Abstract
The use of sisal fibers to reinforce concrete and mortar enables the development of sustainable cement-based materials suitable for various construction elements. However, the high-water absorption of natural fibers can cause dimensional instability and poor fiber–matrix bonding, which reduces strength over time. Physical and chemical treatments can decrease water absorption and enhance the dimensional stability and bonding properties of fibers, but their effects on composite performance require further clarification. This study produced composites with 2%, 3%, and 4% by mass of sisal fibers subjected to different treatments, including hornification, washed alkaline treatment, and unwashed alkaline treatment. Fibers were characterized through water absorption, dimensional variation, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction, thermogravimetric analysis and direct tensile testing. Composites were evaluated by water absorption, capillarity, drying shrinkage, direct tensile and four-point bending tests to assess the influence of fiber treatment and content. Results showed that alkaline treatment significantly improved the physical and mechanical properties of sisal fibers. Consequently, composites reinforced with alkaline-treated fibers achieved superior performance compared to those reinforced with hornified fibers, with the best results observed at the highest fiber mass fraction (4%). These findings demonstrate the potential of treated sisal fibers to enhance the durability and mechanical behavior of natural fiber-reinforced cementitious composites.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the use of plant fibers as reinforcement in cement-based materials has been extensively investigated due to the global search for construction materials aligned with Sustainable Development Goal 11, which addresses “Sustainable Cities and Communities” and aims to make urban areas more inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable. Compared to manufactured fibers, plant fibers are renewable, require low energy for their production, and, being of plant origin, play a beneficial role in mitigating climate change by storing CO2 [1]. Several types of plant fibers can be used as reinforcement in cementitious materials, such as sisal, jute, pineapple, abaca, banana, flax, among others. Used either in the form of fabrics [2,3,4], long fibers [5] or as short fibers dispersed within the matrix [6], plant fiber reinforcement helps inhibit crack propagation in the cementitious matrix, allowing to produce tougher and safer building elements [7]. The low dosage of natural fibers in cementitious composites (up to 5%) contributes to sustainability in several dimensions: environmental, economic, and social. The use of these fibers can drive more sustainable practices and innovative materials in the construction industry [8]
Due to the chemical incompatibility between Portland cement hydration products and plant fibers, new matrices have been developed to increase the durability of composites and enable the production of construction systems with longer service life [9]. However, the high-water absorption capacity of plant fibers, which can reach values of up to 200% [10], leads to dimensional variation in the fibers when exposed to changes in humidity that naturally occur in construction elements exposed to the environment. This phenomenon causes structural damage at the fiber–matrix interface [8,11], which is primarily responsible for stress transfer between the cracked matrix and the fiber, preventing brittle failure of the composite and enhancing toughness. Since the interface is only about a few μm thick, it is easily damaged by fiber expansion and shrinkage during wetting and drying [12]; for this reason, fiber dimensional variation must be controlled.
The reduction in fiber hydrophilicity is therefore essential to provide a more durable and resistant material, and this can be achieved through the application of impermeable coatings, chemical treatments, or thermal treatments of the fibers. The application of polymeric resins on the fiber surface has been shown to reduce water absorption [10,13], but it also decreases fiber–matrix adhesion, which in turn reduces the strength of the composites. Thermal treatments, such as hornification [14] or autoclaving [15], aim to modify the internal structure of the fibers by reducing lumen size and minimizing pores accessible to water. The hornification of plant fibers has shown promising results in reducing water absorption and dimensional variation, leading to improved fiber–matrix adhesion [16]. This process, however, is energy-intensive due to the repeated oven-heating cycles and must be adjusted for each type of plant fiber, as it may lead to fiber cracking.
Among the chemical treatments applied to plant fibers to reduce their hydrophilicity, alkaline treatment is particularly prominent [17]. This method involves exposing the fibers to sodium hydroxide or calcium hydroxide solutions and is primarily intended to clean the fiber surface by removing manufacturing residues, as well as partially eliminating hemicellulose and lignin. The removal of these components improves the packing of cellulose chains, which are responsible for the fiber’s crystallinity. Consequently, alkaline treatment promotes an increase in fiber crystallinity, induces chemical modifications, reduces the fiber diameter [18,19], and significantly influences the physical and mechanical properties of plant fibers.
The application of alkaline treatment with sodium or calcium hydroxide has been shown to reduce water absorption by approximately 15–30% (e.g., NF 154–173% to 123–160% after treatment) [10], increase fiber tensile strength by 17–22% (e.g., from 468.7 MPa for NF to 547.3–573.5 MPa for treated fibers) [20,21] while also enhancing fiber–matrix adhesion, as demonstrated by tensile strength increases of 40–90% in fiber-reinforced composites relative to the plain matrix [10,13]. The extent of these property modifications can be influenced by the type of chemical compounds, concentration, treatment duration, and post-treatment protocol.
While plant fibers offer a path to sustainable construction, it is imperative that treatments be selected and optimized to minimize any environmental impacts, particularly in maintaining a positive environmental impact throughout their life cycle. Calcium hydroxide treatment was applied with different post-treatment protocols: washed fibers (WAF) and unwashed fibers (U-WAF). The aim of this study is to evaluate the effect of different treatments of plant fibers on the physical and mechanical behavior of cement-based composites. To this end, composites reinforced with fibers subjected to hornification and alkaline treatment were produced and evaluated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sisal Fiber Treatments
The sisal fibers used in this study were obtained from Valente City, Bahia, Brazil. Initially, the as-received fibers were immersed in water at 50 °C for 1 h to remove residues from the decortication process. They were then rinsed in running water at room temperature and dried in an oven at 40 °C for 24 h. For use as reinforcement, the fibers were aligned and cut to 40 mm lengths prior to being subjected to the treatments.
In each hornification cycle, the fibers were first saturated in water at ~23 °C for 3 h, then oven-dried with a gradual heating rate of 1 °C/min until reaching 80 °C, where they were maintained for 16 h [22]. The alkaline treatment consisted of immersing the fibers for 50 min in a 0.73% Ca(OH)2 solution prepared with deionized water [10]. After treatment, the fibers were divided into two groups: one was rinsed in water from the supply network to remove excess calcium hydroxide from the fiber surface, while the other remained unwashed. All fibers were subsequently dried at room temperature (≈23 °C).
2.2. Cement Based Composite
To produce the mortar matrix and composites, the following materials were used: (i) Portland cement CPV ARI; (ii) fly ash; (iii) metakaolin; (iv) silica fume; (v) river sand passing through a 600 μm sieve; (vi) sisal fiber; (vii) superplasticizer; (viii) viscosity-modifying agent; (ix) water.
The matrix design followed a binder-to-sand ratio of 1:1 and a water/binder ratio of 0.50. The binder was prepared by replacing 50% of the cement with mineral additions, specifically silica fume (10%), metakaolin (30%), and fly ash (10%). The composites were produced with fiber contents of 3%, 4%, and 5% by weight.
The composites were prepared using a 20 dm3 bench mixer under controlled temperature conditions (21 °C ± 2), following the procedure below: (i) the cement and mineral additions were initially mixed for 1.5 min; (ii) the water and superplasticizer solution was added over 3 min; (iii) a 30 s pause was applied; (iv) sand was gradually added over 2 min; (v) fibers were incorporated gradually.
The matrix was proportioned to achieve a flow spread of approximately 400 mm, ensuring good dispersion and workability of the produced composites. Mechanical evaluation of the matrix indicated a compressive strength of 40 MPa and a Young’s modulus of 19.76 GPa.
2.3. Characterization of the Sisal Fiber
2.3.1. Thermogravimetric Analyses (TGA)
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was conducted on both natural and treated fibers using an SDT Q600 instrument (Water Corporation, New Castle, DE, USA), which allows simultaneous TGA, differential thermal analysis (DTA), and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) to assess the fibers’ thermal stability and decomposition behavior. Samples consisting of 10 mg of cut fibers were placed in an open platinum pan. The test was conducted from 23 °C to 1000 °C at a heating rate of 10 °C/min, using nitrogen at a flow rate of 100 mL/min as the purge gas.
2.3.2. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
The XRD measurements were performed on a Bruker D8 Focus (Bruker Corporation, Karlsruhe, Germany). The analyses were performed in one sample holder per treatment. The diffraction intensity of the radiation was measured in a 2θ between 10° and 40° with step size of 0.05° to 3°/min. To the sample preparation, the fibers were scissor cut to particles sizes less than 1 mm. To determine the crystallinity index (CrI), the intensity peaks corresponding to the crystalline and amorphous regions of the plant fibers were analyzed, according to the following Equation (1):
where Icr corresponds to the intensity of the spectrum in the crystalline region (maximum value at 2θ between 22° and 23°), and Iam corresponds to the intensity in the amorphous region (minimum value at 2θ between 18° and 19°).
2.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
To evaluate the effect of the treatment on fiber morphology, five samples were selected for each treatment and coated with a 20 nm layer of gold. Images of the fiber lateral surfaces were obtained using a Hitachi TM3000 (Hitachi High-Tech, Tokyo, Japan) scanning electron microscope (SEM), operating in a low-vacuum environment at an acceleration voltage of 15 kV.
2.3.4. Water Absorption Capacity
The water absorption capacity of untreated and treated fibers was assessed following this methodology: bundles of fibers (≈40 mm in length, ~1 g) were oven-dried at 60 °C for 24 h, cooled, and immersed in 100 mL of water. Measurements were taken after 3 h of immersion—corresponding to the saturation stage—and again at 24 and 48 h. At each stage, the fibers were removed, lightly dried with absorbent paper to eliminate surface water, and weighed. Each test condition was repeated three times under controlled laboratory conditions.
The water absorption (Wabs) was expressed according to Equation (2), where P0 initial dry weight and P1 weight after water immersion.
2.3.5. Dimensional Variation
The fiber diameter was measured using a QUIMIS Q711FT (QUIMIS, Diadema, São Paulo, Brazil) optical microscope. Fiber monofilaments with 40 mm length were placed on a 2 mm-thick glass slide and observed under a 10× optical lens. Three fibers were analyzed for each treatment. A camera attached to the microscope captured images of the fibers, and the diameter was measured at three distinct points along each fiber using Motic Image Plus 2.0 software.
2.3.6. Direct Tensile Test
Tensile tests were performed on 10 samples for each treatment, with a gauge length of 40 mm, in accordance with ASTM C1557 [23]. A Shimadzu AGX (Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan) universal testing machine with a 5 kN load cell was used at a displacement rate of 0.3 mm/min. The tensile strength was calculated by dividing the maximum force obtained during the test by the cross-sectional area of the fiber, which was determined from the fiber diameter measured using a QUIMIS Q711FT Q711FT (QUIMIS, Diadema, São Paulo, Brazil) optical microscope.
2.4. Characterization of Fiber Reinforced Cement Composites
2.4.1. Water Absorption by Immersion and by Capillarity
The water absorption by immersion was conducted in accordance with NBR 9778 [24] using five cylindrical specimens, for both tests, measuring 75 mm × 150 mm (diameter × height). Specimens were demolded after 24 h and cured for 28 days in a humid chamber at 100% relative humidity prior to testing. From this test, the water absorption of the matrix, as well as the void index and specific mass, were determined. Capillary water absorption was performed following NBR 9779 [25]. To ensure unidirectional water flow and prevent moisture loss, the curved surfaces of the specimens were sealed with plastic film during the test.
2.4.2. Drying Shrinkage Test
For the drying shrinkage test, five specimens were cast with dimensions of 285 mm × 75 mm × 75 mm (length × width × height). The test was conducted in accordance with ASTM C157 [26]. Due to the high flowability of the matrix, casting was performed in a single layer. The specimens were demolded after 24 h, and after 28 days of curing (as performed in the water absorption test), the first measurement of drying shrinkage was taken. Following this initial measurement, the specimens were stored in a room with controlled temperature and humidity (23 ± 2 °C and 60 ± 2% relative humidity).
