Microstructure Evolution Mechanism and Corrosion Resistance of FeCrNi(AlTi)x Medium Entropy Alloy Prepared by Laser Melting Deposition with Al and Ti Content Changes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
3. Results and Discussion
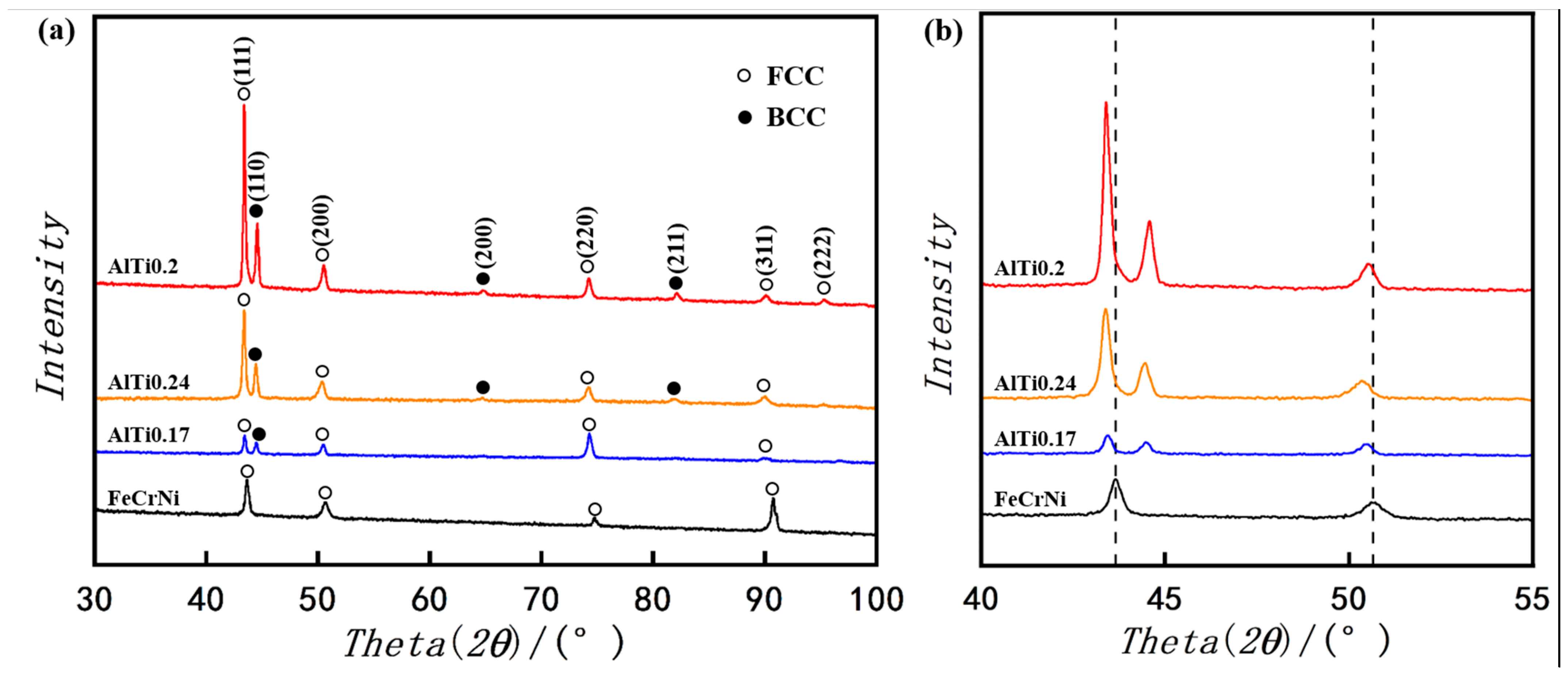
3.1. Phase Identification
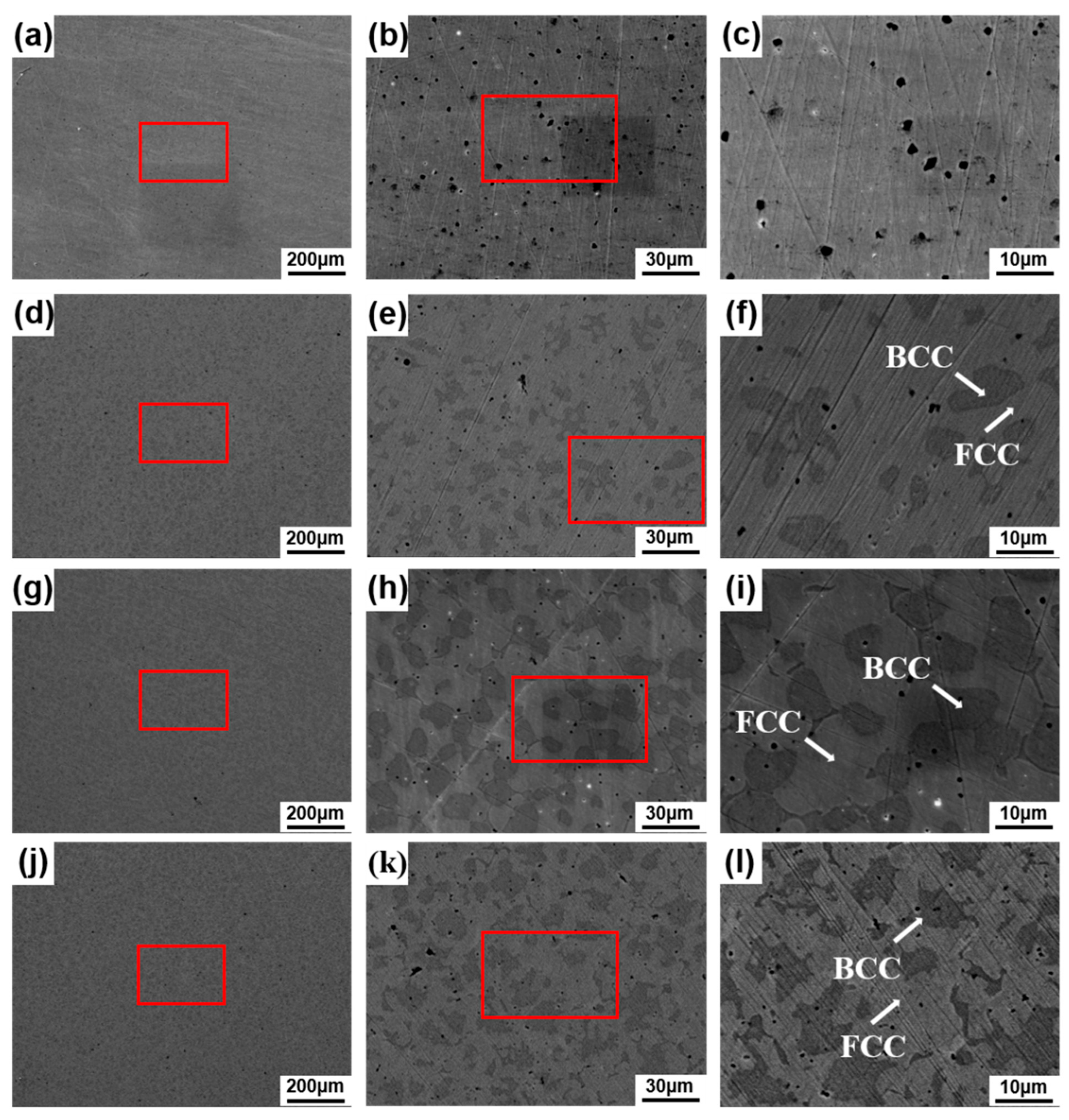
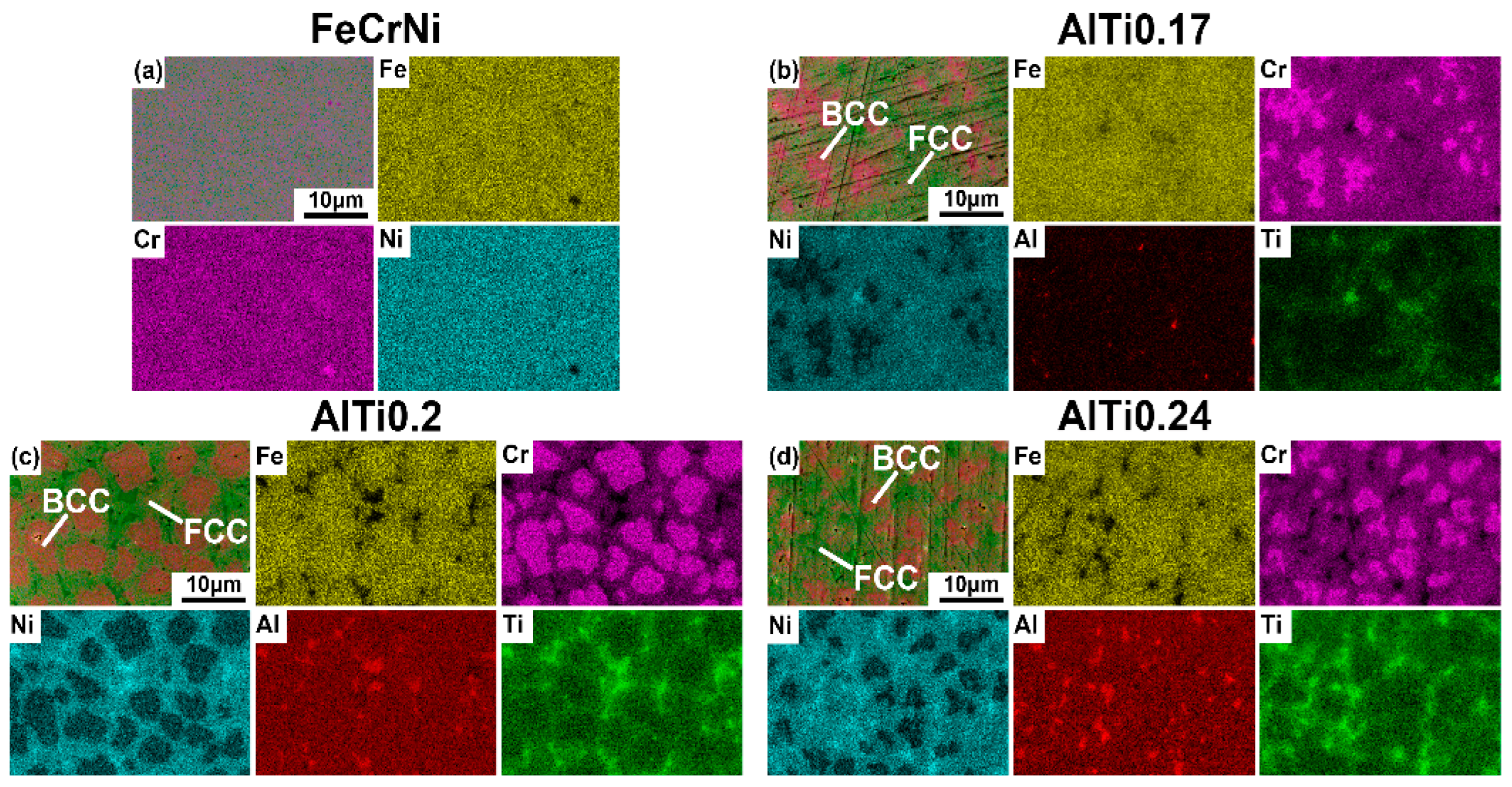
3.2. Surface Morphology and Energy Spectrum Analysis of Alloys
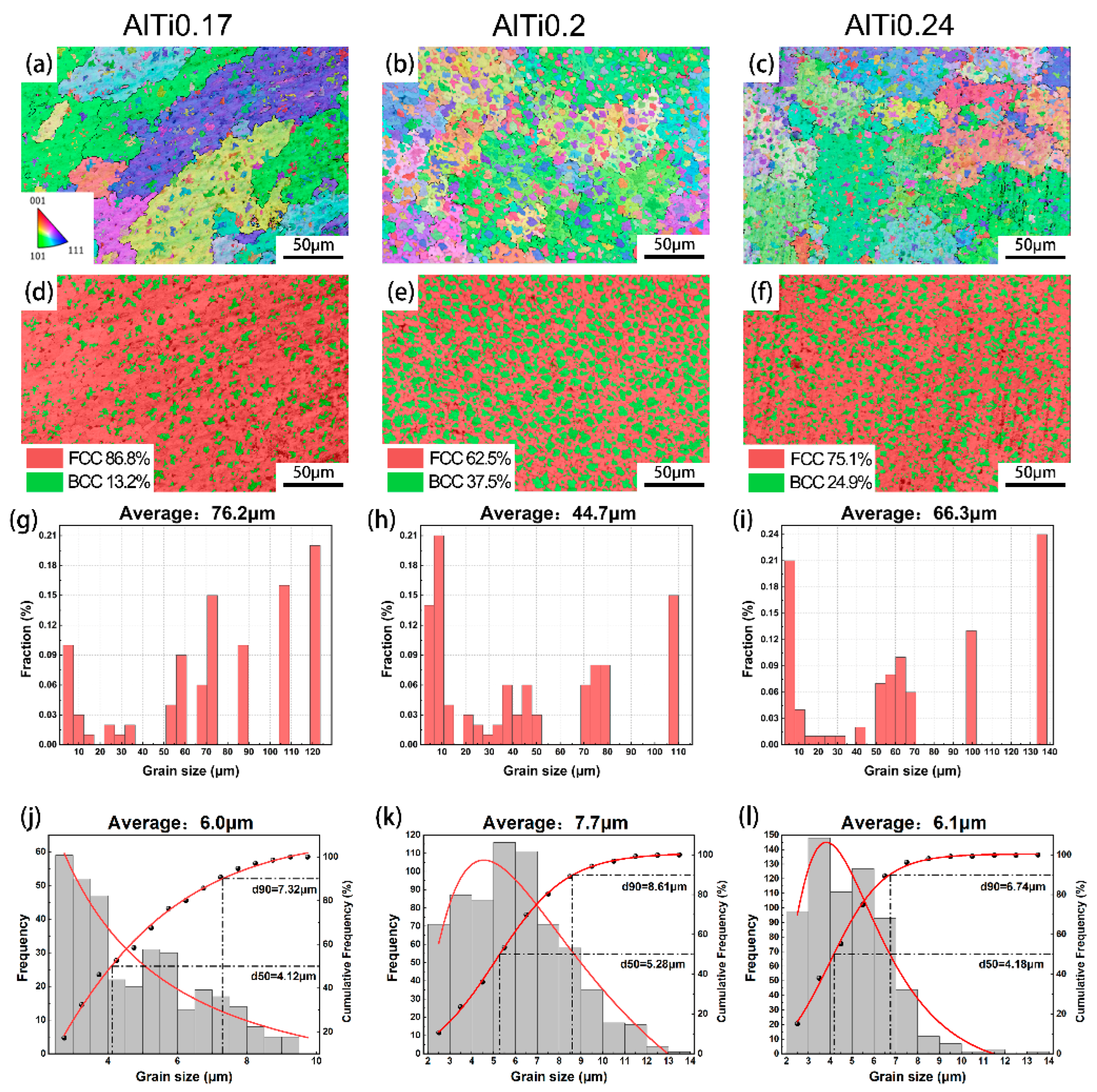
3.3. Microstructure Analysis
3.4. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
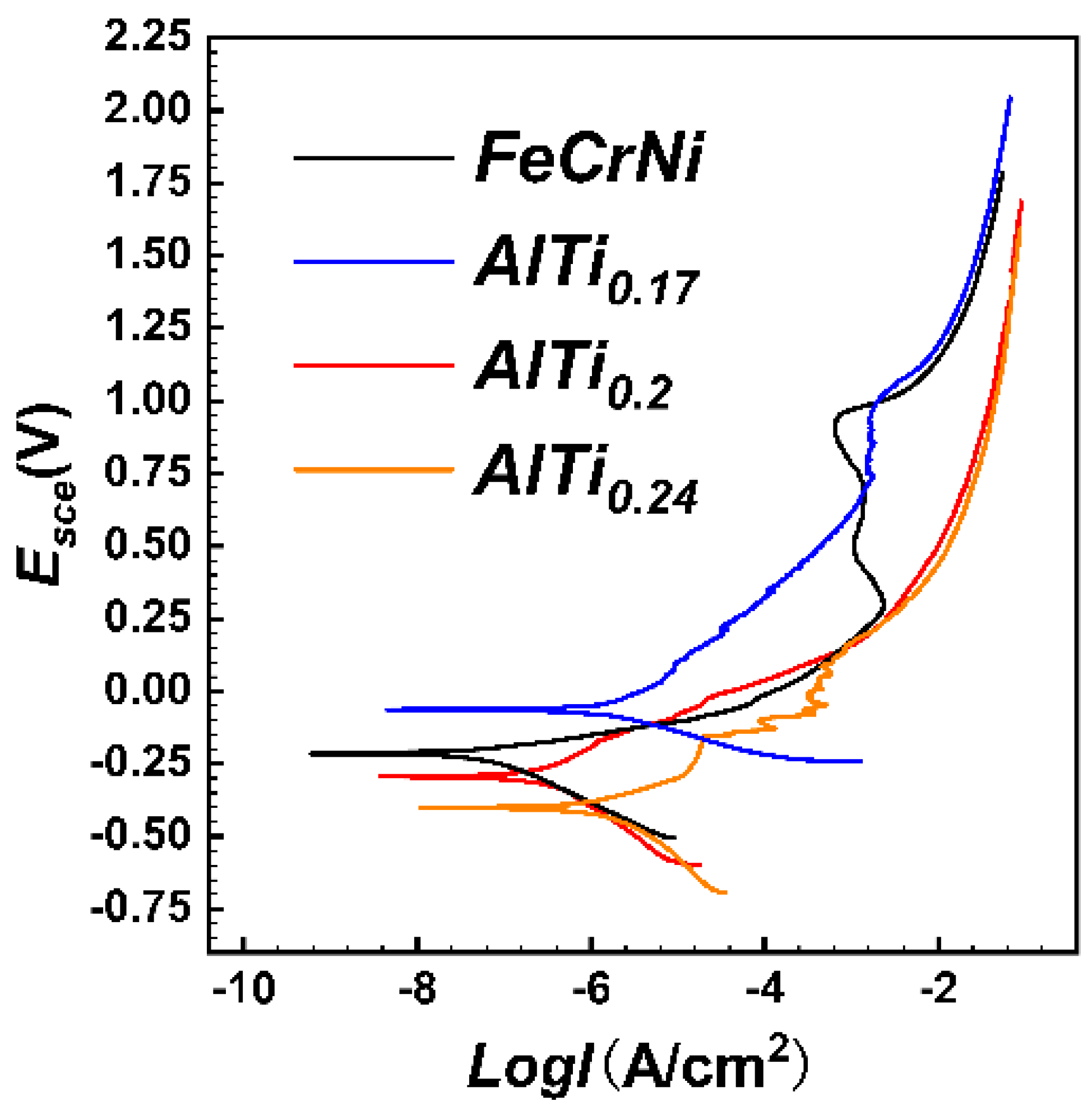
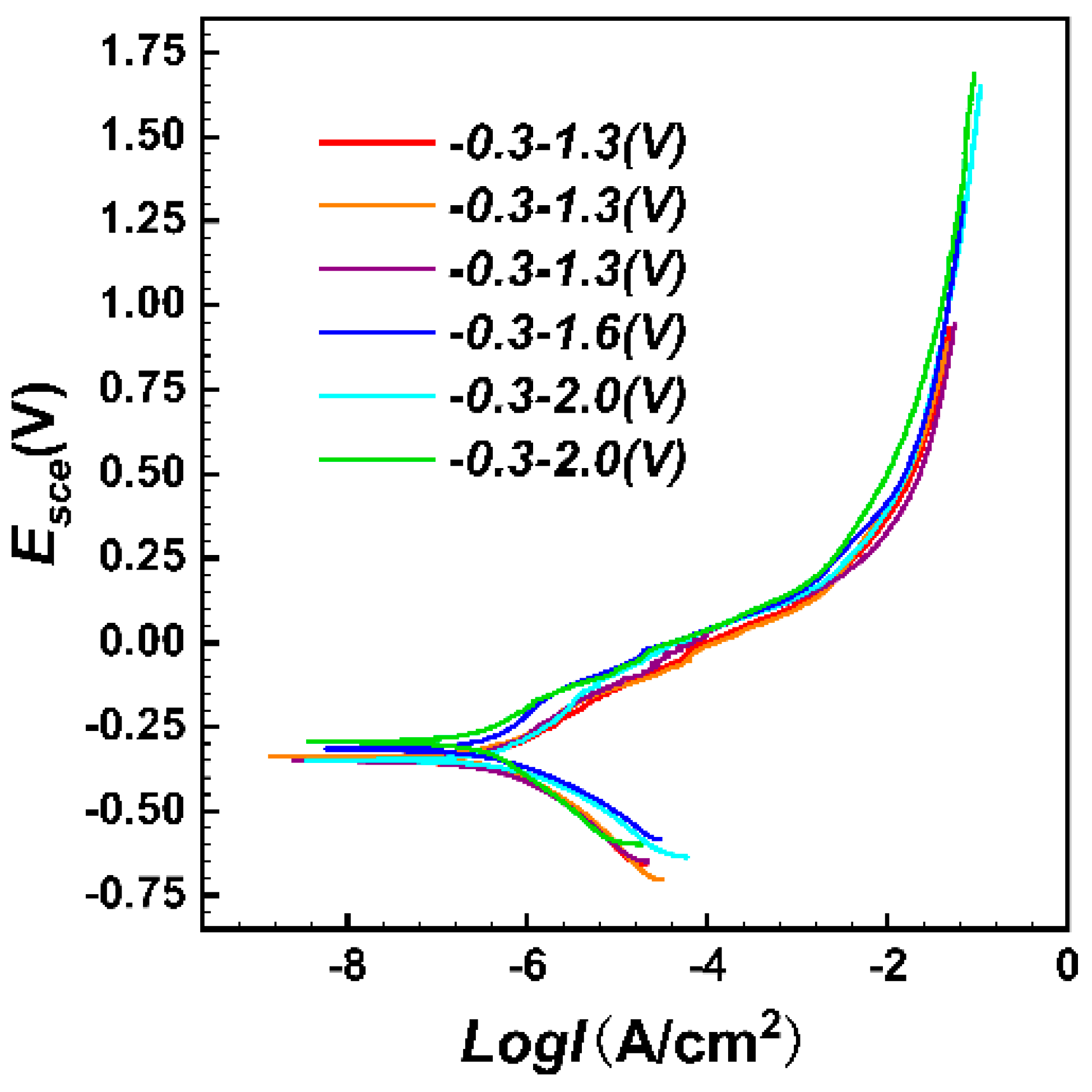
3.5. Potentiodynamic Polarization
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- FeCrNi alloy prepared by laser melting deposition technology shows a single-phase FCC structure. With the addition of Al and Ti elements, the alloy changes from a single FCC phase structure to a biphase FCC + BCC structure. In a certain range, with the increase of the content of Al and Ti elements, the BCC phase ratio continues to increase. After reaching the saturation state, the increase in the content of Al and Ti in the alloy will lead to a decrease in BCC content.
- (2)
- In FeCrNi(AlTi)x medium entropy alloy, the grains of the BCC phase are dispersed in the FCC matrix, and more dislocations accumulate at the interface of the BCC phase and FCC phase, resulting in significantly higher dislocation density. With the increase of the content of Al and Ti, the grain of the alloy can be refined to a certain extent.
- (3)
- The geometrically necessary dislocations (GNDs) of AlTi0.2 alloy are distributed most evenly among the three alloys, and AlTi0.17 and AlTi0.24 both have high-density dislocation regions. The regions with high dislocation density will make them stress-concentrated regions, which will affect their fatigue characteristics, and thus reduce the corrosion resistance of the material. Adjusting the content of Al and Ti elements in the alloy can change the microstructure composition of the alloy, so as to change the corrosion resistance of the alloy.
- (4)
