Multifunctional Protective PVC-ZnO Nanocomposite Coatings Deposited on Aluminum Alloys by Electrospinning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Reagents and Materials
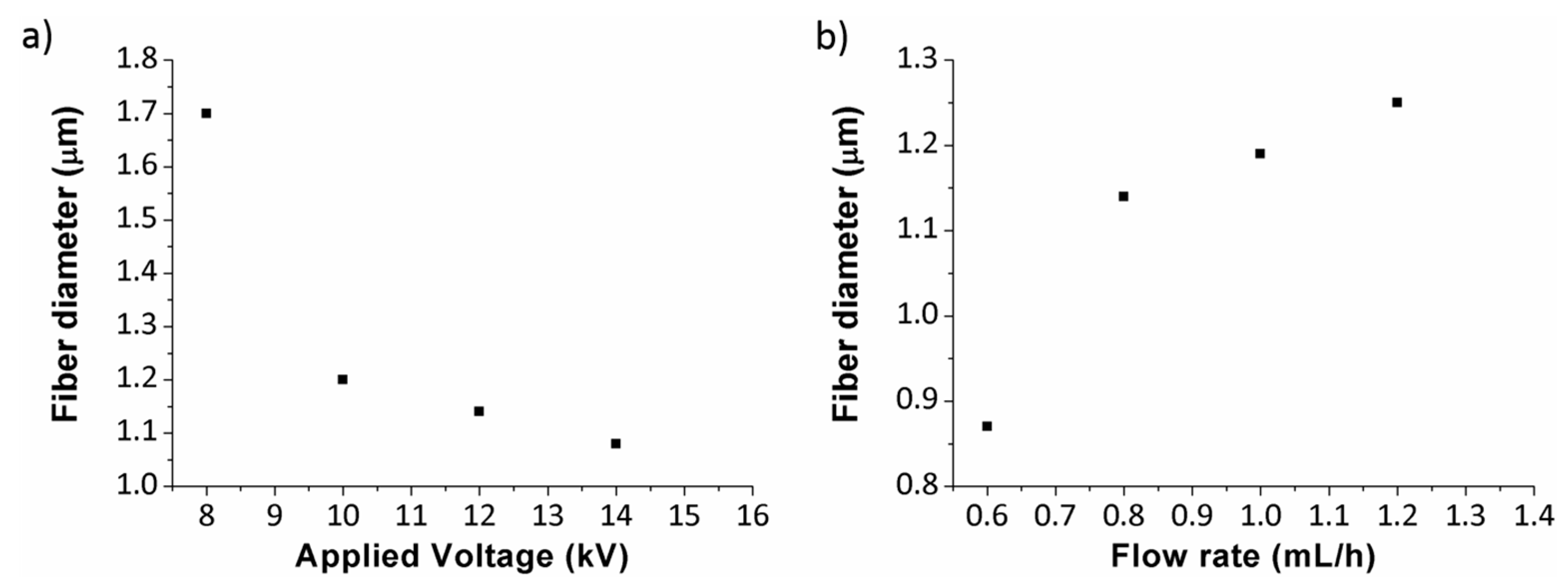
2.2. Deposition of PVC-ZnO Nanocomposite Coatings
2.3. Characterization Techniques
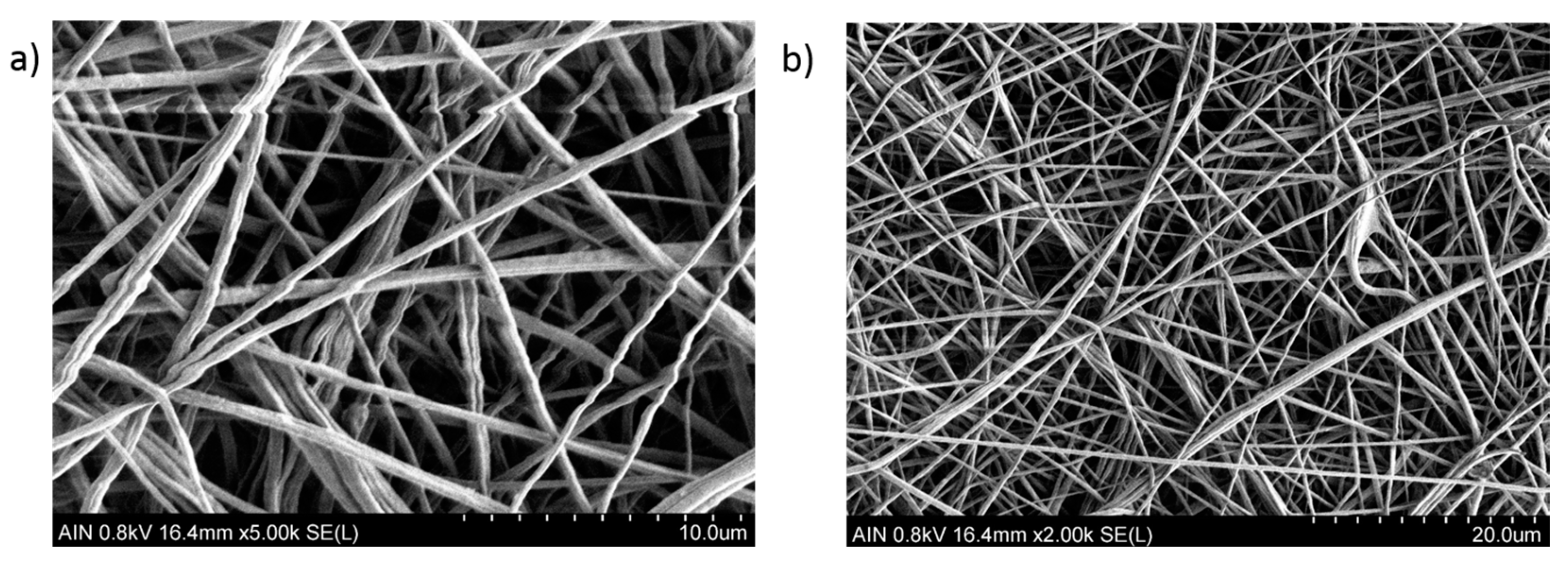
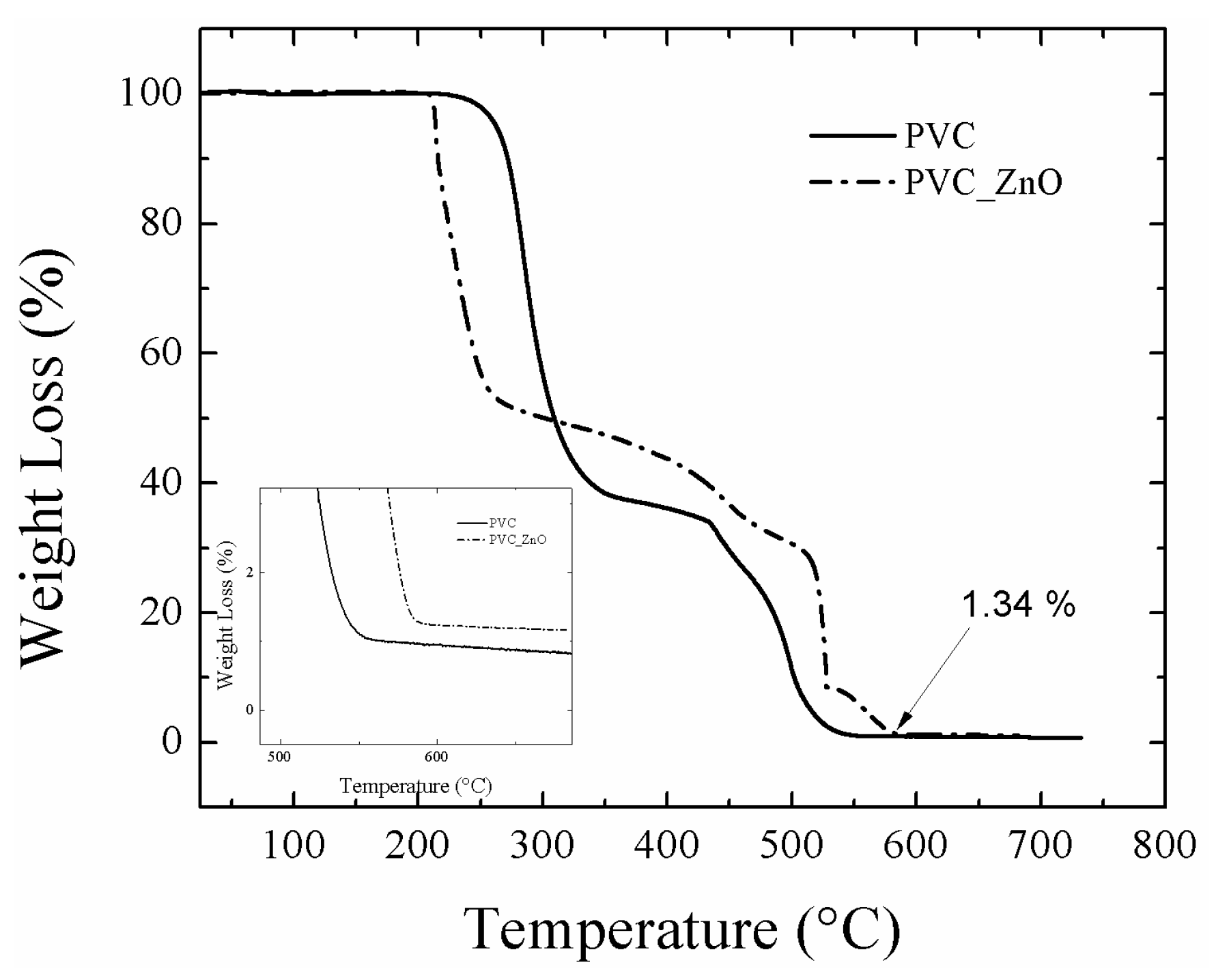
3. Results and Discussion
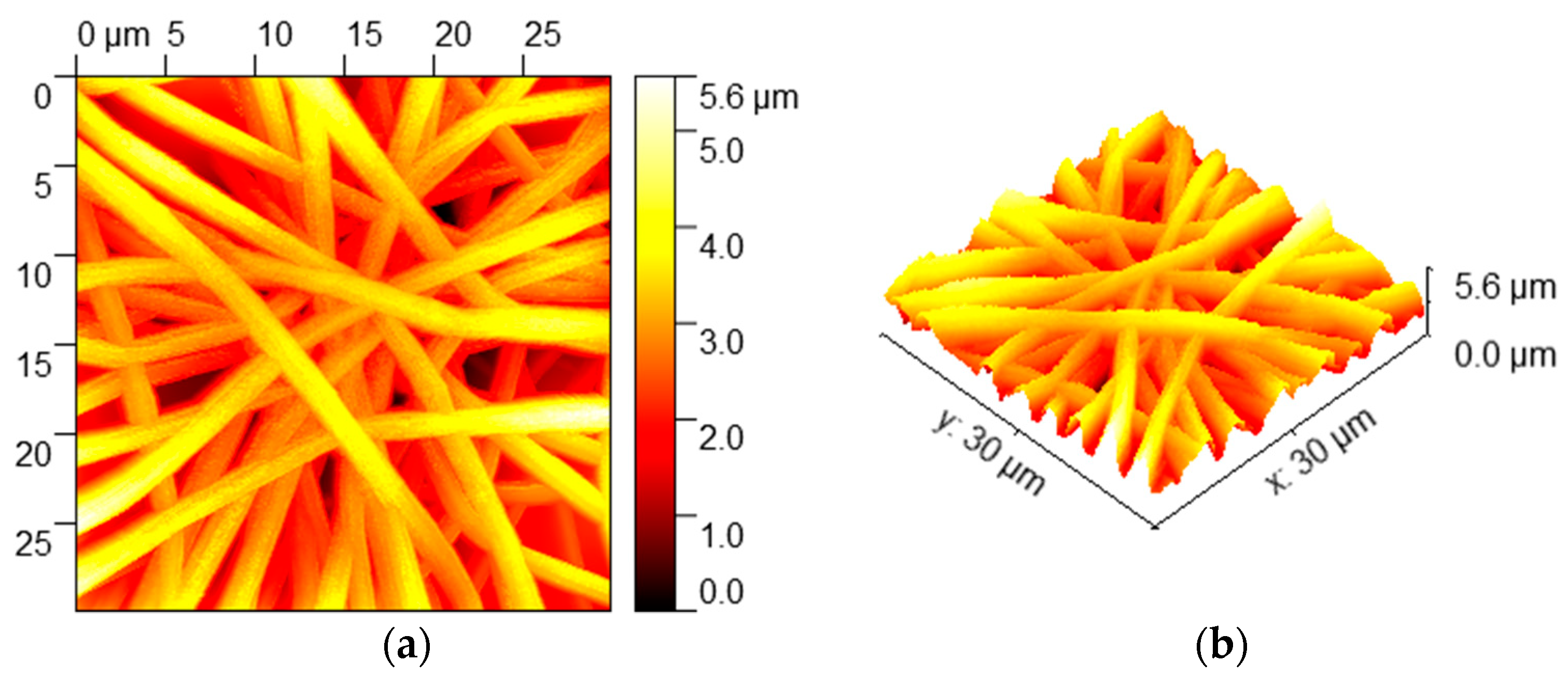
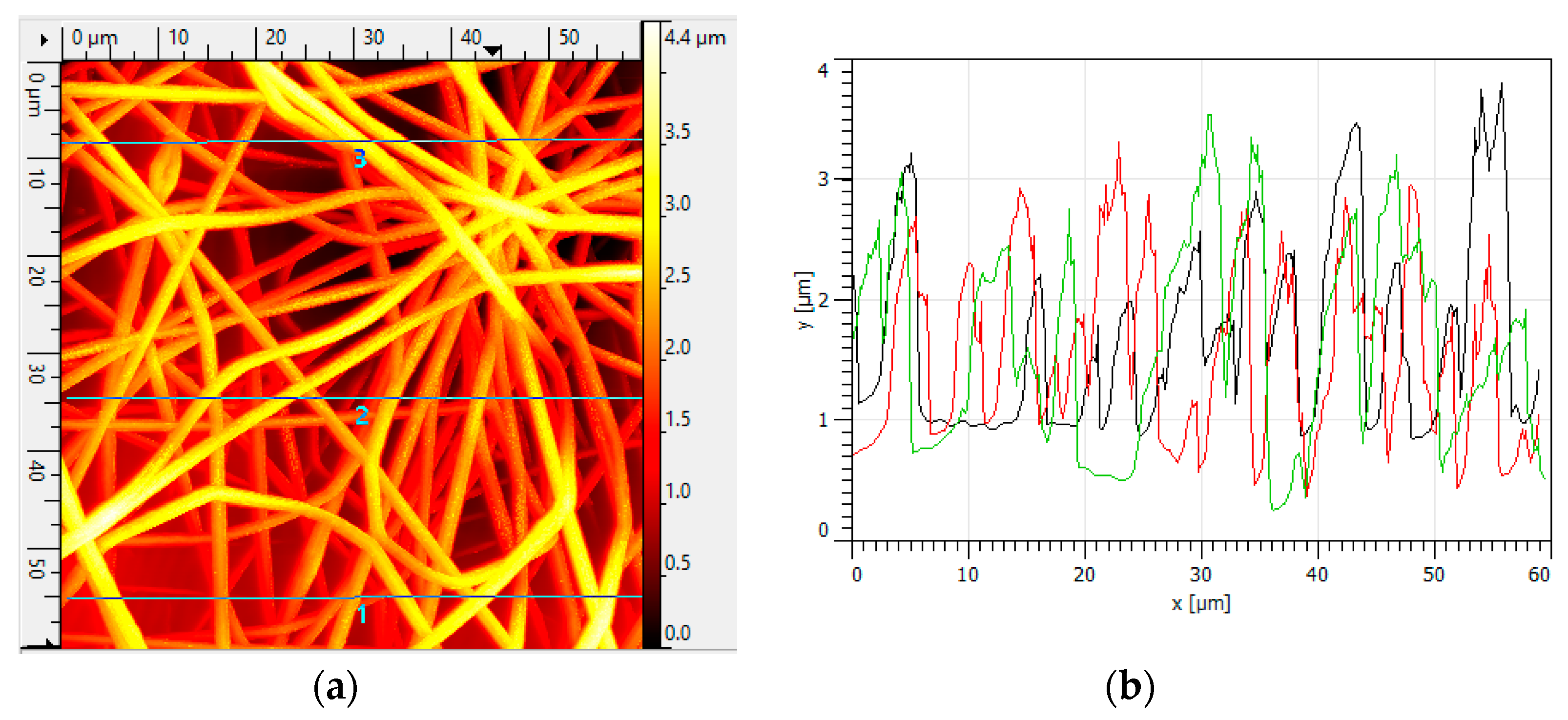
3.1. Morphologies and Wettability
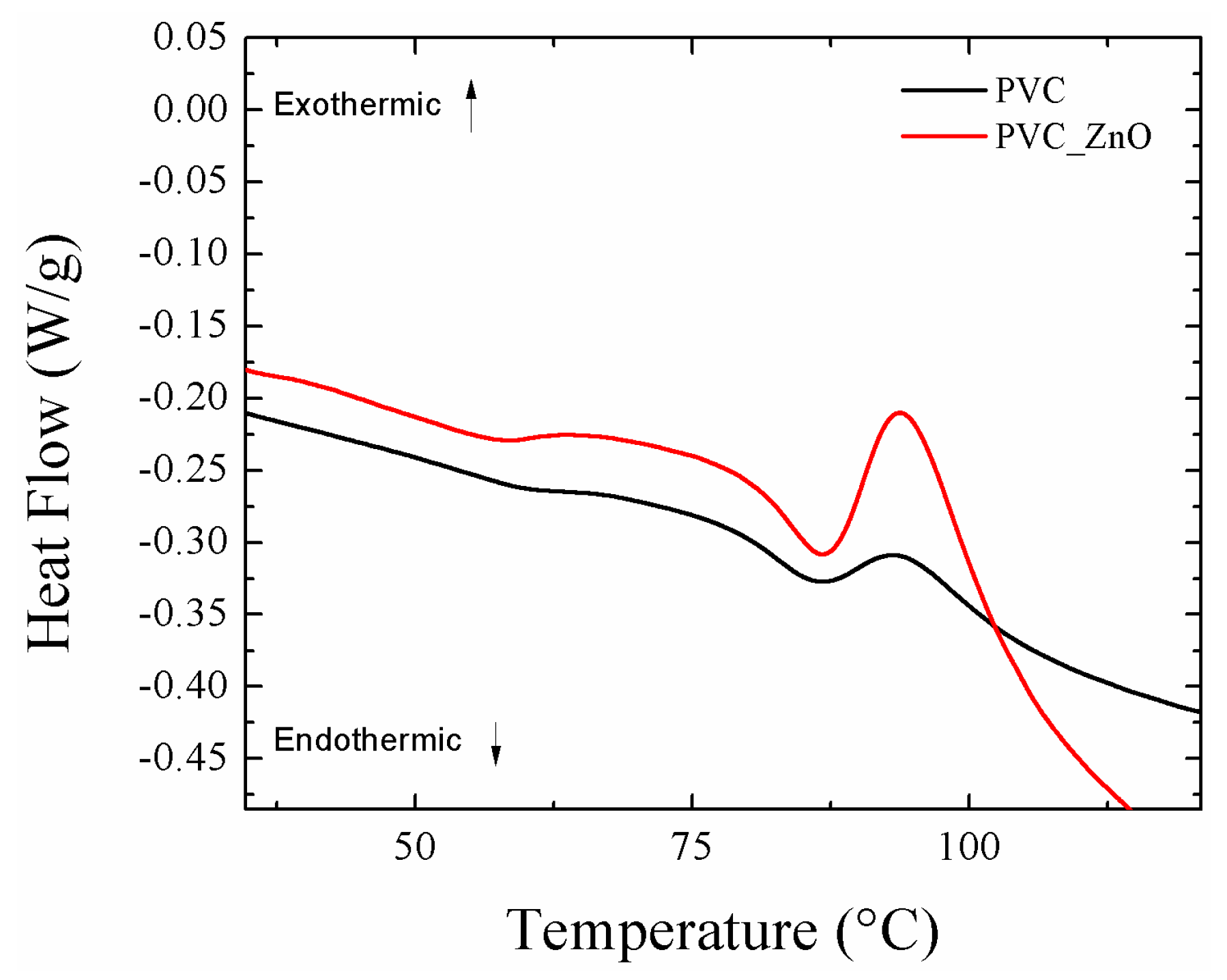
3.2. Effect of Heat Treatment on Hydrophobicity
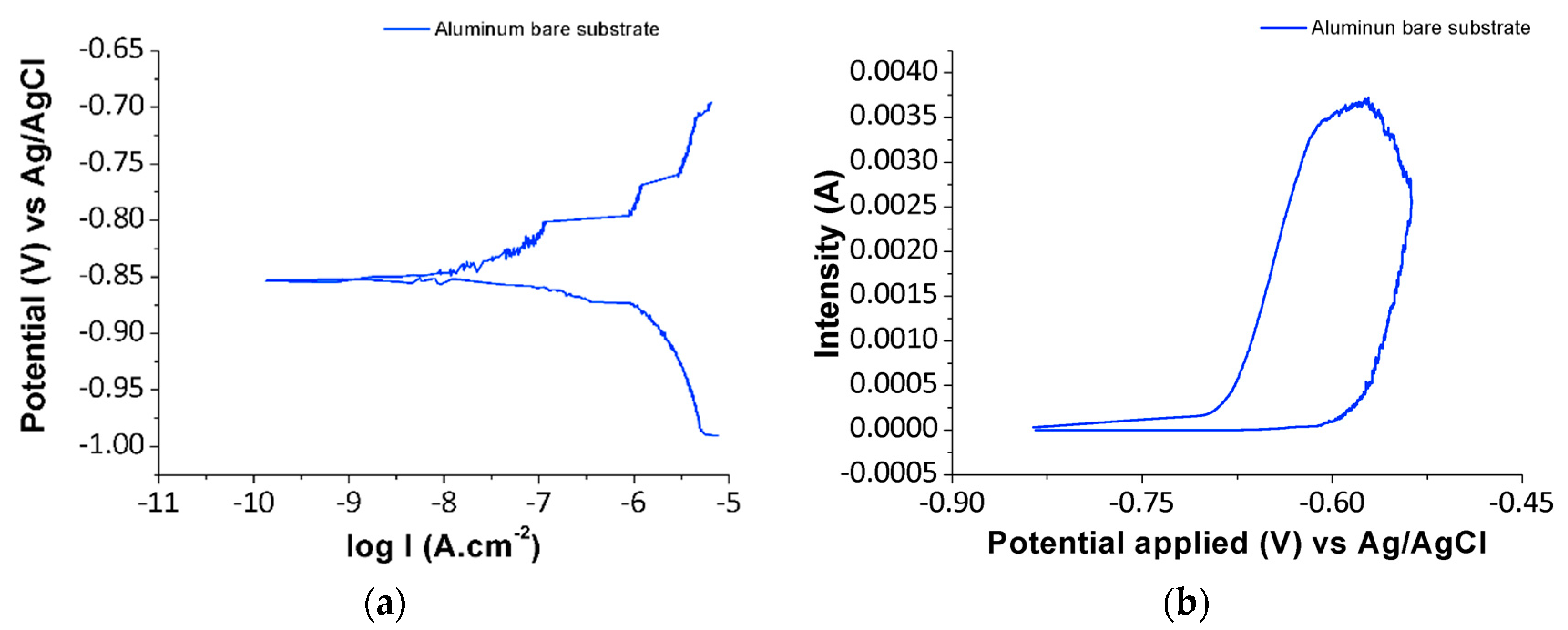
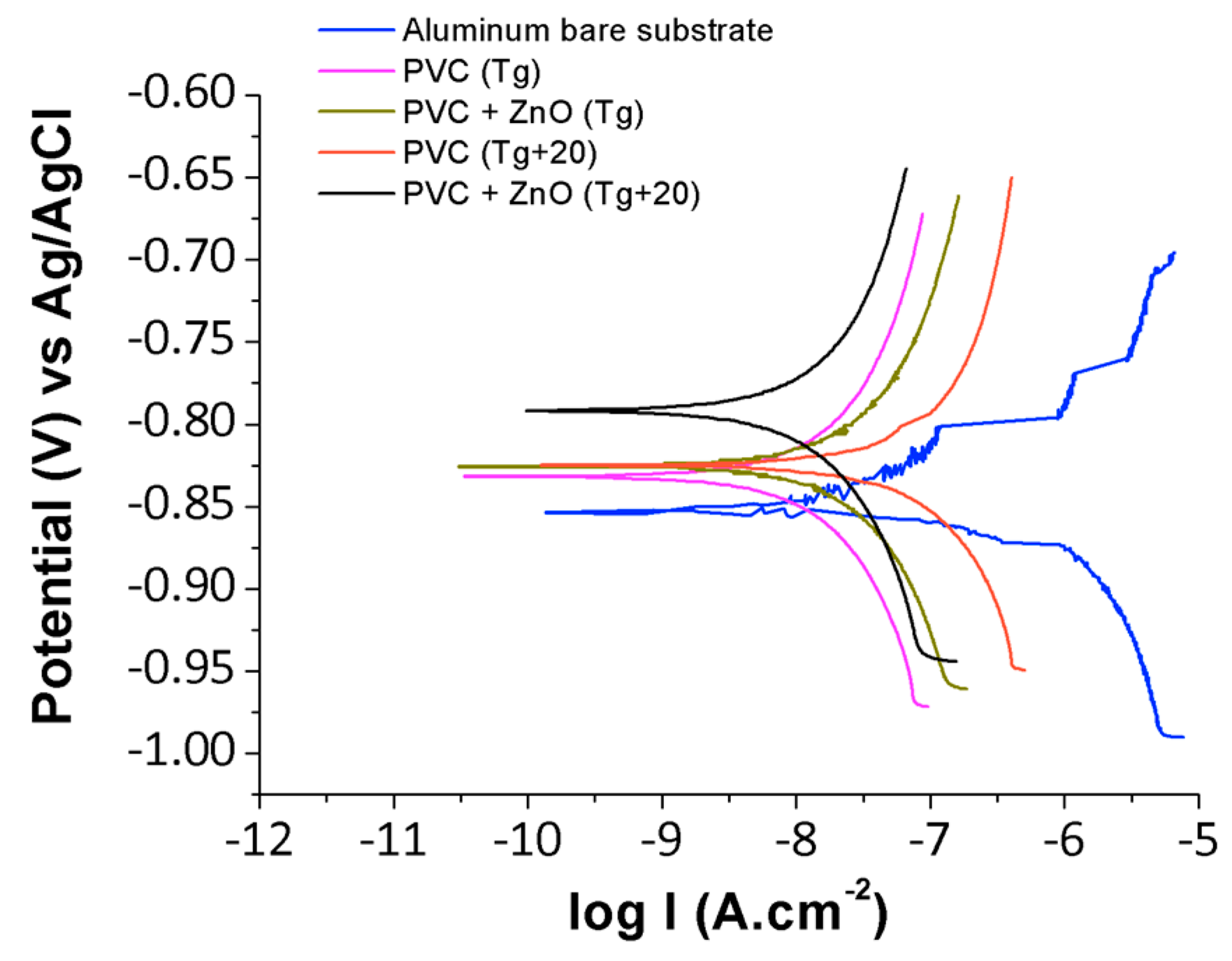
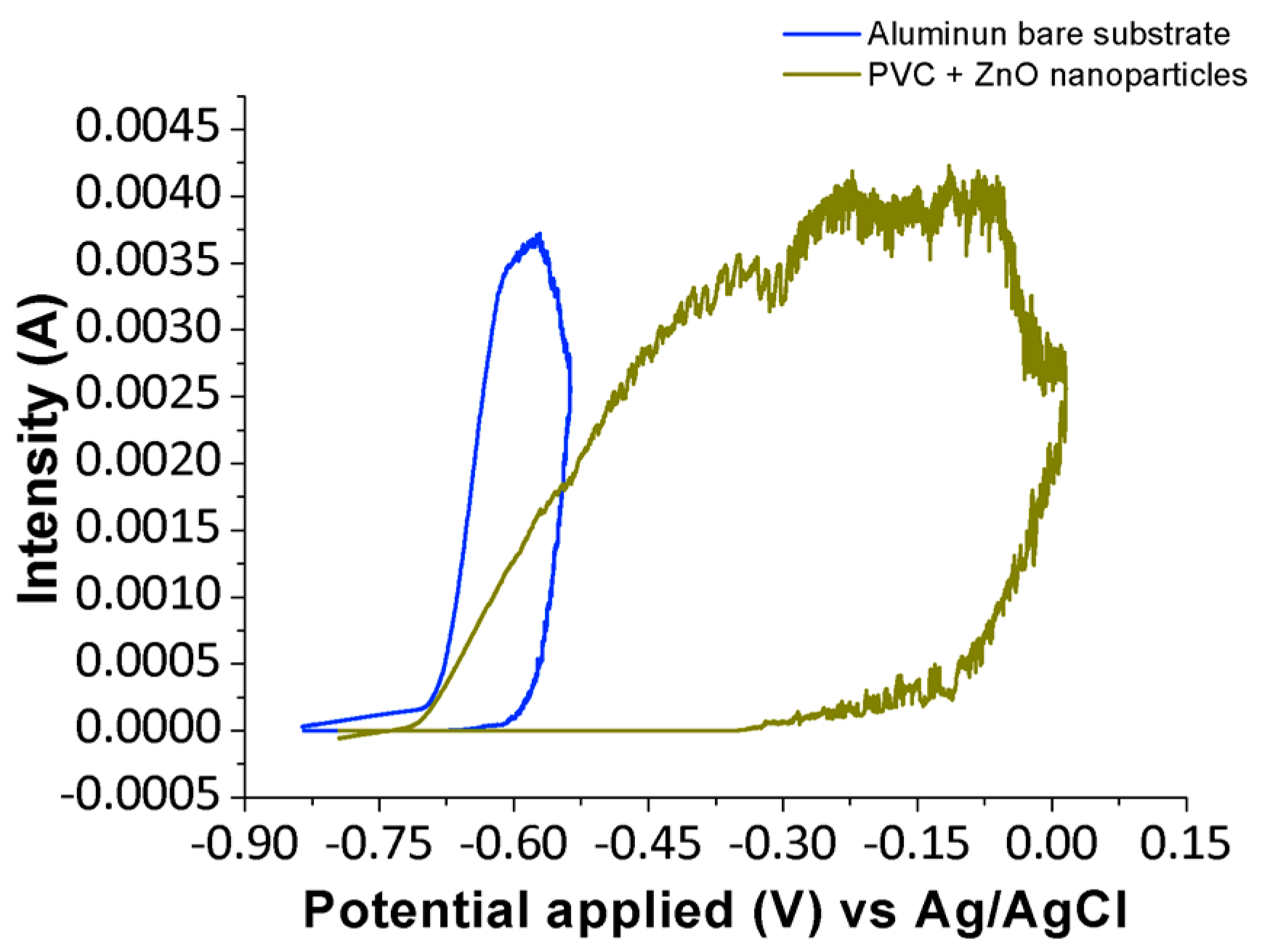
3.3. Anticorrosion Performance of PVC-ZnO Nanostructures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdel-Gaber, A.M.; Abd-El-Nabey, B.A.; Sidahmed, I.M.; El-Zayady, A.M.; Saadawy, M. Kinetics and thermodynamics of aluminium dissolution in 1.0 M sulphuric acid containing chloride ions. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2006, 98, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, W.A.; Al-Kharafi, F.M.; El-Azab, A.S. Electrochemical behaviour and corrosion inhibition of Al, Al-6061 and Al–Cu in neutral aqueous solutions. Corros. Sci. 1999, 41, 709–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NACE International. Corrosion Costs and Preventive Strategies in the United States. Available online: https://www.nace.org/uploadedfiles/publications/ccsupp.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2018).
