Abstract
This research employed triethylenetetramine as a chelating agent to successfully synthesize a chelating-functional waterborne polyurethane (CWPU) dispersion by adjusting the ratio of hard and soft segments and optimizing the molecular structure through the use of a chain extender. This allowed for the establishment of a stable WPU/Ag composite emulsion system upon the addition of silver nitrate, and during the film formation process, the reducing properties of polyols were employed to in situ reduce Ag+, resulting in the formation of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs). Structural characterization analyses, including FTIR and XRD, verified that the reduced AgNPs were evenly distributed in the WPU matrix, and SEM observations revealed the presence of reduced AgNPs on the film. Further, contact angle and TG tests were performed to explore the impact of AgNPs on the hydrophilicity and thermal stability of the film. By applying WPU/Ag to cotton fabric through a padding finishing technique, the fabric retained a breathability of over 64.7% and mechanical properties exceeding 70.9%. Following 20 standardized washes, the antibacterial efficacy against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus remained above 99%. Even after undergoing 1200 abrasion tests, the antibacterial efficacy for both bacteria was sustained at over 93%, and the antibacterial rate continued to exceed 99% after a 6 h immersion in hot water. These findings suggest that the composite material possesses outstanding thermal stability, durability, and mechanical characteristics. This research offers a new methodology for the development of textiles that combine both usability and prolonged antibacterial efficacy.
1. Introduction
In recent years, microbial contamination of material surfaces has become a major threat to human health. It is generally accepted that this contamination mainly arises from the adhesion and proliferation of microbes, leading to biofilm formation. In humid physiological environments, microbes adhered to the surface of materials can quickly reproduce, facilitating biofilm development [1]. Mature biofilms allow bacteria to survive in harsh conditions and show increased resistance to antimicrobial agents and host immune responses. A survey indicated that the average microbial count is 138 CFU/cm2 in rural areas, 72 CFU/cm2 in urban areas, and even higher in public spaces [2]. Thus, there is an urgent need to develop biomaterials that can eliminate bacteria and suppress biofilm formation to prevent the transmission of infectious diseases.
To satisfy the demand for antibacterial performance, researchers have developed various antimicrobial agents, including metal ions [3,4], quaternary ammonium compounds [5,6,7], and guanidine salts [8,9,10]. These antimicrobial agents can effectively prevent the adhesion and spread of microbes on material surfaces. However, there remains ongoing debate about the persistence of their antibacterial effects, as frequent wiping and cleaning can diminish their activity [11]. Recent studies show that fibers containing bioactive silver compounds are gaining popularity due to microbes’ low resistance to silver [12]. These fibers operate by releasing Ag+ into the environment, which inactivates bacteria. While this technology is effective, excessive Ag+ penetration into the system surface can harm beneficial bacteria and damage human tissues [13,14]. Additional research is required to improve the interaction between silver and the polymer matrix to develop suitable and long-lasting materials, ensuring that Ag+ remains securely attached.
Waterborne polyurethane is an eco-friendly material with extensive applications across various industries such as biomedical [15,16], textile [17,18], and construction engineering [19,20]. Its outstanding mechanical properties, emulsion stability, strong adhesion to substrates, and good chemical resistance make it an ideal choice for enhancing material functionality by adhering various substances. Recent studies indicate that enhancing the interaction between silver and the polymer matrix through strong ligands to chelateAg+ is effective. For instance, Tsou et al. [21] construction engineering. synthesized a pyridine-containing chain extender by coordinating bis(3-pyridyl)ethanol with AgNO3. Xu et al. [22] suggested a surface design composed of an antibacterial layer and an anti-fouling layer. The antifouling layer consists of F-SH (1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorodecylthio), which shows remarkable efficacy in eliminating protein and dead bacterial cell residues, thereby displaying outstanding antifouling performance. Concurrently, Ail et al. [23] developed a waterborne polyurethane with contact-active antibacterial and antifouling layers, which offers prolonged stability and antibacterial efficacy. It is noteworthy that due to the hydrophilic and non-toxic nature of DMG, it was designed and synthesized to serve as a chain extender and antibacterial layer, whereas Fluorolink E10H (fluorinated polyether polyol) was included as the soft segment to aid in the elimination of protein and microbial residues.
