Abstract
The pure Cu coating was plated on the surface of silicon carbide particles (SiCP) by two different methods, hydrazine hydrate direct reduction method and hydrazine with glucose pre-reduction method. The hydrazine with glucose pre-reduction method is more suitable for Cu plating on the surface of SiCP in terms of morphology and microstructure. AZ61 composites reinforced with different volume fractions (3~15%) uncoated and Cu-coated SiCP were prepared by powder metallurgy followed by hot extrusion. The effect of Cu coating on the morphology of SiCP/AZ61 composite was analyzed by optical microscope (OM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS), electronic probe micro-analyzer (EPMA) and X-ray diffractometer (XRD). The properties of the composite were characterized by Brinell hardness tester and mechanical testing machine. The effects of Cu coating on the micro-hardness, tensile strength and elongation of SiCP/AZ61 composite were analyzed. The tensile strength of AZ61 composite reinforced with Cu-coated SiCP increased by 3.5~6.3% and the elongation increased by 7.4~35.0% compared with AZ61 composite reinforced with uncoated SiCP. Therefore, the Cu coating can ameliorate the microstructure and properties of the SiCP/AZ61 composite effectively, reduce the defect rate in the composite, and improve the hardness, relative density, tensile strength, elongation of the composite.
1. Introduction
Magnesium and its alloys are widely used as structural materials in the aerospace, automotive, military, and electronics industries due to their light weight, high specific strength, superior machinability, and damping capacity. AZ61 magnesium alloy is one of the most mature Mg–Al–Zn alloy systems with good room temperature strength and ductility [1,2,3]. However, the insufficient elastic modulus, strength, and hardness result in the limited application of these alloys in vehicles and so on. Compared with alloying and heat treatment, the incorporation of ceramic particles is an effective way to improve the mechanical properties of magnesium alloys. Silicon carbide particle (SiCP) is widely used as reinforcement in metal matrix composites (MMCs) owing to its high hardness, strength, elastic modulus, corrosion resistance, wear resistance, high temperature resistance, and low price [4,5,6,7].
There are many researchers who focus their attention on the effect of the properties of the reinforcement (i.e., size, morphology, volume fraction, and distribution, etc.) and the preparation method of the composites [8,9]. While the strong interfacial bonding and homogeneous dispersion of SiC particles are the necessary requirement in achieving excellent performance. One of the effective methods to eliminate the differences in physical and chemical compatibility between SiCP and Mg to enhance the interface strength is the surface modification of reinforcement [10,11]. The coating layer on reinforcement can improve the wetting ability between the reinforcement and the matrix, as well as avoid the brittle intermetallic bond as a result of interfacial reactions. Inspection of the published literature shows that the electroless deposition of a metal layer such as Ni, Cu, and Ti on SiC particles is a popular way to improve the relative density and matrix strength of Al/SiCp composites [12,13,14,15,16,17]. The interfacial bonding as well as the mechanical properties of SiC reinforced metal-based composites is significantly improved after coating the surface of SiC particles with the metal layer. Our group did some research on Ni-coated SiCP reinforced AZ61 composites earlier. The results show that the Ni coating layer enhances the wettability, interface bonding, and the distribution of SiCP [18].
Compared with Ni coating, the compounds of Cu and Mg are more stable since the enthalpy of formation is lower than that of Ni. Moreover, Cu layer can diffuse intoAl element to form continuous solid solution to improve the interfacial bonding strength. However, less work has been performed on the microstructures and mechanical properties of Cu-coated SiCP reinforced AZ61 magnesium composites.
In this work, Cu-coated SiCP reinforced AZ61 magnesium composites are prepared by powder metallurgy and their microstructure as well as properties are compared to AZ61 magnesium composites reinforced by SiCP without Cu-coating. The aim of this work is to analyze the influence of the Cu-coating on the SiCP surface on the properties of SiCP/AZ61 composites.
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Raw Materials
The gas-atomized AZ61 alloy powders (Weihao, Yantai, China) with a nominal composition of Mg–6.6Al–1.1Zn–0.32Mn–0.1Si were used as matrix and the average size of the AZ61 alloy powder was 40 μm. The α-SiC particles (Huarong Ceramics, Weifang, China) with purity of 99.99% and an average size of 14 μm were used as reinforcement [19].
2.2. Surface Modification of SiCP
In this part, surface metallization of SiC particles with copper (Cu-coated SiC) is carried out by two different electroless plating methods, including the hydrazine hydrate direct reduction method and glucose pre-reduction method. The details are as follows.
