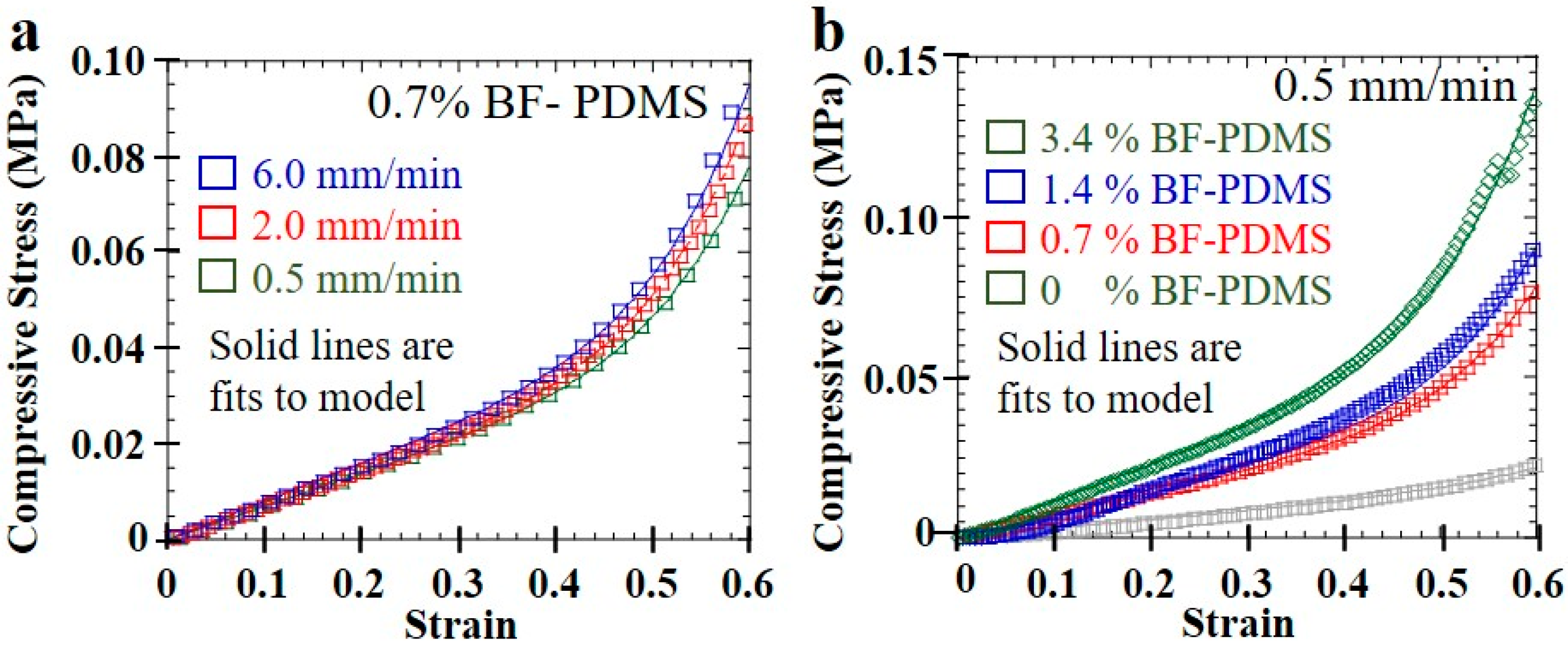
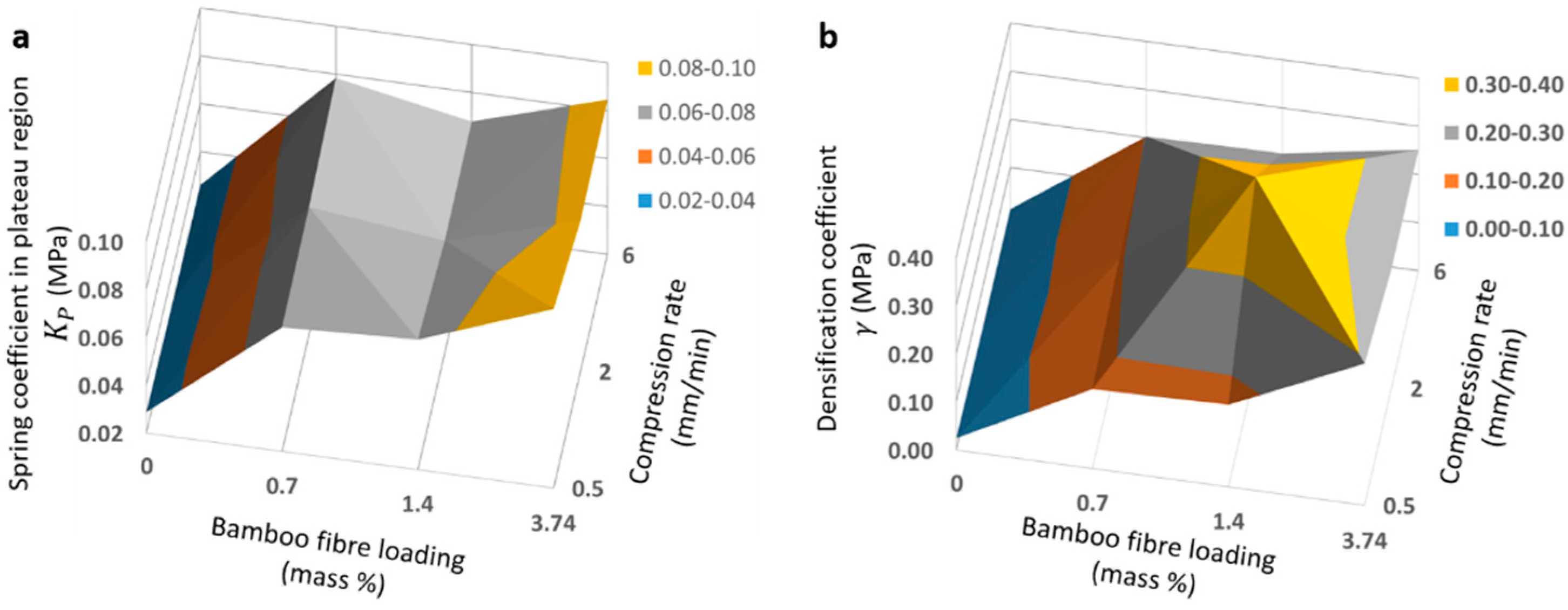
Typical compression stress–strain curves of pristine PDMS and BF-PDMS samples shown in Figure 7. Excellent fits were obtained between the modified phenomenological foam model and stress–strain curves. Figure 8 shows representative stress–strain curves and fits—shown as solid lines—for various compression rates at 0.7% BF loading and for various BF loadings at 0.5 mm/min. For each stress–strain curve, at least 1000 data points were collected for fitting although a fraction of the data points were plotted to aid visualizing the fit solid lines. Fits for 0, 0.7 and 3.4% BF loading have values of 0.99 and those for 1.4% BF loading have values of 0.98. The extracted spring constants in plateau region, , and densification coefficients, , are shown in Table 2 while Figure 9 are the corresponding surface plots.
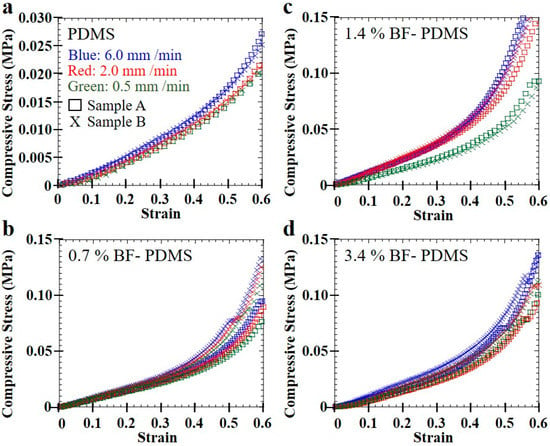
Figure 7.
