Sustainable Marine Coatings: Comparing the Costs, Benefits, and Impacts of Biocidal and Biocide-Free Paints
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
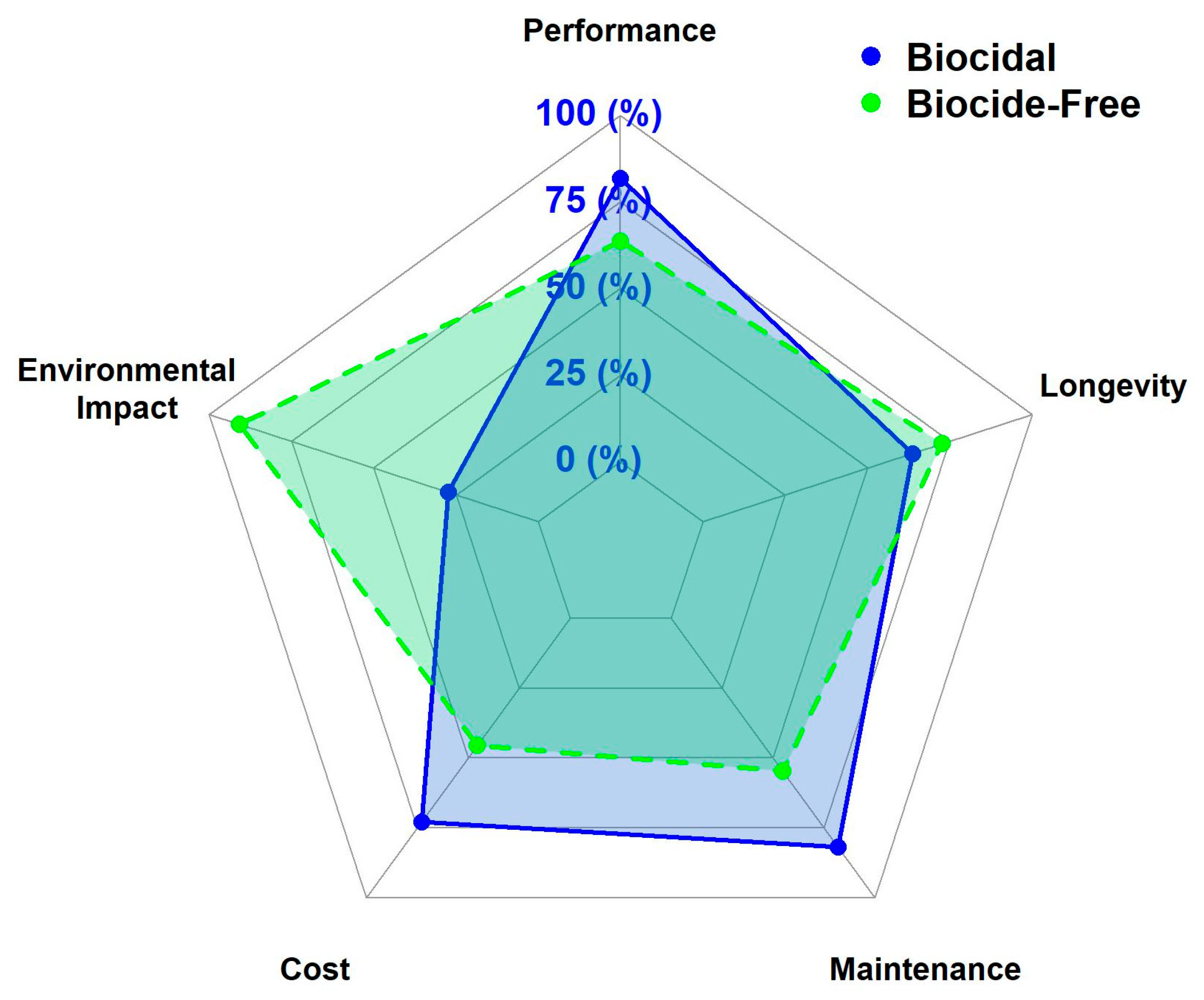
3.1. Comparing Biocidal vs. Biocide-Free Coatings
3.2. Antifouling Performance
3.3. Longevity and Durability
3.4. Adhesion and Surface Properties
3.5. Controlled-Release and Hydrodynamic Strategies in Antifouling Coatings
3.6. Innovations and Emerging Materials
3.7. Toxicity and Environmental Impact
3.8. Economic Considerations of Biocidal and Biocide-Free Antifouling Coatings
3.9. Regulatory Pressures and Policy Trends
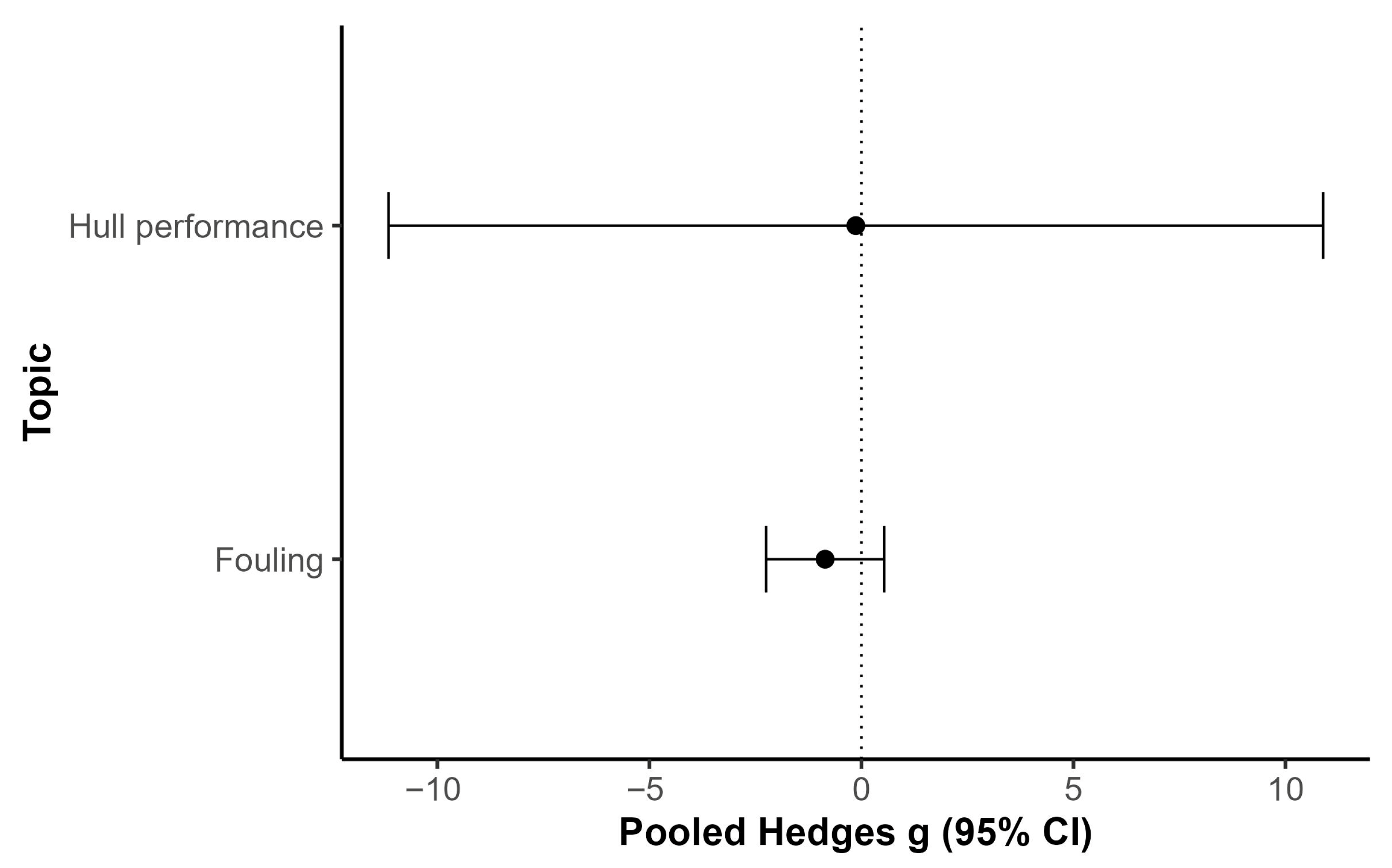
3.10. Meta-Analysis of Biocidal vs. Biocide-Free Coating Performance
3.11. Methodologies, Knowledge Gaps and Future Research
3.12. Limitations of the Database Search Scope
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lindholdt, A.; Dam-Johansen, K.; Olsen, S.M.; Kiil, S. Estimation of long-term drag performance of fouling control coatings using biocide leaching and drag measurements. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2015, 12, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watermann, B.T.; Daehne, B.; Sievers, S.; Dannenberg, R.; Overbeke, J.C.; Heemken, O.; Linders, J. Bioassays and selected chemical analysis of biocide-free antifouling coatings. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 1530–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, L.; Han, B. Zwitterionic Cellulose Nanocrystals/Deacetylated Chitosan Nanospheres Hybrid Coating for Antibiofouling. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2025, 64, 2157–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, M.; Martinelli, E.; Sardo, A.; Gallo, A. Posidonia oceanica (L.) (Delile, 1813) extract in PDMS-based antifouling coatings: Bioactivity and ecological impact. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 18480–18490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; The PRISMA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V. Distribution theory for Glass’s estimator of effect size and related estimators. J. Educ. Stat. 1981, 6, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omae, I. General aspects of tin-free antifouling paints. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 3431–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, H.E.; da Gama, B.A.P.; Pereira, R.C. Antifouling activity of seaweed extracts from the coast of Rio de Janeiro (Brazil) against barnacle larvae. Braz. J. Oceanogr. 2007, 55, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller-Karanassos, C.; Arundell, M.; Readman, J. Environmental concentrations of antifouling paint biocides in estuarine waters of the southwest UK. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 270, 115754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafforn, K.A.; Lewis, J.A.; Johnston, E.L. Antifouling strategies: History and regulation, ecological impacts and mitigation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, K.; Erdogan, U.H.; Cavas, L. Prevention of biofouling on aquaculture nets with eco-friendly antifouling paint formulation. Color. Technol. 2020, 136, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, M.C.; García, M.T.; Stupak, M.E.; Blustein, G. Hacia una reducción del contenido de cobre en pinturas antiincrustantes. Matéria Rio J. 2015, 20, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.G.; Goel, A. Evaluating fouling-resistance and fouling-release performance of amphiphilic polyurethane coatings. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 3693–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, J.; Ytreberg, E.; Eklund, B. Toxicity of anti-fouling paints for use on ships and leisure boats to non-target organisms representing three trophic levels. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, M.; García, M.; del Amo, B.; Blustein, G.; Stupak, M. Core-shell pigments in antifouling paints. Surf. Coat. Int. Part B Coat. Trans. 2003, 86, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkady, E.M.; Tadros, H.R.Z.; Soliman, M.A.; El-Fakharany, E.M. Marine antifouling agents based on bioactive compounds from soft corals: Field evaluation of natural product-based coatings. