Evaluation of Oxinium (Oxidized Zr2.5Nb) Femoral Heads in Hip Endoprostheses—Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Hip Endoprosthesis
1.2. Brief History of Hip Endoprosthesis Biomaterials
1.2.1. Ceramics in Hip Endoprostheses
1.2.2. Oxidized Zirconium Zr2.5Nb Alloy (Oxinium, OxZr)
1.3. Case Presentation
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.1.1. Femoral Stem
- Manufacturer/Provider: Implantcast (Buxtehude, Germany)
- Model: Eco Fit
- Size: 12.5 mm
- Fixation: Cementless
- Material: Ti6Al4V alloy (Titanium alloy)
- Taper: 12/14 (for femoral head connection)
2.1.2. Femoral Head
- Manufacturer: Smith & Nephew (Watford, UK)
- Material: Oxinium (oxidized zirconium)
- Diameter: 32 mm OD+4
2.1.3. Acetabular Cup
- Manufacturer/Provider: Implantcast
- Diameter: 52 mm
- Fixation: Cementless
- Material: Ti6Al4V alloy
2.1.4. Acetabular Inlay (Liner)
- Manufacturer/Provider: Implantcast
- Material: XLPE (cross-linked polyethylene)
- Inner Diameter: 41 mm
2.1.5. New Oxinium Femoral Head (For Comparison) from the Same Manufacturer and of Same Material and Dimensions as Originally Implanted Femoral Head
- Manufacturer: Smith & Nephew
- Material: Oxinium (oxidized zirconium alloy: Zr2.5Nb)
- Diameter: 32 mm OD+4
- 12/14 taper femoral head (for femoral head connection)
- Zr2.5Nb
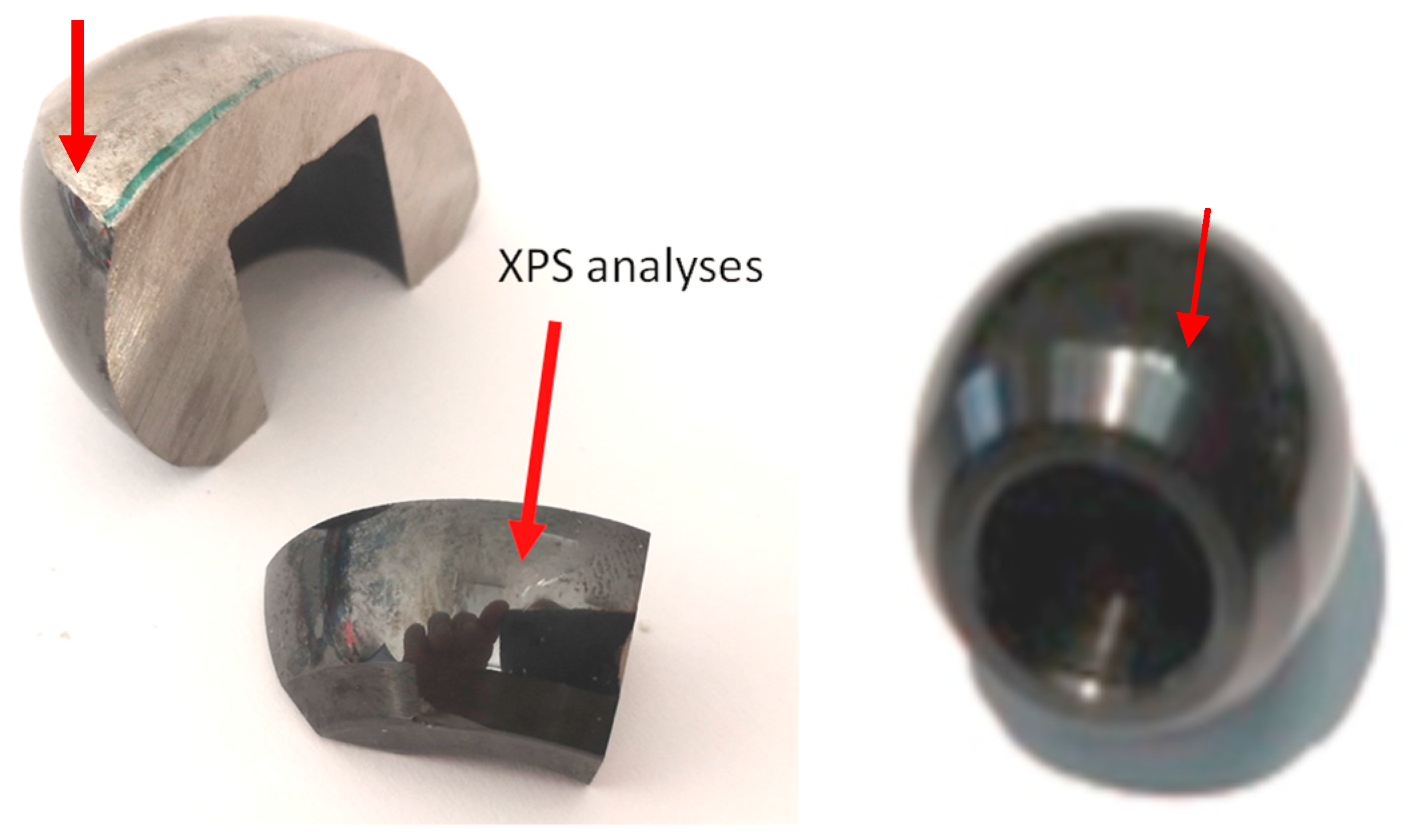
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Microbiological Analysis
2.4. XPS Surface Analysis
2.5. Microindentation—Hardness Measurements
3. Results
3.1. Hardness Measurements
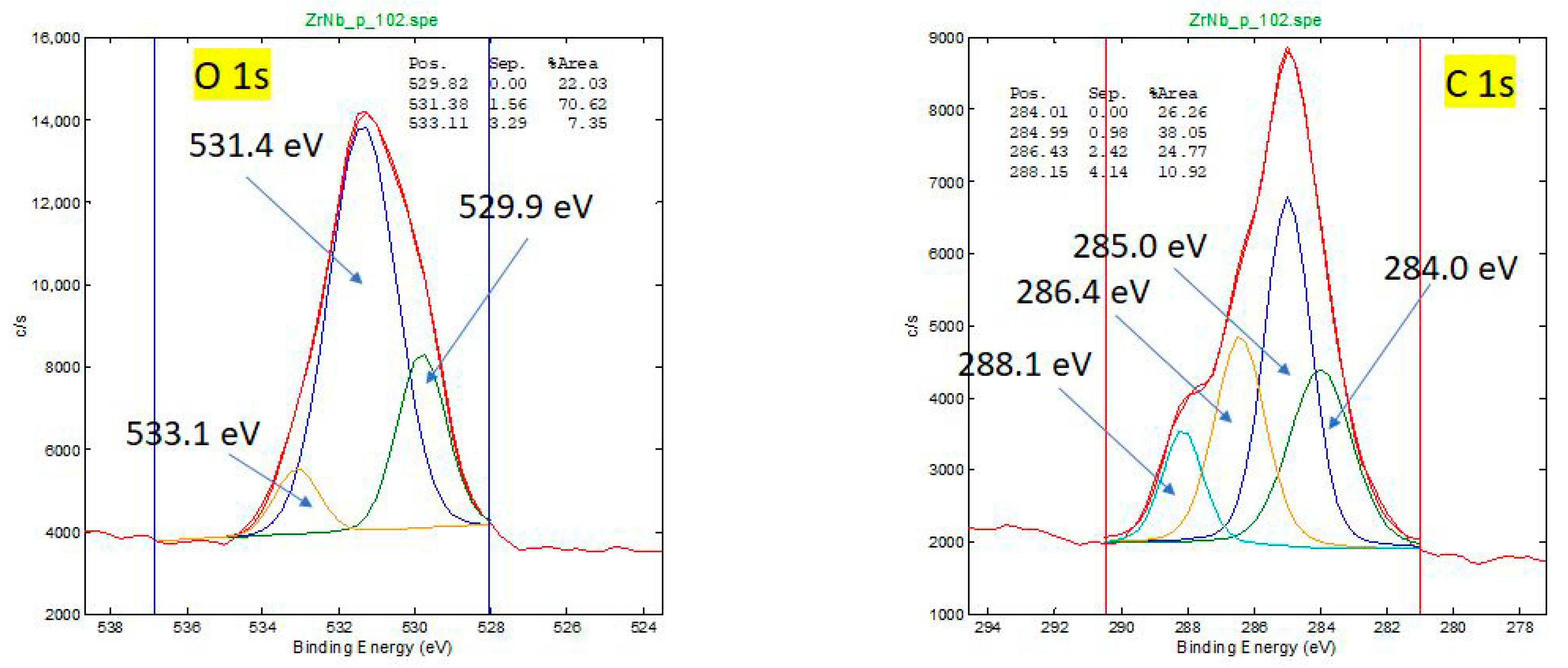
3.2. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy of Retrieved and New Oxinium Femoral Heads
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A



References
- Poulsen, E.; Christensen, H.W.; Roos, E.M.; Vach, W.; Overgaard, S.; Hartvigsen, J. Non-surgical treatment of hip osteoarthritis. Hip school, with or without the addition of manual therapy, in comparison to a minimal control intervention: Protocol for a three-armed randomized clinical trial. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2011, 12, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinic, M. Mayo Clinic: Hip Replacement. 