Abstract
A coating rendering superhydrophobic properties to low-density polyethylene (LDPE) films used in packaging applications was herein generated by means of the electrohydrodynamic processing (EHDP) technique. To this end, electrospun ultrathin poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) fibers, followed by electrosprayed nanostructured silica (SiO2) microparticles, were deposited on top of the LDPE film. Various electrospinning and electrospraying times were tested and optimized followed by a thermal post-treatment to provide physical adhesion between the bilayer coating and the LDPE substrate. The morphology, hydrophobicity, permeance to limonene, and thermal stability of the resultant nanostructured coatings were characterized. It was observed that by controlling both the deposition time of the electrospun ultrathin PCL fibers and the electrosprayed SiO2 microparticles, as well as the conditions of the thermal post-treatment, effective superhydrophobic coatings were developed onto the LDPE films. The resultant multilayer presented a hierarchical micro/nanostructured surface with an apparent contact angle of 157° and a sliding angle of 8°. The addition of silica reduced, to some extent, the limonene (aroma) barrier, likely due to the increased surface-to-volume ratio, which allowed permeant sorption to occur but improved the thermal stability of the LDPE/PCL film. As a result, the developed multilayer system of LDPE/PCL/SiO2 has significant potential for use in easy-to-empty packaging applications of high water activity products.
1. Introduction
Superhydrophobic coatings present surfaces with water contact angles larger than 150° and sliding angles of less than 5° [1]. They have gained popularity over the last few decades to improve the current capabilities of material surfaces for applications in water repellency, self-cleaning, packaging, etc. [2]. Specifically, the use of superhydrophobic coatings has been widely employed in food packaging applications to control desiccation in fruits and vegetables and prevent moist migration or even flavor losses. These coatings represent an attempt to mimic the intrinsic hydrophobic behaviors observed in nature, where structural polysaccharides containing water-repellent properties preserve leaves or fruits internally [3]. In addition, the phenomenon of superhydrophobicity has been popularly observed in the leaves from lotus and silver ragwort [4]. To achieve superhydrophobicity on synthetic surfaces, the chemical and physical compositions of the surface at both the micro- and nanoscales must be efficiently designed. Various superhydrophobic surface coatings have been recently prepared by either modifying the chemistry of the surface to render hydrophobic properties [5,6] or by creating nanometer-scale features on micro-roughened surfaces using different techniques, such as plasma treatment, chemical etching, layer-by-layer (LbL) deposition, chemical vapor deposition (CVD), micropatterning by lithography, and, more recently, electrohydrodynamic processing (EHDP) [1,4,7].
Some of the above-mentioned fabrication methods, such as micropatterning by lithography, chemical etching or plasma treatment, are usually complicated since they require a multistep approach and are not versatile in terms of designing certain surface parameters to obtain a desired coating. In other cases, they can be restricted due to the fact that the superhydrophobic property is not suitable or permanent since the coatings do not cover the entire surface or can be easily damaged. Alternatively, the use of EHDP for both electrospinning and electrospraying processes, has proven to be a straightforward methodology for manufacturing micro- and nanoscale structures from a wide variety of polymer materials in a flexible and controlled manner [8]. Such techniques can particularly allow the fabrication of different polymer-based structures and assemblies in the packaging field [9], in which some of them can additionally display a high degree of complexity in terms of surface morphology and topology [1].
In this sense, the electrospinning technique has shown considerable success in manufacturing polymer nanofibers mats for repelling a wide range of liquids [6,7,10,11,12]. Electrospun nanofibers intrinsically provide at least one length scale of roughness for superhydrophobicity due to their ultrathin dimensions [7]. Likewise, electrospraying has also received a great deal of attention due to its ability to produce either polymer or inorganic small particles, down to the submicron size. These micro- and submicron particles are considered more efficient for achieving an uniform surface coverage due to their small size, allowing a thin and uniform coating to be obtained on films, which ultimately results in better barrier properties [13].
Nowadays, novel and multifunctional polymer/inorganic nanostructured coatings with different surface morphologies and wettabilities, ranging from hydrophobic to superhydrophobic, are produced by EHDP [1,14,15,16]. The common procedure begins with the fabrication of a polymer template made of electrospun fibers, which is then covered with hydrophobic particles prepared by electrospraying [1,4,15,16,17]. This methodology has gained interest due to the formation of composite membranes with different surface morphologies, resulting in a wide range of applications for different sectors, such as membrane technology, packaging, automotive, tissue engineering, and energy storage [18].
Although the use of EHDP to develop highly hydrophobic coatings is certainly very promising, the poor adhesion of the electrosprayed particles to the electrospun fibrilar membranes is an inherent problem that restricts the practical application of these coatings. Thus, this issue needs to be solved in order to retain the hydrophobicity property of the whole surface, especially in flexible packaging applications [1]. Furthermore, the deposition of nanoparticles and fiber coatings onto plastic surfaces, as is the case in low-density polyethylene (LDPE) films, has proven to be challenging because of the low surface energy and non-polar nature of the polyolefins [19].
LDPE films are widely employed in the packaging industry, especially in packaging applications where their easy-to-empty property could be of a significant advantage for devices like toothpaste, pouches or bottles. Hence, one of the most significant challenges for the production of LDPE films is generating a flexible material that is capable of obtaining complete coverage of the target area whilst keeping high barrier properties to prevent water migration through it [3,13]. Although superhydrophobic LDPE surfaces have been prepared from polymer synthesis [5] and by surface treatment with corona discharge and tetrafluoromethane (CF4) plasma [5,19,20], these treatments have only shown a very superficial and short-term effect. In addition, they are expensive, technically complex and are often limited by the nature and geometry of the substrate.
