Development of Iron-Modified Cotton Material: Surface Characterization, Biochemical Activity, and Cytotoxicity Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Modification of Material
2.2.2. Determination of Iron
- M is total iron content (bulk iron content) (mg/kg);
- C is the metal concentration in the tested solution (mg/L);
- V is the volume of the sample solution (mL);
- M is the mass of the mineralized sample (g).
2.2.3. Microscopic Analysis
2.2.4. Specific Surface Area
2.2.5. UV-VIS Analysis and Determination of the Protective Properties Against UV Radiation
- E(λ) is solar irradiance;
- ε(λ) is the erythema action spectrum (a measure of the harmfulness of UV radiation for human skin);
- Δλ is the wavelength interval of the measurements;
- T(λ) is the spectral transmittance at wavelength λ.
2.2.6. Air Permeability and Fabric’s Structure
2.2.7. Biochemical Properties
2.2.8. Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances (TBARS)
2.2.9. Influence on PBM Cells
Preparation of Fabrics for Assessment of Biological Properties
Cell Culture
Cell Viability Resazurin Assay
DNA Damage
Plasmid Relaxation Assay
3. Results and Discussion
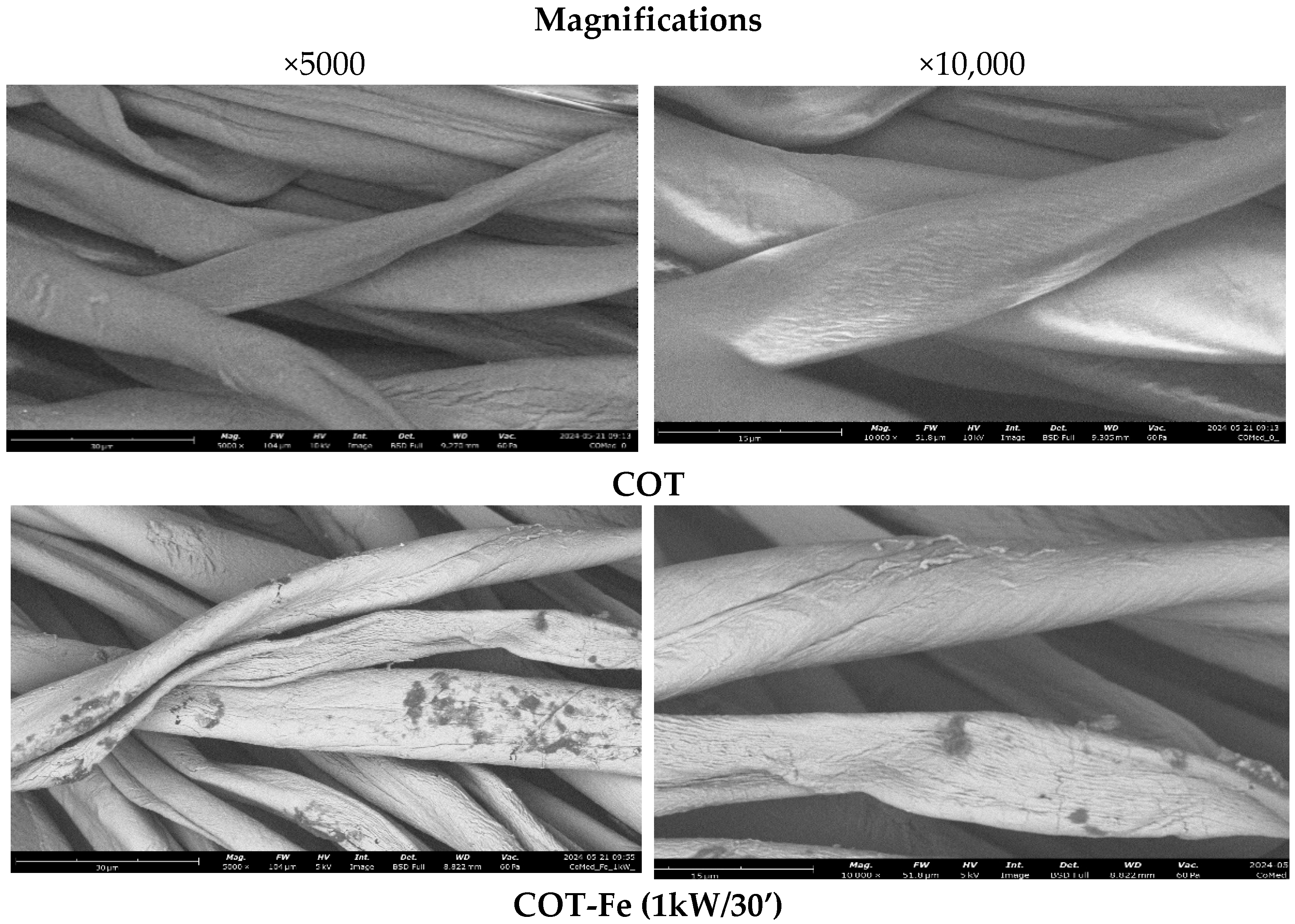
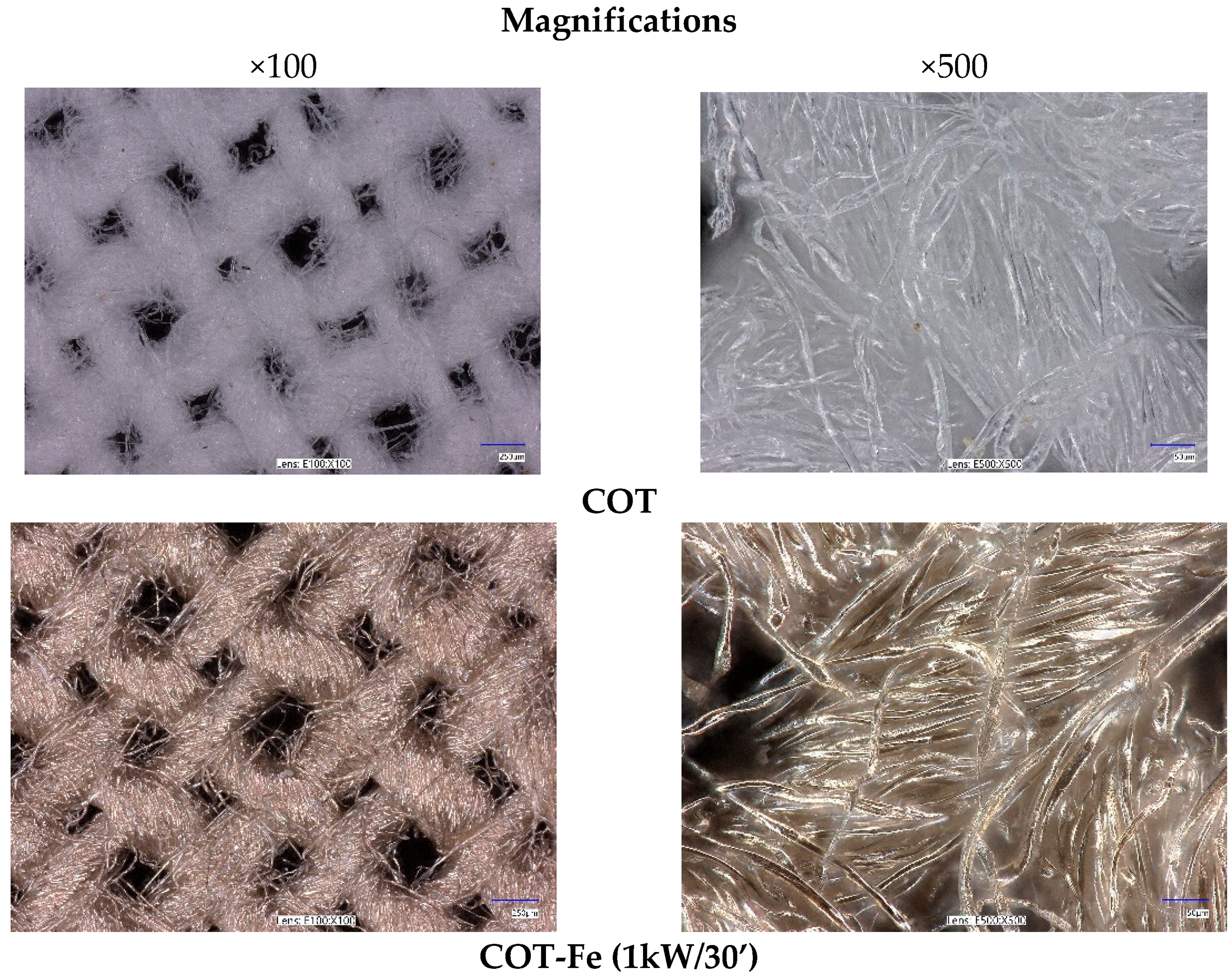
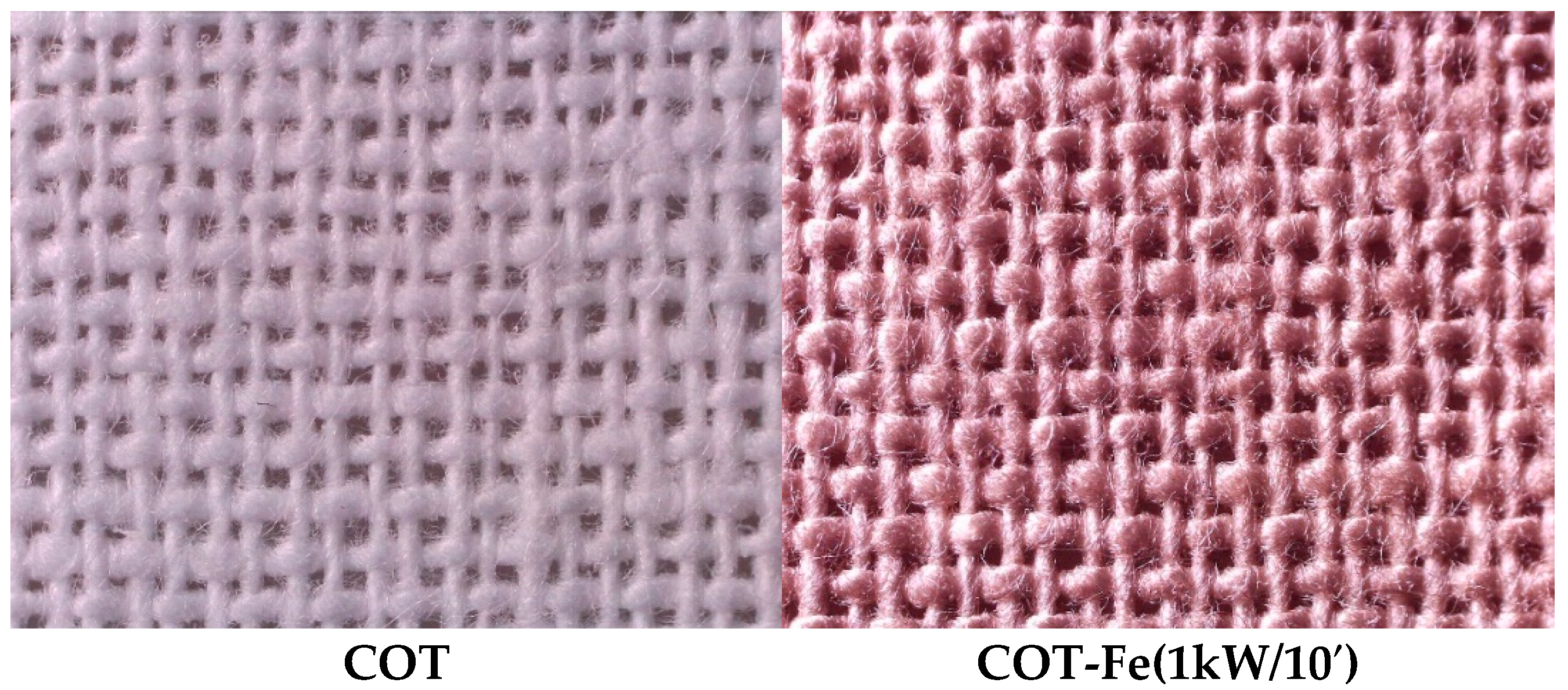
3.1. Microscopic Analysis
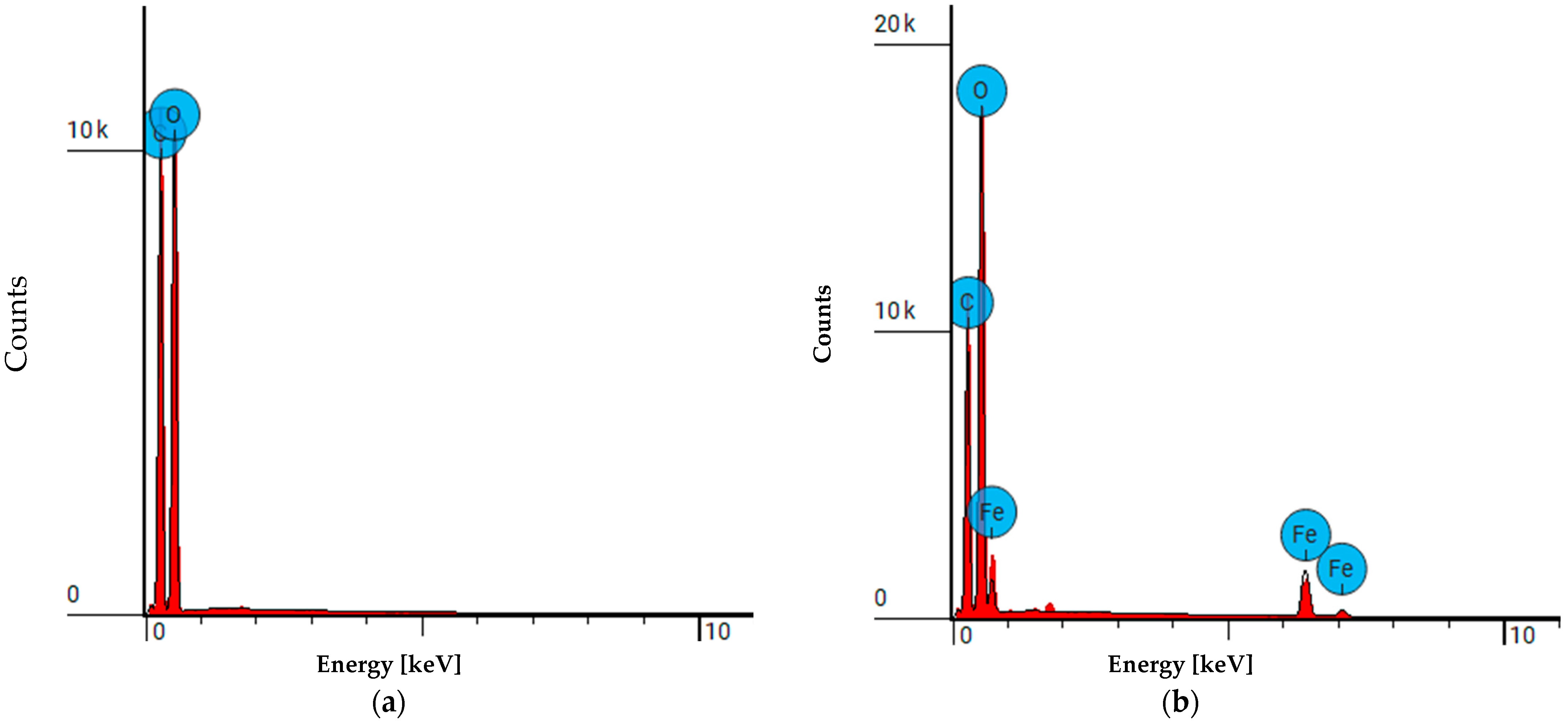
3.2. FAAS Analysis
3.3. Specific Surface Area
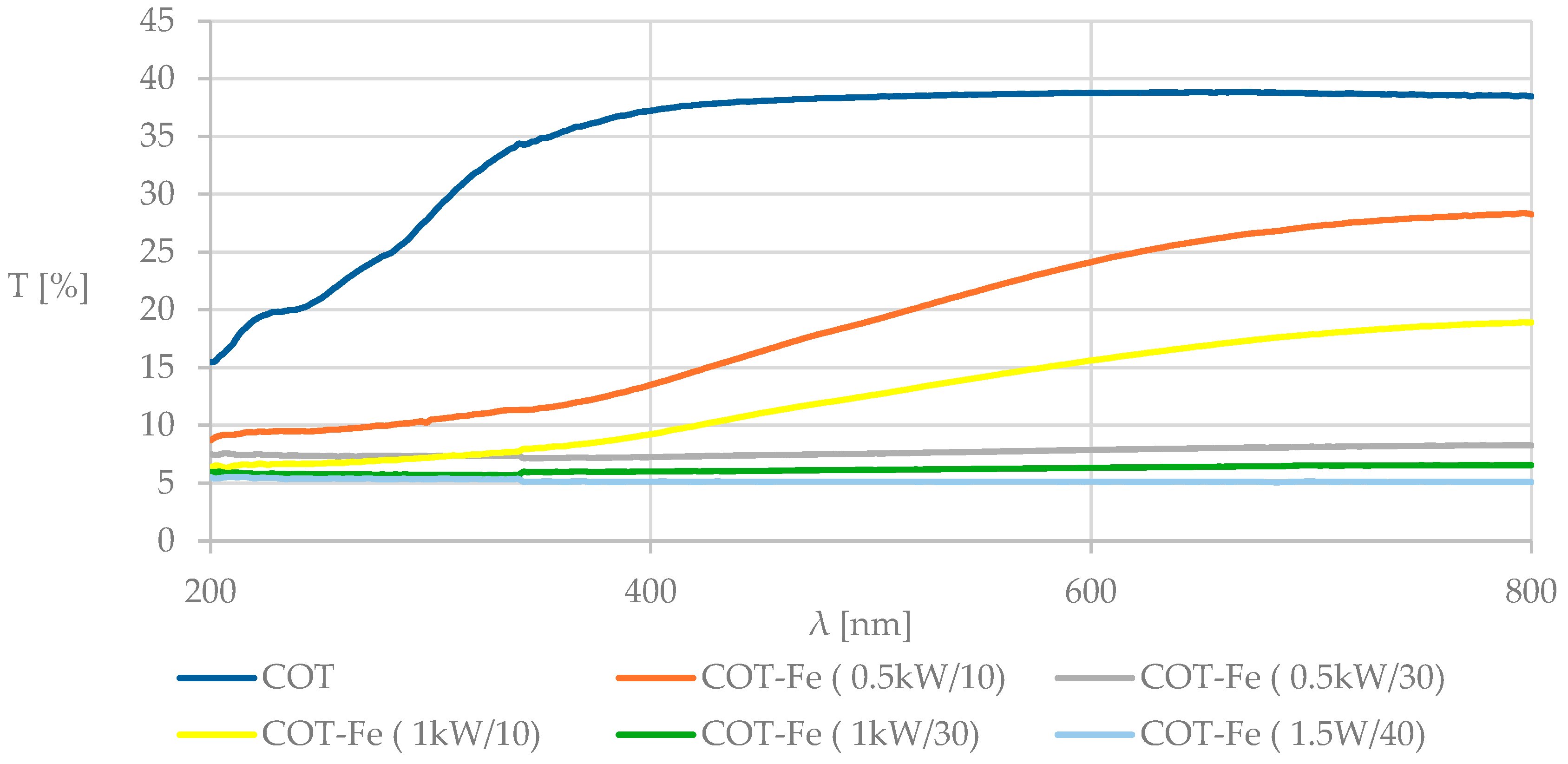
3.4. UV-VIS Analysis and Determination of the Protective Properties Against UV Radiation
3.5. Air Permeability and Fabric’s Structure
3.6. Biochemical Properties
3.7. TBARS
3.8. Effect of COT-Fe Samples on the Viability of PBM Cells
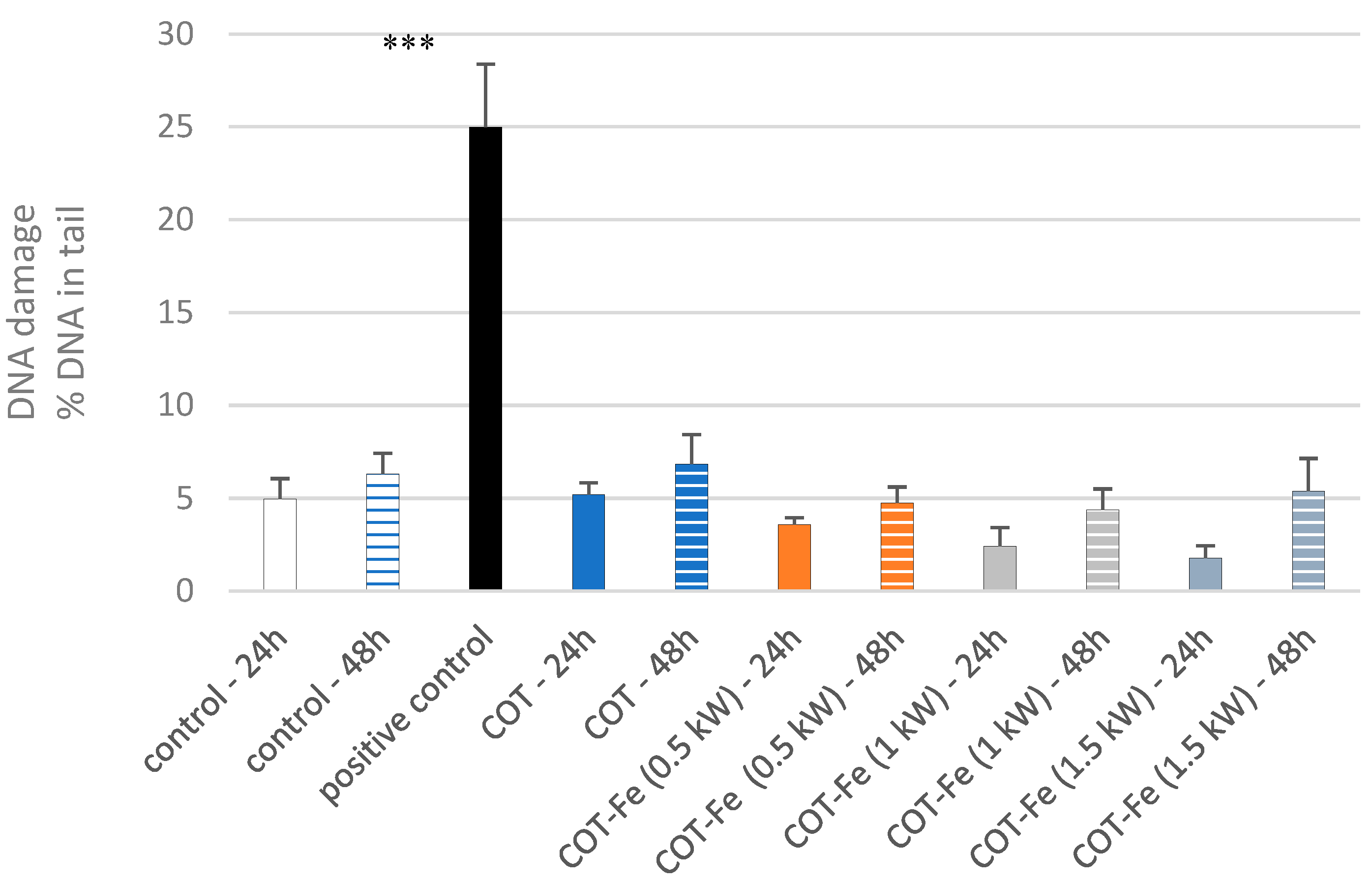
3.9. Effect of COT-Fe Samples on the DNA Damage in PBM Cells
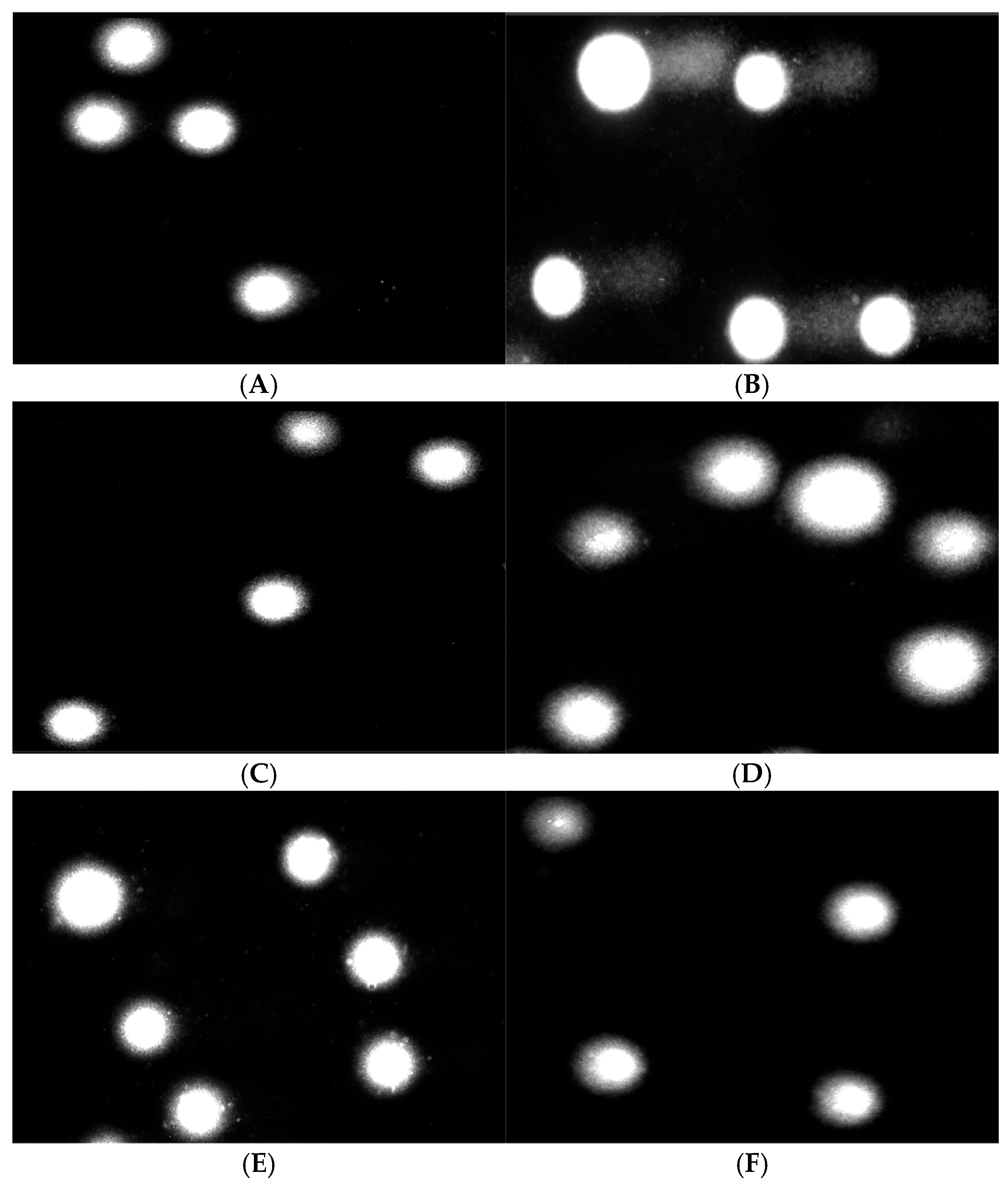
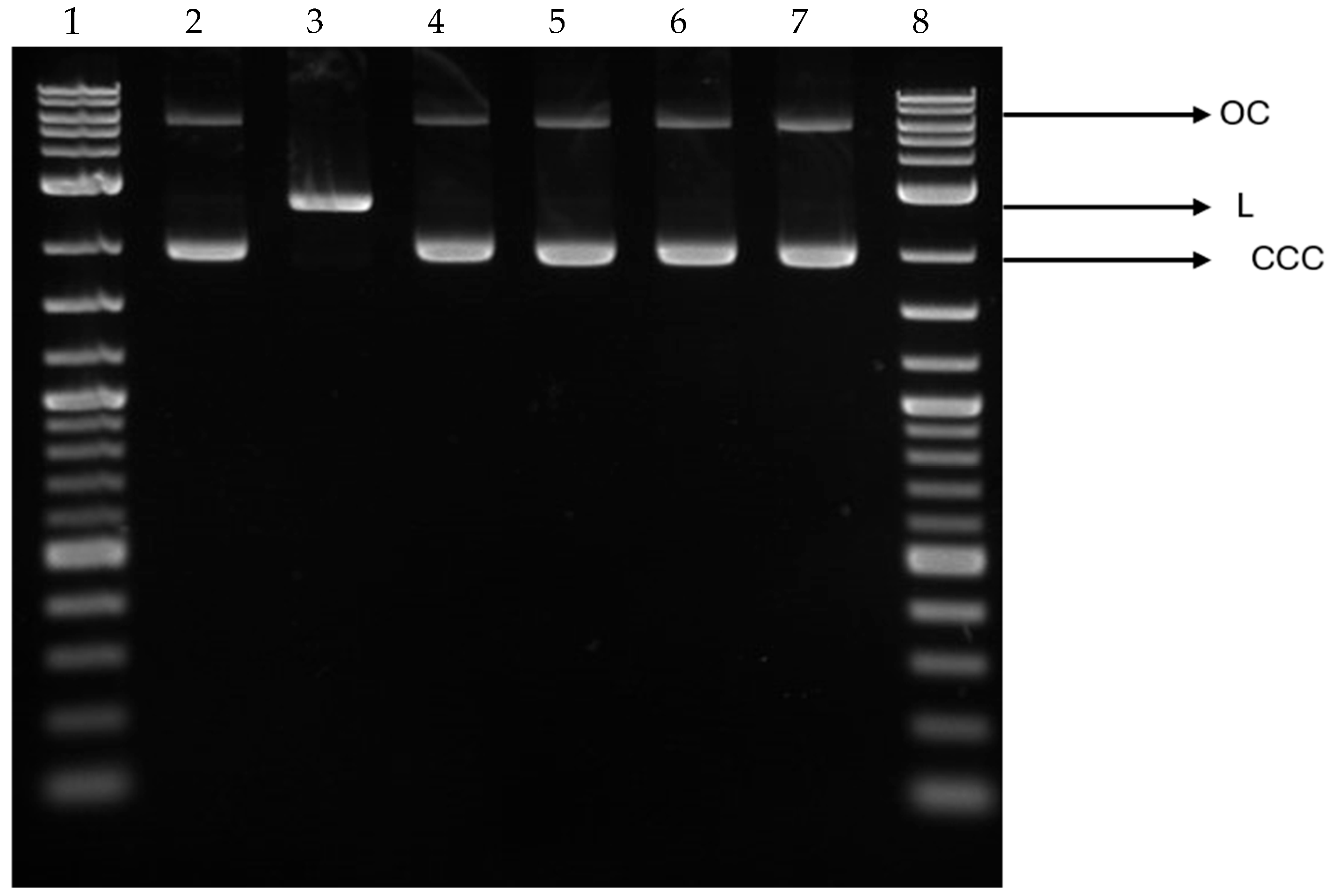
3.10. Effect of COT-Fe Samples on the pUC19 Plasmid Conformation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DC | Direct current |
| aPTT | Activated partial thromboplastin time |
| PT | Prothrombin time |
| TBARS | Linear dichroism |
| PLLA | Poly-L-lactic acid |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| UPF | Ultraviolet protection factor |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| BET | Brunauer–Emmet–Teller method |