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2024, 50, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyazkilic, Z.; Faccini, M.; Escobar, A.M.; Bautista, L. Eco-friendly capsaicin-containing water-based antifouling coatings for marine aquaculture. Coatings 2023, 13, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carteau, D.; Vallée-Réhel, K.; Linossier, I.; Faÿ, F. Development of environmentally friendly antifouling paints using biodegradable polymers. Prog. Org. Coat. 2014, 77, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, C.D.; Truby, K.; Stein, J.; Wiebe, D.; Holm, E.; Wendt, D. Temporal and spatial variations in macrofouling of silicone fouling-release coatings. Biofouling 2000, 16, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, R.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, H.; Song, D.; Wang, J. Photocatalytic antifouling coating based on carbon nitride with dynamic acrylate boron fluorinated polymers. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Hölken, I.; Gapeeva, A.; Filiz, V.; Adelung, R.; Baum, M. Development and characterization of mechanically durable silicone-polythiourethane composites modified with tetrapodal shaped ZnO particles for potential application as fouling-release coating in the marine sector. Materials 2018, 11, 2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.R.; Tulcidas, A.V.; Ferreira, O.; Bayón, R.; Igartua, A.; Mendoza, G.; Mergulhão, F.J.M.; Faria, S.I.; Gomes, L.C.; Carvalho, S.; et al. Assessment of the environmental compatibility and antifouling performance of an innovative biocidal and foul-release multifunctional marine coating. Environ. Res. 2021, 198, 111219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scardino, A.J.; Fletcher, L.E.; Lewis, J.A. Fouling control using air bubble curtains: Protection for stationary vessels. J. Mar. Eng. Technol. 2009, 8, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendt, D.E. Methods of assessing antifouling and foul-release efficacy of non-toxic marine coatings. Green Mater. 2017, 5, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellio, C.; Berge, J.P.; Beaupoil, C.; Le Gal, Y.; Bourgougnon, N. Screening of marine algal extracts for anti-settlement activities against microalgae and macroalgae. Biofouling 2002, 18, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, S.; Oliveira, F.R.; Costa, J.P.; Vilar, V.J.P.; Santos, L.H.M.L.M. Hydrophobic DES Based on Menthol and Natural Oils: Sustainable Solvents for Antifouling Marine Coatings. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 6945–6955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.; Bolam, T. Copper speciation survey from UK marinas, harbours and estuaries. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faÿ, F.; Gouessan, M.; Linossier, I.; Réhel, K. Additives for efficient biodegradable antifouling paints: An eco-design approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vourna, P.; Falara, P.P.; Hristoforou, E.V.; Papadopoulos, N.D. Corrosion and antifouling behavior of a new biocide-free antifouling paint for ship hulls under both artificially simulated and natural marine environment. Materials 2025, 18, 3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, Q.; Han, D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Pei, Y.; Duan, J.; Hou, B. Progress in anti-biofouling materials and coatings for the marine environment. J. Environ. Sci. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venettacci, S.; Ponticelli, G.S.; Tagliaferri, F.; Guarino, S. Environmental and economic impact of an innovative biocide-free antifouling coating for naval applications. Materials 2023, 16, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Wu, S.; Xing, S.; Wang, T.; Hou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, W. Research progress of marine anti-fouling coatings. Coatings 2024, 14, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrier, A.J.; Carve, M.; Shimeta, J.; Walker, T.R.; Zhang, X.; Oakes, K.D.; Jha, K.C.; Charlton, T.; Stenzel, M.H. Transitioning towards environmentally benign marine antifouling coatings. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1175270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F.; Esmaeili, N. Marine biofouling and the role of biocidal coatings in balancing environmental impacts. Biofouling 2023, 39, 661–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, E.; Gardner, H.; Hunsucker, K.Z.; Swain, G. The effect of grooming on five commercial antifouling coatings. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 836555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, B.N.; Thomas, P.J.; Thomas, P.; Greve, M.M. Antibiofouling coatings for marine sensors: Progress and perspectives on materials, methods, impacts, and field trial studies. ACS Sens. 2025, 10, 1600–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, H.; Yagi, M.; Kawachi, M. Application of rotating cylinder method for ecotoxicological evaluation of antifouling paints. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2012, 94, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitworth, P.; Aldred, N. Importance of duration, duty-cycling and threshold intensity for UV-B/C LED antifouling effects on marine biofilm. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 809011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naval Institute. Marine Fouling and Its Prevention. Contribution No. 580 from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution; United States Naval Institute, Prepared for the Bureau of Ships, Navy Department: Annapolis, MD, USA, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Milne, A. Roughness and drag from the marine chemist’s viewpoint. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Marine Roughness and Drag (Paper No. 12), Weir Lecture Hall, Royal Institution of Naval Architects, London, UK, 29 March 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Champ, M.A.; Seligman, P.F. An introduction to organotin compounds and their use in antifouling coatings. In Organotin: Environmental Fate and Effects, 1st ed.; Champ, M.A., Seligman, P.F., Eds.; Chapman & Hall: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, A.; Abel, P.D.; Arnold, D.W.; Milne, A. Cost–benefit analysis of the use of TBT: The case for a treatment approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 258, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champ, M.A. Economic and environmental impacts on ports and harbors from the convention to ban harmful marine anti-fouling systems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 46, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohlander, J. Review of Options for in-Water Cleaning of Ships; MAF Biosecurity New Zealand Technical Paper No. 2009/42; Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry: Wellington, New Zealand, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Candries, M.; Anderson, C.D.; Atlar, M. Foul release systems and drag: Consolidation of technical advances in the protective and marine coatings industry. In Proceedings of the Protective Coatings Europe (PCE) 2001 Conference, Antwerp, Belgium, 5–8 June 2001; pp. 273–286. [Google Scholar]
- Swain, G.; Herpe, S.; Ralston, E.; Tribou, M. Short-term testing of antifouling surfaces: The importance of colour. Biofouling J. Bioadhesion Biofilm Res. 2006, 22, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, M.; Swain, G.W. Managing the use of copper-based antifouling paints. Environ. Manag. 2007, 39, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.-R.-N.; Kim, U.-J.; Lee, I.-S.; Choi, M.; Oh, J.-E. Assessment of organotin and tin-free antifouling paints contamination in the Korean coastal area. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 99, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnie, A.A. Improved estimates of environmental copper release rates from antifouling products. Biofouling 2006, 22, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Coating Type and Examples | Typical Strengths | Typical Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Biocidal Antifouling Paints, e.g., copper-based ablative paints (self-polishing co-polymers), zinc oxides | - Proven high efficacy against a broad range of fouling organisms (hard and soft fouling) by continuously releasing biocides. - Long history of use with well-understood performance; generally lower upfront cost than advanced new coatings. - Self-polishing types renew the active surface by slow erosion, maintaining antifouling effect and a smoother hull (reducing drag) over time. | - Environmental toxicity: leaches toxic biocides (copper, organotins, or booster biocides) into water, harming non-target marine life and accumulating in sediments. Under tightening regulations, many biocides are restricted or banned. - Coating layer wears out and requires regular reapplication (typically every 1–3 years), adding maintenance cost and downtime. - Only mitigates fouling to an extent—microfilm/slime still forms, especially during idle periods, so hulls can still accumulate slime and some fouling if vessel is stationary. Fouling that does occur may transport invasive species. - Optimal performance depends on usage: If the ship operates outside its intended profile (long lay-ups, low speed), heavy growth can still occur. |