Herein, for the first time, a methodology to fabricate mechanically-resistant and thermally-stable superhydrophobic nanostructured bilayer coatings prepared by EHDP to be applied on LDPE or other packaging films is reported. To accomplish this, a commercial LDPE film was initially coated by an electrospun mat of ultrathin poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) fibers. Then, hydrophobic SiO2 particles were electrosprayed on the PCL mat to develop a hierarchical micro/nanostructure surface. Thereafter, an annealing process, that is, a thermal post-treatment below the polymer’s melting point (Tm), was applied to increase the potential usability of the developed composite by physical binding the silica particles to the polymer fibrous mesh and substrate and, thus, allowing physical interlayer adhesion.
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
Corona-treated LDPE films with thicknesses of 150 µm were kindly provided by Lajovic Tuba Embalaža, d.o.o. (Ljubljana, Slovenia). PCL, with a number average molecular weight (MN) of 80,000 g/mol, and 1-butanol (anhydrous, 99.8% purity) were both purchased from Merck KGaA (Darmstadt, Germany). Chloroform (purity > 99.5%) was purchased from Panreac Quimica S.A. (Barcelona, Spain). Hydrophobic pyrogenic SiO2 nanostructured microparticles (HDK H18) with an average particle size of ca. 17 µm and a Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area of 170–230 m2/g were obtained from Wacker Chemie Company (Munich, Germany). The particle size and size distribution of the purchased SiO2 particles were analyzed by laser diffraction with the equipment Malvern Mastersizer MS2000 (Malvern Panalytical, Malvern, UK) (see Figure 1). All materials were used as received without further purification.
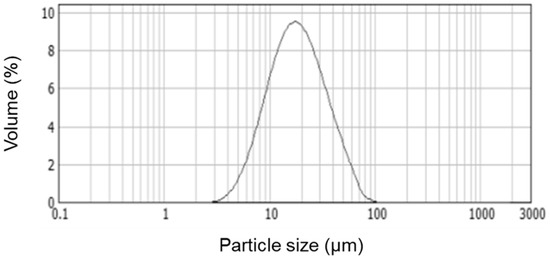
Figure 1.
Particle size distribution of the silica (SiO2) microparticles, as received.
2.2. Fabrication of the Nanostructured Coating
2.2.1. Electrospinning of PCL Fibers onto LDPE Films
In the first stage, a layer of electrospun PCL fibers was deposited onto the corona-treated LDPE films. To this end, a PCL solution was prepared by dissolving 10 wt % of the polymer in a solvent mixture containing 1-butanol and chloroform at 5:1 (v/v) ratio whilst magnetically stirring at room temperature until complete dissolution was achieved.
The resultant PCL solution was then transferred to a 5-mL plastic syringe connected through a PTFE tube to a stainless steel needle (0.603 mm nominal ID—20 G with a blunt tip) and electrospun using a pilot-plant Fluidnatek™ LE-500 apparatus (Bioinicia S.L., Valencia, Spain) with relative humidity (RH) and temperature control. This was operated in lab mode with only one emitter in scanning mode by setting a voltage of 10 kV, a flow-rate of 2 mL/h, and a tip-to-collector distance of 10 cm. During this process, the LDPE film was attached to the roll-to-roll collector so that the fibers were coated directly onto a small rectangular portion of the corona-treated top side of the film. The experiments were performed at 25 °C and 30% RH.
2.2.2. Electrospraying of SiO2 Particles onto LDPE/PCL Films
Secondly, the SiO2 microparticles were electrosprayed on the previously prepared LDPE/PCL films. The electrospraying solution was prepared by dispersing the SiO2 microparticles at 1 wt % in 1-butanol at room temperature whilst magnetically stirring for two hours. Thereafter, the solution was ultrasonicated for 5 min in an Ultraturrax T25 basic from IKA-Werke GmbH & Co. KG (Staufen, Germany) to achieve a stable and homogeneous SiO2 dispersion.
The prepared SiO2 dispersion was thereafter electrosprayed on the bilayer LDPE/PCL film, on the side of the already deposited electrospun fibers. To this end, the same Fluidnatek™ LE-500 equipment described above was used by setting a voltage of 7.6 kV, a flow-rate of 1.1 mL/h, and a tip-to-collector distance of 15 cm. The rest of the conditions were the same as those used for the PCL layer.
2.2.3. Thermal Post-Treatment
The multilayer LDPE/PCL/SiO2 films were annealed under the optimal conditions of 55 °C for 1 min (see Section 3.1) by approaching the top plate to the bottom plate without applying pressure using a hydraulic hot-press (model-4122 from Carver, Inc., Wabash, IN, USA). Samples were placed between Teflon sheets in order to protect the materials from direct contact with the hot plates. Figure 2 illustrates the step-by-step methodology followed to prepare the nanostructured multilayer LDPE/PCL/SiO2 film. Delamination between the coating and the substrate occurred before the annealing process was carried out; however, this was not the case after annealing, where the coated LDPE films could not be delaminated by hand. The annealing process below the melting point has been proven before to promote interfiber coalescence and hence, physical adhesion/lamination, even between materials that are not chemically compatible [21].
