Glass Fibre Strength—A Review with Relation to Composite Recycling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Strength of Glass Fibre
2.1. Flaws
2.2. Strength Loss of Heat-Treated Glass Fibre
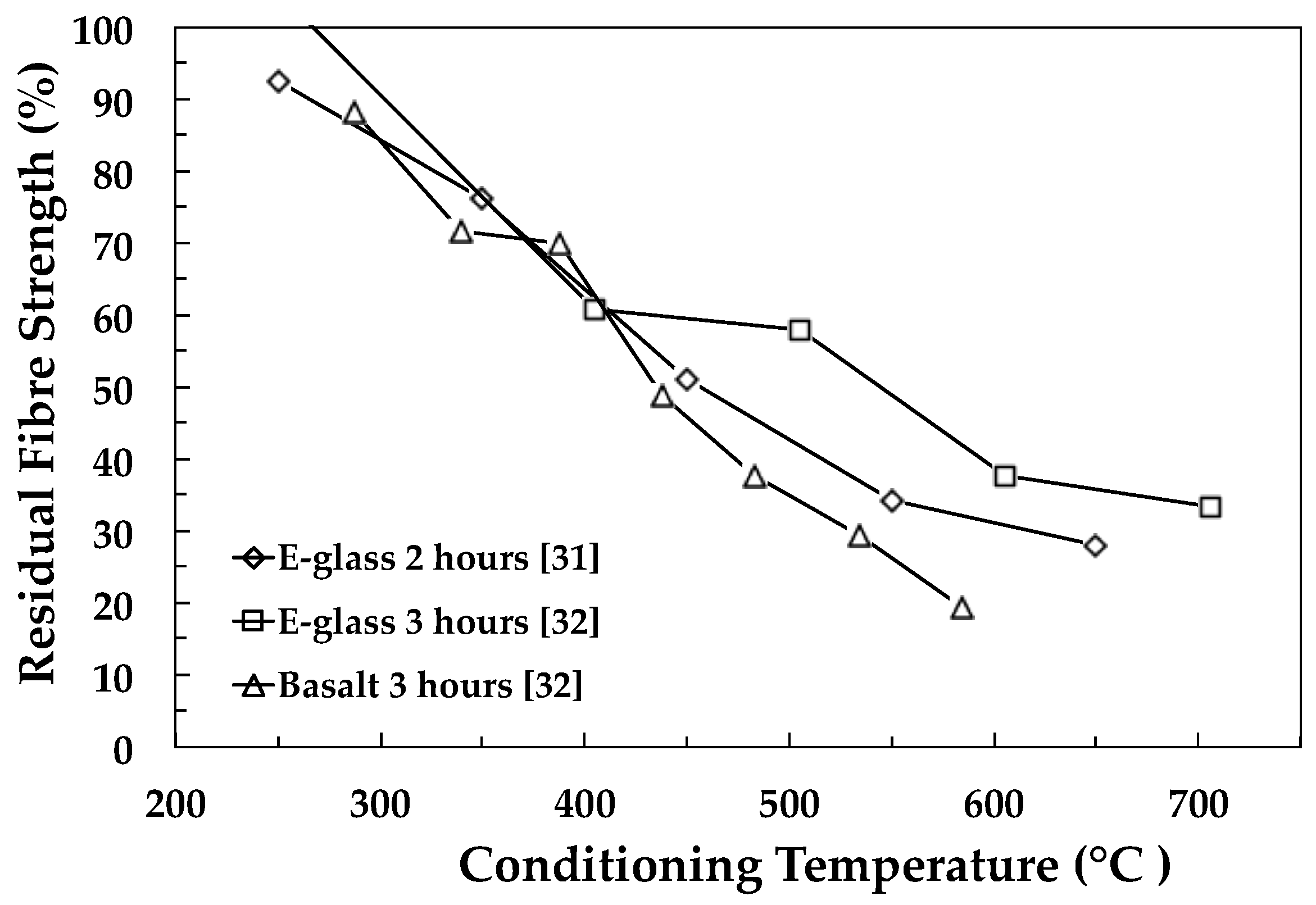
2.2.1. Temperature and Time Effects
2.2.2. The Effect of Heating Atmosphere
2.2.3. The Effect of Heat Treatment under Stress
2.3. Physical Changes Following Heat Treatment
2.3.1. Thermal Compaction or Enthalpy Relaxation
2.3.2. Anisotropy (Birefringence) Relaxation
2.3.3. Crystallisation
2.3.4. Ion Exchange
3. The Role of Water and Hydroxyls
3.1. Hydroxyl Groups
3.2. Interaction with Water
4. The Role of Silanes and Sizings
5. Glass Fibre Recycling and Reuse as Reinforcements
6. Glass Fibre Strength Regeneration and Reuse
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GMT | Glass mat thermoplastic |
| APS | Aminopropylsilane |
| DMC | Dough moulding compound |
| DSC | Differential scanning calorimetry |
| FBC | Fluidized bed combustion |
| GF | Glass fibre |
| RGF | Recycled glass fibre |
| SMC | Sheet moulding compound |
| Tg | Glass transition temperature |
| TGA | Thermo-gravimetric analysis |
References
- Owens Corning Investor Presentation (Slide 22). Available online: http://s1.q4cdn.com/942908807/files/doc_presentations/2015/Q3/Q3-Presentation-v9.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2016).
- Li, H.; Watson, J.C. Continuous glass fibers for reinforcement. In Encyclopaedia of Glass Science, Technology, History and Culture; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Thomason, J.L. Glass Fibre Sizing: A Review of Size Formulation Patents. Blurb Incorporated 2015. Available online: http://www.blurb.co.uk/b/6244662-glass-fibre-sizing (accessed on 3 February 2016).
- Derosa, R.; Telfeyan, E.; Mayes, J.S. Current state of recycling sheet molding compounds and related materials. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2005, 18, 219–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, S.J. Recycling technologies for thermoset composite materials-current status. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 1206–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, J.L.; Perrin, D.; Sonnier, R. Waste management, recycling and regeneration of filled polymers. In Handbook of Multiphase Polymer Systems; Boudenne, A., Ibos, L., Candau, Y., Thomas, S., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 921–957. [Google Scholar]