| TBA | Thiobarbituric acid |
| TCA | Trichloroethanoic acid |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| TBARS | Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances |
| EDS | Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| COT | Cotton sample |
| COT-Fe | Cotton-iron sample |
| IUPAC | International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry |
| PBM cells | Peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
| PBS | Phosphate Buffered Saline |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| LMP | Low-melting-point agarose |
| NMP | Normal-melting-point agarose |
References
- Kauvar, D.S.; Lefering, R.; Wade, C.E. Impact of Hemorrhage on Trauma Outcome: An Overview of Epidemiology, Clinical Presentations, and Therapeutic Considerations. J. Trauma 2006, 60, S3–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Zhou, W.; Gao, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Fang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, W.; Weng, Y.; et al. Efficient, Biosafe and Tissue Adhesive Hemostatic Cotton Gauze with Controlled Balance of Hydrophilicity and Hydrophobicity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granados, A.; Pleixats, R.; Vallribera, A. Recent Advances on Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Cotton Fabrics Containing Nanostructures. Molecules 2021, 26, 3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahriari-Khalaji, M.; Alassod, A.; Nozhat, Z. Cotton-Based Health Care Textile: A Mini Review. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 10409–10432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, A.A.; Patel, V.N.; Pancholi, U.V. In-Vitro Analysis of Hemostatic Cotton Khadi Dressing with Kaolin/Chitosan-Based Composition and Its Application as Prospective Wound Dressing. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, P.; Xiao, D.; Zhu, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sui, X.; Feng, X.; Xu, H.; Mao, Z. Chitosan-Bound Carboxymethylated Cotton Fabric and Its Application as Wound Dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 221, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Shang, X.; Chen, H.; Xiao, L.; Zhu, Y.; Fan, J. A Tightly-Bonded and Flexible Mesoporous Zeolite-Cotton Hybrid Hemostat. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.V.; Prevost, N.; Yager, D.; Nam, S.; Graves, E.; Santiago, M.; Condon, B.; Dacorta, J. Antimicrobial and Hemostatic Activities of Cotton-Based Dressings Designed to Address Prolonged Field Care Applications. Mil. Med. 2021, 186, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutch, N.J.; Waters, E.K.; Morrissey, J.H. Immobilized Transition Metals Stimulate Contact Activation and Drive Factor XII-Mediated Coagulation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 2108–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrozińska, Z.; Ponczek, M.; Kaczmarek, A.; Boguń, M.; Sulak, E.; Kudzin, M.H. Blood Coagulation Activities of Cotton–Alginate–Copper Composites. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrozińska, Z.; Kudzin, M.H.; Ponczek, M.B.; Kaczmarek, A.; Król, P.; Lisiak-Kucińska, A.; Żyłła, R.; Walawska, A. Biochemical Approach to Poly(Lactide)–Copper Composite—Impact on Blood Coagulation Processes. Materials 2024, 17, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrozińska, Z.; Kaczmarek, A.; Świerczyńska, M.; Juszczak, M.; Kudzin, M.H. Biochemical Behavior, Influence on Cell DNA Condition, and Microbiological Properties of Wool and Wool–Copper Materials. Materials 2024, 17, 2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrozińska, Z.; Ponczek, M.B.; Kaczmarek, A.; Świerczyńska, M.; Kudzin, M.H. Activity in the Field of Blood Coagulation Processes of Poly(Lactide)-Zinc Fiber Composite Material Obtained by Magnetron Sputtering. Coatings 2024, 14, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praticò, D.; Pasin, M.; Barry, O.P.; Ghiselli, A.; Sabatino, G.; Iuliano, L.; FitzGerald, G.A.; Violi, F. Iron-Dependent Human Platelet Activation and Hydroxyl Radical Formation: Involvement of Protein Kinase C. Circulation 1999, 99, 3118–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechipurenko, D.Y.; Receveur, N.; Yakimenko, A.O.; Shepelyuk, T.O.; Yakusheva, A.A.; Kerimov, R.R.; Obydennyy, S.I.; Eckly, A.; Léon, C.; Gachet, C.; et al. Clot Contraction Drives the Translocation of Procoagulant Platelets to Thrombus Surface. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Zhou, X.