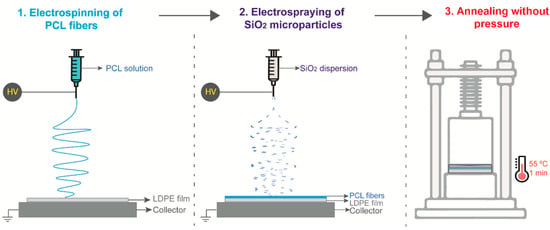
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of (1) deposition of the electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) fibers on the low-density polyethylene (LDPE) film, (2) deposition of the electrosprayed silica (SiO2) microparticles on the LDPE/PCL film, and (3) thermal annealing of the LDPE/PCL/SiO2 film with a hot press without applying pressure.
2.3. Film Characterization
2.3.1. Optical and Scanning Electron Microscopy
The morphologies of the electrospun fibers and resultant films were determined via light microscopy (Eclipse 90i, Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) using a 40× objective as well as a field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM, Hitachi S-4800 from Hitachi High Technologies Corp., Tokyo, Japan). Before FESEM observation, the film samples were cryofractured using nitrogen liquid and subsequently sputtered with a gold-palladium layer for 3 min under vacuum prior to analysis. Samples were observed using an electron beam acceleration voltage of 10 kV. Microanalysis, performed by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS, Hitachi High Technologies Corp., Japan), was used to verify the presence and composition of the inorganic particles. Fiber and particle diameters were determined and averaged using Image J 1.50i software for analysis.
2.3.2. Water Contact Angle Measurements
The wettability of the film samples was evaluated by the measurement of the apparent water contact angle (WCA) using a manual optical tensiometer in a Video-Based Contact Angle Meter, Theta Lite TL 101 model, from Biolin Scientific (Espoo, Finland). Data were obtained by analyzing the shape of a distilled water drop of 5 µL placed over the sample surface, taken after 5 s of droplet–surface contact. Measurements were carried out under room conditions. Image analyses were taken by means of the OneAttension software v 3.1 (Biolin Scientific) and the WCA value reported for each sample was the average of five measurements at different regions of each sample. The sliding angle was determined on a 5-µL water droplet deposited over the surface recorded with a video while being tilted and analyzed with the online software Ergonomics Ruler of the Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV), Valencia, Spain (https://www.ergonautas.upv.es/herramientas/ruler/ruler.php).
2.3.3. Permeability Test
The thicknesses of all films were measured using a digital micrometer Alfa Mirage Absolute series S00014, from Mitutoyo Corporation (Kawasaki, Japan), having ±0.001 mm accuracy. Measurements were performed at five random positions and values were averaged.
The d-Limonene permeance of the film samples was determined using the gravimetric method (ASTM E96-95 [22]). Briefly, 5 mL of d-limonene was placed inside a Payne permeability cup with a diameter of 3.5 cm from Elcometer Sprl (Hermalle-sous-Argenteau, Belgium). The film was introduced in the cups being exposed to the d-limonene vapor on the coated side and secured with silicon rings under environmental conditions of 25 °C and 40% RH. The cups were weighted periodically using an analytical balance (±0.0001 g). Identical cups with aluminum foils were used as control samples to estimate the vapor loss through the sealing. The d-Limonene permeation rate was determined from the steady-state permeation slope obtained from a regression analysis of weight loss data per unit area vs. time, in which the weight loss was calculated as the total cell loss minus the loss through the sealing. The d-Limonene permeance was obtained by correcting the d-Limonene permeation rate for the permeant partial pressure. Three replicates per film sample were determined and averaged.
2.3.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis
The thermal stability was analyzed by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) in a TGA model Q-500 from TA instruments (New Castle, DE, USA). Film samples with a weight between 12–16 mg, were heated from 25 to 900 °C, at a heating rate of 10 °C/min under a nitrogen flow rate of 60 mL/min.
2.3.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
Thermal analyses of the electrospun PCL fiber mat was carried out on a DSC 7 analyzer from PerkinElmer, Inc. (Waltham, MA, USA). The thermal program was applied from −20 to 100 °C in a nitrogen atmosphere using a refrigerating cooling accessory (Intracooler 2, PerkinElmer, Inc.). The scanning rate was 10 °C/min in order to minimize the influence of this parameter on the thermal properties. An empty aluminum cup was used as the reference. Calibration was performed using an indium sample. The endothermic runs were carried out in at least triplicate. From the first heating ramp, the melting point of the PCL fiber mats was measured to be at 58.7 °C, in accordance with previous work [23].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of the Thermal Post-Treatment on the PCL Coating
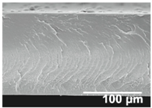
In order to promote the desired hydrophobicity, a layer of electrospun PCL fibers was successfully deposited onto the LDPE films. Figure 3 highlights the morphology of the PCL fibers, as determined by optical microscopy (Figure 3A), as well as by FESEM (Figure 3B). The microscopy results point to well-formed, bead-free, ultrathin fibers with an average fiber diameter of ca. 3 µm.
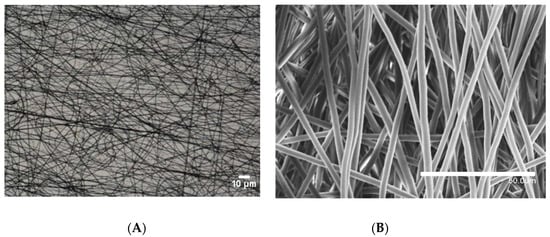
Figure 3.
