Multi-Objective Optimization of Laser Cleaning Quality of Composite Paint Layers Based on Response Surface
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental Design
2.1. Preparation and Treatment of Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Mathematical Modelling and Analysis of Variance
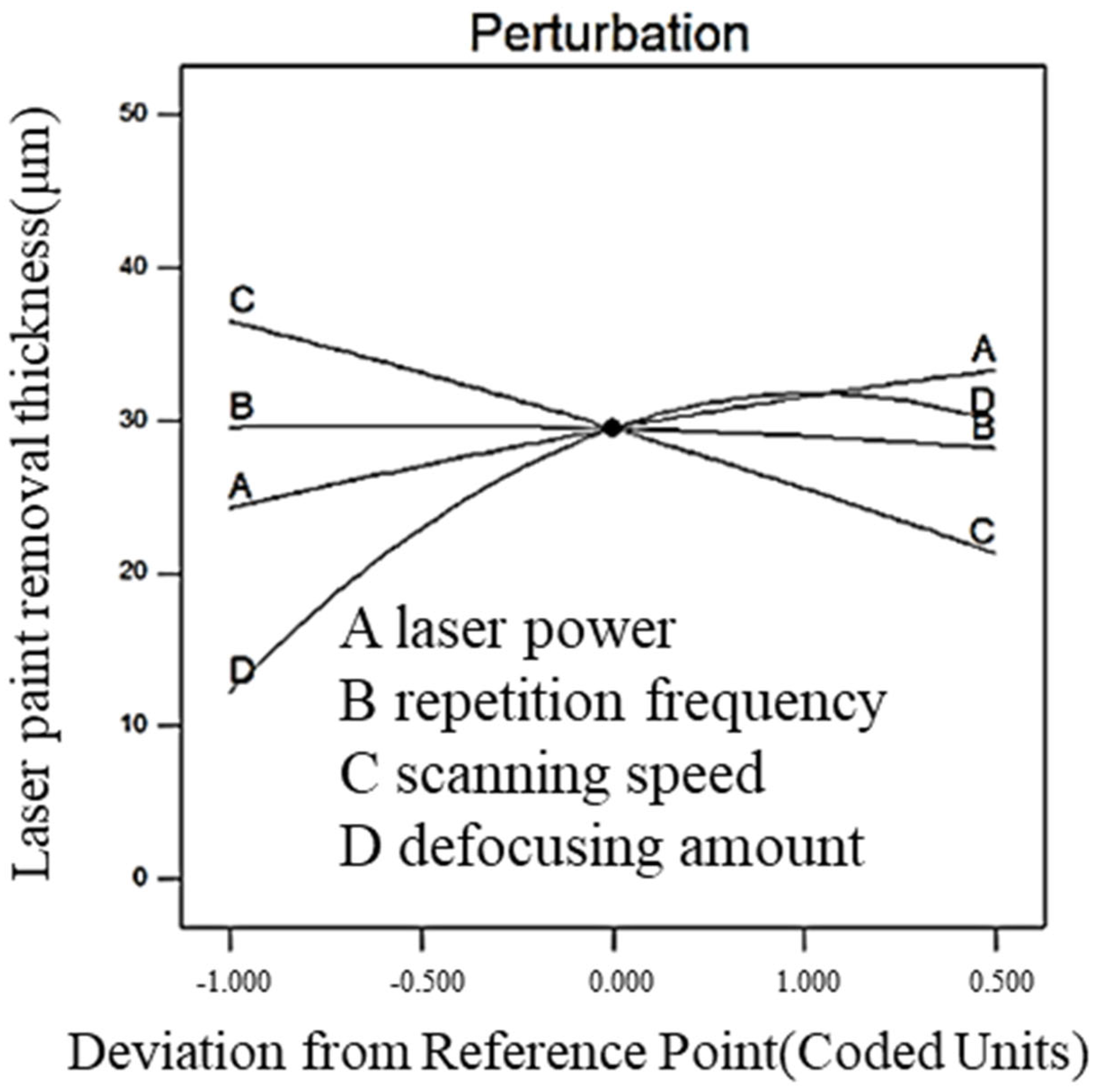
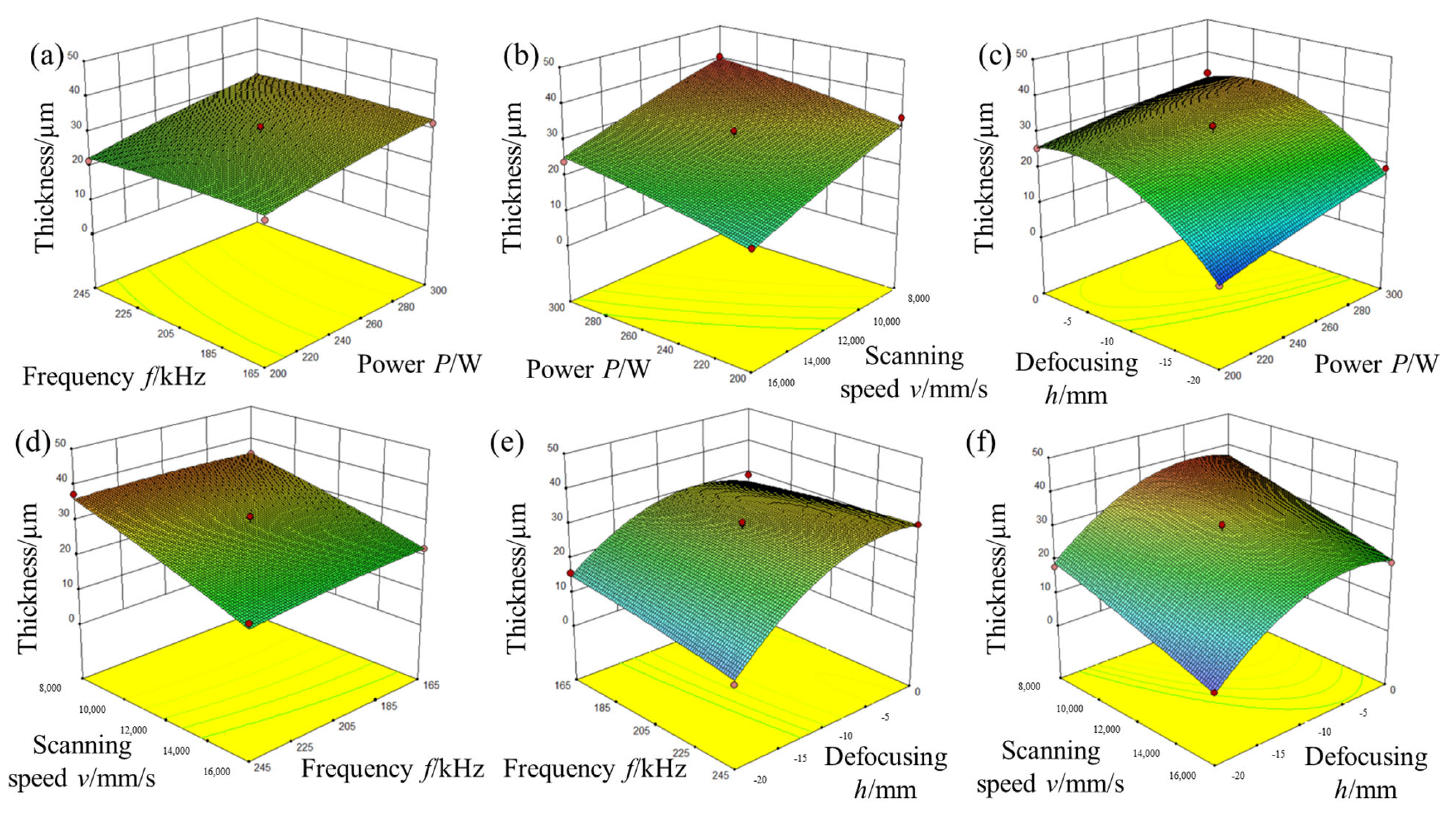
3.2. Influence of Process Parameters on the Amount of Paint Residue
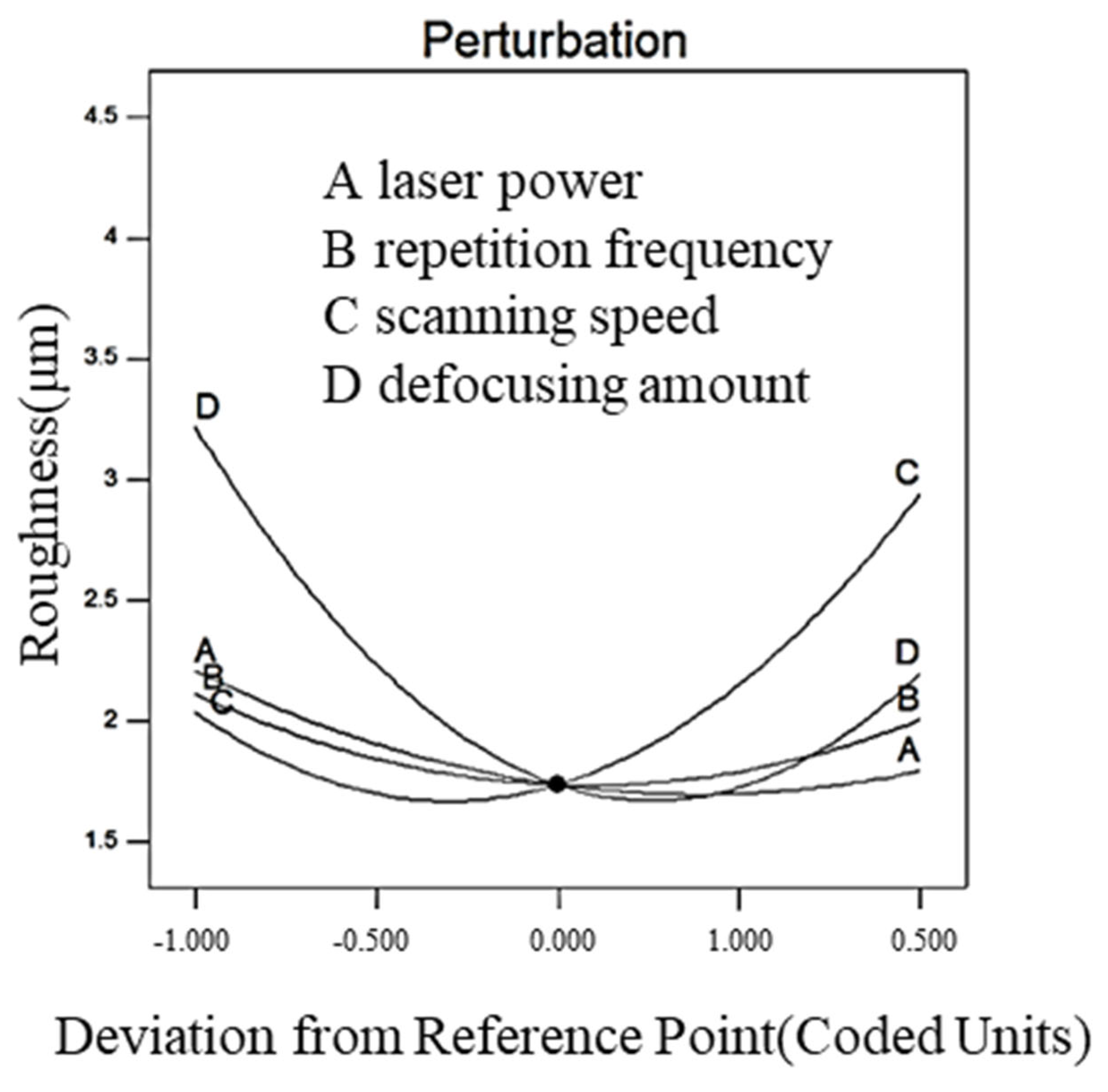