- Goodship, V. Recycling issues in polymer matrix composites. In Failure Mechanisms in Polymer Matrix Composites: Criteria, Testing and Industrial Applications; Robinson, P., Greenhalgh, E., Pinho, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 336–366. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Boom, R.; Irion, B.; van Heerden, D.J.; Kuiper, P.; de Wit, H. Recycling of composite materials. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2012, 51, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, S. Recycling glass fibre reinforced composites—History and progress. Reinf. Plast. 2013, 57, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, S. Recycling composites commercially. Reinf. Plast. 2014, 58, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanbakhsh, A.; Bank, L.C. A critical review of research on reuse of mechanically recycled FRP production and end-of-life waste for construction. Polymers 2014, 6, 1810–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.; Soulliere, K.; Sawyer-Beaulieu, S.; Tseng, S.; Tam, E. Challenges and alternatives to plastics recycling in the automotive sector. Materials 2014, 7, 5883–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmatulu, E.; Twomey, J.; Overcash, M. Recycling of fiber-reinforced composites and direct structural composite recycling concept. J. Compos. Mater. 2014, 48, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauson, J.; Lilholt, H.; Brøndsted, P. Recycling solid residues recovered from glass fibre-reinforced composites—A review applied to wind turbine blade materials. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2014, 33, 1542–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveux, G.; Dandy, L.O.; Leeke, G.A. Current status of recycling of fibre reinforced polymers: Review of technologies, reuse and resulting properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 72, 61–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybicka, J.; Tiwari, A.; Leeke, G.A. Technology readiness level assessment of composites recycling technologies. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, J.L.; Nagel, U.; Yang, L.; Sáez, E. Regenerating the strength of thermally recycled glass fibres using hot sodium hydroxide. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman, B. Strength of Glass (A Review). J. Mater. Sci. 1967, 2, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.K. Strength of glass fibers. In Fiber Fracture; Elices, M., Llorca, J., Eds.; Elsevier Science Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2002; pp. 127–153. [Google Scholar]
- Kurkjian, C.R.; Gupta, P.K.; Brow, R.K.; Lower, N. The intrinsic strength and fatigue of oxide glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2003, 316, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, A.A. The Phenomena of Rupture and Flow in Solids. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1921, 221, 163–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Practice for Fractography and Characterization of Fracture Origins in Advanced Ceramics; ASTM C1322-05b; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010.