(A) Optical microscopy image of the electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) fibers taken at 40×. (B) Field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) image of the PCL fibers taken at 1000×.
Initially, a thermal treatment optimization step was performed on the PCL electrospun fibers coated with LDPE to render adhesion to the substrate and maximize the contact angle. Table 1 indicates that, interestingly, the electrospun fibers were able to promote a higher apparent contact angle than LDPE. However, after the thermal treatment, this hydrophobic enhancement was reduced. Thermal treatment promotes inter-material adhesion in the ultrathin fibers; however, the inter-fiber roughness may diminish, hence decreasing the apparent water contact angle of the structure. Thus, the microfiber structure was lost due to fibers’ coalescence or even melting, especially when the thermal treatment was applied at higher temperatures than the PCL melting point of the fibers and for longer times. This feature prevents the formation of superhydrophobic surfaces by just coating with electrospun PCL fibers. As a result, additional topographical features were created by adding electrosprayed particles on top of the PCL fibers. In any case, the performed experiments served to select the optimal thermal treatment of 55° for 1 min as the annealing step, in order to retain the highest apparent contact angle structure that guaranties adhesion to the LDPE layer.

Table 1.
Apparent water contact angles obtained for the low-density polyethylene (LDPE) film and the electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) fibers deposited for 2 h onto the LDPE films that underwent different thermal post-treatments. The values are reported as means ± standard deviations.
3.2. Deposition of Electrosprayed SiO2
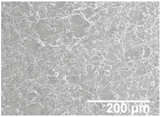
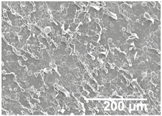
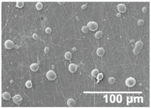
In an attempt to achieve superhydrophobic properties on the LDPE/PCL composite, SiO2 microparticles were electrosprayed onto the LDPE/PCL structure. Once electrosprayed, the morphology of the dried SiO2 particles was characterized by FESEM in Figure 4A. The low concentration used for electrospraying (1 wt %) led to a highly dispersed and distributed coating of the silica, as seen in Figure 4A, obtaining surface aggregates made of nanoparticles with an average diameter of approximately 28 nm (Figure 4B).
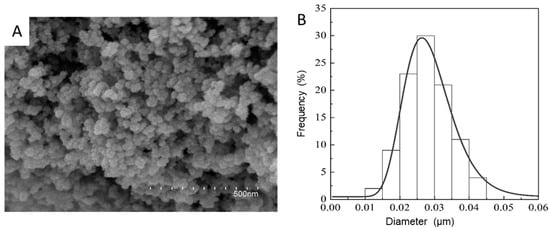
Figure 4.
(A) Field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) image of nanostructured silica (SiO2) microparticles after electrospraying. (B) Histogram showing the particle size distributions of the SiO2 nanoparticles in the aggregates.
3.3. Morphology and Effect of SiO2 Electrospray Time onto LDPE/PCL Films
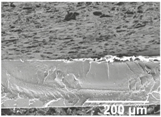
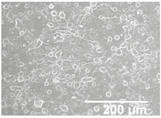
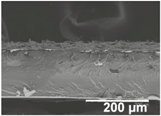
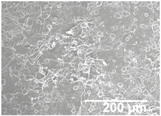
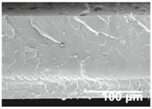
The electrosprayed SiO2 microparticles were deposited at different time intervals (10–60 min) onto the LDPE/PCL films with a PCL deposition time of 2 h. In relation to the top view of the electrosprayed SiO2 layers, it can be observed that the SiO2 microparticles were efficiently distributed onto the surface of the electrospun PCL layer. In Table 2, one can observe that particle agglomerates achieved a mean size of ca. 12.9 μm. This morphology is believed to lead to rough surfaces, especially at the highest deposition time of 1 h [18].

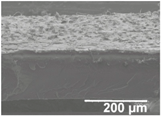
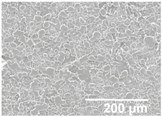
Table 2.
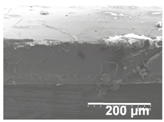
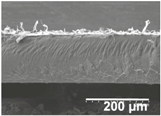
Field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) micrographs of the cryofractured cross-sections and top views of the nanostructured multilayer films of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) coated with electrospun ultrathin poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) fibers and electrosprayed silica (SiO2) microparticles. The PCL deposition time was kept constant at 2 h. The SiO2 nanostructured microparticles were deposited at different time intervals, namely 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, and 60 min, and later, subjected to annealing.
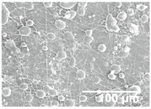
The presence and distribution of the SiO2 microparticles over the electrospun PCL mat was further analyzed by EDS. The comparison of Figure 5A,B further revealed that the SiO2 microparticles were arranged in the form of clusters, randomly distributed on top of the electrospun PCL fiber layer. The here-observed hierarchical micro/nanostructured surface morphology indicates that the coating made of ultrathin PCL fibers and SiO2 microparticles did not only lead to the formation of an organic/inorganic hybrid material but also contributed to the enhancement of the nanostructural features on the LDPE film. This hierarchical topography of the coating, which arises from the micron size of the fibers and nanometric gaps among the fibers as well as across the SiO2 microparticles is expected to increase the solid–liquid interfacial area and, therefore, the apparent surface hydrophobicity, giving rise to a potential superhydrophobic behavior [1,4]. Figure 5C presents the EDS spectrum, which demonstrates the presence of carbon (C), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and silicon (Si), characteristic elements of the electrospun fibers and the electrosprayed particles. In addition, the peak intensities were proportional to the weight content of each element on the sample surface [24]. Furthermore, the appearance of the Si peak confirmed the presence of the SiO2 microparticles on the electrospun PCL membrane surface, as expected.
