Mechanistic Insights into Corrosion and Protective Coating Performance of X80 Pipeline Steel in Xinjiang’s Cyclic Freeze–Thaw Saline Soil Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Steel Selection and Compositional Analysis
2.1.1. Steel Selection
2.1.2. Composition Analysis
2.2. Soil Sample Collection and Pretreatment
2.2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2.2. Soil pH Determination
2.2.3. Soil Composition Analysis
2.3. Experimental Methods, Results, and Discussion
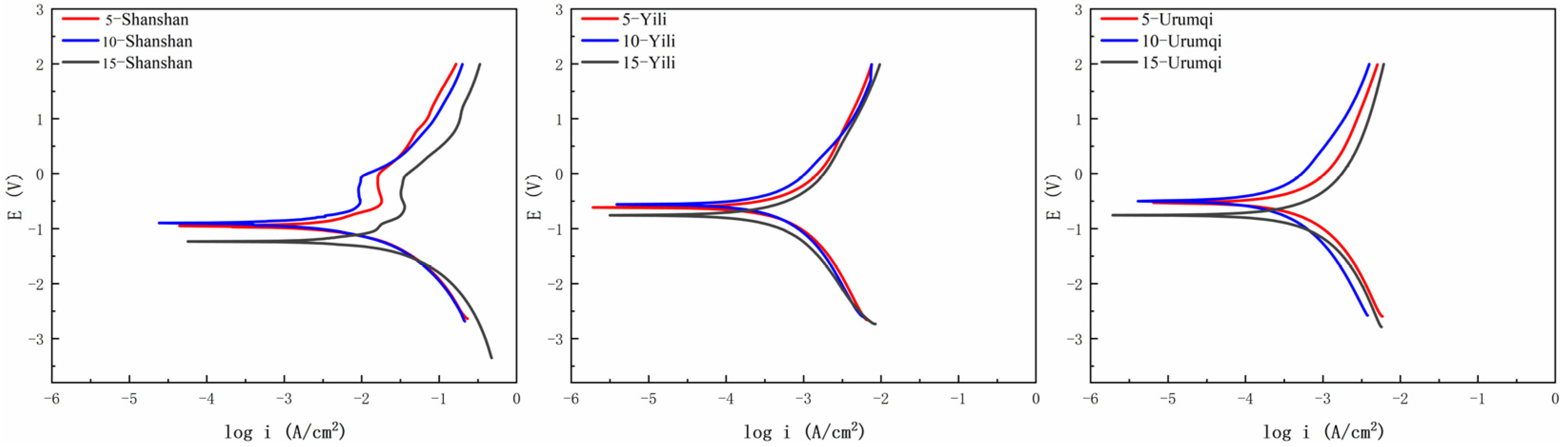
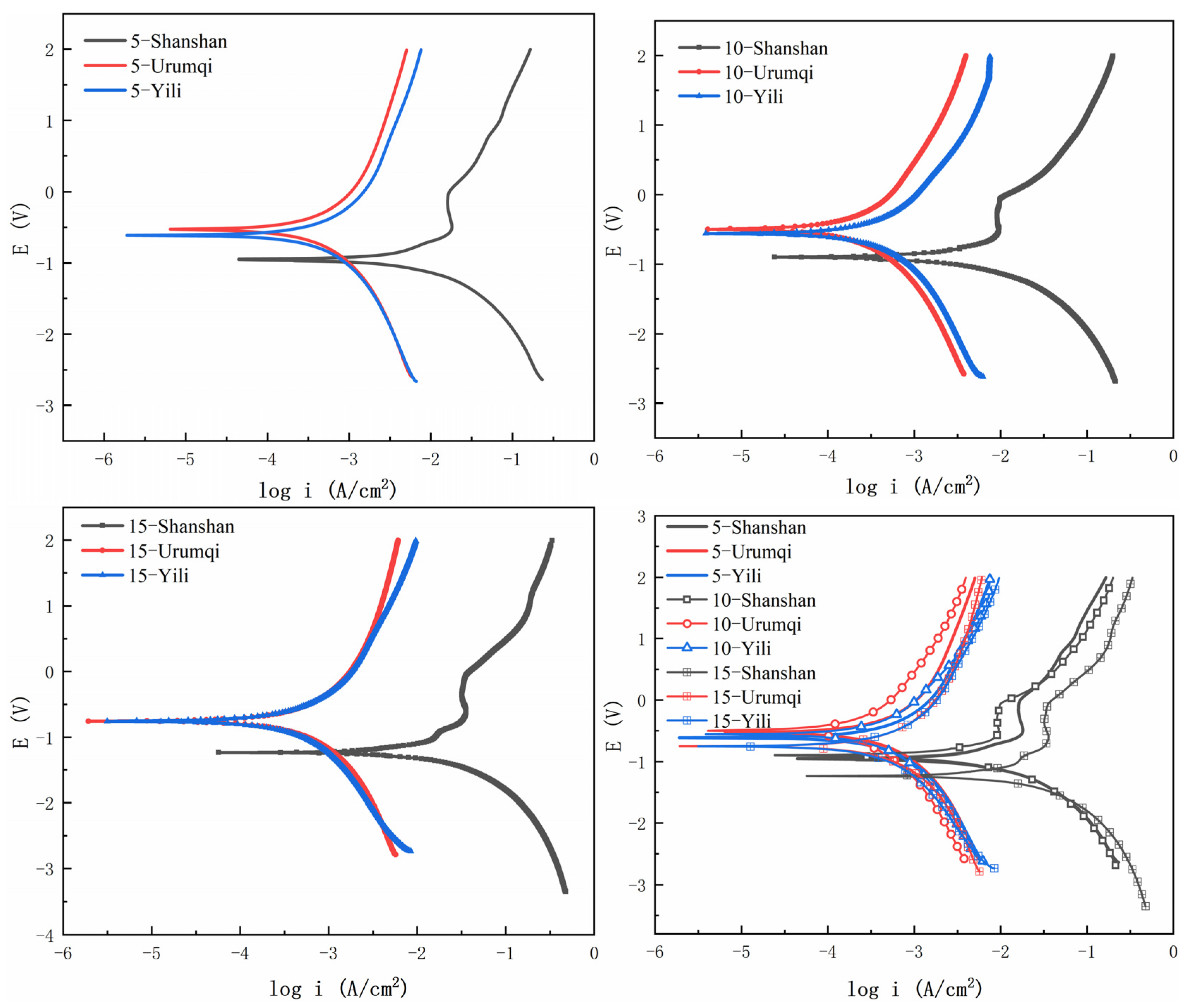
2.3.1. Freeze–Thaw Cycle Experiment and Polarization Curve Test
2.3.2. Microscopic Morphology Observation
2.3.3. Simulation Calculation
3. Results and Discussion
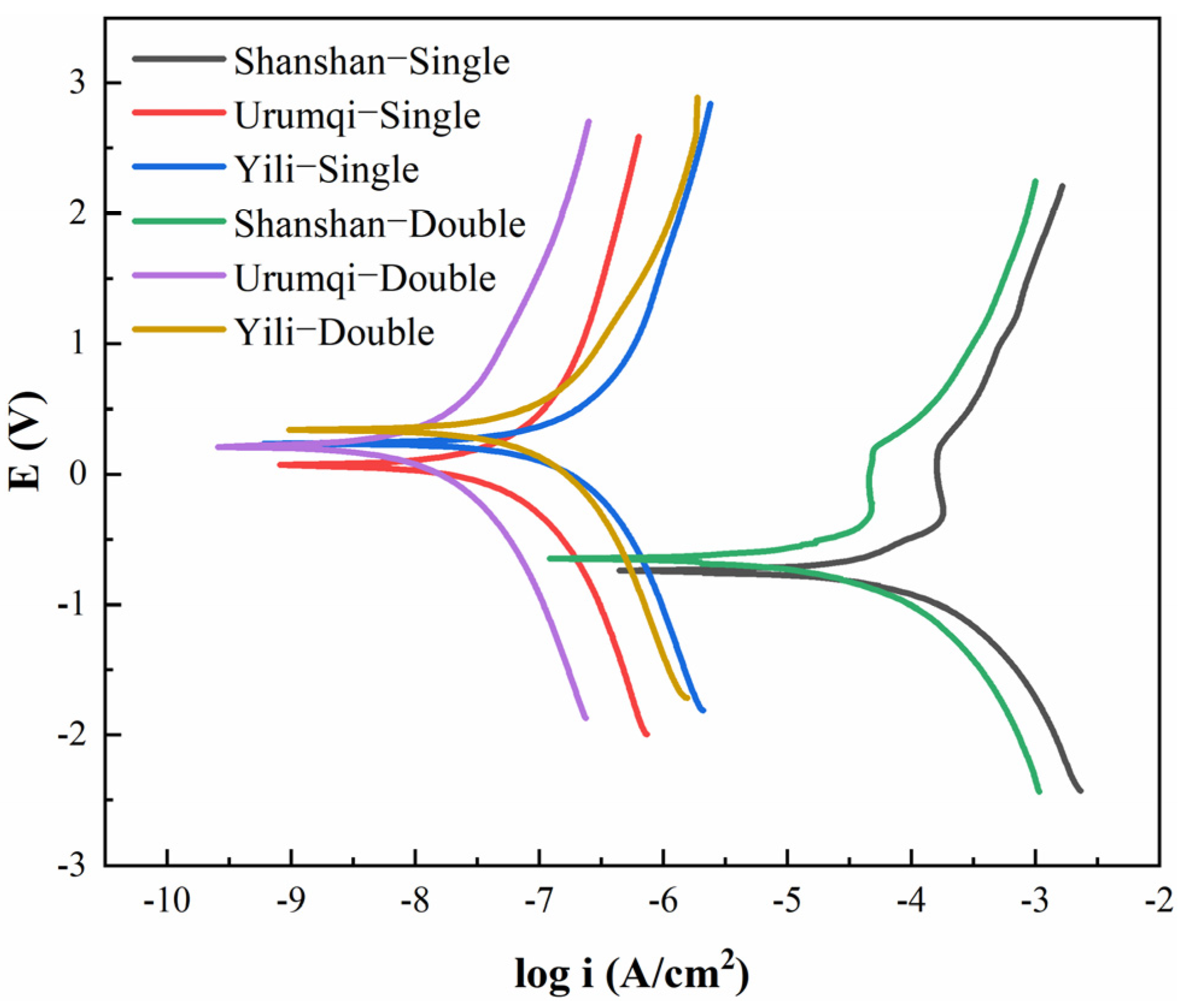
3.1. Corrosion Behavior Analysis
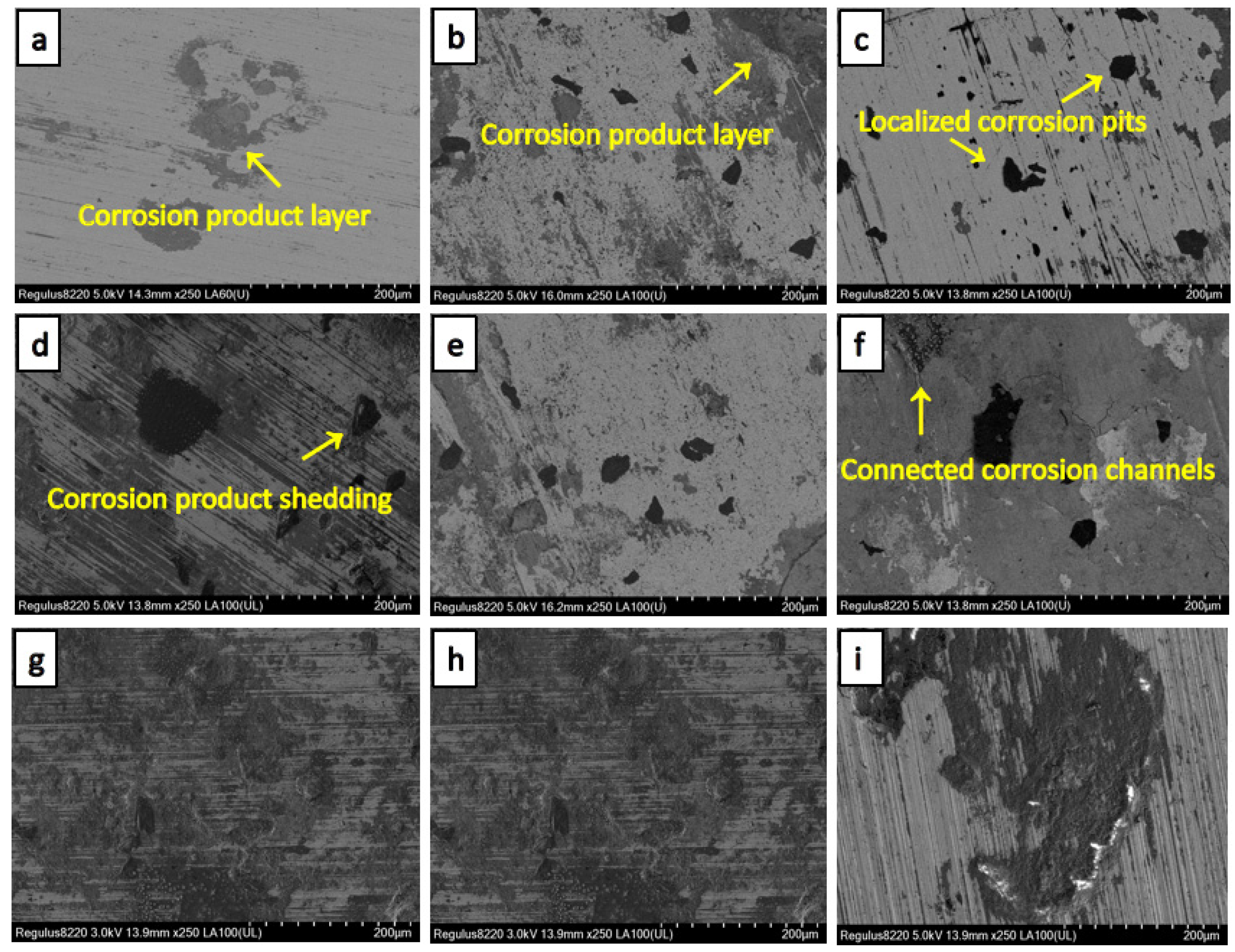
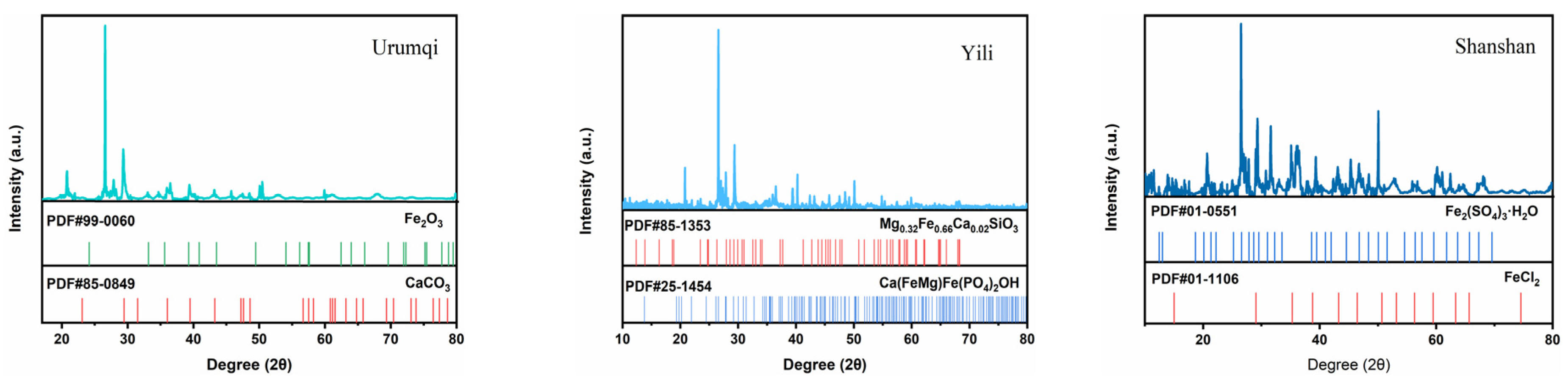
3.2. Micro-Morphology and Corrosion Products
3.3. Performance Evaluation of Anticorrosion Layers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, S. Influence of Xinjiang Saline Soil on Corrosion of X80 Pipeline Steel. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2706, 012086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, A.; Yuan, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Lv, N.; Li, W.; Fan, L.; Li, H. Corrosion of Gathering Pipelines in Oil and Gas Field and Its Mitigation Measures in China. In Proceedings of the AMPP Annual Conference + Expo, San Antonio, TX, USA, 6–10 March 2022; p. D041S037R009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Tian, J.