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Jiao, Z.; Guo, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Biodegradable Alginate-Based Sponge with Antibacterial and Shape Memory Properties for Penetrating Wound Hemostasis. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 247, 110263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, K.; Fu, Y.V.; Xu, T.; Li, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, L.-N.; Lee, C.-S. A Novel Double-Crosslinking-Double-Network Design for Injectable Hydrogels with Enhanced Tissue Adhesion and Antibacterial Capability for Wound Treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1904156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, P.; Chang, S.; Hu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Mao, L.; Yang, H. Emerging Nanoclay Composite for Effective Hemostasis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1704452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simberg, D.; Zhang, W.-M.; Merkulov, S.; McCrae, K.; Park, J.-H.; Sailor, M.J.; Ruoslahti, E. Contact Activation of Kallikrein–Kinin System by Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles In Vitro and In Vivo. J. Control. Release 2009, 140, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meddahi-Pellé, A.; Legrand, A.; Marcellan, A.; Louedec, L.; Letourneur, D.; Leibler, L. Organ Repair, Hemostasis, and In Vivo Bonding of Medical Devices by Aqueous Solutions of Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 6369–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, C.S.; Castro, P.J.; Sousa, S.C.; Pullar, R.C.; Tobaldi, D.M.; Piccirillo, C.; Pintado, M.M. Films of Chitosan and Natural Modified Hydroxyapatite as Effective UV-Protecting, Biocompatible and Antibacterial Wound Dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Fu, X.; Gao, X.; Mao, X.; Li, Z. UV-Shielding Alginate Films Crosslinked with Fe3+ Containing EDTA. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 239, 115480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Hady, M.M.; Farouk, A.; Saeed, S.E.-S.; Zaghloul, S. Antibacterial and UV Protection Properties of Modified Cotton Fabric Using a Curcumin/TiO2 Nanocomposite for Medical Textile Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Xu, L.; Porter, N.A. Free Radical Lipid Peroxidation: Mechanisms and Analysis. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5944–5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Dipietro, L.A. Factors Affecting Wound Healing. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, S.M.; Duquaine, D.; Mundada, L.V.; Menon, R.G.; Khan, B.V.; Rajagopalan, S.; Fay, W.P. Chronic Iron Administration Increases Vascular Oxidative Stress and Accelerates Arterial Thrombosis. Circulation 2003, 107, 2601–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlova, E.; Sherstyukova, E.; Sergunova, V.; Kozlov, A.; Gudkova, O.; Inozemtsev, V.; Chernysh, A. The Toxic Influence of Excess Free Iron on Red Blood Cells in the Biophysical Experiment: An In Vitro Study. J. Toxicol. 2022, 2022, 7113958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 13758-1:2002; Textiles. Solar UV Protective Properties. Method of Test for Apparel Fabrics. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002.
- ISO 9237:1995; Textiles—Determination of the Permeability of Fabrics to Air. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995.
- EN ISO 5084:1996; Textiles. Determination of Thickness of Textiles and Textile Products. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996.
- EN 12127:1997; Textiles—Fabrics—Determination of Mass per Unit Area Using Small Samples. The European Committee for Standardization (CEN): Brussels, Belgium, 1997.
- EN ISO 139:2005; Textiles—Standard Atmospheres for Conditioning and Testing. Amendment 1. Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005.
- Kaals, R.; Priel, M.; Bremser, W.; D’Emilio, S.; Bosch, W.; Bich, W.; Vilalta, E.; Averlant, P.; Bièvre, P.J.D.; Fisicaro, P.; et al. EA Guideline on the Expression of Uncertainty in Quantitative Testing for Up-to-Date Information. In Proceedings of the EALC Meeting, Oslo, Norway, 7–9 September 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrozińska, Z.; Świerczyńska, M.; Juszczak, M.; Woźniak, K.; Kudzin, M.H. Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity, Hemostatic Efficacy, Blood Coagulation Dynamics, and DNA Damage of Linen–Copper Composite Materials. J. Compos Sci. 2025, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluska, M.; Juszczak, M.; Wysokiński, D.; Żuchowski, J.; Stochmal, A.; Woźniak, K. Kaempferol derivatives isolated from Lens culinaris Medik. reduce DNA damage induced by etoposide in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Toxicol. Res. 2019, 8, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.; Wilson, I.; Orton, T.; Pognan, F. Investigation of the Alamar Blue (resazurin) fluorescent dye for the assessment of mammalian cell cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 5421–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarz, P.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.; Kaarniranta, K.; Blasiak, J. All-Trans Retinoic Acid Modulates DNA Damage Response and the Expression of the VEGF-A and MKI67 Genes in ARPE-19 Cells Subjected to Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juszczak, M.; Das, S.; Kosińska, A.; Rybarczyk-Pirek, A.J.; Wzgarda-Raj, K.; Tokarz, P.; Vasudevan, S.; Chworos, A.; Woźniak, K.; Rudolf, B. Piano-stool ruthenium(ii) complexes with maleimide and phosphine or phosphite ligands: Synthesis and activity against normal and cancer cells. Dalton Trans. 2023, 52, 4237–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, A.; Granick, M.S.; Tomaselli, N.L. Wound Dressings and Comparative Effectiveness Data. Adv. Wound Care 2014, 3, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Sanchez, C.; Al Mushref, F.R.A.; Norrito, M.; Yendall, K.; Liu, Y.; Conway, P.P. The Effect of Pore Size and Porosity on Mechanical Properties and Biological Response of Porous Titanium Scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 77, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of Gases, with Special Reference to the Evaluation of Surface Area and Pore Size Distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyama, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Rubiy’atno; Morikawa, M.; Mori, K. Sulfamethoxazole removal and fuel-feedstock biomass production from wastewater in a phyto-Fenton process using duckweed culture. Chemosphere 2024, 361, 142592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, P.D.S.M.; Ko, D.O.; Piao, M.J.; Kang, K.A.; Herath, H.M.U.L.; Hyun, J.W. Protective effect of luteolin against oxidative stressmediated cell injury via enhancing antioxidant systems. Mol. Med. Rep. 2024, 30, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, Q.; Li, X.; Hua, S.; Cao, D.; Chang, Y. Disrupting redox homeostasis for tumor therapy based on PDT/chemo/ferroptosis therapeutic hybrid liposomes. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 20152–20162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.P.; McCoy, M.T.; Tice, R.R.; Schneider, E.L. A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp. Cell Res. 1988, 175, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorska, M.; Ruzycka-Ayoush, M.; Rios-Mondragon, I.; Longhin, E.M.; Meczynska-Wielgosz, S.; Wojewodzka, M.; Kowalczyk, A.; Kasprzak, A.; Nowakowska, J.; Sobczak, K.; et al. Lack of cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of mPEG-silane coated iron(III) oxide nanoparticles doped with magnesium despite cellular uptake in cancerous and noncancerous lung cells. Toxicol. Vitro 2024, 99, 105850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, R.; Niu, J.; Li, Y.; Ke, G.; Huang, H.; Pei, J.; Ding, W.; Yuan, G. In vitro cytocompatibility, hemocompatibility and antibacterial properties of biodegradable Zn-Cu-Fe alloys for cardiovascular stents applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 113, 111007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Xu, L.; Zeng, M.; Dang, H. Application and Development Prospect of Nanoscale Iron Based Metal-Organic Frameworks in Biomedicine. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 4907–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


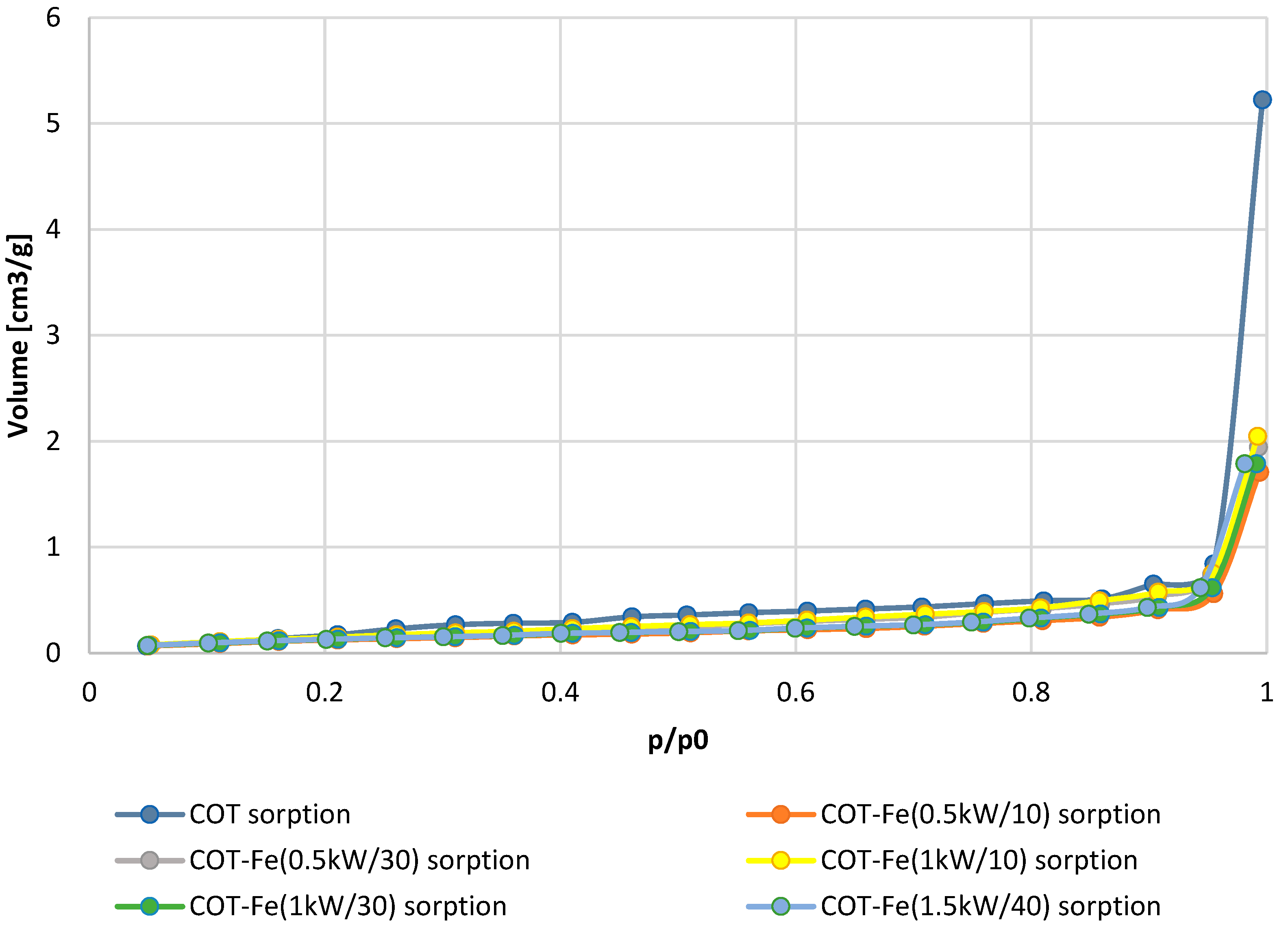

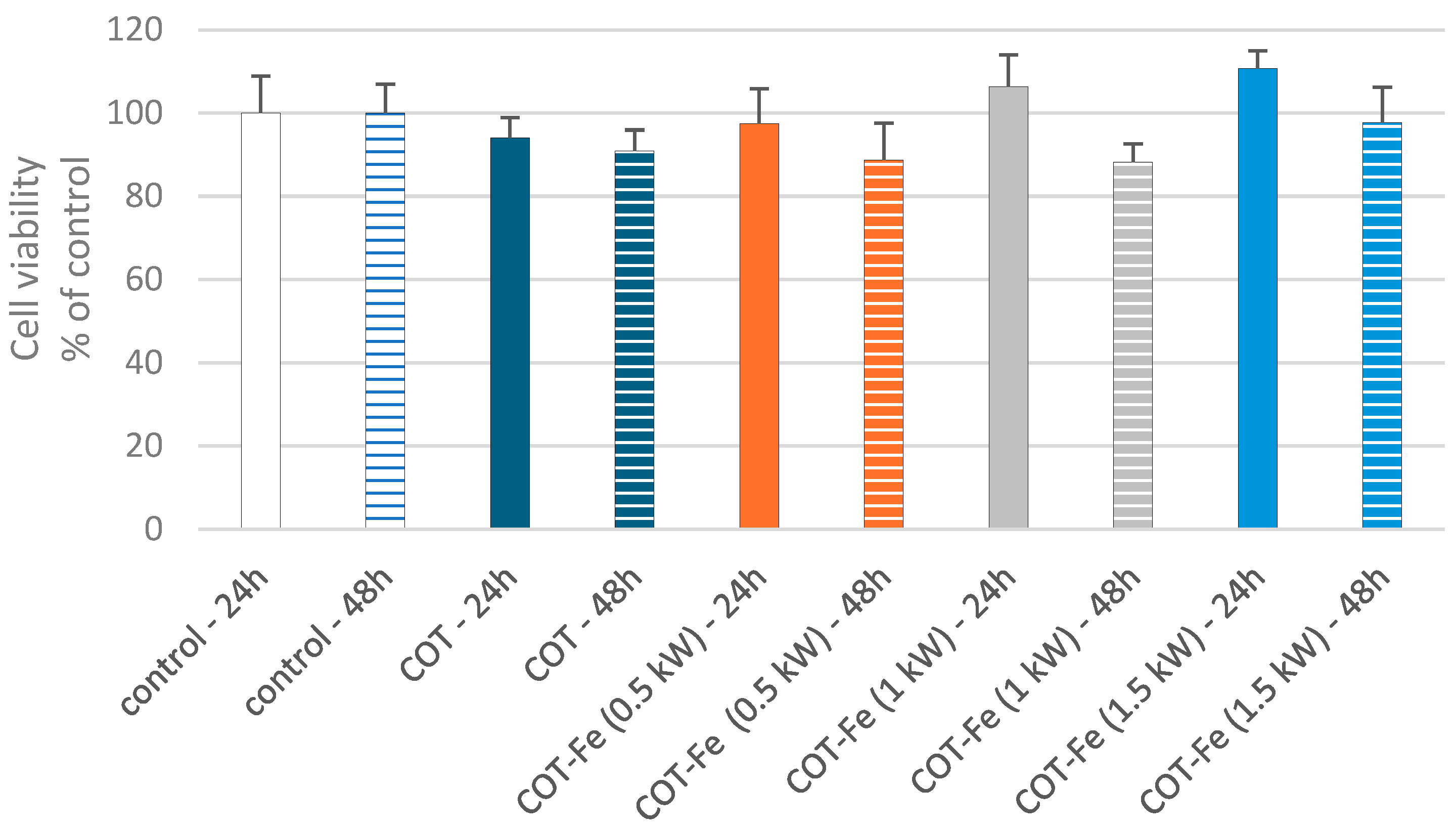
| Sample Name | Fe Concentration [g/kg] | Total Pore Volume [cm3/g] | Specific Surface Area [m2/g] |
| COT | 0 | 7.125 × 10−3 | 0.7216 |
| COT-Fe (0.5kW/10′) | 0.638 | 3.331 × 10−3 | 0.7122 |
| COT-Fe (0.5kW/30′) | 2.187 | 2.643 × 10−3 | 0.6130 |
| COT-Fe (1kW/10′) | 1.043 | 3.249 × 10−3 | 0.7085 |
| COT-Fe (1kW/30′) | 3.562 | 2.411 × 10−3 | 0.6059 |
| COT-Fe (1.5kW/40′) | 20.41 | 2.118 × 10−3 | 0.5155 |
| COT | COT-Fe (0.5kW/10′) | COT-Fe (0.5kW/30′) | COT-Fe (1kW/10′) | COT-Fe (1kW/30′) | COT-Fe (1.5kW/40′) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UPF | 3.29 | 9.27 | 13.62 | 9.97 | 16.75 | 18.22 |
| average %T, λ = 290–400 nm | 31.81 | 10.56 | 6.87 | 9.02 | 5.75 | 4.72 |