| Silicone-Based and Fluoropolymer Foul-Release Coatings, e.g., PDMS silicone elastomers (Intersleek® 700, AkzoNobel, Amsterdam, Netherlands), fluorinated polymers (Intersleek 900, AkzoNobel, Amsterdam, Netherlands), other low-surface-energy non-toxic paints | - Non-toxic, biocide-free: do not poison marine life (environmentally benign). No harmful leaching, aligning with eco-friendly requirements. - Low surface energy and elasticity: organisms attach weakly; water flow can easily shear off fouling. A smooth, “slippery” hull surface means any growth is lightly held and detaches when the vessel is at speed. - This yields fuel savings by reducing drag—e.g., one study saw ~4–8% fuel consumption reduction in the first year with a non-toxic coating. - Commercially available alternatives to biocides; proven effective on fast, active vessels (e.g., naval ships, cruise liners) when operational profiles are suitable. | - Requires activity or cleaning: Optimal performance only at high speeds and sufficient water flow. During long idle periods or low speeds, slime and larvae can settle (no biocidal action to stop them), so fouling still grows if not periodically cleaned. - Fragile coating film: Silicone-based paints have poor adhesion to the hull and are soft, so they are susceptible to damage (scratching, peeling). They often need special primers and careful handling; mechanical abrasion (even aggressive cleaning) can ruin the coating. - High initial cost and application complexity—these coatings are expensive and usually require professional application in drydock (multi-layer systems). - Foul-release means organisms are not killed—they can be carried alive to new regions. Thus, if fouling is not removed promptly, there’s a higher risk of transporting invasive species with these coatings. |
| Hydrogel and Zwitterionic Polymer Coatings, e.g., hydrophilic hydrogel-based paints, PEG- or zwitterion-grafted surfaces, amphoteric polymer brushes | - Hydrophilic “slippery” surface: binds a layer of water, which resists protein and microbe adhesion—effectively reducing biofilm formation and initial fouling settlement. Zwitterionic polymers, for example, show excellent prevention of bacterial and algal biofilms by this mechanism. - No toxic biocides released; truly non-toxic approach (coating itself is benign), so minimal environmental impact. - Has shown strong fouling reduction in tests—preventing buildup of slime can also improve ship fuel efficiency. One study with a hydrogel-like coating noted a 4–8% drag reduction from fouling prevention. - Can be combined with foul-release matrices to get both effects. For instance, silicone–hydrogel hybrids or amphiphilic zwitterionic paints aim to retain durability while achieving ultra-low fouling adhesion. | - Durability issues: Many hydrophilic coatings (hydrogels, polymer brushes) have limited mechanical robustness—they can swell, soften or erode in seawater. Fast degradation or hydrolysis can undermine long-term performance. Balancing water-solubility (for antifouling function) with stability is challenging. - Adhesion and longevity challenges: Grafting or coating hydrophilic polymers onto hull surfaces is complex; coatings may delaminate or wear off. Some require specialized surface chemistry to attach, raising application cost and complexity. Nanoparticle additives can improve strength, but if they agglomerate, effectiveness drops. - Efficacy in real ocean conditions is not yet fully proven—many results come from lab or short field trials. Long-term field data are limited, so uncertainty remains about performance over multiple years and in varied waters. - Often high cost and scaling difficulties: the materials (e.g., PEG, zwitterionic monomers) and techniques involved are expensive. These coatings are mostly experimental or pilot-stage, not widely commercial. |
| Natural Compound-Based Coatings, e.g., paints with bio-based antifoulants like capsaicin, zosteric acid, seaweed extracts, enzyme coatings | - Bio-derived antifoulants: use natural chemicals (from plants, algae, marine organisms) instead of heavy metals. This reduces persistent pollution—they tend to biodegrade and do not bio-accumulate like copper. - Some natural compounds can specifically inhibit fouling processes (e.g., prevent larval attachment or spore germination) with low toxicity to non-target species. For example, coatings with certain algal extracts showed significant mussel attachment reduction without harming test organisms. - Lower environmental impact overall—by replacing copper or synthetic biocides, these coatings aim to meet environmental regulations and avoid broad-spectrum toxicity. Many natural agents are selective or work in synergy with the organism’s biology (often making