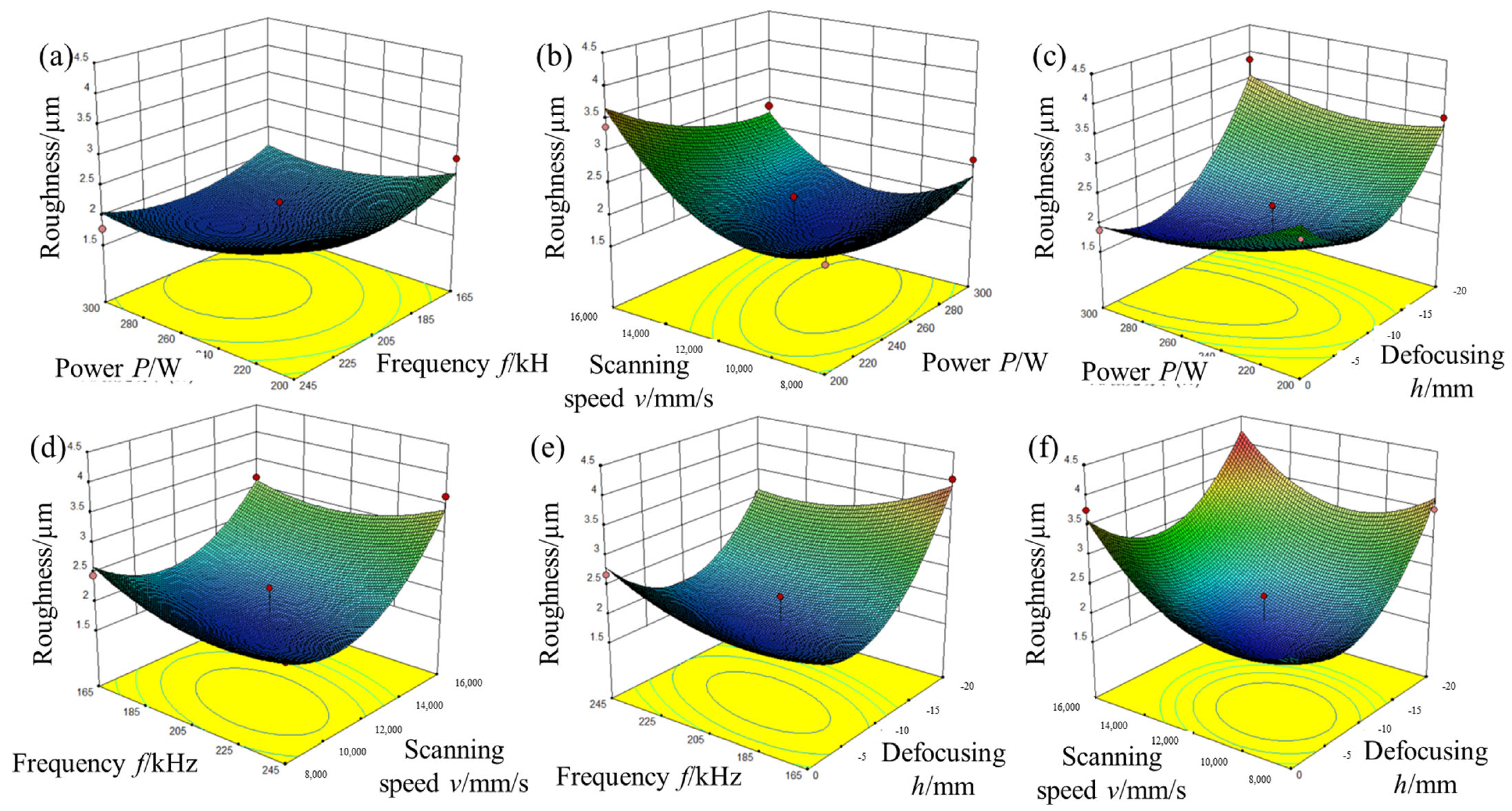
3.3. Effect of Process Parameters on Surface Roughness
3.4. Evaluation Method for Laser Paint Removal from Al Alloy and Its Optimization
4. Conclusions
- Based on the response surface methodology (RSM), a regression prediction model was constructed for the paint layer removal thickness and surface roughness. A model variance analysis showed that both regression models are reliable. This approach can be used for simulating the laser cleaning quality data of composite paint layers.
- The effects of the parameters of the laser cleaning process and their interaction with the thickness of the laser paint removal and the surface roughness of the paint layer after cleaning were examined. The regression predictor model is analyzed and the order of influence on the thickness of the paint stripper is as follows: defocusing rate > scanning speed > laser power > repeat rate. The order of magnitude of the effect on sharpness is as follows: defocusing amount > scanning speed > laser power > repetition rate.