- Sakka, S. Effects of reheating on strength of glass fibers. Bull. Inst. Chem. Res. 1957, 34, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, W.F. An investigation of the factors likely to affect the strength and properties of glass fibres. Phys. Chem. Glasses 1960, 1, 4–18. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, N.M. The effect of environment and temperature on the strength of E-glass fibres. Part 2. Heating and ageing. Glass Technol. 1968, 9, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, N.M. Effect of prior heat treatment on the strength of glass fibers measured at room temperature. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1965, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brearley, W.; Holloway, D.G. The effect of heat-treatment on the breaking strength of glass. Phys. Chem. Glasses 1963, 4, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Piggott, M.R.; Yokom, J.C. The weakening of silica fibres by heat treatment. Glass Technol. 1968, 9, 172–175. [Google Scholar]
- Aslanova, M.S. The effect of different factors on the mechanical properties of glass fibers. Steklo Keram. 1960, 17, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorzhiev, D.B.; Khazanov, V.E.; Gorbachev, V.V. Some features of the structure and strength of a magnesium aluminosilicate fiber. Sov. J. Glass Phys. Chem. 1990, 15, 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Feih, S.; Boiocchi, E.; Mathys, Z.; Gibson, A.G.; Mouritz, A.P. Mechanical properties of thermally-treated and recycled glass fibres. Compos. B Eng. 2011, 42, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, M.D.; Yue, Y. Impact of drawing stress on the tensile strength of oxide glass fibers. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 93, 3236–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, M.D. Tensile Strength of Glass Fibres. Ph.D. Thesis, Aalborg University, Aalborg, Denmark, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Korwin-Edson, M.L.; Hofmann, D.A.; McGinnis, P.B. Strength of high performance glass reinforcement fiber. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 2012, 3, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militky, J.; Kovacic, V.; Rubnerova, J. Influence of thermal treatment on tensile failure of basalt fibers. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2002, 69, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, P.G.; Riopedre-Méndez, S.; Sáez, E.R.; Yang, L.; Thomason, J.L. Investigation of the strength of thermally conditioned basalt and E-glass fibres. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Composite Materials (ICCM20), Copenhagen, Denmark, 19–24 July 2015.
- Sabet, S.M.M.; Akhlaghi, F.; Eslami-Farsani, R. The effect of thermal treatment on tensile properties of basalt fibers. J. Ceram. Sci. Tech. 2015, 6, 245–248. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, N.M. The Effect of Annealing on the Room Temperature Strength of Glass Fibres. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, Champaign, IL, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Thomason, J.L.; Kao, C.C.; Ure, J.; Yang, L. The strength of glass fibre reinforcement after exposure to elevated composite processing temperatures. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, J.L.; Yang, L.; Meier, R. The properties of glass fibres after conditioning at composite recycling temperatures. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 61, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, P.G.; Yang, L.; Liggat, J.J.; Thomason, J.L. Investigation of the strength loss of glass fibre after thermal conditioning. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pico, D.; Bartl, A. Chemical treatment of glass fibers after composite recycling process. In Proceedings of the ISWA World Congress, Hamburg, Germany, 15–18 November 2010.