them less harsh on ecosystems). | - Variable/Lower efficacy: Natural additives are often less potent or broad-spectrum than traditional biocides. A given extract may work well on some fouling species (or microfouling) but not others (e.g., “no effect on macrofouler larvae” was noted in some cases). Copper-free formulations with natural boosters sometimes still perform weaker than copper paint and may allow more growth. - Limited longevity: Bio-based compounds can degrade or leach out faster in water, meaning the antifouling effect might diminish within months. Frequent reapplication or higher loading might be needed to sustain performance. - Many proposals are still unproven at scale—effective largely in lab tests or short-term panels. Field validation is lacking for many natural-product coatings, and some extracts that showed promise in the lab failed to work in real seawater conditions. - Practical challenges: Sourcing and formulating natural compounds can be costly or difficult (some antifoulants come from rare or protected species, limiting availability). Also, “natural” does not guarantee safety—in high doses, these compounds can still affect non-target marine life, so regulatory approval can be an obstacle. |
| Hybrid and Amphiphilic Coatings (Combined-Strategy Coatings), e.g., amphiphilic polymers with both hydrophobic (fluorocarbon, silicone) and hydrophilic (PEG, zwitterion) segments; silicone/fluoropolymer hybrids; fouling-release coatings with tethered or nano-encapsulated biocides | - Multi-mechanism synergy: Hybrid coatings amalgamate different antifouling strategies to cover each other’s gaps. For instance, amphiphilic surfaces present both hydrophobic and hydrophilic domains, deterring a wide range of organisms—the hydrophobic parts make it hard for macrofoulers to stick, while hydrophilic parts resist microbes and slime adhesion. This broad-spectrum approach can outperform single-mechanism coatings in diverse fouling conditions. - Can achieve better overall performance than either component alone. Silicone–fluoropolymer hybrids, for example, combine silicone’s elasticity with fluoropolymer’s harder, lower-energy surface—resulting in a coating with lower surface energy (high water contact angle) and improved foul-release effectiveness compared to pure silicone. Similarly, adding a bit of a hydrophilic or biocidal component to a fouling-release matrix can reduce slime build-up without sacrificing low adhesion for larger organisms. - Often designed for improved durability or adhesion by blending materials. (For example, adding a polyurethane or epoxy element to a silicone can increase hardness and adhesion, addressing silicone’s mechanical weaknesses while retaining foul-release properties.) Some hybrids also incorporate reinforcement (nano-additives, fibers) to extend service life. - May allow lower toxin usage: Hybrid concepts include embedding minimal biocides or anti-microbials in an inert matrix—providing protection against specific fouling (e.g., algal spores) but with far less biocide leaching than a fully toxic paint. This controlled release or contact-kill approach can reduce environmental impact compared to traditional paints. | - Formulation complexity: Combining disparate materials can lead to compatibility issues—phase separation, poor bonding between components, or unpredictable degradation. Such coatings can suffer reduced long-term stability if the ingredients do not integrate well. Achieving a uniform, stable hybrid coating is scientifically challenging. - Higher production cost: Multi-component systems (fluorinated groups + silicone, or polymer blends with nano-additives, etc.) are often expensive to produce and apply. Extra processing steps and specialized ingredients raise costs, which can hinder widespread adoption. - If a hybrid includes any biocidal ingredient, it is not fully non-toxic—it may still leach some chemicals (albeit less), so it does not completely eliminate environmental concerns. For example, a “copper-free” hybrid that still contains a small amount of copper or biocide tethered in the coating is not truly biocide-free. Such coatings could face regulatory scrutiny similar to low-biocide paints. - Potential performance trade-offs: combining traits might dilute the “best” of each. An amphiphilic coating, for instance, might not achieve as ultra-low surface energy as a pure fluoropolymer or as high a hydration layer as a pure hydrogel, so it could still allow some fouling in challenging conditions. Optimization is needed for each hybrid, and some designs may end up being only marginal improvements at high complexity. |