In this research, DETA was incorporated as a metal chelating chain extender into the main chain of WPU, thereby allowing the CWPU/Ag coatings to demonstrate robust antibacterial activity, notable storage stability, minimal aggregation tendency, and a uniform in situ distribution of Ag+. This research explored the impacts of DETA chain extension and Ag+ incorporation on the chemical structure, morphology, crystallinity, thermal characteristics, and wettability of the films, comparing these properties to those of CWPU samples. Additionally, we conducted a comparison between the fabricated coated cotton fabric and untreated cotton fabric to assess the antibacterial effectiveness, durability, and wearing properties of the coated fabric.
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
The cotton fabric was obtained from the market. Silver nitrate (AgNO3) solid particles were sourced from Aladdin. Poly(tetramethylene glycol) (PTMEG) and poly(1,4-cyclohexylene dimethylene succinate) (XCP) were acquired from Hubei Jusheng Technology Co., Ltd. Isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI), trimethylol propane (TMP), and dibutyltin dilaurate (DBDTL) were obtained from China National Pharmaceutical Group. Neopentyl glycol (NPG), dimethylacrylate (DMPA), acetone, diethylenetriamine (DETA), and triethylamine (TEA) were sourced from Macklin. Deionized water was produced in the laboratory.
2.2. Synthesis of WPU and CWPU
We combined IPDI, polyol (PTMEG: XCP = 1:1), TMP, NPG, DMPA, and a specified amount of acetone in a three-neck flask. Heated and stirred the resulting mixture at 250 rpm in a nitrogen atmosphere at 75 °C for 3 h. Subsequently, increased the temperature to 80 °C, introduced the catalyst DBDTL and chain extender NPG, and reacted for 1.5 h. Throughout this period, adjusted the viscosity with acetone based on the system conditions and assessed the mass fraction of NCO using the dibutylamine method. While preparing WPU, the NCO content achieved 0.72–1.01%, and for CWPU, it reached 2.15–2.44%, after which the temperature was reduced to 40 °C. Neutralization to form a salt was carried out by adding TEA (triethylamine), followed by the addition of a measured aqueous solution. Emulsified and dispersed the mixture using high-speed shear for 15 min. The final step involved the rotary evaporation of acetone to yield an anionic waterborne polyurethane (WPU) with a solid content of around 30 wt%. Similar steps were executed, where DETA (diethylene triamine) was added for post-extension prior to the rotary evaporation of acetone, yielding a chelated waterborne polyurethane (CWPU) with a solid content of about 30 wt%. The synthesis pathways for waterborne polyurethane (WPU) and chelated waterborne polyurethane (CWPU) were illustrated in Figure 1.
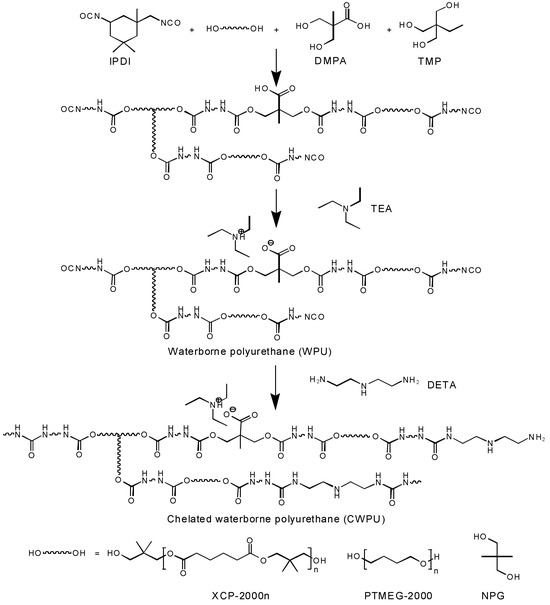
Figure 1.
Synthesis route of WPU and CWPU.
2.3. Preparation of WPU/Ag Dispersion
We used the formula specified in Table 1, and WPU/Ag and CWPU/Ag dispersions were prepared. At temperature nearly 25 °C, 12 mL of both WPU and CWPU (each with a solid content of 30%) were taken, and 4 mL of an aqueous AgNO3 solution (10 mg/mL) was added to each. The mixtures were then stirred for 30 min.

Table 1.
Formula of WPU, CWPU, WPU/Ag, and CWPU/Ag aqueous dispersions.
