Sliding Wear Behavior of Fe-Al Coatings at High Temperatures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
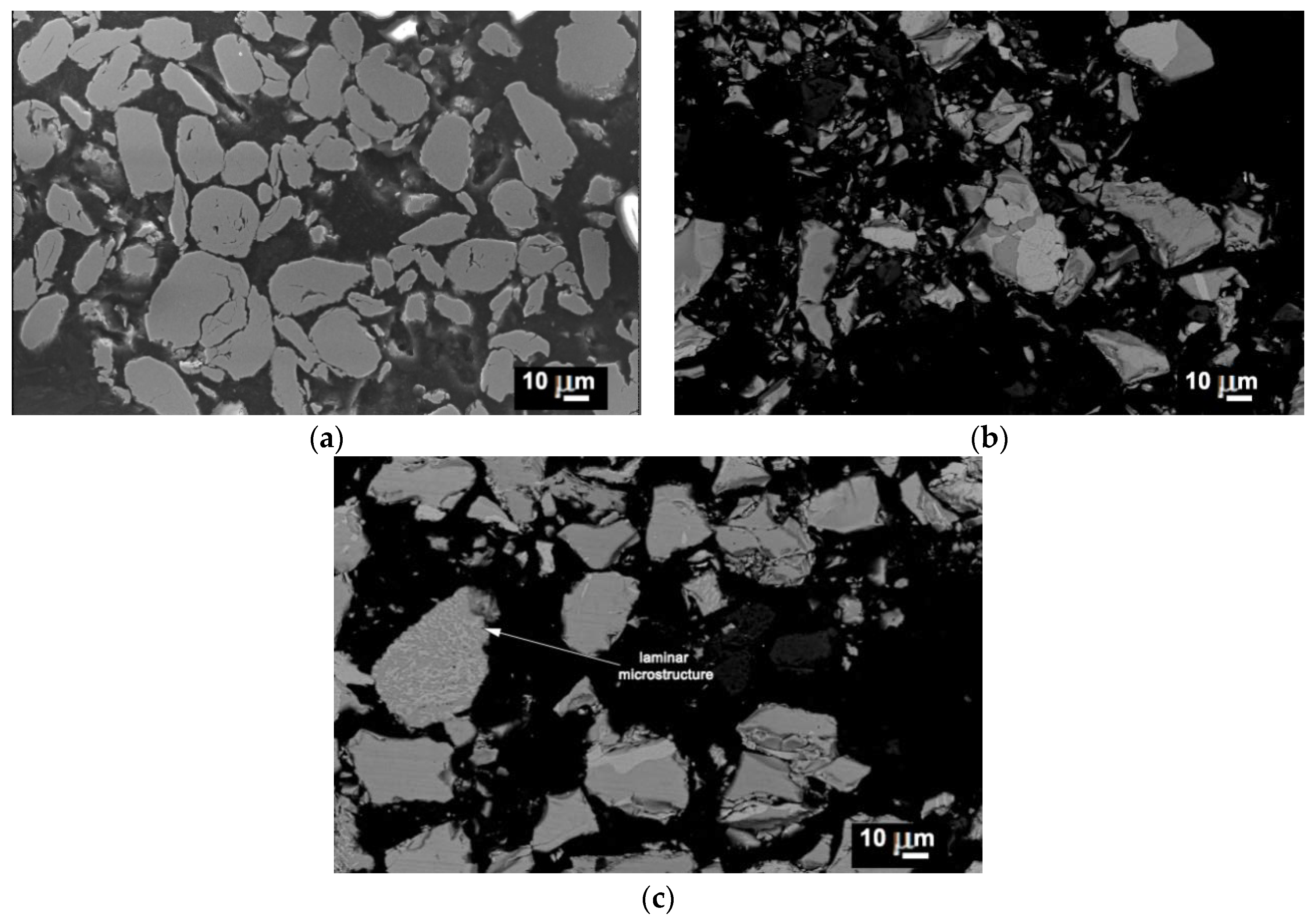
3.1. Powder Deposition
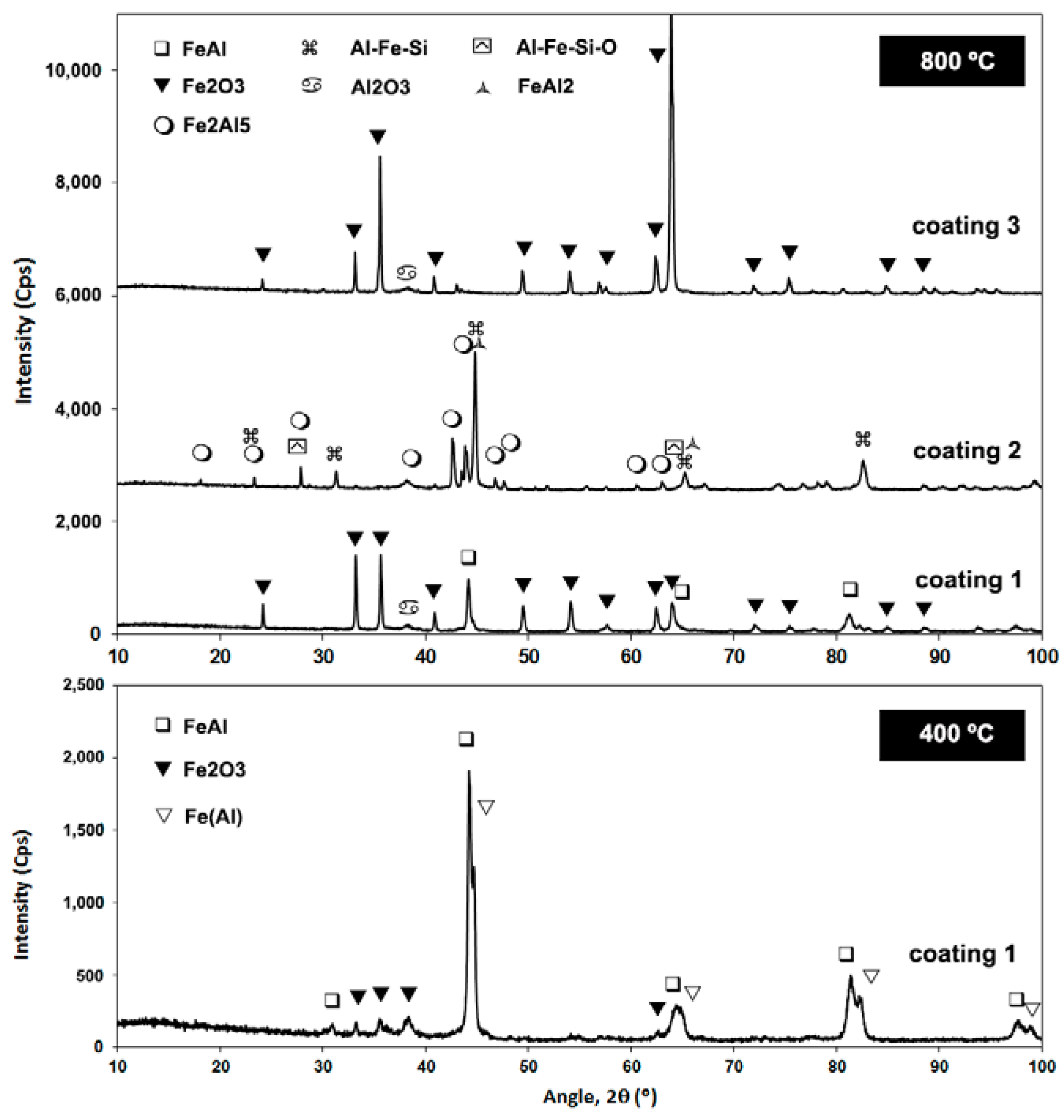
3.2. Coatings Performance
4. Conclusions
- The coating hardness of the sprayed coatings 1 and 2 proved to be very similar, despite their different composition and original powder; this can be explained by heterogeneous balance in the HVOF coating, resulting from the presence of oxide regions as well as Al-depleted regions. The lowest hardness of the sprayed SHS powder came from the higher porosity levels.