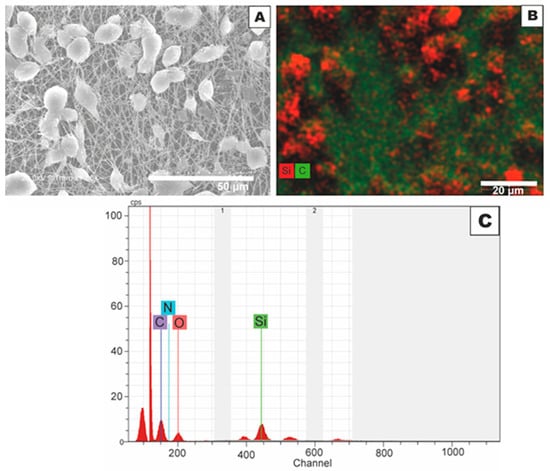
Figure 5.
(A) Field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) micrographs showing a top-view image of the electrospun ultrathin poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) fibers coated with electrosprayed silica (SiO2) microparticles; (B) FESEM micrographs reported in (A) but processed by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS); (C) EDS microanalysis spectrum.
3.4. Surface Wettability of Increasing SiO2 Electrospraying Time over LDPE/PCL
Figure 6 shows the evolution of the apparent water contact angle values at different processing times for the multilayer LDPE/PCL/SiO2 film. The value of the apparent water contact angle for the non-coated LDPE film was 67.3° and this increased to 118.5° when coated with PCL fibers (see previous Table 1). From there, the apparent water contact angle values progressively increased with an increase in the electrospraying time of SiO2 to a value in excess of 150°, supporting a superhydrophobic behavior.
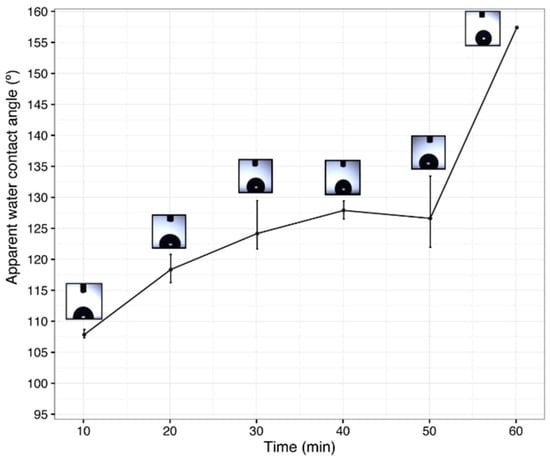
Figure 6.
Apparent water contact angle of the multilayer film based on low-density polyethylene (LDPE), poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) fibers, and silica (SiO2) microparticles for different electrospraying deposition times (10, 20, 30, 40, 50, and 60 min) of SiO2. The profiles of the water droplets are included as insets for each time point. The electrospun PCL deposition time was 2 h, and the thermal treatment was carried out at 55 °C for 1 min.
It can be hypothesized that at deposition times lower than 50 min, the electrosprayed SiO2 microparticles largely filled the voids among the electrospun PCL fibers instead of seating homogeneously over the ultrathin fiber layer. For a silica deposition time of 1 h, the apparent water contact angle was seen to reach a value of 157.4° ± 0.1°. This particular sample exhibited a sliding angle of 8°. This suggests that, for this processing time, the amount of nanostructured SiO2 microparticles exceeded the threshold value required to cover the PCL fiber surface and, thus, generated the necessary surface topology to attain superhydrophobicity. Also, since the inorganic nanostructured microparticles were inserted in a dense layer of PCL fibers, as shown in Table 2, it can be hypothesized that the asperities between the electrospun fibers and the electrosprayed microparticles enhanced the surface roughness of the coated substrate [4]. According to the Cassie–Baxter model, an increase in surface roughness and entrapped air can lead to a reduction in the ratio of the wetting phase to the non-wetting phase [1,25], leading to water repellence. In this regard, further analysis of the contact angle measurements in terms of hysteresis and stability of the Cassie wetting state [26,27,28,29,30] could provide additional valuable information and will be the subject of further work.
3.5. Effect of the Electrospun PCL Deposition Time on Surface Wettability
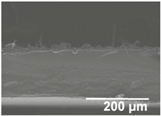
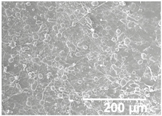
In order to assess the potential effect of the PCL thickness layer on the apparent contact angle for the given optimal SiO2 coating time of 1 h, different electrospinning deposition times of the PCL layer were investigated. Table 3 gathers the FESEM images of the LDPE films coated with the electrospun PCL fibers at different processing times, ranging from 10 to 60 min, and top coated with the optimized electrospraying time of the SiO2 nanostructured microparticles of 60 min, followed by an annealing treatment. From close inspection of the cross-section images, it is estimated that the thickness of the electrospun PCL coatings increased from ca. 3 μm, for the film samples with 10 min of deposition, up to ca. 17 μm for the fibers processed for 60 min. Table 2 shows that the electrospun PCL coated for 2 h presented a thickness of ca. 40 μm, including the SiO2 layer electrosprayed for 60 min.

