Gelatin–Sodium Alginate Composite Hydrogel for Sustained Release of Simvastatin Enabled Osteogenic Differentiation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
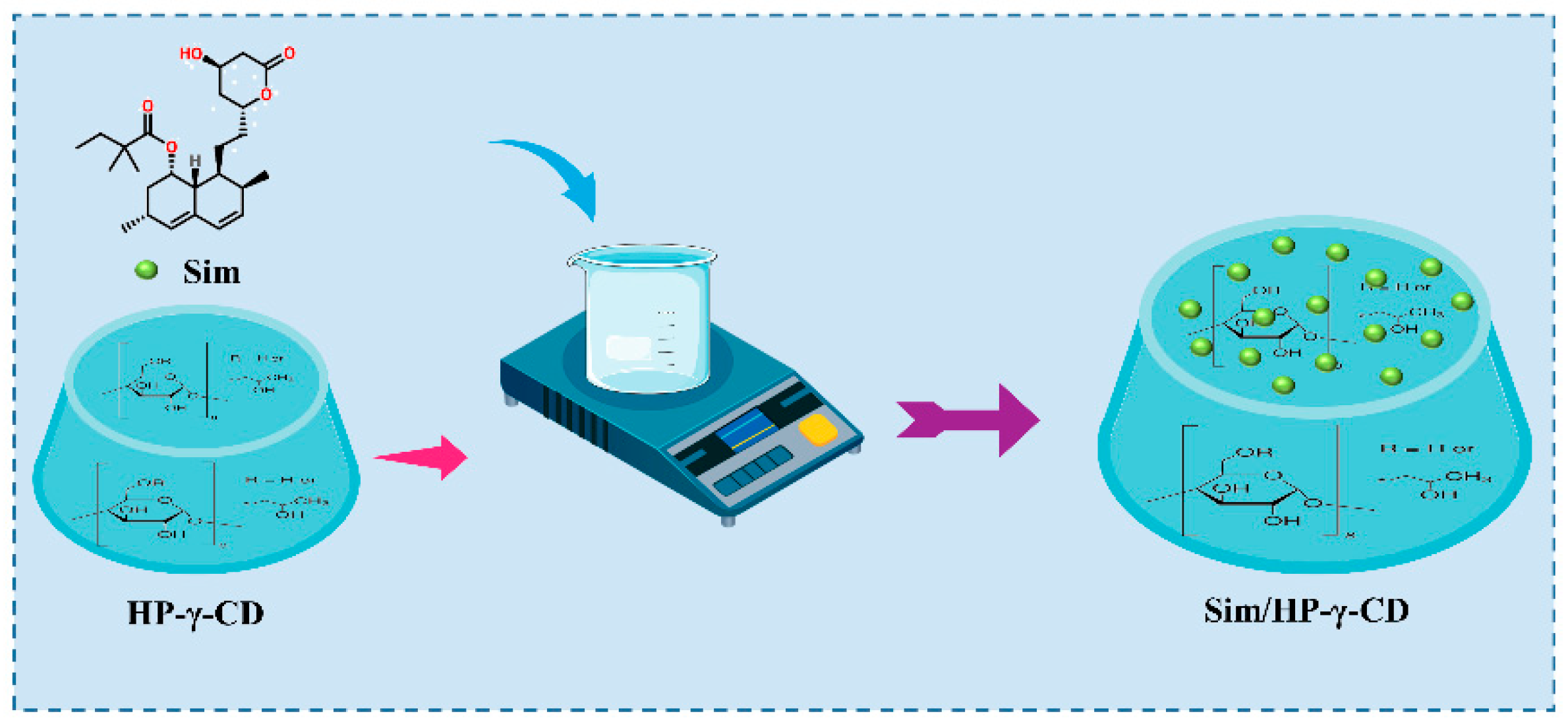
2.1. Preparation of the Sim/HP-γ-CD Inclusion Complex
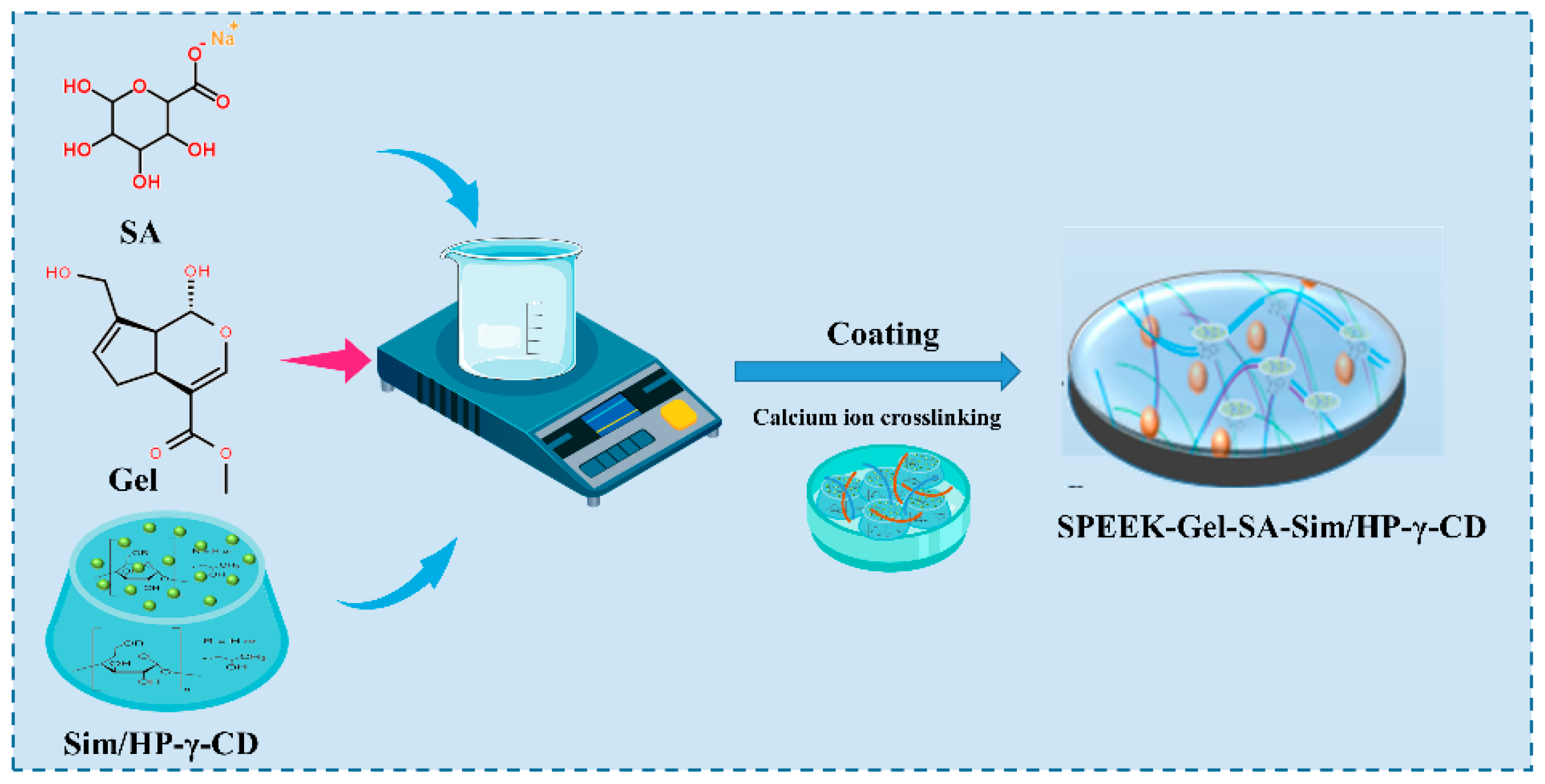
2.2. Fabrication of the Gel-SA-Sim/HP-γ-CD Sustained Release System
2.3. Basic Property Characterization
2.4. Degradation Behavior of Hydrogels
2.5. Mechanical Properties
2.6. Cell Biocompatibility
2.7. In Vitro Osteogenic Differentiation
2.7.1. ALP Staining
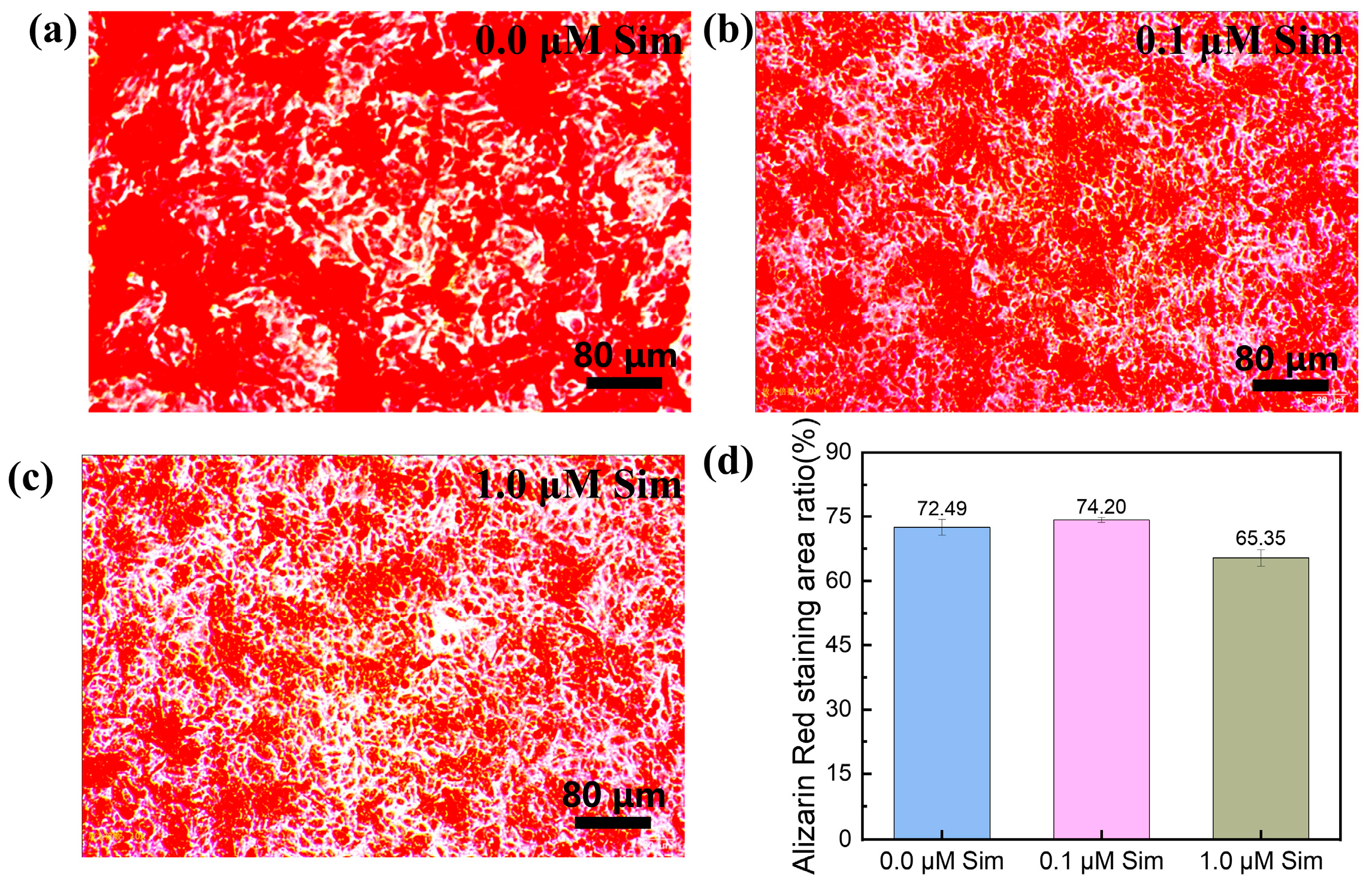
2.7.2. ARS Staining
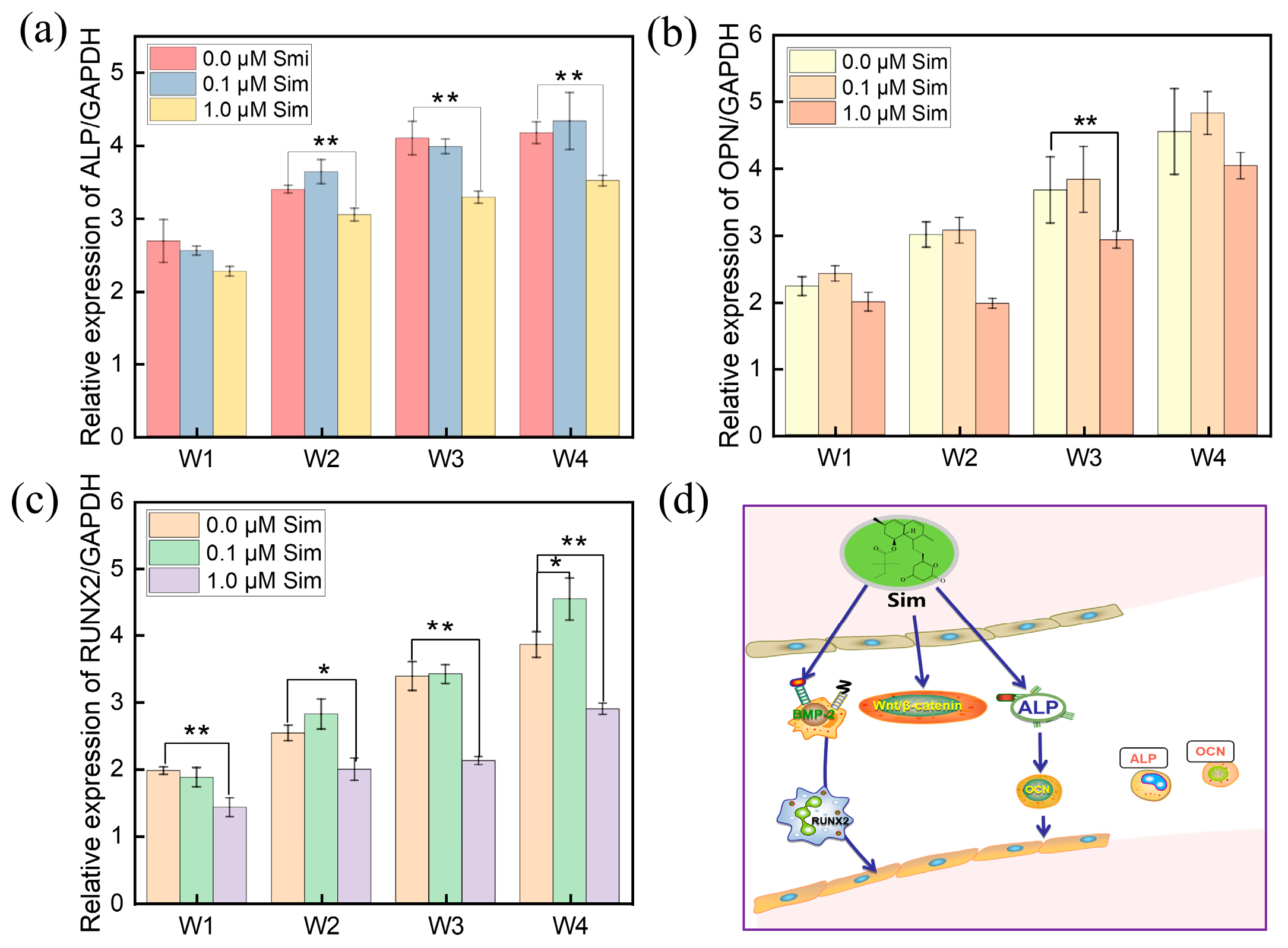
2.8. Osteogenic Gene Expression
3. Results and Discussion
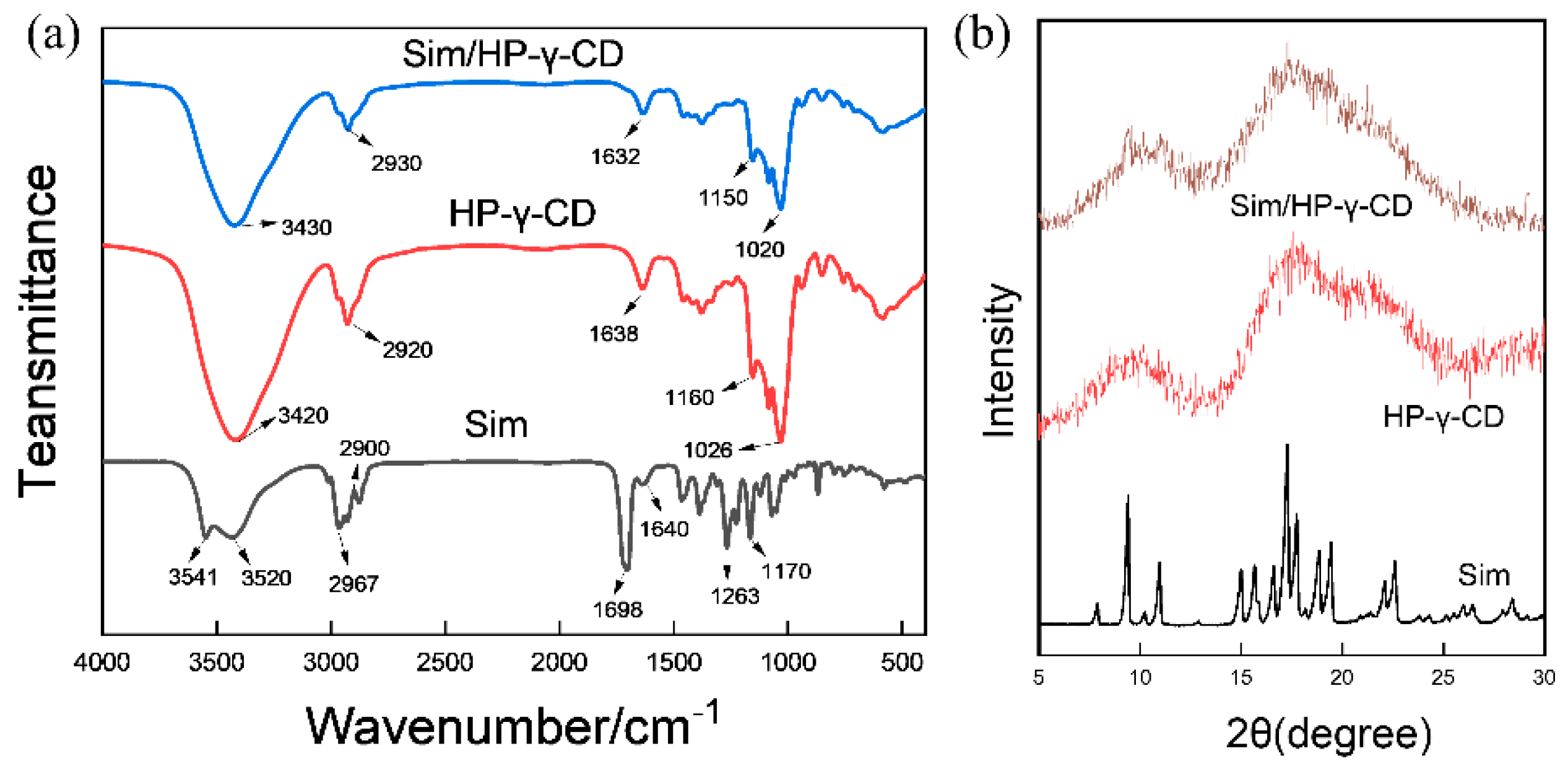
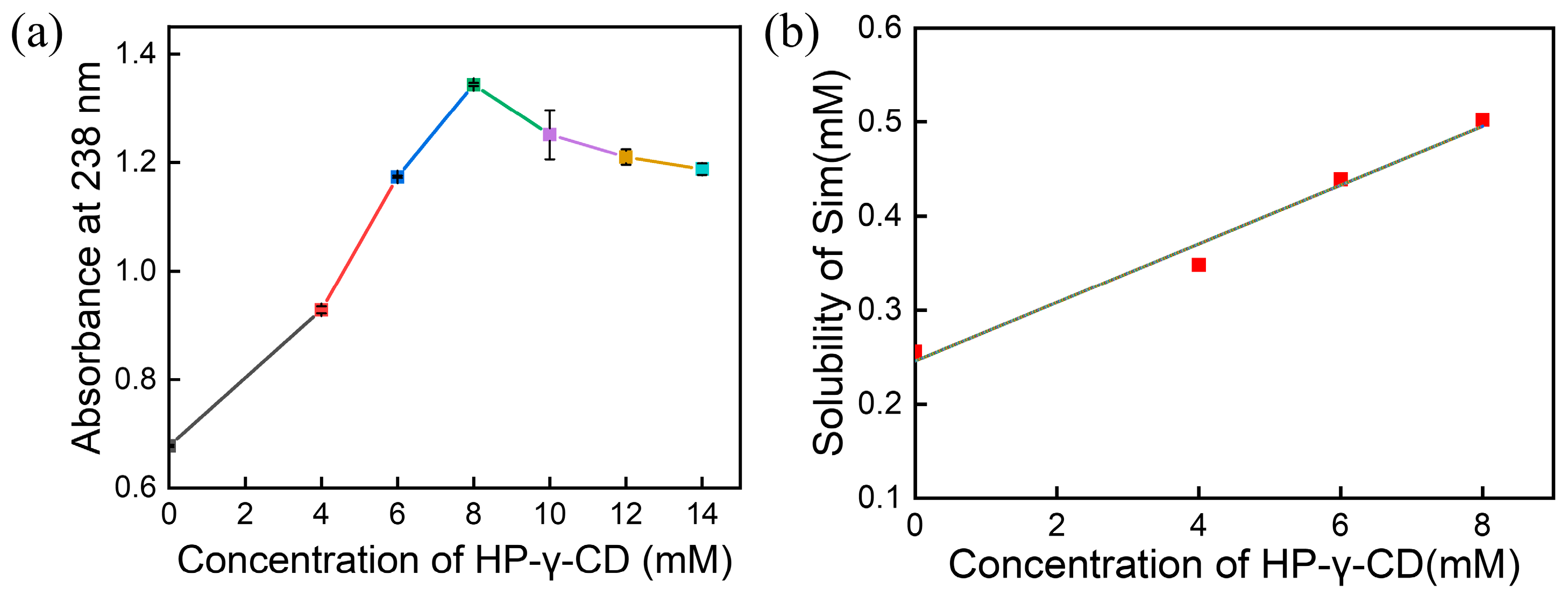
3.1. Characterization and Optimization of the Sim/HP-γ-CD Inclusion Complexes
3.2. Optimization of the Gel-SA-Sim/HP-γ-CD Hydrogel Sustained Release System
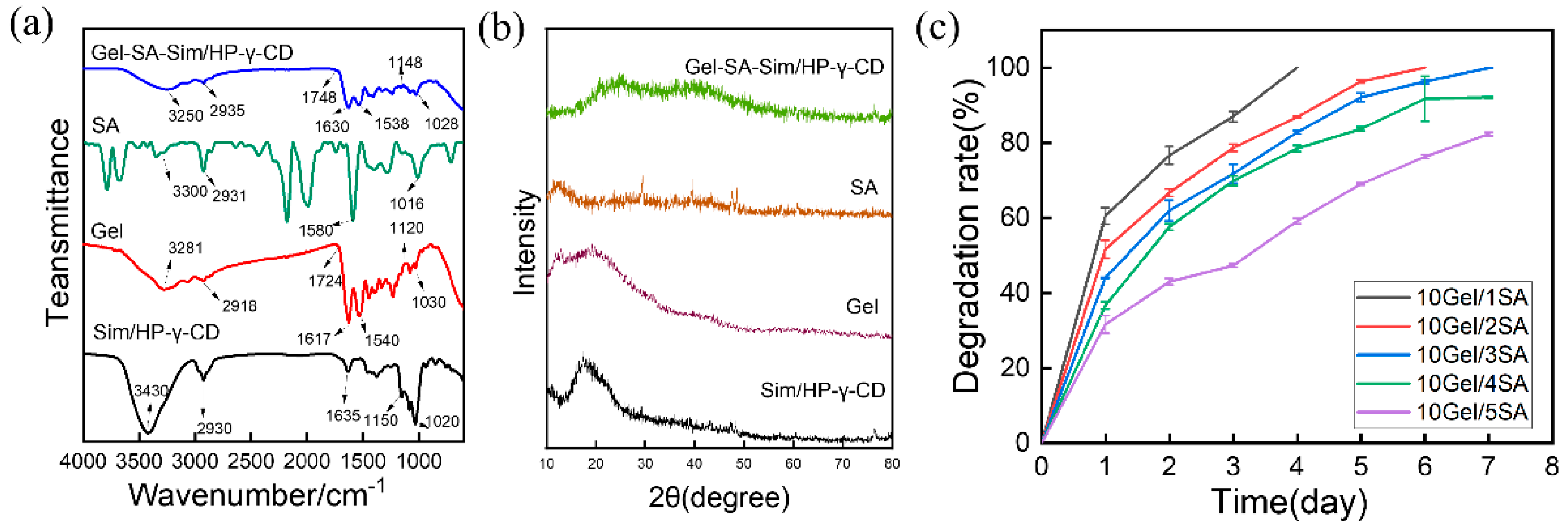
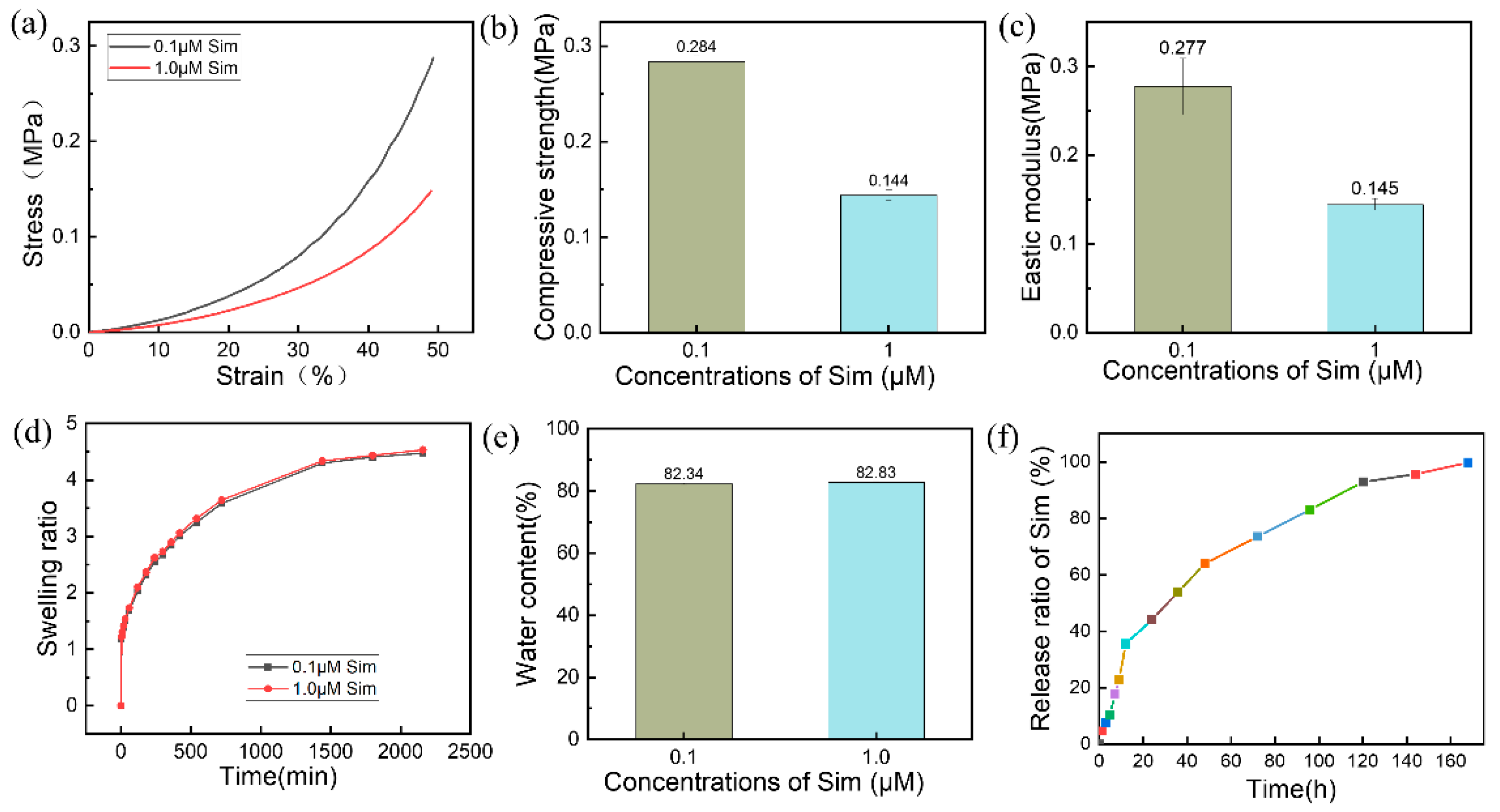
3.3. Characterization of the Gel-SA-Sim/HP-γ-CD Hydrogel Sustained Release System
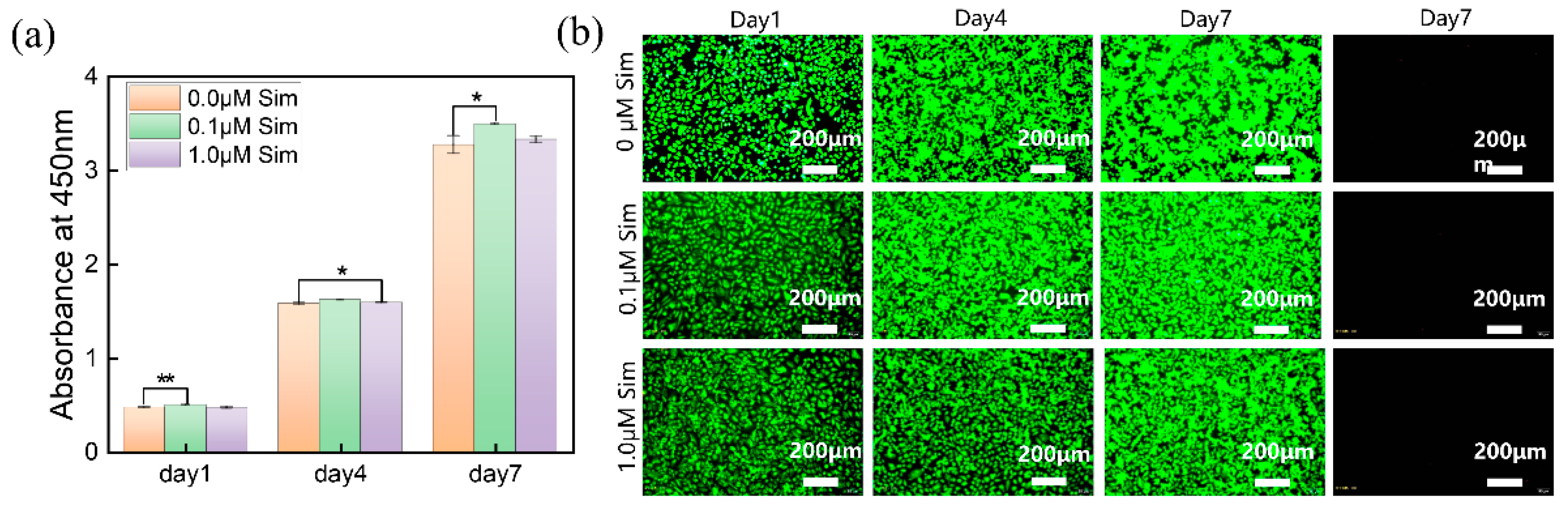
3.4. Cell Biocompatibility of the Gel-SA-Sim/HP-γ-CD Hydrogel Sustained Release System
