Noise Reduction Properties of an Experimental Bituminous Slurry with Crumb Rubber Incorporated by the Dry Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Set up
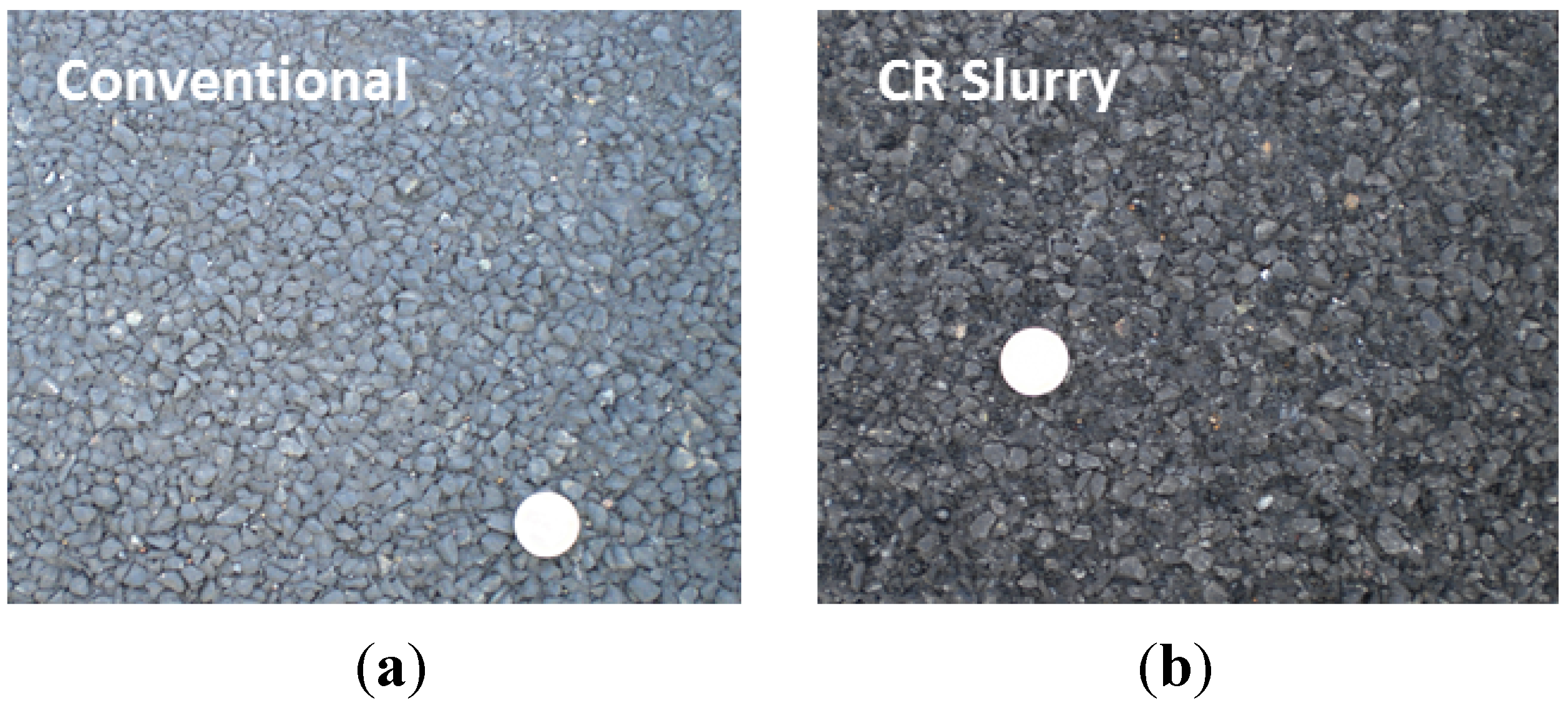
2.1. Test Section and Slurry Surface


2.2. Measurement Equipment
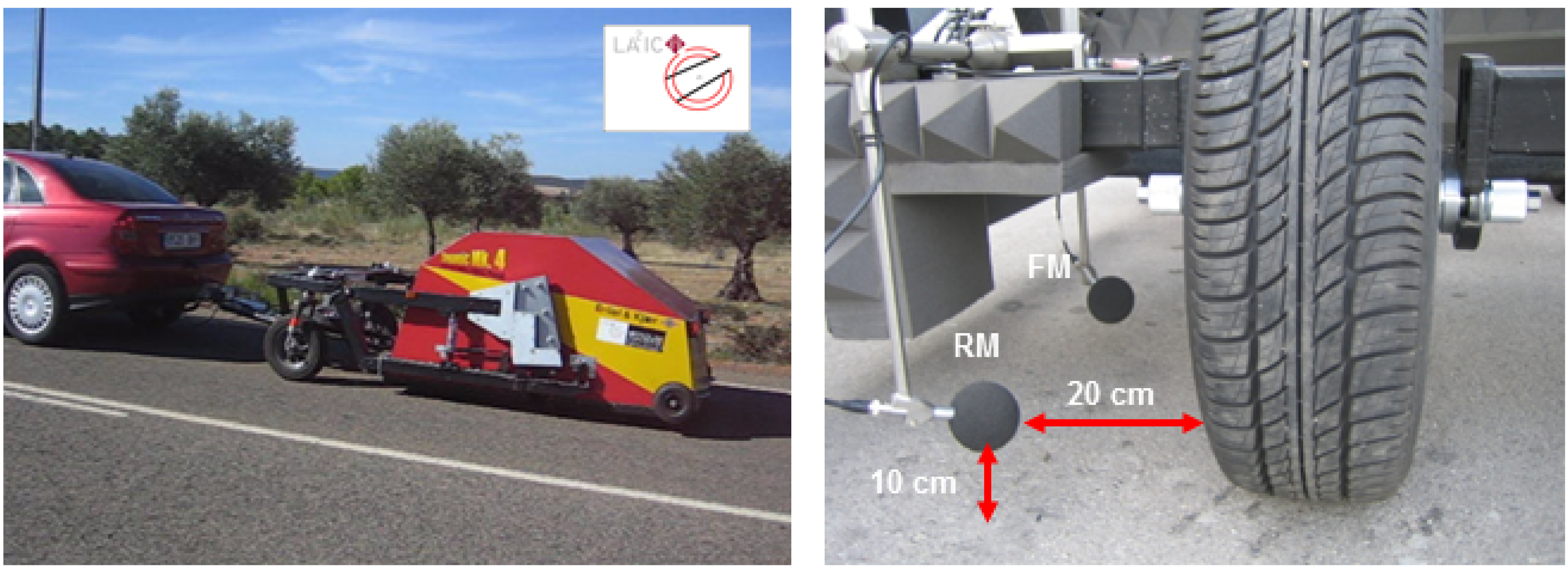
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Texture
| MPD (mm) | Conventional Slurry A | CR Slurry | Conventional Slurry B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | 1.25 | 2.70 | 1.50 |
| After one year | 1.20 | 2.80 | – |
3.2. CPX Sound Levels