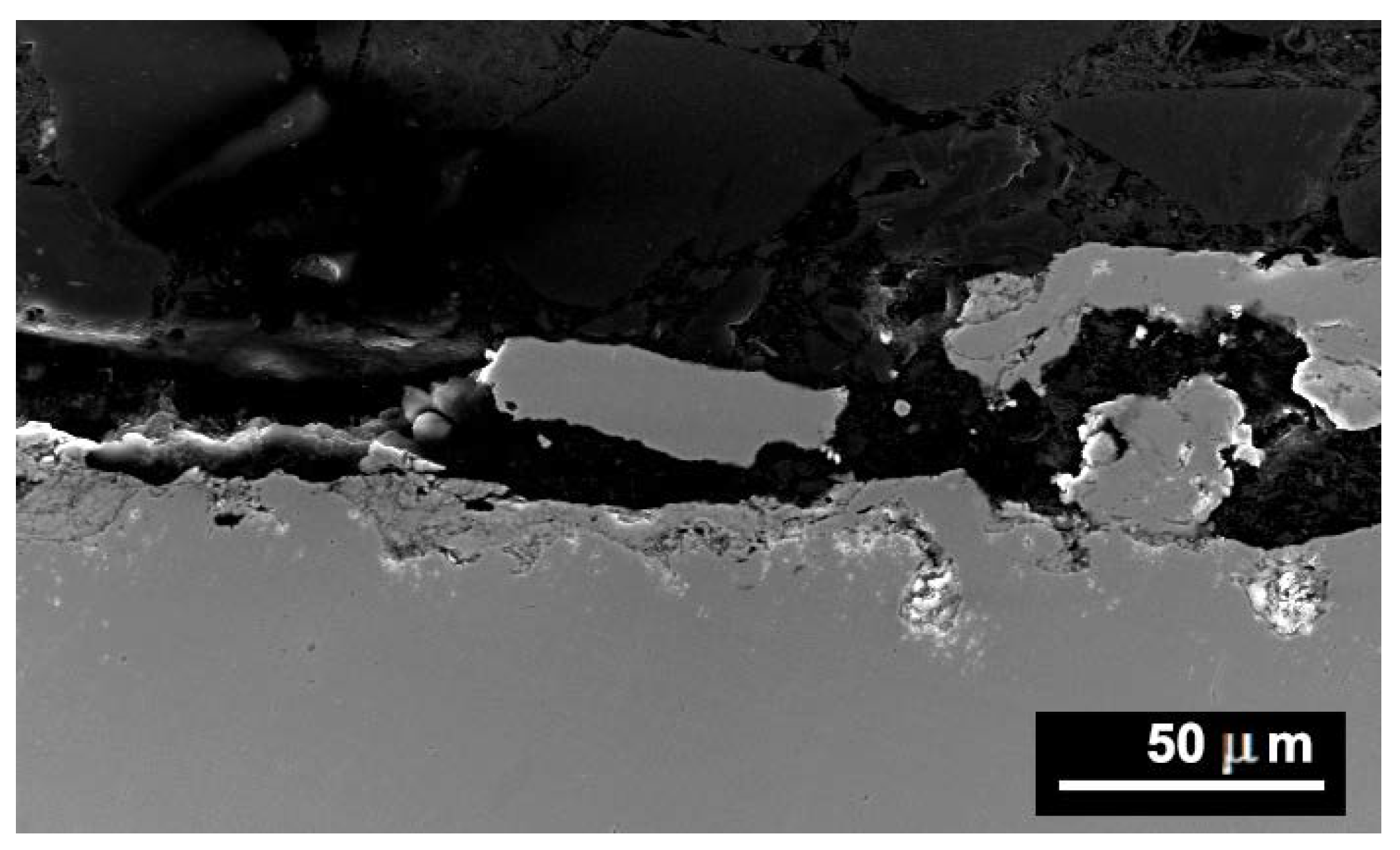
- The self-decomposed and SHS feedstock compositions presented quite brittle phases that were detrimental to wear performance, enabling further penetration of the oxidizing atmosphere, even up to the point that coating 3 finally formed a dense tribofilm (glaze) layer. Delamination and tribo-oxidation were mainly identified as wear mechanisms that resulted from poor substrate cohesion.