| Thickness [mm] | Surface Mass [g/m2] | Air Permeability [mm/s] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 Pa | 200 Pa | |||
| COT | 0.46 ± 0.02 | 183 ± 2 | 802 ± 10 | 1300 ± 20 |
| COT-Fe (0.5kW/10′) | 0.47 ± 0.02 | 184 ± 1 | 841 ± 12 | 1353 ± 16 |
| COT-Fe (0.5kW/30′) | 0.47 ± 0.02 | 184 ± 1 | 847 ± 19 | 1363 ± 38 |
| COT-Fe (1kW/10′) | 0.48 ± 0.02 | 184 ± 1 | 842 ± 10 | 1358 ± 16 |
| COT-Fe (1kW/30′) | 0.47 ± 0.02 | 185 ± 2 | 829 ± 34 | 1368 ± 60 |
| COT-Fe (1.5kW/40′) | 0.47 ± 0.02 | 184 ± 2 | 840 ± 11 | 1358 ± 25 |
| C | COT-Fe (1.5kW/40′) | COT-Fe (1kW/30′) | COT-Fe (1kW/10′) | COT-Fe (0.5kW/30′) | COT-Fe (0.5kW/10′) | COT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.615 | 0.705 | 0.705 | 0.705 | 0.321 | 0.423 | 0.692 | TBARS (nM) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kudzin, M.H.; Mrozińska, Z.; Kaczmarek, A.; Chruściel, J.J.; Pinar, A.; Sulak, E.; Shah, S.A.R.; Juszczak, M.; Woźniak, K.; Ponczek, M.B. Development of Iron-Modified Cotton Material: Surface Characterization, Biochemical Activity, and Cytotoxicity Assessment. Coatings 2025, 15, 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060663
Kudzin MH, Mrozińska Z, Kaczmarek A, Chruściel JJ, Pinar A, Sulak E, Shah SAR, Juszczak M, Woźniak K, Ponczek MB. Development of Iron-Modified Cotton Material: Surface Characterization, Biochemical Activity, and Cytotoxicity Assessment. Coatings. 2025; 15(6):663. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060663
Chicago/Turabian StyleKudzin, Marcin H., Zdzisława Mrozińska, Anna Kaczmarek, Jerzy J. Chruściel, Anna Pinar, Edyta Sulak, Syed Ali Raza Shah, Michał Juszczak, Katarzyna Woźniak, and Michał B. Ponczek. 2025. "Development of Iron-Modified Cotton Material: Surface Characterization, Biochemical Activity, and Cytotoxicity Assessment" Coatings 15, no. 6: 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060663
APA StyleKudzin, M. H., Mrozińska, Z., Kaczmarek, A., Chruściel, J. J., Pinar, A., Sulak, E., Shah, S. A. R., Juszczak, M., Woźniak, K., & Ponczek, M. B. (2025). Development of Iron-Modified Cotton Material: Surface Characterization, Biochemical Activity, and Cytotoxicity Assessment. Coatings, 15(6), 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060663