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Ji, D.; Wang, X.; Li, X. Causes of Corrosion and Anticorrosion Strategies of Pipe String in Coalbed Methane Wells at the Southern Margin of Junggar Basin. Spec. Oil Gas Reserv. 2023, 30, 151. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Yu, H.; Zhu, G.; Wang, P.; Song, S. Investigation on leakage cause of oil pipeline in the west oilfield of China. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 113, 104552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Chen, S.; Gou, L.; Ma, Q. Multi-media environment corrosion mechanism and protection technology of gathering and transportation pipeline in oilfield. Appl. Chem. Ind. 2024, 53, 1612–1615. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, F.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, X.; Guo, D.; Jiang, J. An improvement on direct assessment method for internal corrosion of natural gas pipeline. You-Qi Chuyun 2022, 22, 219–226. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Shao, X.; Xue, C.; Zhang, C.; Fang, F. Effects of pH on Corrosion Behavior of Carbon Steelin Oilfield Water with High Sulphide. J. Chin. Soc. Corros. Prot. 2013, 33, 159–163. [Google Scholar]
- Alamri, A.H. Localized corrosion and mitigation approach of steel materials used in oil and gas pipelines–An overview. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 116, 104735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasim, M.; Djukic, M.B. External corrosion of oil and gas pipelines: A review of failure mechanisms and predictive preventions. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2022, 100, 104467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, M.; Aliofkhazraei, M.; Afroukhteh, S. A comprehensive review on internal corrosion and cracking of oil and gas pipelines. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2019, 71, 102971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papavinasam, S.; Doiron, A.; Revie, R.W. Model to predict internal pitting corrosion of oil and gas pipelines. Corrosion 2010, 66, 035006-1–035006-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unueroh, U.; Omonria, G.; Efosa, O.; Awotunde, M. Pipeline corrosion control in oil and gas industry: A case study of NNPC/PPMC system 2A pipeline. Niger. J. Technol. 2016, 35, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Xu, J.; Wei, B.; Sun, C. A comparative study of sulfate-reducing Desulfovibrio desulfuricans induced corrosion behaviors in Q235, X65, X70, and X80 pipeline steels. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2022, 195, 104599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jin, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Meng, G.; Liu, H. Corrosion inhibition of deposit-covered X80 pipeline steel in seawater containing Pseudomonas stutzeri. Bioelectrochemistry 2023, 149, 108279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefano, R.; Mattia, P.; Massimo, C. Influence of soil chemical characteristics on corrosion behaviour of galvanized steel. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01257. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, F.; Wang, X.; Han, P.; He, B. Combined EIS and BAS-BP neural network analysis of electrochemical corrosion on pipeline steel in silty soil in a Salt–Temperature coupling environment. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2022, 200, 104807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Han, P.; He, B. An analysis of electrochemical corrosion on pipeline steel in silty soil under salt-temperature coupling environments. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2023, 274, 118704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; He, B.; Han, P.; Xie, R.; Sun, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. Corrosion behavior and mechanism of X80 steel in silty soil under the combined effect of salt and temperature. RSC Adv. 2021, 12, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Ai, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, T. Effects of strain on the corrosion behaviour of X80 steel. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 2761–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzaghi, E.; Chia, B.H.; Abaei, M.M.; Abbassi, R.; Garaniya, V. Pitting corrosion modelling of X80 steel utilized in offshore petroleum pipelines. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 141, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.Y.; Ahn, S.S.; Seo, D.H.; Song, W.H.; Kang, K.B. New development of high grade X80 to X120 pipeline steels. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2011, 26, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- API 5L; 46th Edition; Specification for Line Pipe. American Petroleum Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2022.
- GB/T 9711.1; Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries—Pipeline Transportation Systems—Technical Delivery Conditions—Part 1: Pipes of Requirement Class A. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China (SAC): Beijing, China, 2017.
- ISO 18400-205:2018; Soil Quality—Sampling—Part 205: Guidance on the Procedure for Investigation of natural, Near-Natural and Cultivated Sites. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- ASTM D4972-19; Standard Test Method for Determining the Number of Reinforcing Points in a Piece of Pile Yarn Floor Covering. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019.