- Wear rates for coating 1 were in the order of 2.11 × 10−5 ± 2.00 × 10−6 mm3 N−1 m−1 at 400 °C and even lower at 800 °C, where the exact value could not be measured. The other coatings showed wear rates at one order of magnitude higher. The different performance appeared to be related to the microstructural features of the initial composition and the exposure to high temperatures. Cohesive strength in coating 1 as well as its effectiveness in forming a protective layer allowed for the suppression of delamination.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fleischer, R.L.; Dimiduk, D.M.; Lipsitt, H.A. Intermetallic compounds for strong high temperature materials: Status and potential. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1989, 19, 231–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deevi, S.C.; Sikka, V.K.; Liu, C.T. Processing, properties and applications of nickel and iron aluminides. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1997, 42, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deevi, S.C.; Sikka, V.K. Nickel and iron aluminides: An overview on properties, processing, and applications. Intermetallics 1996, 4, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Iwasaki, K.; Kishi, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Tanaka, R. Dry sliding wear behavior of Fe-28Al and Fe-28Al-10Ti alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 366, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Limaye, P.K.; Ramanujan, R.V.; Sundararaman, M.; Prabhu, N. Dry-sliding wear studies of Fe3Al-ordered intermetallic alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 386, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.J.; Kennedy, F.E.; Baker, I. Dry Sliding Wear of NiAl. Wear 1996, 192, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K. A Ni3Al-alloy and Its Composites as Potential Wear Resistant Materials for Advanced Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden, 28 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hawk, J.A.; Alman, D.E. Abrasive wear of intermetallic-based alloys and composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1997, 239, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alman, D.E.; Hawk, J.A.; Tylczak, J.H.; Dogan, C.P.; Wilson, R.D. Wear