Before the surface modification, the SiC particles were all cleaned by NaOH solution and activated by dilute HNO3 solution. Then the SiC particles were washed with distilled water to get neutral pH and dried in hydrogen atmosphere at 300 °C for 1 h to get the cleaned SiC particles. For electroless plating, the sensitization by HCl aqueous solution containing Sn2+ and activation by HCl aqueous solution containing Pd2+ of SiC particles need to be done respectively.
- (1)
- Hydrazine hydrate direct reduction method.
The dried SiC particles were dipped into 40 g/L CuSO4 solution at 50 °C. The prepared hydrazine hydrate solution and the NaOH solution were added at a constant rate, and the mixture was stirred for 30 min till the reaction was finished completely.
- (2)
- Glucose pre-reduction method.
Firstly, the glucose solution were added into the 40 g/L CuSO4 solution which contains SiC particles at 50 °C thermostat. This process lasted about 30 min. Secondly, the hydrazine hydrate solution was added at a constant rate and stirred for 30 min till the reaction was finished completely.
2.3. Preparation of SiCP/AZ61 Composites
The AZ61 powders and Cu-coated SiCP were ball-mixed at 200 rpm for 30 min with a ball-to-powder weight ratio of 10:1. The mixed powders were compressed in a cemented carbide die with a diameter of 32 mm at room temperature. The pressure was 200 MPa and the dwell time was 2 min. Then, the as-received compacts were sintered and densified in a vacuum pressure sintering furnace at 773 K under a pressure of 45 MPa for 30 min and the temperature was monitored by a laser infrared thermometer. The hot-pressed specimens were extruded at 593 K with an extrusion ratio of 10:1. The extruded samples became bars with a diameter of 10 mm. Finally, the extruded specimens were solution-treated at 623 K for 2 h followed by water quenching, and then artificially aged at 453 K for 24 h. For comparative analysis, the SiCP/AZ61 composites with the original SiC particles were prepared under the same processing and aging condition.
2.4. Materials Characterization
The density of the composites was measured by Archimedes method using an accurate balance (1 mg). The hardness of the material was measured using an HBS-62.5-type Brinell hardness tester (HBS-62.5, Yantai, China) with a 5-mm-diameter steel ball under a load of 62.5 kg, and the dwell time was 30 s. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) was performed using a diffractometer (D/max-vb 2500, Tokyo, Japan) with Cu Kα radiation at a scanning speed of 4°/min to detect the phase composition. Detailed microstructures were investigated by optical microscopy (Leica DM2700M, Cologne, Germany). Optical microstructure samples were prepared by sectioning and polishing of the corresponding plane. The microstructures such as the distribution of the Cu-coated SiCP in the AZ61 matrix were observed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM, Quanta-200, Oregon, OR, USA) equipped with energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS). Electron probe microanalysis (EPMA; JXA8230, Tokyo, Japan) was used to demonstrate the distribution of intermetallic phases on the composite samples. The tensile tests at room temperature were conducted using an mechanical testing machine (Instron MTS 810, Minnesota, USA) at a loading rate of 0.2 mm/min.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Investigation on Electroless Methods of Cu Plating
Figure 1 shows the macroscopic contrast of SiC particles with and without electroless copper plating. The color of SiC powder turned from gray-green to dark-red after the surface modification. But, the difference between two electroless plating SiC particles which were placed in the same paper but separated by a black line is not obvious. They both presents a dark-red color which is same with the copper element. Therefore, it is necessary to compare the two plating methods from the microscopic state.
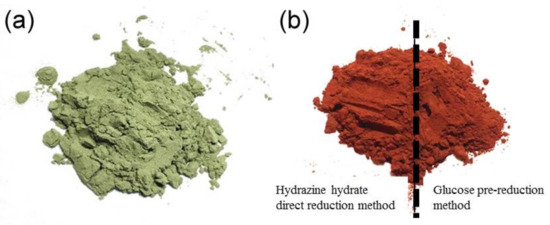
Figure 1.
Macroscopic pictures of (a) original SiC and (b) Cu-coated SiC.
The surface morphologies of the original SiC and the Cu-coated SiC prepared by two plating methods are shown in Figure 2. In Figure 2a, impurities (as indicated by the red circles) and sharp edges (as indicated by the red arrows) can be found on the surface of the original SiC particles. These defects can cause micro-pores and stress concentration in the corresponding composites, which are the main causes of material failure [20]. Figure 2b,c are SEM photographs of copper-coated SiC prepared by the direct hydration method and the glucose pre-reduction method, respectively. The reaction process of the two plating processes is different; while the reaction process of the hydrazine hydrate direct reduction method is shown in the Formula (1), and the reaction process of the glucose pre-reduction method is shown in the Formulas (2)–(4) [21,22,23].