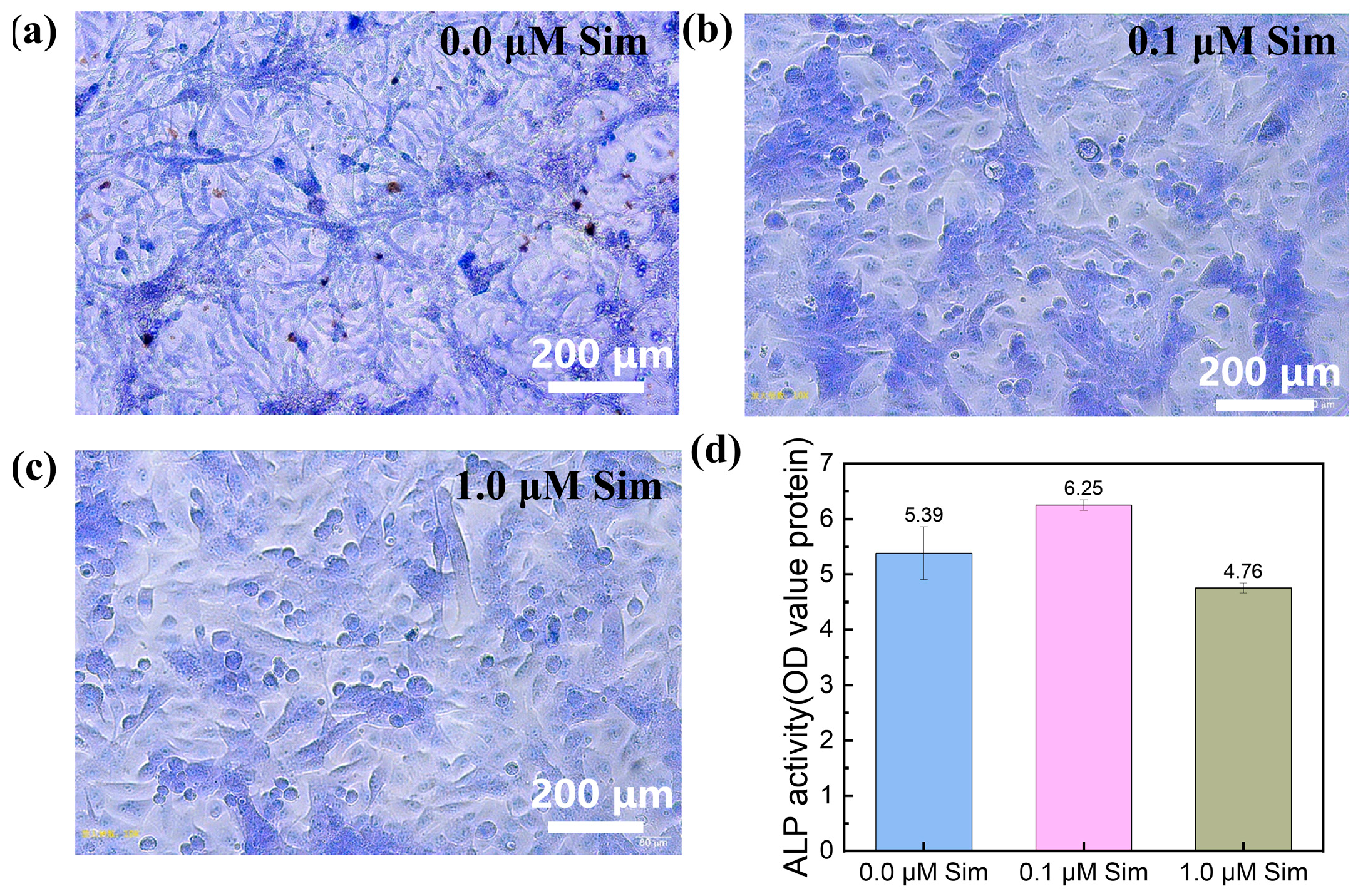
3.5. In Vitro Osteogenic Differentiation of the Gel-SA-Sim/HP-γ-CD Hydrogel Sustained Release System
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, C.H.; Liu, L.S.; Deng, Z.T.; Lei, H.Y.; Yuan, F.Z.; Yang, Y.Q.; Li, Y.Y.; Yu, J.K. Research progress on the design and performance of porous titanium alloy bone implants. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 2626–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.Z.; Wu, D.X.; Zhang, Y.W.; Luo, Y.K.; Yang, L.; Xu, X.R.; Luo, F. Multifunctional modifications of polyetheretherketone implants for bone repair: A comprehensive review. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 154, 213607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, B.H.; Wu, F.G. Hydrogel-based growth factor delivery platforms: Strategies and recent advances. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 202210707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Fahmy-Garcia, S.; Wesdorp, M.A.; Kops, N.; Forte, L.; Luca, C.; Misciagna, M.M.; Dolcini, L.; Filardo, G.; Labberté, M. Effectiveness of BMP-2 and PDGF-BB adsorption onto a collagen/collagen-magnesium-hydroxyapatite scaffold in weight-bearing and non-weight-bearing osteochondral defect bone repair: In vitro, ex vivo and in vivo evaluation. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komai, Y.; Morimoto, S.; Saito, K.; Urushibara, M.; Sakai, K.; Ikeda, S. Possible involvement of bone morphogenetic protein 2 in heterotopic ossification in metastatic lesion from urothelial carcinoma of bladder. Int. J. Urol. 2006, 13, 1126–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Q.; Cao, J.Q.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, C. Transplantation with lentivirus-mediated VEGF-infected rat adipose-derived stem cells through the fourth ventricle ameliorates clinical and pathological features in an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis murine model. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2022, 36, 689–698. [Google Scholar]
- Basarir, K.; Erdemli, B.; Can, A.; Erdemli, E.; Zeyrek, T. Osseointegration in arthroplasty: Can simvastatin promote bone response to implants? Int. Orthop. 2009, 33, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Ji, Y.B.; Cui, Y.T.; Xu, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.C. Simvastatin-Incorporated Drug Delivery Systems for Bone Regeneration. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 2177–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.R.; Werlang, C.A.; Kasper, F.K.; Mikos, A.G. Novel applications of statins for bone regeneration. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2015, 2, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.H.; Yuan, W.Q.; Wang, J.D.; Ni, R.H.; Qin, Y.; Mao, Z.N.; Wei, F.; Song, C.L.; Zheng, Y.F.; Cai, H.; et al. Simvastatin/hydrogel-loaded 3D-printed titanium alloy scaffolds suppress osteosarcoma via TF/NOX2-associated ferroptosis while repairing bone defects. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 34, 463–465. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.; Yang, N.; Fu, X.; Cui, Y.Y.; Guo, Q.; Ma, T.; Yin, X.X.; Leng, H.J.; Song, C.L. Single-dose local simvastatin injection improves implant fixation via increased angiogenesis and bone formation in an ovariectomized rat model. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 1428–1439. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.; Fu, X.; Sun, C.G.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.H.; Cui, Y.Y.; Guo, Q.; Ma, T.; Wang, H.; Du, G.H.; et al. A single CT-guided percutaneous intraosseous injection of thermosensitive simvastatin/poloxamer 407 hydrogel enhances vertebral bone formation in ovariectomized minipigs. Osteoporos. Int. 