Effect of Additives Ag and Rare‐Earth Elements Y and Sc on the Properties of Hydrogen Sensors Based on Thin SnO2 Films during Long‐Term Testing
Abstract
1. Introduction
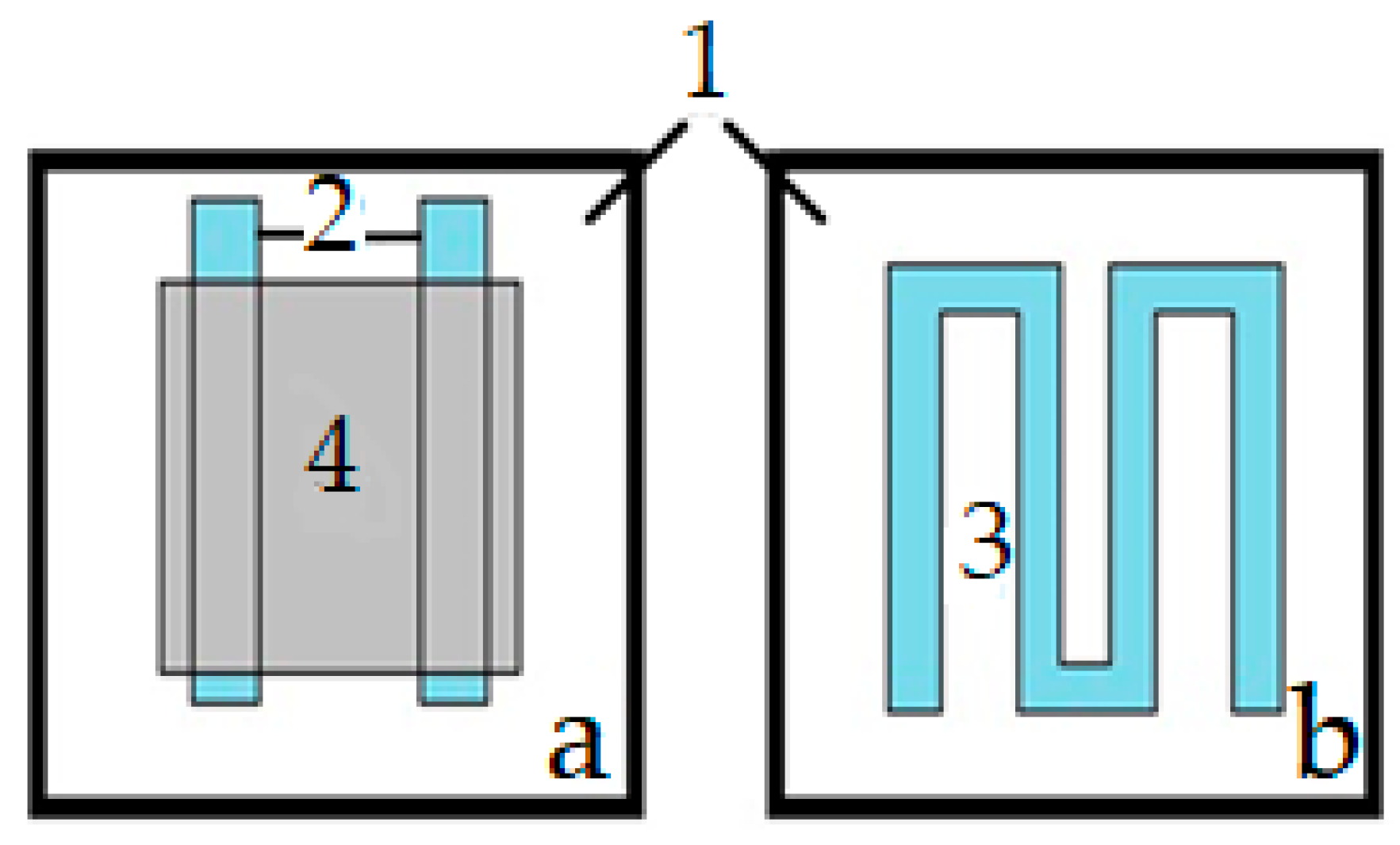
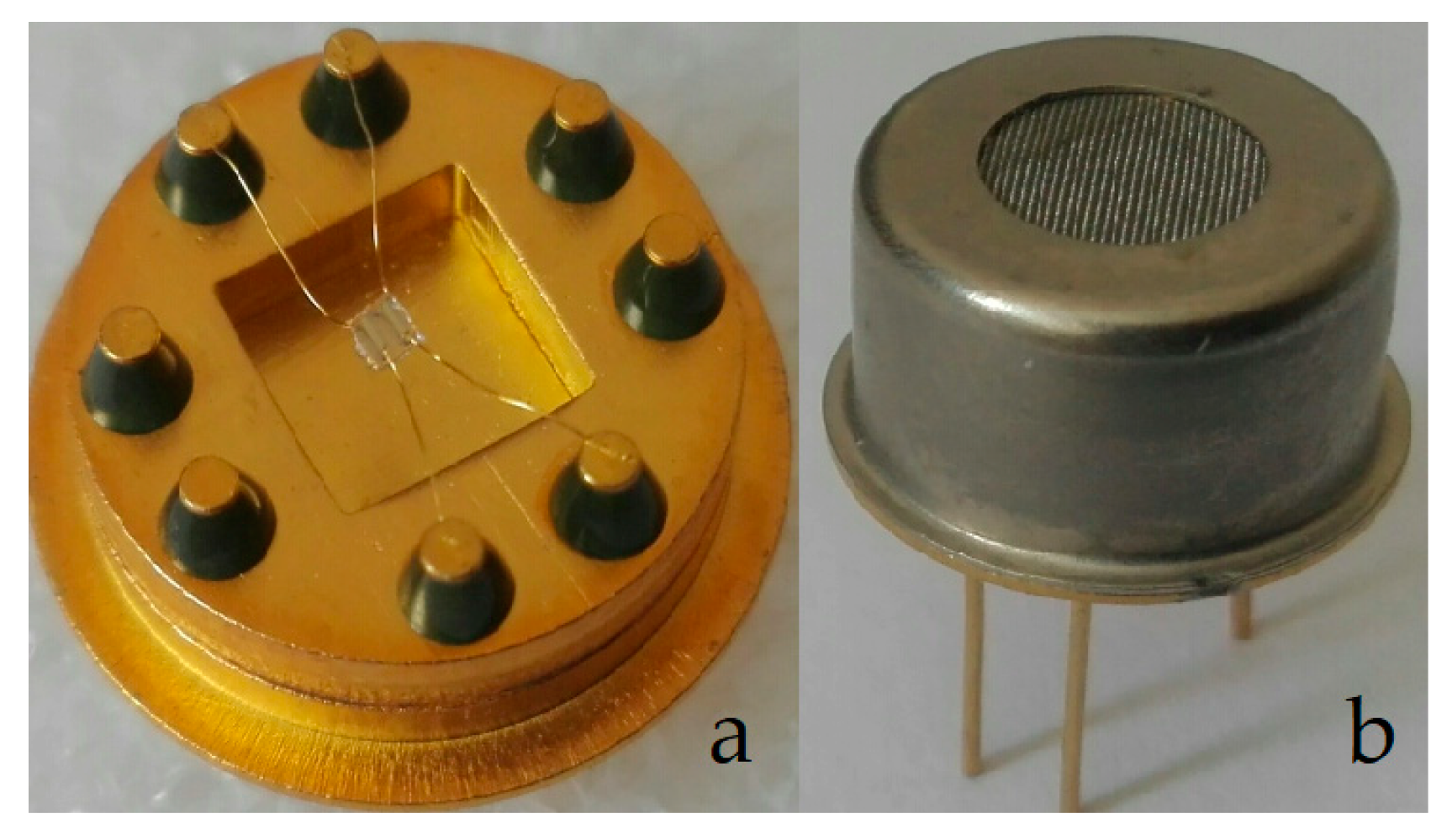
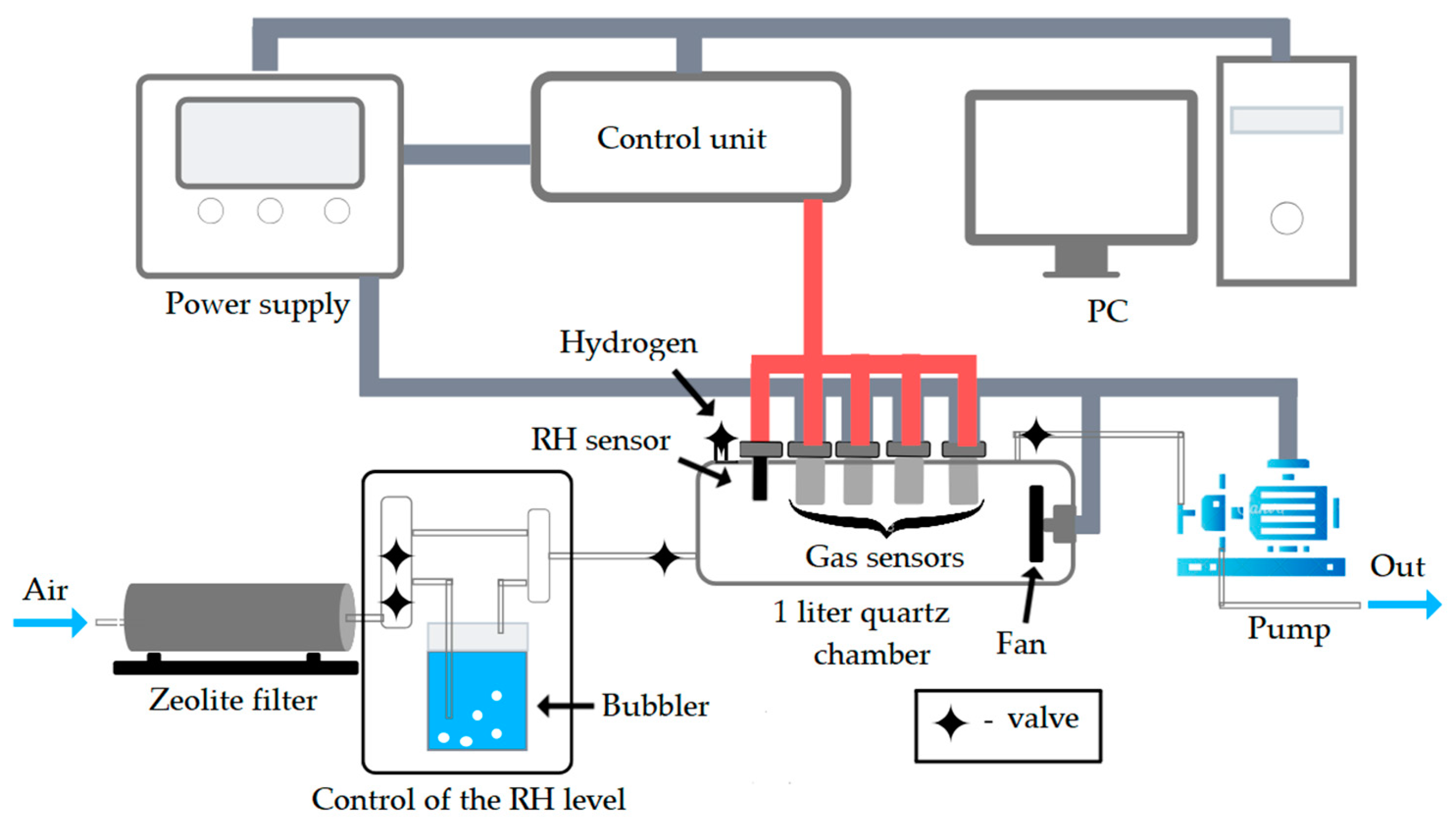
2. Materials and Methods
- Pt/Pd/SnO2:Sb;
- Pt/Pd/SnO2:Sb, Ag;
- Pt/Pd/SnO2:Sb, Y;
- Pt/Pd/SnO2:Sb, Sc;
- Pt/Pd/SnO2:Sb, Ag, Y;
- Pt/Pd/SnO2:Sb, Ag, Sc.
3. Results
3.1. Nanostructure and Composition of the Films
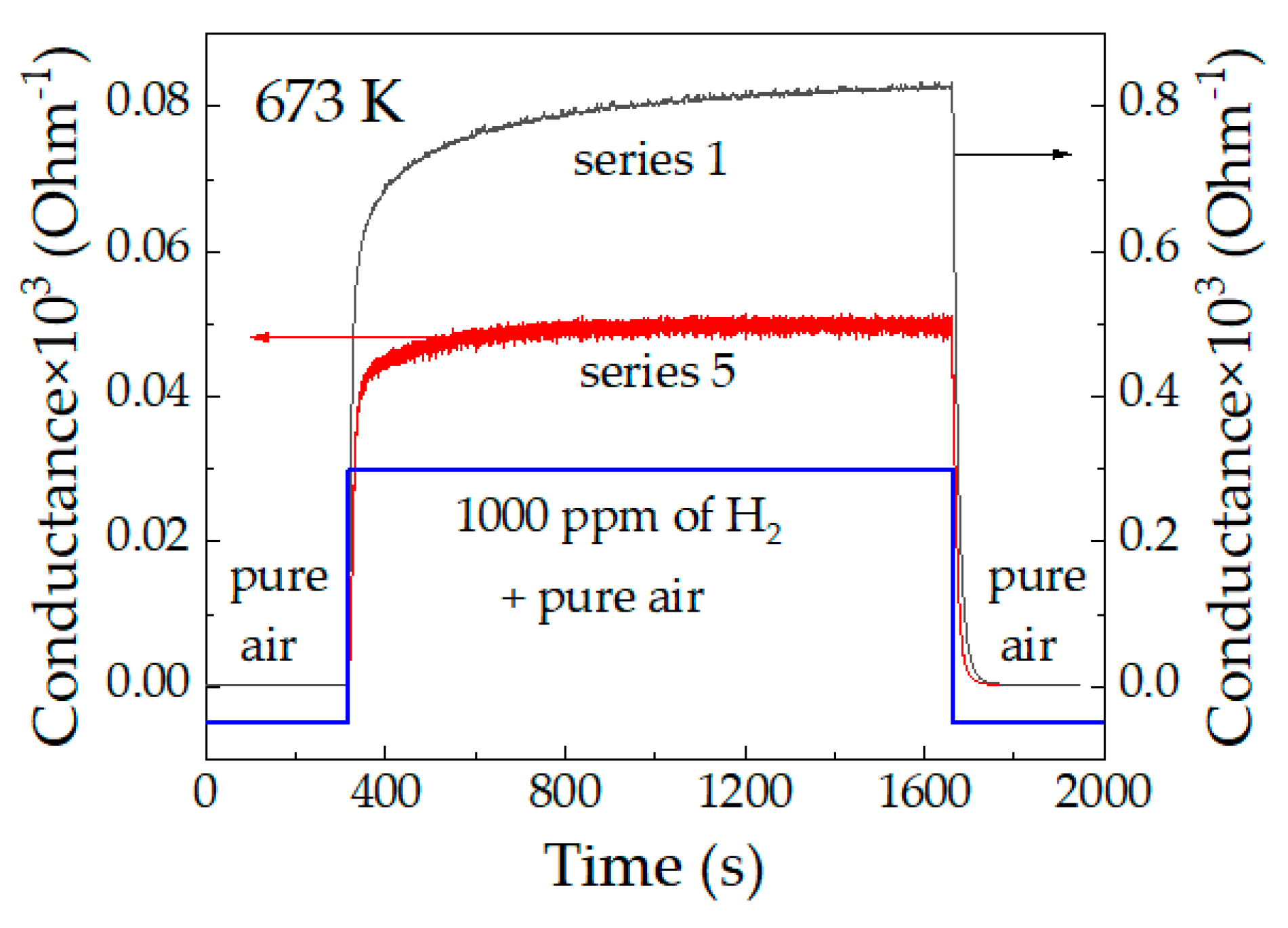
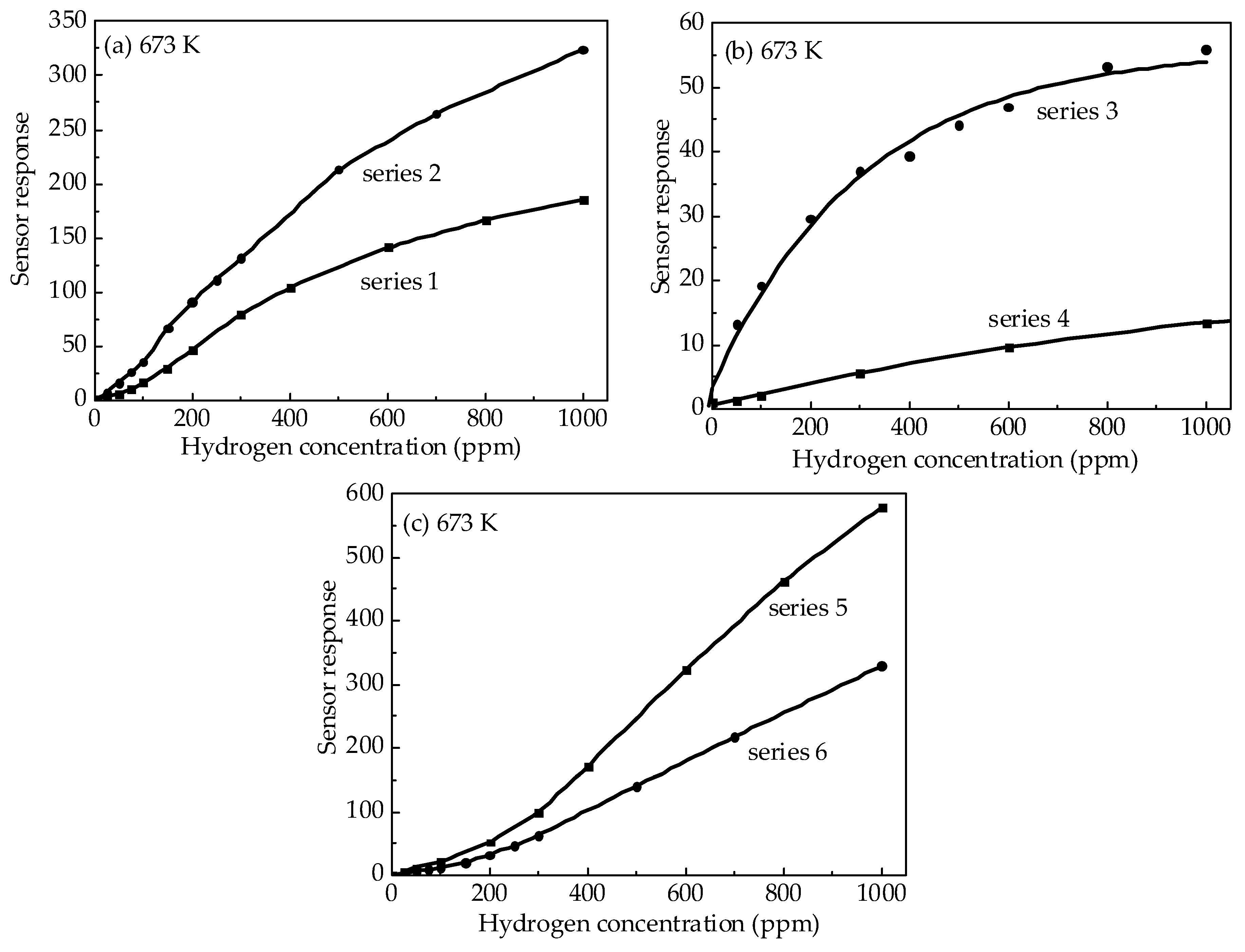
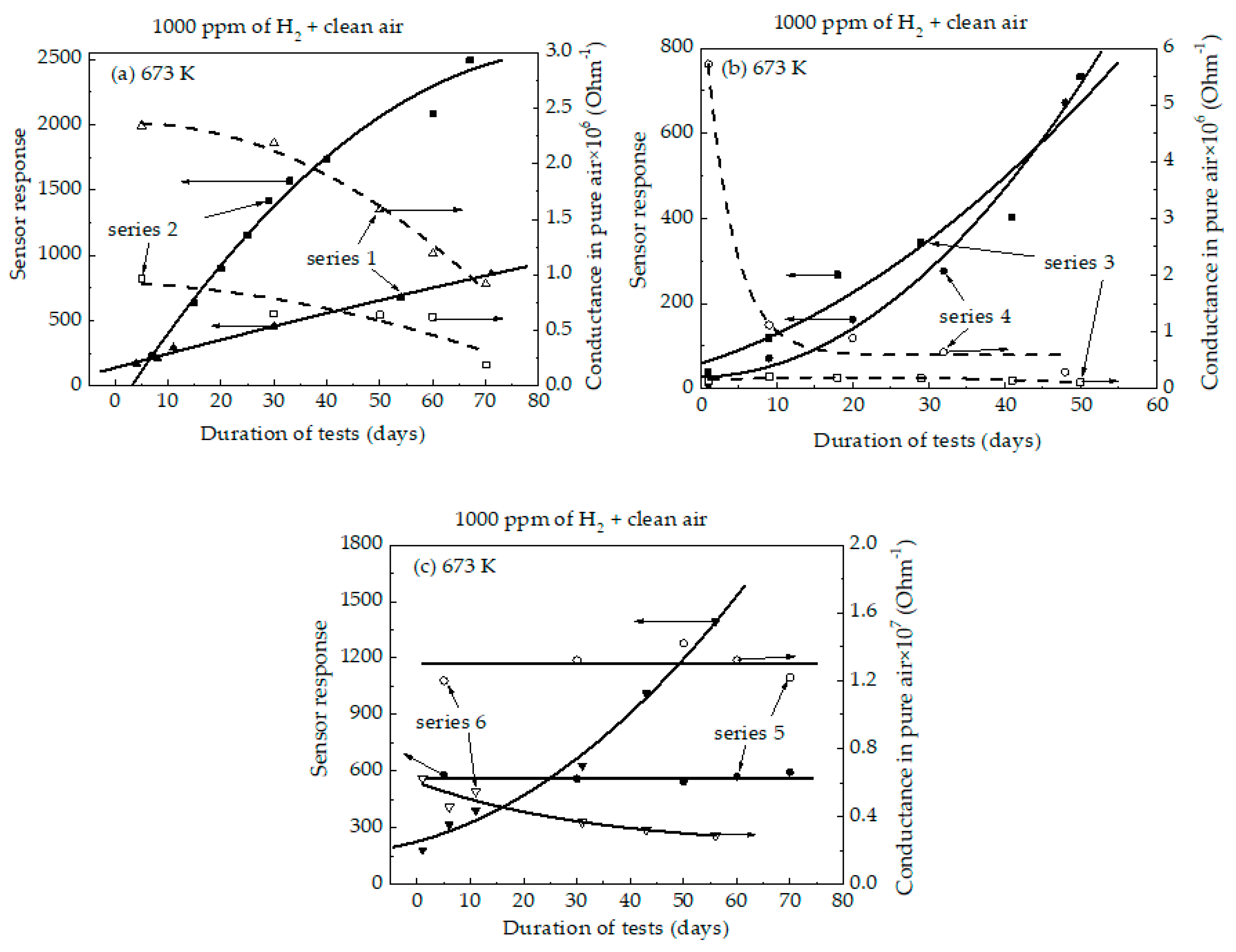
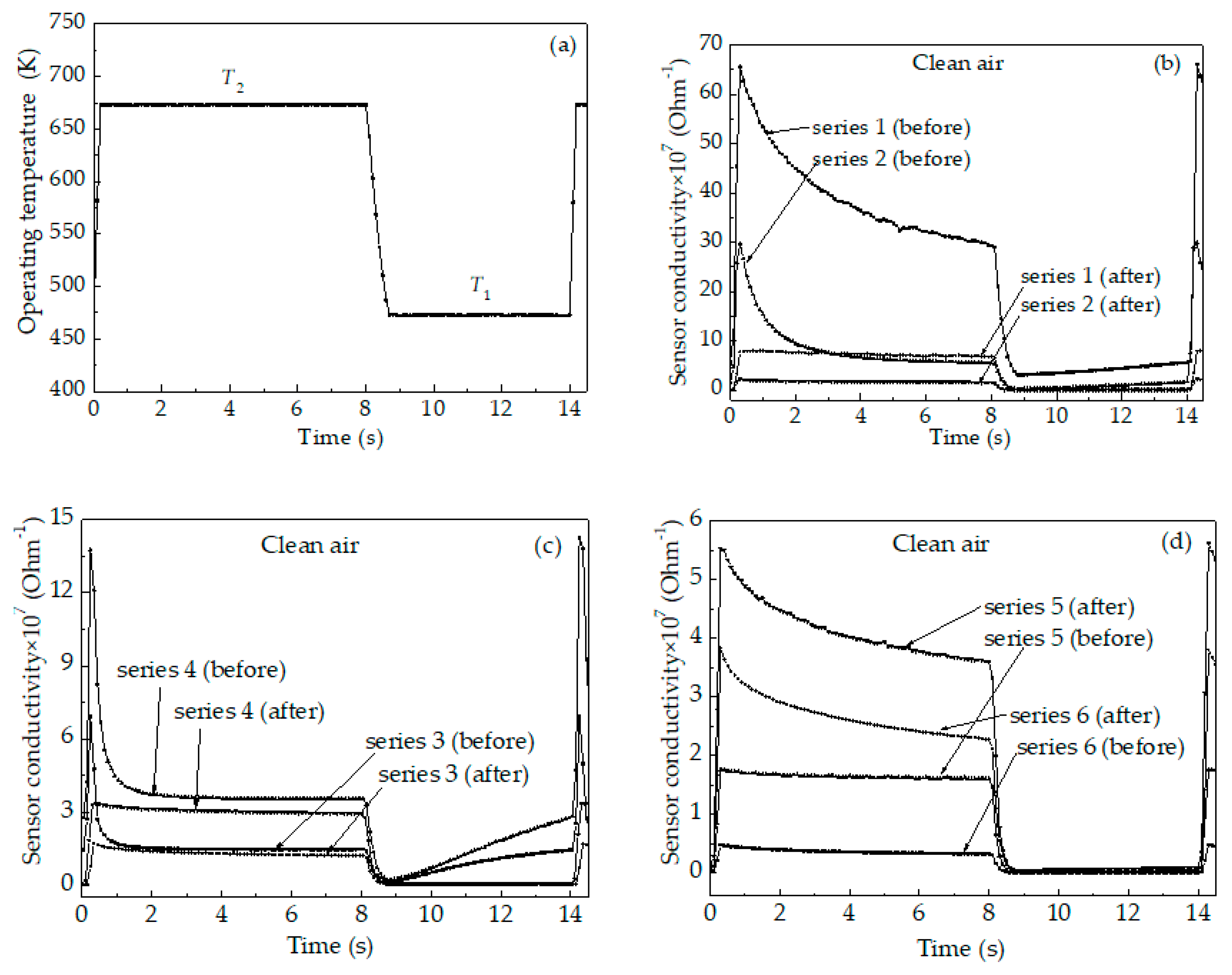
3.2. Characterization of the Sensors
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Physical Models of Sensors
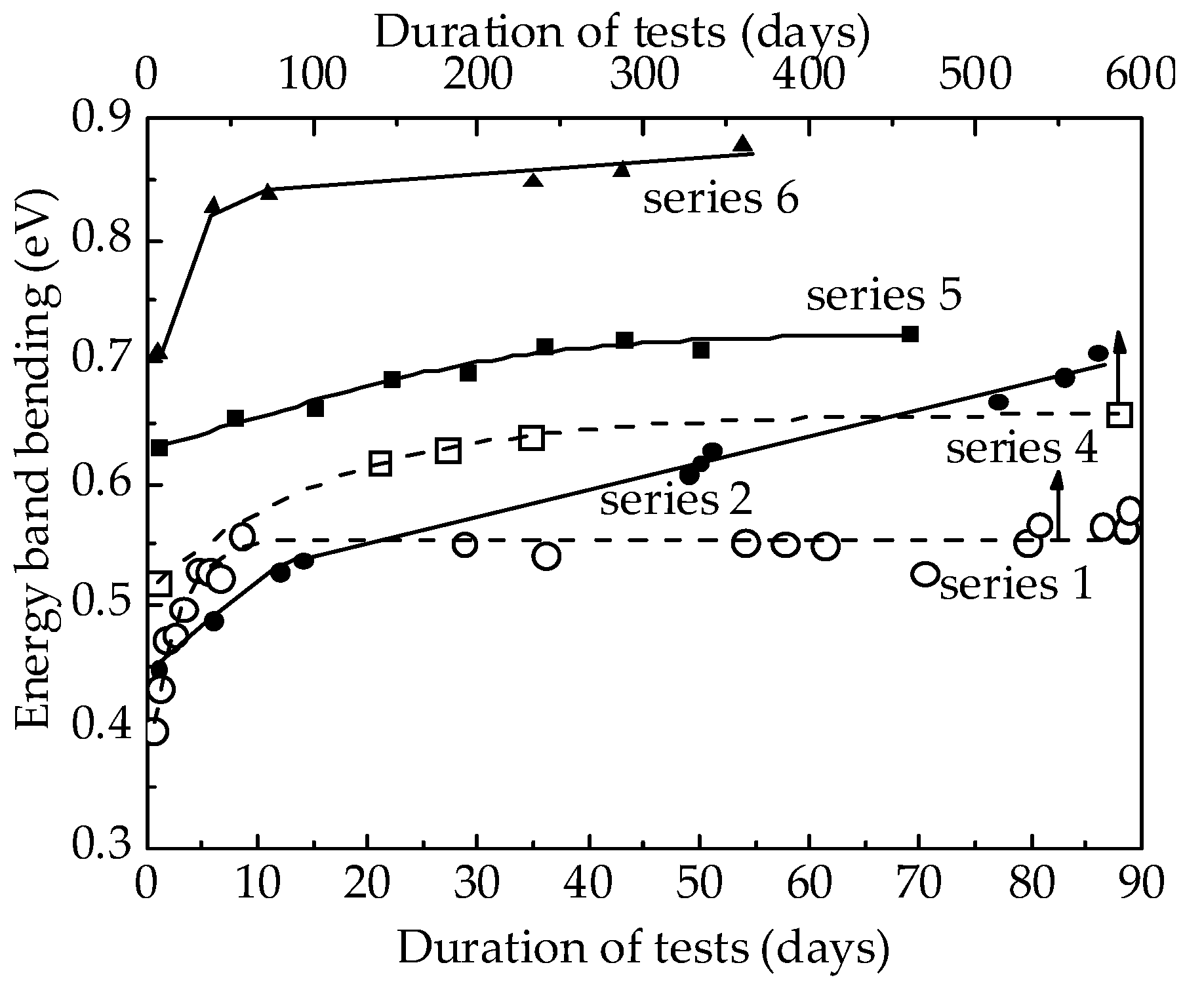
4.2. Method for Determining the Energy Band Bending
4.3. Mechanisms of the Influence of Ag, Y, and Sc in the Volume of SnO2 on the Properties and Stability of Hydrogen Sensors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hübner, M.; Bârsan, N.; Weimar, U. Influences of Al, Pd and Pt additives on the conduction mechanism as well as the surface and bulk properties of SnO2 based polycrystalline thick film gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 171, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübner, M.; Pavelko, R.; Kemmler, J.; Bârsan, N.; Weimar, U. Influence of material properties on hydrogen sensing for SnO2 nanomaterials. Proced. Chem. 2009, 1, 1423–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bârsan, N. Transduction in semiconducting metal oxide based gas sensors—Implications of the conduction mechanism. Proced. Eng. 2011, 25, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübner, M.; Hafner, S.; Bârsan, N.; Weimar, U. The influence of Pt doping on the sensing and conduction mechanism of SnO2 based thick film sensors. Proced. Eng. 2011, 25, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, S.R. Selectivity in semiconductor gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1987, 12, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivetskiy, V.V.; Ponzoni, A.; Comini, E.; Badalyan, S.M.; Rumyantseva, M.N.; Gaskov, A.M. Materials based on modified SnO2 for selective gas sensors. Inorg. Mater. 2010, 46, 1100–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotcenkov, G.; Cho, B.K. Instability of metal oxide-based conductometric gas sensors and approaches to stability improvement (short survey). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 156, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Choi, S.-J.; Park, K.-M.; Lee, S.S.; Choi, S.; Kim, I.-D.; Park, C.O. The stability, sensitivity and response transients of ZnO, SnO2 and WO3 sensors under acetone, toluene and H2S environments. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 197, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T.; Matsubara, I.; Kadosaki, M.; Sakai, Y.; Shin, W.; Izu, N. Effects of high-humidity aging on platinum, palladium, and gold loaded tin oxide-volatile organic compound sensors. Sensors 2010, 10, 6513–6521. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220/10/7/6513 (accessed on 2 July 2019). [CrossRef]
- Gaman, V.I.; Sevast’yanov, Е.Y.; Маksimova, N.K.; Аlmaev, А.V.; Sergeichenko, N.S. Characteristics of the semiconductor resistive hydrogen sensors in the thermo-cyclic operation mode. Russ. Phys. J. 2014, 56, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevast’yanov, E.Y.; Maksimova, N.K.; Novikov, V.A.; Rudov, F.V.; Sergeychenko, N.V.; Chernikov, E.V. Effect of Pt, Pd, Au additives on the surface and in the bulk of tin dioxide thin films on the electrical and gas-sensitive properties. Semiconductors 2012, 46, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchigami, M.; Kasahara, N. The Fukushima nuclear power plant accident: The main sequence of events. In The 2011 Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant Accident; Elsevier: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 21–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübert, T.; Boon-Brett, L.; Black, G.; Banach, U. Hydrogen sensors—A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 157, 329–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, O.; Östberg, C.; Pagels, J.; Sebastian, A. Air contaminants in a submarine equipped with air independent propulsion. J. Environ. Monit. 2006, 8, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenmann, A.; Amann, A.; Said, M.; Datta, B.; Ledochowski, M. Implementation and interpretation of hydrogen breath tests. J. Breath Res. 2008, 2, 046002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kien, N.; Hung, C.M.; Ngoc, T.M.; Le, D.T.T.; Hoa, N.D.; Duy, N.V.; Hieu, N.V. Low-temperature prototype hydrogen sensors using Pd-decorated SnO2 nanowires for exhaled breath applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 253, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaman, V.I.; Almaev, A.V.; Maksimova, N.K. Stability of characteristics of resistive hydrogen sensors based on thin tin dioxide films with deposited catalysts Pt and Pd. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Siberian Conference on Control and Communications (SIBCON), Omsk, Russia, 21–23 May 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potekaev, A.I.; Sevast’yanov, Е.Y.; Маksimova, N.K.; Chernikov, E.V.; Sergeychenko, N.V. Stability of characteristics of CO sensors based on tin dioxide thin films in the thermo-cyclic mode. Russ. Phys. J. 2017, 59, 2177–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevast’yanov, Е.Y.; Маksimova, N.K.; Chernikov, E.V.; Sergeychenko, N.V.; Rudov, F.V. Properties of hydrogen sulfide sensors based on thin films of tin dioxide and tungsten trioxide. Russ. Phys. J. 2016, 59, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevast’yanov, Е.Y.; Маksimova, N.K.; Potekaev, A.I.; Khludkova, L.S.; Chernikov, E.V.; Davydova, T.A. Effect of various catalysts on the stability of characteristics of acetone sensors based on thin nanocrystalline SnO2 films. Russ. Phys. J. 2018, 60, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevast’yanov, Е.Y.; Маksimova, N.K.; Potekaev, A.I.; Sergeychenko, N.V.; Chernikov, E.V.; Аlmaev, А.V.; Kushnarev, B.O. Properties of resistive hydrogen sensors as a function of additives of 3d-metals introduced in the volume of thin nanocrystalline SnO2 films. Russ. Phys. J. 2017, 59, 1094–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreno, N.L.V.; Maciel, A.P.; Leite, E.R.; Lisboa-Filho, P.N.; Longo, E.; Valentino, A.; Probst, L.E.D.; Paiva-Santos, C.O.; Schreiner, W.H. The influence of cation segregation on the methanol decomposition on nanostructured SnO2. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 86, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotcenkov, G.; Cho, B.K. Metal oxide composites in conductometric gas sensors: Achievements and challenges. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 244, 182–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, R.; Maciel, A.P.; Weber, I.T.; Lisboa-Filho, P.N.; Longo, E.; Paiva-Santos, C.O.; Andrade, A.V.C.; Pakoscimas, C.A.; Maniette, Y.; Schreiner, W.H. Development of metal oxide nanoparticles with high stability against particle growth using a metastable solid solution. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Ma, S.Y.; Li, X.B.; Luo, J.; Li, W.Q.; Li, F.M.; Mao, Y.Z.; Wang, T.T.; Li, Y.F. Highly sensitive acetone sensors based on Y-doped SnO2 prismatic hollow nanofibers synthesized by electrospinning. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 2014, 200, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Ma, S.Y.; Wang, T.T.; Luo, J.; Li, X.B.; Li, W.Q.; Mao, Y.Z.; Gz, D.J. Highly sensitive acetic acid gas sensor based on coral-like and Y-doped SnO2 nanoparticles prepared by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2014, 137, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotcenkov, G.; Cho, B.K.; Gulina, L.B.; Tolstoy, V.P. Gas sensor application of Ag nanoclusters synthesized by SILD method. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 166–167, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Chen, Q.; Lian, M.-R.; Liu, N.-C.; Stevenson, R.G.; Adami, F. Micromachined nanocrystalline silver doped SnO2 H2S sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 114, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiduk, P.I.; Chevallier, J.; Prokopyev, S.L.; Nylandsted Larsen, A. Plasmonic-based SnO2 gas sensor with in-void segregated silver nanoparticles. Microelectron. Eng. 2014, 125, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.N.; Mehta, B.R.; Joshi, R.K.; Kruis, F.; Shivaprasad, S.M. Enhanced gas sensing properties of In2O3: Ag composite nanoparticle layers; electronic interaction, size and surface induced effects. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 125, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushima, S.; Teraoka, Y.; Miura, N.; Yamazoe, N. Electronic interaction between metal additives and tin dioxide in tin dioxide-based gas sensors. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 27, 1798–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.D.; Riggs, W.M.; Davis, L.E.; Moulder, J.F.; Mullenberg, G.E. Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy; Perkin-Elder Corp., Physical Electronics Division: Eden Prairie, MN, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turishchev, S.Y.; Chuvenkova, O.A.; Parinova, E.V.; Koyuda, D.A.; Chumakov, R.G.; Presselt, M.; Schleusener, A.; Sivakov, V. XPS investigations of MOCVD tin oxide thin layers on Si nanowires array. Results Phys. 2018, 11, 507–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, D.; Seah, M.P. Practical Surface Analysis by Auger and X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R.; Smart, R.S.C. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Sc, Ti, V, Cu and Zn. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batzill, M.; Diebold, U. The surface and materials science of tin oxide. Prog. Surf. Sci. 2005, 79, 47–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domashevskaya, E.P.; Ryabtsev, S.V.; Yurakov, Y.A.; Chuvenkova, O.A.; Kashkarov, V.M.; Turishchev, S.Y.; Kushev, S.B.; Lukin, A.N. SnOx obtaining by thermal oxidation of nanoscale tin films in the air and its characterization. Thin Solid Films 2007, 515, 6350–6355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, K.B.; Bhagavat, G.K. Optical absorption studies on tin oxide films. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 1981, 14, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.-H.; Choe, Y.-S.; Kim, D.-S. Effect of low energy oxygen ion beam on optical and electrical characteristics of dual ion beam sputtered SnO2 thin films. Thin Solid Films 1999, 349, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanon, G.; Rup, R.; Mansingh, A. Band-gap narrowing and band structure in degenerate tin oxide (SnO2) films. Phys. Rev. B 1991, 44, 5672–5680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Neri, G.; Pinna, N. Nanostructured materials for room-temperature gas sensors. Adv. Mater. 2018, 185, 795–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaman, V.I.; Аlmaev, А.V. Dependences of characteristics of sensors based on tin dioxide on the hydrogen concentration and humidity of gas mixture. Russ. Phys. J. 2017, 60, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaman, V.I. Basic physics of semiconductor hydrogen sensors. Russ. Phys. J. 2008, 51, 425–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotcenkov, G.; Brinzari, V.; Golovanov, V.; Blinov, Y. Kinetics of gas response to reducing gases of SnO2 films, deposited by