- Ates, M. A review on conducting polymer coatings for corrosion protection. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2016, 30, 1510–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkarter, E.; Saul, C.K.; Thomazi, F.; Cruz, N.C.; Roman, L.S.; Schreiner, W.H. Superhydrophobic electrosprayed PTFE. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 202, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, B.; Shen, Z. Fabrication of superhydrophobic surfaces by dislocation-selective chemical etching on aluminum, copper, and zinc substrates. Langmuir 2005, 21, 9007–9009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.Y.; Park, S.J. Effect of fluorination of carbon nanotubes on superhydrophobic properties of fluoro-based films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 342, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acatay, K.; Simsek, E.; Ow-Yang, C.; Menceloglu, Y.Z. Tunable, superhydrophobically stable polymeric surfaces by electrospinning. Angew. Chem. 2004, 43, 5210–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, P.J.; Garcia, J.A.; Quintana, I.; Rodriguez, R. Design of nanostructured functional coatings by using wet-chemistry methods. Coatings 2018, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Li, Y.S.; Xiang, C.B. Preparation of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) ultrafiltration membrane modified by nano-sized alumina (Al2O3) and its anti-fouling research. Polymer 2005, 46, 7701–7706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, N.T.K.; Vasudevan, T.; Subramania, A. Synthesis of ZrO2 nano particles in microwave hydrolysis of Zr (IV) salt solutions-ionic conductivity of PVDF-co-HFP- based polymer electrolyte by the inclusion of ZrO2 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2007, 68, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, N.A.; Liu, Y.; Li, K. Preparation of PVDF hollow fiber membranes using SiO2 particles: The effect of acid and alkali treatment on the membrane performances. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 3035–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.S.; Yu, S.L.; Shi, W.X.; Sun, N.; Jin, L.M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, B.; Ma, C.; Sun, L.P. The influence of important factors on ultrafiltration of oil/water emulsion using PVDF membrane modified by nano-sized TiO2/Al2O3. Desalination 2011, 281, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Tao, C.Y.; Sun, C.X. Preparation and characterization of Fe3O4/PVDF magnetic composite membrane. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2004, 20, 598–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigo, C.E.L.; Porto, A.O.; De Lima, G.M. Characterization of CdS nanoparticles in solutions of P(TFE-co-PVDF/co-Prop)/N,N-dimethylformadine. Eur. Polym. J. 2004, 40, 2465–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.M.A.; Jafari, R.; Farzaneh, M. An optimization of superhydrophobic polyvinylidene fluoride/zinc oxide