2.4. Preparation of Polyurethane Film
We added suitable amounts of anionic polyurethane, EDTA-extended polyurethane, and EDTA-extended WPU/Ag dispersion into Petri dishes, dried them in an oven for 8 h to form films, and subsequently conducted further analysis on the films, determining that the mass percentage of silver ions in the WPU/Ag films was 0.64%.
2.5. Preparation of Antibacterial Cotton Fabric
First, the CWPU/Ag dispersion was prepared following the formulation indicated in Table 1. Next, two pieces of cotton fabric of equal dimensions were cut, and a desizing process was carried out initially. After the desizing process, the cotton fabric was soaked in the prepared CWPU/Ag dispersion. Once adequately soaked, a small roller was employed to eliminate excess liquid. Subsequently, the fabric was dried in an oven set at 60 °C.
2.6. Characterization of WPU, CWPU and CWPU/Ag Thin Films
We conducted an analysis of the prepared films utilizing a scanning electron microscope (SEM, JEM-2100, Hitachi High-Technologies, Shanghai, China). Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) measurements of WPU, CWPU, and CWPU/Ag films were conducted using a Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (Thermo Nicolet IS5), with spectral wavenumbers ranging from 4000 to 550 cm−1. X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements were performed at room temperature employing a Bruker D8 Advance diffractometer using CuKα radiation (λ = 1.540598 Å) at a scanning rate of 1°/min over a 2θ range of 5° to 80° [24]. A contact angle goniometer was utilized to measure the contact angles (CA) of water droplets on the fabric surface, allowing for the assessment of the varying contact angle performances of each film. For the qualitative and quantitative evaluation of the antibacterial efficacy of CWPU and CWPU/Ag, we performed antibacterial tests on Escherichia coli (Gram-negative bacteria) and Staphylococcus aureus (Gram-positive bacteria) utilizing the shaking method (GB/T 20944.3-200). The samples and control groups were introduced into flasks containing a defined concentration of antibacterial solution, shaken for a specified time at an optimal temperature, and the corresponding antibacterial rates were calculated accordingly. The wear resistance test is performed using a fabric wear machine. The material used for abrasion is pure cotton fabric, with an applied pressure of 12 KPa. The wear rate between the upper pure cotton fabric (diameter 120 mm) and the treated fabric surface (diameter 20 mm) is set at 50 rpm. The procedure for the wash durability test consists of soaking a fabric sample (20 mm × 20 mm) in a beaker with a diameter of 50 mm, adding 50 mL of soap solution (concentration of 2 g/L) into the beaker, and stirring at 400 rpm using a magnetic stirrer. Following the stirring, the sample is rinsed with deionized water for 10 min, and this step is regarded as one cycle. The water contact angle (WCA) of deionized water droplets (about 5 μL) was measured at room temperature with an optical contact angle measuring instrument (SCI4000, Beijing Global Hengda Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). The average contact angle value was calculated by taking measurements at three distinct locations on the same sample. A thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA, STA6000, PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA) was employed to measure the weight loss of the polyurethane films in a nitrogen atmosphere, with the samples being heated from room temperature to 800 °C at a rate of 10 °C/min. Furthermore, following the GB/T 5453-1997 standard, the air permeability of the samples was assessed using a YG461E fully automatic air permeability tester at a testing pressure of 100 Pa. The tensile performance of fabric specimens sized 150 × 50 mm2 was evaluated using a universal testing machine in accordance with the GB/T 3923.1-2013 standard.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of WPU/Ag and CWPU/Ag Dispersions
Figure 2 shows the appearance of the AgNO3 solution dispersion at immediate and 24 h intervals following the incorporation of WPU and CWPU dispersions. As shown in Figure 2a, during the preparation of the WPU/Ag dispersion, the addition of AgNO3 into the WPU dispersion led to the development of a cohesive gel-like structure within the WPU/Ag dispersion. After 24 h, the solution transitioned to a brown color, and the precipitate altered from white to black. This phenomenon was presumably a result of the interaction between Ag+ ions and the polyurethane bonds, thereby initiating crosslinking. As illustrated in Figure 2b, following the addition of AgNO3 to the CWPU dispersion, the CWPU/Ag dispersion continued to maintain its clarity, although its color shifted from transparent to brown after a duration of 24 h. This phenomenon was believed to result from the addition of DETA into the system, where DETA segments in the CWPU chains formed complexes with Ag, thus maintaining the stability of the CWPU dispersion (Figure 2c). Notably, the quantity of Ag+ introduced into both the WPU and CWPU dispersions was equimolar, with both being 2500 ppm.
