Plasma-Induced Amino HBP/Ag Nanoparticle-Grafted PP Melt-Blown Nonwoven Fabric and Its Antibacterial Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
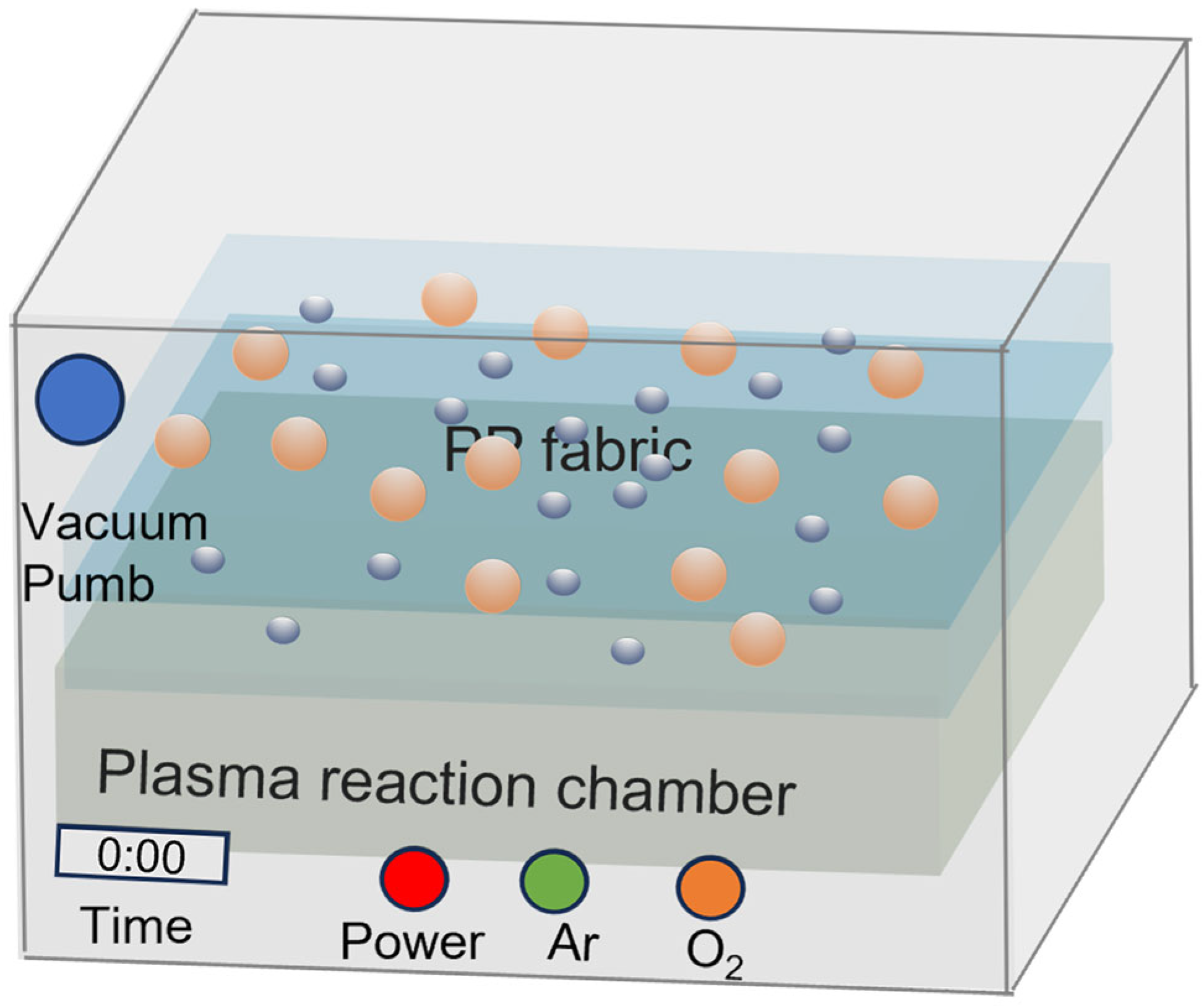
2.2. Preparation of Ag NP-Grafted PP Fabrics
2.3. Characterization of Ag NP-Coated PP Fabric
3. Results and Discussion
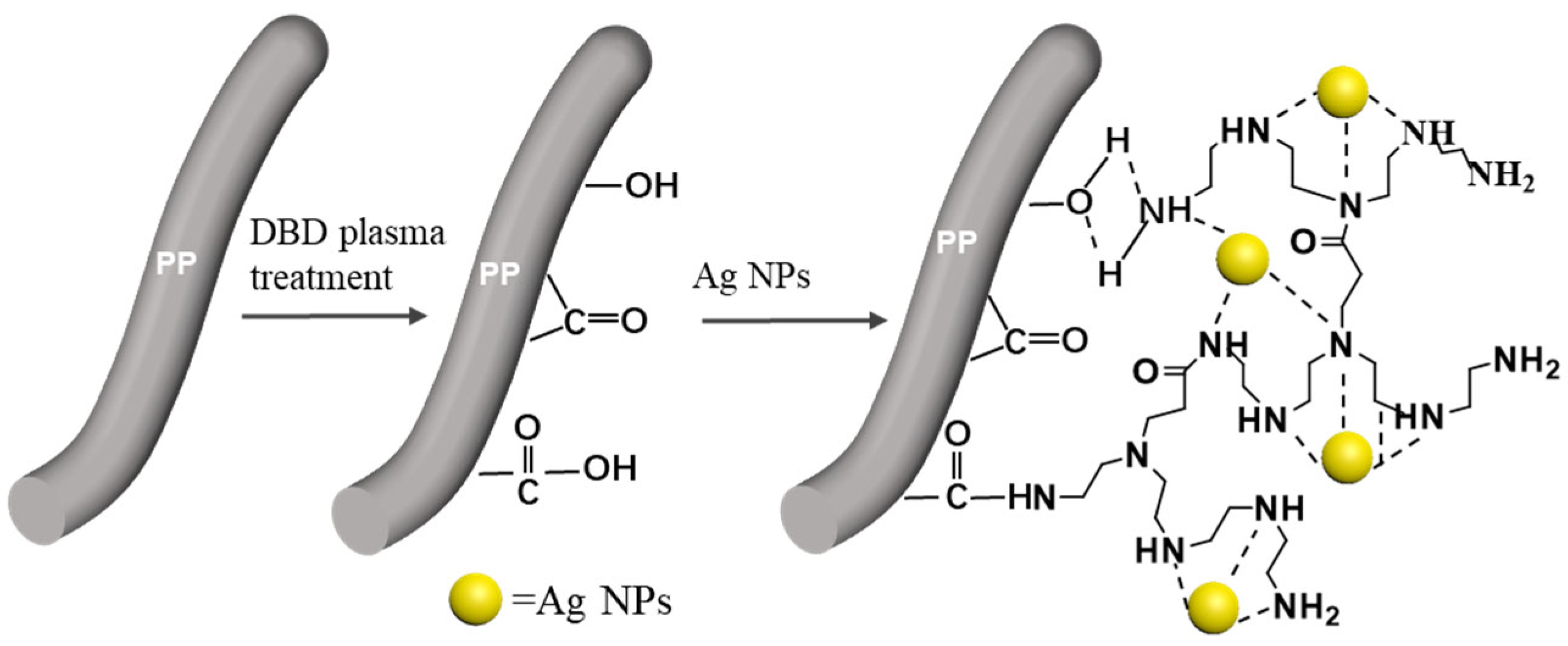
3.1. Mechanism of Plasma Treatment
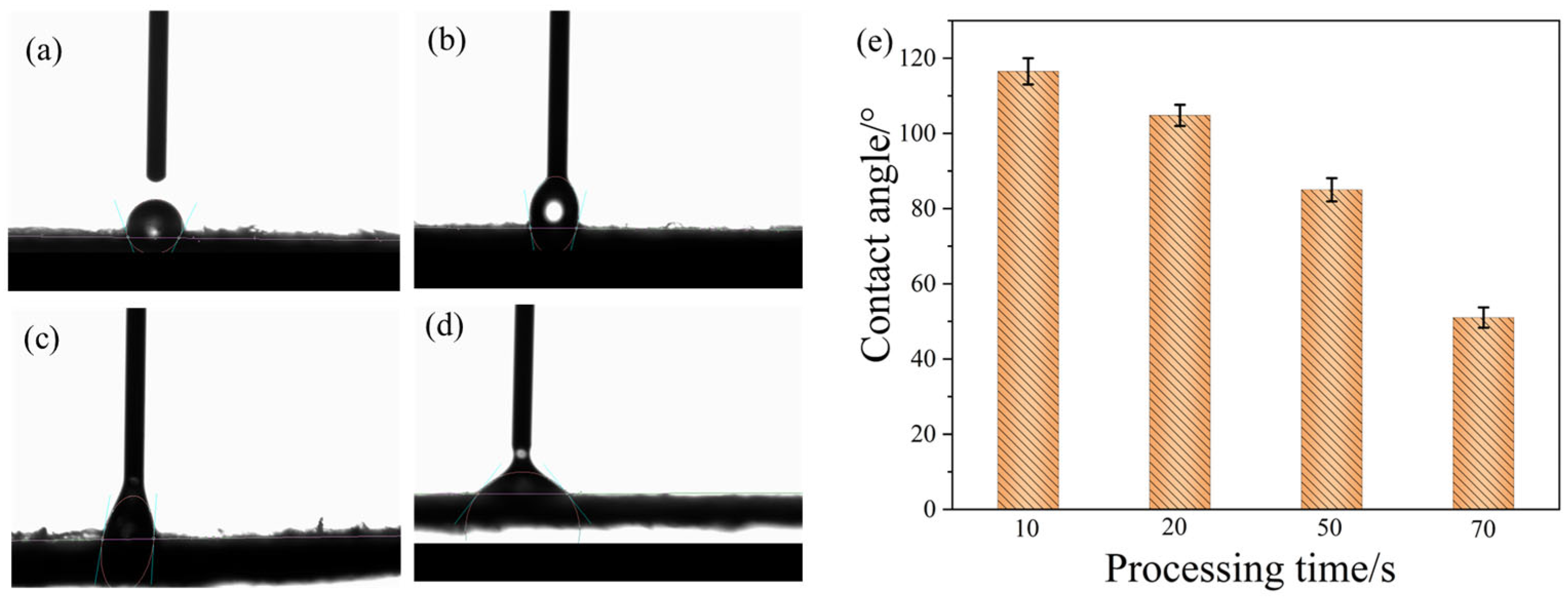
3.2. Surface Wettability Testing of the PP Fabric
3.3. Breaking Strength of the PP Fabric
3.4. Mechanism of Impregnation Finishing
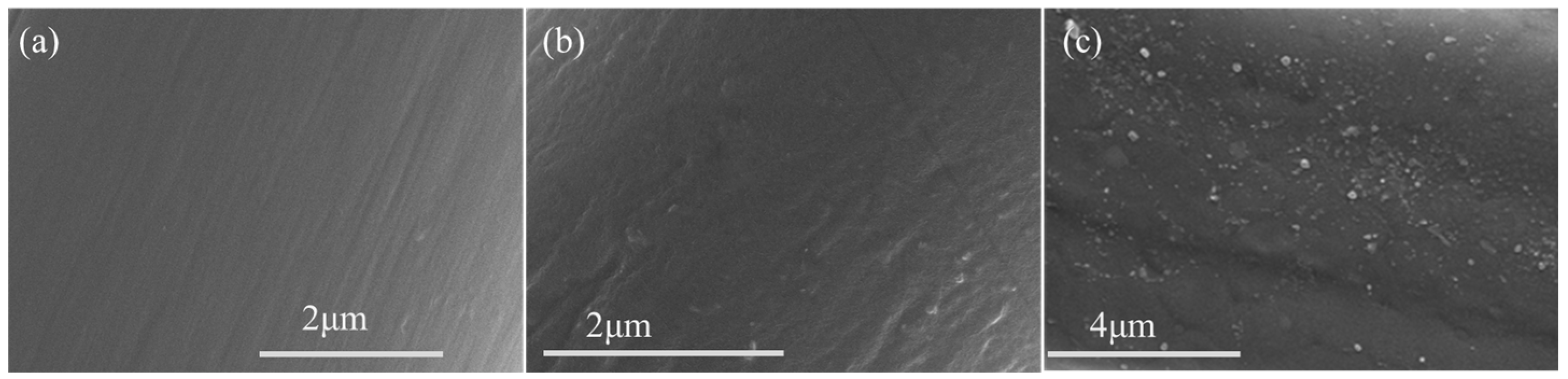
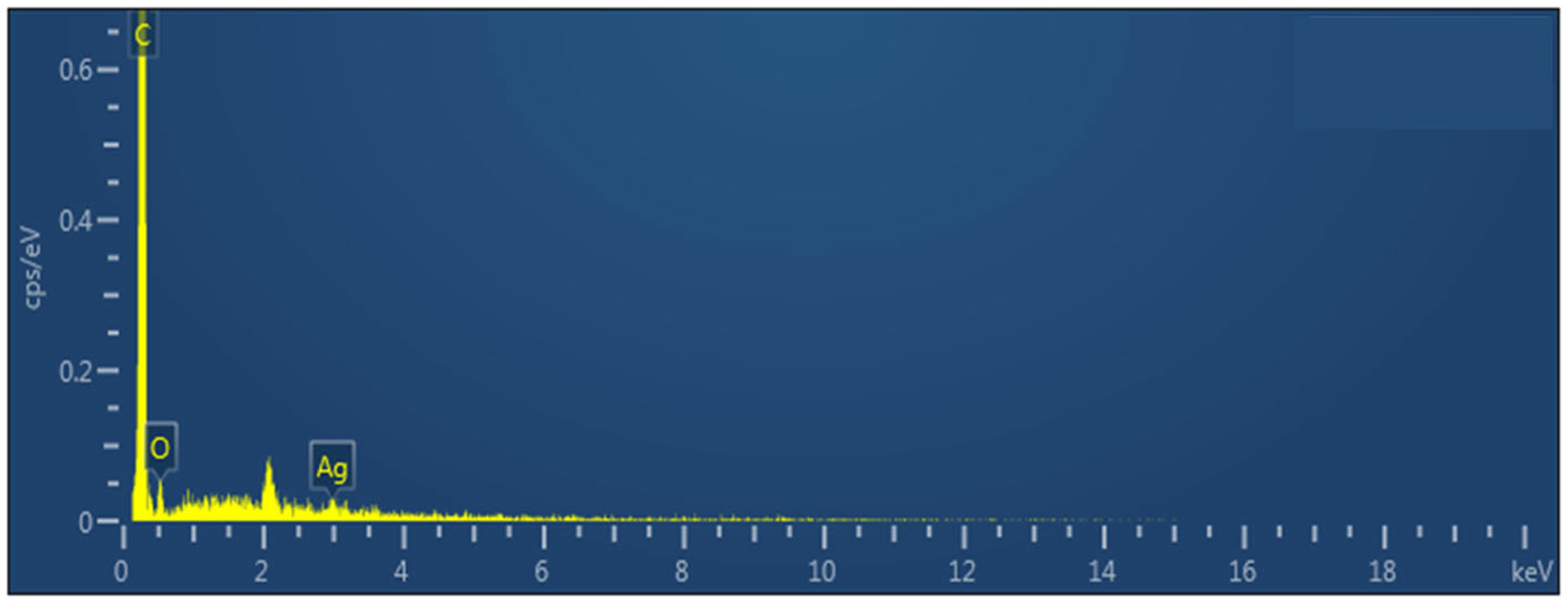
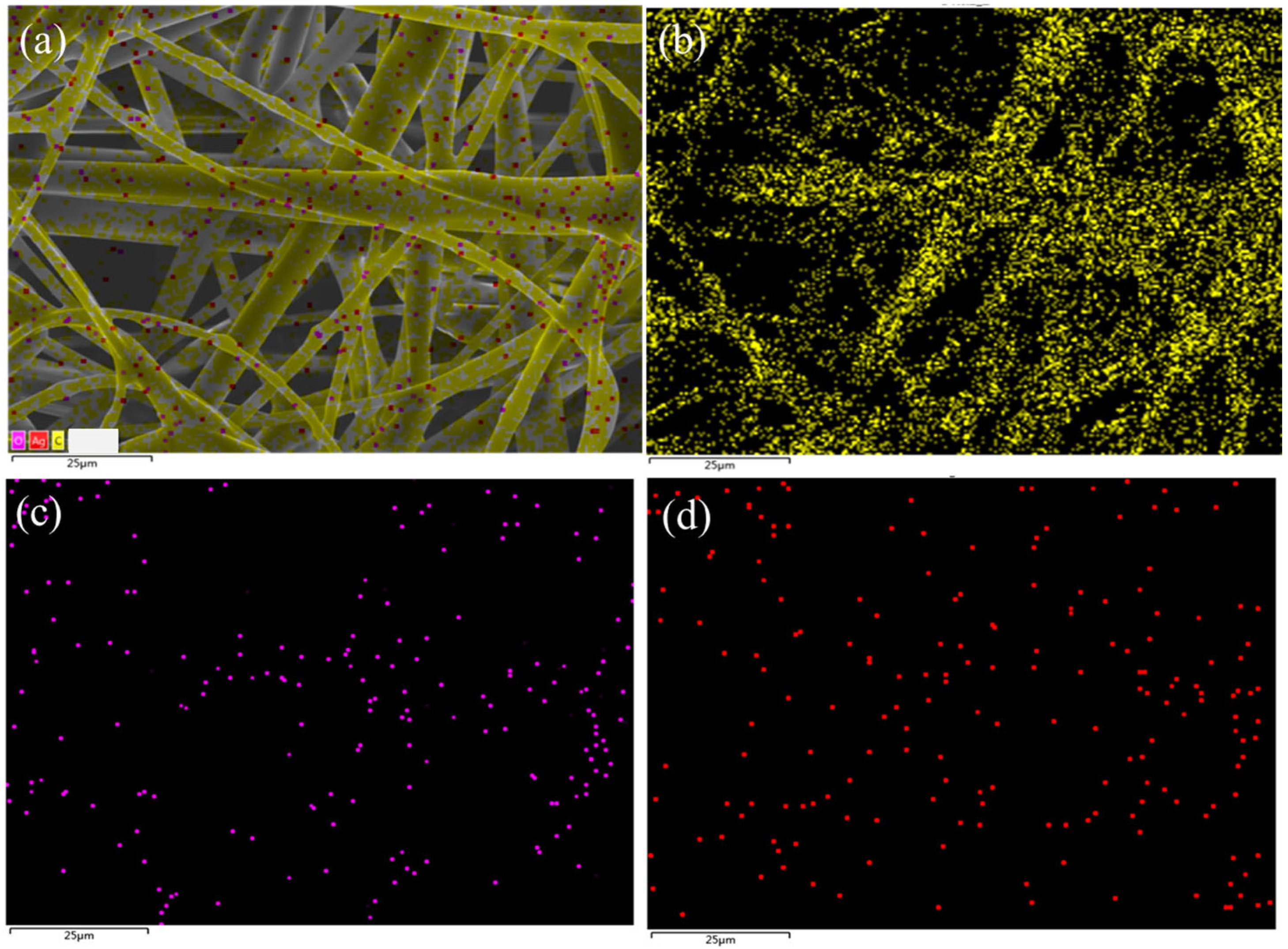
3.5. Characterization of Ag NP-Coated PP Fabric
3.6. Antibacterial Properties of Ag NP-Coated PP Fabric
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alassod, A.; Abedalwafa, M.; Xu, G. Evaluation of polypropylene melt blown nonwoven as the interceptor for oil. Environ. Technol. 2021, 42, 2784–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łatwińska, M.; Sójka-Ledakowicz, J..; Chruściel, J. PLA and PP composite nonwoven with antimicrobial activity for filtration applications. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 2016, 2510372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Shahid, M.; Mahmud, N. Research and application of polypropylene: A review. Discov. Nano 2024, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkataraman, D.; Shabani, E.; Park, J. Advancement of nonwoven fabrics in personal protective equipment. Materials 2023, 16, 3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Pei, J.; Li, X.; Guo, Q. Preparation, mechanical and electric