| “Smart” Coatings (Self-Healing and Stimuli-Responsive), e.g., self-healing silicone-polyurethane that repairs scratches via dynamic bonds; light-responsive coatings that change wettability; enzyme or bacteria-triggered release coatings | - Self-repairing capability: Coatings with self-healing chemistries (e.g., reversible covalent bonds, microcapsules) can automatically fix minor damage. This preserves a continuous antifouling surface and prolongs the coating’s lifetime. For example, a PDMS-polyurethane elastomer with disulfide bonds achieved rapid self-healing (within minutes to hours) of scratches, maintaining its antifouling function. Such coatings can also double as anticorrosive layers by healing barrier defects. - Stimuli-responsive antifouling: Some smart coatings actively change properties in response to environmental triggers. A prototype silicone with photo-sensitive additives can reversibly switch surface stiffness and wettability under UV/visible light, enhancing its fouling release when needed. This kind of “on-demand” adaptation can help counter different fouling scenarios (e.g., become more hydrophilic to shed biofilm, then revert to hydrophobic). - Multi-functional and adaptive: Smart coatings often integrate multiple functions—e.g., foul-release + self-healing + anti-corrosion. These advanced materials aim to extend service intervals and maintain performance over time by either repairing damage or adjusting to conditions. They represent a cutting-edge approach aligned with the future trend of responsive, sensor-enabled hull coatings. - Early studies show that such designs can significantly improve both antifouling efficacy and durability. For instance, an amphiphilic self-healing silicone-based coating achieved strong adhesion to the substrate and resisted both bacterial biofilm and algal adhesion, while also being highly elastic and tough. This demonstrates the promise of marrying fouling resistance with mechanical resilience. | - High complexity and cost: Smart coatings rely on novel chemistries (e.g., special polymers, functional microcapsules, nano-sensors) that are currently expensive and complicated to manufacture. Scaling these lab concepts to practical, affordable marine paints is non-trivial. The added complexity also raises chances of something failing (e.g., an encapsulated agent not releasing at the right time). - Unproven long-term in real conditions: Most such coatings are at the R&D or prototype stage. Their performance over multiple years in saltwater, under abrasion, UV exposure, etc., is largely unknown. For example, one self-healing coating showed slower healing in seawater vs. air, and excessive amounts of healing agent led to reduced flexibility/adhesion of the coating. These sensitive trade-offs need real-world validation. - Potential trade-offs in material properties: Embedding self-healing or responsive components can affect the coating’s hardness, strength, or adhesion. There is often a balance between having dynamic, mobile components and maintaining a robust coating. Achieving a smart coating that is as tough as conventional paints is a challenge (though progress is being made with new chemistries). - Not yet commercially available: As of now, these are mostly experimental. Regulatory approval, cost-effectiveness, and ease of application remain to be addressed. Field trials are needed to ensure that the “smart” features deliver tangible antifouling benefits in practice and do not degrade quickly under operational stresses. |
| Photocatalytic Coatings (Light-Activated Antifouling), e.g., TiO2 or ZnO nanoparticle-infused paints, doped visible-light photocatalysts, graphitic carbon nitride additives; UV-illuminated surfaces | - Active biofilm inhibition: Photocatalytic coatings contain light-activated catalysts that generate reactive oxygen species (e.g., OH· radicals) under illumination. These radicals kill or inhibit microorganisms on the surface, preventing biofilm (slime) formation and early-stage fouling. In effect, the coating continuously self-disinfects when exposed to light. This approach can dramatically reduce bacterial fouling on illuminated surfaces. - Non-depleting, eco-friendly mechanism: Unlike biocides, the catalyst is not consumed in the reaction—it can function as long as light is available. There is no ongoing release of toxic chemicals into the water, making it an environmentally friendly strategy. Only fouling organisms and organics at the surface are targeted (via oxidation), with minimal persistent