- Bartenev, G.M.; Motorina, L.I. Effect of tensile stresses on the strength of heat-treated glass fibers. Mekhanika Polim. 1965, 1, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezzi, P.J.; Xiao, Q.R.; Tomozawa, M.; Blanchet, T.A.; Kurkjian, C.R. Strength increase of silica glass fibers by surface stress relaxation: A new mechanical strengthening method. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2013, 379, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezzi, P.J.; Seaman, J.H.; Tomozawa, M. Strengthening of E-glass fibers by surface stress relaxation. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2014, 402, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, W.H. Compaction effects in glass fibers. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1961, 44, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, W.H.; Preston, F.W. Evidence against oriented structure in glass fibres. J. Soc. Glass Technol. 1950, 34, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Aslanova, M.S.; Ivanov, N.V.; Balashov, Y.S. Effect of chemical composition on the relaxation properties of thin glass fibers. Steklo Keram. 1970, 8, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Stockhorst, H.; Brückner, R. Structure sensitive measurements on E-glass fibers. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1982, 49, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya, M.; Deubener, J.; Yue, Y. Enthalpy and anisotropy relaxation of glass fibers. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 91, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Jensen, S.L.; Christiansen, J. Physical aging in a hyperquenched glass. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 2983–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y. Features of the relaxation in hyperquenched inorganic glasses during annealing. Phys. Chem. Glasses 2005, 46, 354–358. [Google Scholar]
- Deubener, J.; Yue, Y.; Bornhöft, H.; Ya, M. Decoupling between birefringence decay, enthalpy relaxation and viscous flow in calcium boroalumosilicate glasses. Chem. Geol. 2008, 256, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Thomason, J.L. The thermal behaviour of glass fibre investigated by thermomechanical analysis. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 5768–5775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Arruda, E.M.; Schultz, W.W. The effect of processing parameters on glass fiber birefringence development and relaxation. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 1999, 86, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Korsgaard, M.; Kirkegaard, L.F.; Heide, G. Formation of a nanocrystalline layer on the surface of stone wool fibers. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 92, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakasugi, T.; Burgner, L.L.; Weinberg, M.C. A DTA study of crystal nucleation in Na2O-SiO2 glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1999, 244, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Olabi, A.G. Effect of nucleation temperature and time on crystallization behaviour of zirconia/zircon added borosilicate glass. In Proceedings of the ECCM15—15th European Conference on Composite Materials, Venice, Italy, 24–28 June 2012.
- Gy, R. Ion exchange for glass strengthening. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2008, 149, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshneya, A.K. Chemical strengthening of glass: Lessons learned and yet to be learned. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 2010, 1, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallenberger, F.T.; Watson, J.C.; Hong, L. Glass Fibers. In ASM Handbook, Volume 21: Composites; ASM International: Novelty, OH, USA, 2001; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kistler, S.S. Stresses in glass produced by nonuniform exchange of monovalent ions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1962, 45, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, D.; Hercules, D.M.; Peek, R.C.; Vaughan, D.J. Application of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy to the study of fiberglass surfaces. Appl. Spectrosc. 1974, 28, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, A.C.; Stratton, R.P.; Lewis, D.B. Investigation of elemental diffusion during the drawing and heat treatment of glass optical fibres. J. Mater. Sci. 1994, 29, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R. Recent aspects of glass fiber-resin interfaces. J. Adhes. 1972, 4, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, J.L.; Dwight, D.W. The use of XPS for characterisation of glass fibre coatings. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1999, 30, 1401–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Thomason, J.L.; Jones, F.R. XPS and AFM study of interaction of organosilane and sizing with E-Glass fibre surface. J. Adhes. 2008, 84, 322–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Jones, F.R.; Denison, P. TOF SIMS and XPS study of the interaction of hydrolysed γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane with E-glass surfaces. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 1992, 6, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesson, S.P.; Jen, J.S.; Nishioka, G.M. Acid-base characteristics of silane- treated E glass fiber surfaces. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 1992, 6, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, M.L. Hydroxyl groups on silica surface. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1975, 19, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, R.A.; Tsomaia, N.; Pantano, C.G.; Mueller, K.T. 19F MAS NMR quantification of accessible hydroxyl sites on fiberglass surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 2378–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, R.S. Surface functionality of amorphous silica by infrared spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. 1956, 62, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Qisui, W.; Xi, L.; Chaocan, Z. Investigation of the states of water and OH groups on the surface of silica. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 334, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakaev, V.A.; Pantano, C.G. Inverse reaction chromatography 2. Hydrogen/Deuterium exchange with silanol groups on the surface of fumed silica. J. Phys. Chem. 2009, 113, 13894–13898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravlev, L.T. Surface characterization of amorphous silica—A review of work from the former USSR. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1993, 74, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantano, C.G. Effect of boron oxide on surface hydroxyl coverage of aluminoborosilicate glass fibres: A (19)F solid state NMR study. Phys. Chem. Glasses 2003, 44, 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Carré, A.; Lacarrière, V.; Birch, W. Molecular interactions between DNA and an aminated glass substrate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 260, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.M.; Thomason, J.L.; Jones, F.R. The concentration of hydroxyl groups on glass surfaces and their effect on the structure of silane deposits. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Silanes and Other Coupling Agents, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 13–15 June 2007.