spray pyrolysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 98, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Аlmaev, А.V.; Gaman, V.I. Characteristics of hydrogen sensors based on thin tin dioxide films modified with gold. Russ. Phys. J. 2017, 60, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.R. Comprehensive Handbook of Chemical Bond Energies; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
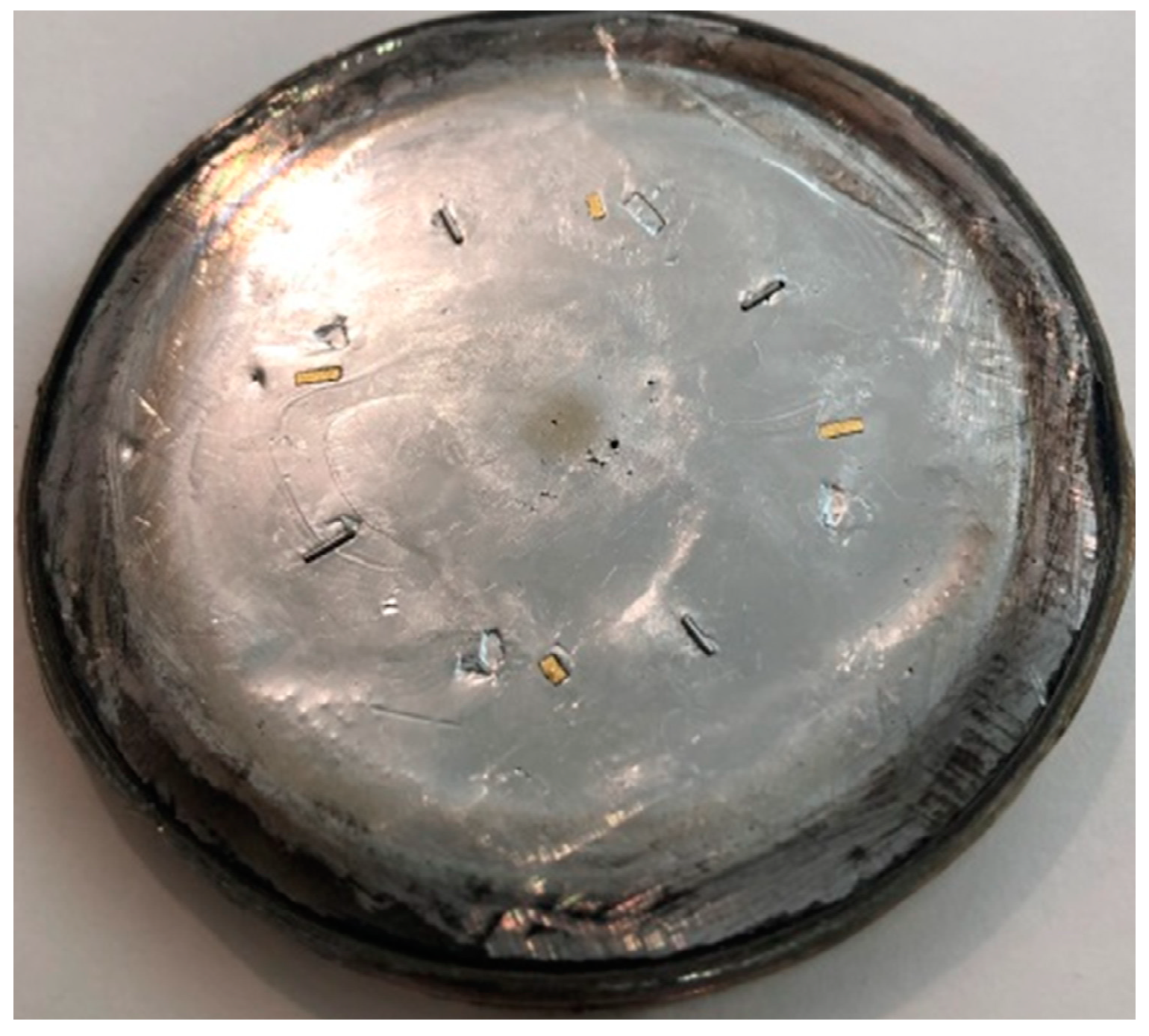

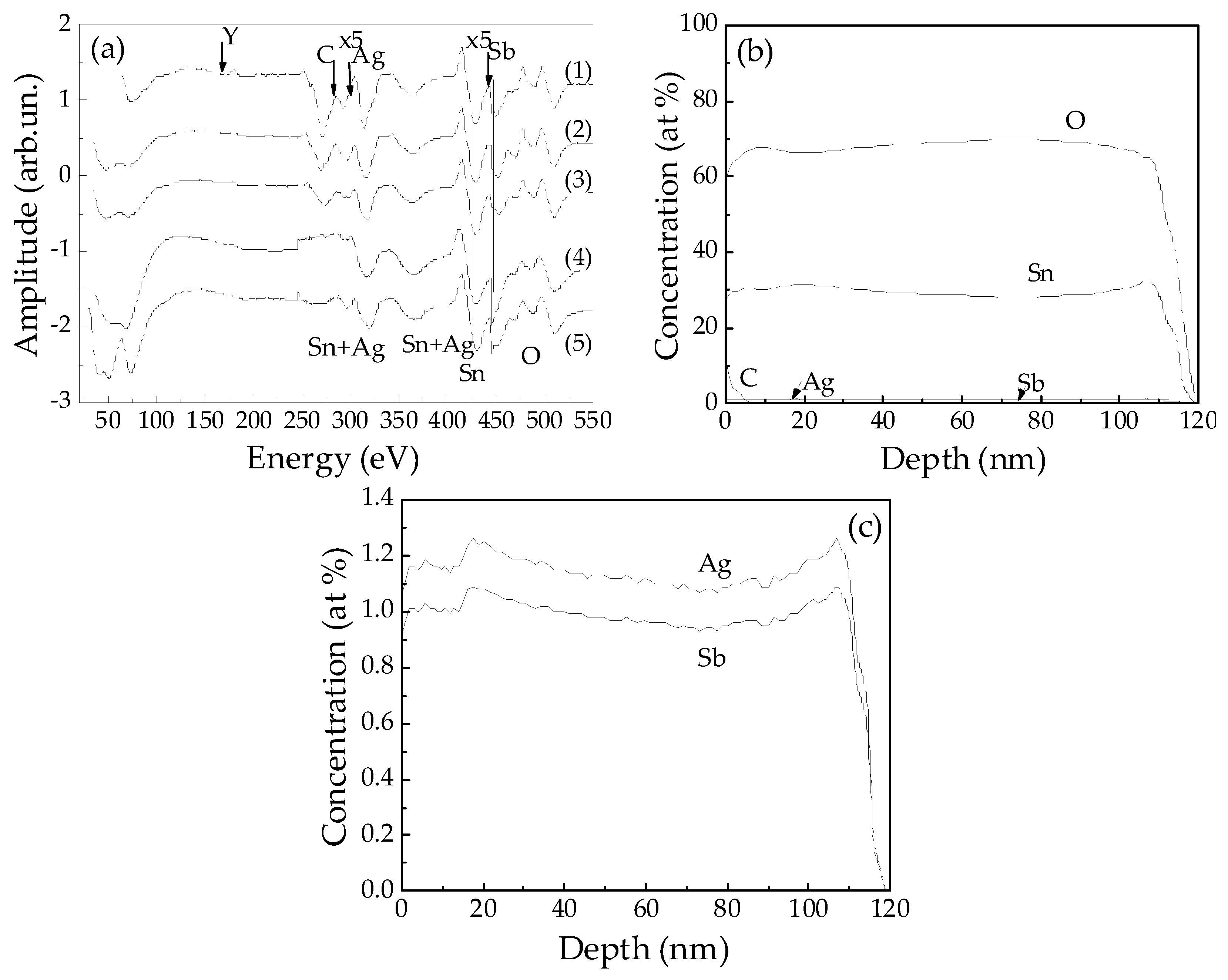
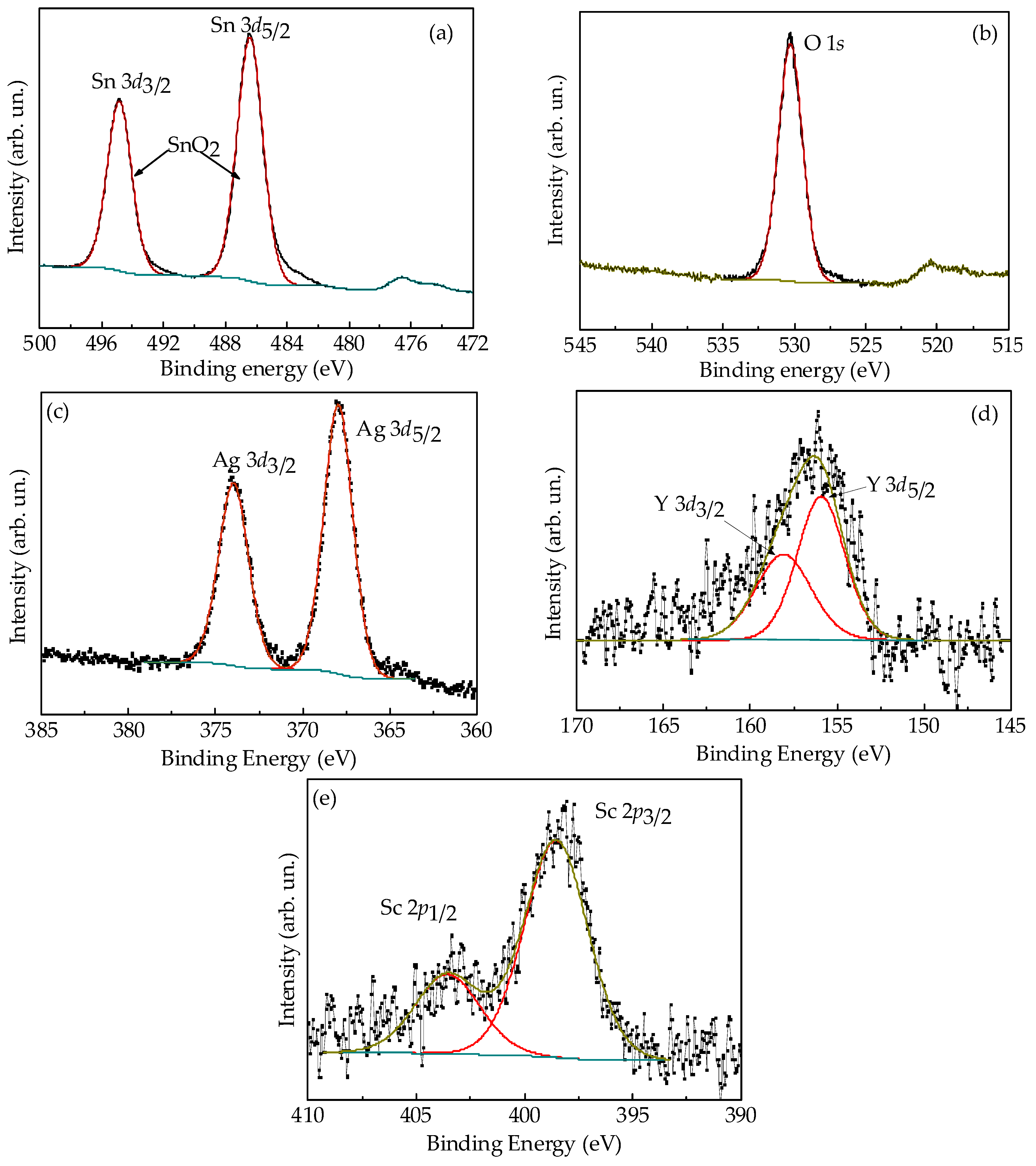
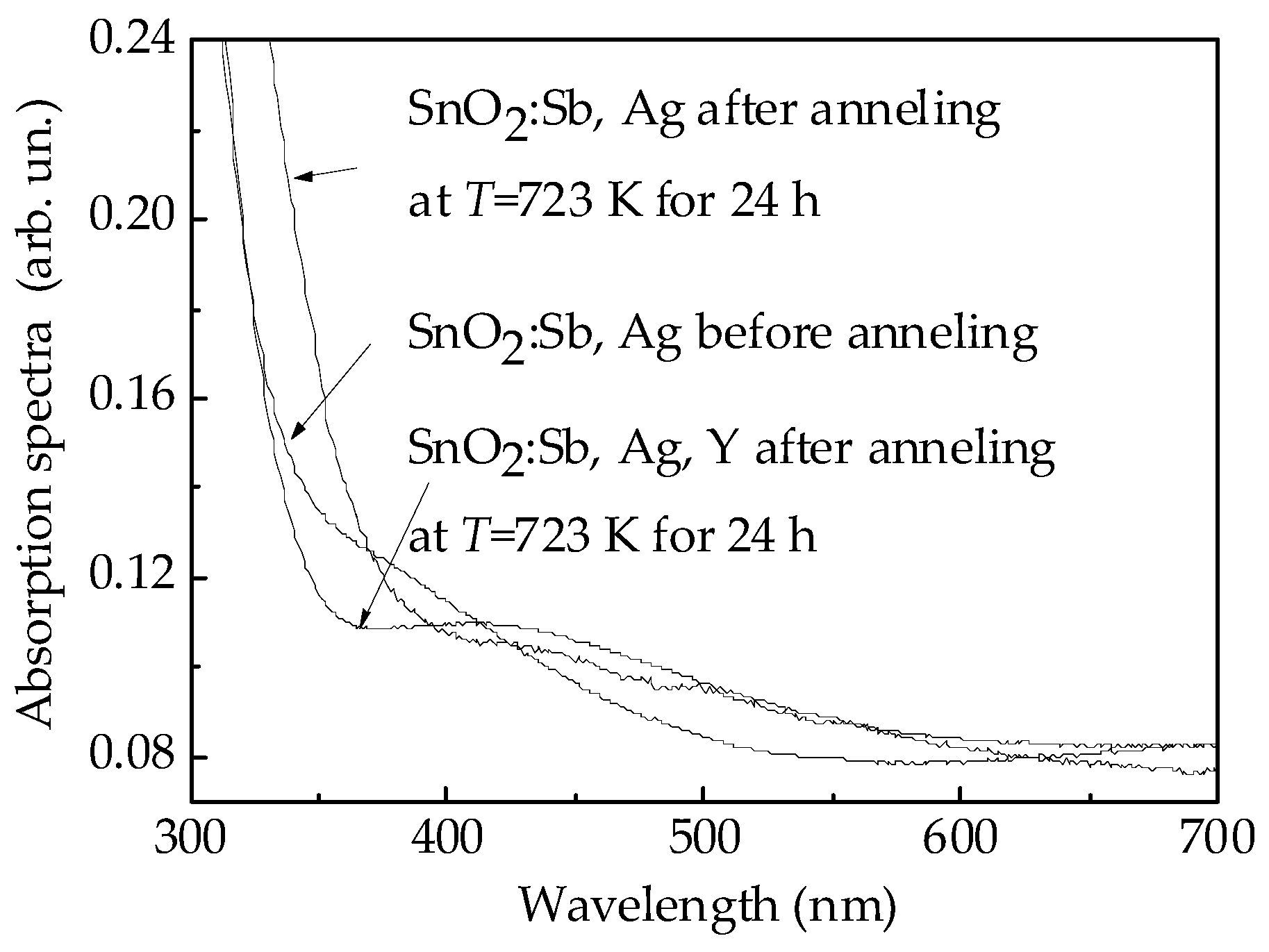
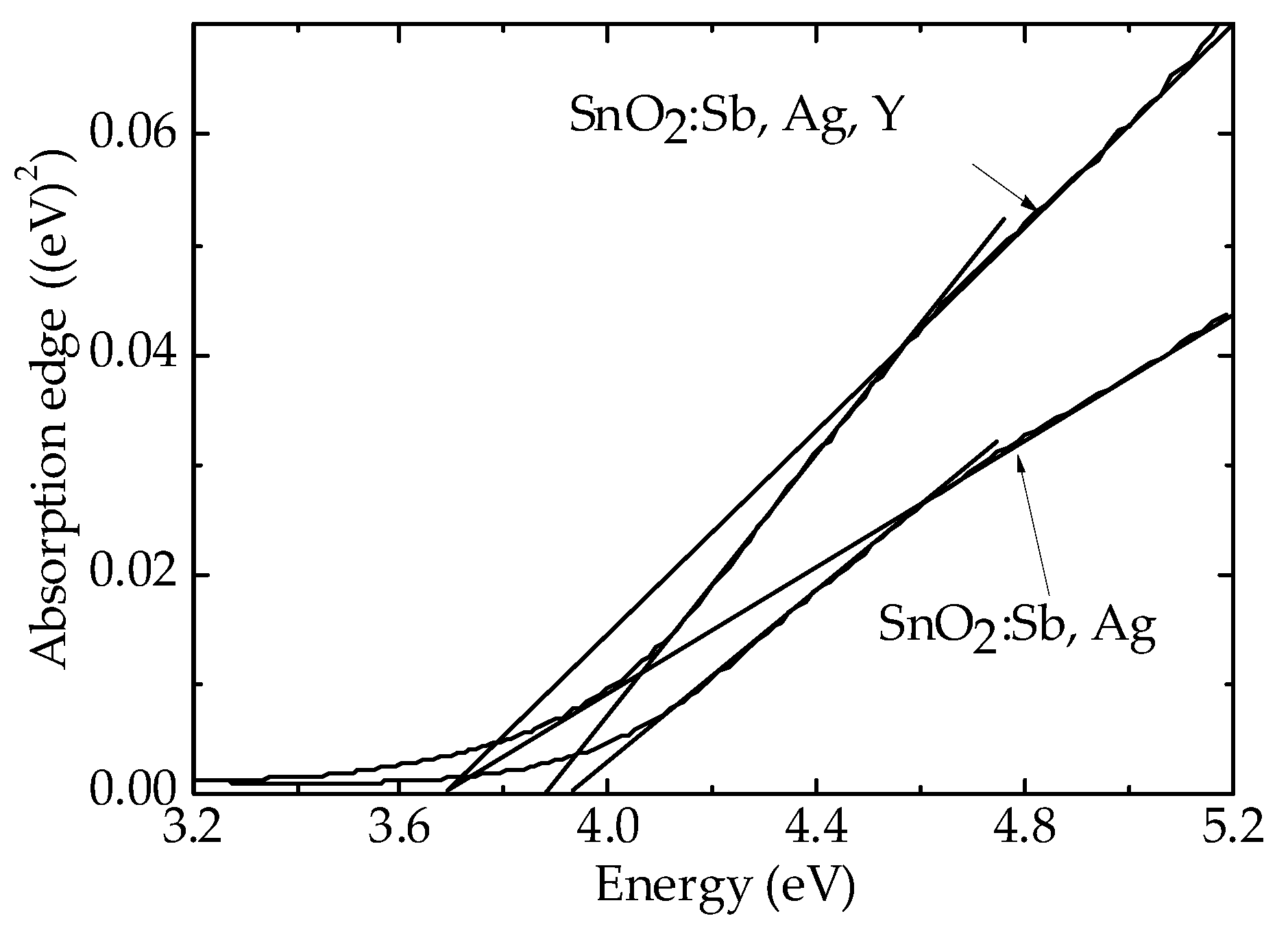
| The Core Levels | Composition of the Films | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| SnO2:Sb, Sc | SnO2:Sb, Ag, Y | SnO2:Sb, Ag, Sc | |
| Bending Energy (eV) | |||
| Sn 3d5/2 | 486.7 | 486.4 | 486.4 |
| O 1s | 531.0 | 530.2 | 529.8 |
| Ag 3d5/2 | – | 368.1 | 368.0 |
| Sc 2p3/2 | 398.5 | – | 398.5 |
| Y 3d5/2 | – | 155.8 | – |
| Series | 1 Pt/Pd/SnO2:Sb | 2 Pt/Pd/SnO2:Sb, Ag | 3 Pt/Pd/SnO2:Sb, Y |
| d1 (nm) | 18–20 | 30–60 | 200–350 |
| d2 (nm) | 70–100 | – | – |
| R0 (MΩ) | 1.5–5 | 2.5–3.7 | 5–15 |
| Tmax (K) | 670–690 | 570–600 | 690–730 |
| R0* (МΩ) | 0.5–0.7 | 1.5–2.5 | 3.5–4.5 |
| G1/G0* | 16–18 | 19–30 | 18–20 |
| G1/G0** | 170–180 | 290–330 | 42–45 |
| eφs(eV) | 0.40 | 0.44 | 0.46 |
| Series | 4 Pt/Pd/SnO2:Sb, Sc | 5 Pt/Pd/SnO2:Sb, Ag, Y | 6 Pt/Pd/SnO2:Sb, Ag, Sc |
| d1 (nm) | 40–60 | 18–30 | 20–40 |
| d2 (nm) | – | 120–200 | 120–210 |
| R0 (MΩ) | 7–8 | 26–30 | – |
| Tmax (K) | 620–630 | 670–690 | 620–680 |
| R0* (МΩ) | 0.17 | 5.9–6.5 | 15–17 |
| G1/G0* | 2.4–3.5 | 30–35 | 10–13 |
| G1/G0** | 10–17 | 580–590 | 230–240 |
| eφs(eV) | 0.52 | 0.64 | 0.74 |
| Series | 1 Pt/Pd/SnO2:Sb | 2Pt/Pd/SnO2:Sb, Ag | 3 Pt/Pd/SnO2:Sb, Y |
| t (days) | 600 | 67 | 50 |
| Tmax (K) | 670–690 | 640–650 | 690–730 |
| R0* (MΩ) | 1.5–3.5 | 9.1–10 | 3.5–4.5 |
| G1/G0* | 14–16 | 130–139 | 18–20 |