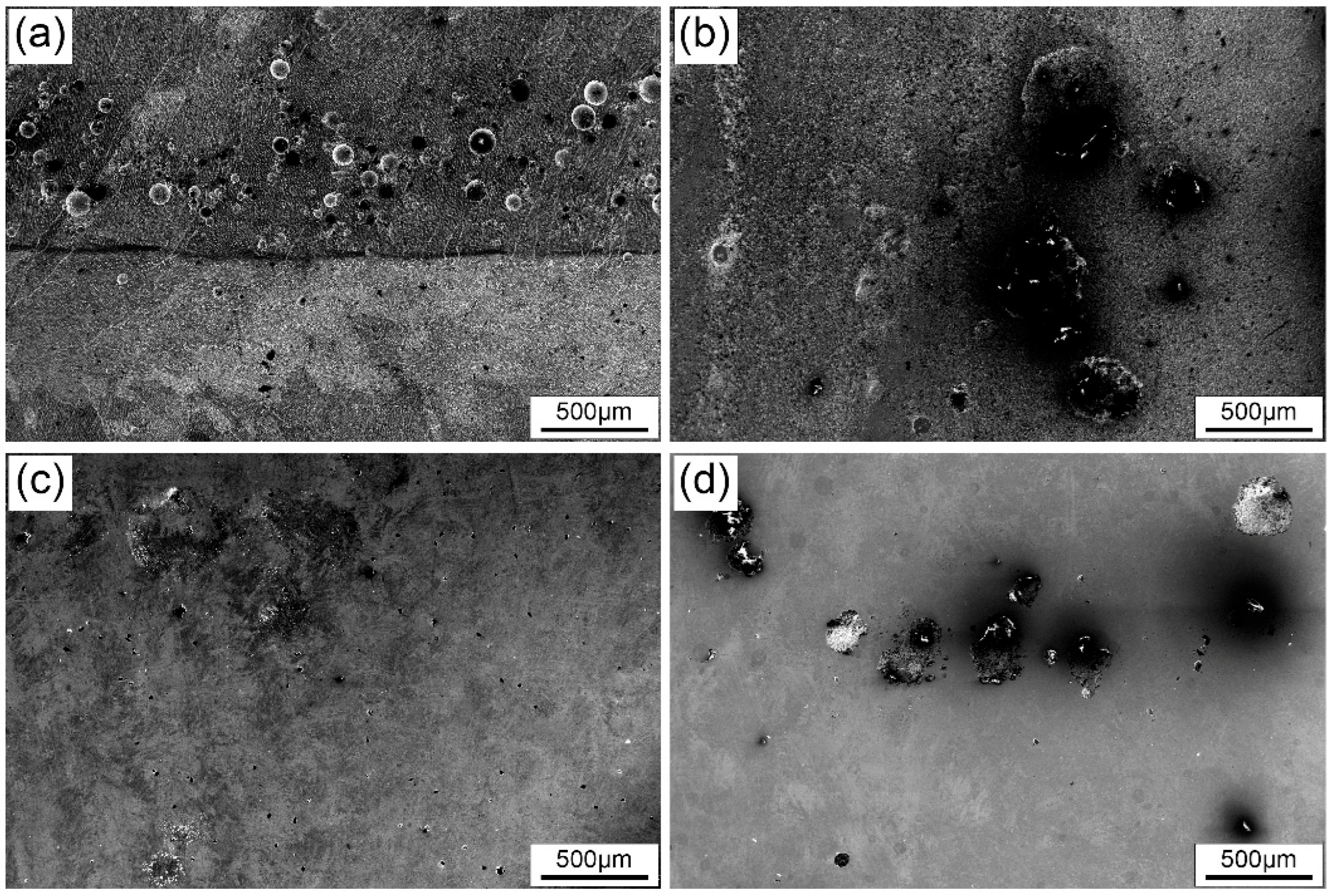
- FeCrNi(AlTi)x medium entropy alloy has good corrosion resistance and can be spontaneously passivated in 3.5 wt.%NaCl solution to form a corrosion-resistant passivated film. With the increase of the content of Al and Ti, the protection of the passivation film on the surface of FeCrNi(AlTi)x can be effectively improved, and the corrosion rate of the alloy surface can be reduced. Among the alloys with different contents of Al and Ti, the AlTi0.2 alloy has the best corrosion resistance. After the high-potential potentiodynamic corrosion test, the surface of other alloys has a large-scale corrosion phenomenon, and only part of the alloy has a random pitting morphology.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Yu, Q.; Asta, M.; Ritchie, R.O. Tunable stacking fault energies by tailoring local chemical order in CrCoNi medium-entropy alloys. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 8919–8924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, S.; Ritchie, R.O. Mechanical properties of high-entropy alloys with emphasis on face-centered cubic alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 102, 296–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Huang, C.; Du, C.; Li, J.; Dai, C.; Luo, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, X. Evolution in microstructure, wear, corrosion, and tribocorrosion behavior of Mo-containing high-entropy alloy coatings fabricated by laser cladding. Corros. Sci. 2021, 191, 109727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.J.; Chen, Y.L.; Yeh, J.W.; Lin, S.J.; Chen, S.K.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H. Chang Microstructure characterization of AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multiprincipal elements. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Liu, W.H.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Nieh, T.G.; Lu, Z.P. Effects of Al addition on structural evolution and tensile properties of the FeCoNiCrMn high-entropy alloy system. Acta Mater. 2014, 62, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brif, Y.; Thomas, M.; Todd, I. The use of high-entropy alloys in additive manufacturing. Scr. Mater. 