2CuSO4 + N2H4·H2O + 4NaOH = Cu + N2 + 2Na2SO4 + 5H2O,
CuSO4 + 2NaOH = Cu(OH)2 + Na2SO4,
CH2OH(CHOH)4CHO + 2Cu(OH)2 = Cu2O + CH2OH(CHOH)4COOH + 2H2O,
N2H4·H2O + 2Cu2O = 4Cu + N2 + 3H2O
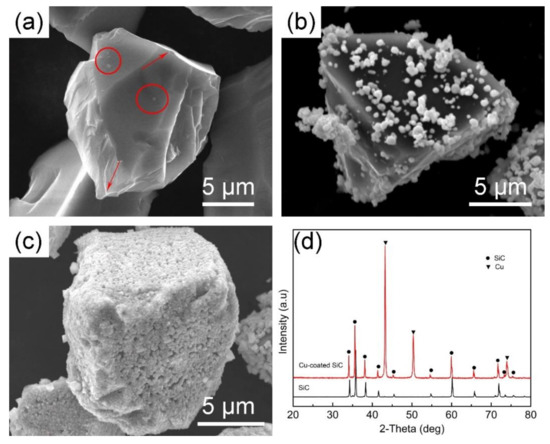
Figure 2.
SEM morphologies of (a) original SiC and copperplated SiC obtained by (b) hydrazine dir-reduction method, (c) hydrazine with glucose pre-reduction method; (d) XRD patterns of uncoated and Cu-coated SiCP.
As shown in Figure 2b, the copper particles formed by the hydrazine hydrate direct reduction method are agglomerated together while the distribution is loosely on the surface of the SiC particles. It is consistent with the reaction mechanism which is shown in Formula (1) indicting a rapid and intense reaction. As a comparison, the surface of Cu-coated SiC prepared by glucose pre-reduction method is covered by a uniform and intact coating layer. Figure 2d shows the XRD patterns of the original SiC particles and the copper-plated SiC particles prepared by the glucose pre-reduction method. It reveals that there are no impurities in the original SiC particles due to the limitation of the X-ray detection accuracy [24]. Diffraction peaks of copper were discovered at 43°, 50°, and 74°, indicting the existence of pure copper in the Cu-coated SiC powder and there is no Cu2O phase since the completion of the reaction shown in Formula (4).
Since the purpose of this paper is to study the effect of Cu-coating layer on the microstructure and mechanical properties of SiCP/AZ61 composites, we chose glucose pre-reduction method to prepare a uniform and intact Cu coating layer on the surface of SiC particles.
3.2. Microstructures of SiCP/AZ61 Composites
The metallographic morphologies of Cu-coated SiCP/AZ61 composites with a volume fraction of 3% to 15% are shown in Figure 3a–e. The distribution of SiC particles is discrete and uniform when the volume fraction is 3~9%. As indicated by the red circle in Figure 3d–e, there is a slight agglomeration in 12 vol% Cu-coated SiCP/AZ61 composites. The situation became more serious when the volume fraction is 15% and pits left by the peel off of SiC particles can be observed indicating a weak bonding strength in the SiC agglomeration region. Since the better the dispersibility of the reinforcing phase in the metal matrix, the better strengthening effect on the composite, the microstructure of the composites has a positive correlation on determining the final properties of the composites [25,26,27].
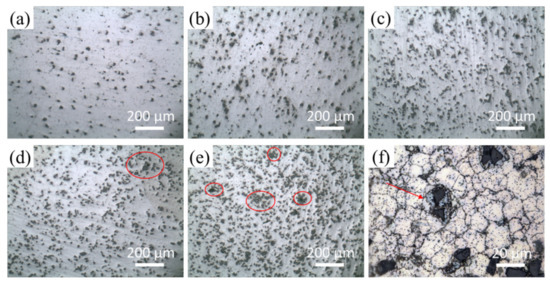
Figure 3.
Optical microstructures of AZ61 composites reinforced with different volume fractions: (a) 3%, (b) 6%, (c) 9%, (d) 12%, (e) 15% Cu-coated SiCP; (f) corrosion morphology of AZ61 composite reinforced with 9% Cu-coated SiCP.
