Heat Transfer in Directional Water Transport Fabrics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
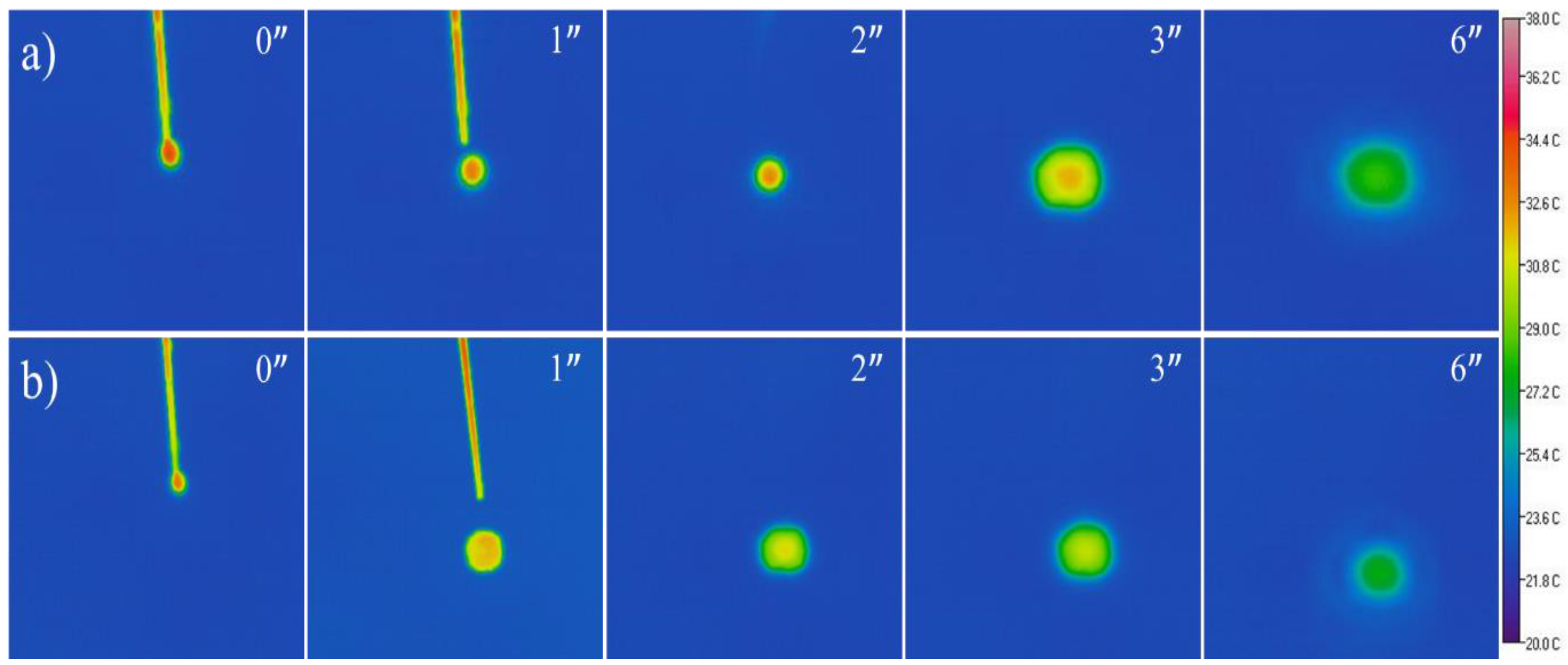
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.; Ding, J.; Dai, L.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Directional water-transfer through fabrics induced by asymmetric wettability. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 7938–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xin, J.H. Fabrics with self-adaptive wettability controlled by “light-and-dark”. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 17978–17987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Dong, H.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L. Unidirectional water-penetration composite fibrous film via electrospinning. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 5996–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Unidirectional water transfer effect from fabrics having a superhydrophobic-to-hydrophilic gradient. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 839–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, H.; Niu, H.; Lin, T. Superphobicity/philicity janus fabrics with switchable, spontaneous, directional transport ability to water and oil fluids. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Jin, H.; Sainio, J.; Ras, R.H.; Ikkala, O. Droplet and fluid gating by biomimetic janus membranes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 6023–6028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Niu, H.; Zhang, J.; Du, Y.; Lin, T. Dual-layer superamphiphobic/superhydrophobic-oleophilic nanofibrous membranes with unidirectional oil-transport ability and strengthened oil-water separation performance. Adv. Mater. Inter. 2015, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Barboiu, M. Dynameric asymmetric membranes for directional water transport. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 15925–15927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenceau, É.; Quéré, D. Drops on a conical wire. J. Fluid Mech. 2004, 510, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Bai, H.; Huang, Z.; Tian, X.; Nie, F.-Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, L. Directional water collection on wetted spider silk. Nature 2010, 463, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.; Tian, X.; Zheng, Y.; Ju, J.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L. Direction controlled driving of tiny water drops on bioinspired artificial spider silks. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 5521–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.; Sun, R.; Ju, J.; Yao, X.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, L. Large-scale fabrication of bioinspired fibers for directional water collection. Small 2011, 7, 3429–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, J.; Bai, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, T.; Fang, R.; Jiang, L. A multi-structural and multi-functional integrated fog collection system in cactus. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Xue, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired spindle-knotted fibers with a strong water-collecting ability from a humid environment. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 11450–11454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Bai, H.; Wu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired electrospun knotted microfibers for fog harvesting. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2012, 13, 1153–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Gao, L.; Feng, S.; Chen, Y.; Xue, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zheng, Y. Temperature-triggered directional motion of tiny water droplets on bioinspired fibers in humidity. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 5253–5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Xue, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zheng, Y. Bioinspired tilt-angle fabricated structure gradient fibers: Micro-drops fast transport in a long-distance. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhury, M.K.; Whitesides, G.M. How to make water run uphill. Science 1992, 256, 1539–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, S.; Chaudhury, M.K.; Chen, J.C. Fast drop movements resulting from the phase change on a gradient surface. Science 2001, 291, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.-H.; Zhang Newby, B.-M. Micrometer-scaled gradient surfaces generated using contact printing of octadecyltrichlorosilane. Langmuir 2003, 19, 7427–7435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, T.; Stutz, R.; Balmer, T.E.; Schmid, H.; Malaquin, L.; Spencer, N.D.; Wolf, H. Printing chemical gradients. Langmuir 2005, 21, 7796–7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, X. Surface gradient material: From superhydrophobicity to superhydrophilicity. Langmuir 2006, 22, 4483–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blondiaux, N.; Zürcher, S.; Liley, M.; Spencer, N.D. Fabrication of multiscale surface-chemical gradients by means of photocatalytic lithography. Langmuir 2007, 23, 3489–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Feng, Y.; Ye, X.; Zhou, Z. Tuning wettability and getting superhydrophobic surface by controlling surface roughness with well-designed microstructures. Sens. Actuators A 2006, 130, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhao, X.-W.; Han, Y.-H.; Gu, Z.-Z. Control of water droplet motion by alteration of roughness gradient on silicon wafer by laser surface treatment. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 4059–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncombe, T.A.; Erdem, E.Y.; Shastry, A.; Baskaran, R.; Böhringer, K.F. Controlling liquid drops with texture ratchets. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1545–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommers, A.; Brest, T.; Eid, K. Topography-based surface tension gradients to facilitate water droplet movement on laser-etched copper substrates. Langmuir 2013, 29, 12043–12050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Ju, J.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, L. Asymmetric ratchet effect for directional transport of fog drops on static and dynamic butterfly wings. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Kong, J.; Phua, S.L.; Zhao, C.; Thomas, N.L.; Lu, X. Tailoring surface hydrophilicity of porous electrospun nanofibers to enhance capillary and push–pull effects for moisture wicking. ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 14087–14095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Yang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Fang, J.; Lin, T. Selective, Spontaneous One-Way Oil-Transport Fabrics and Their Novel Use for Gauging Liquid Surface Tension. ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 22874–22880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.; Han, K.; Heng, L.; Cao, M.; Jiang, L. Ordered porous structure hybrid films generated by breath figures for directional water penetration. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 88471–88476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Xiao, J.; Yu, C.; Li, K.; Jiang, L. Hydrophobic/hydrophilic cooperative Janus system for enhancement of fog collection. Small 2015, 11, 4379–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, C.; Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Lin, T. Directional Water Transport Fabrics with Durable Ultra-High One-Way Transport Capacity. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 3, 1600036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mates, J.E.; Schutzius, T.M.; Qin, J.; Waldroup, D.E.; Megaridis, C.M. The fluid diode: Tunable unidirectional flow through porous substrates. ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 12837–12843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Fan, J. Study of heat and moisture transfer within multi-layer clothing assemblies consisting of different types of battings. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2008, 47, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanković, S.B.; Popović, D.; Poparić, G.B. Thermal properties of textile fabrics made of natural and regenerated cellulose fibers. Polym. Test. 2008, 27, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhang, W. Clothing thermal insulation during sweating. Text. Res. J. 2003, 73, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Yadav, R. Thermal properties of knitted fabrics made from cotton and regenerated bamboo cellulosic fibres. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2010, 49, 2042–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath, M.; Aruputharaj, A.; Senthilkumar, M.; Nalankilli, G. Analysis of thermal comfort characteristics of moisture management finished knitted fabrics made from different yarns. J. Ind. Text. 2012, 42, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Improving thermal conductivity of cotton fabrics using composite coatings containing graphene, multiwall carbon nanotube or boron nitride fine particles. Fibers Polym. 2013, 14, 1641–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Lin, T. Self-cleaning, superhydrophobic cotton fabrics with excellent washing durability, solvent resistance and chemical stability prepared from an SU-8 derived surface coating. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 61044–61050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