Compression stress–strain curves of (a) PDMS, (b) 0.7%, (c) 1.4%, and (d) 3.4% BF-PDMS.
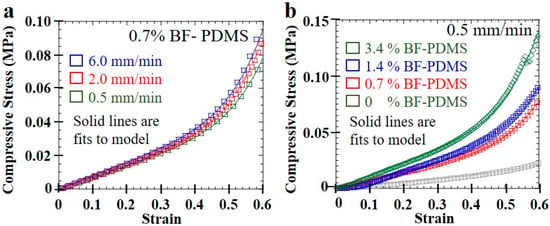
Figure 8.
Fits of modified phenomenological model to compression stress–strain curves of (a) 0.7% BF-PDMS samples at various compression rates and (b) BF-PDMS samples with various BF loadings at 0.5 mm/min compression rate.

Table 2.
Computed best fit values of and .
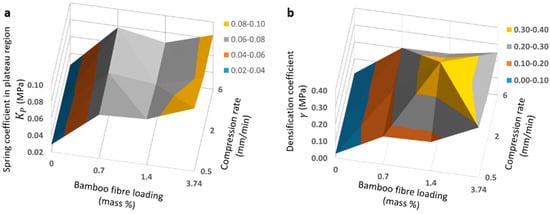
Figure 9.
Surface plots visualizes effect of compression rate and bamboo fiber loading on (a) spring coefficient in plateau region and (b) densification coefficient .
In general, values of extracted spring constants in plateau region, , and densification coefficients, , increase with BF loading for all compression rates. Only values at 2.0 mm/min and 6.0 mm/min and value at 2.0 mm/min for 1.4% BF-PDMS foam do not follow this trend. Compared to PDMS foam, the and of BF-PDMS foams are larger. and of 0.7% BF-PDMS foam is approximately 2.5- and 7-fold greater than those of the PDMS foam which explains why the compressive stress for BF-PDMS is approximately 5-fold greater than that for PDMS foams.
The larger ratio for suggests presence of bamboo fibers has a greater effect on mechanical response during densification than during the plateau region. In contrast, there is no apparent trend in and with compression rate. However, compression test results suggest dependence of mechanical response on compression rates. Stress–strain curves of a sample are highest when foams were compressed at 6.0 mm/min and the lowest when compressed at 0.5 mm/min although the difference between them is small.
Rate-dependence of elastic response in polymer systems is well known and has been explained on the basis of different molecular motions at various time regimes [24]. Recent studies have reported dependence of elastic moduli on strain rate for virgin and prestrained pristine PDMS [25]. With its emergence as a leading material for flexible pressure sensors, the strain-rate dependence of mechanical properties of carbon-filled PDMS have been reported [14]. Increasing the cross-head speed from 1 to 32 mm/min increased the stiffness and compressive strengths to a small extent especially at higher strains; similar trends are observed in the current study [14]. Strain-rate dependence in PDMS and its composite are not completely understood. While the current study is not focused on elucidating the mechanism for strain-rate dependence on mechanical property of foams, it is postulated that confinement of PDMS molecules in walls of foams and compounding with bamboo fiber further impede molecular motion; this may further amplify strain-rate dependence.
