Influence of Cooling Methods on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TiB2@Ti/AlCoCrFeNi2.1 Eutectic High-Entropy Alloy Matrix Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. XRD Results
3.2. Microstructure
3.3. Mechanical Properties
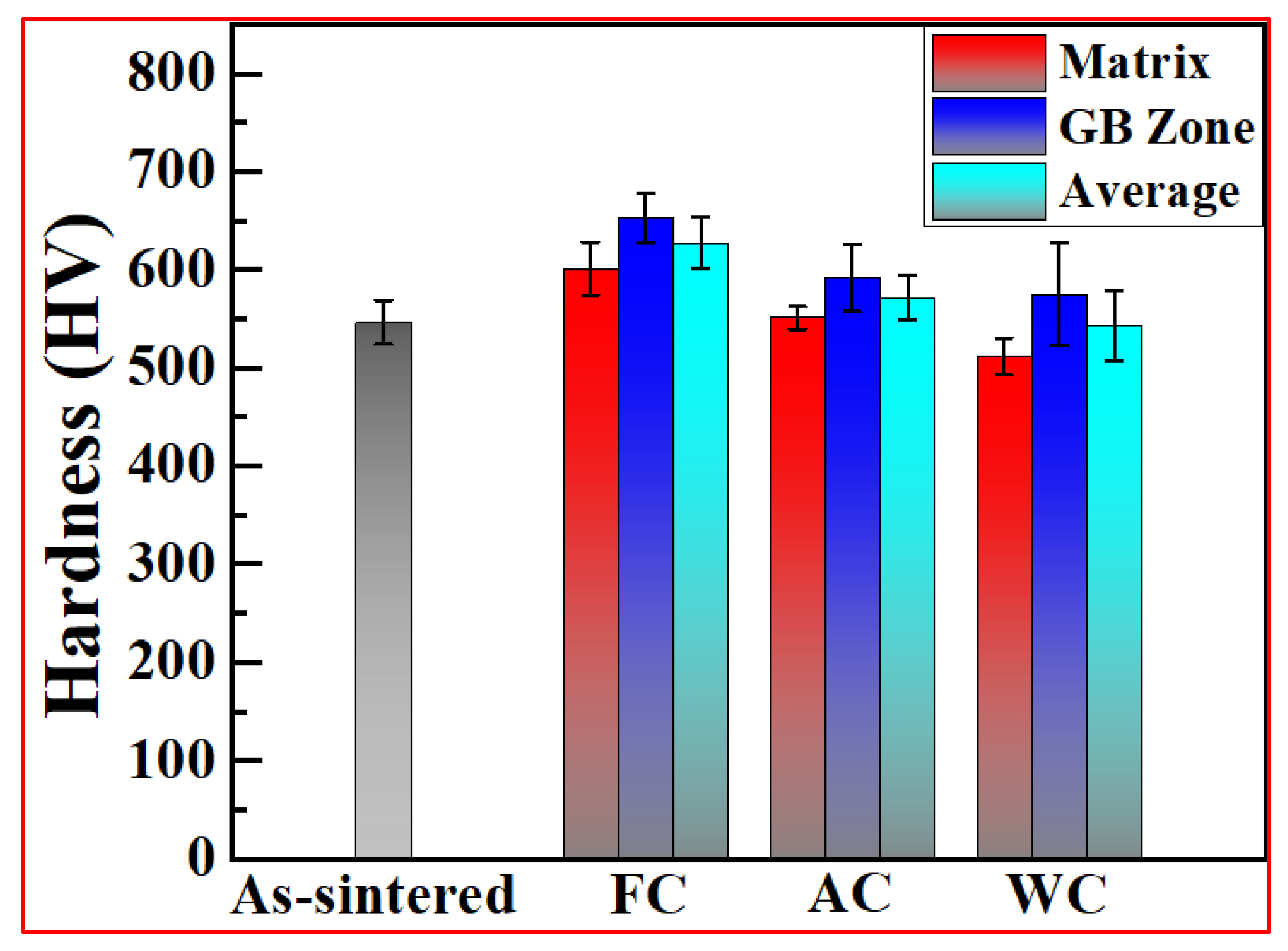
3.3.1. Hardness
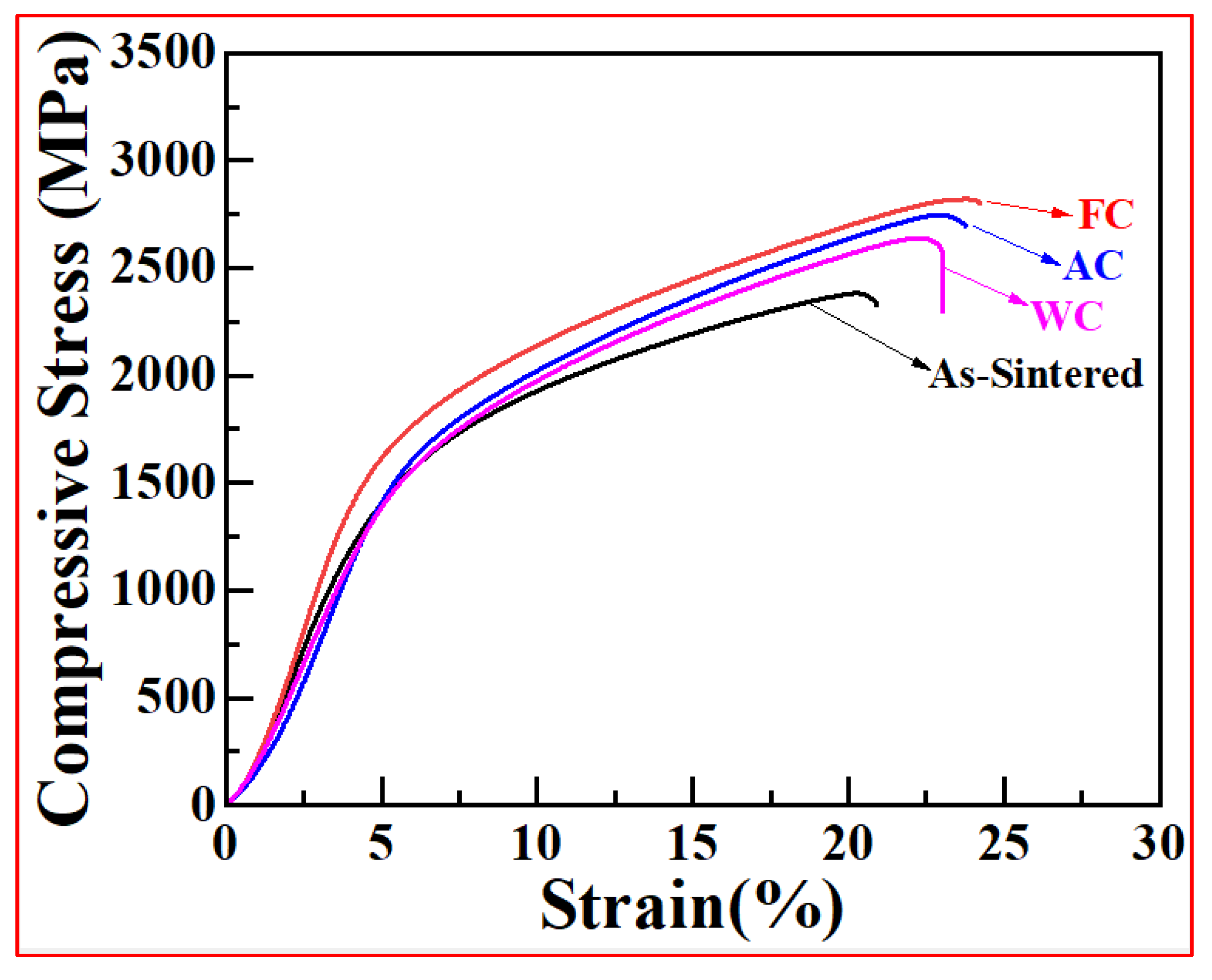
3.3.2. Room-Temperature Compression Property
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured high entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, S. Alloyed pleasures: Multimetallic cocktails. Curr. Sci. 2003, 85, 1404–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 448–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.P.; Dong, Y.; Guo, S.; Jiang, L.; Kang, H.J.; Wang, T.M.; Wen, B.; Wang, Z.J.; Jie, J.C.; Cao, Z.Q.; et al. A promising new class of high-temperature alloys: Eutectic high-entropy alloys. Sci. Rep. 2014, 78, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, H.; Lu, Y.P.; Wang, T.M.; Li, T.J. Effects of annealing treatment on microstructure and hardness of bulk AlCrFeNiMo0.2 eutectic high-entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 2015, 82, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.T.; Chen, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.Q. A quantitative understanding on the mechanical behavior of AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high-entropy alloy. J. Alloy Compd. 