| vref 80 km/h | Initial | After One Year | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCPtr dB(A) | σ dB(A) | ∆ dB(A) | LCPtr dB(A) | σ dB(A) | ∆ dB(A) | |
| Conventional slurry A (reference) | 96.6 | 0.6 | 2.0 | 98.3 | 0.8 | 3.1 |
| CR Slurry | 95.2 | 0.8 | 2.6 | 97.3 | 0.8 | 3.0 |
| Conventional slurry B | 98.2 | 0.9 | 3.3 | 99.4 | 0.7 | 3.1 |
3.3. CPX Sound Spectra
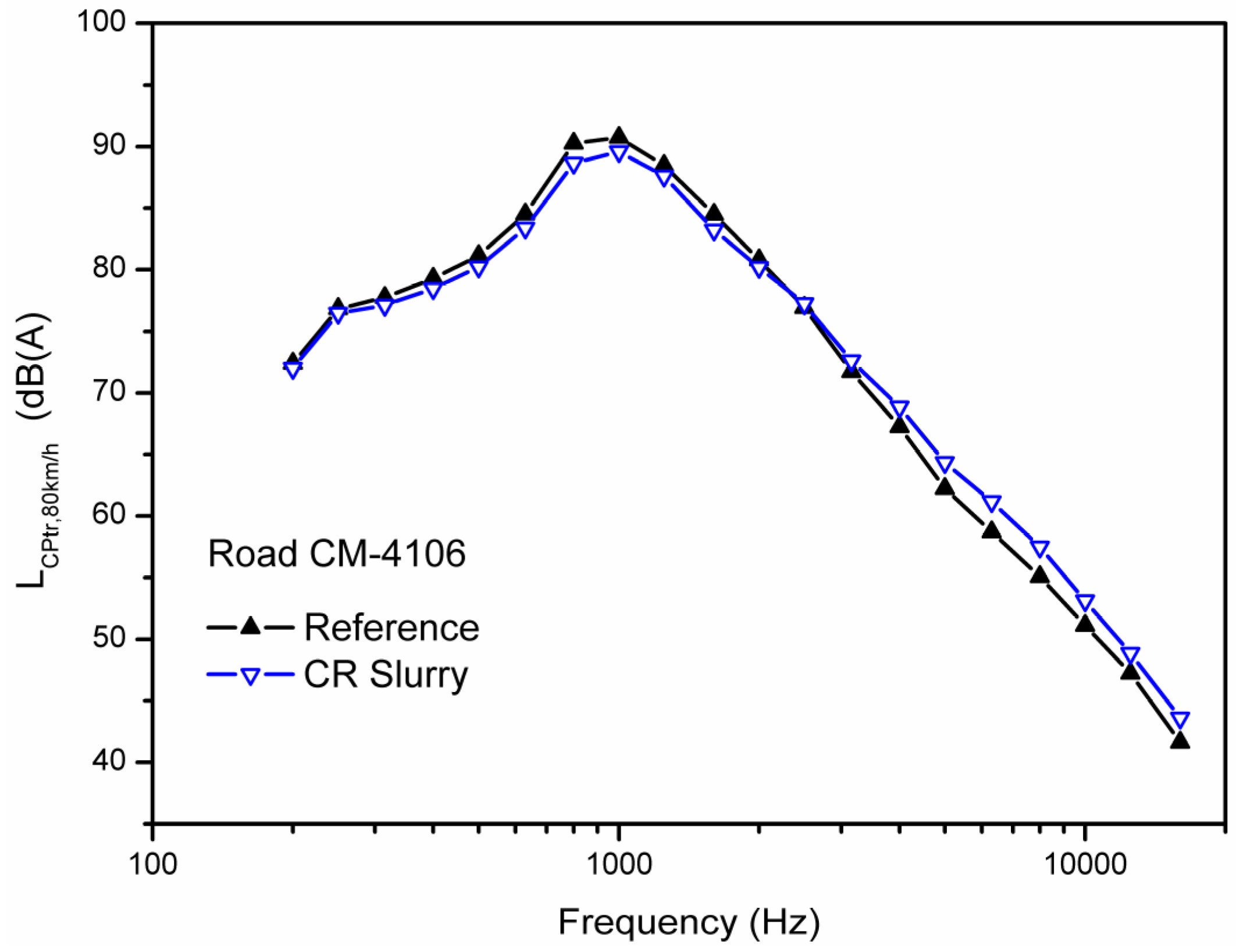
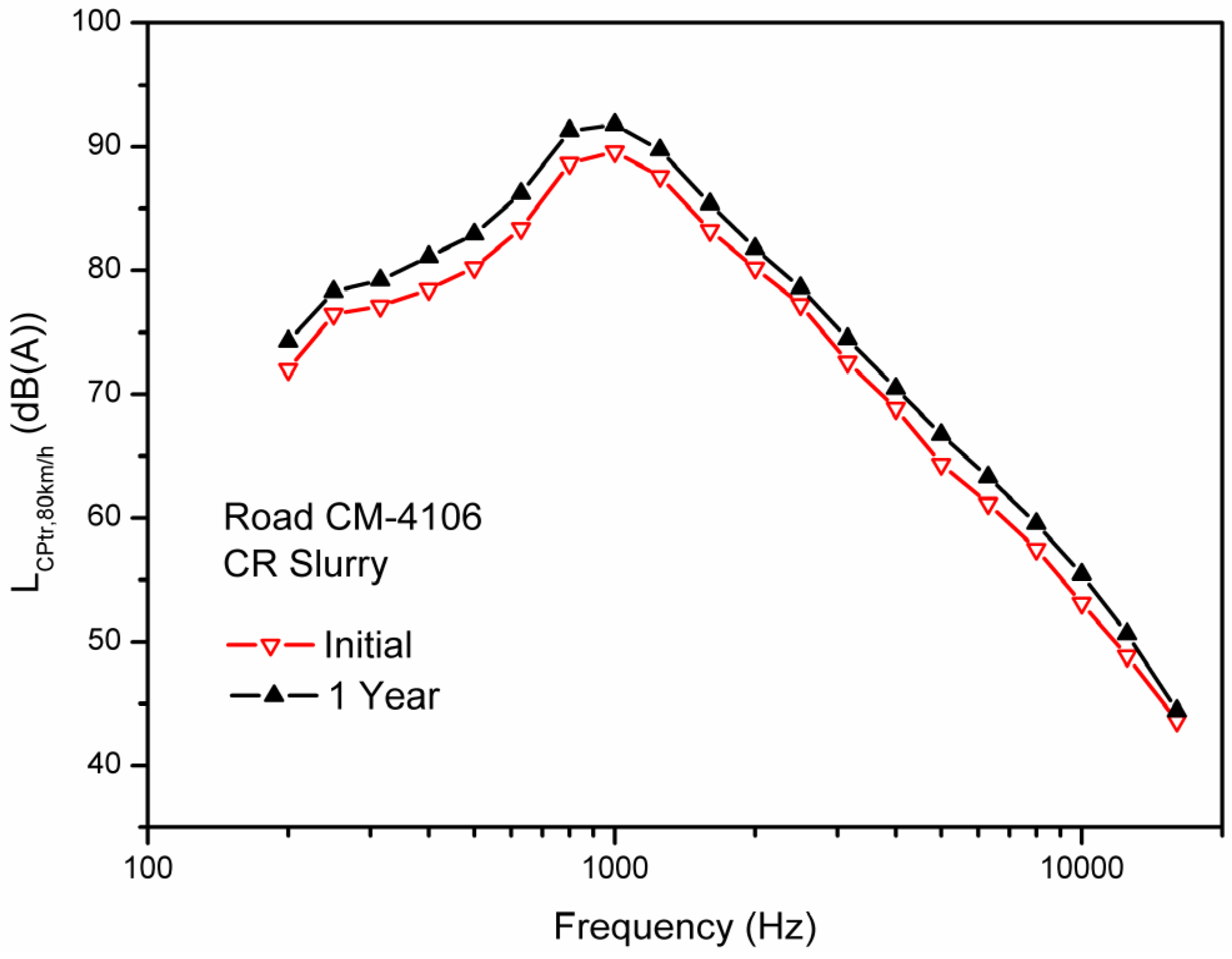
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNE-EN 12273:2009 Slurry Surfacing Requirements; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2009.
- Smith, R.E.; Beatty, C.K. Microsurfacing usage guidelines. Transp. Res. Rec. 1999, 1680, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Nebrada-Rodrigo, F.J.; Santos, J. Slurry seal and microsurfacing (Lechadas bituminosas y microaglomerados en frío). Carreteras 2005, 4, 78–87. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Van Kirk, J. Multi-layer pavement preservation strategies using slurry surfacing and chip seals. In Proceedings of the 7th ISSA World Congress, Lyon, France, October 2010.
- Sandberg, U.; Ejsmont, J.A. Tyre/Road Noise Reference Book; Informex: Kisa, Sweden, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mun, S.; Cho, D.S.; Choi, T.M. Influence of pavement surface noise: The Korea highway corporation test road. Can. J. Civil Eng. 2007, 34, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahammed, A.M.; Tighe, S.L. Pavement surface friction and noise: Integration into the pavement management system. Can. J. Civil Eng. 2010, 37, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Smith, G.; Shores, R. Pavement noise investigation on North Carolina highways: An on-board sound intensity approach. Can. J. Civil Eng. 2012, 39, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takallou, H.B.; Rayner, G.L.; Takallou, M.B. Development of design and construction guidelines for rubberized emulsified asphalt slurry seal. In Proceedings of the 4th ISSA World Congress, Paris, France, March 1997.