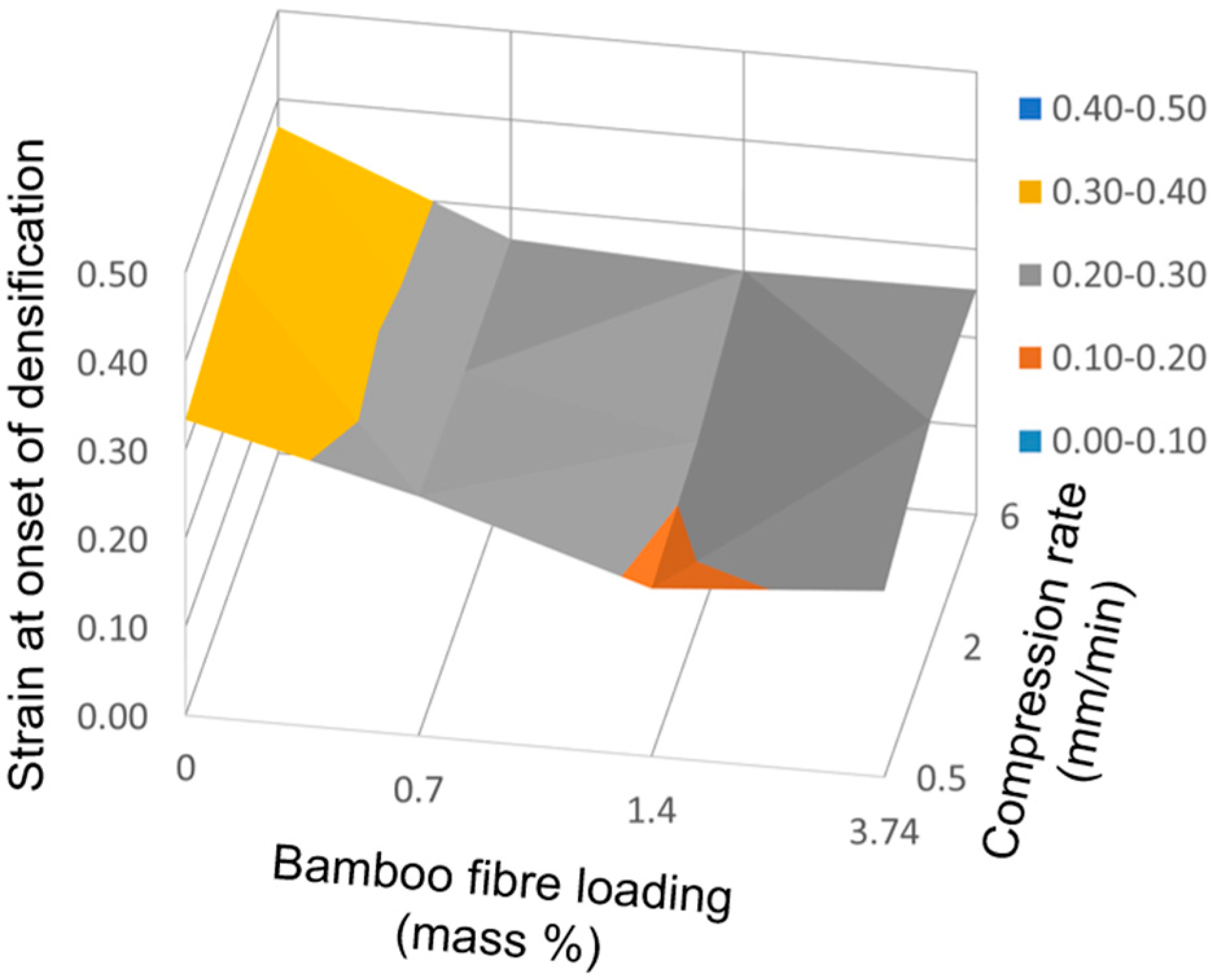
Addition of bamboo fiber hastens onset of densification. Increase in stress with strain is more gradual for PDMS foam and there is no sharp or distinct transition from the plateau region to densification. In contrast, there is a more discernible stress increase once densification starts in BF-PDMS foams, Figure 7. Using the and values computed earlier, we define the strain at onset of densification, , as corresponding to the strain at which the densification stress component is equal to 2% of the total stress. Strain at onset of densification decreases as fiber loading increases. However, no clear effect dependence on compression rate was observed is shown in Figure 10.
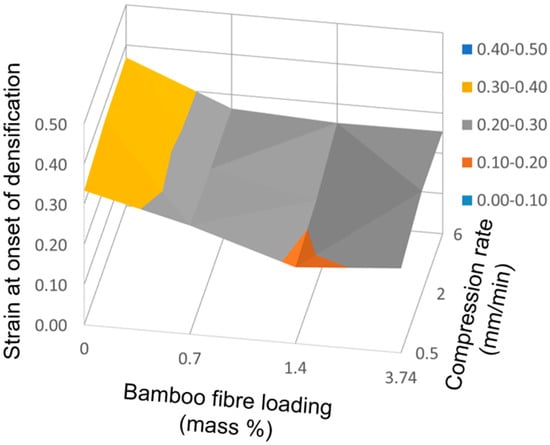
Figure 10.