2021, 850, 156610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, I.S.; Bhattacharjee, T.; Sheikh, S.; Bhattacharjee, P.P.; Guo, S.; Tsuji, N. Tailoring nanostructures and mechanical properties of AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high entropy alloy using thermo-mechanical processin. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 675, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.Y.; Chen, J.; Ding, R.G.; Yao, Y.H.; Wang, W.L.; Zhang, T.; He, J.H.; Liu, Y.Z.; Liu, J.N. Achieving high yield strength in a directly cast eutectic high entropy alloy via introducing κ′ nano-precipitates. J. Alloy Compd. 2025, 1036, 181935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.D.; Ye, X.C.; Yang, J.K.; Kang, H.J.; Sun, L.; Wu, G.X.; Guo, J.J.; Rong, Y.R.; Zhu, F.H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a novel lightweight eutectic high-entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2025, 185, 108925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Liu, E.S.; Peng, C.; Han, C.; Zhou, G.T.; Li, C.J.; Qi, L.; Li, R.; Ke, Y.J. Synthesis and characterization of TiB2-reinforced AlCoCrFeNi2.1 high-entropy-alloy matrix composite. Metals 2024, 14, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Zhao, L.; Wan, D.; Guan, S.; Chan, K.C. Additive manufacturing of TiB2-containing CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy matrix composites with high density and enhanced mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 825, 141871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.N.; Su, H.J.; Gao, H.L.; Shen, Z.L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Yang, P.X.; Hu, Q.D.; Zhang, Z. Cracking behavior of newly-developed high strength eutectic high entropy alloy matrix composites manufactured by laser powder bed fusion. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 163, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhao, R.F.; Zhang, H.S. Microstructure and friction properties of TiB2@Ti/CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy matrix composite. Met. Mater. Int. 2025, 31, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.Y.; Feng, S.; Jiang, Z.F.; Ren, J.; Zhang, S.B.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhang, L.; He, W.Y.; Liu, Z.Q.; Guan, S.; et al. High strength and ductility in a dual-phase hetero-structured AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high-entropy alloy by powder metallurgy. Mater. Res. Lett. 2024, 12, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.C.; Chen, H.S.; Zhou, J.; Wang, W.X.; Xi, S.X.; Chen, X.C. Interfacial bonding