Figure 3f shows the corroded metallography of 9 vol% Cu-coated SiCP/AZ61 composites after etching by the etching solution which contains 1 mL HNO3, 1 mL CH3COOH, 1 g H2C2O4 and 95 mL distilled water for 5 s. The grain boundary, second phase particles and SiC/AZ61 matrix interface were preferential corrosion sites which were displayed clearly in black. It is obvious that the grains around the SiC particles are much finer than the matrix free of SiC particles. The grain size around the SiC particles is measured to be only 4 μm while the grains far from the SiC particles can reach 40 μm at largest. This phenomenon can be attributed to the following reasons: (1) micron-sized SiCP can induce recrystallization of the AZ61 matrix alloy by accelerating the particle nucleation at the interface between SiCP and AZ61 matrix; (2) the addition of SiCP can limit or delay the growth of the grains during the heating process effectively.
The red arrow in Figure 3f shows the transition layer between SiC and AZ61matrix. The color is lighter than the grain boundary which means the degree of corrosion is not as severe as the grain boundary and indicates the transition layer is tightly bonded to SiC particles and AZ61matrix.
Figure 4 shows the microstructure of the composites reinforced with 9 vol% SiCP with and without copper coating. It can be observed that there are visible flaws (shown in Figure 4a with the arrows and circles) in the composites, including micro-sized pores around the untreated SiC particles and triangular-shape pits in the AZ61 matrix. These defects all indicates the weak interfacial bonding between the reinforcement and the matrix. The micro-pores can be caused in the hot pressing due to the insufficient wettability of SiC particles and magnesium matrix, and the pits might be the abscission of the SiC particles during polishing. This is consistent with research that it is difficult to achieve the densification of SiC particles reinforced aluminum and magnesium composites even the temperature is above the liquidus temperature [28].
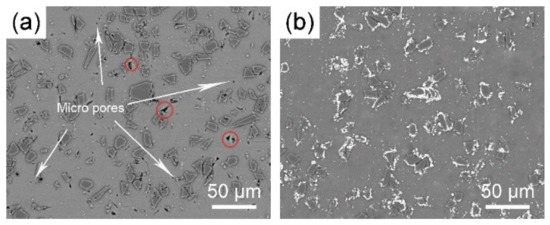
Figure 4.
SEM images of AZ61 composites reinforced with 12% (a) uncoated and (b) Cu coated SiCP.
In contrast, there are little porosities or flaws in the composites reinforced with Cu-coated SiC particles as shown in Figure 4b. However, the phenomenon of SiC particles agglomeration has not changed significantly. But the situation is different owing to the copper layer on the surface of SiC particles. Compared to the direct contact of original SiC particles, there is always a metal transition layer which can help to avoid the generation of micro-pores and local stress concentration during tensile load was applied. This is benefit to the relative density and the ultimate tensile strength of the composites. Details are described in Section 3.3 as follows.
3.3. Interface of SiCP/AZ61 Composites
Figure 5 shows the interface morphology and corresponding energy spectrum of the composites reinforced with 9 vol% SiCP with and without copper coating. It can be seen from Figure 5a that the SiC particles are almost contacting directly in the agglomeration area while there is a copper transition layer between two Cu-coated SiC particles to avoid direct contact. The corresponding EDS line scanning map verified the existence of copper layer in Figure 5d. There is always a sudden drop of Si intensity on the edge of SiC particles. As shown in Figure 5c, Mg element can be detected between two edges of SiC particles, but the intensity is little which indicates the direct contact of two SiC particles. In contrast, a peak of Cu element appeares at the same position where the Si element showes a sharp drop. This provides evidence for the existence of copper in the interface and the thickness of the transition layer is approximately 2 μm. The copper layer can avoid the direct contact of SiCP when the particles are agglomerated due to the increase of the volume fraction of SiCP. Whereas, the generation of micro-pores and local stress concentration were avoided during tensile load was applied.
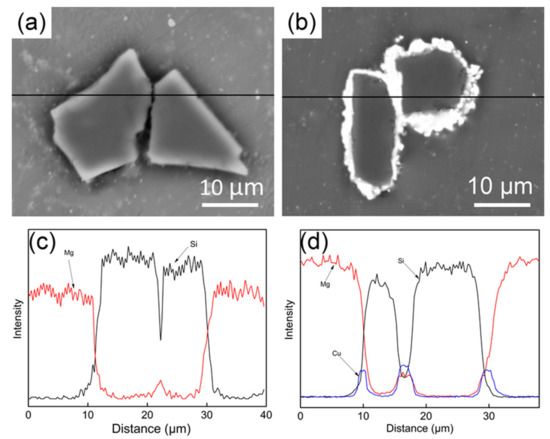
Figure 5.