- Martin, D.M.; Akinc, M.; Oh, S.M. Effect of forming and aging atmospheres on E-glass strength. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1978, 61, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, B.A.; Whitney, I.; Johnson, J.W. The strength of fused silica. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1967, 297, 534–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orowan, E. Fracture and strength of solids. Rep. Prog. Phys. 1948, 12, 185–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomozawa, M. Stress corrosion reaction of silica glass and water. Phys. Chem. Glasses 1998, 39, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Michalske, T.A.; Freiman, S.W. A molecular interpretation of stress corrosion in silica. Nature 1982, 295, 511–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naraev, V.N. The influence of water on the glass properties. Glass Phys. Chem. 2004, 30, 367–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelby, J.E. A limited review of water diffusivity and solubility in glasses and melts. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 91, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.M.; Tomozawa, M. An infrared spectroscopic study of water-related species in silica glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1996, 201, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.M.; Tomozawa, M. Water diffusion into silica glass: Structural changes in silica glass and their effect on water solubility and diffusivity. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1995, 185, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehler, A.; Tomozawa, M. Water diffusion into silica glass at a low temperature under high water vapor pressure. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2004, 347, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Tomozawa, M. Dynamic fatigue of sodium-silicate glasses with high water content. J. Phys. 1982, C9, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, D.E.; Stevels, J.M. Effect of dissolved water on the internal friction of glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1974, 14, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomozawa, M.; Kim, D.-L.; Agarwal, A.; Davis, K.M. Water diffusion and surface structural relaxation of silica glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2001, 288, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mould, R.E. Strength and static fatigue of abraded glass under controlled ambient conditions: III, aging of fresh abrasions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1960, 43, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Tomozawa, M. Crack blunting of high-silica glass. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1982, 65, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tomozawa, M. Mechanical strength increase of abraded silica glass by high pressure water vapor treatment. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1994, 168, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirao, K.; Tomozawa, M. Dynamic Fatigue of treated high-silica glass: Explanation by crack tip blunting. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1987, 70, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederhorn, S.M.; Fett, T.; Rizzi, G.; Fuenfschilling, S.; Hoffmann, M.J.; Guin, J.P. Effect of water penetration on the strength and toughness of silica glass. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 94, S196–S203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fett, T.; Rizzi, G.; Hoffmann, M.J.; Wagner, S.; Wiederhorn, S.M. Effect of water on the inert strength of silica glass: Role of water penetration. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 95, 3847–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederhorn, S.M.; Yi, F.; LaVan, D.; Richter, L.J.; Fett, T.; Hoffmann, M.J. Volume expansion caused by water penetration into silica glass. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 98, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, G.M.; Schramke, J.A. Desorption of water from glass fibers. In Molecular Characterization of Composite Interfaces; Ishida, H., Kumar, G., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 387–400. [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka, G.M.; Schramke, J.A. Thermodesorption of water from silicate surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1985, 105, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trens, P.; Denoyel, R.; Guilloteau, E. Evolution of surface composition, porosity, and surface area of glass fibers in a moist atmosphere. Langmuir 1996, 12, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, J.L. Glass Fibre Sizing: A Review of the Literature. Blurb Incorporated 2015. Available online: http://www.blurb.co.uk/b/6244677-glass-fibre-sizing (accessed on 3 February 2016).