2015, 99, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Niu, S.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, C. Solid solution island of the Co-Cr-Fe-Ni high entropy alloy system. Scr. Mater. 2017, 131, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Q.L. Effect of preparation technology on corrosion resistance of entropy alloy in powder metallurgy FeCrNi. Powder Metall. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 28, 490–499. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gu, S.; Huang, H.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Hsieh, C.-A.; Panda, P.K.; Chang, J.-K.; Hsieh, C.-T. High-entropy alloys with low platinum content: Novel catalysts for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions. Emergent Mater 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.J.; Tian, Y.Z.; An, X.H.; Lin, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z. Ultrahigh cryogenic strength and exceptional ductility in ultrafine-grained CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy with fully recrystallized structure. Mater. Today Nano 2018, 4, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.J.; Tian, Y.Z.; Lin, H.R.; Dong, X.G.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhang, Z.F. Enhanced strength and ductility of bulk CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy having fully recrystallized ultrafine-grained structure. Mater. Des. 2017, 133, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shun, T.T.; Du, Y.C. Microstructure and tensile behaviors of FCC Al0.3CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 479, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, M.; Zhou, Y.M.; Shen, Y.F. Thermal stability of eutectic FeNiCoCrTi0.6N0.4 high-entropy alloy coating. Powder Metall. 2022, 65, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, B.B.; Li, C.L.; Hao, J.M.; Li, X.N.; Dong, C.; Nieh, T.G. Controlled formation of coherent cuboidal nanoprecipitates in bodycentered cubic high-entropy alloys based on Al2(Ni,Co,Fe,Cr)14 compositions. Acta Mater. 