SEM images of AZ61 composites reinforced with 12% (a) uncoated and (b) Cu-coated SiCP; corresponding energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) analysis of (c) uncoated and (d) Cu–SiCP reinforced composite.
The magnesium matrix we used in the study is AZ61 magnesium which mainly contains Mg element, Al element, and Zn element. EPMA mapping was carried out to figure out the microstructure of the composites reinforced with Cu-coated SiCP. As shown in Figure 6, the distribution of Mg element is relatively uniform, and there is no obvious segregation around the SiCP. The energy spectrum of Si element is mainly onSiC particles and is not detected in the matrix, indicating that the phenomenon of Si diffusion to the matrix does not occur during hot pressing, hot extrusion, and heat treatment. The energy spectrum of Cu distributed around the SiC particles indicates that the copper layer is wrapped with SiCP tightly and no diffusion occures. The energy intensity of Cu varies with the thickness of copper coating on the surface of SiC which is uniform overall. Obvious segregation of Al and Zn element can be observed at the interface region since the intensity values of Al and Zn element in the matrix and interface changed from 3.22, 0.742 to 8.84 and 2.976 respectively. These segregations must be generated during the preparation processes such as hot-pressing, hot-extrusion, and heat treatment. New phases may be generated in the segregation area.
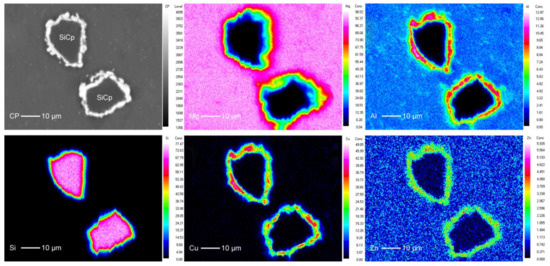
Figure 6.
Back scattered electron (BSE) images and electron probe microanalysis (EPMA) X-ray elemental color mapping images for Mg, Al, Si, Cu, and Zn from Cu–SiCP/AZ61 composites.
EDS and XRD analysis were carried out to figure out the possible new phases generated in the interface of Cu-coated SiCP/AZ61composites. The results are shown in Figure 7 and Figure 8, respectively. According to Figure 7b, the interface region of the Cu-coated SiCP/AZ61 composites containes four elements of Mg, Al, Cu, and Zn. This indicates that a new phase is formed at the interface, and the new phase of the interface layer is judged to be the θ phase (Al2Cu) and the η phase (MgZn2) in combination with the literature [29,30]. The XRD pattern of Cu–SiCP/AZ61 composite has three peaks at 43°, 50°, and 74°, corresponding to the elemental Cu while peaks appearing near 21° and 43° can be indexed to be Al2Cu phase. This indicates that the Cu layer produced by electroless plating reacts with Al in the AZ61 alloy matrix and formes a binary alloy phase Al2Cu. The reaction product η phase (MgZn2) could not be detected by X-ray diffractometer since the mass fraction of Zn in the AZ61 alloy was 1.1% as shown in Figure 8.
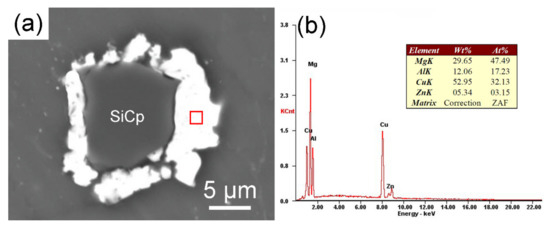
Figure 7.
SEM images (a) and EDS spectra (b) of interfacial layer of Cu–SiCP/AZ61.
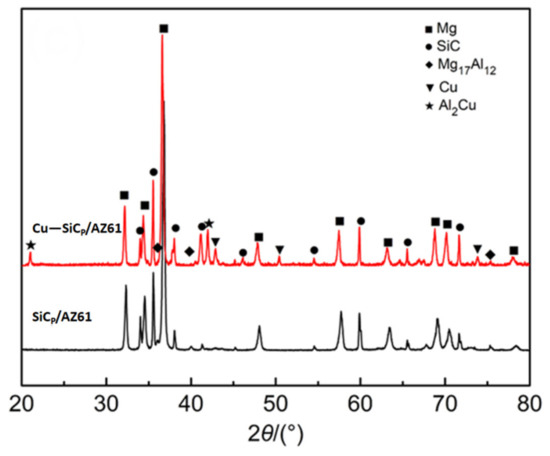
Figure 8.