materials using Taguchi method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 288, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelke, V.; Bhole, M.P.; Patil, D.S. Effect of open air annealing on spin coated aluminum doped ZnO nanostructure. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2013, 141, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelke, V.; Bhole, M.P.; Patil, D.S. Opto-electrical characterization of transparent conducting sand dune shaped indium doped ZnO nanostructures. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 560, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelke, V.; Bhole, M.P.; Patil, D.S. Open air annealing effect on the electrical and optical properties of tin doped ZnO nanostructure. Solid State Sci. 2012, 14, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzi, A.; Impagnatiello, A.; Del Gaudio, C.; Lamastra, F.R.; Bianco, A.; Montesperelli, G. Electrospun protective self-healing coatings for light alloys: A better understanding of the intrinsic potential of the technology. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarus, B.; Fadel, N.; Al-Oufy, A.; El-Messiry, M. Effect of polymer concentration on the morphology and mechanical characteristics of electrospun cellulose acetate and poly (vinyl chloride) nanofiber mats. Alex. Eng. J. 2016, 55, 2975–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Haleem, S.A.; El Wanees, S.A.; Bahgat, A. Environmental factors affecting the corrosion behaviour of reinforcing steel. VI. Benzotriazole and its derivatives as corrosion inhibitors of steel. Corros. Sci. 2014, 87, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampetti, E.; Pantalei, S.; Scalese, S.; Bearzotti, A.; de Cesare, F.; Spinella, C.; Macagnano, A. Biometic sensing layer based on electrospun conductive polymer webs. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2460–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sill, T.J.; von Recum, H.A. Electrospinning: Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1989–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kim, H.Y.; La, Y.M.; Lee, D.R.; Sung, N.H. Influence of a mixing solvent with tetrahydrofuran and N,N-dimethylformamide on electrospun poly(vinyl chloride) nonwoven mats. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2002, 40, 2259–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megelski, S.; Stephens, J.S.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Micro and nanostructured surface morphology on electrospun polymer fibers. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 8456–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Mao, Y.; Gupta, M.; Gleason, K.; Rutledge, G.C. Superhydrophobic fabrics produced by electrospinning and chemical vapor deposition. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 9742–9748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.N. Surface roughness and contact angle. J. Phys. Chem. 1949, 53, 1466–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; McCarthy, T.J. An Attempt to correct