behavior of WC/AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high-entropy alloy matrix composites fabricated by fast hot pressing sintering. Vacuum 2023, 217, 112574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, S.X.; Chen, H.S.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, L.W.; Wang, W.X.; Nie, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, B.C. A novel eutectic high-entropy matrix composites were prepared by selective laser melting: Microstructure evolution, strengthening and fracture mechanism. J. Manu. Process. 2024, 120, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.Q.; Zhou, Y.J.; Jiang, Q.G.; Chen, P.F.; Ren, B. Influence of Heat Treatment Temperature on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TiB2@Ti/AlCoCrFeNi2.1 Eutectic High-Entropy Alloy Matrix Composites. Metals 2025, 15, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Zhao, R.F.; Geng, H.C.; Ren, B.; Liu, Z.X.; Liu, J.X.; Jiang, A.Y.; Zhang, B.F. Effect of cooling method on microstructure and microhardness of CuCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Coatings 2024, 14, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.F.; Wang, W.H.; Qi, X.L.; Lv, Y.K.; Yang, W.; Li, T.Y.; Chen, J. Effects of heat treatment cooling methods on precipitated phase and mechanical properties of CoCrFeMnNi-Mo5C0.5 high entropy alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 29, 3566–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.L.; Sun, Y.; Cao, P.P.