- To achieve the optimum values of laser paint removal thickness and surface roughness of the paint layer after cleaning, Design-expert software was used to solve the parameters of the laser cleaning process under the optimal target. The parameters for the laser cleaning process that are most reliable were selected: laser power P = 291 W, frequency of repetition f = 166 kHz, scanning speed v = 8425 mm/s, and refractive index h = −17 mm. The optimal parameters of the process were verified via randomization. The relative error for the thickness of the paint stripper is 1.9–3.8 m and the relative error for roughness is −0.573–−0.419 m. This demonstrates that the response surface method can be used to predict and optimize the surface quality of laser paint removal.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, H.; Liu, H.; Gao, R.; Liu, X.; Yu, X.; Song, F.; Liu, L. Numerical simulation of paint stripping on CFRP by pulsed laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 145, 107450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Ouyang, W.; Jiao, J.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X.; Luo, W.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y. Investigation on repairing 30CrMnSiNi2A steel with laser additive and subtractive hybrid remanufacturing technology. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2023, 160, 107254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, T.; Ban, G.; Zou, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, C. Effect of scanning speed on laser cleaning of composite paint layer on aluminum alloy. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 171, 110470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, S.; Pan, Y.; Li, Z.; Yu, L. Current research status of laser cleaning of carbon fiber reinforced polymers. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 39, 109312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, T.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Q. Influence of Different Spot Pattern Lasers on Cleaning Effect of TC4 Titanium Alloy. Materials 2025, 18, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Xu, L.; Su, L.; Ouyang, W.; Sun, S.; Cheng, W.; Guo, W.; Ma, X.; Zhang, W.; Jiao, J. Enhancing high-temperature performance of Inconel 718 LDED samples through hybrid laser polishing post-treatment. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2024, 19, 2345391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Qin, X.; Liu, X.; Su, L.; Sun, Z.; Li, W.; Ma, X.; Guo, W.; Cheng, W. Effect of surface morphology and microstructure on the corrosion behavior of Inconel 718 superalloy prepared by laser additive and subtractive hybrid manufacturing. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 44, 112176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Lu, Y.; Duan, X. Electrical discharge-mechanical hybrid drilling of micro-holes in carbon fibre-reinforced polymers. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2025, 205, 104243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zou, J.; Liu, T.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Z. Single-pulse and multi-pulse cleaning mechanism study on laser paint removal of composite paint layer on surface of 2A12 aluminum alloy. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 45, 112292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, M.P.; Ctvrtnickova, T.; Fernandez, E.; Ramos, J.; Yáñez, A.; Nicolas, G. Laser cleaning of varnishes and contaminants on brass. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 5579–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Qiao, H.; Lu, Y. Effects of Laser De-painting on Microstructure and Properties of Ti17 Alloy. Surf. Technol. 2018, 47, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Jasim, H.; Demir, A.; Previtali, B.; Taha, Z.A. Process development and monitoring in stripping of a highly transparent polymeric paint with ns-pulsed fiber laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2017, 93, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brygo, F.; Dutouquet, C.; Le Guern, F.; Oltra, R.; Semerok, A.; Weulersse, J. Laser fluence, repetition rate and pulse duration effects on paint ablation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 2131–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razab, M.; Jaafar, M.; Abdullah, N.; Amin, M.F.M.; Mohamed, M. Influence of elemental compositions in laser cleaning for automotive coating systems. J. Russ. Laser Res. 2016, 37, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Du, P.; Li, W.; Song, F.; Wang, C.; Chen, N. Research on Paint Removal with 1064 nm Quasi-Continuous-Wave Laser. Chin. J. Lasers 2012, 39, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Huang, T.; Chong, A.W.; Zhou, R.; Choo, Y.S.; Hong, M. Laser cleaning of steel structure surface for paint removal and repaint adhesion. Opto-Electron. Eng. 2017, 44, 340–344. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Q.; Meng, X.; Zhu, M.; Guo, Z.; Fu, Q. Laser Paint Removal Process Parameter Optimization via Response Surface Methodology. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2019, 56, 190–197. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Dai, Z.; Ding, J.; Xu, J. Multi-objective optimization of laser cleaning quality based on response surface and genetic algorithm. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2022, 1–13. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/31.1690.tn.20220713.1645.454.html (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Yang, W.; Lin, D.; Zhong, M.; Li, S.; Qian, Z.; Liu, G.; Cao, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G. Controllability of Laser Removal of Aircraft Skin Paint Layer Based on Response Surface Analysis. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2023, 60, 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, H. Optimization of Laser Cleaning Process Parameters for Petroleum Pipe Threads Based on Response Surface Method and Particle Swarm Algorithm. Chin. J. Lasers 2022, 49, 40–52. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, M.; Bian, H.; Zhang, D. Laser cleaning Technology of 2A12 Aluminum Alloy Composite Paint Layer. Chin. J. Lasers 2022, 49, 140–150. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Du, R.; Li, C.; Zhang, T.; Liu, H.; Wu, D. Optimizing laser cleaning quality for composite paint layer on aluminum alloy surface using response surface methodology. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 183, 112386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Deng, J.; Lei, J.; Tang, W.; Zhou, W.; Lei, Z. Multi Objective Optimization of Laser Cleaning Quality of Q390 Steel Rust Layer Based on Response Surface Methodology and NSGA-II Algorithm. Materials 2024, 17, 3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, Z.; Kang, M.; Shi, M.; Deng, R.; Yan, Y.; Zhu, Q. Research on multivariate nonlinear regression model of specific energy of rock with laser drilling based on response surface methodology. Opt. Commun. 2021, 489, 126865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
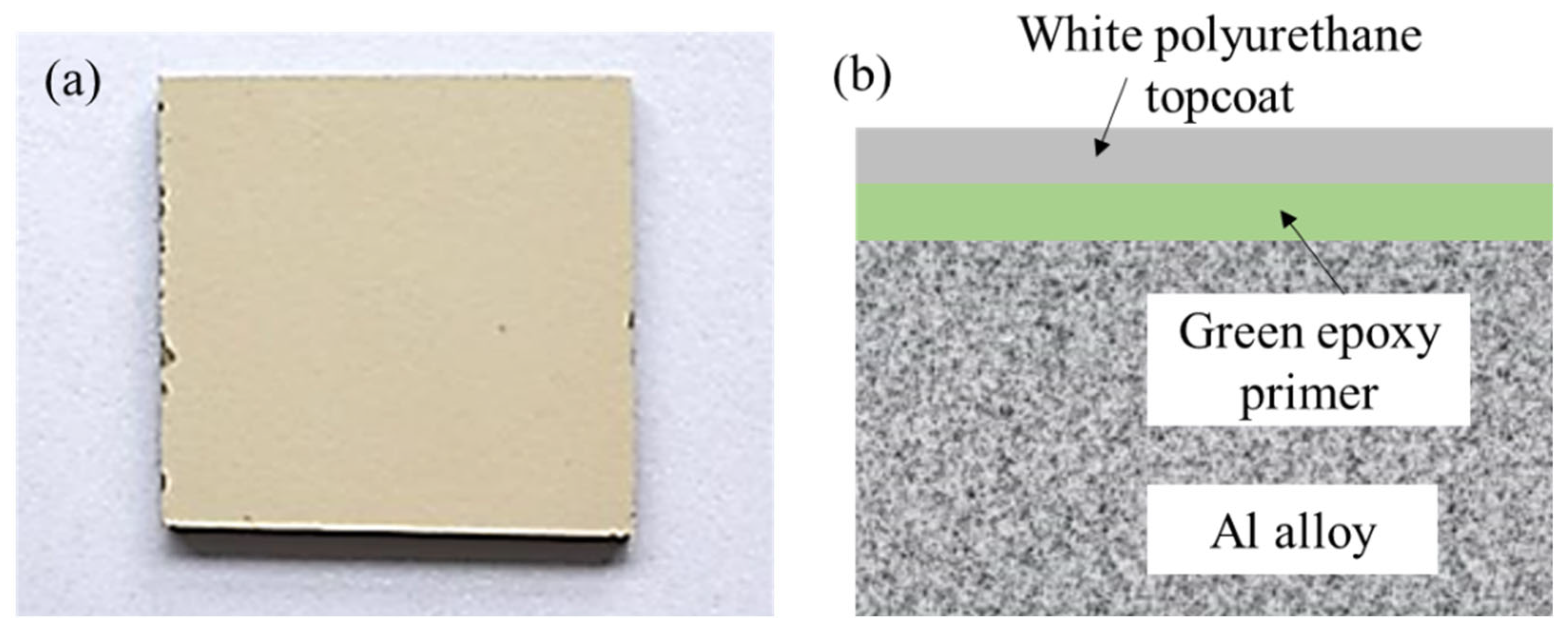
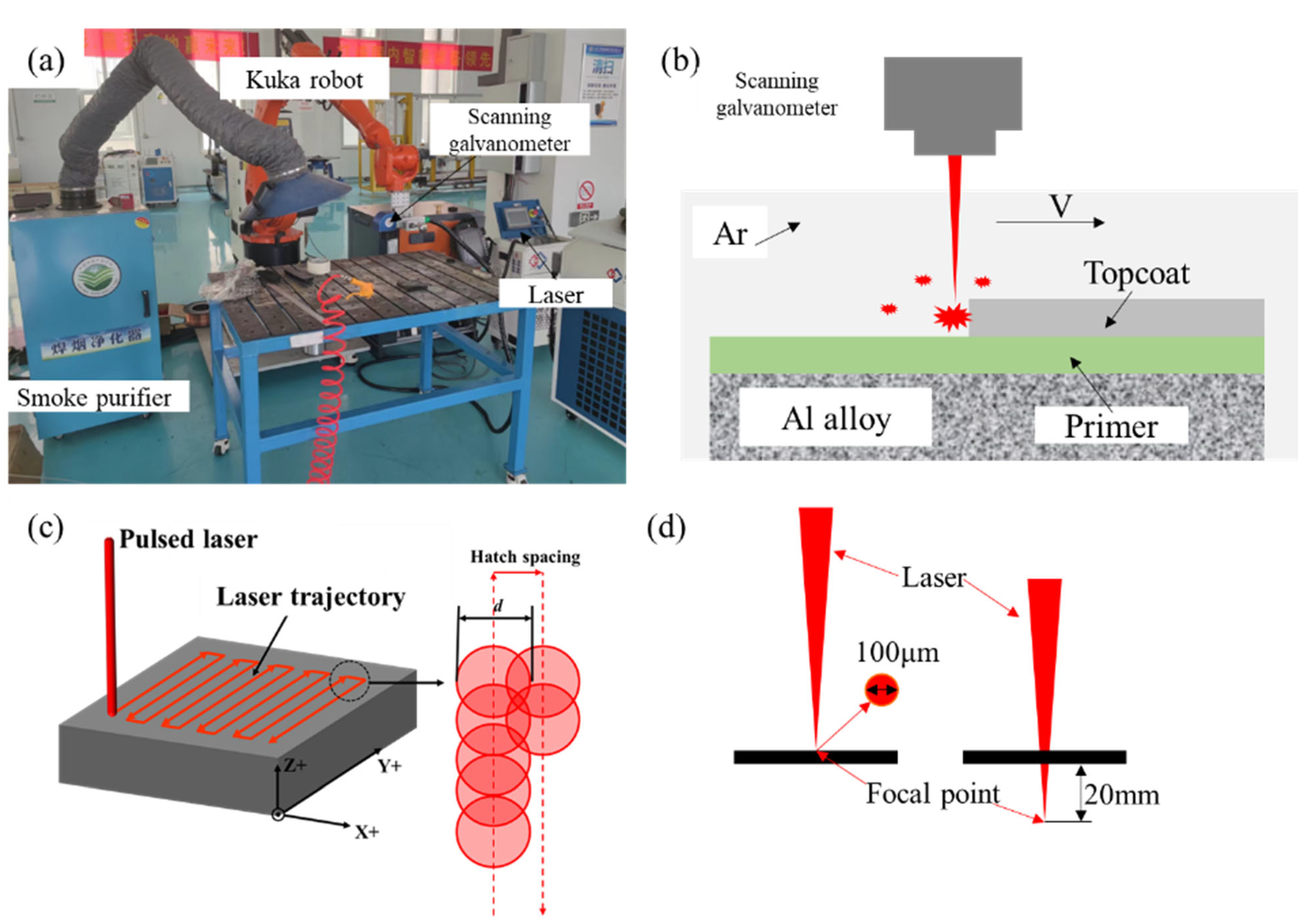
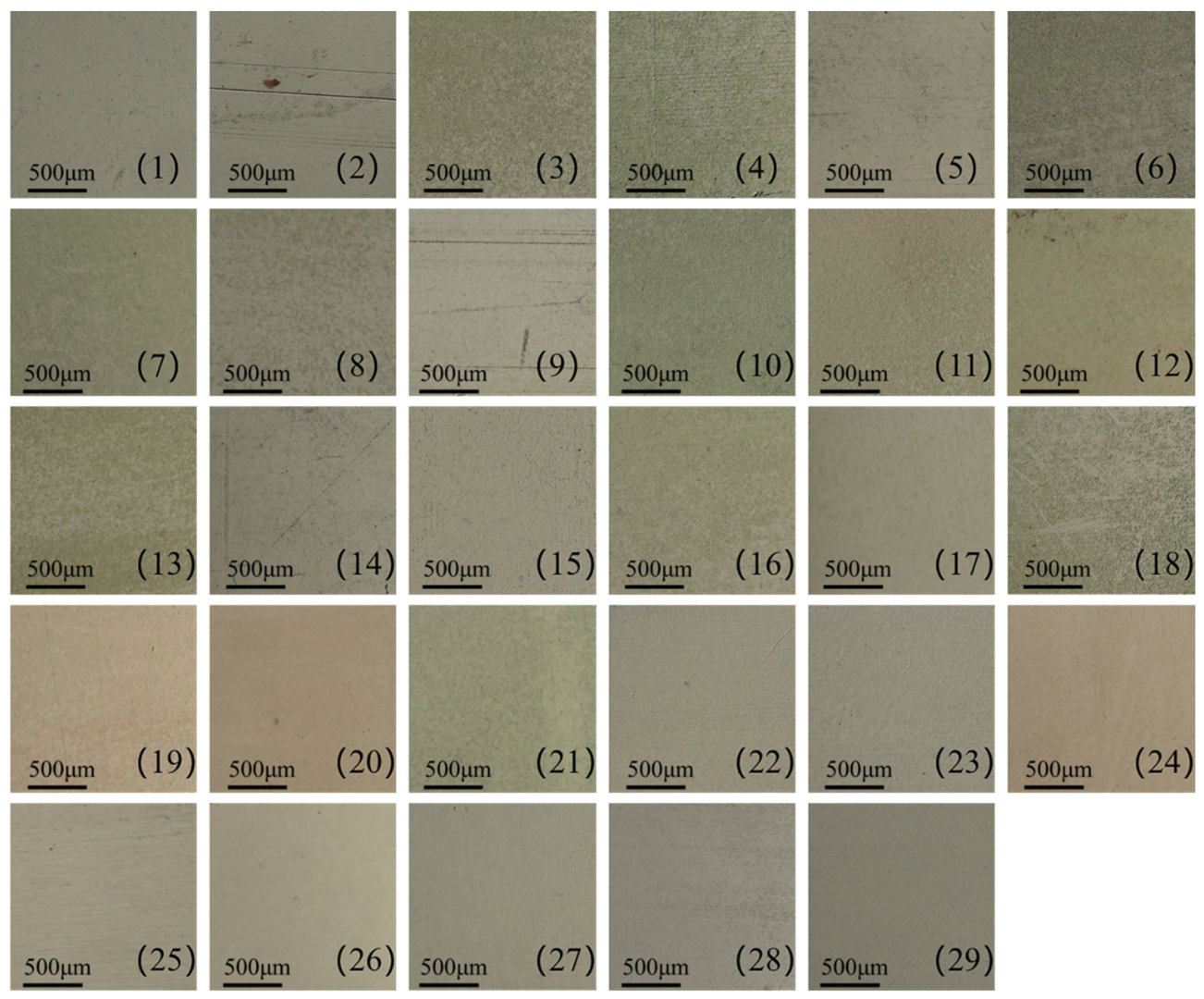
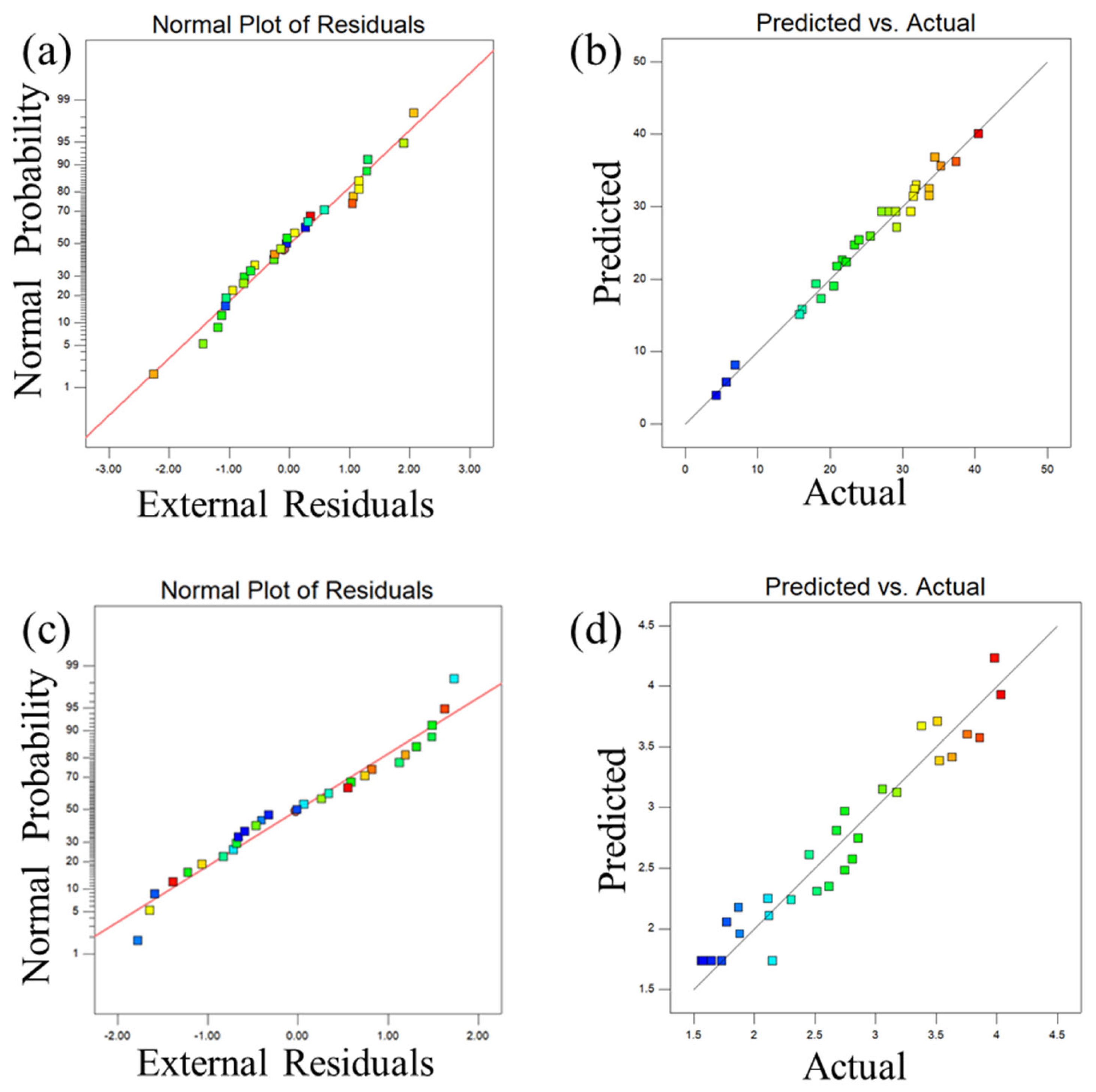
| Symbol | Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| λ | Laser wavelength | 1060 | nm |
| D | Spot diameter | 100 | μm |
| P | Laser power | 0–300 | W |
| f | Repetition frequency | 0–300 | kHz |
| n | Pulse width | 70 | ns |