- Zinck, P.; Mader, E.; Gerard, J.F. Role of silane coupling agent and polymeric film former for tailoring glass fiber sizings from tensile strength measurements. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 5245–5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinck, P.; Pays, M.F.; Rezakhanlou, R.; Gerard, J.F. Mechanical characterisation of glass fibres as an indirect analysis of the effect of surface treatment. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 2121–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Thomason, J.L. Effect of silane coupling agent on mechanical performance of glass fibre. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 48, 1947–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiefenthaler, A.; Urban, M.W. Thermal stability of silane coupling agents on Nextel fibres. Composites 1989, 20, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Benito, J.; Baselga, J.; Aznar, A.J. Microstructural and wettability study of surface pretreated glass fibres. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1999, 92–93, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennerley, J.R.; Fenwick, N.J.; Pickering, S.J.; Rudd, C.D. The properties of glass fibers recycled from the thermal processing of scrap thermoset composites. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 1997, 3, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennerley, J.R.; Kelly, R.M.; Fenwick, N.J.; Pickering, S.J.; Rudd, C.D. The characterisation and reuse of glass fibres recycled from scrap composites by the action of a fluidised bed process. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1998, 29A, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, S.J.; Kelly, R.M.; Kennerley, J.R.; Rudd, C.D.; Fenwick, N.J. A fuidised bed process for the recovery of glass fibres from scrap thermoset composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2000, 60, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.T.; Cunliffe, A.; Jones, N. Recovery of value-added products from the pyrolytic recycling of glass-fibre-reinforced composite plastic waste. J. Energy Inst. 2005, 78, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunliffe, A.M.; Williams, P.T. Characterisation of products from the recycling of glass fibre reinforced polyester waste by pyrolysis. Fuel 2003, 82, 2223–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, D.; Guillermain, C.; Bergeret, A.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.-M.; Tersac, G. SMC composites waste management as reinforcing fillers in polypropylene by combination of mechanical and chemical recycling processes. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 3593–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkesson, D.; Foltynowicz, Z.; Christéen, J.; Skrifvars, M. Microwave pyrolysis as a method of recycling glass fibre from used blades of wind turbines. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2012, 31, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveux, G.; Bailleul, J.-L.; Salle, E.L.G.L. Chemical recycling of glass fibre reinforced composites using subcritical water. Compos. A. Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 1809–1818. [Google Scholar]
- Kao, C.C.; Ghita, O.R.; Hallam, K.R.; Heard, P.J.; Evans, K.E. Mechanical studies of single glass fibres recycled from hydrolysis process using sub-critical water. Compos. Part A. Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.C.; Thomason, J.L. Regeneration of thermally recycled glass fibre for cost-effective composite recycling: Performance of fibre recyclates from thermoset composites and with subsequent ReCoVeR treatments. In Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Composite Materials (ECCM16), Seville, Spain, 22–26 June 2014.
- Beauson, J.; Fraisse, A.; Toncelli, C.; Bech, J.I.; Brøndsted, P. Thermoset composite recycling: Properties of recovered glass fiber. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Composite Materials (ICCM20), Copenhagen, Denmark, 19–24 July 2015.
- Thomason, J.L.; Sáez-Rodríguez, E.; Kao, C.C.; Nagel, U.; Yang, L. ReCoVeR: Regenerating the strength of glass fibres thermally recycled from end-of-life composites. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Composite Materials (ICCM20), Copenhagen, Denmark, 19–24 July 2015.