2.4.3. Mechanical Testing
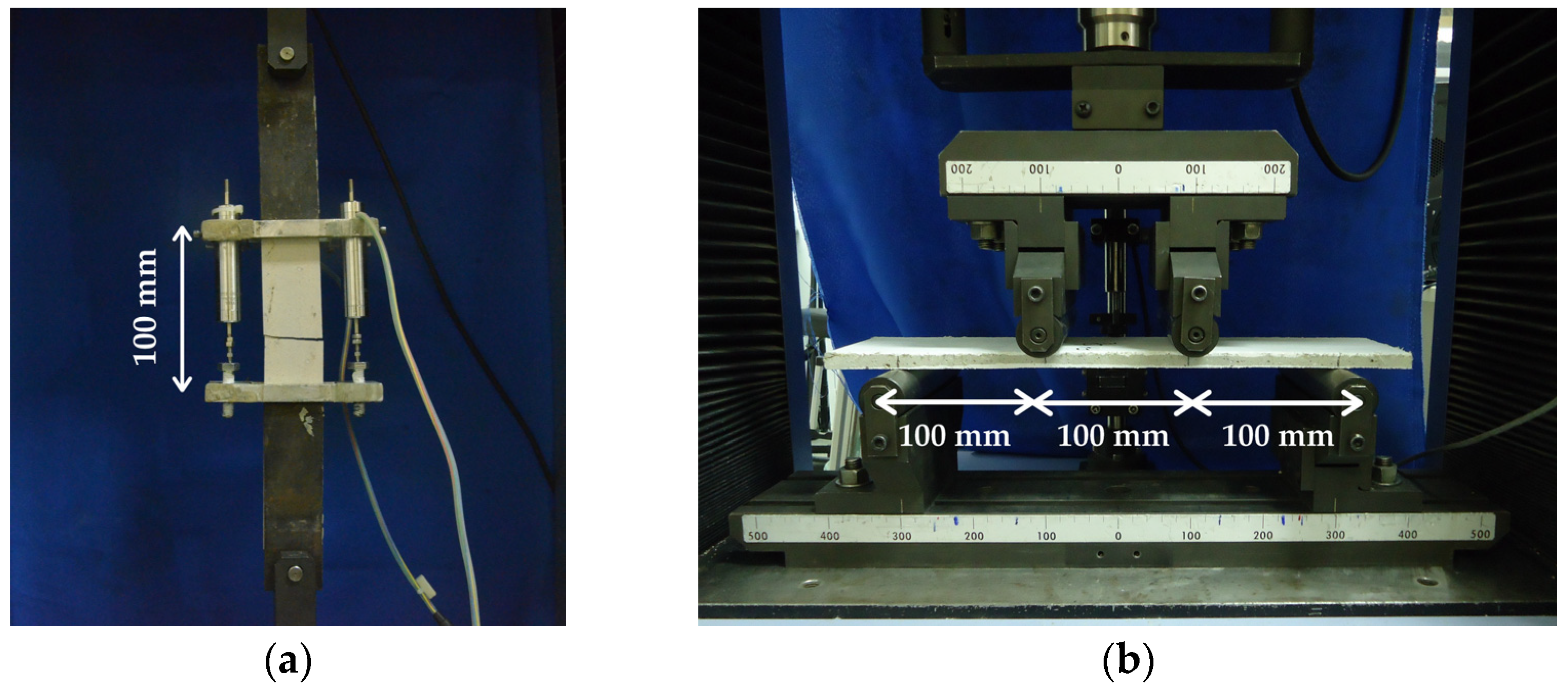
The direct tensile test was performed using an electromechanical testing machine Shimadzu AGX (Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan), with 100 kN capacity, under displacement control at 0.1 mm/min, with a 100 kN load cell. For data acquisition, two LVDTs were mounted on an aluminum support positioned at the central region of the specimen, as shown in Figure 1a.
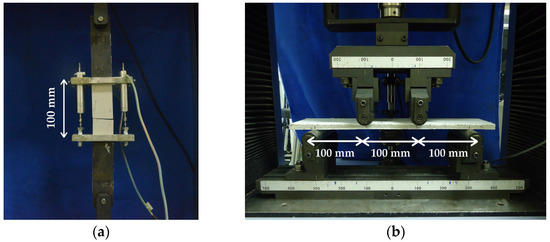
Figure 1.
Setup configuration of mechanical tests: (a) tensile test; (b) bending test.
The four-point bending test was carried out on the same electromechanical machine Shimadzu AGX (Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan) under displacement control at 0.3 mm/min. The distance between the load application points was 100 mm, with a total span of 300 mm (Figure 1b). Data were recorded using the Trapezium software, version 1.3.0, which enabled measurement of the mid-span deflection via an LVDT attached to the device. Specimens were demolded after 24 h and cured for 28 days, for each test, five specimens were tested. In both tests, the 100 kN load cell was employed due to calibration reliability and compatibility with other mechanical tests conducted on the same equipment.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of Sisal Fibers
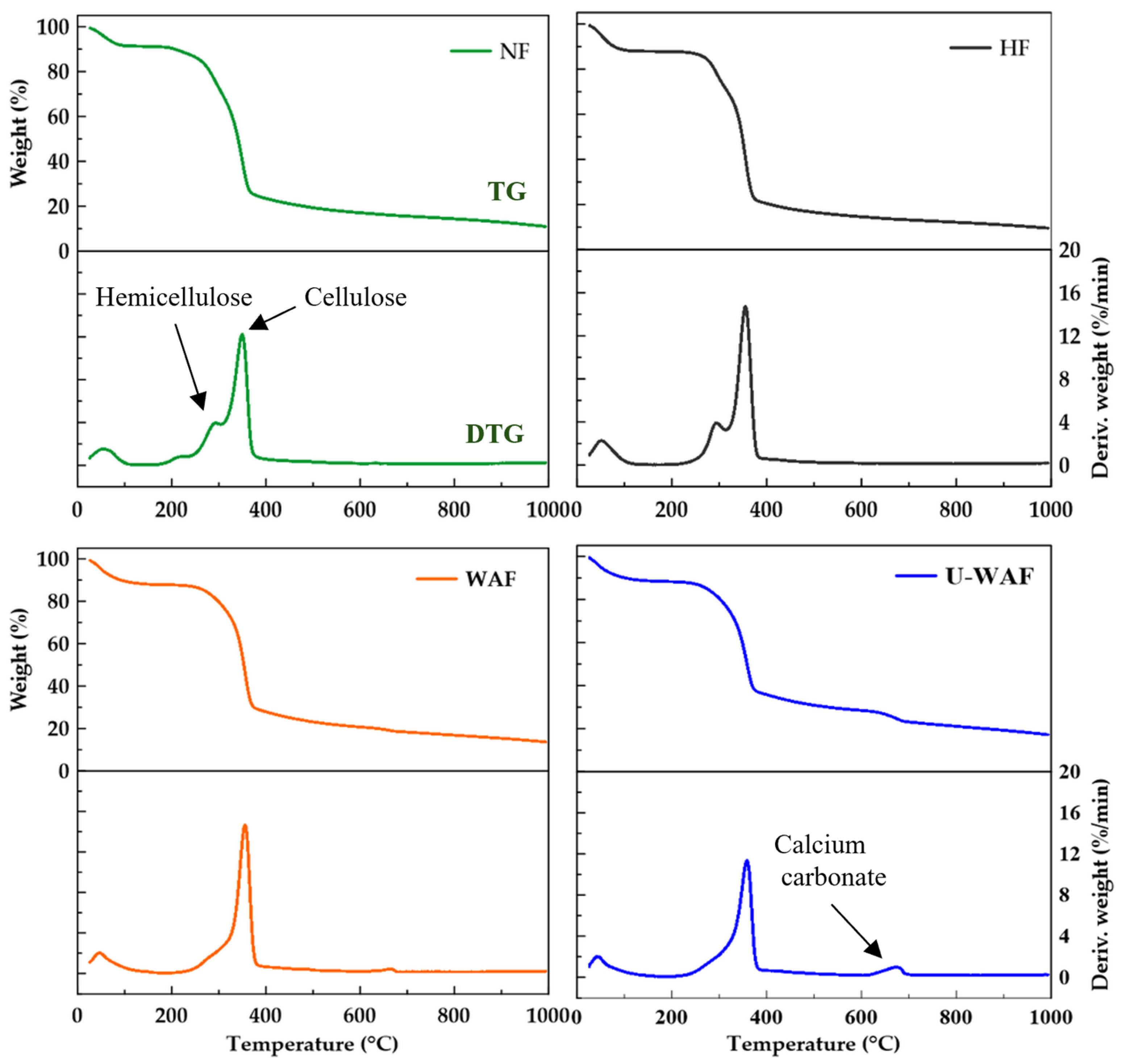
Figure 2 presents the thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) of natural and treated sisal fibers, showing both the mass loss curve (TG) and the derivative mass loss curve (DTG) as a function of temperature. In the DTG, a peak between 230–315 °C is linked to hemicellulose breakdown, while another between 315–350 °C reflects cellulose decomposition [27]. In the DTGs of the samples subjected to alkaline treatment, a small peak can also be observed at around 700 °C, corresponding to calcium carbonate particles originating from the chemical treatment.
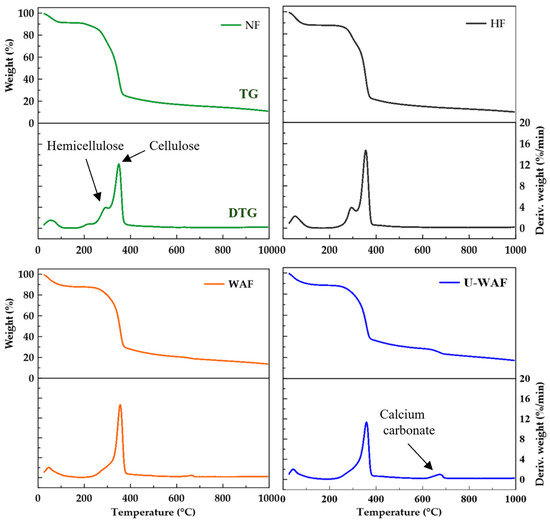
Figure 2.
Thermogravimetry analysis of sisal fiber before and after treatments.
The natural fiber exhibited a mass loss of 15.83% associated with hemicellulose decomposition, while the fibers subjected to hornification treatment showed a similar value of 16.66%, indicating no significant alteration. In contrast, the alkaline treatment, both unwashed (U-WAF) and washed (WAF), reduced these values to 7.9% and 7.6%, respectively. This result demonstrates the effectiveness of the chemical treatment, achieving approximately a 50% reduction in the mass loss associated with hemicellulose. The degradation of natural fibers following alkaline treatment has been investigated using thermogravimetric analysis by other researchers [10,13,28], confirming that alkaline treatment modifies the thermal stability of the fibers.
The effect of the washing process after alkaline treatment can be observed in the mass loss values associated with calcium carbonate. For the washed fibers (WAF), the mass loss was 2.40%, whereas the unwashed fibers exhibited nearly twice this amount, with a mass loss of 5.36%. Alkaline treatment is a chemical modification process used to remove amorphous constituents—namely hemicellulose and lignin—from natural fibers. The treatment enhances the solubility of these components; hemicellulose is solubilized via saponification of ester and acetyl groups [18,29], while lignin is partially depolymerized through the cleavage of ether bonds [19,28]. The removal of these binding materials improves the fiber’s structural integrity and thermal stability, as evidenced by reduced mass loss during thermogravimetric analysis. Consequently, this enhanced stability is correlated with improved mechanical performance, including greater tensile strength and reduced dimensional variation.