Table 3.
Field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) micrographs of the cryofractured cross-sections and top views of the nanostructured multilayer films of low-density polyethylene (LDPE), coated with electrospun ultrathin poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) fibers and electrosprayed silica (SiO2) microparticles. The PCL fibers were deposited at different time intervals, namely 10, 30, and 60 min, and later subjected to annealing. The SiO2 deposition time was kept constant at 1 h.
For all processing times, the PCL fibers strongly adhered to the substrate, an effect that is, again, ascribed to the thermal post-treatment. The top-view pictures of Table 3 (in comparison with previous Table 2) suggest that low PCL deposition times after annealing do not seem to create a substrate with enough fibers for the SiO2 microparticles to generate the continuous voided topology required for superhydrophobicity.
Table 4 gathers the apparent contact angle of the films after coating with increasing deposition times of PCL, ranging from 10 to 120 min, and 60 min of electrospraying of SiO2 microparticles. Thus, for an electrospinning deposition time of 10 min, the apparent contact angle value reached a value of 98.8° and thus, was clearly not superhydrophobic. The use of longer electrospun PCL deposition times further increased the apparent water contact angle values, perhaps due to the presence of more fibrous structures, leading to enhanced roughness and a reduction in porosity [31] and showing values above 130°. However, as explained above, only 120 min of PCL deposition generated the required morphology to achieve superhydrophobicity.

Table 4.
Apparent water contact angles of the nanostructured multilayer films of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) coated with electrospun ultrathin poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) fibers and electrosprayed silica (SiO2) microparticles with varied PCL deposition times. *: The SiO2 microparticles were deposited for 1 h for all the samples. **: The thermal treatment was 55 °C for 1 min. Values are reported as means ± standard deviations.
Thus, the dual-size surface structure introduced by both micro/nanostructures is thought to efficiently ensure a large liquid-vapor fraction in the interface. Additionally, PCL has an inherently low surface energy due to its chemical structure, so its hydrophobic fibers may also prevent water droplets from penetrating into the valleys between the ultrathin fibers and microparticles, which could help to further enhance the surface hydrophobicity [5,6]. In terms of previous works that have described hydrophobic surfaces prepared by EHDP with the additional incorporation of SiO2 particles, Zhu et al. [31] reported an apparent water contact angle of 152° for a membrane consisting of SiO2 nanoparticles bonded to an electrospun polyimide (PI) membrane by electrostatic attraction. Similarly, Su et al. [16] successfully created highly porous membranes with superhydrophobic structures via simultaneous electrospraying of SiO2/dimethylacetamide (DMAc) colloids and electrospinning of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF)/DMAc solutions, which exhibited a water contact angle of 163°. Also, previously, Wang et al. [32] fabricated superhydrophobic membranes with apparent water contact angles of up to 161.2° by electrospinning of PVDF incorporating SiO2 nanoparticles modified by epoxy-siloxane without any low surface energy substance. In all of these previous studies, the SiO2 particles introduced a second length scale to the structure due to their fibrous membranes, thereby developing the superhydrophobic behavior. However, none of these works employed additional methods to ensure adhesion between the SiO2 particles, the polymer fibers, and the substrate.
3.6. Barrier Properties
Table 5 gathers the permeance to d-limonene for the LDPE, LDPE/PCL(2 h), and the selected superhydrophobic film: LDPE/PCL(2 h)/SiO2(1 h). The barrier’s performance against d-limonene is, indeed, one of the main parameters of interest in the food/health care packaging field, since it is considering a standard to assess aroma barrier. It is known that LDPE and PCL are low barrier materials to gases and organic vapors but are extremely good barrier materials to water [33]. As one can observe, the three films, namely the monolayer LDPE film, the bilayer LDPE/PCL film, and the multilayer LDPE/PCL/SiO2 film, presented values of d-limonene permeance in the same range. The ca. 150-µm monolayer LDPE film presented a permeance of 1.44 × 10−9 kg·Pa−1·s−1·m−2, which corresponds to a d-limonene permeability of 2.16 × 10−13 kg·m·Pa−1·s−1·m−2. The deposition of the electrospun coating of PCL fibers onto LDPE exhibited a similar film permeance value, albeit with a higher thickness sample, that is, 1.35 × 10−9 kg·Pa−1·s−1·m−2. In this sense, it should be taken into account that PCL is very permeable to limonene vapors, even more so than LDPE, since uptake of this organic compound is very high, that is, 9.8% [23]. However, with the presence of the SiO2 particles, the films showed a slightly increased permeance with a higher sample thickness, reaching a value of 1.48 × 10−9 kg·Pa−1·s−1·m−2. This result could be related to the increased surface-to-volume ratio available for sorption for the permeant in the coated thicker film.

Table 5.
Mean thicknesses and d-limonene permeances of the films based on low-density polyethylene (LDPE), poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) fibers, and silica (SiO2) microparticles. PCL and SiO2 layers were electrospun for 120 min and electrosprayed for 60 min, respectively. Values are reported as means ± standard deviations.