residues. - Can be combined with other coating features for synergy. For example, integrating photocatalytic particles into a superhydrophobic coating yielded a dual effect: the superhydrophobicity prevented many spores from attaching initially and the photocatalysis killed micro-organisms, together effectively preventing biofilm establishment. Such hybrid designs show significantly improved performance in tests. | - Needs light to work: A major limitation is the requirement for UV or high-intensity light. Ship hulls receive very little UV light underwater (especially on the bottom in deep or turbid water), so photocatalytic antifouling is mostly effective on sun-lit areas or stationary structures near the surface. In low-light conditions or at night, the coating provides no active antifouling effect. - Limited spectrum efficiency: Many photocatalysts (like standard TiO2) only activate under UV radiation. Visible-light-activated variants exist, but still typically need strong illumination to be effective. This dependence on environmental conditions makes consistent performance hard to ensure on a moving vessel. - Fouling can shield the light: If organisms do start to grow (e.g., during dark periods or in shaded spots), they can form a film that blocks light from reaching the catalyst, thus stopping the protective effect. The method is better at preventing initial settlement than removing established fouling. - Material and durability challenges: Incorporating photocatalytic nanoparticles into paint must be done carefully—agglomeration of particles can reduce effectiveness, and particles must be securely embedded to avoid leaching. Long-term exposure to UV can also degrade the binder resin of coatings if not formulated properly. To date, these coatings are largely experimental; scaling them up and ensuring they maintain antifouling action over years (despite uneven light exposure) are ongoing challenges. |
| Superhydrophobic Coatings (Micro-Textured Water-Repellent Surfaces), e.g., nanostructured silicone or fluoropolymer coatings with lotus-leaf effect; rough hydrophobic sprays creating >150° water contact angle; slippery lubricant-infused surfaces (SLIPS) | - Extreme water repellency = self-cleaning: Superhydrophobic surfaces are engineered to repel water so strongly (contact angles often 150–170°) that water beads up and rolls off, carrying away dirt and organisms. This prevents initial fouling adhesion—marine algal spores and bacteria have trouble attaching because the surface is effectively “dry” and any contaminants are swept off by rolling droplets or flow. In early-stage fouling trials, superhydrophobic coatings have shown drastically reduced biofilm accumulation. - Low adhesion strength: Even if some fouling does attach, the adhesion is extremely weak due to the tiny contact area. Organisms can be removed with minimal force (sometimes even by the motion of the ship or gentle wiping). The coating thus makes cleaning very easy and can maintain a smooth, low-drag state in between cleanings. - No biocides needed: This approach is purely physical—no toxic additives. It is inspired by natural surfaces (lotus leaves, shark skin) and can achieve antifouling without environmental harm from chemicals. Some superhydrophobic formulations also trap a layer of air when submerged, potentially reducing fluid friction (though this “air layer” may be temporary). | - Fragile microstructure: Superhydrophobic coatings rely on micro/nano-scale surface textures (and often special low-energy chemistries). These textures are easily damaged by mechanical wear, impact, or abrasion—a swipe with a brush or contact with a rough surface can destroy the surface topology and with it the water-repellent effect. Maintaining the microstructure in harsh marine service is difficult. - Contamination sensitivity: If the surface becomes contaminated by oils, sediments, or a biofilm matrix, it can lose its water repellency (water will wet the surface), at which point fouling can start attaching normally. In practice, marine oils or microbial secretions can negate the superhydrophobic effect, so these coatings may require frequent gentle cleaning to restore repellency. - Performance decay over time: Prolonged immersion tends to eventually penetrate or collapse the air-trapping surface features, especially under pressure at depth. Thus, the superhydrophobic effect may diminish over long deployments. Repeated wetting/drying cycles or exposure to rough conditions can further degrade performance. - Scaling and cost issues: Fabricating a robust superhydrophobic surface over an entire ship hull is not yet commercially feasible. The processes to create nano-textures can be complex and costly. Some approaches use coatings with particles or patterns, but ensuring uniformity and durability at large scale is challenging. As a result, these coatings are still mostly in the research or niche-prototype stage. |