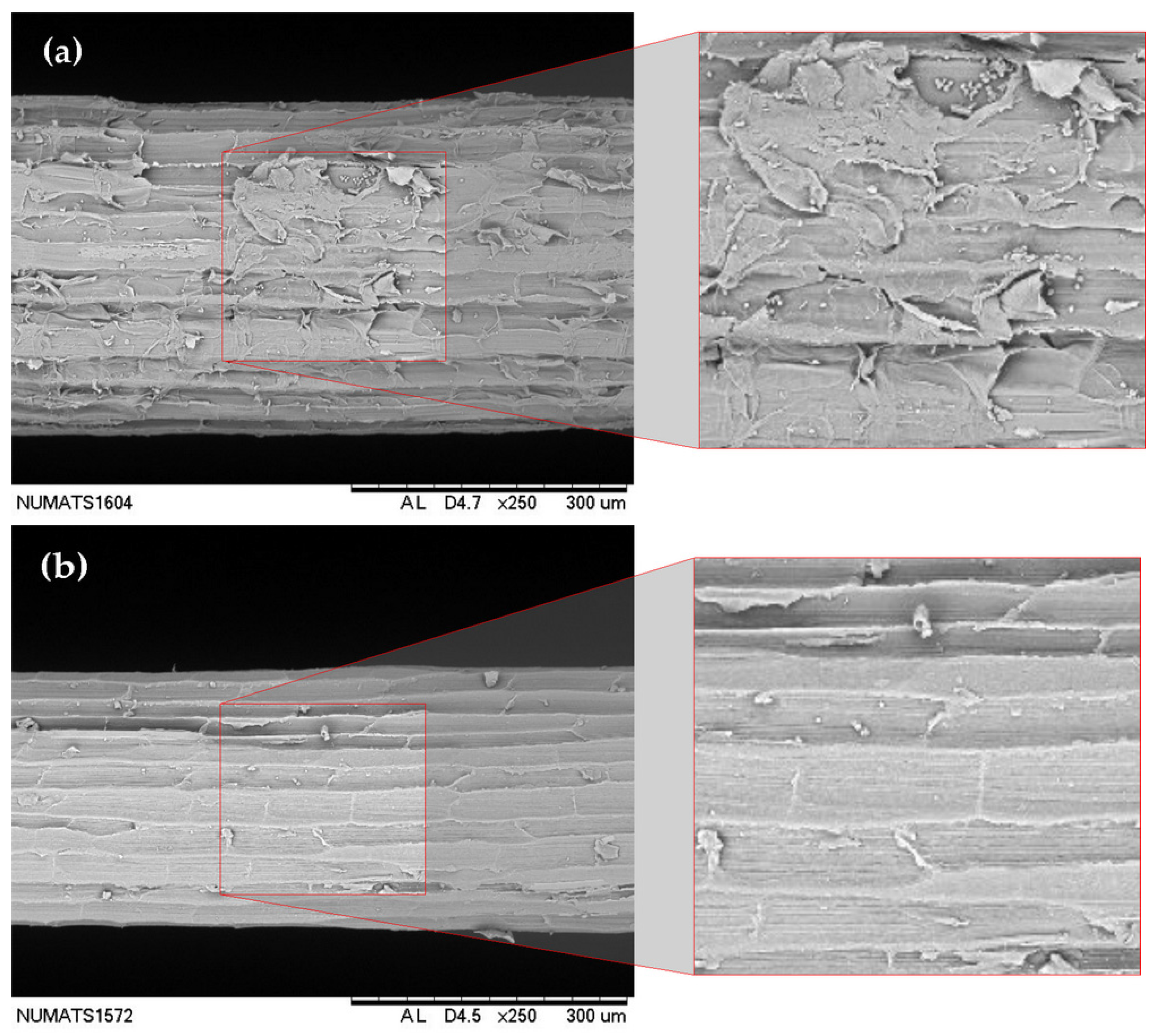
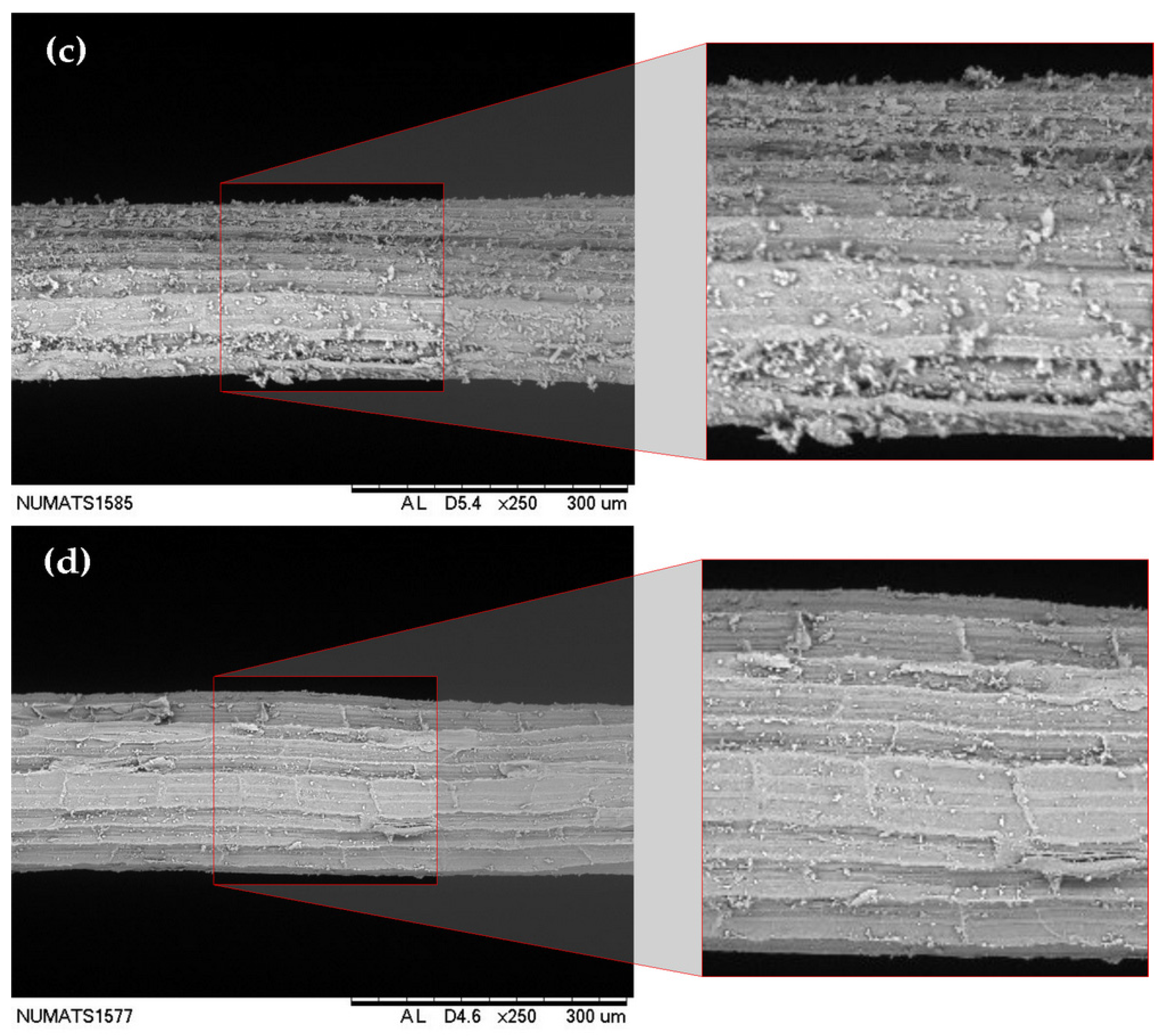
Indeed, the greater presence of calcium carbonate particles on the fiber surface can be visually identified in the scanning electron microscopy images shown in Figure 3. The natural fiber (Figure 3a) exhibits a surface covered with parenchyma cells, along with residues and impurities from the beneficiation process. In contrast, the U-WAF fiber (Figure 3c) shows a noticeable change in surface morphology, becoming rougher due to the deposition of calcium hydroxide on its surface.
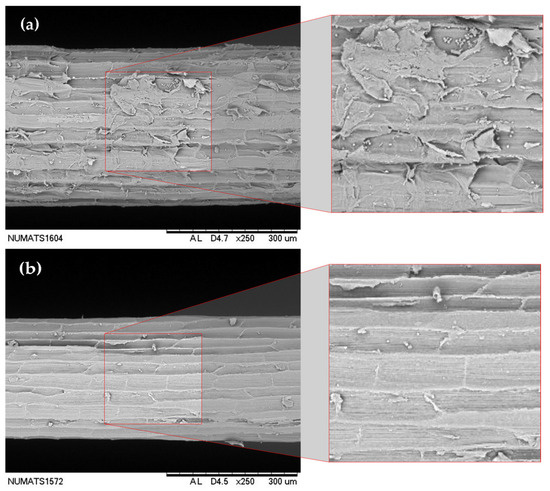

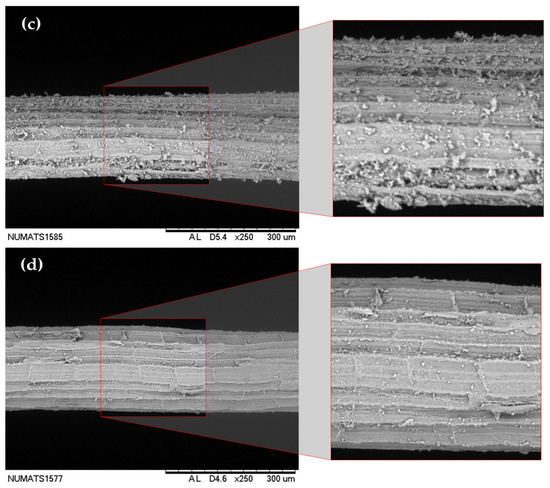
Figure 3.
Micrograph showing the sisal fiber surface after treatments; (a) NF—natural fiber; (b) HF—hornified fiber; (c) U-WAF—unwashed alkaline fiber; (d) WAF—washed alkaline fiber.
Figure 3b demonstrates that the hornification process effectively removes the processing residues present in the natural fiber, leaving the parenchyma cells exposed in a manner similar to that observed for the WAF fiber (Figure 3d). However, fibers subjected to this latter treatment still display small calcium carbonate particles dispersed across the surface.