- Henry, H.A.L. Soil freeze–thaw cycle experiments: Trends, methodological weaknesses and suggested improvements. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y. Deterioration of concrete under the coupling effects of freeze–thaw cycles and other actions: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 319, 126045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Niu, D. Influence of freeze–thaw cycles and sulfate corrosion resistance on shotcrete with and without steel fiber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 122, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, J.J. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Atactic Polystyrene Using an All-Atom Model Within Materials Studio. Master’s Thesis, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, J.; Hanke, F.; Ji, H.; McLendon, R.; Todd, S.; Dalrymple, T.; Salazar-Tio, R.; Persson, M.; Chiavaccini, E.; Wescott, J.; et al. Multiscale modeling for the science and engineering of materials. Int. J. Multiscale Comput. Eng. 2021, 19, 1–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, B.; Hong, Q. Molecular dynamics simulation of distribution and adhesion of asphalt components on steel slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 255, 119332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Chen, J.; Hu, E.; Zeng, F. A reactive molecular dynamics simulation study on corrosion behaviors of carbon steel in salt spray. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2022, 203, 111142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Cui, X.; Jin, G.; Dong, M.; Li, J.; Yang, Y. Study on micro-mechanism of carbon atom diffusion in surface nanocrystallization low carbon alloy steel using molecular dynamics simulation. Vacuum 2021, 184, 109889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S. Atomistic investigation on diffusion welding between stainless steel and pure Ni based on molecular dynamics simulation. Materials 2018, 11, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Cong, P.; Wu, S. Laboratory investigation of the properties of asphalt modified with epoxy resin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 3557–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.; Li, X. A review of high-quality epoxy resins for corrosion-resistant applications. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2024, 21, 461–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagdag, O.; Haldhar, R.; Kim, S.C.; Guo, L.; El Gouri, M.; Berdimurodov, E.; Hamed, O.; Jodeh, S.; Akpan, E.D.; Ebenso, E.E. Recent progress in epoxy resins as corrosion inhibitors: Design and performance. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2023, 37, 923–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, S.; Veith, L.; Baier, R.; Dietrich, C.; Schmid, M.J.; Ternes, T.A. New methodical approaches for the investigation of weathered epoxy resins used for corrosion protection of steel constructions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 395, 122289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Li, T.; Yin, H.; Hu, L.; Tang, J.; Ren, K. Preparation and corrosion protection of three different acids doped polyaniline/epoxy resin composite coatings on carbon steel. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 612, 126069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Wei, L.; Pu, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Fan, J.; Ding, T.; Guo, Z. Alternating multilayer structural epoxy composite coating for corrosion protection of steel. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 304, 1900374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

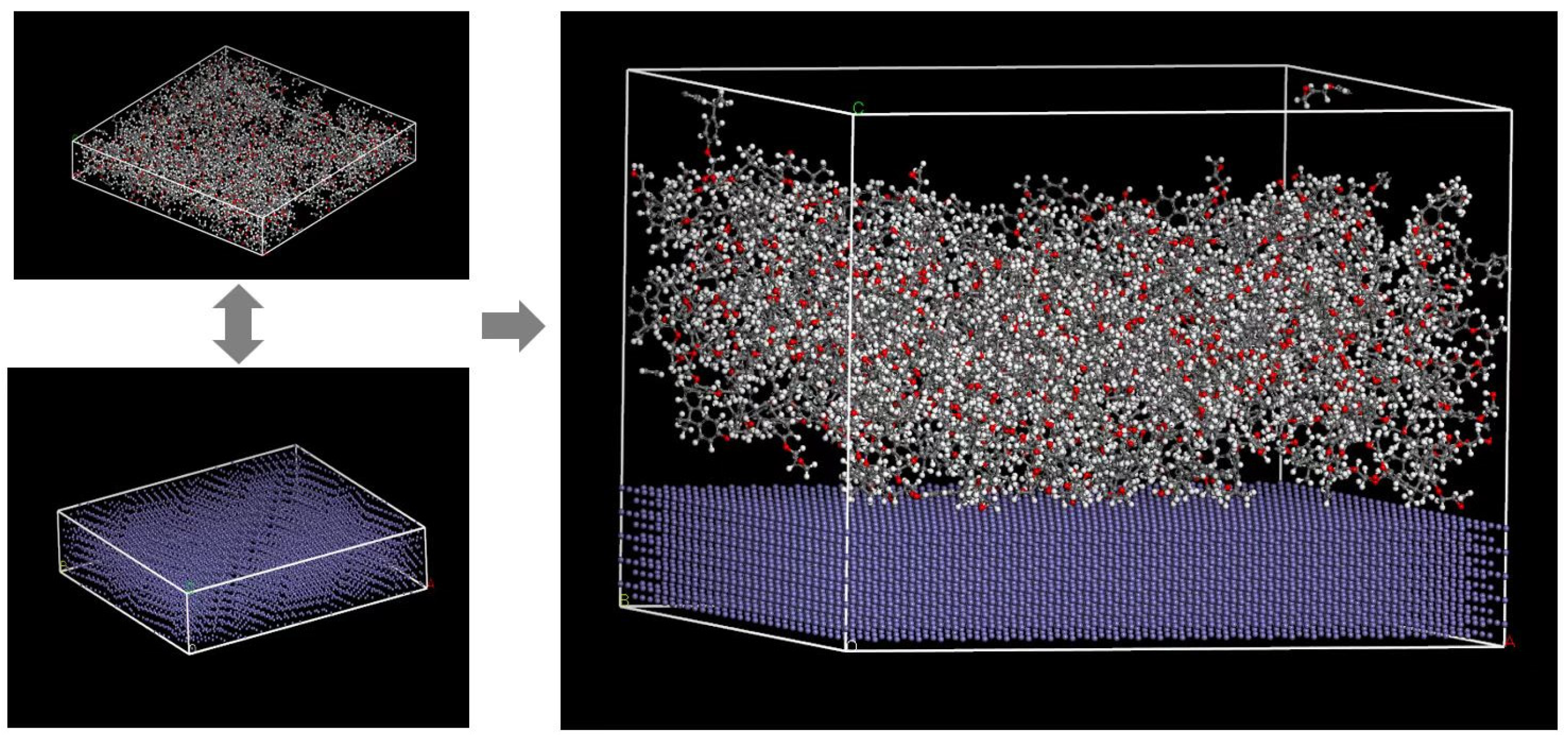
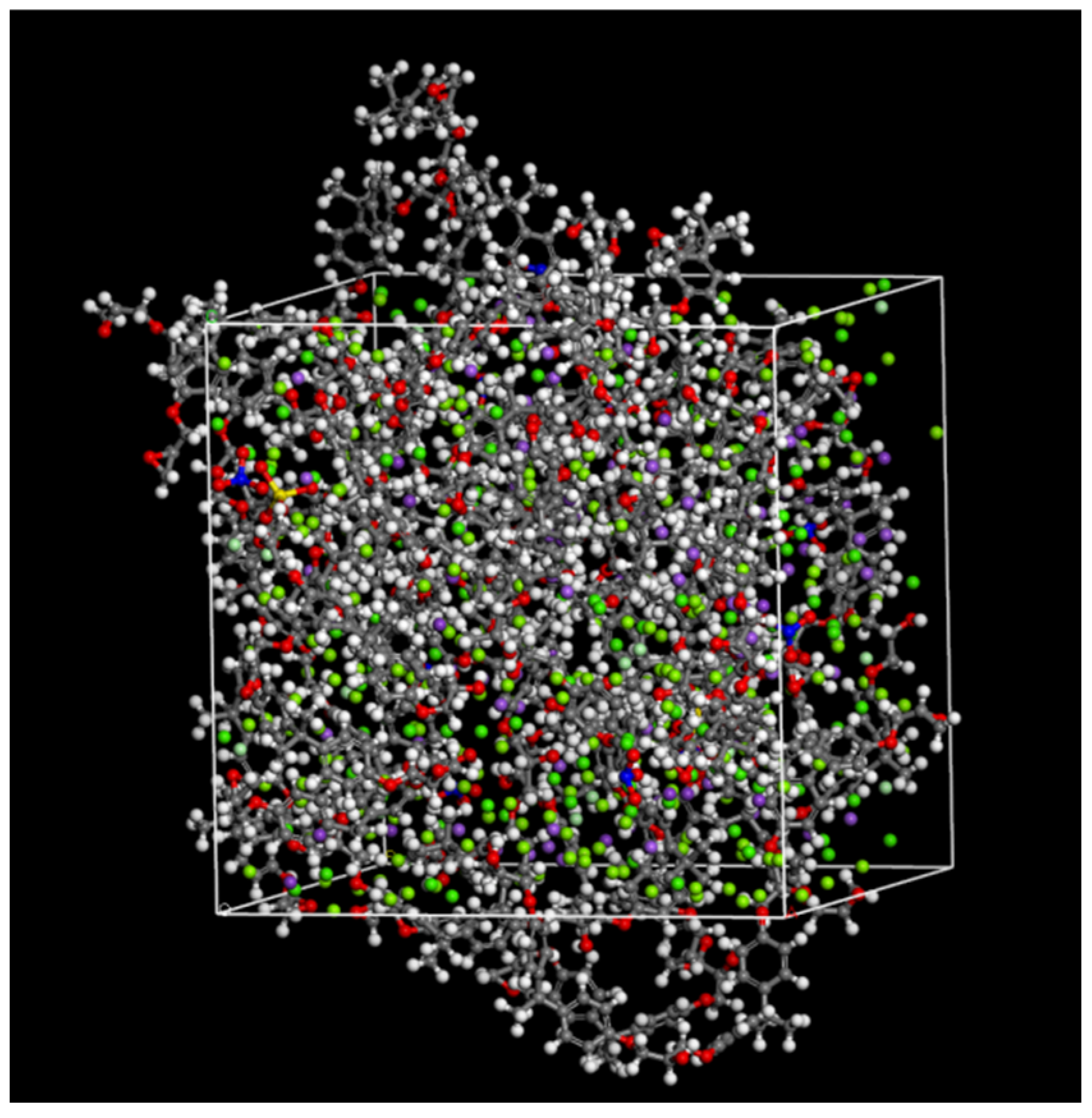

| Element | Fe | Mn | Si | Mo | C | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 97.39% | 1.83% | 0.28% | 0.22% | 0.063% | <0.22% |
| Serial Number | Soil Samples | pH Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Urumqi | 7.58 |