Surface plot showing variation of strain at onset of densification with compression rate and bamboo fiber loading.
Addition of bamboo fibers affects the mechanical behavior of PDMS foams during compression as shown in Figure 11. Pores in PDMS foams and BF-PDMS composite foams collapse upon application of a compressive force. This compresses fibers as the materials around them folds. The fibers in turn exert a back response on the surrounding material which increases compressive stress and spring coefficient of during the plateau region. This is not present in pristine PDMS and this explains the why for 0.7% BF-PDMS is 2.5 times that of PDMS foam. A larger BF loading would lead to a greater back response and hence, . As compression continues, fibers are packed more closely and facilitate completion of collapse of the porous structure. This in turn lowers the strain at which densification starts and the back response results in a discernible increase in compressive stress for the same amount of strain. As densification proceeds, bamboo fibers are more tightly packed and the back response increases at a higher rate than during the plateau region. Consequently, densification coefficients, , are larger than the spring constants in plateau region, .
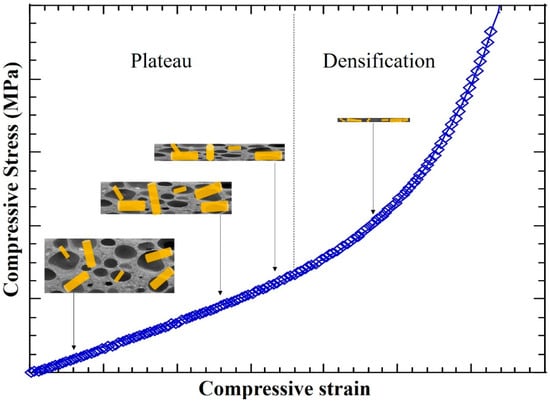
Figure 11.
Visualization of bamboo fiber effect during plateau and densification regions.
5. Conclusions
In summary, mechanical behavior of bamboo fiber reinforced polydimethylsiloxane (BF-PDMS) foams at low fiber loading has been investigated. Pristine PDMS foams and BF-PDMS composite foams were fabricated using a sugar leaching method. Compression test results of pristine PDMS and BF-PDMS composite foams display plateau and densification regions. Predictions of a modified phenomenological foam (PF) model based on Maxwell and Kelvin–Voight models are in good agreement with compression test results. Stiffness coefficients were extracted by fitting results of compression tests to the modified PF model. Spring and densification coefficients of BF-PDMS composite foams are, ~2.5- and 15-fold greater than those of pristine PDMS foams, respectively. Strains corresponding to onset of densification computed were 35% and 25% for pristine PDMS foams and BF-PDMS composite foams, respectively. Compressing foams at 6.0 and 0.5 mm/min results in highest and lowest compressive stress, respectively.