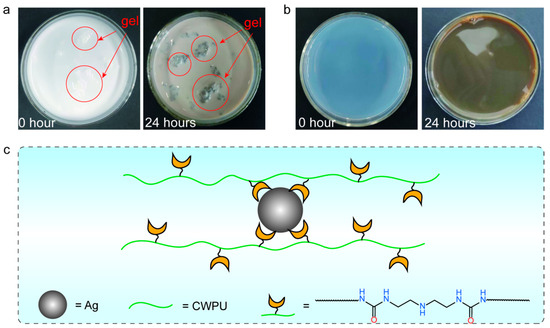
Figure 2.
(a) WPU/Ag and (b) CWPU/Ag dispersions at different times, and (c) the complex structure between CWPU and Ag.
3.2. Surface Morphology of Films
Figure 3a shows the SEM images of CWPU, CWPU/Ag films, and CWPU/Ag-coated cotton fabric. As seen in Figure 3b, the CWPU film surface smooth after film formation. Upon the addition of AgNO3, numerous regularly shaped particles were evenly dispersed on the CWPU/Ag film surface, with particle sizes smaller than 1 micron. The even dispersion of nanoparticles was essential for the film’s performance, likely because Ag+ ions first coordinate with the DETA structure in the WPU chain prior to in situ reduction by PTMEG polyether polyol in the soft segment [25]. Figure 3c presents the morphology of cotton fabric treated with CWPU/Ag. As seen in the image, Ag nanoparticles were successfully reduced on the cotton fabric surface after treatment.
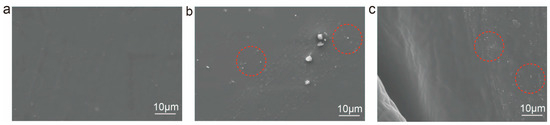
Figure 3.
SEM images of (a) CWPU, (b) CWPU/Ag films, and (c) CWPU/Ag-coated cotton fabric.
3.3. Chemical Compositions of Films
3.3.1. FTIR Study
Figure 4 presents the infrared spectra of the synthesized WPU, CWPU, and CWPU/Ag films. The spectra indicate the -NH2 hydrogen bond stretching vibration at 3326 cm−1, the C-H stretching vibration at 2849 cm−1, the stretching vibration of the amide carbonyl group associated with hydrogen bonding at 1729 cm−1, and the bending vibration of the amino hydrogen bond at 1530 cm−1. Furthermore, the bending and rocking vibrations of CH2 were detected at 1451 cm−1 and 1360 cm−1, respectively, whereas the asymmetric stretching vibration of C-O-C was identified at 1254 cm−1. The characteristic spectral bands of the CWPU and CWPU/Ag samples closely resemble those of the WPU sample, with only minor shifts in peak positions. Additionally, in comparison with the WPU sample, the intensity of the spectral band associated with the hydrogen-bonded polyurethane carbonyl at 1729 cm−1 decreases in the CWPU sample. This suggests that incorporating DETA into the main chain of WPU reduces the degree of hydrogen bonding between the polyurethane linkages (hard segments), leading to decreased microphase separation and increased hydrophobicity of CWPU within the hard segments. Furthermore, the infrared spectrum of the CWPU/Ag film features an additional characteristic peak at 460 cm−1 when compared to the CWPU, which is generated by the vibration of Ag-O.
3.3.2. XRD Study
The impact of DETA chain extender and AgNO3 addition on the crystallinity of CWPU and CWPU/Ag films was studied through XRD. The crystallinity of polyurethane is typically dictated by the degree of microphase separation between the soft and hard segments. As illustrated in Figure 4b, all samples displayed broad peaks of varying intensities at 19.5°, suggesting they have semicrystalline characteristics due to reduced microphase separation. In addition, the peak position at 19.5° is perfectly aligned with the crystallization peak of PTMEG at 2θ = 19.6°, suggesting that crystallized soft segments are present, dispersed in the amorphous matrix of all samples. Moreover, the XRD spectra indicated that the introduction of the DETA chain extender and the presence of in situ generated Ag+ affect the crystallinity and microphase separation of CWPU and CWPU/Ag samples. The large DETA structure disrupts the hydrogen bonds within the hard segments, obstructing the formation of more compact and orderly hard segments. Therefore, the extent of microphase separation is lower than that observed in WPU samples. Furthermore, the incorporation of DETA facilitates a limited mixing of hard segments with PTMEG polyether polyol, improving microphase mixing and leading to a reduction in peak intensity of CWPU at 19.5° relative to WPU. Additionally, the XRD spectra of the CWPU/Ag films exhibited several diffraction peaks at 2θ = 38.4°, 44.8°, 64.72°, and 77.6°, which correspond to the (111), (200), (220), and (311) planes [23] of the face-centered cubic structure of Ag, with other peaks resulting from residual AgNO3. Figure 4c,d depict the XPS spectra of the CWPU/Ag films.