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Jiang, S.H.; Wang, H.; Lu, Z.P. On cooling rates dependence of microstructure and mechanical properties of refractory high-entropy alloys HfTaTiZr and HfNbTiZr. Scr. Mater. 2022, 211, 114506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Jia, T.; Qiu, H.; Zhu, H.G.; Xie, Z.H. Effect of cooling rate upon the microstructure and mechanical properties of in-situ TiC reinforced high entropy alloy CoCrFeNi. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 42, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Inoue, A. Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying element. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 2817–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

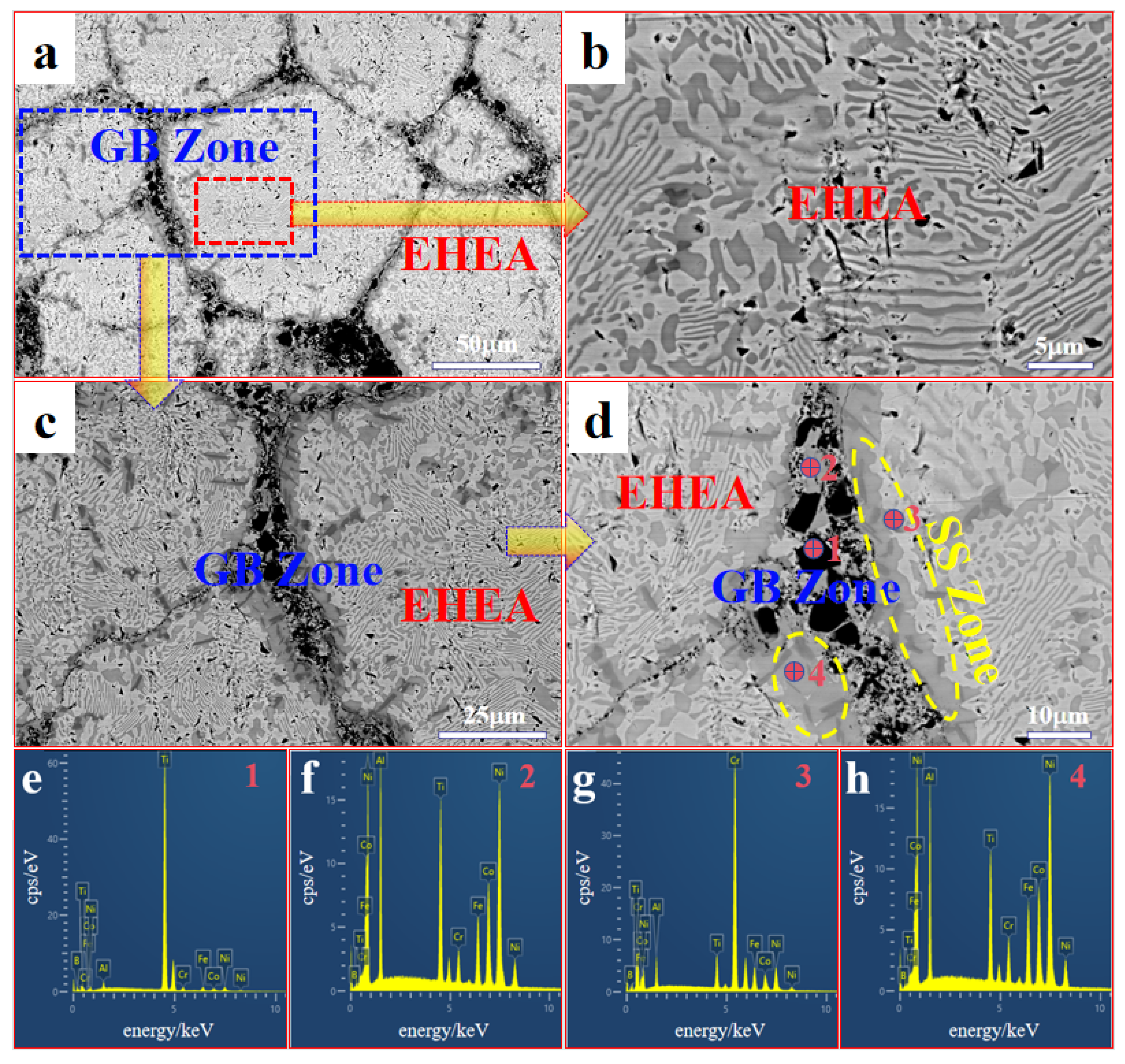

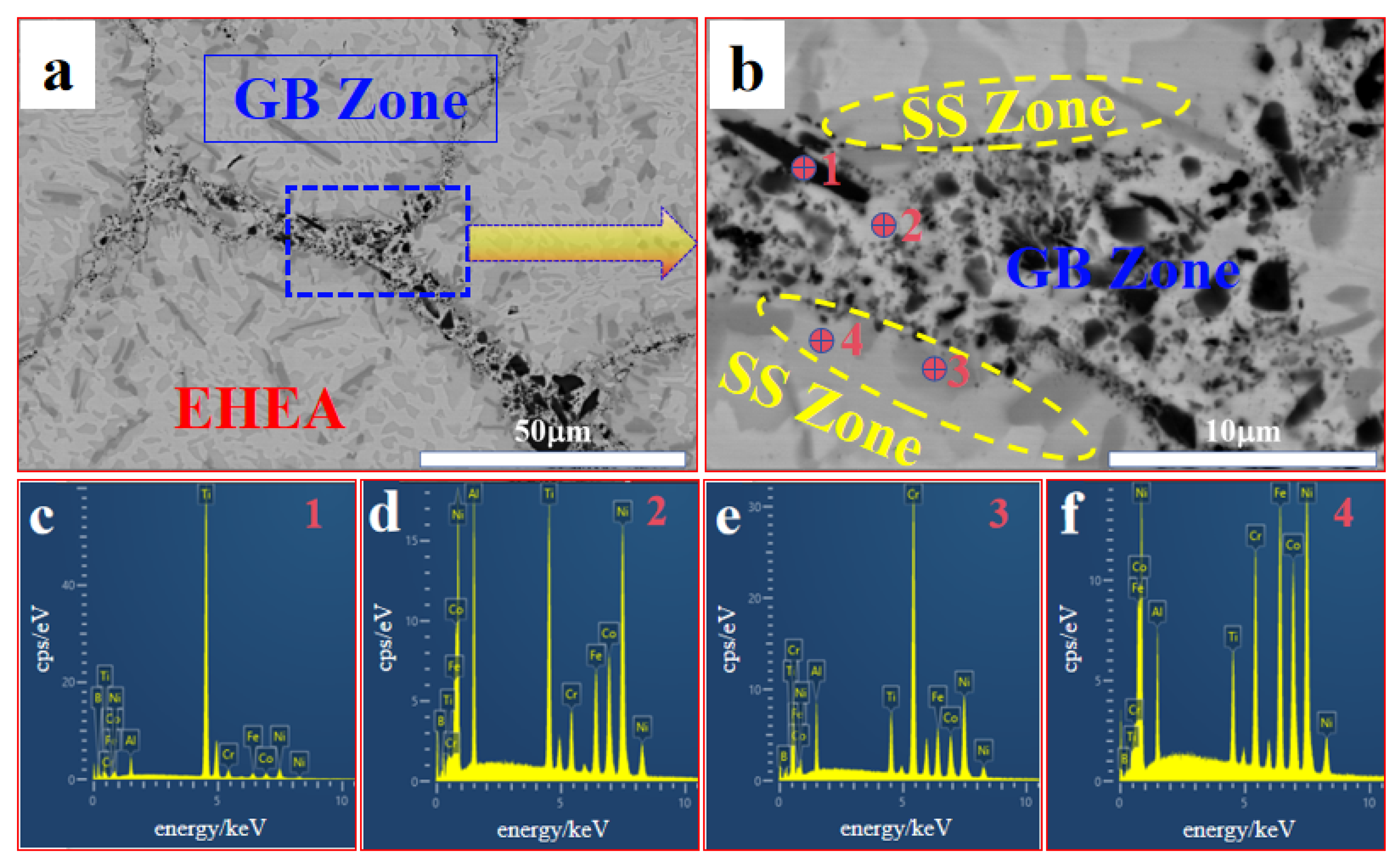
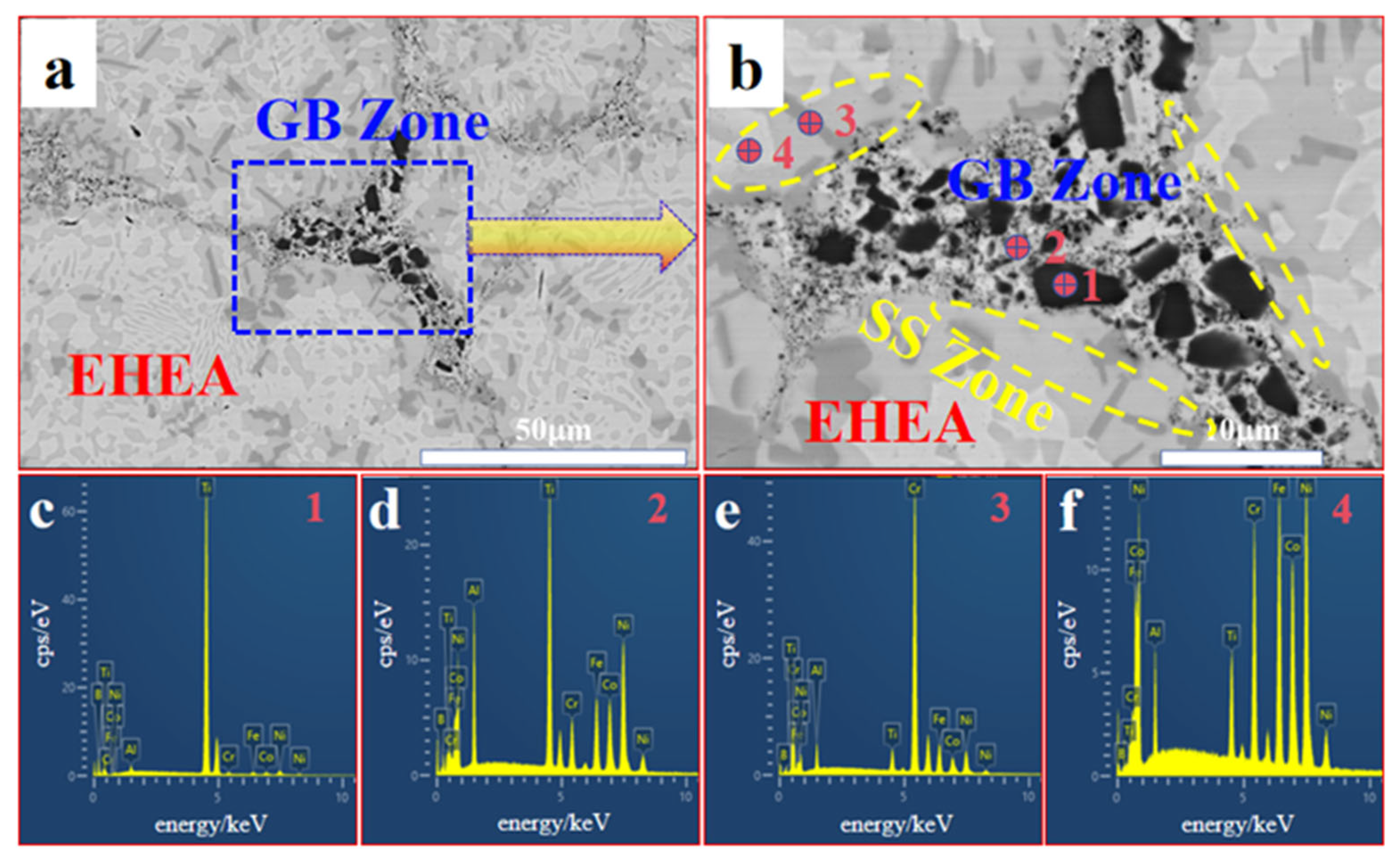
| Sample | Point | Al | Co | Cr | Fe | Ni | Ti | B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-Sintered | 1 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.7 | 2.3 | 75.5 | 16.5 |
| 2 | 16.5 | 16.5 | 3.4 | 9.1 | 38.0 | 16.3 | 0.2 | |
| 3 | 5.2 | 6.1 | 58.0 | 8.0 | 10.6 | 6.6 | 5.5 | |