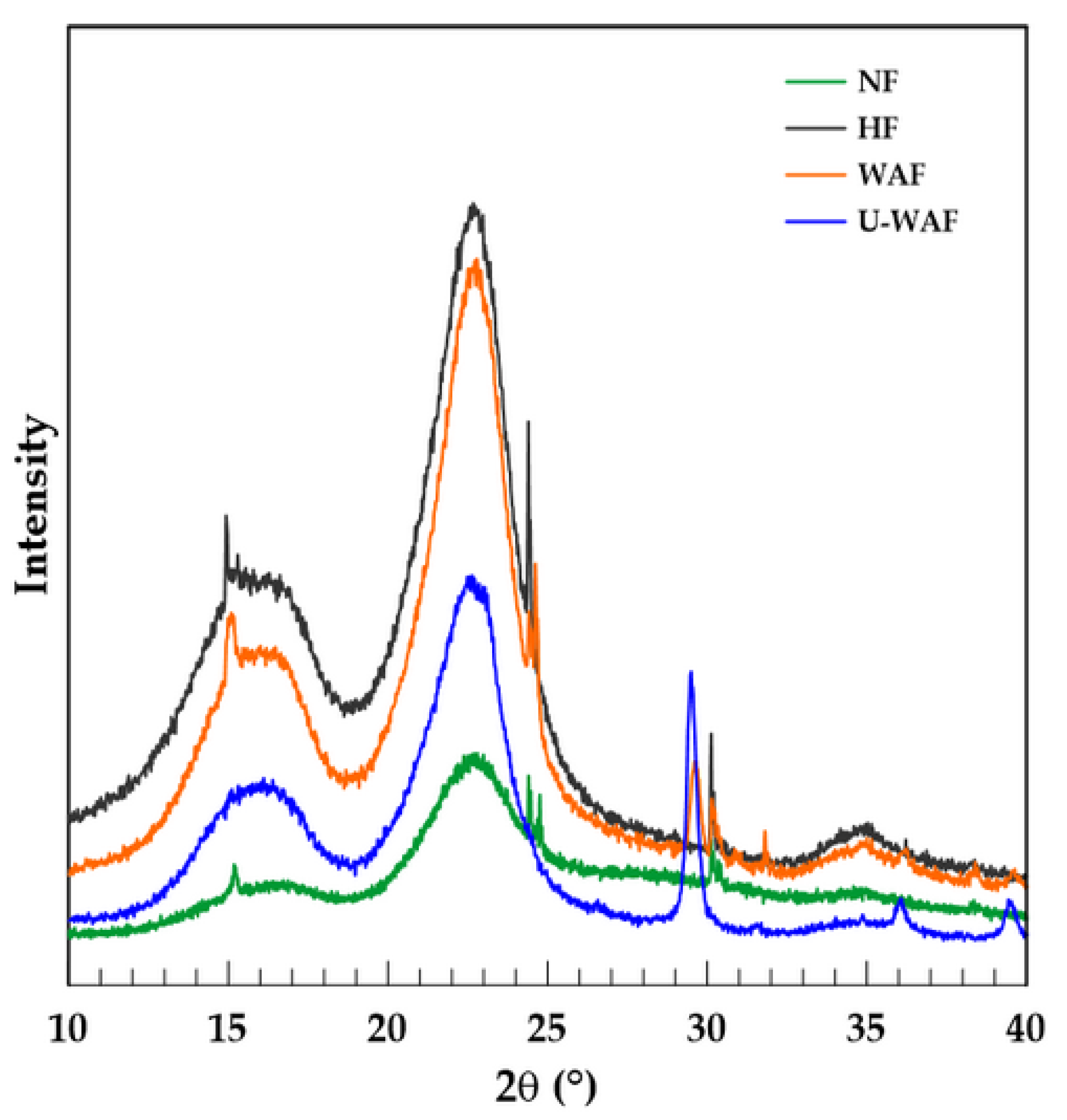
The modifications in the chemical composition and surface of the fibers resulting from the applied treatments directly affect their crystalline structure, as evidenced by the X-ray diffraction patterns shown in Figure 4. The graph presents the peaks that represent the crystalline planes of the cellulose (2θ = 17° and 23°) and an amorphous phase characterized mainly by lignin. For the fibers subjected to alkaline treatment U-WAF, an additional peak can be observed at 2θ = 29°, corresponding to calcium carbonate, similar to observed by [29]. Peaks not characteristic of the crystallographic planes of the lignocellulosic components and calcium carbonate can be attributed to the occurrence of fiber contamination or some inorganic impurity.
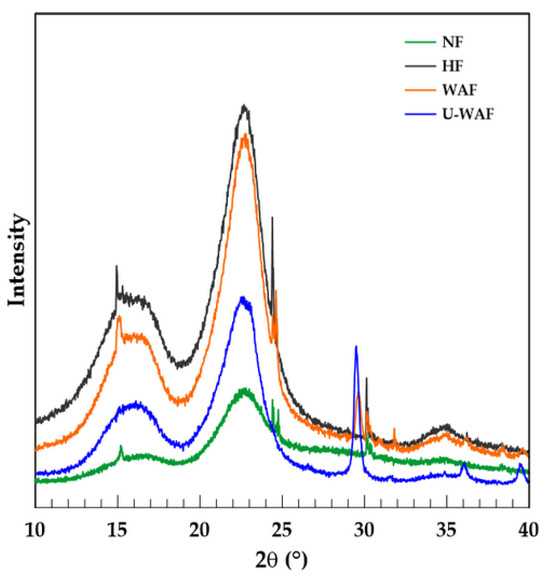
Figure 4.
X-ray diffractograms of the sisal fibers before and after treatments.
The diffraction patterns of the treated fibers exhibit noticeable modifications compared to those of the natural fibers, evidencing an increase in the crystallinity index, as reported in Table 1.

Table 1.
Crystallinity index of natural and treated sisal fiber.
The increase in the crystallinity index is consistent with the findings of [10,29], who reported that alkaline treatment with NaOH on sisal fibers enhanced the cellulose content and the crystalline fraction by partially removing the amorphous components. For piassava fibers, on the other hand, treatment with 2% NaOH resulted in an increase in the crystallinity index, whereas treatment with 2% Ca(OH)2 led to a decrease in crystallinity [30]. This indicates that the chemical interaction between the alkaline solution and plant fibers can vary depending on the type of fiber and the solution used. The hornification treatment typically increases the crystallinity index of plant fibers, but the extent of this increase depends on the number of cycles applied and the type of fiber [16].
The treatments, by removing amorphous components in the fibers, affect the crystalline structure of the sisal. From the determination of the crystallinity index, it is possible to estimate the mechanical behavior of natural fibers, since cellulose is responsible for their stiffness and tensile strength [31]. Additionally, these mechanical properties influence the fiber–matrix interaction, indicating that fiber crystallinity affects the composite’s performance after the onset of initial cracks.
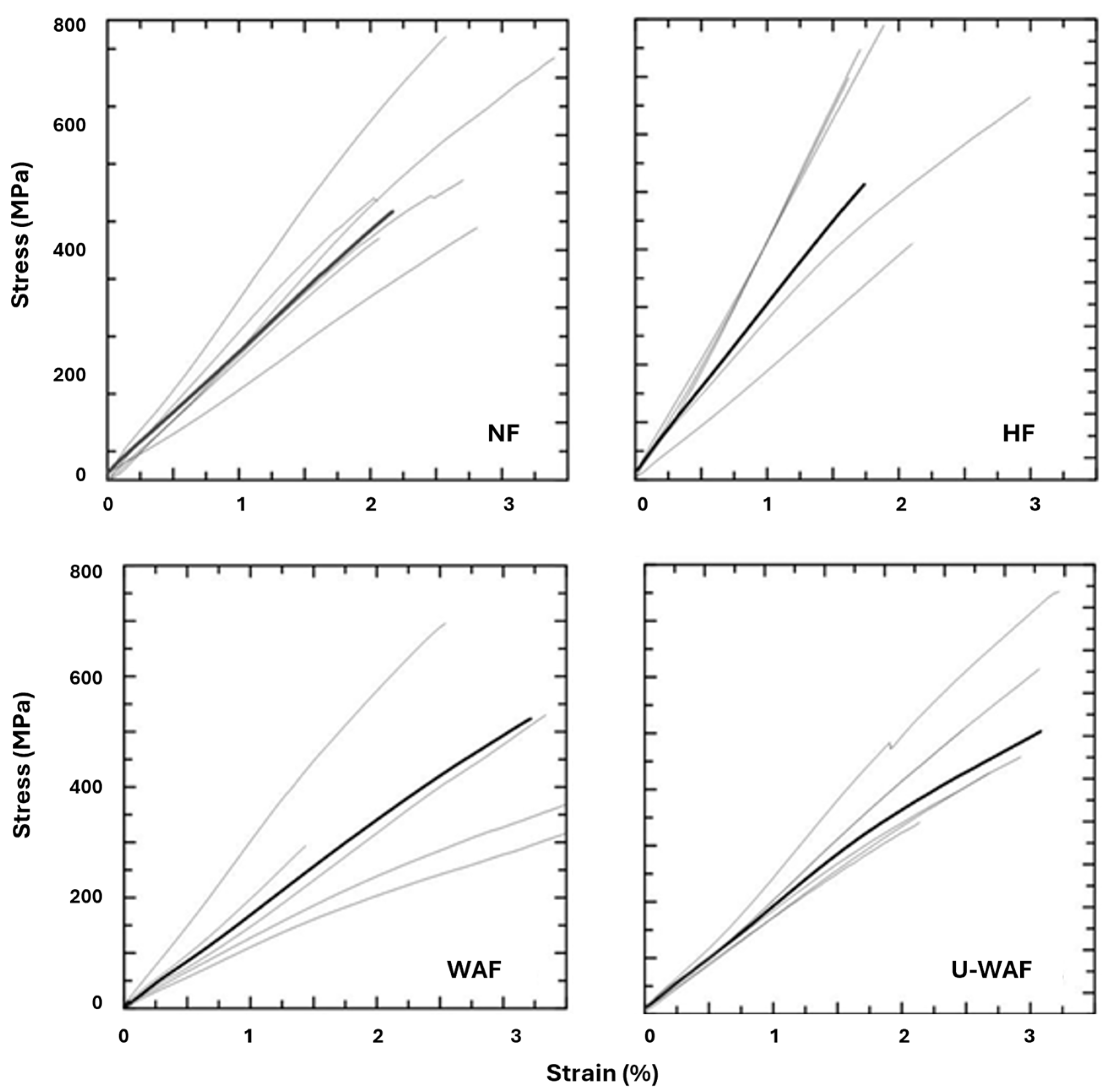
The typical tensile test curves of natural and treated sisal fibers are presented in Figure 5, the results are presented with a smaller number of samples, as some were lost during assembly in the setup or discarded during the test. The fibers exhibit an approximately linear response up to rupture, which occurs abruptly, indicating a brittle material.
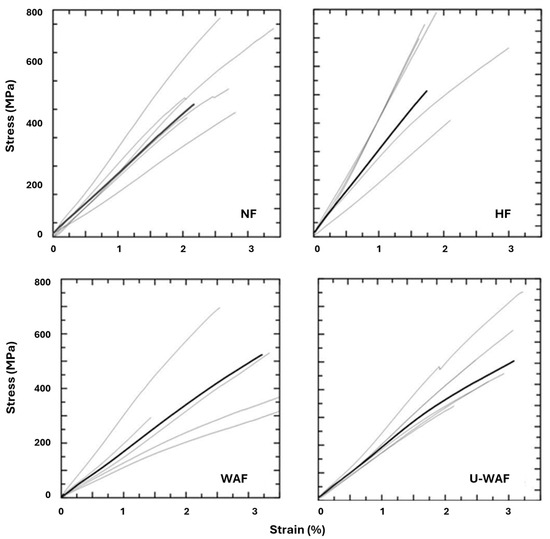
Figure 5.
Tensile stress–strain of fibers (Black curves = average response; gray curves = individual tested samples).
The experimental results of tensile test of fibers are summarized in Table 2, which presents the mean values together with the coefficients of variation (in percentage, shown in parentheses).

Table 2.
Experimental results of the direct tensile test of the fibers.