3.3.3. XPS Study
In Figure 4c, the full spectrum of the CWPU/Ag film shows four peaks at 284.1 eV, 365.9 eV, 397.1 eV, and 531.2 eV, attributed to the C 1s, Ag 3d, N 1s, and O 1s signals. The Ag content in the sample is calculated to be 0.63%, which is nearly identical to the Ag content employed in the preparation process. Figure 4d displays the Ag 3d XPS spectrum of the CWPU/Ag film, with peaks at 368.3 eV and 374.2 eV corresponding to the Ag 3d5/2 and Ag 3d3/2 states, respectively. This spectrum is characteristic of the typical Ag 3d doublet structure. Therefore, based on the XRD and XPS analysis, we confirm the presence of Ag+ ions in the CWPU/Ag film.
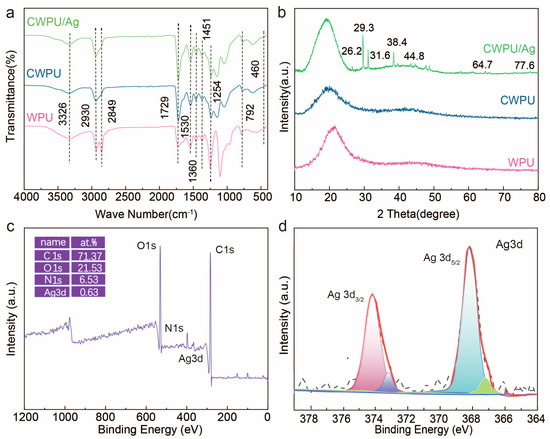
Figure 4.
(a) FTIR and (b) XRD curves of WPU, CWPU, and CWPU/Ag. (c) XPS spectra and (d) high-resolution Ag 3d of CWPU/Ag film.
3.4. TGA Analysis of the Treated Film
To examine the impact of DETA as a chain extender and the addition of Ag+ on the thermal stability and decomposition behavior of WPU membranes, this research performed TGA on anionic WPU, CWPU, and CWPU/Ag samples in a nitrogen atmosphere. Figure 5 shows the TGA and DTG curves for WPU, CWPU, and CWPU/Ag membranes, and the corresponding data are compiled in Table 2. Thermal degradation of polyurethane generally initiates with the breakdown of the hard segments [26]. In this research, the temperature corresponding to a 5% weight loss (T5%) was utilized as a reference point for evaluating thermal stability [27]. The T5% for WPU samples was found to be 279 °C. Meanwhile, for CWPU utilizing DETA as a chain extender, T5% was reduced to 250 °C. The decline in thermal stability of CWPU could be due to diminished hydrogen bonding interactions within the hard segments [28], resulting in a decreased temperature for the onset of weight loss. Furthermore, the T5% of WPU/Ag membranes was markedly reduced to 224 °C, mainly due to the catalytic role of Ag+, which sped up the thermal degradation of the polymer, causing CWPU/Ag to degrade more rapidly than WPU and CWPU samples.
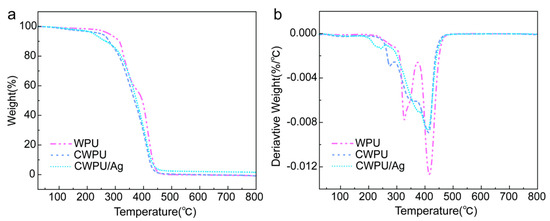
Figure 5.
(a) TG and (b) DTG curves of WPU, CWPU, and CWPU/Ag.

Table 2.
TGA data analysis of polyurethane film.