XRD patterns of AZ61 composites reinforced with 15% uncoated and Cu-coated SiCP.
3.4. Mechanical Properties of SiCP/AZ61 Composites
Figure 9 shows the hardness and relative density of the AZ61 matrix composites reinforced with different volume fractions of SiCP with and without Cu coating, respectively.
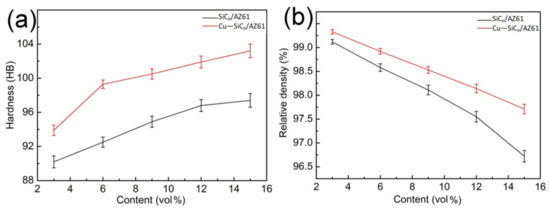
Figure 9.
Variations in (a) relative density, (b) hardness for AZ61 composites reinforced with different volume fractions of uncoated and Cu-coated SiCP.
There is a significant increment in the hardness of the SiCP/AZ61composites with the increase in volume fraction of reinforcement, as seen in Figure 9a. This enhanced hardness can be primarily attributed to: (a) the presence of relatively harder ceramic particles in the matrix [27,29], (b) a higher constraint to the localized matrix deformation during indentation. It should be noted that intermetallic is extremely hard relative to their pure components [30]. Higher concentration of reaction product and reinforcement particles causes a further increment of hardness.
The relative density of the composites decreases with the increase in the volume fraction of SiCP. However, the composites with Cu-SiCP shows_ a higher density than that with uncoated ones at the same content of SiCP. According to the result of differential thermal analysis, liquid phase is formed at 703 K which is beneficial for densification of the composites [31]. Compared with uncoated SiCP, the Cu-coated SiCP shows a positive cooperativity with the AZ61 matrix during the densification. The liquidus phase can be better spread on the surface of the Cu-coated SiCP, reducing defects such as voids in the composite material, thereby increasing the density of the composites. The relationship between the viscosity of the composites and the volume fraction of the reinforce particles can be summarize by the following equation [32].
where is the viscosity of the composite, is the viscosity of the matrix, and is the volume fraction of the particles.
As shown in Figure 5, the Cu layer on the surface of the SiCP can improve the wettability between the magnesium alloy substrate and SiC. The molten AZ61 alloy can effectively spread on the surface of the Cu–SiCP, reducing defects such as voids in the composite material, thereby increasing the density of the composite material [31].
Figure 10 exhibits the stress-strain curves upon tensile loading of the AZ61 matrix composites reinforced with different volume fractions of SiCP with and without Cu coating, respectively. It can be observed that ultimate tensile strength and elongation of Cu-SiCP/AZ61 composites were both higher than SiCP/AZ61 ones. This indicates that the Cu layer can improve the bonding strength of the interface, reduced the possibility of the interface peeling, and transferred the load from the matrix to the hard reinforcement particles effectively. The ultimate tensile strength of SiCP/AZ61 composites increases with the increasing of SiCP content since the attribution of load transfer enhancement is from the matrix to the SiCP [33]. However, as shown in Equation (5), the viscosity of the composites increases exponentially with the volume fraction of SiCP, and the melt fluidity deteriorates during the preparation process, resulting in an increase in defects such as pores which decreased the relative density of the composite. Therefore, the best mechanical properties were obtained when the appropriate volume fraction of SiCP is 9%.
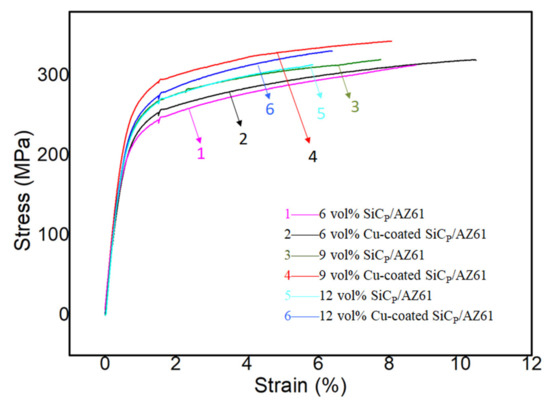
Figure 10.
The stress–strain curves upon tensile loading of the AZ61 matrix composites reinforced with different volume fractions of SiCP with and without Cu coating.