| v | Scanning speed | 0–20,000 | mm/s |
| Horizontal Coding of Each Factor/Factor | Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Low (−1) | Medium (0) | High (1) | |
| Laser power P/W | 200 | 250 | 300 |
| Repetition frequency f/kHz | 165 | 205 | 245 |
| Scanning speed v/mm/s | 8000 | 12,000 | 16,000 |
| Defocusing h/mm | −20 | −10 | 0 |
| No | Process Parameters | Result | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P/W | f/kHz | v/mm/s | h/mm | H/µm | Ra/µm | |
| 1 | 250 | 205 | 12,000 | −10 | 31.2 | 1.563 |
| 2 | 250 | 205 | 12,000 | −10 | 29.1 | 1.650 |
| 3 | 250 | 245 | 16,000 | −10 | 20.5 | 3.631 |
| 4 | 300 | 205 | 16,000 | −10 | 24.0 | 2.859 |
| 5 | 300 | 245 | 12,000 | −10 | 31.7 | 1.776 |
| 6 | 250 | 245 | 12,000 | 0 | 31.5 | 2.680 |
| 7 | 250 | 205 | 16,000 | 0 | 21.0 | 3.756 |
| 8 | 200 | 205 | 12,000 | 0 | 25.6 | 2.746 |
| 9 | 250 | 165 | 12,000 | 0 | 29.2 | 2.305 |
| 10 | 250 | 165 | 16,000 | −10 | 22.3 | 3.175 |
| 11 | 250 | 165 | 12,000 | −20 | 15.8 | 4.035 |
| 12 | 250 | 205 | 8000 | −20 | 18.1 | 3.511 |
| 13 | 300 | 205 | 12,000 | −20 | 18.8 | 3.859 |
| 14 | 200 | 205 | 8000 | −10 | 33.7 | 2.113 |
| 15 | 250 | 205 | 12,000 | −10 | 31.2 | 1.733 |
| 16 | 200 | 165 | 12,000 | −10 | 23.4 | 2.811 |
| 17 | 250 | 205 | 12,000 | −10 | 27.1 | 2.153 |
| 18 | 200 | 245 | 12,000 | −10 | 21.7 | 2.748 |
| 19 | 250 | 205 | 16,000 | −20 | 4.3 | 3.984 |
| 20 | 250 | 245 | 12,000 | −20 | 6.9 | 3.059 |
| 21 | 200 | 205 | 16,000 | −10 | 16.2 | 3.382 |
| 22 | 250 | 165 | 8000 | −10 | 35.3 | 2.455 |
| 23 | 250 | 205 | 8000 | 0 | 34.5 | 2.517 |
| 24 | 200 | 205 | 12,000 | −20 | 5.7 | 3.525 |
| 25 | 300 | 205 | 8000 | −10 | 40.5 | 2.615 |
| 26 | 250 | 245 | 8000 | −10 | 37.4 | 2.122 |
| 27 | 300 | 165 | 12,000 | −10 | 31.9 | 1.871 |
| 28 | 300 | 205 | 12,000 | 0 | 33.7 | 1.882 |
| 29 | 250 | 205 | 12,000 | −10 | 28.1 | 1.581 |
| Variance Source | Response Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paint Layer Removal Thickness | Roughness | |||
| F-Value | p-Value | F-Value | p-Value | |
| Model | 51.85 | <0.0001 | 13.66 | <0.0001 |
| x1 | 74.64 | <0.0001 | 6.11 | 0.0269 |
| x2 | 1.7 | 0.2131 | 0.41 | 0.5335 |
| x3 | 210.54 | <0.0001 | 29.97 | <0.0001 |
| x4 | 283.88 | <0.0001 | 37.33 | <0.0001 |
| x1x2 | 0.17 | 0.6856 | 3.095 × 10−3 | 0.9564 |
| x1x3 | 0.076 | 0.7869 | 3.18 | 0.0965 |
| x1x4 | 1.9 | 0.1899 | 4.34 | 0.0561 |
| x2x3 | 1.16 | 0.3007 | 1.88 | 0.1918 |
| x2x4 | 9.53 | 0.008 | 5.52 | 0.034 |
| x3x4 | 0.006835 | 0.9353 | 1.77 | 0.2042 |