| 4 | 5.5 | 19.1 | 14.3 | 20.9 | 33.6 | 6.6 | 0 | |
| FC | 1 | 3.3 | 2.7 | 1.0 | 2.4 | 6.4 | 46.2 | 38.1 |
| 2 | 13.7 | 15.9 | 11.2 | 16.7 | 30.8 | 11.3 | 0.3 | |
| 3 | 3.7 | 6.7 | 56.1 | 9.5 | 12.0 | 3.9 | 8.1 | |
| 4 | 6.9 | 19.7 | 12.8 | 20.3 | 32.9 | 7.4 | 0 | |
| AC | 1 | 2.4 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1.4 | 3.8 | 58.0 | 30.9 |
| 2 | 15.0 | 14.3 | 4.8 | 10.3 | 35.3 | 17.5 | 2.8 | |
| 3 | 6.5 | 9.2 | 40.5 | 8.8 | 21.0 | 6.7 | 7.4 | |
| 4 | 5.8 | 20.1 | 13.2 | 21.4 | 33.5 | 6.0 | 0 | |
| WC | 1 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 1.9 | 61.2 | 34.0 |
| 2 | 11.6 | 11.9 | 5.6 | 10.2 | 25.9 | 26.2 | 8.6 | |
| 3 | 3.7 | 5.2 | 65.3 | 8.9 | 9.0 | 3.6 | 4.3 | |
| 4 | 4.7 | 20.1 | 14.4 | 22.0 | 34.2 | 4.6 | 0 |
| Status | Zone | Harness |
|---|---|---|
| As-Sintered | 546.5 ± 22.3 | |
| FC | Matrix | 601.0 ± 27.3 |
| GB Zone | 653.1 ± 24.8 | |
| Average | 627.0 ± 26.1 | |
| AC | Matrix | 551.3 ± 11.8 |
| GB Zone | 591.2 ± 34.3 | |
| Average | 571.3 ± 23.1 | |
| WC | Matrix | 511.6 ± 18.9 |
| GB Zone | 574.7 ± 51.9 | |
| Average | 543.2 ± 35.4 |
| Status | Zone | Harness |
|---|---|---|
| As-Sintered | 546.5 ± 22.3 | |
| FC | Matrix | 601.0 ± 27.3 |
| GB Zone | 653.1 ± 24.8 | |
| Average | 627.0 ± 26.1 | |
| AC | Matrix | 551.3 ± 11.8 |
| GB Zone | 591.2 ± 34.3 | |
| Average | 571.3 ± 23.1 | |
| WC | Matrix | 511.6 ± 18.9 |
| GB Zone | 574.7 ± 51.9 | |
| Average | 543.2 ± 35.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, F.; Zhou, Y.; Shao, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Ren, B. Influence of Cooling Methods on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TiB2@Ti/AlCoCrFeNi2.1 Eutectic High-Entropy Alloy Matrix Composites. Coatings 2025, 15, 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091002
Guo F, Zhou Y, Shao Y, Jiang Q, Ren B. Influence of Cooling Methods on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TiB2@Ti/AlCoCrFeNi2.1 Eutectic High-Entropy Alloy Matrix Composites. Coatings. 2025; 15(9):1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091002
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Fuqiang, Yajun Zhou, Yayun Shao, Qinggang Jiang, and Bo Ren. 2025. "Influence of Cooling Methods on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TiB2@Ti/AlCoCrFeNi2.1 Eutectic High-Entropy Alloy Matrix Composites" Coatings 15, no. 9: 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091002
APA StyleGuo, F., Zhou, Y., Shao, Y., Jiang, Q., & Ren, B. (2025). Influence of Cooling Methods on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TiB2@Ti/AlCoCrFeNi2.1 Eutectic High-Entropy Alloy Matrix Composites. Coatings, 15(9), 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091002