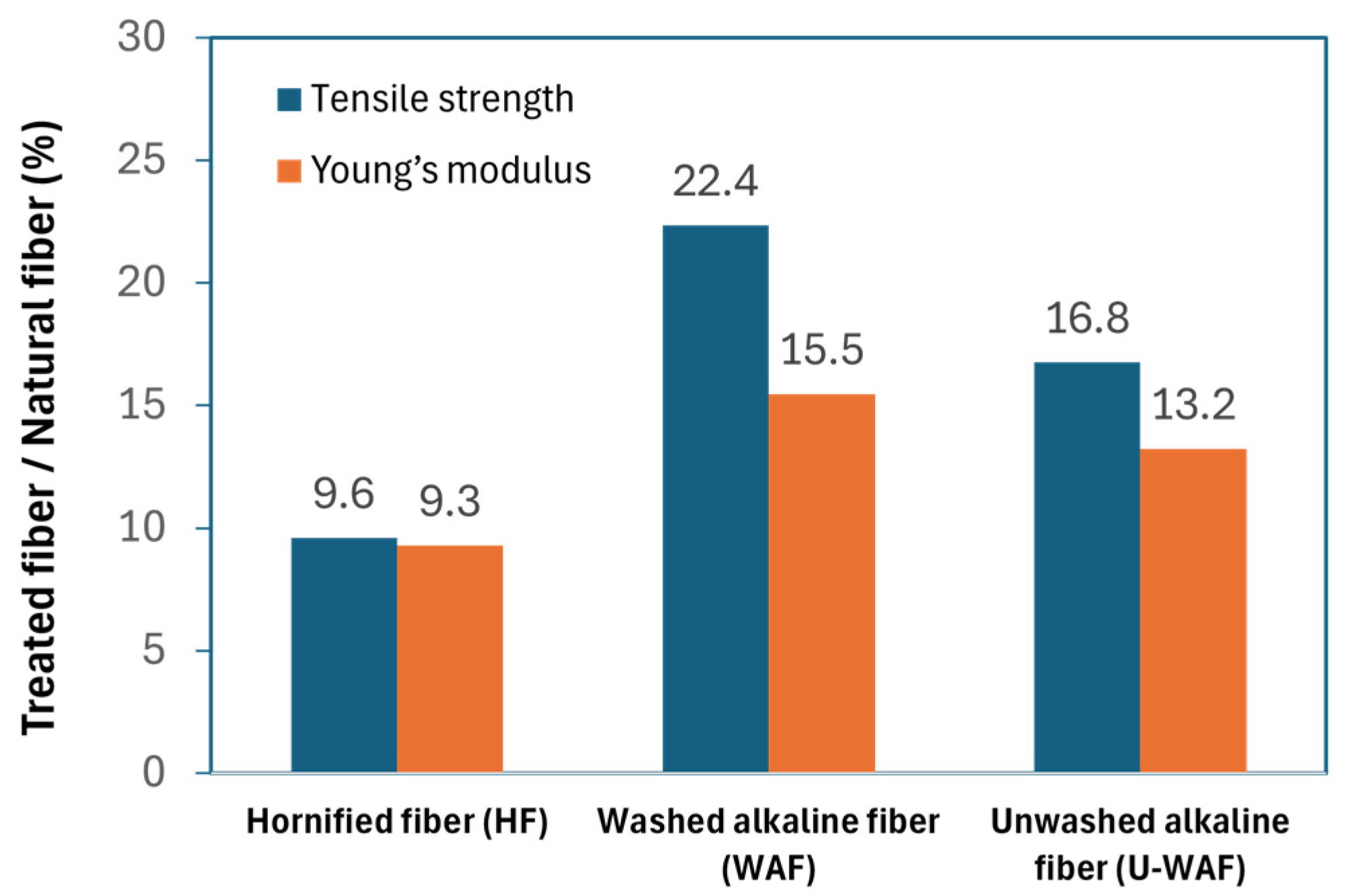
Figure 6 shows the effect of the three fiber treatments on the tensile strength and elastic modulus of the fibers. All treatments improved the fiber properties, with the alkaline treatment followed by washing (WAF) being the most effective, resulting in an increase of approximately 22% in tensile strength and 15% in elastic modulus compared to the untreated fibers. These results are consistent with the crystallinity index values, indicating that this treatment was more effective in removing non-cellulosic materials and impurities.
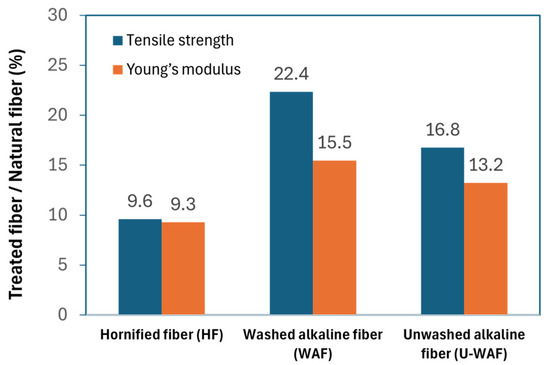
Figure 6.
Effect of treatment on mechanical properties of fibers.
Hornification and alkaline treatments led to higher stress resistance and stiffness compared to untreated fibers [13,32]. This enhancement in mechanical performance can be attributed to changes in cellulose crystallinity and the formation of potential bonds between polymer chains within the internal fiber structures, including fibrils and microfibrils.
3.2. Effect of Fiber Treatment on Physical Properties of Fibers and Composite
Despite the increases in strength and stiffness of the fibers resulting from the applied treatments, one of the most significant improvements expected from treating natural fibers for use in cement-based composites is the reduction in their water absorption. This property directly influences the workability of the composites in the fresh state, as well as fiber–matrix adhesion and water absorption in the hardened composites. Figure 7 presents the water absorption results of natural fibers and fibers subjected to the various treatments.
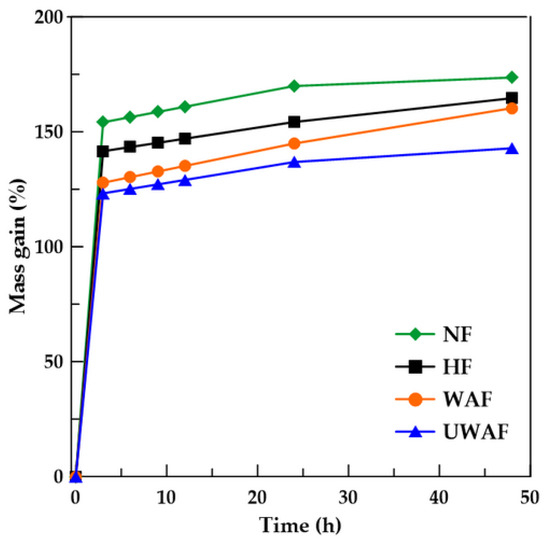
Figure 7.
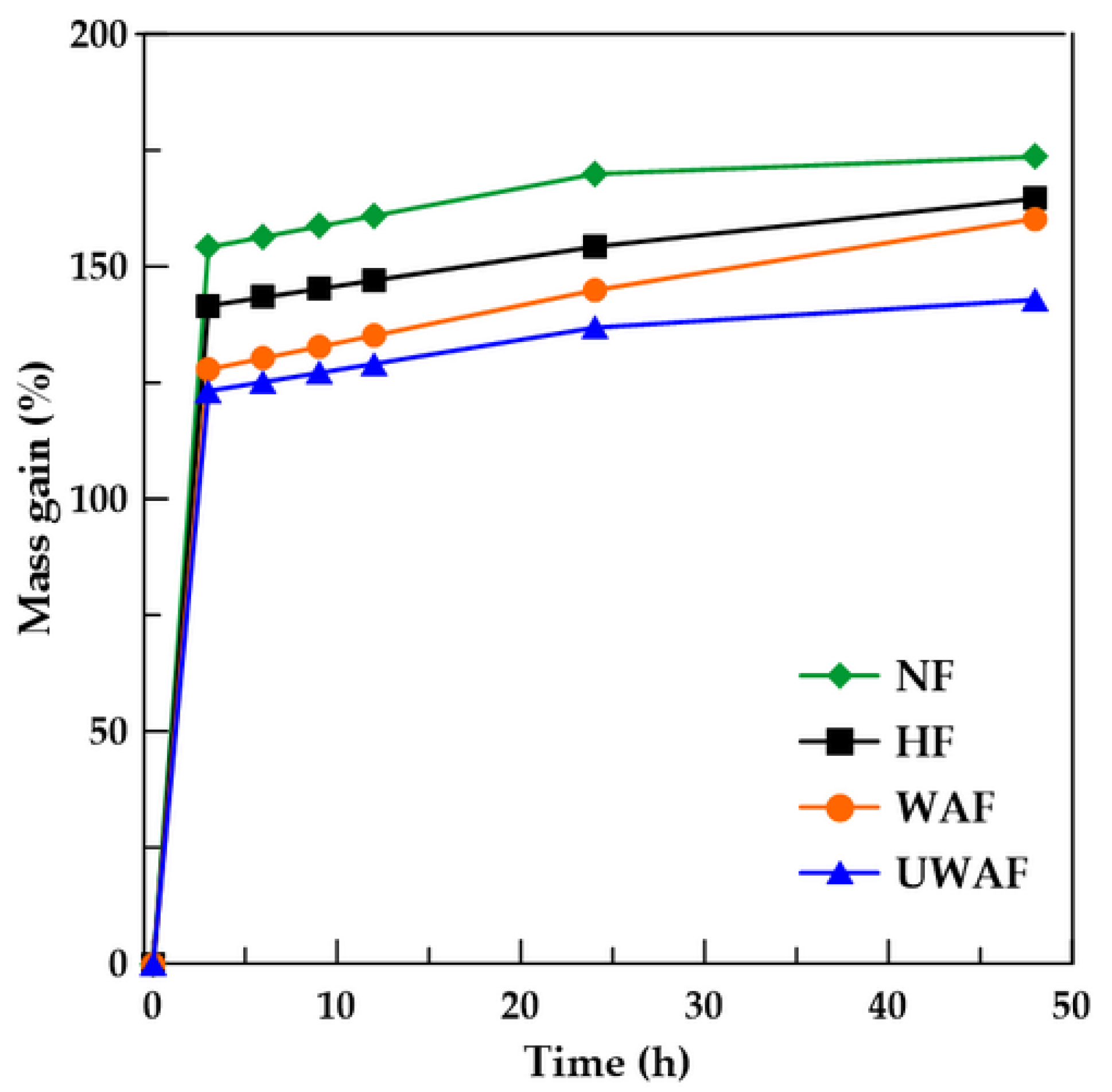
Mass gain of sisal fiber before and after treatments at different times of immersion.
From the absorption curves, it is possible to state that in 3 h the NF absorbs 154.12%, the HF absorbs 141.54%, the WAF absorbs 127.81% and the U-WAF absorbs 123.19%. This time is sufficient for the fibers to practically reach about 90% of the total absorption capacity after 48 h of immersion, which was 173% for NF, 164% for HF, 160% and 142% for WAF and U-WAF, respectively. The treatments used reduce hydrophilic components (hydroxyl groups—OH), decreasing the water absorption capacity of the fiber. In the case of hornification treatment, the fiber cells become more densely packed, and the lumen is reduced after the process, which consequently decreases the fiber’s water absorption capacity [22]. It is observed that alkaline treatment is more effective than hornification in removing hydroxyl groups, as previously reported by [10].
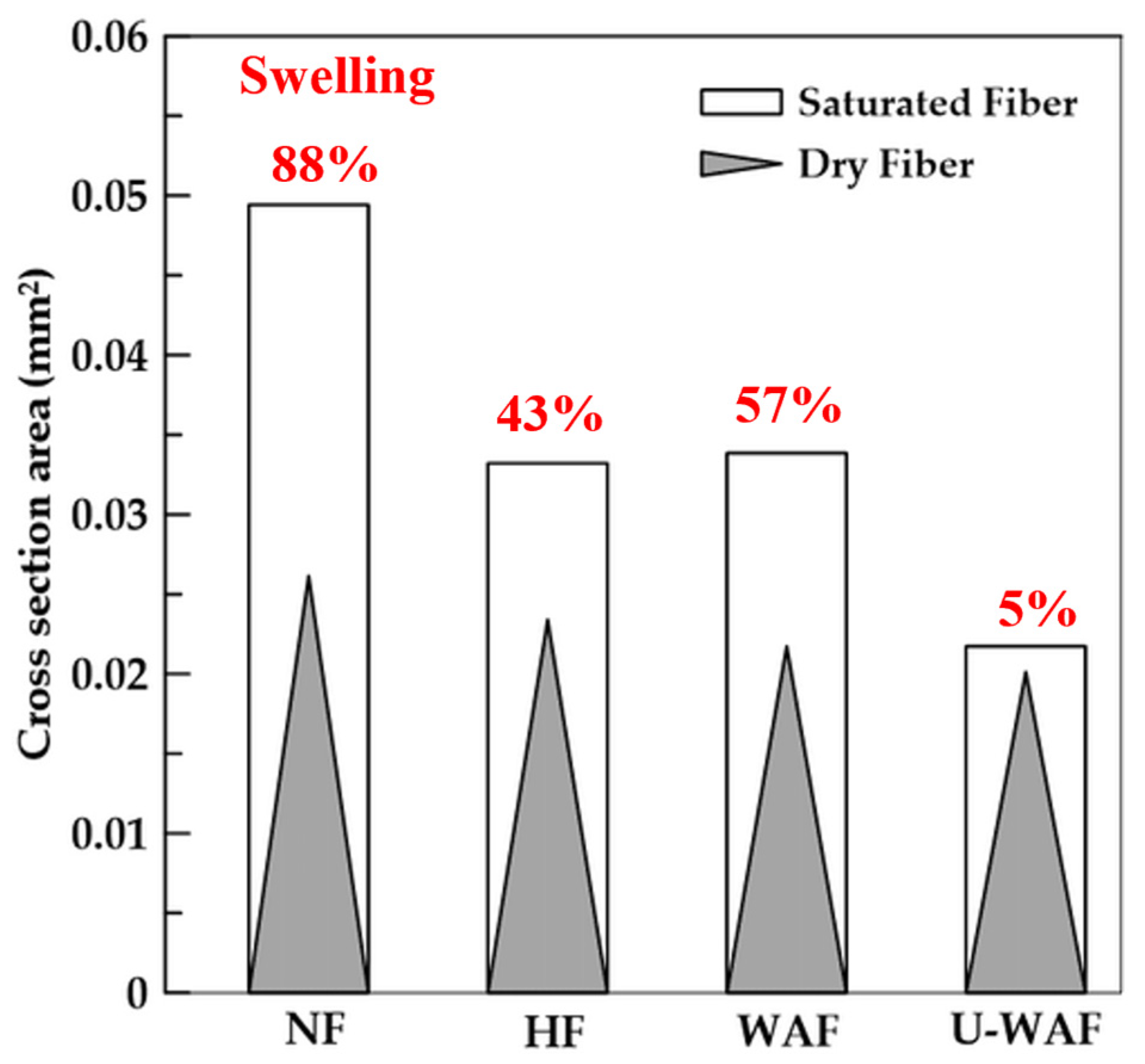
In Figure 8, the average values of the cross-sectional areas of the natural fibers and after the treatments are presented. For natural fiber (NF), the average area of dry fibers was 0.026 mm2 and the area of saturated fibers after 48 h was 0.049 mm2. For dry hornified fibers (HF), they presented an average section of 0.023 mm2 and saturated section of 0.033 mm2. In the fibers with alkaline treatment the average section of the dry fibers were 0.021 mm2 and 0.020 mm2 for the washed alkaline (WAF) and unwashed alkaline fiber (U-WAF), respectively, after saturation the fibers presented average section of 0.033 mm2 and 0.021 mm2.