3.7. Thermal Stability
The thermal stabilities of the different prepared LDPE based films were measured by TGA and their curves are gathered in Figure 7. From these results, it can be determined that the monolayer LDPE film presented the highest thermal stability, showing an onset degradation temperature (Tonset), considered as the temperature at which a weight loss of 5% occurs, at 430 °C, and a degradation temperature (Tdeg), that is, the temperature at which the decomposition rate is the highest, at 495 °C. The presence of the electrospun PCL fibers layer significantly reduced the thermal stability of the multilayer, showing values of Tonset and Tdeg at 397.1 and 489.9 °C, respectively. The observed reduction in thermal stability can be related to the inherent low thermal stability of PCL, which is known to start decomposing at approximately 362 °C [34].
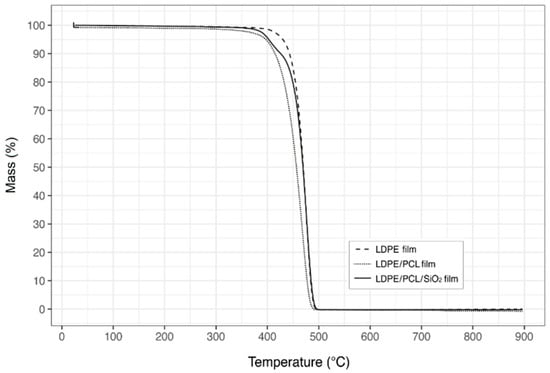
Figure 7.
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) curves of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) (dashed line), LDPE/poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) film (dotted line), and of LDPE/PCL/silica (SiO2) (black line) films. PCL and SiO2 layers were electrospun and electrosprayed for 120 and 60 min, respectively, and then annealed.
Interestingly, the incorporation of the SiO2 microparticles coating improved the thermal stability of the LDPE/PCL film since the degradation temperature occurred at a higher temperature, that is, at 496.6 °C, similar to that of the pure LDPE. This thermal-oxidative stabilization could be due to the capacity of the SiO2 microparticles to play stabilization roles, such as trapping volatile products, issued from the decomposition of the polymers, based on their nanosized porous features [35].
4. Conclusions
A superhydrophobic LDPE film with a composite micro/nanostructured surface consisting of PCL fibers and SiO2 microparticles has been prepared by EHDP, followed by a thermal annealing step to promote binding of the coating layers to themselves and to the LDPE substrate due to the ultrathin PCL fiber coalescence process. This generated a coated LDPE film that could not be delaminated by hand. The surface morphologies of the prepared films were controlled by adjusting the deposition times of the electrospun PCL fibers and electrosprayed nanostructured SiO2 microparticles. The FESEM micrographs and EDS analysis showed that the incorporation of the PCL fibers and SiO2 microparticles successfully changed the morphology of the coated LDPE films. It was particularly observed that a deposition time of 120 min for the electrospun PCL fibers followed by 60 min of electrospraying of the nanostructured SiO2 microparticles generated a superhydrophobic surface with an apparent contact angle of 157.4°. The results achieved here were ascribed to the fact that the electrospun PCL fibers formed a 3D network with trapped air, which prevented water from penetrating and spreading over the mat. In addition, it was suggested that the electrosprayed SiO2 microparticles were wrapped on the dense layer of the electrospun PCL fibers, increasing the tortuosity that contributed to the manifestation of the superhydrophobic behavior. Additionally, the electrospraying of the SiO2 microparticles improved the thermal stability of the LDPE/PCL films but decreased, to a small extent, the aroma barrier of the film. Therefore, the here-applied EHDP-based methodology can be regarded as a potential new process for creating permanent and thermally stable superhydrophobic films that could be easily applied in a wide variety of food packaging applications with, for instance, easy-emptying properties for high water activity goods.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization was devised by J.M.L.; Methodology, Validation and Formal Analysis was carried out by J.L.-B., S.T.-G., M.P.-F., M.Á.-L. and J.M.L. Investigation, Resources, Data Curation, Writing-Original Draft Preparation and Writing-Review & Editing was performed by J.L.-B., S.T.-G., M.P.-F., M.Á.-L. and J.M.L.; Supervision J.M.L.; Project Administration, J.M.L.
Funding
This study was funded by the EU H2020 project OPTINANOPRO (reference number 686116) and the MINECO project AGL2015-63855-C2-1-R.