2016, 27, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nantavisai, S.; Rodprasert, W.; Pathanachai, K.; Wikran, P.; Kitcharoenthaworn, P.; Smithiwong, S.; Archasappawat, S.; Sawangmake, C. Corrigendum to “Simvastatin enhances proliferation and pluripotent gene expression by canine bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (cBM-MSCs) in vitro”. Heliyon 2019, 5, e2805. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.J.; Wu, Y.L.; He, X.H.; Xie, K.N.; Xie, L.; Deng, Y. Simvastatin delivery on PEEK for bioactivity and osteogenesis enhancements. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2018, 29, 2237–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajihasani Biouki, M.; Mobedi, H.; Karkhaneh, A.; Joupari, M.D. Development of a simvastatin loaded injectable porous scaffold in situ formed by phase inversion method for bone tissue regeneration. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2019, 42, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Wu, G.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, Y. Human adipose-derived stem cells and simvastatin-functionalized biomimetic calcium phosphate to construct a novel tissue-engineered bone. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 1264–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.G. Simvastatin: Present and future perspectives. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2007, 8, 2159–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.L.; Guan, Y.Y.; Dong, Q.P.; An, R.; Wang, J.C. Chitosan-based biomaterials promote bone regeneration by regulating macrophage fate. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 7480–7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepthi, S.; Venkatesan, J.; Kim, S.K.; Bumgardner, J.D.; Jayakumar, R. An overview of chitin or chitosan/nano ceramic composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 1338–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qiang, T.; Chen, X.; Ren, W.; Zhang, H.J. Tough and biodegradable gelatin-based film via the synergistic effect of multi-cross-linking. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipal, J.; Pu’ad, N.A.S.M.; Lee, T.C.; Nayan, N.H.M.; Sahari, N.; Basri, H.; Idris, M.I.; Abdullah, H.Z. A review of gelatin: Properties, sources, process, applications, and commercialization. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 42, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkoc, P.; Uvak, I.; Nazeer, M.A.; Batool, S.R.; Odeh, Y.N.; Akdogan, O.; Kizilel, S. 3D printing of cytocompatible gelation-cellulose-alginate blend hydrogels. Food Rev. Int. 2020, 38, 812–855. [Google Scholar]
