Fabrication of Self-healing Superhydrophobic Surfaces from Water-Soluble Polymer Suspensions Free of Inorganic Particles through Polymer Thermal Reconstruction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Colloidal Polymer Spheres
2.3. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Surfaces
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
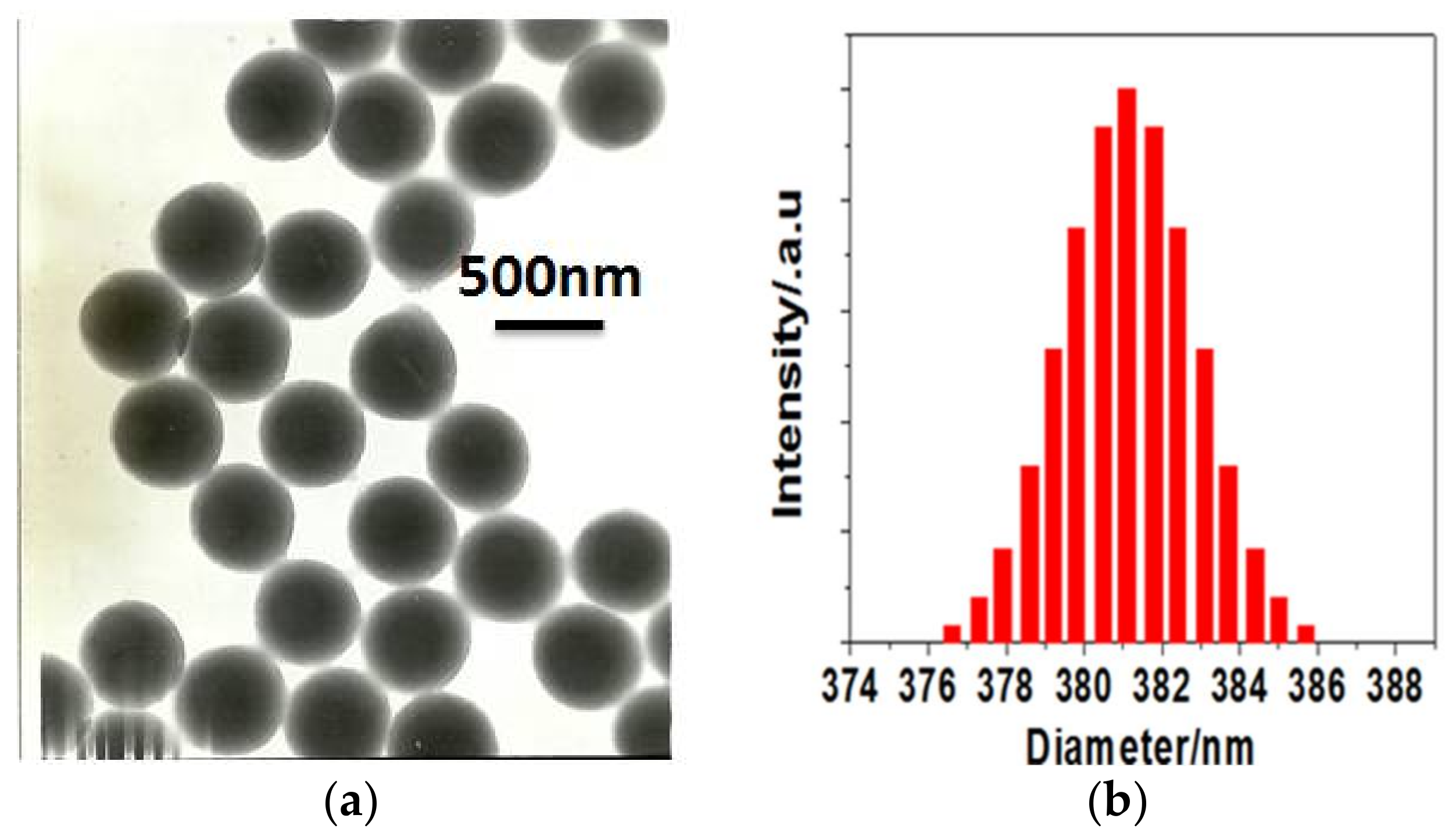
3.1. Synthesis and Morphology of Water-Soluble Amphiphilic Polymer Spheres
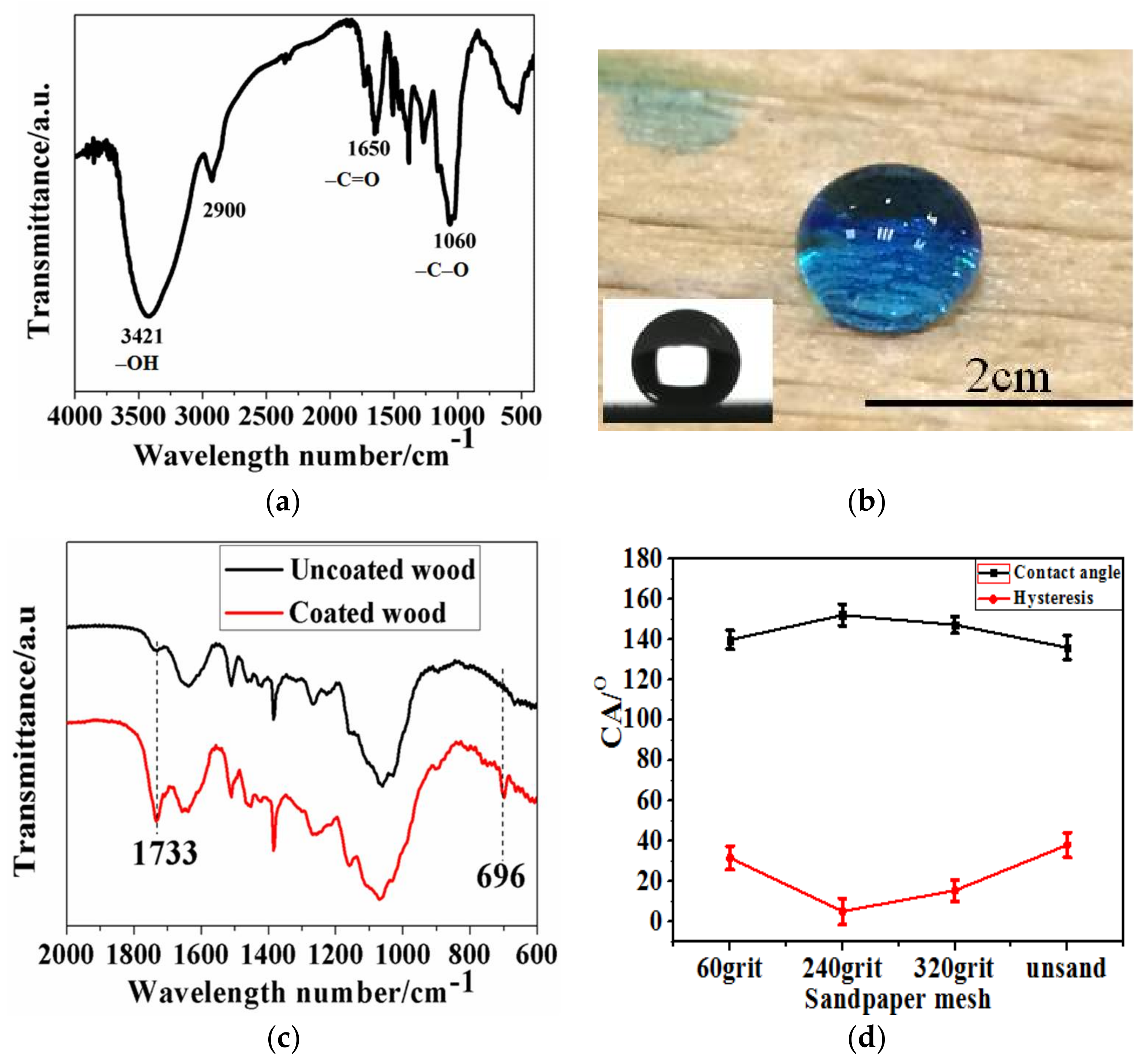
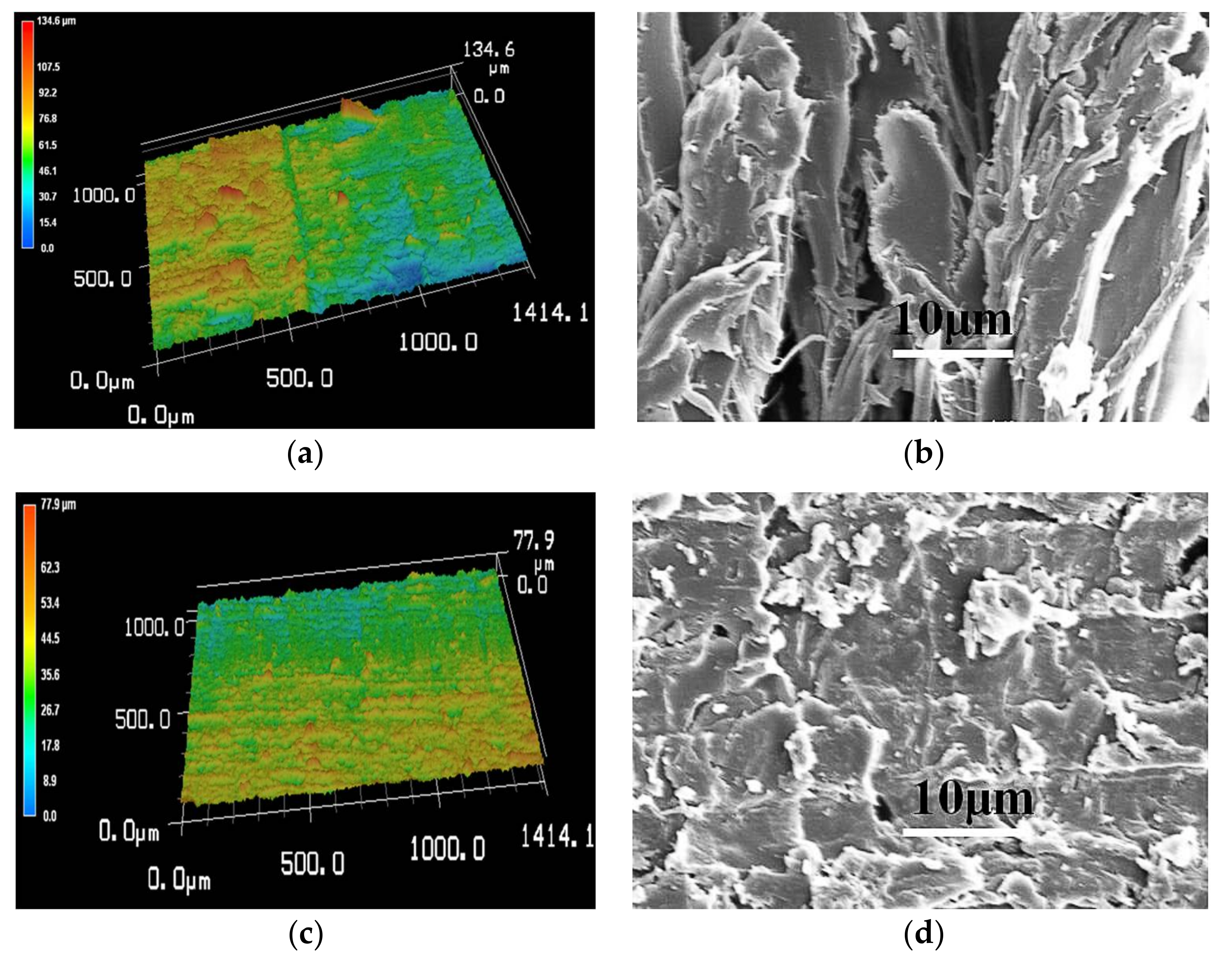
3.2. The fabrication of Superhydrophobic Surfaces through Polymer Thermal Reconstruction and the Effect of Surface Roughness on Wettability
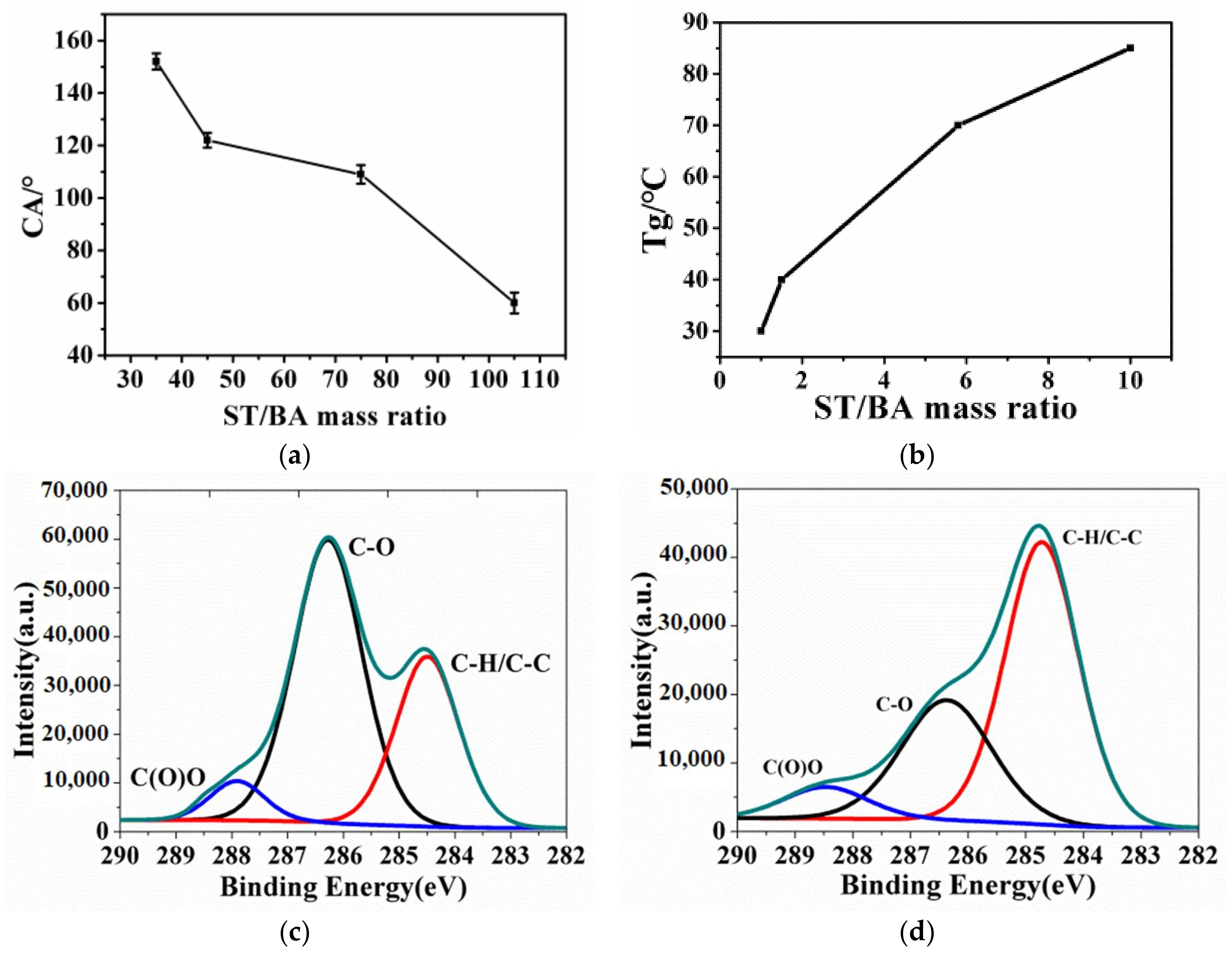
3.3. Effect of ST/BA Mass Ratio on Wettability
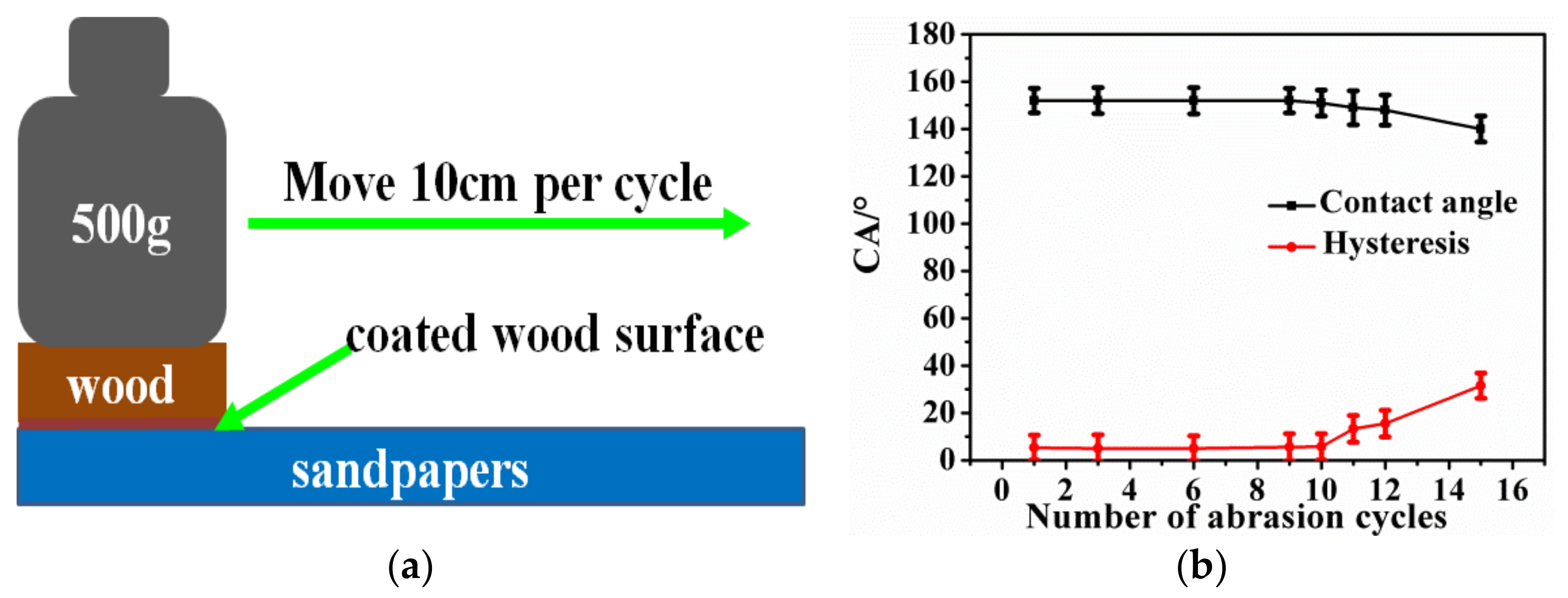
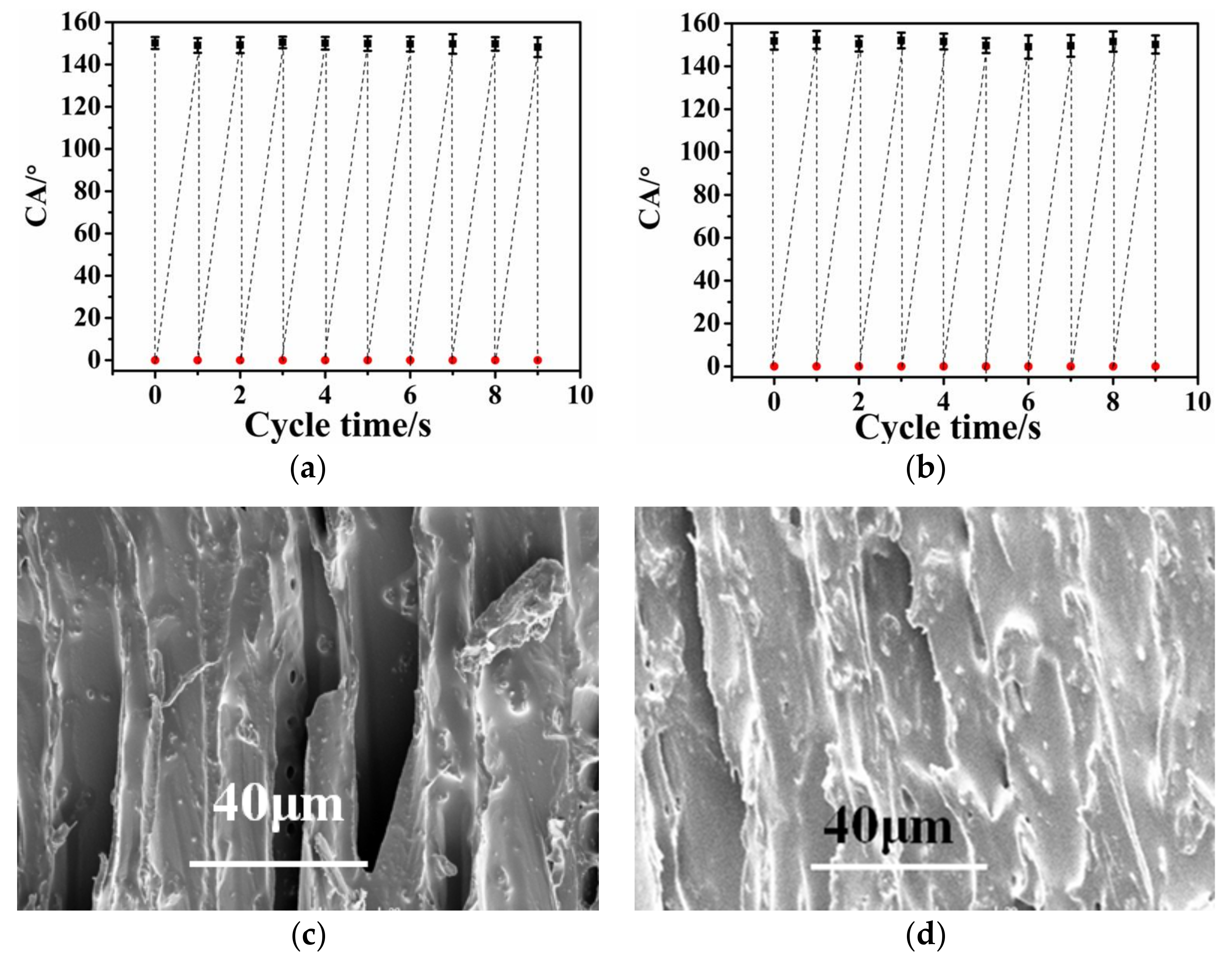
3.4. The Roubustness and Self-Replenishment of Superhydrophobic Surfaces
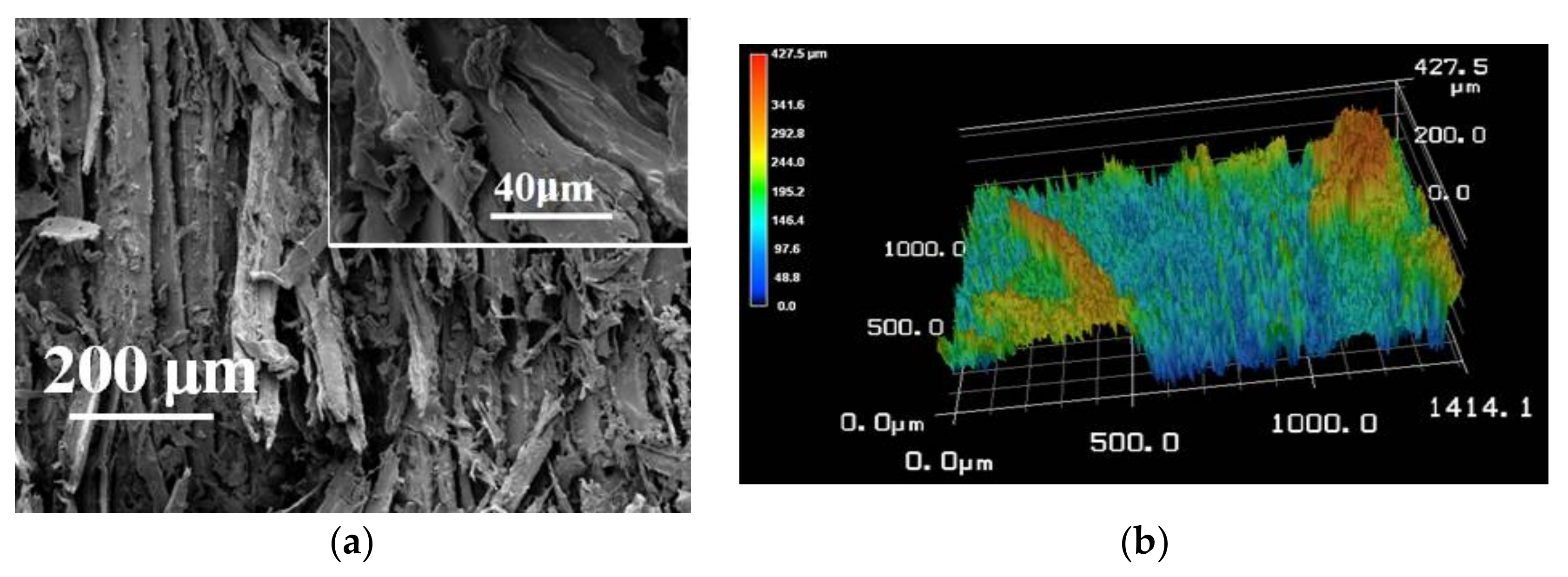
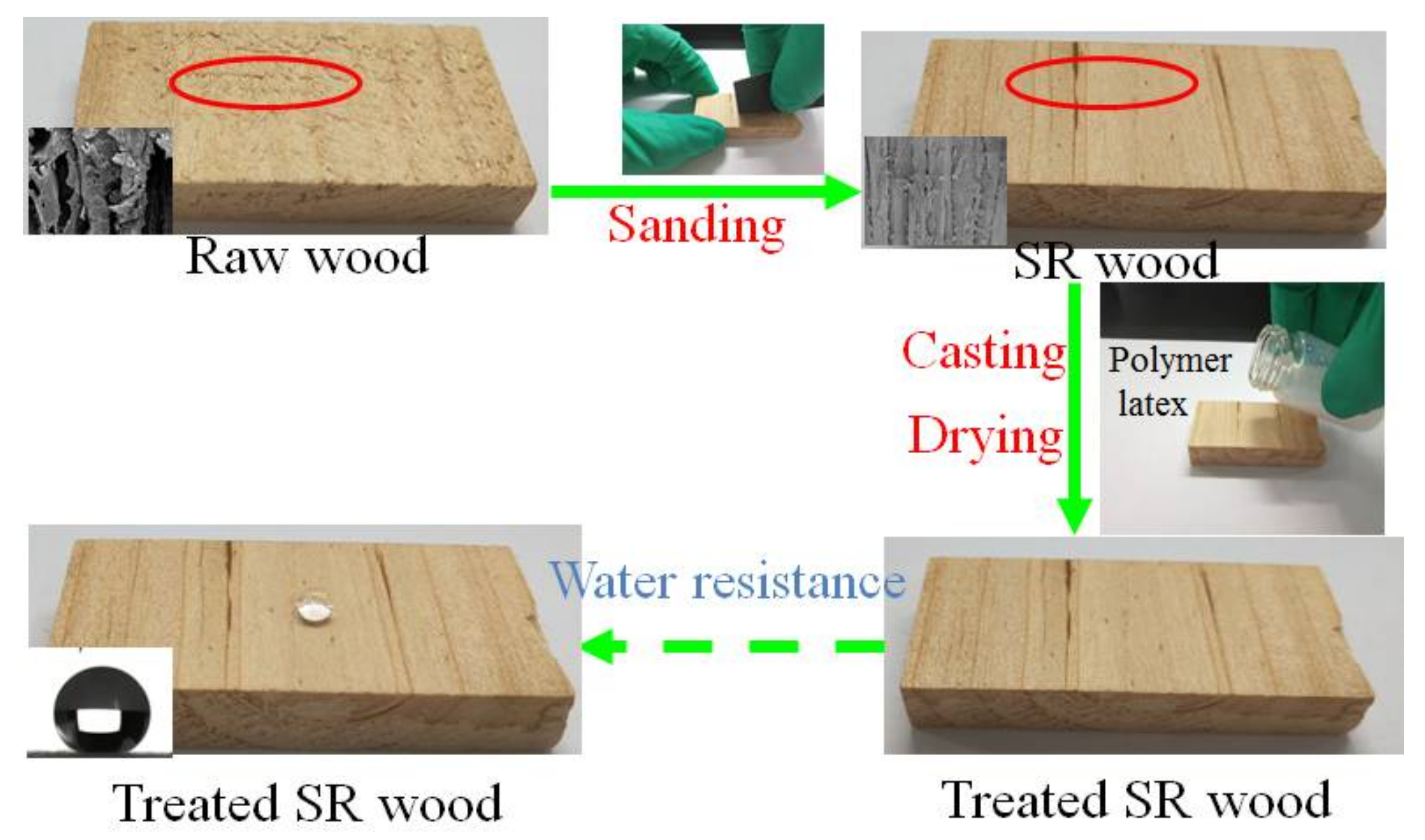
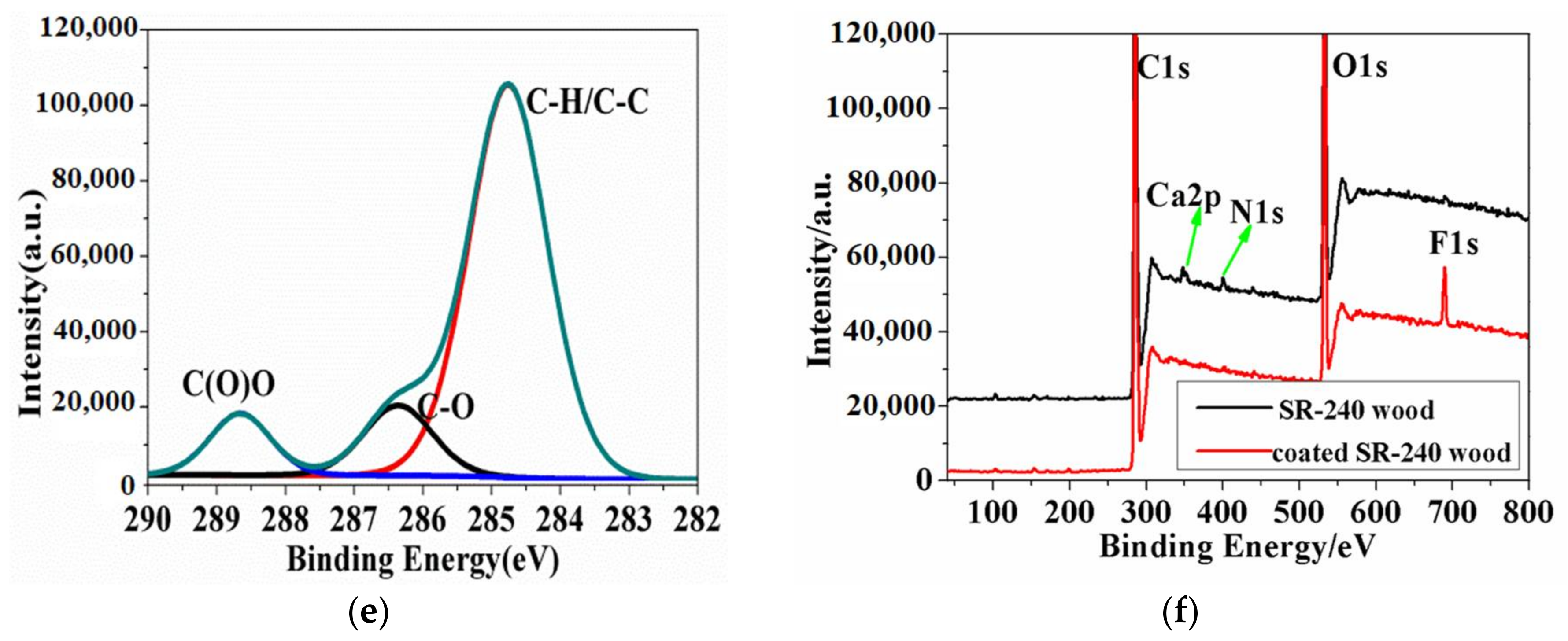
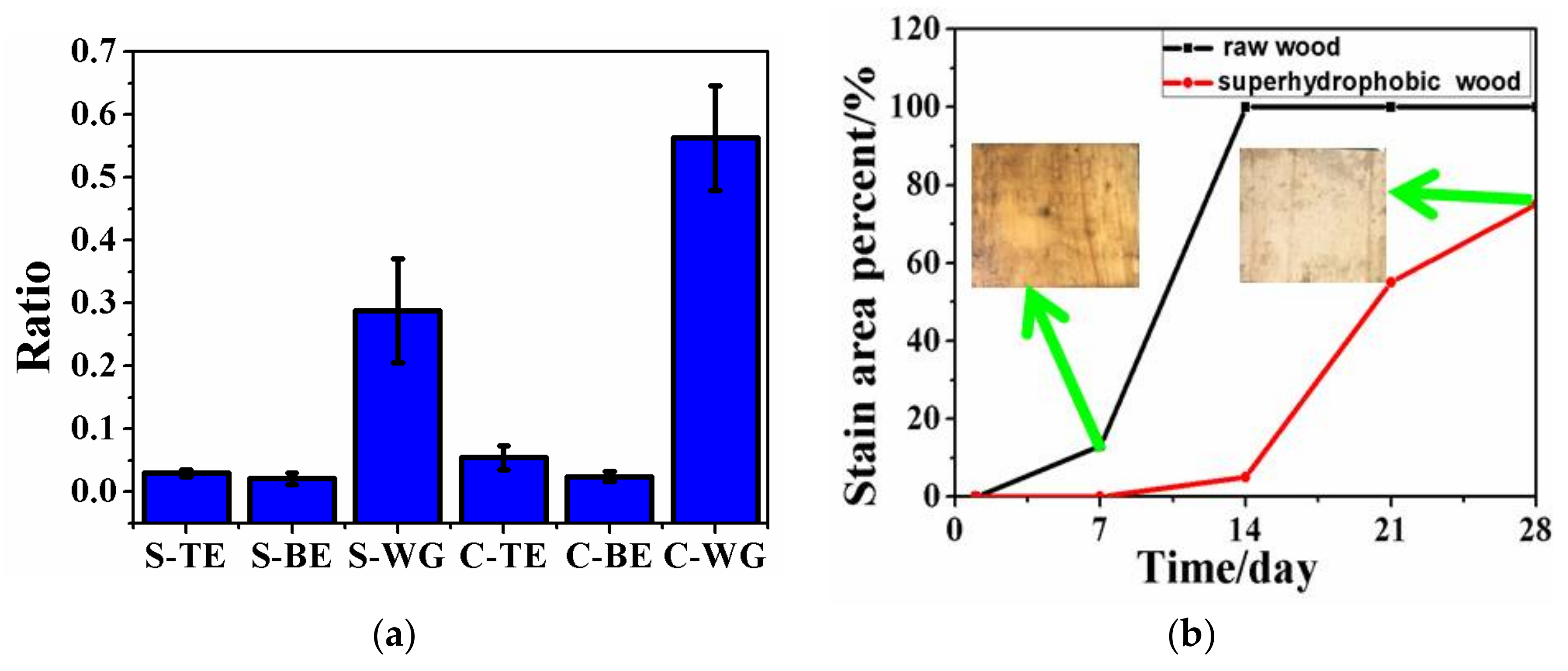
3.5. The Improved Water and Mildew Resistance of Wood with Superhydrophobic Surfaces
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, M.; Ma, B.; Pan, T.; Chen, S.; Sun, J. Silver-nanoparticle-colored cotton fabrics with tunable colors and durable antibacterial and self-healing superhydrophobic properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellinas, K.; Kefallinou, D.; Stamatakis, K.; Gogolides, E.; Tserepi, A. Is there a threshold in the antibacterial action of superhydrophobic surfaces? ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 39781–39789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Hays, M.P.; Hardwidge, P.R.; Kim, J. Surface characteristics influencing bacterial adhesion to polymeric substrates. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14254–14261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Levanen, E. Superhydrophobic surfaces for the reduction of bacterial adhesion. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 12003–12020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Pan, L.; Yang, M.; Peng, L.; Zong, S.; Shi, Y.; Yu, G. Multifunctional superhydrophobic surfaces templated from innately microstructured hydrogel matrix. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 4803–4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Hu, Y.; Grinthal, A.; Khan, M.; Aizenberg, J. Liquid-based gating mechanism with tunable multiphase selectivity and antifouling behaviour. Nature 2015, 519, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Fei, B.; Hu, H.; Lai, C.; Xin, J. Bioinspired, stimuli-responsive, multifunctional superhydrophobic surface with directional wetting, adhesion, and transport of water. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 5047–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, K.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired multifunctional foam with self-cleaning and oil/water separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 2881–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, C.; Ai, K.; Li, X.; Lu, L. A Superhydrophobic sponge with excellent absorbency and flame retardancy. Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 5556–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Sathasivam, S.; Song, J.; Crick, C.R.; Carmalt, C.J.; Parkin, I.P. Robust self-cleaning surfaces that function when exposed to either air or oil. Science 2015, 347, 1132–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildirim, A.; Khudiyev, T.; Daglar, B.; Budunoglu, H.; Okyay, A.K.; Bayindir, M. Superhydrophobic and omnidirectional antireflective surfaces from nanostructured ormosil colloids. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youngblood, J.P.; McCarthy, T.J. Ultrahydrophobic polymer surfaces prepared by simultaneous ablation of polypropylene and sputtering of poly(tetrafluoroethylene) using radio frequency plasma. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 6800–6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellinas, K.; Pujari, S.P.; Dragatogiannis, D.A.; Charitidis, C.A.; Tserepi, A.; Zuilhof, H.; Gogolides, E. Plasma micro-nanotextured, scratch, water and hexadecane resistant, superhydrophobic, and superamphiphobic polymeric surfaces with perfluorinated monolayers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 6510–6524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shon, Y.-S.; Lee, S.; Colorado, R.; Perry, S.S.; Lee, T.R. Spiroalkanedithiol-based sams reveal unique insight into the wettabilities and frictional properties of organic thin films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 7556–7563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyauchi, M.; Kieda, N.; Hishita, S.; Mitsuhashi, T.; Nakajima, A.; Watanabe, T.; Hashimoto, K. Reversible wettability control of TiO2 surface by light irradiation. Surf. Sci. 2002, 511, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutel, B.; Taleb, A.B.; Dessaux, O.; Goudmand, P.; Gengembre, L.; Grimblot, J. Characterization of mixed zinc-oxidized zinc thin films deposited by a cold remote nitrogen plasma. Thin Solid Films 1995, 266, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, I.S.; Davis, A.J.; Loth, E.; Steele, A. Water jet resistant superhydrophobic carbonaceous films by flame synthesis and tribocharging. Mater. Today Commun. 