4. Conclusions
In the present work, SiCP/AZ61composites were prepared by hot pressing followed by hot extrusion using the mixture of rapidly solidified AZ61 alloy powder and different volume fractions of SiCP with and without Cu coating, respectively. The extruded and heat-treated materials were characterized for their microstructural and mechanical properties. And the following conclusions can be summarized.
- (1)
- The Cu layer prepared by the pre-reduction method of glucose using hydrazine hydrate as reducing agent is more uniform and complete than the one prepared by direct reduction of hydrazine hydrate. Therefore, the pre-reduction method is more suitable for copper plating on the surface of SiCP.
- (2)
- The Cu layer fabricated by electroless plating is beneficial for the wettability and interfacial bonding strength between the SiCP and AZ61 matrix. The microstructure of Cu–SiCP/AZ61 composites shows a significant decrease in micro-porosity and other defects.
- (3)
- XRD phase analysis shows that θ phase (Al2Cu) has formed in Cu–SiCP/AZ61. Combined with the EPMA element mapping and EDS spectrum quantitative analysis, it is further inferred the formation of η phase (MgZn2).
- (4)
- Cu plating on the surface of SiCP has positive effect on the hardness, relative density, tensile strength, and elongation of the composite. With the increase of SiCP volume content, defects such as voidsare more likely to occur in the composite. While the Cu layer on the surface of SiCP can reduce the porosity effectively and enhanced the interfacial bonding strength between SiCP and AZ61 matrix. Besides, the Cu coating on the surface of SiCP plays as a transition layer to make sure the load transfersfrom the matrix to the SiC particles effectively, thereby increasing the ultimate tensile strength, and elongation of the composite. The best mechanical properties are obtained when the appropriate volume fraction of SiCP is 9% and the hardness, ultimate tensile strength, and elongation are 100.5 HB, 335.67 MPa, and 7.91%, respectively.
Author Contributions
Data creation: C.D. and S.G.; Writing—original draft: C.D.; Writing—review& editing: R.W.
Funding
This research was funded by the Science and Technology Program of Shenzhen, China (CXZZ20140506150310438), the Science and Technology Program of Hunan, China (2017GK2261) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University, China (2017zzts111).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cui, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Gong, D.; Wang, W. Microstructure, mechanical, corrosion properties and cytotoxicity of betacalcium polyphosphate reinforced ZK61 magnesium alloy composite by spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 99, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, P.N.; Lam, R.N.; Zheng, Y.F.; Thian, E.S. Magnesium-calcium/hydroxyapatite (Mg-Ca/HA) composites with enhanced bone differentiation properties for orthopedic applications. Mater. Lett. 2016, 172, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwinski, F. Controlling the ignition and flammability of magnesium for aerospace applications. Corros. Sci. 2014, 86, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, A.; Tun, K.S.; Gupta, M. Deformation behaviour of Mg/Y2O3 nanocomposite at elevated temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 551, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommala, V.K.; Krishna, M.G.; Rao, C.T. Magnesium matrix composites for biomedical applications: A review. J. Magnes. Alloys 2019, 7, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.Z.; Liu, X.Y. Review of recent studies in magnesium matrix composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 6153–6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, G.; Han, F.; Xia, X.; Wu, Y. Microstructures, mechanical properties, and wear resistances of thixoextruded SiCP/WE43 magnesium matrix composites. Miner. Met. Meter. Soc. ASM Int. 2017, 48, 3497–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Huang, S.-J.; Wu, Y.-J.; Kang, C.-W. Particle Size and Particle Percentage Effect of AZ61/SiCp Magnesium Matrix Micro- and Nano-Composites on Their Mechanical Properties Due to Extrusion and Subsequent Annealing. Metals 2017, 7, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkoffli, Z.; Syarif, J.; Sajuri, Z. Fabrication of AZ61/SiC composites by powder metallurgy process. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Eng. 2009, 4, 156–159. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.W.; Liu, X.R.; Zhang, R.L.; Su, Z.Z. Preparation and Properties of Magnesium-Aluminum Matrix Composites Reinforced with Silicon Carbon Particles. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 583, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, H.; He, B.L.; Hong, Y. Rheological behavior of semi-solid Mg 2Si/AM60 magnesium matrix composites at steady state. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. Chin. 2010, 20, s883–s887. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Xu, H.; Lu, H.; Guan, S. Preparation of Al-based Metal Matrix Composites Reinforced by Cu Coated SiC Particles. Key Eng. Mater. 2005, 280, 1493–1496. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, M.; Lai, M.O.; Saravanaranganathan, D. Synthesis, microstructure and properties characterization of disintegrated melt deposited Mg/SiC composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 2155–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Liao, W.; Guo, W.; Ye, B.; Li, W.; Jiang, H.; Ding, W. Effects of cyclic extrusion and compression on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ91D magnesium composites reinforced by SiC nanoparticles. Mater. Charact. 2017, 126, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaily, M.; Mortazavi, N.; Svensson, J.E.; Halvarsson, M.; Wessén, M.; Johansson, L.G.; Jarfors, A.E. A new semi-solid casting technique for fabricating SiC-reinforced Mg alloys matrix composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 94, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojanová, Z.; Gärtnerová, V.; Jäger, A.; Námešný, A.; Chalupová, M.; Palček, P.; Lukáč, P. Mechanical and fracture properties of an AZ91 Magnesium alloy reinforced by Si and SiC particles. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 2256–2264. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.Y.; Zha, X.W. Influence of nickel coating on the interfacial bonding characteristics of carbon nanotube–aluminum composites. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2010, 49, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.Q.; Wang, R.C.; Peng, C.Q.; Cai, Z.Y.; Dong, C.G. Microstructures and mechanical properties of Ni-coated SiC particles reinforced AZ61 alloy composites. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. Chin. 2019, 29, 1854–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Li, X.R.; An, D.; Liang, J.; Liu, C.S. Preparation and Wear Performance of Novel Graphite/Copper Alloy-Matrix Self-Lubricating Composite Materials. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 941, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.W.; Kim, S.K.; Ha, H.S.; Kim, M.G.; Lee, D.B.; Kim, Y.J. Microstructural evolution and semisolid forming of SiC particulate reinforced AZ91HP magnesium composites. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2000, 16, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, P.P.; Shaik, A.H.; Chakraborty, J. Preparation of stable sub 10 nm copper nanopowders redispersible in polar and non-polar solvents. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 466, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikova, S.V.; Vorob’ev, S.A.; Nikolaeva, R.B.; Mikhlin, Y.L. Conditions for the formation of copper nanoparticles by reduction of copper (II) ions with hydrazine hydrate solutions. Russ. J Gen. Chem. 2010, 80, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.H.; Lee, C.H.; Popuri, S.R.; Kumar, K.N.S. Preparation of High-Purity Ultrafine Copper Powder in Mass-Production by Chemical Reduction Method: Taguchi Robust Design Optimization. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 2016, 55, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.F.; Gupta, M. Development of high strength magnesium based composites using elemental nickel particulates as reinforcement. J. Mater. Sci. 2002, 37, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Konishi, H.; Fehrenbacher, A.; Ma, C.; Xu, J.Q.; Choi, H.; Xu, H.F.; Pfefferkorn, F.E.; Li, X.C. Novel nanoprocessing route for bulk graphene nanoplatelets reinforced metal matrix nanocomposites. Scr. Mater. 2012, 67, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Boselli, J.; Sinclair, I. Simulation and quantitative assessment of homogeneous and inhomogeneous particle distributions in particulate metal matrix composites. J. Microsc. 2001, 201, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacob, G.; Ghica, V.G.; Buzatu, M.; Buzatu, T.; Petrescu, M.I. Studies on wear rate and micro-hardness of the Al/Al2O3/Gr hybrid composites produced via powder metallurgy. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 69, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W. Determination of densification behavior of Al–SiC metal matrix composites during consolidation processes. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 483, 648–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaubey, A.K.; Mohapatra, S.; Jayasankar, K.; Pradhan, S.K.; Satpati, B.; Sahay, S.S.; Mishra, B.K.; Mukherjee, P.S. Effect of cerium addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2009, 62, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cao, F.; Guo, S.; Ning, Z.; Liu, Z.; Jia, Y.; Scudino, S.; Gemming, T.; Sun, J. Microstructures and properties evolution of spray-deposited Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloys with scandium addition. J. Alloys. Compd. 2017, 691, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, M.; Mirkovic, D.; Schmidfetzer, R. Liquidus and solidus temperatures of Mg-rich Mg–Al–Mn–Zn alloys. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 3883–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Ma, L.; Yan, J.; Chen, W.; Yang, S. Solidification microstructure of SiC particulate reinforced Zn–Al composites under ultrasonic exposure. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 148, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, S.; Imai, H.; Jia, L.; Umeda, J.; Takahashi, M.; Kondoh, K. Load transfer strengthening in carbon nanotubes reinforced metal matrix composites via in-situ tensile tests. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 113, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).