Acknowledgments
The authors would also like to thank to Colciencias through the National Ph.D. scholarship program and EAFIT University for the financial support of this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wu, J.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Liao, G.; Johnston, P.; Topham, P.D.; Wang, L. Rinse-resistant superhydrophobic block copolymer fabrics by electrospinning, electrospraying and thermally-induced self-assembly. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 422, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darband, G.B.; Aliofkhazraei, M.; Khorsand, S.; Sokhanvar, S.; Kaboli, A. Science and engineering of superhydrophobic surfaces: Review of corrosion resistance, chemical and mechanical stability. Arab. J. Chem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Polo, M.; Voilley, A.; Blond, G.; Colas, B.; Mesnier, M.; Floquet, N. Hydrophobic films and their efficiency against moisture transfer. 2. Influence of the physical state. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1992, 40, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Huang, X.; Xue, H.; Tang, L.; Li, R.K.Y. Facile preparation of hybrid microspheres for super-hydrophobic coating and oil-water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 326, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Wu, D.; Ming, W.; Niemantsverdriet, J.W.; Thüne, P.C. Direct catalytic route to superhydrophobic polyethylene films. Langmuir 2006, 22, 7956–7959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhai, J. A lotus-leaf-like superhydrophobic surface: A porous microsphere/nanofiber composite film prepared by electrohydrodynamics. Angew. Chem. 2004, 116, 4438–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Gupta, M.; Li, Z.; Zhai, L.; Gleason, K.K.; Cohen, R.E.; Rubner, M.F.; Rutledge, G.C. Decorated electrospun fibers exhibiting superhydrophobicity. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Giner, S.; Pérez-Masiá, R.; Lagaron, J.M. A review on electrospun polymer nanostructures as advanced bioactive platforms. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2016, 56, 500–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Giner, S. 5—Electrospun nanofibers for food packaging applications. In Multifunctional and Nanoreinforced Polymers for Food Packaging; Lagarón, J.-M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 108–125. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, S.; Horst, S.; Bognitzki, M. Electrospinning of fluorinated polymers: Formation of superhydrophobic surfaces. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2006, 291, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Jung, R.; Kim, H.-S.; Jin, H.-J. Preparation of superhydrophobic polystyrene membranes by electrospinning. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 313, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasprilla-Botero, J.; Álvarez-Láinez, M.; Lagaron, J.M. The influence of electrospinning parameters and solvent selection on the morphology and diameter of polyimide nanofibers. Mater. Today Commun. 2018, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.K.I.; Schutyser, M.A.I.; Schroën, K.; Boom, R. The potential of electrospraying for hydrophobic film coating on foods. J. Food Eng. 2012, 108, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wu, X.-F. Electrospinning superhydrophobic–superoleophilic fibrous PVDF membranes for high-efficiency water-oil separation. Mater. Lett. 2015, 160, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavielle, N.; Hébraud, A.; Schlatter, G.; Thöny-Meyer, L.; Rossi, R.M.; Popa, A.-M. Simultaneous electrospinning and electrospraying: A straightforward approach for fabricating hierarchically structured composite membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 10090–10097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Li, Y.; Dai, Y.; Gao, F.; Tang, K.; Cao, H. Fabrication of three-dimensional superhydrophobic membranes with high porosity via simultaneous electrospraying and electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2016, 170, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.-M.; Moon, J.H.; Yi, G.-R.; Heo, C.-J.; Yang, S.-M. Fabrication of one-dimensional colloidal assemblies from electrospun nanofibers. Langmuir 2006, 22, 3445–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Zhang, X. Ultrafine polyacrylonitrile/silica composite fibers via electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 2161–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqa, A.J.; Chaudhury, K.; Adhikari, B. Hydrophilic low density polyethylene (LDPE) films for cell adhesion and proliferation. Res. Rev. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 1, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Fresnais, J.; Benyahia, L.; Chapel, J.P.; Poncin-Epaillard, F. Polyethylene ultrahydrophobic surface: Synthesis and original properties. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 26, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echegoyen, Y.; Fabra, M.J.; Castro-Mayorga, J.L.; Cherpinski, A.; Lagaron, J.M. High throughput electro-hydrodynamic processing in food encapsulation and food packaging applications: Viewpoint. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 60, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E96–95 Standard Test Methods for Water Vapor Transmission of Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011.
- Sanchez-Garcia, M.D.; Gimenez, E.; Lagaron, J.M. Morphology and barrier properties of solvent cast composites of thermoplastic biopolymers and purified cellulose fibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccaria, M.; Fabiani, D.; Cannucciari, G.; Gualandi, C.; Focarete, M.L.; Arbizzani, C.; De Giorgio, F.; Mastragostino, M. Effect of silica and tin oxide nanoparticles on properties of nanofibrous electrospun separators. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, A915–A920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko, E. Progress in understanding wetting transitions on rough surfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friberg, S.E. Wetting of real surfaces, by Edward Yu. Bormashenko. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2015, 36, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, K. A guide to the equilibrium contact angles maze. In Contact Angle, Wettability and Adhesion; Mittal, K.L., Ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2009; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Quéré, D.; Lv, C.; Zheng, Q. Monostable superrepellent materials. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 3387–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gennes, P.-G.; Brochard-Wyart, F.; Quere, D. Capillarity and Wetting Phenomena: Drops, Bubbles, Pearls, Waves; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hou, H.; Shi, W.; Qu, F.; Cui, F.; Wang, W. Dual-bioinspired design for constructing membranes with superhydrophobicity for direct contact membrane distillation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3027–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhao, H.; Wang, W. Preparation of superhydrophobic nanocomposite fiber membranes by electrospinning poly(vinylidene fluoride)/silane coupling agent modified SiO2 nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Číhal, P.; Vopicka, O.; Pilnacek, K.; Poustka, J.; Friess, K.; Hajslova, J.; Dobias, J.; Dole, P. Aroma scalping characteristics of polybutylene succinate based films. Polym. Test. 2015, 46, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadj-Hamou, A.S.; Metref, F.; Yahiaoui, F. Thermal stability and decomposition kinetic studies of antimicrobial PCL/nanoclay packaging films. Polym. Bull. 2017, 74, 3833–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolbukh, Y.; Kuzema, P.; Tertykh, V.; Laguta, I. Thermal degradation of polyethylene containing antioxidant and hydrophilic/hydrophobic silica. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2008, 94, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).