2015, 3, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, I.S.; Brandi, F.; Cingolani, R.; Athanassiou, A. Modification of wetting properties of laser-textured surfaces by depositing triboelectrically charged teflon particles. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.-Z.; Uetsuka, H.; Takahashi, K.; Nakajima, R.; Onishi, H.; Fujishima, A.; Sato, O. Structural color and the lotus effect. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 894–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wen, Y.; Feng, X.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L. Control over the wettability of colloidal crystal films by assembly temperature. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wen, Y.; Hu, J.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L. Fine control of the wettability transition temperature of colloidal-crystal films: From superhydrophilic to superhydrophobic. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latthe, S.; Terashima, C.; Nakata, K.; Sakai, M.; Fujishima, A. Development of sol-gel processed semi-transparent and self-cleaning superhydrophobic coatings. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 5548–5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Z.; He, J.; Xu, L.; Yao, L. Rational design and elaborate construction of surface nano-structures toward highly antireflective superamphiphobic coatings. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 8721–8724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, X.; Hang, J.; Jin, L.; Shang, D.; Shi, L. Large-scale fabrication of robust superhydrophobic coatings with high rigidity and good flexibility. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 3, 500718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellinas, K.; Tserepi, A.; Gogolides, E. Durable superhydrophobic and superamphiphobic polymeric surfaces and their applications: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 250, 132–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verho, T.; Bower, C.; Andrew, P.; Franssila, S.; Ikkala, O.; Ras, R.H. Mechanically durable superhydrophobic surfaces. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayer, I.S.; Krishnan, K.G.; Robison, R.; Loth, E.; Berry, D.H.; Farrell, T.E.; Crouch, J.D. Thermal alternating polymer nanocomposite (TAPNC) coating designed to prevent aerodynamic insect fouling. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Sun, J. Bioinspired self-healing superhydrophobic coatings. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6129–6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xue, Y.; Ding, J.; Feng, L.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Durable, self-healing superhydrophobic and superoleophobic surfaces from fluorinated-decyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane and hydrolyzed fluorinated alkyl silane. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11433–11436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteves, A.C.C.; Luo, Y.; Put, M.W.P.V.D.; Carcouët, C.C.M.; With, G.D. Self-replenishing dual structured superhydrophobic coatings prepared by drop-casting of an all-in-one dispersion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Wu, M.; Sun, J. All spraying processes for the fabrication of robust, self-healing, superhydrophobic coatings. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3344–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Ma, C.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, G. Self-repairing silicone coatings for marine anti-biofouling. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 15855–15861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Mammen, L.; Butt, H.J.; Vollmer, D. Candle soot as a template for a transparent robust superamphiphobic coating. Science 2012, 335, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Zhou, S.; Yang, S.; Wu, L. Fabrication of all-water-based sel-repairing superhydrophobic coatings based on UV-responsive microcapsules. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.H.; Bai, X.; Jia, S.T. Robust, self-healing superhydrophobic fabrics prepared by one-step coating of pdms and octadecylamine. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Urban, M.W. Self-healing polymeric materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7446–7467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.Y.; Rong, M.Z.; Zhang, M.Q. Self-healing polymeric materials based on microencapsulated healing agents: From design to preparation. Prog. Chem. Sci. 2015, 49–50, 175–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M.; Yang, S. Directed water shedding on high-aspect-ratio shape memory polymer micropillar arrays. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Salazar, J.; Vahabi, H.; Joshiimre, A.; Voit, W.E.; Kota, A.K. Metamorphic superomniphobic surfaces. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, U.; Lynn, D.M. Restoration of superhydrophobicity in crushed polymer films by treatment with water: Self-healing and recovery of damaged topographic features aided by an unlikely source. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5104–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Lu, F.; Bao, B.; You, B. Self-assembly of binary particles and application as structural colors. Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 2495–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Lu, F.; Bao, B.; You, B.; Shi, L. Self-assembly of colloidal spheres and application as solvent responding polymer film. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 389, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, B.; Liu, D.; Yang, Y.; Shen, Z.; You, B. Self-assembly of ternary particles for tough colloidal crystals with vivid structure colors. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.; Bai, N.; Xu, L.; Tan, C.; Li, Q. Fabrication of superhydrophobic wood surface with enhanced environmental adaptability through a solution-immersion process. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 277, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Tu, K.; Wang, X.; Liu, J. Fabrication of mechanically durable superhydrophobic wood surfaces using polydimethylsiloxane and silica nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 30647–30653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shi, J.; Liu, C.; Cheng, X.; Wang, C. Fabrication of a superhydrophobic surface on a wood substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 9362–9365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, K.; Wang, X.; Kong, L.; Guan, H. Facile preparation of mechanically durable, self-healing and multifunctional superhydrophobic surfaces on solid wood. Mater. Des. 2018, 140, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surface Roughness Standard (JIS B0601:1994). Available online: https://us.misumi-ec.com/pdf/tech/mech/US2010_fa_p3541_3542.pdf (accessed on 11 March 2018).
- Plötze, M.; Niemz, P. Porosity and pore size distribution of different wood types as determined by mercury intrusion porosimetry. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2011, 69, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperry, P.R.; Snyder, B.S.; O’Dowd, M.L.; Lesko, P.M. Role of water in particle deformation and compaction in latex film formation. Langmuir 1994, 10, 2619–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhs, C. Developing environmentally benign and effective organic wood preservatives by understanding the biocidal and non-biocidal properties of extractives in naturally durable heartwood. Holzforschung 2008, 62, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, T.P.; Nicholas, D.D. Development of environmentally-benign wood preservatives based on the combination of organic biocides with antioxidants and metal chelators. Phytochemistry 2002, 61, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Shen, Z.; Chen, H. Fabrication of Self-healing Superhydrophobic Surfaces from Water-Soluble Polymer Suspensions Free of Inorganic Particles through Polymer Thermal Reconstruction. Coatings 2018, 8, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8040144
Shen Y, Wu Y, Shen Z, Chen H. Fabrication of Self-healing Superhydrophobic Surfaces from Water-Soluble Polymer Suspensions Free of Inorganic Particles through Polymer Thermal Reconstruction. Coatings. 2018; 8(4):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8040144
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Yalun, Yitian Wu, Zhehong Shen, and Hao Chen. 2018. "Fabrication of Self-healing Superhydrophobic Surfaces from Water-Soluble Polymer Suspensions Free of Inorganic Particles through Polymer Thermal Reconstruction" Coatings 8, no. 4: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8040144
APA StyleShen, Y., Wu, Y., Shen, Z., & Chen, H. (2018). Fabrication of Self-healing Superhydrophobic Surfaces from Water-Soluble Polymer Suspensions Free of Inorganic Particles through Polymer Thermal Reconstruction. Coatings, 8(4), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8040144