| x12 | 0.78 | 0.3927 | 5.42 | 0.0354 |
| x22 | 0.58 | 0.4604 | 8.19 | 0.0126 |
| x32 | 0.52 | 0.481 | 44.65 | <0.0001 |
| x42 | 137.48 | <0.0001 | 74.09 | <0.0001 |
| Lack of Fit | 0.96 | 0.5659 | 1.57 | 0.3523 |
| R2 | 0.9811 | 0.9318 | ||
| Adjusted R2 | 0.9622 | 0.8636 | ||
| Predicted R2 | 0.9143 | 0.6654 | ||
| Adeq Precision | 27.665 | 12.071 | ||
| Technical Parameter | Goal | Parameter | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser power P/W | In range | 200~300 | 1 |
| Repetition frequency f/kHz | In range | 165~245 | 1 |
| Scanning speed v/mm/s | In range | 8000~16,000 | 1 |
| Defocusing h/mm | In range | −20~0 | 1 |
| Paint layer removal thickness H/μm | Target | 30 | 1 |
| Surface roughness Ra/μm | Maximize | Max | 1 |
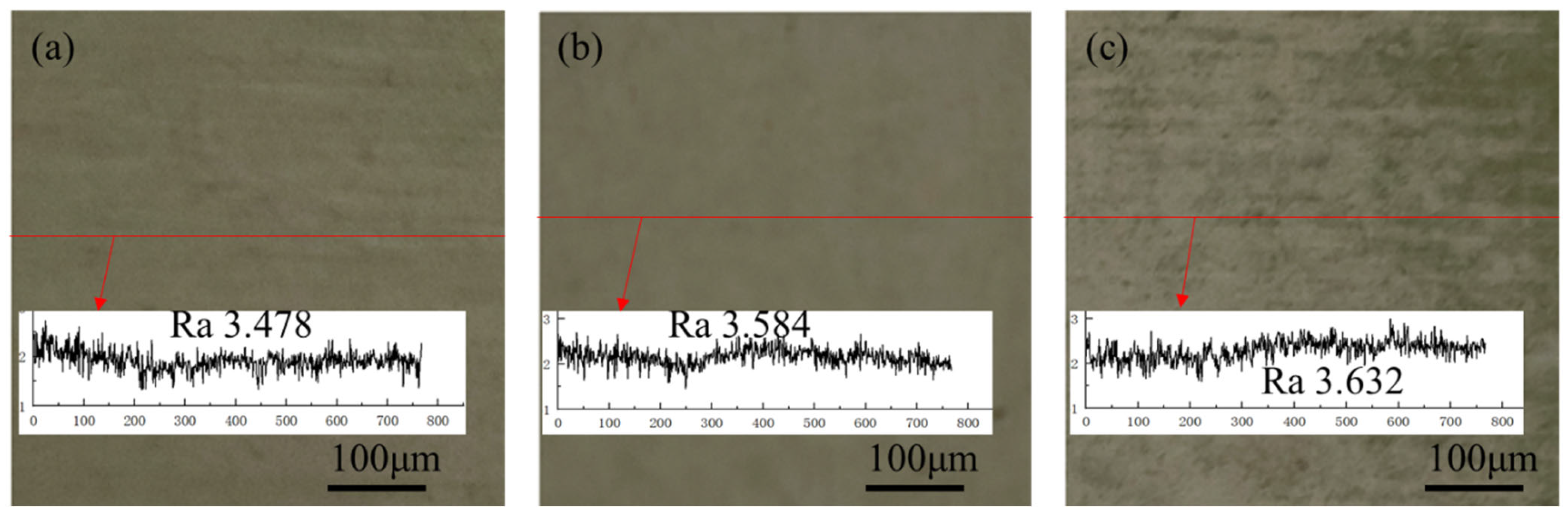
| Sample | Paint Layer Removal Thickness H | Surface Roughness Ra | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimal | Actual | Relative Error | Optimal | Actual | Relative Error | |
| 1 | 30 μm | 32.6 ± 1.2 μm | 2.6 μm | 4.051 μm | 3.478 ± 0.53 μm | −0.573 μm |
| 2 | 30 μm | 31.9 ± 2.4 μm | 1.9 μm | 4.051 μm | 3.584 ± 0.75 μm | −0.467 μm |
| 3 | 30 μm | 33.8 ± 0.8 μm | 3.8 μm | 4.051 μm | 3.632 ± 0.35 μm | −0.419 μm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, X.; Ren, Y.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, W.; Qin, X.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Q. Multi-Objective Optimization of Laser Cleaning Quality of Composite Paint Layers Based on Response Surface. Coatings 2025, 15, 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060647
Ma X, Zhang Y, Hou X, Ren Y, Xu Z, Cheng W, Qin X, Guo W, Zhang Q. Multi-Objective Optimization of Laser Cleaning Quality of Composite Paint Layers Based on Response Surface. Coatings. 2025; 15(6):647. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060647
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xinqiang, Yanlu Zhang, Xingqiang Hou, Yuan Ren, Zifa Xu, Wei Cheng, Xiangli Qin, Wei Guo, and Qinhe Zhang. 2025. "Multi-Objective Optimization of Laser Cleaning Quality of Composite Paint Layers Based on Response Surface" Coatings 15, no. 6: 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060647
APA StyleMa, X., Zhang, Y., Hou, X., Ren, Y., Xu, Z., Cheng, W., Qin, X., Guo, W., & Zhang, Q. (2025). Multi-Objective Optimization of Laser Cleaning Quality of Composite Paint Layers Based on Response Surface. Coatings, 15(6), 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15060647