2018, 147, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; An, J.; Chua, C.K. Fundamentals and applications of 3D printing for novel materials. Appl. Mater. Today 2017, 7, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Fang, Q.; Shi, Y.; Tor, S.B.; Chua, C.K.; Zhou, K. Recent advances on high entropy alloys for 3D printing. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1903855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.Q.; Zhao, H. 4D printing: Future insight in additive manufacturing. Met. Mater. Int. 2020, 26, 564–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.B.; Zhao, K.; Huang, Y.L. Microstructures and mechanical properties of doubled annealed laser melting deposited TC11 titanium alloy. Chin. J. Lasers 2021, 48, 2202001. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.H.; Song, C.H.; Liu, L.Q. Research progress of selective laser melting of nitinol. Chin. J. Lasers 2020, 47, 1202005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorehead, M.; Bertsch, K.; Niezgoda, M.; Parkin, C.; Elbakhshwan, M.; Sridharan, K.; Zhang, C.; Thoma, D.; Couet, A. High-throughput synthesis of Mo-Nb-Ta-Whigh-entropy alloys via additive manufacturing. Mater. Des. 2020, 187, 108358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Laplanche, G. Effects of temperature on mechanical properties and deformation mechanisms of the equiatomic CrFeNi medium-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2021, 204, 116470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, W.; Wei, P.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Ren, F. Overcoming the strength-ductility trade-off via the formation of nanoscale Cr-rich precipitates in an ultrafine-grained FCC CrFeNi medium entropy alloy matrix. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 762, 138107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Bei, H.; Otto, F.; Pharr, G.M.; George, E.P. Recovery, recrystallization, grain growth and phase stability of a family of FCC-structured multi-component equiatomic solid solution alloys. Intermetallics 2014, 46, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Inoue, A. Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying element. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 2817–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, R.C. The Superalloys: Fundamentals and Applications; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Zhao, Y.L.; Li, W.P.; Yu, C.Y.; Luan, J.H.; Lin, D.Y.; Fan, L.; Jiao, Z.B.; Liu, W.H.; Liu, X.J.; et al. Ultrahigh-strength and ductile superlattice alloys with nanoscale disordered interfaces. Science 2020, 369, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, A.; Cao, Y.K.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Wang, J.; Khanlari, K.; Wang, B.; Liu, B. Corrosion behavior of FeCrNi medium-entropy alloy fabricated by laser powder bed fusion. Mater. Commun. 2024, 38, 108558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Li, Z.M.; Mingers, A.M.; Raabe, D. Corrosion behavior of an equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy compared with 304 stainless steel in sulfuric acid solution. Corros. Sci. 2018, 134, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzdor, V.; Sridharan, K.; Cao, G.; Anderson, M.; Allen, T. Corrosion of a stainless steel and nickel-based alloys in high temperature supercritical carbon dioxide environment. Corros. Sci. 2013, 69, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.-Y.; Peng, K.; Hu, A.-P.; Zhou, L.-P.; Zhu, J.-J.; Li, D.-Y. Structure and properties of FeCoNiCrCu0.5Alx high-entropy alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.Y.; Li, C.W.; Ye, Z.H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; Gu, J. Strength-ductility synergy of additively manufactured (CoCrNi)87Al13 medium entropy alloy with heterogeneous multiphase microstructure. Scr. Mater. 2023, 222, 115016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Pint, B.A.; Terrani, K.A.; Field, K.; Yang, Y.; Snead, L. Development and property evaluation of nuclear grade wrought FeCrAl fuel cladding for light water reactors. J. Nucl. Mater. 