- MacLeod, D.; Ho, S.; Wirth, R.; Zanzotto, L. Study of crumb rubber materials as paving asphalt modifiers. Can. J. Civil Eng. 2007, 34, 1276–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Olivares, F.; Witoszek-Schultz, B.; Alonso-Fernández, M.; Benito-Moro, C. Rubber-modified hot-mix asphalt pavement by dry process. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2009, 10, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, E.; Canestrari, F.; Cardone, F.; Santagata, F.A. Performance evaluation of gap graded asphalt rubber mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 2014–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, F.; Rubio, M.C. Influence of crumb rubber on the indirect tensile strength and stiffness modulus of hot bituminous mixes. J. Mater. Civil Eng. 2012, 24, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miró, R.; Pérez-Jiménez, F.; Martínez, A.H.; Reyes, O.; Paje, S.E.; Bueno, M. Effect of using crumb rubber bituminous mixes on functional characteristics of road pavements. Transp. Res. Rec. 2009, 2126, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Ahammed, A.M.; Tighe, S.L.; Klement, T. Quiet and durable pavements: Findings from an Ontario study. Can. J. Civil Eng. 2010, 37, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paje, S.E.; Bueno, M.; Terán, F.; Miró, R.; Pérez-Jiménez, F.; Martínez, A.H. Acoustic field evaluation of asphalt mixtures with crumb rubber. Appl. Acoust. 2010, 71, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, E.F. The effect of time on the contribution of asphalt rubber mixtures to noise abatement. Noise Control Eng. J. 2012, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasetto, M.; Spinoglio, S. The use of a synthetic aggregate in non-skid and noise abatement microsurfacings for road maintenance. Performance improvements and environmental impact. In Proceedings of the 4th ISSA World Congress, Paris, France, March 1997.
- Esch, D.C. Construction and benefits of rubber modified-asphalt pavements. Transp. Res. Rec. 1982, 1680, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Amirkhanian, S.N.; Arnold, L.C. A Laboratory and Field Investigation of Rubberized Asphalt Concretes Mixtures (Pelham road); Final Report No. FHWA-SC-93-02; South Carolina Department of Highways and Public Transportation: South Carolina, SC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W. Study on properties of recycled tire rubber modified asphalt mixtures using dry process. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, F.; Rubio, M.C.; Martinez-Echevarría, M.J. The mechanical performance of dry-process crumb rubber modified hot bituminous mixes: The influence of digestion time and crumb rubber percentage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 26, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, J. Evaluation of rubber asphalt demonstration projects. Transp. Res. Rec. 1995, 1515, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Centre for the Development of Industrial Technology (CDTI). FENIX Project. Strategic Research on Safer and More Sustainable Roads. 2009. Available online: http://www.proyectofenix.es/ (accessed on 4 August 2014).
- Bueno, M.; Luong, J.; Viñuela, U.; Terán, F.; Paje, S.E. Pavement temperature influence on close proximity tire/road noise. Appl. Acoust. 2011, 72, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN ISO 13473–1:2004 Characterization of Pavement Texture by Use of Surface Profiles. Part 1: Determination of Mean Profile Depth; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2004.
- Paje, S.E.; Bueno, M.; Terán, F.; Viñuela, U. Monitoring road surfaces by close proximity noise of the tire/road interaction. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 122, 2636–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biligiri, K.P.; Kalman, B.; Samuelsson, A. Understanding the fundamental material properties of low-noise poroelastic road surfaces. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2013, 14, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Bueno, M.; Luong, J.; Terán, F.; Viñuela, U.; Vázquez, V.F.; Paje, S.E. Noise Reduction Properties of an Experimental Bituminous Slurry with Crumb Rubber Incorporated by the Dry Process. Coatings 2014, 4, 602-613. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings4030602
Bueno M, Luong J, Terán F, Viñuela U, Vázquez VF, Paje SE. Noise Reduction Properties of an Experimental Bituminous Slurry with Crumb Rubber Incorporated by the Dry Process. Coatings. 2014; 4(3):602-613. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings4030602
Chicago/Turabian StyleBueno, Moisés, Jeanne Luong, Fernando Terán, Urbano Viñuela, Víctor F. Vázquez, and Santiago E. Paje. 2014. "Noise Reduction Properties of an Experimental Bituminous Slurry with Crumb Rubber Incorporated by the Dry Process" Coatings 4, no. 3: 602-613. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings4030602
APA StyleBueno, M., Luong, J., Terán, F., Viñuela, U., Vázquez, V. F., & Paje, S. E. (2014). Noise Reduction Properties of an Experimental Bituminous Slurry with Crumb Rubber Incorporated by the Dry Process. Coatings, 4(3), 602-613. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings4030602