the faulty intuition perpetuated by the Wenzel and Cassie “laws”. Langmuir 2009, 25, 7249–7255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbil, H.Y. The debate on the dependence of apparent contact angles on drop contact area or three-phase contact line: A review. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2014, 69, 325–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Choi, S.O.; Kim, J. Analysis of contact area between water and irregular fibrous surface for prediction of wettability. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 73313–73322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomello, A.; Meloni, S.; Chinappi, M.; Casciola, C.M. Cassie−Baxter and Wenzel states on a nanostructured surface: Phase diagram, metastabilities, and transition mechanism by atomistic free energy calculations. Langmuir 2012, 28, 10764–10772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, A.J.B.; Amirfazli, A. The Cassie equation: How it is meant to be used. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 170, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, P.K.; Ura, D.P.; Metwally, S.; Knapczyk-Korczak, J.; Gajek, M.; Marzec, M.M.; Bernasik, A.; Stachewicz, U. Roughness and fiber fraction dominated wetting of electrospun fiber-based porous meshes. Polymers 2019, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homaeigohar, S.; Koll, J.; Lilleodden, E.T.; Elbahri, M. The solvent induced interfiber adhesion and its influence on the mechanical and filtration properties of polyethersulfone electrospun nanofibrous microfiltration membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 98, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Pan, F.; Wang, D.; Pan, Z. Effects of heat treatment on the morphology and performance of PSU electrospun nanofibrous membrane. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2012, 7, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, N.R.; Gaikwad, V.L.; Nair, K.J.; Kadam, H.W. Glass transition temperature: Basics and application in pharmaceutical sector. Asian J. Pharm. 2009, 3, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmatulu, R.; Ceylan, M.; Nuraje, N. Study of superhydrophobic electrospun nanocomposite fibers for energy systems. Langmuir 2011, 27, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, J.; Budiansky, N.; Tiwary, Y.; Mikhailov, A.; Hudson, J. An alternate explanation for the abrupt current increase at the pitting potential. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
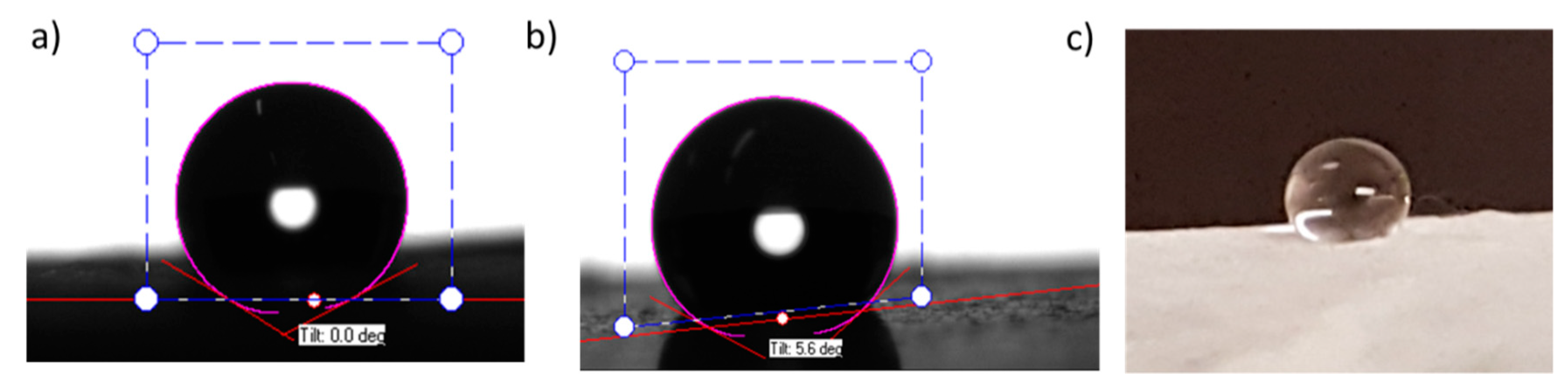
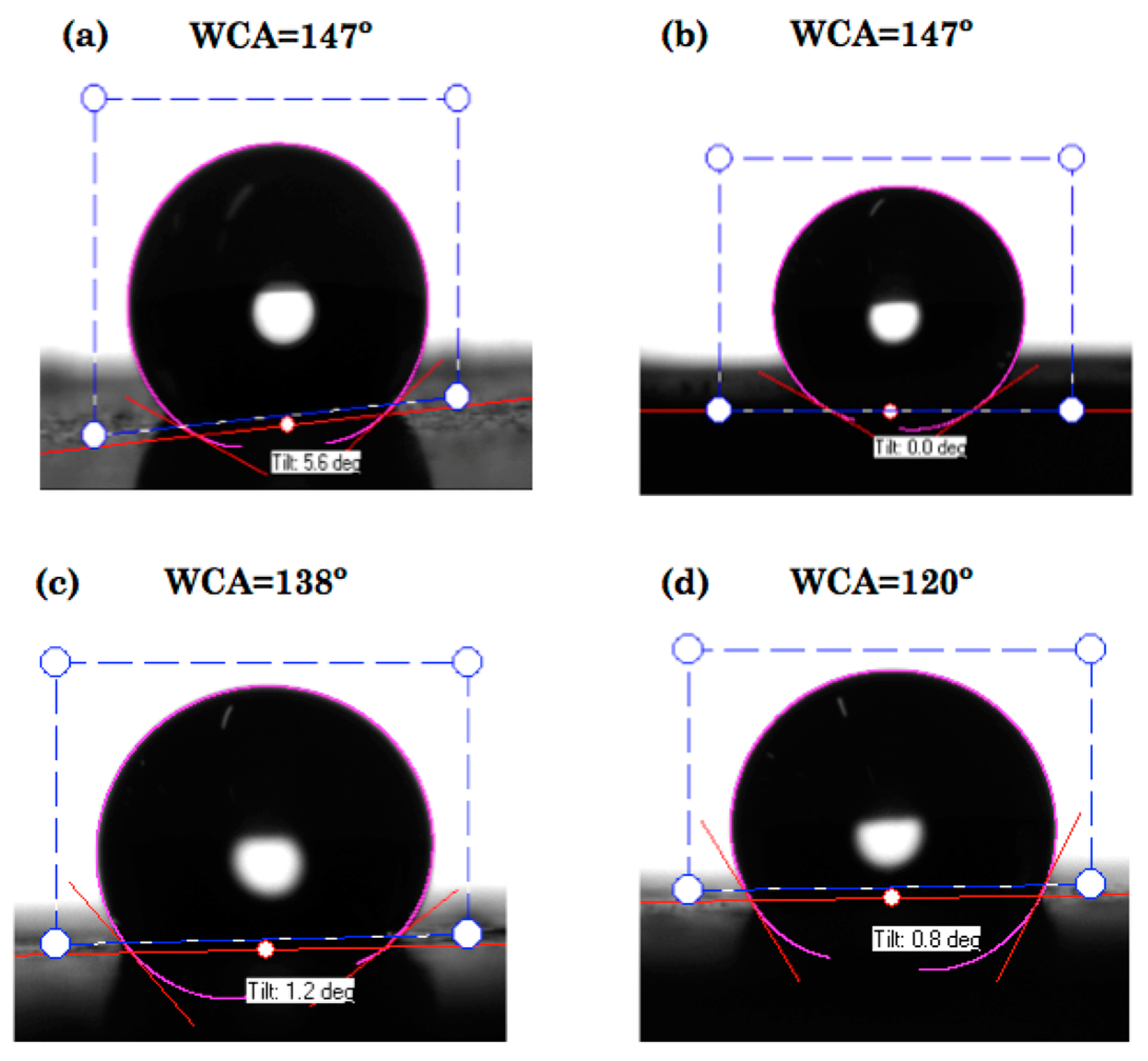
| Contact Angle Values at Different Temperatures | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| WCA | 147 | 149 | 147 | 139 | 138 | 135 | 120 |
| Sample | βa (mV/dec) | βc (mV/dec) | icorr (µA/cm2) | Ecorr (V) | η (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al substrate | 56 | 150 | 1.107 | −0.856 | – |
| PVC (Tg) | 155 | 143 | 0.011 | −0.833 | 99.01 |
| PVC (Tg + 20) | 197 | 172 | 0.029 | −0.827 | 97.38 |