2015, 467, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Mao, H.; Nieh, T.; Lu, Z. Precipitation behavior and its effects on tensile properties of FeCoNiCr high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2016, 79, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; Lin, J.P.; Chen, G.L.; Liaw, P.K. Solid-solution phase formation rules for multi-component alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 511–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.B.; Yang, X. Advanced High Entropy Alloy Technology; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2018; pp. 115–117. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sunkari, U.; Reddy, S.R.; Rathod, B.D.S.; Kumar, S.S.S.; Saha, R.; Chatterjee, S.; Bhattacharjee, P.P. Heterogeneous precipitation mediated heterogeneous nanostructure enhances strength-ductility synergy in severely cryo-rolled and annealed CoCrFeNi2.1Nb0.2 high entropy alloy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Kosiba, K.; Suryanarayana, C.; Lu, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Prashanth, K.G. Prashanth, Feedstock preparation, microstructures and mechanical properties for laser-based additive manufacturing of steel matrix composites. Int. Mater. Rev. 2023, 68, 1192–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DebRoy, T.; Mukherjee, T.; Wei, H.L.; Elmer, J.W.; Milewski, J.O. mechanistic models and machine learning in metal printing. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 48–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.Q.; Zhou, R.; Wei, B.Q. Nanosized precipitates and dislocation networks reinforced C-containing CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy fabricated by selective laser melting. Mater. Charact. 2018, 144, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommersbach, P.; Alemany-dumont, C.; Millet, J.P.; Normand, B. Formation and behaviour study of an environmentfriendly corrosion inhibitor by electrochemical methods. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 51, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Huang, H.; Ji, S.; Ruan, J.; Liu, Z. Corrosion behavior of CoCrNi medium-entropy alloy compared with 304 stainless steel in H2SO4 and NaOH solutions. Corros. Sci. 2020, 177, 108973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.H.; Ren, W.N.; Yang, J.; Tian, A.; Du, Y.; Liu, G.; Wei, R.; Zhang, G.; Chen, Y. The