| 2 | Shanshan | 7.66 |
| 3 | Yili | 7.80 |
| Serial Number | Soil Samples | K+ | Ca2+ | Na+ | Mg2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g/kg | g/kg | g/kg | g/kg | ||
| 1 | Urumqi | 0.017 | 0.057 | 0.074 | 0.892 |
| 2 | Shanshan | 0.045 | 0.456 | 0.033 | 0.756 |
| 3 | Yili | 0.074 | 0.106 | 0.080 | 0.274 |
| Serial Number | Soil Samples | Cl− | SO42− | NO3− |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| g/kg | g/kg | g/kg | ||
| 1 | Urumqi | 0.01 | 1.13 | 0.03 |
| 2 | Shanshan | 0.57 | 1.28 | 0.17 |
| 3 | Yili | 0.06 | 0.47 | 0.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, G.; Wang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wei, B.; Xiao, C.; Zhang, X. Mechanistic Insights into Corrosion and Protective Coating Performance of X80 Pipeline Steel in Xinjiang’s Cyclic Freeze–Thaw Saline Soil Environments. Coatings 2025, 15, 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15080881
Cheng G, Wang Y, Dai Y, Zhang S, Wei B, Xiao C, Zhang X. Mechanistic Insights into Corrosion and Protective Coating Performance of X80 Pipeline Steel in Xinjiang’s Cyclic Freeze–Thaw Saline Soil Environments. Coatings. 2025; 15(8):881. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15080881
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Gang, Yuqi Wang, Yiming Dai, Shiyi Zhang, Bin Wei, Chang Xiao, and Xian Zhang. 2025. "Mechanistic Insights into Corrosion and Protective Coating Performance of X80 Pipeline Steel in Xinjiang’s Cyclic Freeze–Thaw Saline Soil Environments" Coatings 15, no. 8: 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15080881
APA StyleCheng, G., Wang, Y., Dai, Y., Zhang, S., Wei, B., Xiao, C., & Zhang, X. (2025). Mechanistic Insights into Corrosion and Protective Coating Performance of X80 Pipeline Steel in Xinjiang’s Cyclic Freeze–Thaw Saline Soil Environments. Coatings, 15(8), 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15080881