2022. Available online: https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/hip-replacement/about/pac-20385042 (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Hip Replacement Surgery. 2023. Available online: https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/hip-replacement-surgery (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Total Hip Replacement. 2020. Available online: https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/treatment/total-hip-replacement/ (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Merola, M.; Affatato, S. Materials for Hip Prostheses: A Review of Wear and Loading Considerations. Materials 2019, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration. Recognized Consensus Standards: Medical Devices. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfStandards/detail.cfm?standard__identification_no=42378 (accessed on 29 May 2023).
- Hunter, G.; Jones, W.M.; Spector, M. Oxidized Zirconium. In Total Knee Arthroplasty; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 370–377. [Google Scholar]
- Good, V.; Widding, K.; Hunter, G.; Heuer, D. Oxidized zirconium: A potentially longer lasting hip implant. Mater. Des. 2004, 26, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baura, G. Total Hip Prostheses; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 451–482. [Google Scholar]
- Gibon, E.; Scemama, C.; David, B.; Hamadouche, M. Oxinium femoral head damage generated by a metallic foreign body within the polyethylene cup following recurrent dislocation episodes. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2013, 99, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Innocenti, M.; Civinini, R.; Carulli, C.; Matassi, F.; Villano, M. The 5-year Results of an Oxidized Zirconium Femoral Component for TKA. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2009, 468, 1258–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, A.; Hunter, G. Laboratory and Clinical Performance of Oxidized Zirconium Alloy. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2010, 7, 169. [Google Scholar]