properties of polypropylene fiber reinforced lead zirconate titanate flexible materials. Ferroelectrics 2019, 540, 162–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Song, L.; Shi, Q.; Luan, S.; Yin, J. Antibacterial and Hemocompatibility Switchable Polypropylene Nonwoven Fabric Membrane Surface. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2013, 5, 5260–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernakova, L.; Szabova, R.; Wolfova, M.; Bucek, A.; Cernak, M. Surface modification of polypropylene nonwoven after plasma activation at atmospheric pressure. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2007, 15, 64–65. [Google Scholar]
- Brindha, R.; Thilagavathi, G.; Viju, S. Development of Nettle-Polypropylene-Blended Needle-Punched Nonwoven Fabrics for Oil Spill Cleanup Applications. J. Nat. Fibers 2020, 17, 1439–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Wan, L.; Xu, Z. Surface hydrophilization of microporous polypropylene membrane by grafting zwitterionic polymer for anti -biofouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 362, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yu, H.; Tang, Z.; Liu, L.; Yan, M.; Gu, J.; Wei, X. Reducing protein fouling of a polypropylene microporous membrane by CO2 plasma surface modification. Desalination 2009, 244, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wan, L.; Xu, Z. Surface engineering of microporous polypropylene membrane for antifouling: A mini-review. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2011, 25, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, T.; Kellermann, S.; Münstedt, M. Different surface treatments to improve the adhesion of polypropylene. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2000, 14, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, R.; Yoshitani, Y.; Mitani, K.; Niibe, M.; Nakano, Y.; Azuma, C.; Mukai, T. Effects of air-based nonequilibrium atmospheric pressure plasma jet treatment characteristics of polypropylene film surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 509, 144910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, S.; Ge, M. Surface modification of polypropylene non-woven fabric for improving its hydrophilicity. Surf. Eng. 2018, 34, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Russo, P.; Ferraro, P.; Pagliarulo, V. Plasma treatment application to improve interfacial adhesion in polypropyle-flax fabric composite laminates. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 1787–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Jelil, R. A review of low-temperature plasma treatment of textile materials. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 5913–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Cheng, C.; Wang, R.; Li, X. Effect of Fiber Surface Morphology on the Hydrophilicity Modification of Cold Plasma-Treated Polypropylene Nonwoven Fabrics. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 2480–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ráhel’, J.; Šimor, M.; Černák, M.; Štefečka, M.; Imahori, Y.; Kando, K. Hydrophilization of polypropylene nonwoven fabric using surface barrier discharge. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 169, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaleh, B.; Parvin, P.; Wanichapichart, P.; Pourakbar, S.; Reyhani, A. Induced super hydrophilicity due to surface modification of polypropylene membrane treated by O2 plasma. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 1655–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Jiao, Y.; Sun, Q.; Li, J. Preparation, characterization, and antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles embedded into cellulose aerogels. Polym. Compos. 2016, 37, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Hua, B.; Ji, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, M. Preparation of silver nanoparticles with hydrophobic surface and their polyester based nanocomposite fibres with excellent antibacterial properties. Mater. Res. Innov. 2014, 18, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, R.; Shen, L.; Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Fu, F.; Fu, Y.; Liu, X. Enhancing the surface affinity with silver nano-particles for antibacterial cotton fabric by coating carboxymethyl chitosan and L-cysteine. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 497, 143673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Lu, F.; Zou, Y.; Liu, J.; Rong, B.; Li, Z.; Dai, F.; Wu, D.; Lan, L. In situ reduction of silver nanoparticles by chitosan-l-glutamic acid/hyaluronic acid: Enhancing antimicrobial and wound-healing activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 173, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanshenas, M.; Shateri-Khalilabad, M. The effect of alkali pre-treatment on formation and adsorption of silver nanoparticles on cotton surface. Fibers Polym. 2012, 13, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rafie, M.; Shaheen, T.; Mohamed, A.; Hebeish, A. Bio-synthesis and applications of silver nanoparticles onto cotton fabrics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, C.; Windler, L.; von Goetz, N.; Lehmann, R.; Schuppler, M.; Hungerbühler, K.; Heuberger, M.; Nowack, B. Characterization of silver release from commercially available functional (nano)textiles. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montazer, M.; Shamei, A.; Alimohammadi, F. Synthesizing and stabilizing silver nanoparticles on polyamide fabric using silver-ammonia/PVP/UVC. Prog. Org. Coat. 2012, 75, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Gu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ke, X.; Liu, X. Antibacterial cotton fabric with enhanced durability prepared using L-cysteine and silver nanoparticles. Fibers Polym. 2017, 18, 2204–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadadi, B.; Bordbar, M.; Yeganeh-Faal, A.; Nasrollahzadeh, M. Green synthesis of Ag nanoparticles/clinoptilolite using Vaccinium macrocarpon fruit extract and its excellent catalytic activity for reduction of organic dyes. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 719, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X.; Chen, Y. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles and antibacterial property of silk fabrics treated by silver nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Ke, H.; Yang, T.; Peng, Q.; Ge, J.; Yao, L.; Xu, S.; Ding, Z.; Pan, G. Enhanced thermal and antibacterial properties of stereo-complexed polylactide fibers doped with nano-silver. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 775333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, D.R.; Santese, F.; Toth, R. Simple, fast, and accurate in silico estimations of contact angle, surface tension, and work of adhesion of water and oil nanodroplets on amorphous polypropylene surfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2855–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Tang, T.; Amirfazli, A. Fabrication of polymeric surfaces with similar contact angles but dissimilar contact angle hysteresis. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 408, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, H.T.; Vu Thi Hong, K.; Nguyen, T.B. Surface modification by the DBD plasma to improve the flame-retardant treatment for dyed polyester fabric. Polymers 2021, 13, 3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Nie, X.; Jin, Z. Dual dielectric barrier discharge plasma treatments for synthesis of Ag–TiO2 functionalized polypropylene fabrics. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 7734–7741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relvas, C.; Castro, G.; Rana, S. Characterization of physical, mechanical and chemical properties of quiscal fibres: The influence of atmospheric DBD plasma treatment. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2015, 35, 863–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, K.V.; Chandwani, N.; Kikani, P. Optimization and surface modification of silk fabric using DBD air plasma for improving wicking properties. J. Text. Inst. 2018, 109, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Xu, W.; Huang, F. Polyester fabric coated with Ag/ZnO composite film by magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 390, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Fabrication of cotton fabrics with durable antibacterial activities finishing by Ag nanoparticles. Text. Res. J. 2019, 89, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radić, N.; Obradović, B.M.; Kostić, M. Deposition of silver ions onto DBD and DCSBD plasma treated nonwoven polypropylene. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 5006–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Samples | Ag Contents (mg/Kg) | Bacterial Colonies (cfu/mL) | Ratio (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. coli | S. aureus | E. coli | ||
| PP fabric | - | 2.27 × 106 | 1.8 × 105 | - | - |
| Ag NP-coated | 20 | 1.21 × 104 | 1.27 × 102 | 99.5 | 99.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Gao, W.; Zhang, G. Plasma-Induced Amino HBP/Ag Nanoparticle-Grafted PP Melt-Blown Nonwoven Fabric and Its Antibacterial Performance. Coatings 2025, 15, 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15080947
Chen H, Zhang W, Gao W, Zhang G. Plasma-Induced Amino HBP/Ag Nanoparticle-Grafted PP Melt-Blown Nonwoven Fabric and Its Antibacterial Performance. Coatings. 2025; 15(8):947. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15080947
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Hongxia, Wei Zhang, Weidong Gao, and Guangyu Zhang. 2025. "Plasma-Induced Amino HBP/Ag Nanoparticle-Grafted PP Melt-Blown Nonwoven Fabric and Its Antibacterial Performance" Coatings 15, no. 8: 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15080947
APA StyleChen, H., Zhang, W., Gao, W., & Zhang, G. (2025). Plasma-Induced Amino HBP/Ag Nanoparticle-Grafted PP Melt-Blown Nonwoven Fabric and Its Antibacterial Performance. Coatings, 15(8), 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15080947