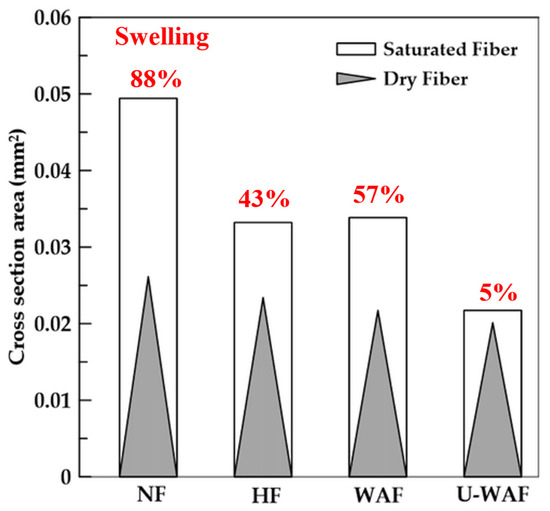
Figure 8.
Dimensional variation (and swelling) of sisal fiber before and after treatment.
It can be observed that the treatments reduced the fiber cross-sectional area and decreased fiber swelling, that is, the variation in this area between the dry and saturated states. The reductions were 88% for natural fibers, 43% for hornified fibers, and 57% and 16.8% for alkaline treatments with and without washing, respectively. These variations are proportional to the water absorption capacity of the fibers, as shown in Figure 7, and demonstrate that the treatments effectively decreased fiber swelling. This effect can be attributed to the reduction in hemicellulose and lignin, as confirmed in this study through thermogravimetric and X-ray diffraction analyses. According [33], alkaline treatment alters the composition of plant fibers and can reduce their swelling, with the magnitude of this effect depending on the solution concentration and exposure time.
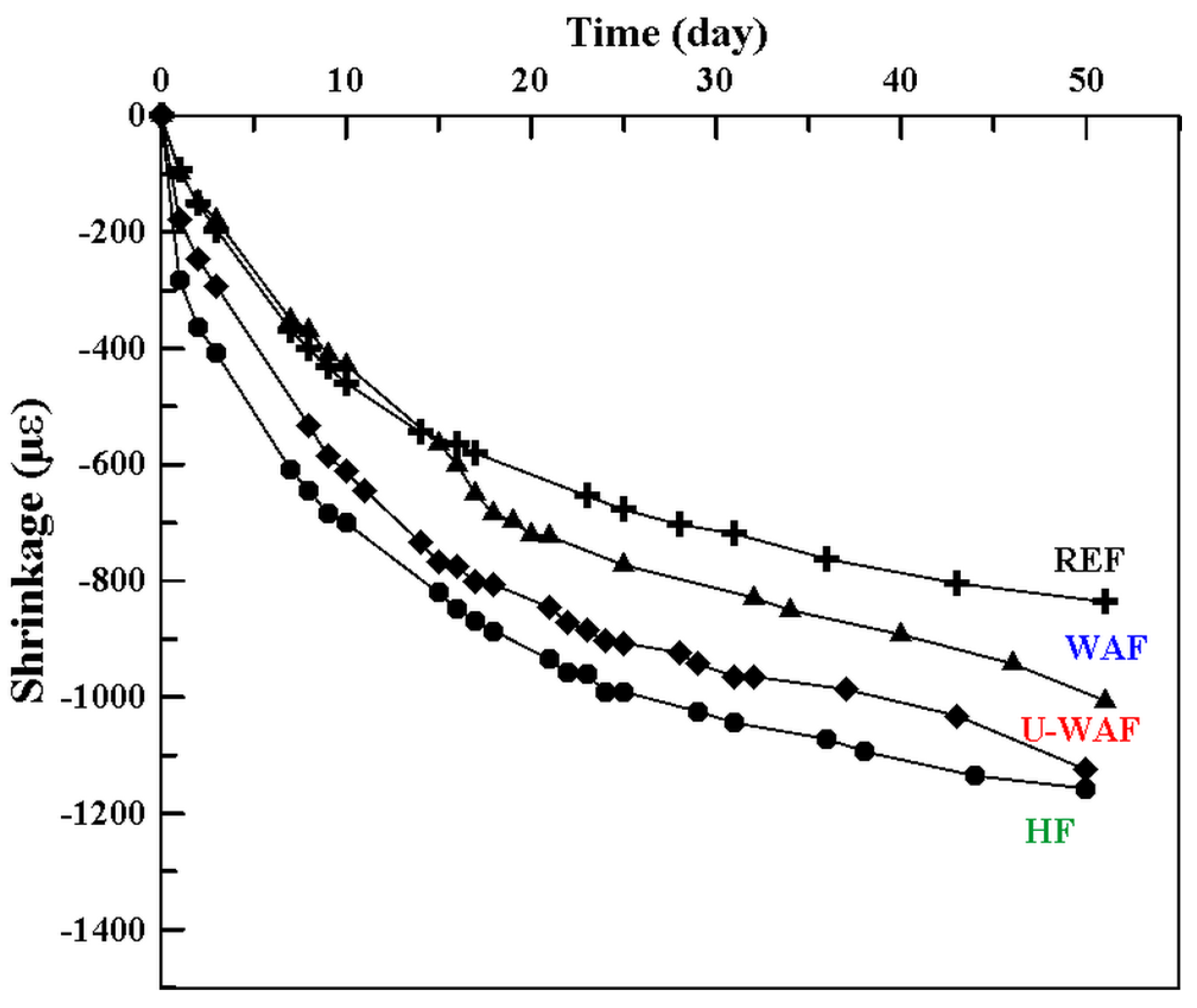
The effect of fiber treatment on the physical properties of fiber-reinforced composites (FRC) was evaluated in composites with a higher fiber content (4%), in comparison with the reference matrix (REF) without fiber reinforcement. In addition to water absorption by capillarity, whose results are presented in Table 3, the drying shrinkage of the composites was also assessed up to an age of 50 days, as shown in Figure 9.

Table 3.
Experimental results of water absorption tests.
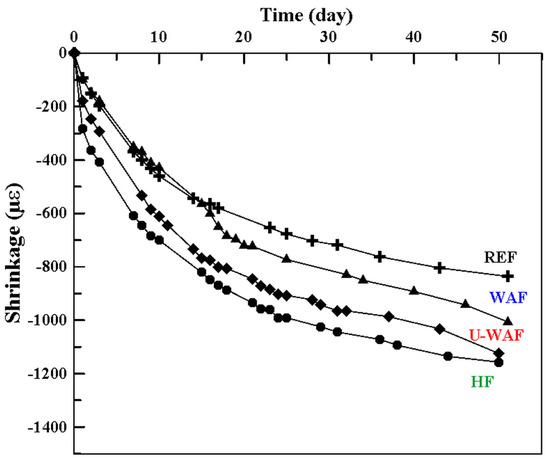
Figure 9.
Shrinkage of cement based composite reinforced with treated fibers.
Incorporating natural fibers into cement-based composites generally promotes a substantial increase in porosity and water absorption capacity, with the effect being more pronounced at higher fiber contents [34,35]. In this study, when treated fibers were used, the increase in water absorption ranged from only 6% to 27%. Among them, alkaline-treated fibers—characterized by lower intrinsic water absorption (see Figure 3)—produced only a minor effect on the overall water absorption of the composites. Typically, the addition of fibers increases porosity and water uptake due to changes in the consistency of the fresh mix, which promotes air entrapment during mixing and casting [36], combined with the high water absorption capacity of the fibers themselves. Since all composites were produced using the same mixing procedure, the reduction in water absorption observed here can be directly attributed to the fiber treatments, particularly the alkaline treatment.
The capillary behavior of the composites is associated with both their water absorption capacity and the dimensions of the capillary pores. The incorporation of fibers resulted in capillarity values 1.7 to 2.2 times higher than those of the reference matrix, indicating a modification in the capillary structure of the matrix within the composite compared to the plain matrix. In addition, due to the porosity and water absorption capacity of the fibers, the composites contain more internally available water than the fiber-free matrix. Consequently, an increase in drying shrinkage was observed in the fiber-reinforced composites, as shown in Figure 9.
At 50 days, the drying shrinkage ranged from 861.87 µε for the reference matrix to 1062 µε, 1005.97 µε, and 1023.93 µε for the WAF, U-WAF, and UH composites, respectively. Notably, composites reinforced with alkaline-treated fibers showed lower drying shrinkage than those reinforced with hornified fibers, reflecting the reduced water absorption capacity of the fibers following alkaline treatment.