| Hard Inert Coatings (Non-Toxic Hard Films), e.g., glass-flake reinforced epoxy, ceramic-epoxy blends, silicone-epoxy hybrids without biocide | - Highly durable protection: These coatings cure into a very hard, impact- and abrasion-resistant layer on the hull. They can withstand mechanical damage that would ruin softer coatings—even in ice-prone waters or with frequent in-water cleanings, they hold up well. Their toughness gives them a much longer service life (often 5–10 years) before reapplication, far exceeding typical biocidal paints. - Completely inert and non-toxic: Hard inert coatings contain no biocides; they do not release any harmful substances into the environment. This makes them environmentally safe during operation—the only environmental consideration is the biofouling that grows on them and how it is managed. - Tolerant of frequent cleaning: Since the coating itself does not polish away or dissolve, ships can be cleaned regularly (by divers or hull cleaning robots) without rapidly degrading the coating. In fact, the strategy with these coatings is to allow fouling to grow and then periodically clean it off. The coating’s hardness lets it survive repeated cleanings that would wear down conventional paints. - Simplified re-coating cycle: With no need to refresh biocide, these coatings do not rely on yearly re-painting. They serve more as a durable lining—which can be cost-effective long-term if an appropriate cleaning schedule is maintained instead of repainting. They are often used in niche applications like ice-breakers or vessels in sensitive waters where biocides are undesired, providing basic hull protection and fouling management via cleaning. | - No antifouling function unless cleaned: These coatings do not actively prevent biofouling—organisms will settle and thrive on the hull as if it were any unprotected surface. This can lead to very heavy fouling and severe drag penalties if not frequently removed. Essentially, the bonus is on maintenance: the coating just ensures the hull can handle that maintenance. - Requires committed cleaning schedule: Ships using hard inert coatings must be prepared for regular in-water cleaning (e.g., every few weeks or months depending on fouling rate) to avoid performance loss. This adds operational costs and logistics (dive teams or robotics), and cleaning in port may be restricted by local regulations (due to biosecurity or debris concerns). - If cleaning is neglected, the vessel will incur significant fuel penalties and risk spreading invasive species. The coating itself will not stop accumulation, so the ship’s efficiency can quickly deteriorate between cleanings. - Niche use and initial cost: These coatings are mostly favored for special cases (e.g., in very cold waters where biocides are less effective or where hulls see physical abuse). The application of glass-flake epoxies, for example, can be as costly and involved as other high-performance coatings. Without a fouling-release property, their benefit is purely in durability—making them unsuitable for many commercial ships unless a robust maintenance plan is in place. Some ports allow cleaning of these coatings without capture of debris since no biocides are released, but the biofouling still must be managed responsibly. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kontus, O.; Kotta, J. Sustainable Marine Coatings: Comparing the Costs, Benefits, and Impacts of Biocidal and Biocide-Free Paints. Coatings 2025, 15, 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15080931
Kontus O, Kotta J. Sustainable Marine Coatings: Comparing the Costs, Benefits, and Impacts of Biocidal and Biocide-Free Paints. Coatings. 2025; 15(8):931. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15080931
Chicago/Turabian StyleKontus, Oskar, and Jonne Kotta. 2025. "Sustainable Marine Coatings: Comparing the Costs, Benefits, and Impacts of Biocidal and Biocide-Free Paints" Coatings 15, no. 8: 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15080931
APA StyleKontus, O., & Kotta, J. (2025). Sustainable Marine Coatings: Comparing the Costs, Benefits, and Impacts of Biocidal and Biocide-Free Paints. Coatings, 15(8), 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15080931