Based on the DTG curves, thermal degradation of the three samples predominantly takes place in two stages. The first stage corresponds to the degradation of hard segments (polyurethane and urea bonds), which normally takes place prior to 350 °C, resulting in the formation of primary amines, olefins, and carbon dioxide [29]. Additionally, the second stage, ranging from 350 °C to 500 °C, is related to the degradation of the soft segments [26]. Table 2 lists the values of Tmax,1 (maximum temperature of degradation rate for the hard segments) and Tmax,2 (maximum temperature of degradation rate for the soft segments). The table clearly shows that the values of Tmax,1 and Tmax,2 for CWPU/Ag are both lower than those for WPU and CWPU, which further validates the idea that Ag+ catalyzes the acceleration of the thermal degradation of the polymer.
3.5. Antibacterial Activity of the Treated Cotton Fabrics
We chosed Gram-negative bacteria (E. coli) and Gram-positive one (S. aureus) to evaluate the antibacterial performance of CWPU films, CWPU/Ag films, and CWPU/AgCF. Additionally, to more clearly illustrate the antibacterial properties, we used a viable cell counting method to quantify the antibacterial effects of the fabrics. As showed in Figure 6a, both the CWPU/Ag and CWPU/Ag cotton fabrics displayed substantial antibacterial activity against S. aureus and E. coli, achieving antibacterial rates greater than 99.9% for both bacteria, while the Ag+-free control group lacked significant antibacterial activity, resulting in easy colony formation on the culture plates. The antibacterial mechanism of the modified fabrics is attributed to the electrostatic interactions between the negatively charged bacterial cell walls and the positively charged silver ions, which disrupt the charge equilibrium of the cell wall, ultimately resulting in its rupture. In addition, silver ions penetrate bacterial cells and quickly coordinate with thiol or amino groups found in proteins, resulting in their inactivation and subsequent bacterial death.
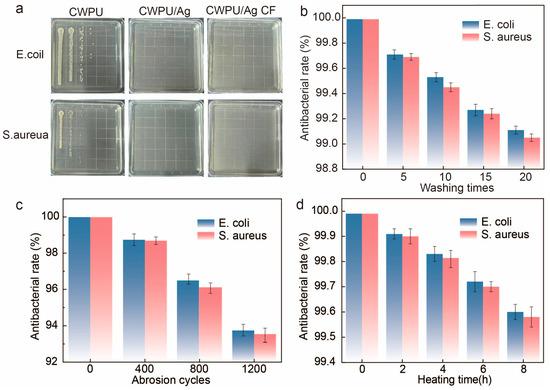
Figure 6.
(a) Antibacterial test of CWPU films, CWPU/Ag films and CWPU/AgCF against E. coil and S. aureus, and the antibacterial rate of CWPU/Ag CF against S. aureus and E. coli after (b) washing, (c) abrasion, and (d) heating.
In order to assess the antibacterial durability of the treated fabric, we performed a series of tests. When unwashed, the antibacterial efficacy of CWPU/Ag cotton fabric against S. aureus and E. coli reaches 99.99% (Figure 6b). Even after 20 washes, the antibacterial efficacy remains at 99.13% and 99.06% against S. aureus and E. coli, respectively. As illustrated in Figure 6c, the treated fabric retains an antibacterial rate exceeding 93% against both bacterial strains after 1200 rubbing cycles, demonstrating remarkable wear resistance. Figure 6d reveals the thermal stability of the treated fabric, showing that after being heated at 100 °C for 6 h, the antibacterial rate against both bacterial strains stays above 99.5%, indicating its remarkable heat resistance. This suggests that the finishing treatment of cotton fabrics not only improves their antibacterial performance, but also provides them with enduring antibacterial properties, ensuring that the fabrics can effectively retain their antibacterial efficacy in diverse environments, highlighting their broad application potential. In addition, these results also validate that the synthesized CWPU dispersion creates a stable and solid WPU/Ag system after the incorporation of silver nitrate.
3.6. Wettability of Films
The wettability of WPU, CWPU, and CWPU/Ag films was assessed by measuring the contact angle formed between water droplets and the surface of the films [30]. As depicted in Figure 7a, the contact angle of the CWPU film rose from 62.62° to 72.14°. This finding can be attributed to the increased hydrophobicity conferred by the DETA structure. However, when Ag+ ions were formed in situ within the CWPU matrix, the contact angle sharply dropped to 6.56°. This phenomenon suggests that the incorporation of Ag+ into the polyurethane results in a significant change in the wettability characteristics of the film surface, rendering it more hydrophilic.