corrosion behavior of ultra-fine grained CoNiFeCrMn high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 816, 152583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, C.E.B.; Maascaro, L.H. EIS characterization of a Ti-dental implant in artificial saliva media: Dissolution process of the oxide barrier. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2004, 568, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.N.; Zhang, J.Q. Introduction to Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.K.; Choudhari, A.; Rane, A.; Tiwari, A.; Sharma, P.; Gupta, A.; Sapale, P.; Tirumala, R.T.A.; Muthaiah, R.; Kumar, A. Advances in Nickel-Containing High-Entropy Alloys: From Fundamentals to Additive Manufacturing. Materials 2024, 17, 3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Fe | Cr | Ni | Al | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeCrNi | 33.33 | 33.34 | 33.33 | - | - |
| AlTi0.17 | 30.00 | 30.02 | 29.98 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| AlTi0.2 | 29.41 | 29.42 | 29.41 | 5.88 | 5.88 |
| AlTi0.24 | 28.67 | 28.70 | 28.63 | 7.01 | 6.99 |
| Laser Power (W) | Scanning Speed (mm/s) | Spot Diameter (mm) | Overlap Rate (%) | Powder Feed Rate (g/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1800 | 5 | 2.12 | 45 | 3.7 |
| Sample | Phase | Detected Composition/at.% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | Cr | Ni | Al | Ti | ||
| FeCrNi | FCC | 30.9 ± 0.3 | 31.1 ± 0.3 | 38.0 ± 0.3 | - | - |
| BCC | - | - | - | - | - | |
| AlTi0.17 | FCC | 30.6 ± 0.3 | 28.5 ± 0.3 | 32.0 ± 0.3 | 6.6 ± 0.2 | 2.3 ± 0.2 |
| BCC | 32.4 ± 0.3 | 34.3 ± 0.3 | 22.7 ± 0.3 | 7.2 ± 0.2 | 3.4 ± 0.2 | |
| AlTi0.2 | FCC | 30.9 ± 0.3 | 23.2 ± 0.3 | 37.2 ± 0.3 | 3.0 ± 0.2 | 5.7 ± 0.2 |
| BCC | 35.1 ± 0.3 | 35.7 ± 0.3 | 23.3 ± 0.3 | 2.3 ± 0.2 | 3.6 ± 0.2 | |
| AlTi0.24 | FCC | 29.6 ± 0.3 | 22.2 ± 0.3 | 34.6 ± 0.3 | 7.5 ± 0.2 | 6.1 ± 0.2 |
| BCC | 30.7 ± 0.3 | 41.5 ± 0.3 | 18.8 ± 0.3 | 5.7 ± 0.2 | 3.3 ± 0.2 | |