- Willmann, G. Ceramics for total hip replacement—what a surgeon should know. Orthopedics 1998, 21, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Affatato, S.; Goldoni, M.; Testoni, M.; Toni, A. Mixed oxides prosthetic ceramic ball heads. Part 3: Effect of the ZrO2 fraction on the wear of ceramic on ceramic hip joint prostheses. A long-term in vitro wear study. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamadouche, M.; Sedel, L. Ceramics in orthopaedics. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2000, 82, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piconi, C.; Maccauro, G.; Muratori, F.; Del Prever, E.B. Alumina and zirconia ceramics in joint replacements. J. Appl. Biomater. Biomech. 2003, 1, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- De Aza, A.H.; Chevalier, J.; Fantozzi, G.; Schehl, M.; Torrecillas, R. Crack growth resistance of alumina, zirconia and zirconia toughened alumina ceramics for joint prostheses. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Affatato, S.; Torrecillas, R.; Taddei, P.; Rocchi, M.; Fagnano, C.; Ciapetti, G.; Toni, A. Advanced nanocomposite materials for orthopaedic applications. I. A long-term in vitro wear study of zirconia-toughened alumina. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2006, 78, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernigou, P.; Nogier, A.; Manicom, O.; Poignard, A.; De Abreu, L.; Filippini, P. Alternative femoral bearing surface options for knee replacement in young patients. Knee 2004, 11, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Good, V.; Ries, M.; Barrack, R.L.; Widding, K.; Hunter, G.; Heuer, D. Reduced wear with oxidized zirconium femoral heads. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2003, 85, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith & Nephew. 2020. Available online: https://www.smith-nephew.com/en/health-care-professionals/products (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Avsec, K.; Conradi, M.; Jenko, M.; Kocjančič, B.; Debeljak, M.; Gorenšek, M.; Dolinar, D. Effect of sterilization on the surface properties of Ti6Al7Nb alloy femoral stems. Mater. Technol. 2021, 55, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozden, V.E.; Saglam, N.; Dikmen, G.Ö.K.S.E.L.; Tozun, I.R. Oxidized zirconium on ceramic; Catastrophic coupling. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2017, 103, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, W.L.; Strauss, E.J.; Cardinale, M.; Herrera, L.; Kummer, F.J. Surface oxidized zirconium total hip arthroplasty head damage due to closed reduction effects on polyethylene wear. Arthroplasty 2009, 24, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frye, B.M.; Laughery, K.R.; Klein, A.E. The Oxinium Arthrogram: A Sign of Oxidized Zirconium Implant Failure. Arthroplast. Today 2021, 8, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kop, A.M.; Whitewood, C.; Johnston, D.J. Damage of oxinium femoral heads subsequent to hip arthroplasty dislocation three retrieval case studies. J. Arthroplast. 2007, 22, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potparić, I.; Jenko, M.; Dolinar, D.; Avsec, K.; Debeljak, M.; Godec, M.; Kocjančič, B. Severe metallosis after polyethylene liner dislocation in ceramic-on-Ti6Al4V total hip arthroplasty. A case study. Mater. Technol. 2025, 59, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| HV | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Base/HV 1 | 191 | 195 | 192 |
| Base/HV 0.01 | 198 | 204 | 201 |
| Edge/HV/0.01 | 262 | 252 | 267/279 |
| Distance µm | HV 0.01 |
|---|---|
| 15 | 283 |
| 25 | 265 |
| 50 | 230 |
| 75 | 229 |
| 100 | 221 |
| 125 | 228 |
| 150 | 231 |
| 200 | 215 |
| 300 | 215 |
| 500 | 190 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kocjančič, B.; Kocjančič, E.; Tadel Kocjančič, Š.; Kovač, J.; Jenko, M.; Debeljak, M. Evaluation of Oxinium (Oxidized Zr2.5Nb) Femoral Heads in Hip Endoprostheses—Case Report. Coatings 2025, 15, 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091087
Kocjančič B, Kocjančič E, Tadel Kocjančič Š, Kovač J, Jenko M, Debeljak M. Evaluation of Oxinium (Oxidized Zr2.5Nb) Femoral Heads in Hip Endoprostheses—Case Report. Coatings. 2025; 15(9):1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091087
Chicago/Turabian StyleKocjančič, Boštjan, Ema Kocjančič, Špela Tadel Kocjančič, Janez Kovač, Monika Jenko, and Mojca Debeljak. 2025. "Evaluation of Oxinium (Oxidized Zr2.5Nb) Femoral Heads in Hip Endoprostheses—Case Report" Coatings 15, no. 9: 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091087
APA StyleKocjančič, B., Kocjančič, E., Tadel Kocjančič, Š., Kovač, J., Jenko, M., & Debeljak, M. (2025). Evaluation of Oxinium (Oxidized Zr2.5Nb) Femoral Heads in Hip Endoprostheses—Case Report. Coatings, 15(9), 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091087