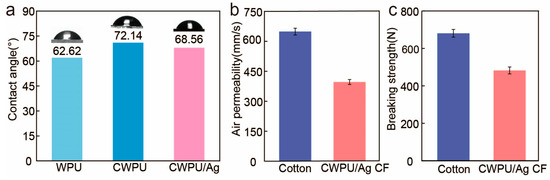
Figure 7.
(a) Contact angles of WPU, CWPU, and WPU/Ag films. (b) Air permeability and (c) breaking strength of cotton fabric and treated fabric.
3.7. Service Performance of the Treated Fabrics
To assess the mechanical properties and breathability of cotton fabrics following coating treatment, breathability, and tensile strength tests were performed on both untreated and treated cotton fabrics. The average values from ten breathability tests are illustrated in Figure 7b, indicating that the average breathability of the treated fabric decreased from 673.2 ± 23.1 mm/s to 435.6 ± 17.6 mm/s. This reduction is due to the coating treatment applied to the fabric; nonetheless, the coating did not completely block the spaces between the yarns, permitting many pores to remain in the fabric. Consequently, although the breathability was reduced, the average value across the ten tests was still 435.6 ±17.6 mm/s, demonstrating that the treated fabric retains satisfactory breathability. Figure 7c illustrates the tensile strength of untreated and treated cotton fabrics, where the average results from five tests show that the tensile strength of the treated fabric dropped from 680.78 ± 20.62 N to 482.57 ± 18.51 N. Although there is some loss in strength compared to before, the treated fabric still possesses satisfactory breathability and strength.
4. Conclusions
In this research, DETA was incorporated as a metal chelating chain extender into the main chain of waterborne polyurethane (WPU), thereby allowing the CWPU/Ag coatings to demonstrate robust antibacterial activity, notable storage stability, minimal aggregation tendency, and a uniform in situ distribution of Ag+. This research explored the impacts of DETA chain extension and Ag+ incorporation on the chemical structure, morphology, crystallinity, thermal characteristics, and wettability of the films, comparing these properties to those of CWPU samples. Additionally, we conducted a comparison between the fabricated coated cotton fabric and untreated cotton fabric to assess the antibacterial effectiveness, durability, and wearing properties of the coated fabric.
Author Contributions
Validation, Y.W. and J.W.; Investigation, Z.L.; Resources, J.C.; Data curation, J.S. and X.L.; Writing—original draft, Q.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the PhD Research Startup Foundation of Xinjiang University [620323013], and the Scientific Research Program of the Higher Education Institution of Xinjiang, China (XJEDU2023P030), The Program of Tianchi Talent of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region [5105240151n].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhao, A.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y. Understanding bacterial biofilms: From definition to treatment strategies. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 6, 1137947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, D.; Liu, X.; Hawkey, P.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Mao, Z.; Sun, J. Use of and microbial resistance to antibiotics in China: A path to reducing antimicrobial resistance. Int. Med. Res. 2017, 45, 1768–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, S.; Gunaskara, T.; Holton, J. Antimicrobial nanoparticles: Applications mechanisms of action Sri Lankan. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 8, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, A.L.; Adams, D.; Karpanen, T.J.; Lambert, P.A.; Cookson, B.D.; Nightingale, P.; Elliott, T.S.J. Role of copper in reducing hospital environment contamination. J. Hosp. Infect. 2010, 74, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Tan, H.; Wang, K.; Fu, Q. Synthesis and antibacterial characterization of waterborne polyurethanes with gemini quaternary ammonium salt. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Xu, J.; Luo, Q.; Hou, C.; Qiao, S.; Fu, S.; Liu, J. Constructing antibacterial polymer nanocapsules based on pyridine quaternary ammonium salt. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 108, 110383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Liu, J.L.; Liu, Y.Y.; He, W.Z.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.J. Durable antibacterial cotton fabrics with good performance enabled by quaternary ammonium salts. Cellulose 2024, 31, 6551–6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathuria, D.; Raul, A.D.; Wanjari, P.; Bharatam, P.V. Biguanides: Species with versatile therapeutic applications. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 219, 113378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; He, S.; Wu, M.; Hou, M.; Li, R.; Zhang, A. Amphiphilic polysiloxane graft guanidine salts with a combination of low environmental toxicity and high antifungal activity. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 216, 113258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajie, W.; Qiang, G.; Jiqiang, C.; Xin, X.; Ying, W.; Han, S.; Lei, T.; Xiang, L. Superhydrophobic Antibacterial Aramid Fabric with Self-Cleaning, Ultraviolet Protection and Oil-water separation Functionalities. Text. Res. J. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J. Development of a novel silver ions-nanosilver complementary composite as antimicrobial additive for powder coating. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Fan, C.; Tang, X.; Zhao, J.; Song, Y.; Shao, Z.; Xu, L. Characterization and antibacterial properties of porous fibers containing silver ions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 387, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panáček, A.; Kvítek, L.; Prucek, R.; Kolář, M.; Večeřová, R.; Pizúrová, N.; Zbořil, R. Silver colloid nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and their antibacterial activity. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 16248–16253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franci, G.; Falanga, A.; Galdiero, S.; Palomba, L.; Rai, M.; Morelli, G.; Galdiero, M. Silver nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 8856–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Gu, L.; Nguyen, L.T.; Cao, J.; Liu, H.; Zhaoqun, D.; Weidong, Y. A superhydrophobic and flame-retardant cotton fabric fabricated by an eco-friendly assembling method. Text. Res. J. 2022, 92, 2873–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaee, F.; Khorasani, M.; Ebrahimi, M.; González, A.; Irusta, L.; Sardon, H. Synthesis and comprehensive study on industrially relevant flame retardant waterborne polyurethanes based on phosphorus chemistry. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 131, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Tu, Y.; Li, Z.; Wu, H.; Mao, H.; Wang, C. Synthesis and application of multifunctional lignin-modified cationic waterborne polyurethane in textiles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 262, 130063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Hu, J. Waterborne polyurethane based thermoelectric composites and their application potential in wearable thermoelectric textiles. Compos. Part. B Eng. 2016, 107, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, Y.; Luo, X.; Xiong, Y.; Xu, C.A.; Yuan, T. A Novel Polyfunctional Polyurethane Acrylate Derived from Castor Oil-Based Polyols for Waterborne UV-Curable Coating Application. Polymers 2024, 16, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wei, H.; Wang, L.; Gao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xiang, J.; Fan, H. Anti-smudge and self-cleaning characteristics of waterborne polyurethane coating and its construction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 628, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, C.H.; Lee, H.T.; Hung, W.S.; Wang, C.C.; Shu, C.C.; Suen, M.C.; De Guzman, M. Synthesis and properties of antibacterial polyurethane with novel Bis (3-pyridinemethanol) silver chain extender. Polymer 2016, 85, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, W. Synthesis of vegetable oil-based waterborne polyurethane/silver-halloysite antibacterial nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 126, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Amin, B.U.; Yu, W.; Gui, T.; Cong, W.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Q. Eco-friendly biodegradable polyurethane based coating for antibacterial and antifouling performance. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 54, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Du, Y.; Lei, J.; Zhou, L.; Du, X. Oxidative Desulfurization of Fuel Oil at Room Temperature Catalyzed by Ordered Meso-macroporous HPW/SiO2. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. -Mater. Sci. Ed. 2019, 34, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gies, A.P.; Hercules, D.M.; Raghuraman, A.; Kosanovich, A.J.; Baker, M.A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Paradkar, M. Microstructure characterization and mechanistic insight into polyether polyols and their associated polyurethanes. Mass. Spectrom. Rev. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, Z.S.; Javni, I.; Divjaković, V. Structure and physical properties of segmented polyurethane elastomers containing chemical crosslinks in the hard segment. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Phys. 1998, 36, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosu, D.; Rosu, L.; Varganici, C. The thermal stability of some semi-interpenetrated polymer networks based on epoxy resin and aromatic polyurethane. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 100, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macocinschi, D.; Filip, D.; Zaltariov, M.F.; Varganici, C.D. Thermal and hydrolytic stability of silver nanoparticle polyurethane biocomposites for medical applications. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 121, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Doctorsafaei, A.H.; Burujeny, S.B.; Rudbari, H.A.; Kordestani, N.; Najafabadi, S.A.A. Silver(I) complex with a Schiff base ligand extended waterborne polyurethane: A developed strategy to obtain a highly stable antibacterial dispersion impregnated with in situ formed silver nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitaer, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, Q.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Cao, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X. Preparation of Superhydrophobic Flame-Retardant UHMWPE Fabrics with Excellent Mechanical Stability by Simple Coating Method. Coatings 2025, 15, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).