- Yang, L.; Sáez, E.R.; Nagel, U.; Thomason, J.L. Can thermally degraded glass fibre be regenerated for closed-loop recycling of thermosetting composites? Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 72, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.P.; Ghita, O.R.; Savage, L.; Evans, K.E. Successful closed-loop recycling of thermoset composites. Compos. A. Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2009, 40, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado, M.; Garcia-Dáz, I.; Bastidas, J.M.; Alguacil, F.J.; López, F.A.; Monticelli, C. Effect of recycled glass fiber on the corrosion behavior of reinforced mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 64, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, I.W. Methods for improving the mechanical properties of oxide glasses. J. Mater. Sci. 1989, 24, 4177–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, S.; Jonson, B.; Stålhandske, C. The technology of chemical glass strengthening—A review. Glass Technol. Eur. J. Glass Sci. Technol. 2010, 51, 41–54. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, A.R.; Krohn, D.A. Strengthening of glass fibers: Part 2, ion exchange. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1969, 52, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennerley, J. Recycling Fibres Recovered from Composite Materials Using a Fluidised Bed Process. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Jenkins, P.G.; Liggat, J.J.; Thomason, J.L. Strength of thermally conditioned glass fibre degradation, retention and regeneration. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Composite Materials (ICCM20), Copenhagen, Denmark, 19–24 July 2015.
| Ref. | Fibre Type | Fibre Diameter (microns) | Coating, Sizing | Maximum Conditioning Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Maximum Strength Loss (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [28] | Silica | 50 | unsized | 600 | 60 | 65 |
| [34] | Silica | – | unsized | 650 | 60 | 79 |
| [34] | S-glass | – | – | 650 | 60 | 71 |
| [24] | E-glass | 12 | unsized | 600 | 240 | 67 |
| [31] | E-glass | 12 | 111A | 650 | 15 | 70 |
| [32] | E-glass | 8–16 | unsized | 600 | 180 | 62 |
| [34] | E-glass | – | unsized | 650 | 60 | 80 |
| [38] | E-glass | 6–17 | unsized | 273 | 240 | 40 |
| [39] | E-glass | 17 | unsized | 400 | 25 | 45 |
| [39] | E-glass | 17 | aminosilane | 400 | 25 | 55 |
| [40] | E glass | 17 | unsized | 600 | 25 | 45 |
| [40] | E-glass | 17 | aminosilane | 600 | 25 | 73 |
| [41] | E-glass | 17 | unsized | 600 | 25 | 65 |
| [41] | E-glass | 17 | aminosilane | 600 | 25 | 75 |
| [42] | E-glass | 17 | SE1500 | 600 | 25 | 65 |
| [32] | Basalt | 9–16 | unsized | 600 | ? | 80 |
| [34] | Basalt | – | unsized | 650 | 60 | 97 |
| [35] | Basalt | 9 | – | 500 | 60 | 90 |
| [37] | Basalt | 10 | – | 500 | 5 | 77 |
| [37] | Basalt | 10 | – | 500 | 20 | 89 |
| [42] | Basalt | 15 | epoxy | 600 | ? | 80 |
| [23] | NA-ABG * | 12 | unsized | 650 | ? | 75 |
| [23] | NA-ABG * | 22 | unsized | 650 | 60 | 70 |
| [27] | Soda-lime | 3000 | unsized | 530 | 60 | 70 |
| [29] | NA-ABG * | – | – | 550 | ? | 55 |
| [43] | Alkaline | 20 | unsized | 500 | 60 | 70 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thomason, J.; Jenkins, P.; Yang, L. Glass Fibre Strength—A Review with Relation to Composite Recycling. Fibers 2016, 4, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib4020018
Thomason J, Jenkins P, Yang L. Glass Fibre Strength—A Review with Relation to Composite Recycling. Fibers. 2016; 4(2):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib4020018
Chicago/Turabian StyleThomason, James, Peter Jenkins, and Liu Yang. 2016. "Glass Fibre Strength—A Review with Relation to Composite Recycling" Fibers 4, no. 2: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib4020018
APA StyleThomason, J., Jenkins, P., & Yang, L. (2016). Glass Fibre Strength—A Review with Relation to Composite Recycling. Fibers, 4(2), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib4020018