3.3. Mechanical Behavior of Composites
3.3.1. Direct Tensile
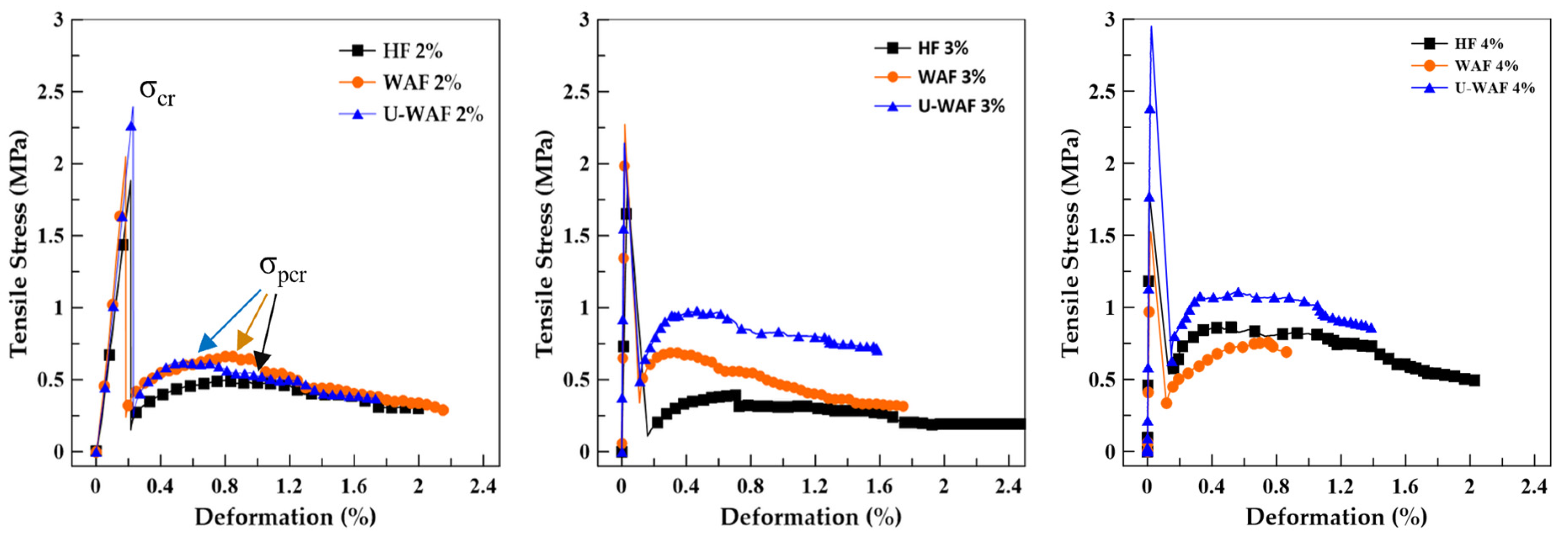
Figure 10 presents the typical stress–strain curves obtained from direct tensile tests of composites reinforced with 2%, 3%, and 4% treated fibers. The tests were terminated upon reaching the maximum deformation of the specimen and/or prior to the LVDT attaining its maximum displacement. Figure 11 illustrates the fracture modes of the composites under tensile loading, where in all cases the formation of a single crack was observed. Initially, the composites exhibit a linear elastic response up to the first-cracking point (σcr), followed by a sudden stress drop associated with the transfer of stresses from the brittle cementitious matrix to the fibers, which is characterized by a strain-softening behavior. With increasing deformation, a subsequent rise in stress is observed until the maximum post-cracking strength (σpcr) is reached. Beyond this point, the fibers bridging the cracks begin to be pulled out from the matrix, leading to a gradual reduction in stress. Similar behavior under tensile testing was observed by [35] for sisal fiber-reinforced mortar.
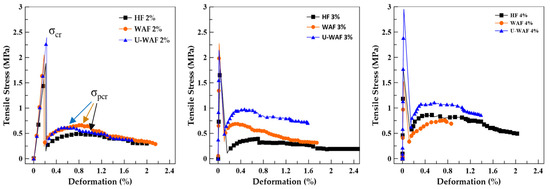
Figure 10.
Typical tensile stress curves for treated fiber composites.

Figure 11.
Fracture of composites subjected to tensile stresses.
Table 4 presents the values of first-cracking strength (σcr) and maximum post-cracking strength (σpcr) of the composites. The matrix exhibited a low direct tensile strength (1.36 MPa) and limited deformation capacity (0.020%), confirming the brittle nature of cement-based materials. The incorporation of sisal fibers, regardless of treatment, led to significant improvements in tensile strength, evidencing the fibers’ ability to bridge cracks and transfer tensile stresses across the fracture plane.

Table 4.
Experimental results of the direct tensile test of matrix and composites.
For hornification fibers (HF), tensile strength increased progressively with fiber content, reaching 1.94 MPa at 4% volume fraction (+42.6% compared to the matrix). Deformation capacity was maintained or slightly increased, with a peak value of 0.023% for HF 3%, indicating an enhancement in ductility without compromising stiffness.
Composites reinforced with washed alkaline fibers (WAF) also showed notable strength gains, with maximum tensile strength of 1.91 MPa at 3% fiber content (+40.4%). However, WAF composites generally exhibited lower deformation capacities (0.012–0.016%) than HFs, suggesting a stiffer tensile response. This behavior may be attributed to the higher crystallinity of WAFs and improved fiber–matrix adhesion, which promote efficient stress transfer but limit strain localization.
Unwashed alkaline fibers (U-WAF) produced the most significant improvements, achieving 2.16 MPa at 2% fiber content and a maximum of 2.56 MPa at 4%, representing an 88.2% increase relative to the matrix. At lower fiber contents (2% and 3%), deformation capacity remained limited (0.012–0.014%), whereas at 4% volume fraction, it increased to 0.022%, comparable to HF composites. This suggests that, at higher fiber volumes, the greater number of crack-bridging elements compensates for the stiffer individual fiber behavior, allowing for increased overall composite ductility.
These results demonstrate that alkaline treatments, particularly U-WAF, enhance fiber tensile performance and, consequently, the tensile strength of cementitious composites. Nevertheless, the ductility response is treatment- and content-dependent, with HF maintaining better strain capacity at lower fiber contents and U-WAF excelling in strength enhancement, especially at higher fiber volumes. The observed trends align with previous reports that attribute the improved tensile behavior of natural fiber composites to the removal of amorphous components, increased surface roughness, and improved fiber–matrix bonding.
Liang [35] reported that alkaline treatment enhances the fiber–matrix interface in plant fibers, as evidenced by the improved mechanical performance of composites reinforced with treated fibers compared to untreated ones. However, the tensile strength of these composites remains lower than that of the plain matrix, a reduction attributed to defects and voids likely caused by fiber agglomeration and processing difficulties.
3.3.2. Four-Point Bending Test
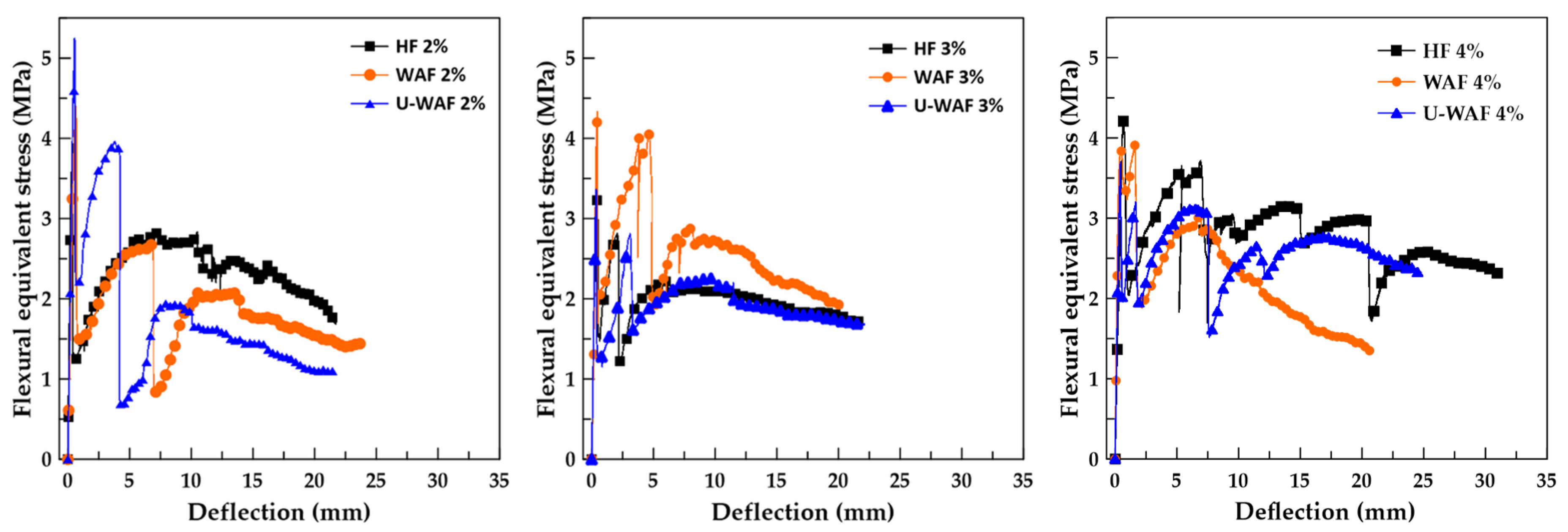
Figure 12 shows the stress–displacement curves under bending, with an initial linear elastic response up to the first-crack strength (σf), followed by a sudden stress drop. At this stage, the fibers are mobilized and begin to bridge the cracks, allowing the composite to sustain additional loads beyond matrix cracking until reaching a maximum stress value (σp), after which the gradual reduction in flexural strength begins. Similar flexural behavior was observed for cement mortar reinforced with sisal fiber treated with alkaline treatment and silane [11].
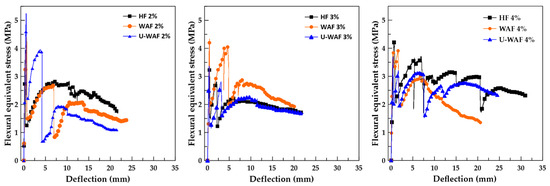
Figure 12.
Typical stress-displacement curves of composites.
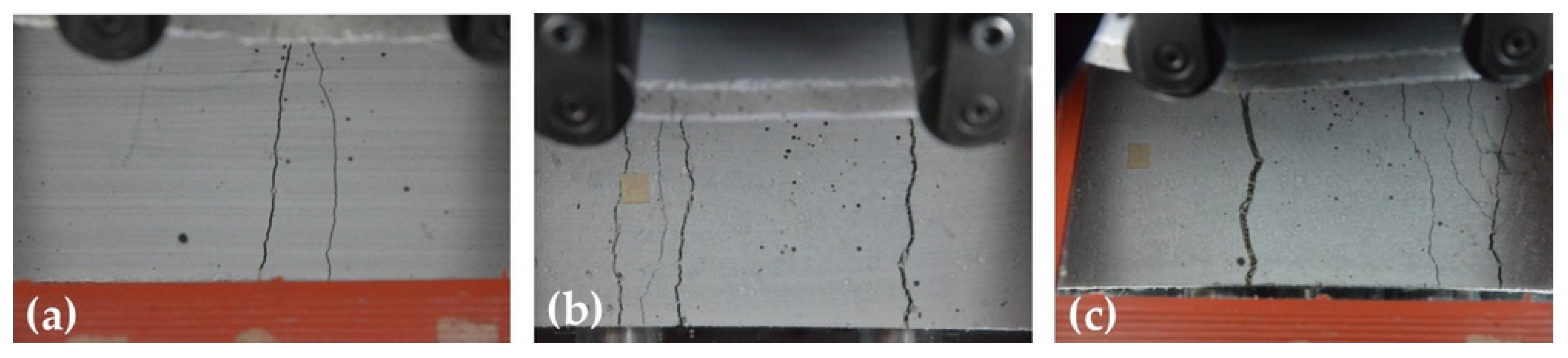
Unlike the behavior observed under direct tensile loading, which was characterized by the formation of a single dominant crack, the bending tests revealed the development of multiple cracks (multiple cracking phenomenon), particularly in composites with higher fiber contents. Figure 13 shows the fracture modes of U-WAF composites with varying fiber contents, highlighting the role of fiber bridging in enhancing post-cracking load capacity and overall ductility.

Figure 13.
Fracture mode of U-WAF composites subjected to four-point bending test: (a) 2%, (b) 3% and (c) 4%.
Table 5 presents the average experimental results obtained from the curve analysis. The toughness index T20 was calculated as the area under the stress–displacement curve for a deflection of 20 mm.

Table 5.
Experimental results of the bending test of composites.
The matrix exhibited a peak flexural strength of 4.37 MPa, a limited peak deflection of 0.19 mm, and negligible toughness (T20 = 0.007 kJ/m2), confirming its brittle failure mode. Fiber addition markedly improved the post-cracking response, with increases in deflection capacity and energy absorption across all treatments. Composites reinforced with hornified fibers (HF) showed improvements in flexural strength, with the highest value at 2% fiber content (4.73 MPa, +8.2% compared to the matrix). Peak deflection more than doubled (0.40–0.66 mm), and toughness increased substantially (T20 up to 1.79 kJ/m2), indicating a clear enhancement in ductility.