Author Contributions
I.Z. and A.S.Z. conceptualized the project. I.Z., A.N., S.N.Z.A., and N.Z. developed the methodology and collected data. I.Z., A.N., S.N.Z.A., N.Z., and A.S.Z. contributed to writing the manuscript. A.S.Z. supervised the project.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge technical support received from the Mechanical Engineering Programme Area, Universiti Teknologi Brunei.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ba, A.; Kovalenko, A.; Aristégui, C.; Mondain-Monval, O.; Brunet, T. Soft porous silicone rubbers with ultra-low sound speeds in acoustic metamaterials. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuruzi, A.S.; Tuah, M.H.; Daruis, A.; Amirul, A.; Norfatriah, A.; Nurmawati, M.H. Towards wearable pressure sensors using multiwall carbon nanotube/polydimethylsiloxane nanocomposite foams. Mater. Des. 2017, 132, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Handschuh-Wang, S.; Zhou, X. Recent progress in fabrication and application of polydimethylsiloxane sponges. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 16467–16497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-J.; Kwon, T.-H.; Im, H.; Moon, D.-I.; Baek, D.J.; Seol, M.-L.; Duarte, J.P.; Choi, Y.-K. A Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Sponge for the Selective Absorption of Oil from Water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 4552–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Wu, P.; Zhang, S.; Geng, B. Facile preparation of superhydrophobic and superoleophilic porous polymer membranes for oil/water separation from a polyarylester polydimethylsiloxane block copolymer. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 3211–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Cui, L.; Song, Z.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, L. Facile Preparation of the Porous PDMS Oil-Absorbent for Oil/Water Separation. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1600862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Weibel, J.A.; Garimella, S.V. Continuous Oil–Water Separation Using Polydimethylsiloxane-Functionalized Melamine Sponge. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 3596–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.N.H.; Kabiri, S.; Sim, T.R.; Losic, D. Selective adsorption of oil–water mixtures using polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)–graphene sponges. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2015, 1, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Rivera, J.; Iglio, R.; Barillaro, G.; Duce, C.; Tinè, R.M. Structural and Thermoanalytical Characterization of 3D Porous PDMS Foam Materials: The Effect of Impurities Derived from a Sugar Templating Process. Polymers 2018, 10, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, I.; McCluskey, D.; Tan, C.K.L.; Tracey, M. Mechanical characterization of bulk Sylgard 184 for microfluidics and microengineering. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2014, 24, 035017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lötters, J.C.; Olthuis, W.; Veltink, P.H.; Bergveld, P. The mechanical properties of the rubber elastic polymer polydimethylsiloxane for sensor applications. J. Micromech. Microeng. 1997, 7, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, A.; Fleischman, A.J.; Roy, S. Characterization of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Properties. Biomed. Microdevices 2005, 7, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Bian, Z.; Fang, C.; Zhou, X.; Song, J. Experimental and Theoretical Study on Mechanical Properties of Porous PDMS. J. Appl. Mech. 2018, 85, 041009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, A.; Tamburrano, A.; Fortunato, M.; Sarto, M.S. A Flexible and Highly Sensitive Pressure Sensor Based on a PDMS Foam Coated with Graphene Nanoplatelets. Sensors 2016, 16, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghavami, K. Bamboo as Reinforcement in Structural Concrete Elements. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2005, 27, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Guo, Q.; Mi, Y. Bamboo fiber-reinforced polypropylene composites: A study of the mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 69, 1891–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md Shah, A.U.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Jawaid, M.; Cardona, F.; Abu Talib, A.R. A review of on the tensile properties of bamboo fiber reinforced polymer composites. BioResources 2016, 11, 10654–10676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Acosta, D. Sylgard® Cure Inhibition Characterization; Project Report LA-UR-12-25325; Los Alomos National Laboratory: Los Alomos, NM, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzoubi, M.F.; Al-Hallaj, S.; Abu-Ayyad, M. Modeling of Compression Curves of Flexible Polyurethane Foam with Variable Density Chemical Formulations and Strain Rates. J. Solid Mech. 2014, 6, 82–97. [Google Scholar]
- Planes, M.; Le Coz, C.; Soum, A.; Carlotti, S.; Rejsek-Riba, V.; Lewandowski, S.; Remaury, S.; Solé, S. Polydimethylsiloxane/Additive Systems for Thermal and Ultraviolet Stability in Geostationary Environment. J. Spacecr. Rockets 2017, 53, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, F.; Liang, W.; Wang, Z.; Duan, Z.; Yang, B. Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Bamboo Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites. Polymers 2018, 10, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Martins, M.; da Silva, O.; Mattoso, L. Studies on the thermal properties of sisal fiber and its constituents. Thermochim. Acta 2010, 506, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yan, R.; Chen, H.; Lee, D.H.; Zheng, C. Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel 2007, 86, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulliken, A.D.; Boyce, M.C. Mechanics of the rate-dependent elastic–plastic deformation of glassy polymers from low to high strain rates. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2006, 43, 1331–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolini, L.; Iannuzzi, D.; Mattei, G. Comparison of frequency and strain-rate domain mechanical characterization. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).