- Safari, B.; Aghanejad, A. Porous gelatin-based phosphorylated scaffold: Microstructure, cell response and osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 99, 106008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, P.; Tang, J.J.; Xue, Y.F.; Luo, H.S.; Dai, R.; Jin, J.L.; Liu, J. 3D printed heterogeneous hybrid hydrogel scaffolds for sequential tumor photothermal-chemotherapy and wound healing. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 5648–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alishahi, M.; Xiao, R.B.; Kreismanis, M.; Chowdhury, R.; Aboelkheir, M.; Lopez, S.; Altier, C.; Bonassar, L.J.; Shen, H.Q.; Uyar, T. Antibacterial, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antioxidant Cotton-Based Wound Dressing Coated with Chitosan/Cyclodextrin-Quercetin Inclusion Complex Nanofibers. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 5662–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Yan, H.L.; Xiu, Y.; Li, F.R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.C.; Zhao, L.X.; Ye, F.; Fu, Y. Electrospun Nanofibers Incorporated with HPγCD Inclusion Complex for Improved Water Solubility and Activity of Hydrophobic Fungicides Pyrimethanil. Molecules 2025, 30, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Guan, N.; Chen, Q.; Chen, K.; Feng, C.; Zhang, D. Gelatin–Sodium Alginate Composite Hydrogel for Sustained Release of Simvastatin Enabled Osteogenic Differentiation. Coatings 2025, 15, 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091004
Zhang X, Guan N, Chen Q, Chen K, Feng C, Zhang D. Gelatin–Sodium Alginate Composite Hydrogel for Sustained Release of Simvastatin Enabled Osteogenic Differentiation. Coatings. 2025; 15(9):1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091004
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xinyue, Ning Guan, Qin Chen, Kai Chen, Cunao Feng, and Dekun Zhang. 2025. "Gelatin–Sodium Alginate Composite Hydrogel for Sustained Release of Simvastatin Enabled Osteogenic Differentiation" Coatings 15, no. 9: 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091004
APA StyleZhang, X., Guan, N., Chen, Q., Chen, K., Feng, C., & Zhang, D. (2025). Gelatin–Sodium Alginate Composite Hydrogel for Sustained Release of Simvastatin Enabled Osteogenic Differentiation. Coatings, 15(9), 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091004