Washed alkaline fiber (WAF) composites presented the highest toughness among all groups, particularly at 3% fiber volume, which reached T20 = 1.94 kJ/m2 alongside a peak strength of 4.47 MPa. However, at 4% fiber content, flexural strength decreased to 3.83 MPa and peak deflection was significantly reduced, suggesting that excessive fiber content may lead to fiber agglomeration and weak zones in the matrix. Unwashed alkaline fiber (U-WAF) composites showed intermediate performance. While their toughness values (T20 up to 1.89 kJ/m2) and deflections were higher than those of the matrix, they remained below the WAF composites.
Overall, the results demonstrate that fiber treatment and volume fraction have a direct influence on flexural behavior. WAF at 3% fiber content provided the most favorable balance between flexural strength and energy absorption, while HF treatment excelled in enhancing ductility, and U-WAF achieved consistent but moderate improvements. These findings are consistent with literature reports that alkaline treatments and hornification improve the crack-bridging efficiency of natural fibers [10,13], leading to greater post-cracking toughness in cementitious composites.
Increasing fiber content consistently improves the toughness of composites across all treatments, in agreement with [6,11], who reported that sisal fibers enhance post-cracking behavior in cement-based composites.
4. Conclusions
This study evaluated the effect of sisal fiber treatment types on their physical and mechanical properties, as well as on the mechanical behavior of cement-based composites reinforced with the treated fibers. Based on the results obtained, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- Alkali treatments and hornification led to changes in the crystalline structure of the fibers, modifying the crystallinity index due to hemicellulose removal, which was confirmed by changes in fiber behavior in thermogravimetric analysis. As a result, the fibers showed reduced water absorption capacity and increased tensile strength. Alkali treatment without post-treatment washing was the most effective in improving the properties for application in cement-based composites.
- Composites reinforced with 4% treated fibers exhibited higher water absorption by immersion and capillarity compared to the fiber-free matrix, with composites containing U-WAFs showing the lowest values. Due to higher water absorption, the drying shrinkage of the composites was also higher than that of the matrix, whereas composites containing alkali-treated fibers showed lower shrinkage.
- The addition of fibers resulted in a ductile material, maintaining residual stress after the appearance of the first crack. In direct tension tests, the post-cracking stress was proportional to the fiber content added to the composite and was higher when U-WAFs were used.
- In bending tests, the fibers allowed for stress redistribution with the formation of multiple cracks in the composites, and toughness increased proportionally to the fiber content. No treatment proved superior to the others in achieving the best properties.
The findings of this study confirm that treated sisal fibers act as effective reinforcement in cementitious composites, significantly enhancing crack control and toughness. These improvements position the composite as a viable and sustainable alternative to asbestos cement and fiberglass for non-structural components, such as facade panels. The material’s profile is further strengthened by the use of sisal, a renewable and biodegradable resource. Although the applied treatment conditions proved effective, further research is essential to optimize the protocols and assess long-term durability. Future work, including a life cycle assessment and scalability studies, will be crucial to validate its industrial adoption in real-world structures.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.R.L.L. and R.D.T.F.; methodology, D.O.J.d.S.; validation, P.R.L.L. and D.O.J.d.S.; formal analysis, P.R.L.L. and D.O.J.d.S.; investigation, D.O.J.d.S.; resources, R.D.T.F.; data curation, P.R.L.L. and D.O.J.d.S.; writing—original draft preparation, D.O.J.d.S.; writing—review and editing, P.R.L.L. and R.D.T.F.; supervision, P.R.L.L. and R.D.T.F.; project administration, R.D.T.F.; funding acquisition, R.D.T.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior for the scholarships. P.R.L.L. thanks CNPq for a fellowship (Grant number 304631/2022-1).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| Ca(OH)2 | Calcium Hydroxide |
| Crl | Crystallinity index |
| DTG | Derivative Thermogravimetry |
| E | Young’s modulus |
| ε | Strain |
| FRC | Fiber-Reinforced Composite |
| HF | Hornified Fiber |
| LVDT | Linear Variable Differential Transformer |
| NF | Natural Fiber |
| REF | Reference matrix without fibers |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| σcr | First-cracking strength |
| σf | First-crack flexural strength |
| σp | Maximum flexural strength |
| σpcr | Maximum post-cracking tensile strength |
| T20 | Toughness index |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric Analysis |
| U-WAF | Unwashed Alkaline Fiber |
| WAF | Washed Alkaline Fiber |
| Wabs | Water absorption capacity |
| XRD | X-Ray Diffraction |
References
- Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Zhu, L.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, L. Carbon Neutrality Potential of Textile Products Made from Plant-Derived Fibers. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, F.; Pinheiro, R.; Silva, A. Strengthening and Repair of RC Beams Using Natural Sisal Fabric-Reinforced Cementitious Matrix Composite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 447, 138047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, G.; Coppola, B.; Di Maio, L.; Incarnato, L.; Martinelli, E. Tensile strength of flax fabrics to be used as reinforcement in cement-based composites: Experimental tests under different environmental exposures. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 168, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohan, L.; Fioroni, C.A.; Azevedo, A.G.D.S.; Leonardi, B.; Baruque-Ramos, J.; Fangueiro, R.; Savastano, H., Jr. Jute Textiles with Enhanced Interfacial Bonding as Reinforcement for Cementitious Composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2024, 58, 1847–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, F.P.; de Andrade Silva, F. On the use of natural curauá reinforced cement based composites for structural applications. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 114, 103775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biskri, Y.; Babouri, L.; Boukhelf, F.; Charradi, K.; Annaba, K.; El Mendili, Y. On the Physical-Mechanical Behavior of Fiber Cement Composite: Effect of Chemical Treatment of Sisal Fibers. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 101, 111978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, P.R.L.; Silva, J.M.; Barros, J.A.; Roque, A.B.; Fontes, C.M.; Lima, J.M. Short Sisal Fiber Reinforced Recycled Concrete Block for One-Way Precast Concrete Slabs. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 187, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Yadav, B.P. Sustainable Innovations and Future Prospects in Construction Material: A Review on Natural Fiber-Reinforced Cement Composites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 62549–62587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsalu Fode, T.; Ali, R.; Chande Jande, Y.A.; Kivevele, T.; Rahbar, N. A Review on Degradation Improvement of Sisal Fiber by Alkali and Pozzolana for Cement Composite Materials. J. Nat. Fibers 2024, 21, 2335327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.R.; Lima, P.R.L.; de Andrade Silva, F.; Lima, P.R.L.; Filho, R.D.T. Effect of Fiber Treatments on the Sisal Fiber Properties and Fiber–Matrix Bond in Cement-Based Systems. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 101, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Ding, Y.; Li, S.; Song, Y.; Gong, H.; Zhang, Y. Silane Treatment for Sisal Fibers to Improve the Degradation Resistance and Interface with Cement Matrix. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 429, 136435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savastano, H., Jr.; Santos, S.F.; Radonjic, M.; Soboyejo, W.O. Fracture and Fatigue of Natural Fiber-Reinforced Cementitious Composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Castoldi, R.; Liebscher, M.; de Souza, L.M.S.; Mechtcherine, V.; Menezes, R.P.; de Andrade Silva, F. Effect of Polymeric Fiber Coating on the Mechanical Performance, Water Absorption, and Interfacial Bond with Cement-Based Matrices. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 404, 133222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Amaral, L.M.; de Souza Rodrigues, C.; Poggiali, F.S.J. Hornification on Vegetable Fibers to Improve Fiber-Cement Composites: A Critical Review. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 48, 103947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda Filho, A.B.; Dantas, C.L.D.E.R.; Lima, P.R.L.; Fontes, C.M.A. Autoclave Treatment of Sisal Fiber and Its Effect on Fiber Properties and on the Pull-Out Behavior from Cementitious Matrix. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 11204–11217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.R.; de Andrade Silva, F.; Lima, P.R.L.; Filho, R.D.T. Effect of Hornification on the Structure, Tensile Behavior and Fiber-Matrix Bond of Sisal, Jute and Curauá Fiber Cement-Based Composite Systems. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 139, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, H.A.; Tanni, T.R.; Shahid, M.A. Analysis of Water Absorption of Different Natural Fibers. J. Text. Sci. Technol. 2021, 7, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledzki, A.K.; Gassan, J. Composites Reinforced with Cellulose-Based Fibres. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1999, 24, 221–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindole, C.F.; Bigambo, P.N. Effect of Alkali Treatment on the Chemical Composition and Dyeability of Sisal Fibers. Tanz. J. Sci. 2024, 50, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raharjo, W.P.; Raharjo, W.W.; Kusharjanta, B. Characterization of Calcium Hydroxide-Treated Zalacca Fibers for Improving Properties as Reinforcement for Composites. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1096, 012036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Guru, S.; Padmakaran, P.; Mishra, D.; Mudgal, M.; Dhakad, S. Characterisation Studies and Impact of Chemical Treatment on Mechanical Properties of Sisal Fiber. Compos. Interfaces 2011, 18, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.R. Influência da Hornificação na Aderência Fibra-Matriz e no Comportamento Mecânico de Compósitos Cimentícios Reforçados com Fibras Curtas de Sisal. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Estadual de Feira de Santana, Feira de Santana, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM C1557-03; Standard Test Method for Tensile Strength and Young’s Modulus of Fibers. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2003.
- Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. Argamassa e Concreto Endurecidos: Determinação da Absorção de Água, Índice de Vazios e Massa Específica; NBR 9778; ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. Argamassa e Concreto Endurecidos: Determinação da Absorção de Água por Capilaridade; NBR 9779; ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM Subcommittee C09.68; Standard Test Method for Length Change of Hardened Hydraulic-Cement Mortar and Concrete. ASTM C157-08. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2008.
- Martin, A.R.; Martins, M.A.; da Silva, O.R.; Mattoso, L.H. Studies on the Thermal Properties of Sisal Fiber and Its Constituents. Thermochim. Acta 2010, 506, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J. Degradation Behavior and Kinetics of Sisal Fiber in Pore Solutions of Sustainable Cementitious Composite Containing Metakaolin. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 150, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, A.C.H.; Rosa, D.; Fechine, P.; Mazzetto, S. Properties of Sisal Fibers Treated by Alkali Solution and Their Application into Cardanol-Based Bio-Composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Santos, E.B.; Gomes Moreno, C.; Pereira Barros, J.J.; de Moura, D.A.; de Carvalho Fim, F.; Ries, A.; Ramos Wellen, R.M.; da Silva, L.B. Effect of Alkaline and Hot Water Treatments on the Structure and Morphology of Piassava Fibers. Mater. Res. 2018, 21, e20170365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Zeng, J.; Wang, B.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, K. Cellulosic Fiber: Mechanical Fibrillation-Morphology-Rheology Relationships. Cellulose 2021, 28, 7651–7662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, B.W.; Chakraborty, S.; Kim, H. Efficacy of Alkali-Treated Jute as Fibre Reinforcement in Enhancing the Mechanical Properties of Cement Mortar. Mater. Struct. 2016, 49, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Chen, F.; Ma, Y.; Roselli, A.; Enqvist, E.; Hassi, H. Single Fiber Swelling Behavior for Natural and Man-Made Cellulose Fibers under Alkaline Treatment. Cellulose 2021, 28, 11287–11298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshaid, H.; Mishra, R.K.; Raza, A.; Hussain, U.; Rahman, M.L.; Nazari, S.; Chandan, V.; Muller, M.; Choteborsky, R. Natural Cellulosic Fiber Reinforced Concrete: Influence of Fiber Type and Loading Percentage on Mechanical and Water Absorption Performance. Materials 2022, 15, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Fu, Z.; Li, Z.; Liang, L.; Luo, Q.; Long, W. Enhancing the Applicability of Sisal Fibers in Cement-Based Materials through Alkali Treatment and Penetrating Crystallization. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 490, 144736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Saidi, T.; Jamil, M.; Amalia, Z.; Mubarak, A. Mechanical Properties and Absorption of High-Strength Fiber-Reinforced Concrete (HSFRC) with Sustainable Natural Fibers. Buildings 2022, 12, 2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).