| PVC-ZnO (Tg) | 140 | 96 | 0.054 | −0.826 | 95.12 |
| PVC-ZnO (Tg + 20) | 175 | 159 | 0.009 | −0.793 | 99.19 |
| Sample | Ep (V) | Ecutoff (V) | (mA/V) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al substrate | −0.656 | −0.538 | 21.10 |
| PVC-ZnO (Tg + 20) | −0.341 | 0.015 | 6.99 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iribarren, A.; Rivero, P.J.; Berlanga, C.; Larumbe, S.; Miguel, A.; Palacio, J.F.; Rodriguez, R. Multifunctional Protective PVC-ZnO Nanocomposite Coatings Deposited on Aluminum Alloys by Electrospinning. Coatings 2019, 9, 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9040216
Iribarren A, Rivero PJ, Berlanga C, Larumbe S, Miguel A, Palacio JF, Rodriguez R. Multifunctional Protective PVC-ZnO Nanocomposite Coatings Deposited on Aluminum Alloys by Electrospinning. Coatings. 2019; 9(4):216. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9040216
Chicago/Turabian StyleIribarren, Alvaro, Pedro J. Rivero, Carlos Berlanga, Silvia Larumbe, Adrian Miguel, Jose F. Palacio, and Rafael Rodriguez. 2019. "Multifunctional Protective PVC-ZnO Nanocomposite Coatings Deposited on Aluminum Alloys by Electrospinning" Coatings 9, no. 4: 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9040216
APA StyleIribarren, A., Rivero, P. J., Berlanga, C., Larumbe, S., Miguel, A., Palacio, J. F., & Rodriguez, R. (2019). Multifunctional Protective PVC-ZnO Nanocomposite Coatings Deposited on Aluminum Alloys by Electrospinning. Coatings, 9(4), 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9040216