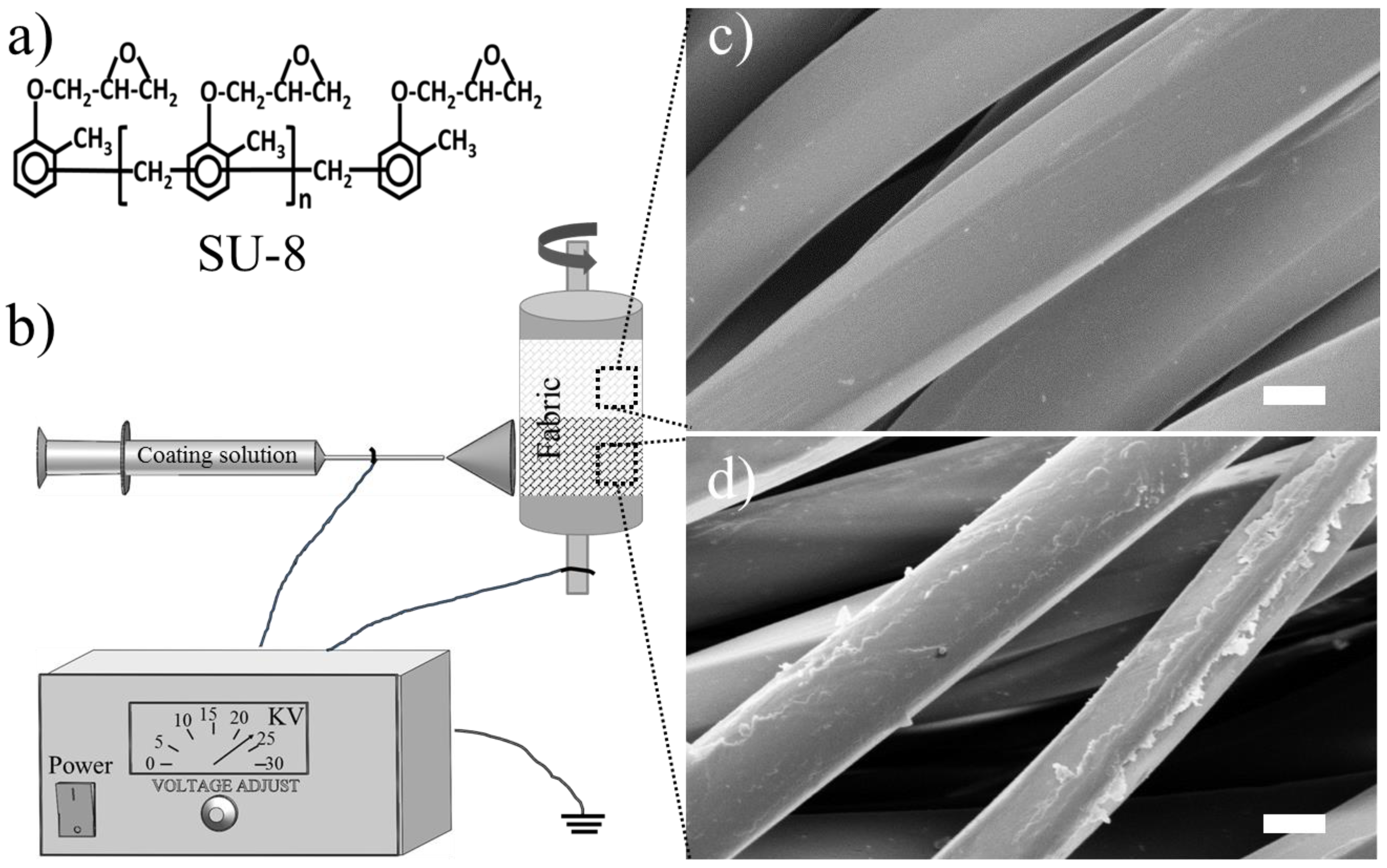
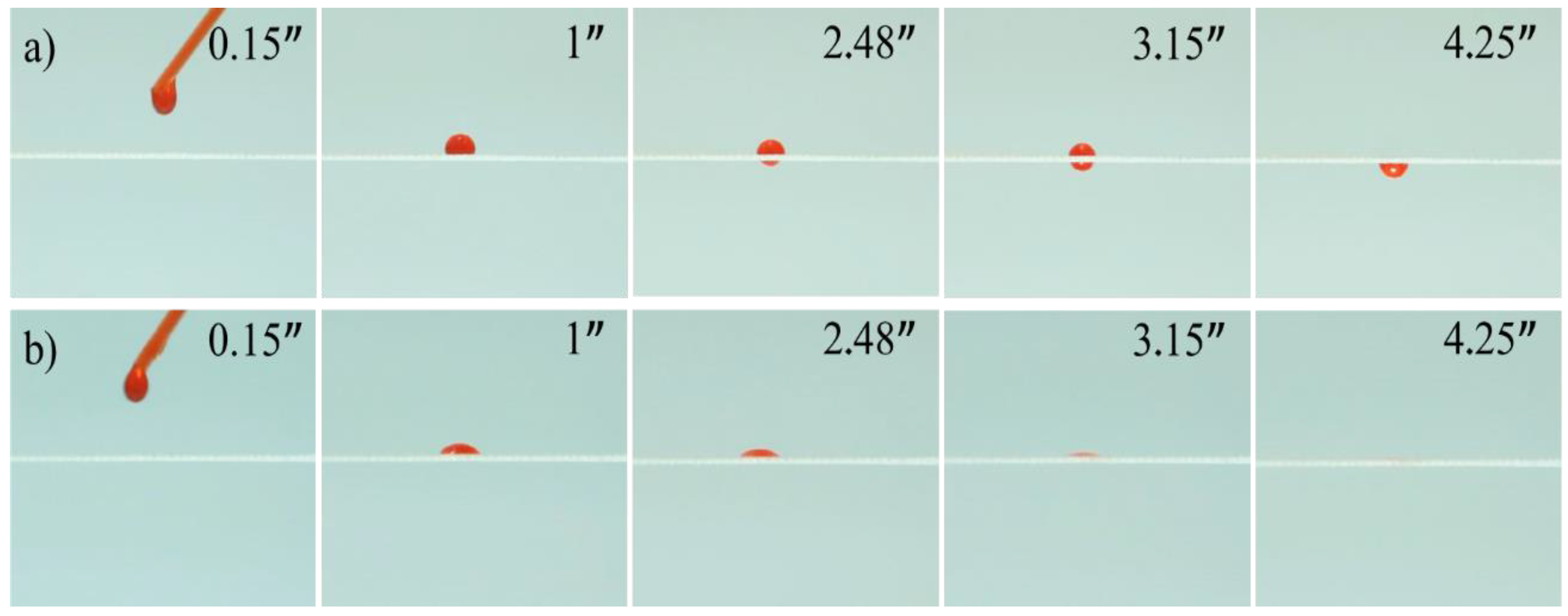
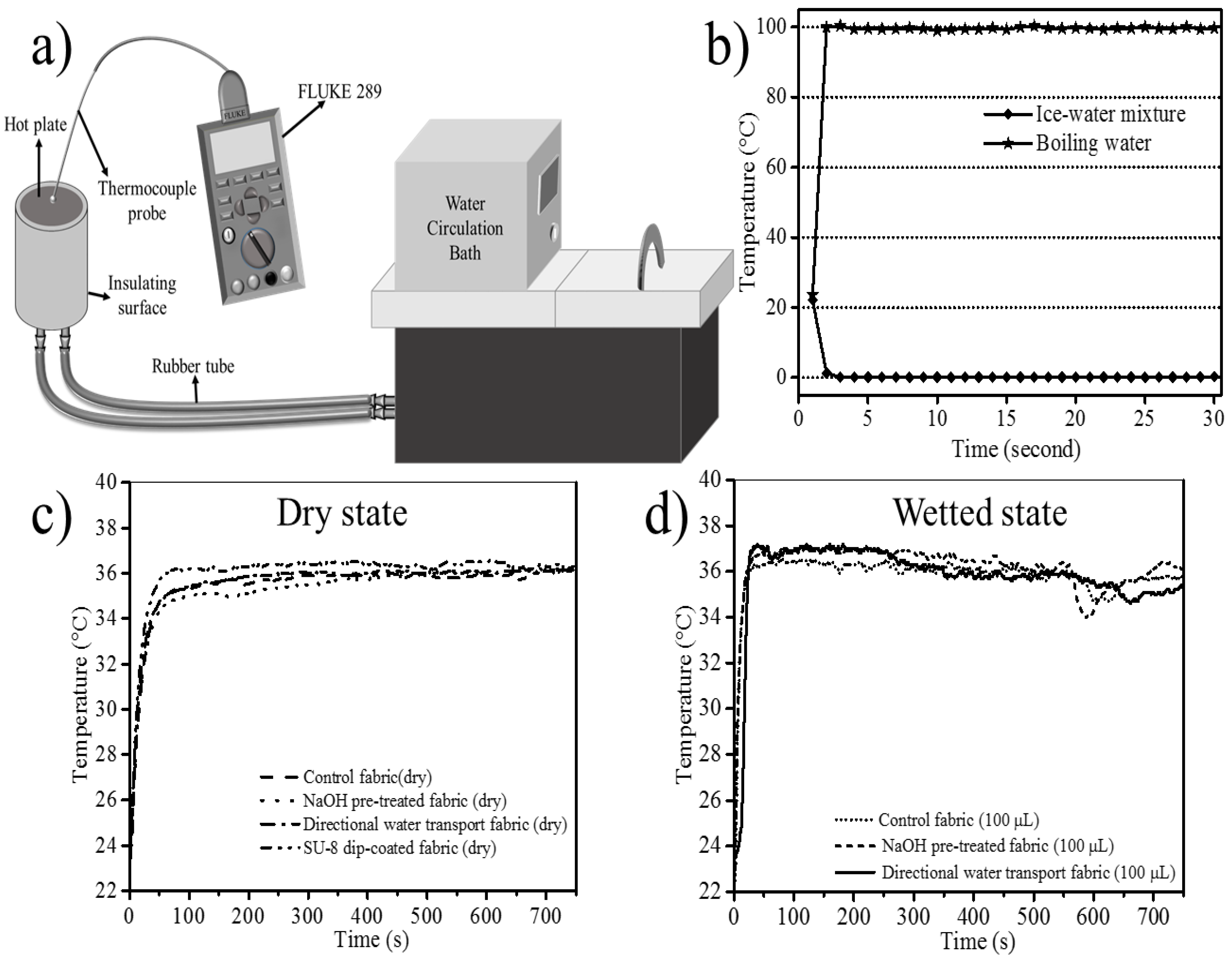
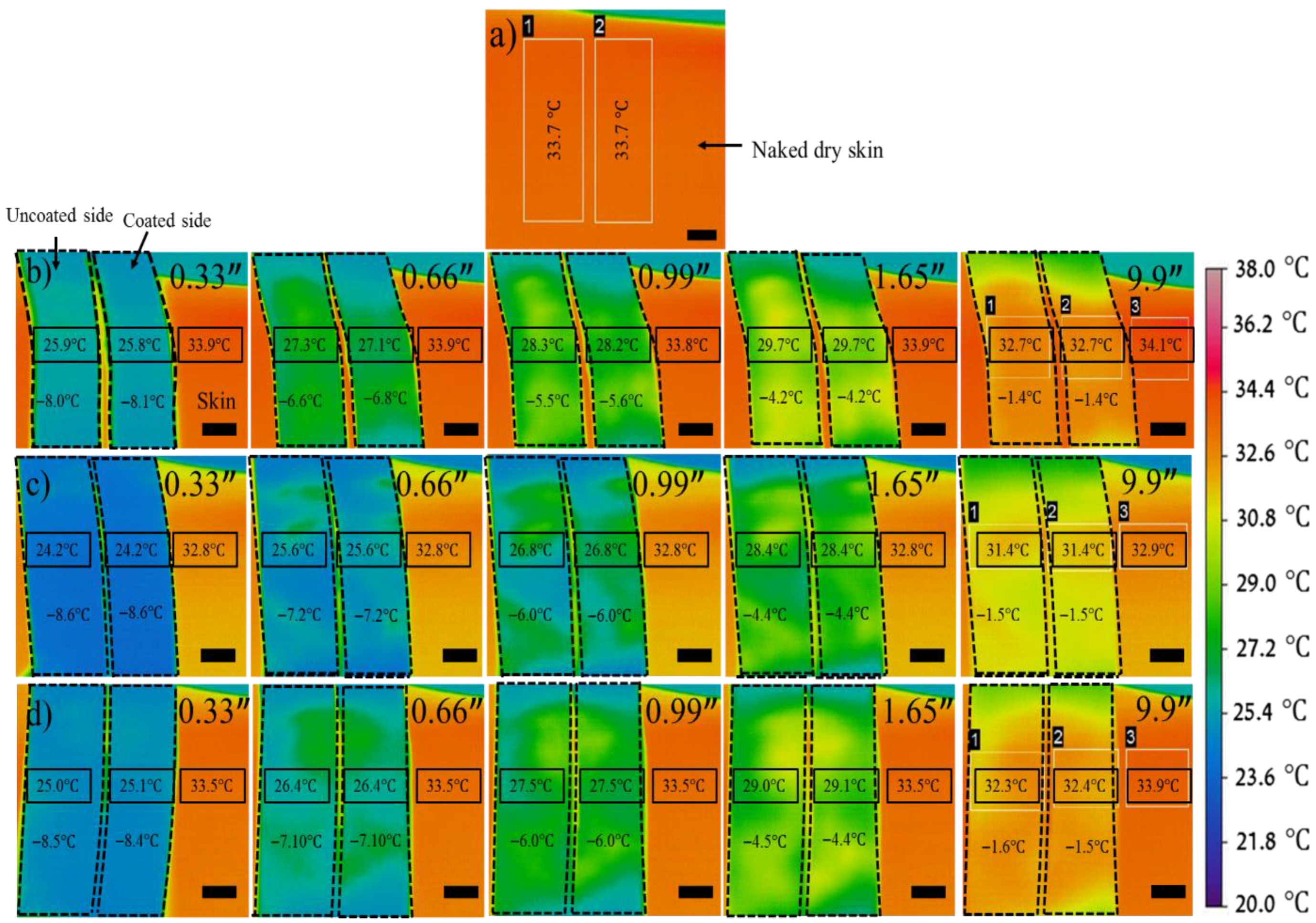
| Fabric Type | Method | WCA (°) | Water Transport | Thermal Conductivity (mW/mK) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | - | 118 | Bidirectional | 59.7 ± 1.0 (dry) |
| 405.4 ± 4.2 (wetted) | ||||
| NaOH treated | Immersing in NaOH solution | 0 | Bidirectional | 54.6 ± 1.4 (dry) |
| 436.2 ± 5.6 (wetted) | ||||
| Directional water transport | SU-8 single-side electrospraying | 131 * on the coated side, and 0 on uncoated side | Unidirectional (from the coating to uncoated) | 61.3 ± 1.5 (dry) |
| 316.3 ± 3.2 (wetted) | ||||
| SU-8 dip-coated | SU-8 dip coating | 131 on both sides | No transport | 62.5 ± 1.0 (dry) |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, C.; Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Lin, T. Heat Transfer in Directional Water Transport Fabrics. Fibers 2016, 4, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib4040026
Zeng C, Wang H, Zhou H, Lin T. Heat Transfer in Directional Water Transport Fabrics. Fibers. 2016; 4(4):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib4040026
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Chao, Hongxia Wang, Hua Zhou, and Tong Lin. 2016. "Heat Transfer in Directional Water Transport Fabrics" Fibers 4, no. 4: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib4040026
APA StyleZeng, C., Wang, H., Zhou, H., & Lin, T. (2016). Heat Transfer in Directional Water Transport Fabrics. Fibers, 4(4), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib4040026