| Phase | Rs (Ω·cm2) | Rp (Ω·cm2) | Qp Y0 (sn·Ω−1·cm−2) | n1 | Rct (Ω·cm2) | Qct Y0 (sn·Ω−1·cm−2) | n2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeCrNi | 5.151 × 10−6 | 14.21 | 6.960 × 10−9 | 1 | 1.201 × 104 | 7.530 × 10−5 | 0.8752 |
| AlTi0.17 | 4.201 × 10−6 | 15.61 | 5.001 × 10−9 | 1 | 1.412 × 104 | 3.273 × 10−5 | 0.8414 |
| AlTi0.2 | 1.132 × 10−6 | 11.32 | 6.881 × 10−9 | 1 | 4.049 × 104 | 4.133 × 10−5 | 0.9189 |
| AlTi0.24 | 4.257 × 10−5 | 99.23 | 7.347 × 10−10 | 1 | 3.034 × 104 | 1.230 × 10−5 | 0.8038 |
| Phase | Ecorr (VSCE) | Ep-s (VSCE) | Ebr (VSCE) | Ebr-Ecorr (VSCE) | Icorr (A/cm2) | Itr (A/cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeCrNi | −0.2147 | 0.2881 | 0.9569 | 0.6688 | 5.992 × 10−10 | 7.901 × 10−4 |
| AlTi0.17 | −0.4696 | 0.7371 | 1.0597 | 0.3226 | 4.527 × 10−9 | 3.185 × 10−3 |
| AlTi0.2 | −0.2935 | 0.1089 | — | — | 3.668 × 10−9 | — |
| AlTi0.24 | −0.4009 | −0.2841 | −0.1543 | 0.1298 | 1.083 × 10−8 | 2.094 × 10−5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Liu, M.; Liu, C.; Li, X.; Shao, G. Microstructure Evolution Mechanism and Corrosion Resistance of FeCrNi(AlTi)x Medium Entropy Alloy Prepared by Laser Melting Deposition with Al and Ti Content Changes. Coatings 2025, 15, 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070851
Wang K, Liu M, Liu C, Li X, Shao G. Microstructure Evolution Mechanism and Corrosion Resistance of FeCrNi(AlTi)x Medium Entropy Alloy Prepared by Laser Melting Deposition with Al and Ti Content Changes. Coatings. 2025; 15(7):851. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070851
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kai, Mingjie Liu, Chuan Liu, Xiaohui Li, and Guanghui Shao. 2025. "Microstructure Evolution Mechanism and Corrosion Resistance of FeCrNi(AlTi)x Medium Entropy Alloy Prepared by Laser Melting Deposition with Al and Ti Content Changes" Coatings 15, no. 7: 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070851
APA StyleWang, K., Liu, M., Liu, C., Li, X., & Shao, G. (2025). Microstructure Evolution Mechanism and Corrosion Resistance of FeCrNi(AlTi)x Medium Entropy Alloy Prepared by Laser Melting Deposition with Al and Ti Content Changes. Coatings, 15(7), 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070851