of iron-aluminide intermetallic-based alloys and composites by hard particles. Wear 2001, 251, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, R.; Schneibel, J.H. FeAl-TiC and FeAl-WC composites—Melt infiltration processing, microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 244, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, M.; Wexler, D.; Chandra, T.; Calka, A. Abrasive wear of WC-FeAl-B and WC-Ni3Al-B composites. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2005, 23, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, J.; Fu, L.; Zhu, S.; Li, F.; Yang, J.; Liu, W. High temperature wear resistance of Fe–28Al–5Cr alloy and its composites reinforced by TiC. Tribol. Int. 2013, 61, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosbah, A.Y.; Wexler, D.; Calka, A. Abrasive wear of WC-FeAl composites. Wear 2005, 258, 1337–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Baker, I.; Kennedy, F.E.; Liu, Y.; Munroe, P.R. The effects of stoichiometry on the dry sliding wear of FeAl. Intermetallics 2013, 40, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M. The influence of temperature on the wear of Cr3C2−25(Ni20Cr) coating-comparison between nanocrystalline grains and conventional grains. Wear 2004, 257, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taktak, S. Tribological behaviour of borided bearing steels at elevated temperatures. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 2230–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.G.; Muñoz-Morris, M.A. Intermetallics: Past, present and future. Rev. Metal. 2005, 41, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasalmonie, A. Intermetallics: Why is it so difficult to introduce them in gas turbine engines? Intermetallics 2006, 14, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C. Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2001, 46, 1–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, S.E.; Janghorban, K.; Izadi, S. Order-sintering of mechanically alloyed FeAl nanostructures. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 503, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lee, S.W. Erosion-corrosion behaviour of HVOF NiAl-Al2O3 intermetallic-ceramic coating. Wear 2000, 239, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, K.; Wang, J.; Tian, B.; Wang, H.; Yin, Y. Sliding wear behavior of plasma sprayed Fe3Al-Al2O3 graded coatings. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 5681–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, M. The effect of CeO2 on the erosion and abrasive wear of thermal sprayed FeAl intermetallic alloy coatings. Wear 2006, 261, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearley, J.A.; Little, J.A.; Sturgeon, A.J. The erosion behaviour of NiAl intermetallic coatings produced by high velocity oxy-fuel thermal spraying. Wear 1999, 233, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinca, N.; Guilemany, J.M. Thermal spraying of transition metal aluminides: An overview. Intermetallics 2012, 24, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Ma, S.; Zhang, W.; Liu, W. Sliding wear behavior of FeAl and FeAl/WC coatings prepared by high velocity arc spraying. Wear 2004, 257, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.-H.; Liu, P.; Xu, B.S.; Ma, S.-N.; Zhang, W.; Li, S.Z. Tribological properties of thermal spray formed Fe3Al-based coatings at elevated temperature. Chin. J. Nonferr. Met. 2003, 13, 974–978. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Amiriyan, M.; Blais, C.; Savoie, S.; Schulz, R.; Gariépy, M.; Alamdari, H. Tribo-Mechanical Properties of HVOF Deposited Fe3Al Coatings Reinforced with TiB2 Particles for Wear-Resistant Applications. Materials 2016, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinush, G.; Achutha, M.V.; Rakash, K.R. Dry Sliding Wear Behaviour of Nickel Aluminide coated on Zinc Aluminium alloy Metal Matrix Composite for Anti friction Applications. Int. J. Curr. Eng. Technol. 2015, 5, 1836–1840. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, L. Micro-Indentation and Erosion Properties of Thermal Sprayed NiAl Intermetallic-Based Alloy Coatings. Wear 2003, 254, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilemany, J.M.; Cinca, N.; Fernandez, J.; Sampath, S. Erosion, abrasive, and Friction Wear Behavior of Iron Aluminide Coatings Sprayed by HVOF. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2008, 17, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanzade, M.; Barnoush, A.; Christian, M. A review on the Properties of Iron Aluminide Intermetallics. Crystals 2016, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senderowski, C.; Zasada, D.; Durejko, T.; Bojar, Z. Characterization of as-synthesized and mechanically milled Fe–Al powders produced by the self-disintegration method. Powder Technol. 2014, 263, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKamey, C.G.; DeVan, J.H.; Tortorelli, P.F.; Sikka, V.K. A review of recent developments in Fe3Al-based alloys. J. Mater. Res. 1991, 6, 1779–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozańska, M.; Kościelniak, B.; Swadźba, L. Evaluation of Hot Corrosion Resistance of Directionally Solidified Nickel-Based Superalloy. Solid State Phenom. 2015, 227, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilemany, J.M.; Lima, C.R.C.; Cinca, N.; Miguel, J.R. Studies of Fe-40Al coatings obtained by high velocity oxy-fuel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 2072–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinca, N.; Dosta, S.; Guilemany, J.M. Nanoscale characterization of FeAl-HVOF coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senderowski, C.; Bojar, Z.; Wolczynski, W.; Pawlowski, A. Microstructure characterization of D-gun sprayed Fe-Al intermetallic coatings. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1405–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, I.; Shipway, P. Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering Materials, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2017; ISBN 9780081009109. [Google Scholar]
- Pauschitz, A.; Roy, M.; Franek, F. Mechanisms of sliding wear of metals and alloys at elevated temperatures. Tribol. Int. 2008, 41, 584–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Guan, X.; Shibata, K.; Iwasaki, K. Microstructure and mechanical and tribological properties of high carbon Fe3Al and FeAl intermetallic alloys. Mater. Trans. 2002, 43, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassatelli, P.; Bolelli, G.; Lassinantti Gualtieri, M.; Heinonen, E.; Honkanen, M.; Lusvarghi, L.; Manfredini, T.; Rigone, R.; Vippola, M. Properties of HVOF-sprayed Stellite-6 coatings. Surf. Coat. Techol. 2018, 338, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
