Chemical and Structural Characterization of Sandlasted Surface of Dental Implant using ZrO2 Particle with Different Shape
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sandblasting Process
2.3. Alloy Chemical Compound
2.4. Surface Erosion Assessment
2.5. Optical Microscopy
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.7. Surface Roughness Measurement
2.8. Contact Angle Measurement
2.9. Cell Culture Experiment
2.10. Statistic
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optical Microscopy
3.2. Chemical Composition of the Surface after Treatment
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.4. Contact Angle and Roughness
3.5. Cell Culture
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
- The results demonstrate the potential of using granular powders that are based on zirconium dioxide as an abrasive to create a rough surface with a low contact angle; also being absent of cell toxicity on the endosseous part of dental implants made from zirconium-based alloys.
- Sandblasting with the abrasive, as proposed in this paper, does not lead to a significant change in the chemical composition of the surface layer of the alloy and it does not require subsequent etching in order to remove abrasive particles, as in the case of a traditional abrasive on the basis of aluminum oxide, which should have a positive effect on the corrosion characteristics of the implants (biocompatibility).
- It was found that it is preferable to use round shaped powder of ZrO2 pellets of tetragonal form, with small sharp protrusions over the entire surface, with a size of 250 μm, at an operating pressure of not more than 4 atm and an exposure time of 5 s.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albrektsson, T.; Branemark, P.I.; Hansson, H.A.; Lindstrom, J. Osseointegrated titanium implants. Requirements for ensuring a long-lasting, direct bone-to-implant anchorage in man. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1981, 52, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrin, Y.; Vinogradov, A. Extreme grain refinement by severe plastic deformation: A wealth of challenging science. Acta Materialia 2013, 61, 782–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Sabirov, I.; Zhilyaev, A.P.; Langdon, T.G. Bulk Nanostructured Metals for Innovative Applications. JOM 2012, 64, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Alexandrov, I.V.; Zhu, Y.T.; Lowe, T.C. Paradox of strength and ductility in metals processed by severe plastic deformation. J. Mater. Res. 2002, 17, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindu, S.; Sanosh, K.P.; Balakrishnan, A.; Kim, T.N. An in vivo evaluation of ultra-fine grained titanium implants. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2009, 25, 556–560. [Google Scholar]
- Estrin, Y.; Ivanova, E.P.; Michalska, A.; Truong, V.K.; Lapovok, R.; Boyd, R. Accelerated stem cell attachment to ultrafine grained titanium. Acta Biomaterialia 2011, 7, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrin, Y.; Kasper, C.; Diederichs, S.; Lapovok, R. Accelerated growth of preosteoblastic cells on ultrafine grained titanium. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2009, 90, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Semenova, I.P.; Latysh, V.V.; Rack, H.; Lowe, T.C.; Petruzelka, J.; Dluhos, L.; Hrusak, D.; Sochova, J. Nanostructured titanium for biomedical applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, B15–B17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, D.L.; Schenk, R.K.; Lussi, A.; Higginbottom, F.L.; Buser, D. Bone response to unloaded and loaded titanium implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched surface: A histometric study in the canine mandible. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998, 40, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennerberg, A.; Hallgren, C.; Johansson, C.; Danelli, S. A histomorphometric evaluation of screw-shaped implants each prepared with two surface roughnesses. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1998, 9, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, D.; Schenk, R.K.; Steinemann, S.; Fiorellini, J.P.; Fox, C.H.; Stich, H. Influence of surface characteristics on bone integration of titanium implants. A histomorphometric study in miniature pigs. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1991, 25, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotfredson, K.; Wennerberg, A.; Johansson, C.; Skovgaard, L.T.; Hjørting-Hansen, E.; Hjørting-Hansen, E. Anchorage of TiO2-blasted, HA-coated, and machined implants: An experimental study with rabbits. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1995, 29, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennerberg, A.; Albrektsson, T.; Albrektsson, B.; Krol, J.J. Histomorphometric and removal torque study of screw-shaped titanium implants with three different surface topographies. Clin. Oral. Implants Res. 1996, 6, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testori, T.; Wiseman, L.; Woolfe, S.; Porter, S.S. A prospective multicenter clinical study of the Osseotite implant: Four-year interim report. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2001, 16, 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Conner, K.A.; Sabatini, R.; Mealey, B.L.; Takacs, V.J.; Mills, M.P.; Cochrann, D.L. Guided Bone Regeneration Around Titanium Plasma-Sprayed, Acid-Etched, and Hydroxyapatite-Coated Implants in the Canine Model. J. Periodontol. 2003, 74, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulthard, P.; Thomsen, P.; Worthington, H.V. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: Different types of dental implants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2005, 25, CD003815. [Google Scholar]
- Aparicio, C.; Gil, F.J.; Fonseca, C.; Barbosa, M.; Planell, J.A. Corrosion behavior of commercially pure titanium shot blasted with different materials and size of shot particles for dental implant applications. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanoff, C.-J.; Widmark, G.; Hallgren, C.; Sennerby, L.; Wennerberg, A. Histologic evaluation of the bone integration of TiO2 blasted and turned titanium microimplants in humans. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2001, 12, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmusson, L.; Kahnberg, K.-E.; Tan, A. Effects of Implant design and surface on bone regeneration and implant stability: An experimental study in the dog mandible. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2001, 3, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotfredsen, K.; Karlsson, U. A prospective 5-year study of fixed partial prostheses supported by implants with machined and TiO2-blasted surface. J. Prosthodont. 2001, 10, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmusson, L.; Roos, J.; Bystedt, H. A 10-year follow-up study of titanium dioxide–blasted implants. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2005, 7, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abron, A.; Hopfensperger, M.; Thompson, J.; Cooper, L.F. Evaluation of a predictive model for implant surface topography effects on early osseointegration in the rat tibia model. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2001, 85, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, S.; Özcan, M.; Maleki Dizaj, S.; Sharifi, S.; Al-Haj Husain, N.; Eftekhari, A.; Ahmadian, E. A review on potential toxicity of dental material and screening their biocompatibility. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2019, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, A.; Elie, A.-M.; Plawinski, L.; Serro, A.P.; Botelho do Rego, A.M.; Almeida, A.; Urdaci, M.C.; Durrieu, M.-C.; Vilar, R. Femtosecond laser surface texturing of titanium as a method to reduce the adhesion of Staphylococcus aureus and biofilm formation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 360, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branemark, P.I.; Hansson, B.O.; Adell, R.; Breine, U.; Lindström, J.; Hallén, O.; Ohman, A. Osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Experience from a 10-year period. Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Suppl. 1977, 16, 1–132. [Google Scholar]
- Mavrogenis, A.F.; Dimitriou, R.; Parvizi, J.; Babis, G.C. Biology of implant osseointegration. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2009, 9, 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, L.; Sun, Y.; Guan, S.; Liu, B.; Kong, L. The effect of hierarchical micro/nanosurface titanium implant on osseointegration in ovariectomized sheep. Osteoporos. Int. 2011, 22, 1907–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liu, X.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Guo, H.; Li, P.; Hu, T.; Chung, C.Y.; Chu, P.K. Surface nano-architectures and their effects on the mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of Ti-based orthopedic implants. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 233, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverwood, R.K.; Fairhurst, P.G.; Sjöström, T.; Welsh, F.; Sun, Y.; Li, G.; Yu, B.; Young, P.S.; Su, B.; Meek, R.M.; et al. Analysis of osteoclastogenesis/osteoblastogenesis on nanotopographical titania surfaces. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Pérez, R.; Bartolomé, J.F.; Ferreiroa, A.; Salido, M.P.; Pradíes, G. Original vs. non-original abutments for screw-retained single implant crowns: An in vitro evaluation of internal fit, mechanical behaviour and screw loosening. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, A.V.; Dudnik, E.V.; Tsukrenko, V.V.; Ruban, A.K.; Red’ko, V.P.; Lopato, L.M. Microstructural design of bioinert composites in the ZrO2–Y2O3–CeO2–Al2O3–CoO system. Powder Metall. Metal Ceram. 2013, 51, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Shi, X.; Mao, M.; Yang, W.; Han, S.; Guo, H.; Guo, J. Investigation of the Oxidation Behaviour of Ti and Al in Inconel 718 Superalloy During Electroslag Remelting. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
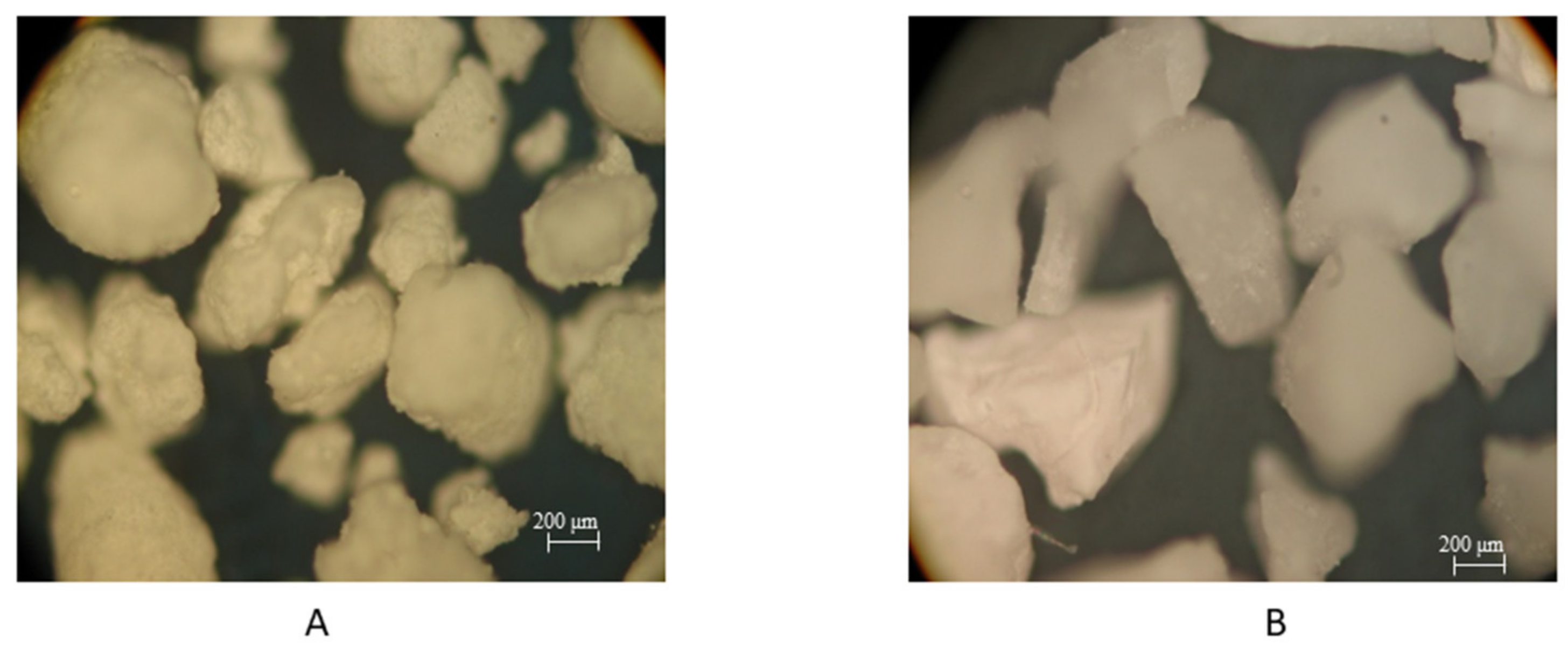

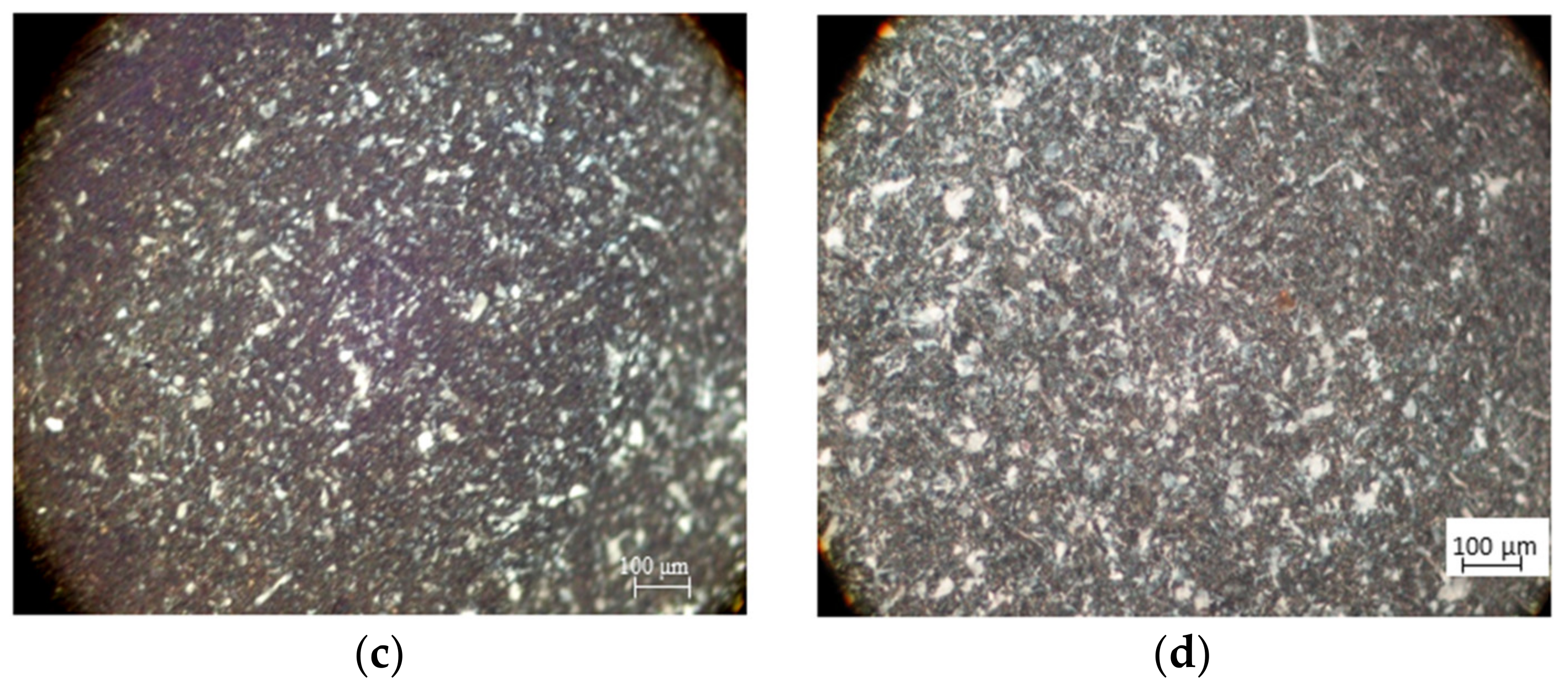


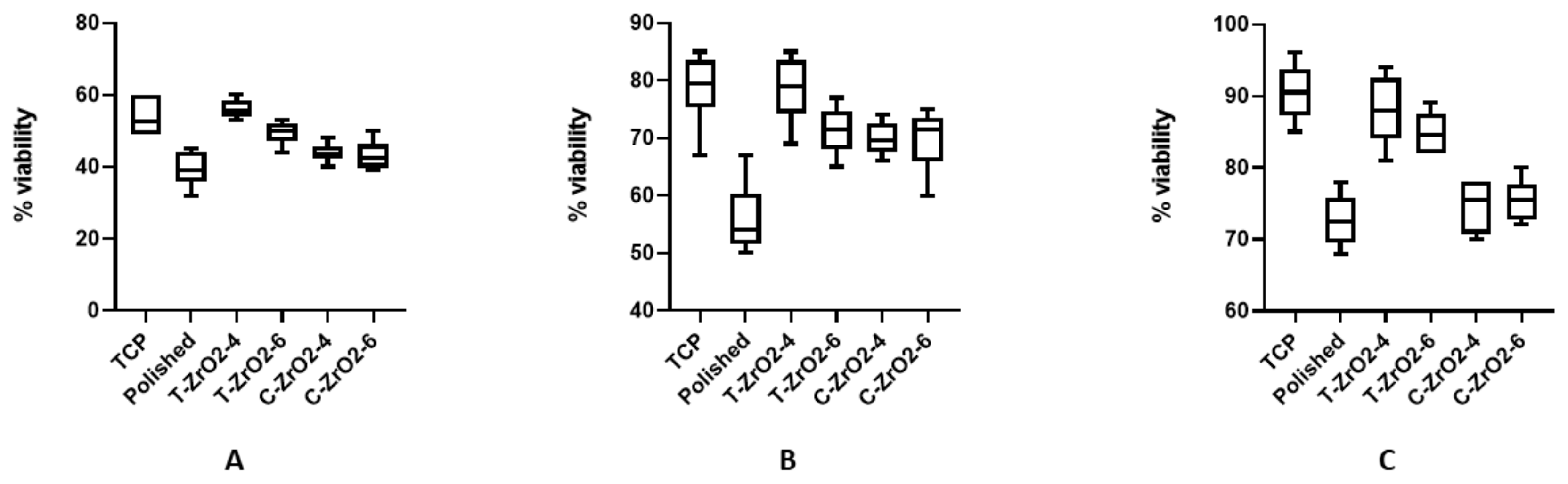
| Characteristic | Abrasive | |
|---|---|---|
| ZrO2 Tetragonal | ZrO2 Cubic | |
| Density, g/cm3 | 6.0–6.05 | 6.5–10 |
| Modulus of rupture in bending, MPa | 750–1050 | – |
| Young’s modulus, GPa | 200–210 | – |
| Vickers hardness, GPa | 12–13 | – |
| Crack resistance, MPa m½ | 8.0–10.0 | – |
| Moh’s hardness | – | 7.5–8.5 |
| Parameter | Polished | ZrO2 Tetragonal | ZrO2 Cubic | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 atm | 6 atm | 4 atm | 6 atm | ||
| Ra Values (μm) | 0.45 ± 0.092 | 3.57 ± 0.12 | 3.86 ± 0.35 | 2.19 ± 0.28 | 2.76 ± 0.44 |
| CA (°) | 92.17 ± 2.78 | 76.83 ± 2.63 | 82.13 ± 5.10 | 81.17 ± 4.66 | 86.5 ± 3.20 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mishchenko, O.; Filatova, V.; Vasylyev, M.; Deineka, V.; Pogorielov, M. Chemical and Structural Characterization of Sandlasted Surface of Dental Implant using ZrO2 Particle with Different Shape. Coatings 2019, 9, 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9040223
Mishchenko O, Filatova V, Vasylyev M, Deineka V, Pogorielov M. Chemical and Structural Characterization of Sandlasted Surface of Dental Implant using ZrO2 Particle with Different Shape. Coatings. 2019; 9(4):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9040223
Chicago/Turabian StyleMishchenko, Oleg, Vira Filatova, Mykhaylo Vasylyev, Volodymyr Deineka, and Maksym Pogorielov. 2019. "Chemical and Structural Characterization of Sandlasted Surface of Dental Implant using ZrO2 Particle with Different Shape" Coatings 9, no. 4: 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9040223
APA StyleMishchenko, O., Filatova, V., Vasylyev, M., Deineka, V., & Pogorielov, M. (2019). Chemical and Structural Characterization of Sandlasted Surface of Dental Implant using ZrO2 Particle with Different Shape. Coatings, 9(4), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9040223