| G1/G0** | 840–860 | 2480–2490 | 621–730 |
| eφs(eV) | 0.56 | 0.71 | 0.71 |
| Series | 4 Pt/Pd/SnO2:Sb, Sc | 5 Pt/Pd/SnO2:Sb, Ag, Y | 6 Pt/Pd/SnO2:Sb, Ag, Sc |
| t (days) | 590 | 70 | 50 |
| Tmax (K) | 620–680 | 670–690 | 670–690 |
| R0* (MΩ) | 1.2 | 6.2–7.1 | 33–35 |
| G1/G0* | 5.5–7.6 | 30–35 | 46–54 |
| G1/G0** | 640–711 | 590–597 | 1500–1600 |
| eφs(eV) | 0.66 | 0.72 | 0.88 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maksimova, N.K.; Almaev, A.V.; Sevastyanov, E.Y.; Potekaev, A.I.; Chernikov, E.V.; Sergeychenko, N.V.; Korusenko, P.M.; Nesov, S.N. Effect of Additives Ag and Rare‐Earth Elements Y and Sc on the Properties of Hydrogen Sensors Based on Thin SnO2 Films during Long‐Term Testing. Coatings 2019, 9, 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9070423
Maksimova NK, Almaev AV, Sevastyanov EY, Potekaev AI, Chernikov EV, Sergeychenko NV, Korusenko PM, Nesov SN. Effect of Additives Ag and Rare‐Earth Elements Y and Sc on the Properties of Hydrogen Sensors Based on Thin SnO2 Films during Long‐Term Testing. Coatings. 2019; 9(7):423. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9070423
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaksimova, Nadezhda K., Aleksei V. Almaev, Evgeniy Yu. Sevastyanov, Aleksandr I. Potekaev, Evgeniy V. Chernikov, Nadezhda V. Sergeychenko, Petr M. Korusenko, and Sergey N. Nesov. 2019. "Effect of Additives Ag and Rare‐Earth Elements Y and Sc on the Properties of Hydrogen Sensors Based on Thin SnO2 Films during Long‐Term Testing" Coatings 9, no. 7: 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9070423
APA StyleMaksimova, N. K., Almaev, A. V., Sevastyanov, E. Y., Potekaev, A. I., Chernikov, E. V., Sergeychenko, N. V., Korusenko, P. M., & Nesov, S. N. (2019). Effect of Additives Ag and Rare‐Earth Elements Y and Sc on the Properties of Hydrogen Sensors Based on Thin SnO2 Films during Long‐Term Testing. Coatings, 9(7), 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9070423