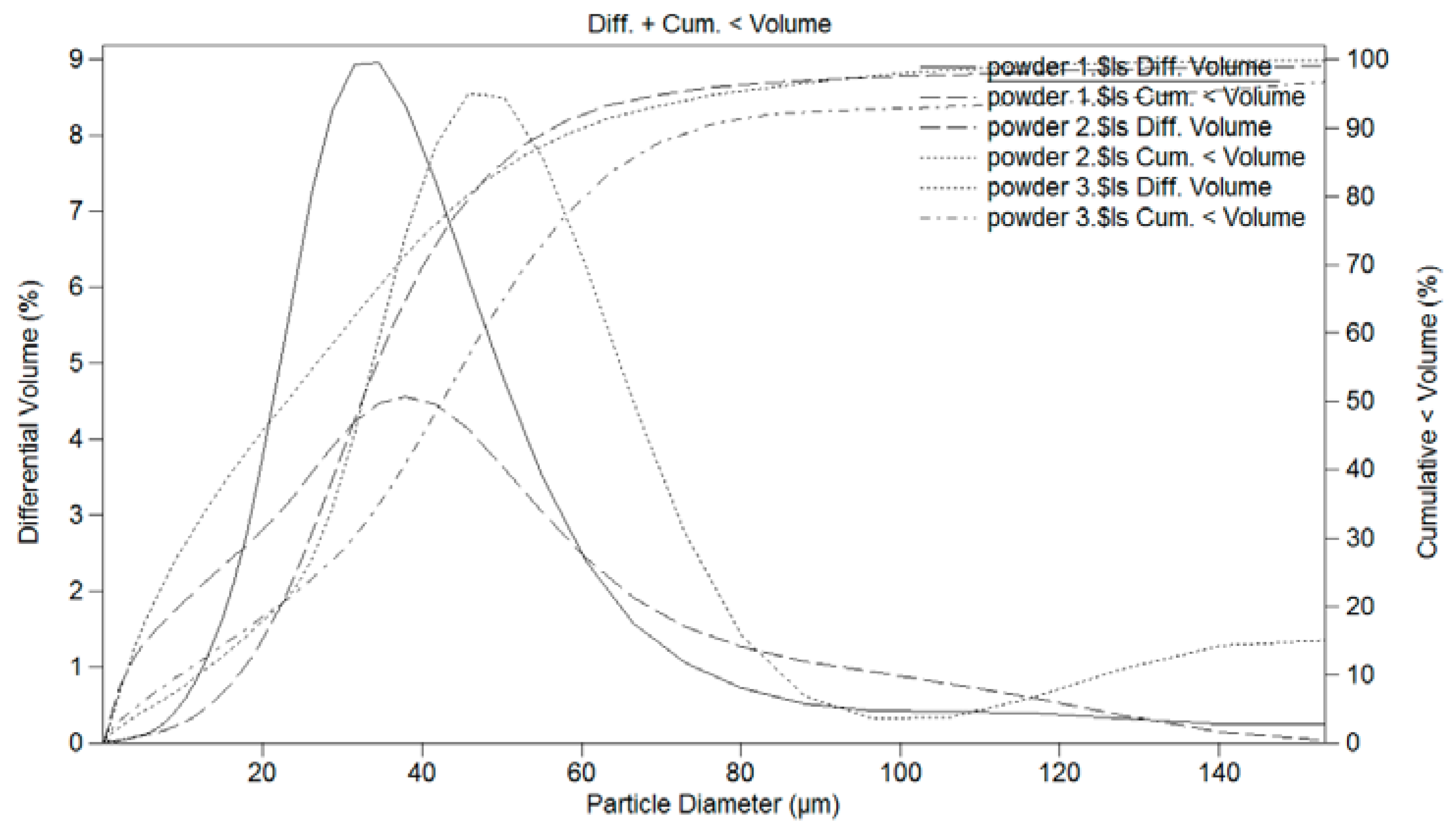
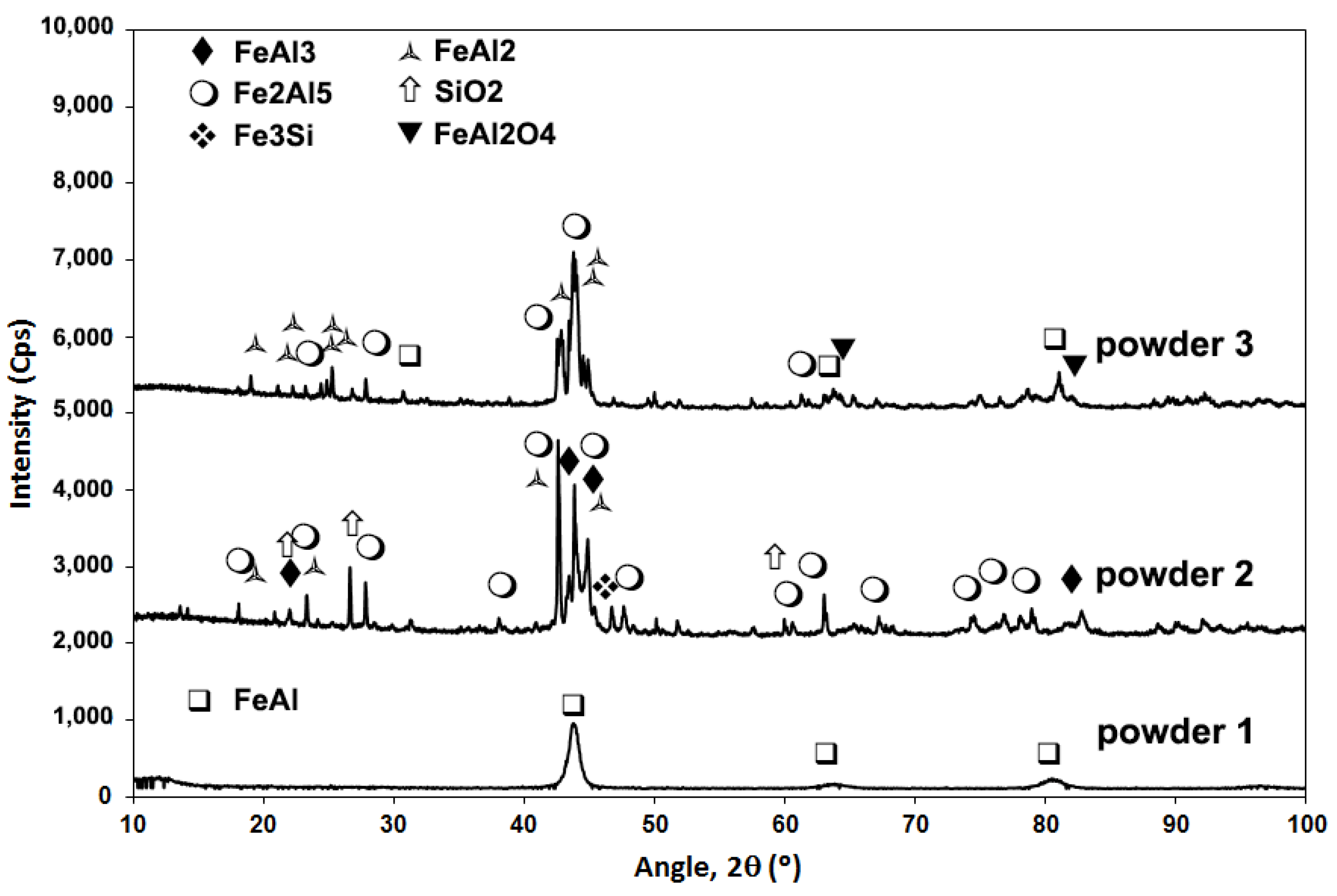





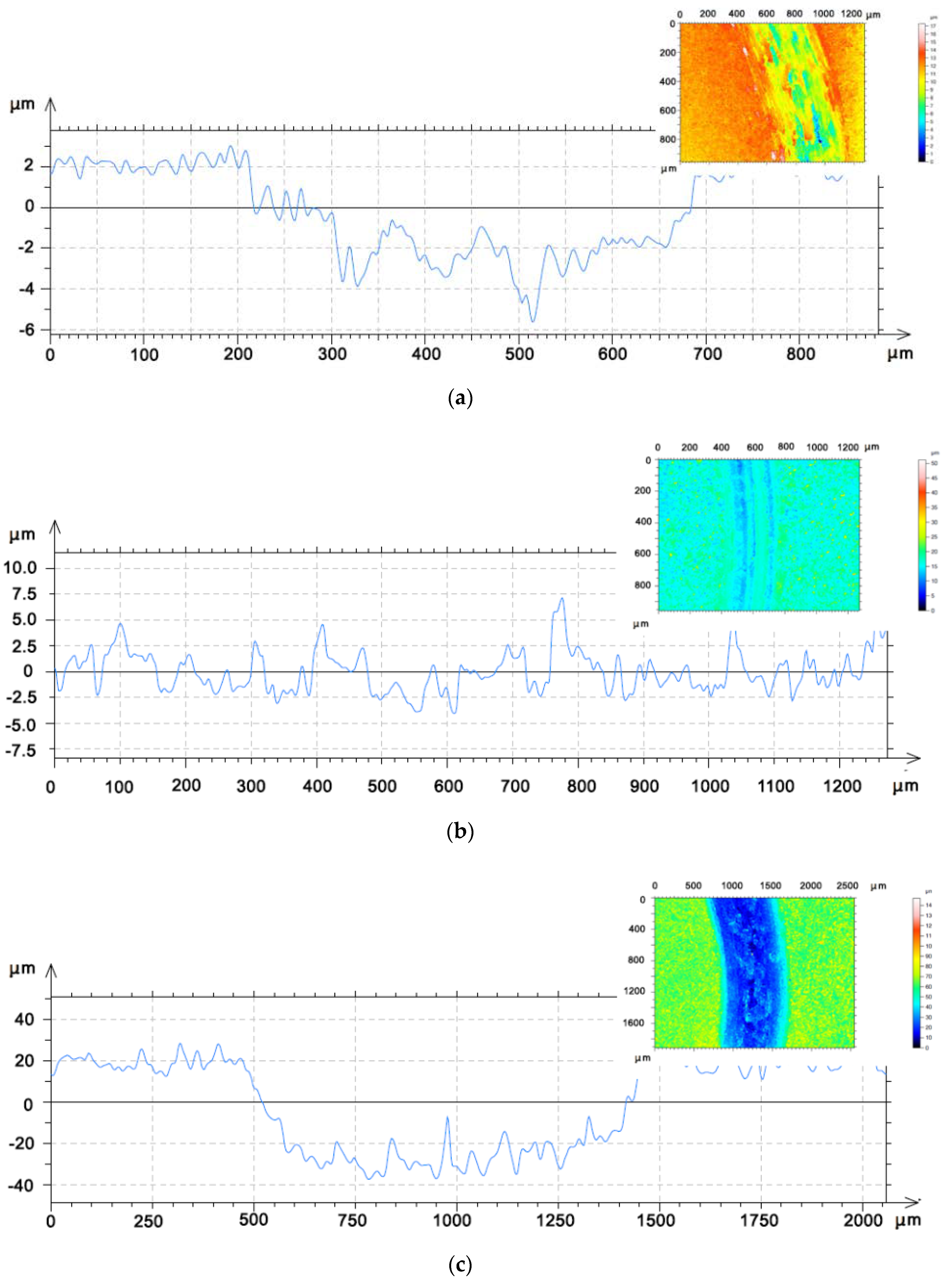

| Powder Nomenclature | Nominal Composition | Particle Size (µm) | Obtaining Procedure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Powder 1 (FeAl Grade 3) | Fe-40Al-0.05Zr (at.%) + 50 ppm B + 1 wt.% Y2O3 | <50 | Atomising + Ball milling |
| Powder 2 | Fe-46Al-6.55Si (at.%) | <40 | self-decomposed |
| Powder 3 | FexAly | −53 + 38 | SHS multi-phases FexAly type powder |
| Coating Nomenclature | HV 0.2 |
|---|---|
| Coating 1 | 505 ± 28 |
| Coating 2 | 502 ± 35 |
| Coating 3 | 423 ± 39 |
| Coating Nomenclature | T (°C) | Friction Coefficient | Wear Track Width (µm) | Wear Track Depth (µm) | Wear Rate (mm3 N−1 m−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coating 1 | 400 | 0.72 ± 0.06 | 625 ± 38 | 7.1 ± 0.1 | 2.11 × 10−5 ± 2.00 × 10−6 |
| Coating 1 | 800 | 0.47 ± 0.05 | 480 ± 15 | – | – |
| Coating 2 | 800 | 0.8 ± 0.13 | 1021 ±30 | 48.5 ± 7.06 | 4.67 × 10−4 ± 5.02 × 10−5 |
| Coating 3 | 800 | 0.43 ± 0.05 | 1399 ± 60 | 49 | 3.87 × 10−4 ± 1.68 × 10−4 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cinca, N.; Cygan, S.; Senderowski, C.; Jaworska, L.; Dosta, S.; G. Cano, I.; Guilemany, J.M. Sliding Wear Behavior of Fe-Al Coatings at High Temperatures. Coatings 2018, 8, 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8080268
Cinca N, Cygan S, Senderowski C, Jaworska L, Dosta S, G. Cano I, Guilemany JM. Sliding Wear Behavior of Fe-Al Coatings at High Temperatures. Coatings. 2018; 8(8):268. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8080268
Chicago/Turabian StyleCinca, Núria, Slawomir Cygan, Cezary Senderowski, Lucyna Jaworska, Sergi Dosta, Irene G. Cano, and Josep M. Guilemany. 2018. "Sliding Wear Behavior of Fe-Al Coatings at High Temperatures" Coatings 8, no. 8: 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8080268
APA StyleCinca, N., Cygan, S., Senderowski, C., Jaworska, L., Dosta, S., G. Cano, I., & Guilemany, J. M. (2018). Sliding Wear Behavior of Fe-Al Coatings at High Temperatures. Coatings, 8(8), 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8080268









