Abstract
This study explores a novel method for removing Al metal coatings by using nanosecond pulsed lasers to clean Al metal layers from ceramic substrate surfaces. The impact of laser power and pulse width on the effectiveness of the removal of the Al metal layer from the ceramic substrate was examined. The findings revealed that a laser with a power of 120 W, a pulse width of 200 ns, a frequency of 240 kHz, and a speed of 6000 mm/s could effectively remove the Al metal layer (50 μm) in a single laser cleaning cycle without causing damage to the ceramic substrate. The mechanism behind the removal of the Al metal layer from the ceramic substrate surface was also investigated. It was discovered that local high temperatures caused by laser irradiation and the difference in thermal expansion coefficients between the metal layer and the ceramic substrate both contribute to the removal of the Al metal layer during the laser cleaning process. This research provides an effective process for removing the Al metal layer.
1. Introduction
The aluminum (Al) metal layer on ceramic-based coatings is subject to progressive aging, thinning, and structural degradation (including cracking and delamination) due to climatic variations, prolonged exposure, and particle erosion [1,2,3]. This deterioration severely compromises its performance. Therefore, the effective removal of damaged Al layers is a critical aspect of maintenance operations. With recent advancements in industrial technologies, various ceramic surface-cleaning methods have emerged, such as physical grinding [4,5] and chemical cleaning [6]. However, these methods present several challenges, including the difficulty in localizing coating removal areas, high residues, low efficiency, uneven removal edges, significant environmental pollution, and health hazards [7]. Consequently, laser cleaning technology has emerged as a research hotspot in the field of ceramic surface cleaning, owing to its advantages of high efficiency, environmental friendliness, and high precision [8,9,10,11,12,13].
Laser cleaning technology employs a high-energy laser beam to irradiate ceramic surfaces, leading to the immediate vaporization and removal of surface contaminants and metal layers [14,15]. This method not only effectively eliminates surface coatings without harming the underlying substrate but also augments the surface roughness of ceramics, thereby improving the adhesion strength with subsequent repair layers [16,17]. Notably, this technology is well suited for cleaning intricate surfaces and precision components [18].
The inception of laser cleaning technology dates back to the 1970s, when initial attempts were made to employ high-energy laser beams for the removal of oxide layers and contaminants from metal surfaces [19]. These early techniques, however, were impeded by limitations such as a low laser power and inadequate stability, thereby narrowing their range of applications. The situation evolved substantially in the 1990s due to the rapid progression of laser technology. The introduction of high-power and pulsed lasers facilitated the gradual proliferation of laser cleaning across diverse fields. In the subsequent two decades, considerable advances have been registered in sectors like aerospace, automotive manufacturing, and electronics, among others [20,21,22,23]. Nie et al. [24] utilized nanosecond pulsed lasers to clean inorganic thermal control coatings off aluminum alloys, evaluating the post-cleaning surface condition at varying laser fluences. Delmdahl et al. [25] provided an overview of laser cleaning’s application to carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRPs), discussing the bond strength results post-laser cleaning. Their findings suggested that laser cleaning and ablation present a viable alternative, producing a pristine surface suitable for adhesive bonding. Wang et al. [26] deployed a nanosecond pulsed laser in an air environment to clean the oxide film off TC4 titanium alloy, examining the impact of laser energy density on the cleaning efficacy. They recommended laser process parameters with short pulse widths and high frequencies for the effective cleaning of the titanium alloy TC4 in an air environment. Lu et al. [27] used a nanosecond ultraviolet (UV) laser to clean micro biofouling from the Fe substrate surface, contributing significantly to our understanding of the theoretical model and mechanism behind UV laser-assisted micro biofouling surface cleaning.
Prior research has not addressed the removal of metal layers from ceramic-based substrates. This study employs nano-pulsed laser cleaning to eliminate the Al metal layer from such substrates, examining the impact of laser power, pulse width, cleaning speed, and the number of cleaning cycles on cleaning efficiency. Additionally, the morphology and roughness of the substrate post-cleaning under varying parameters are analyzed to ascertain the optimal laser cleaning process parameters. This investigation offers pivotal insights for the broader application of laser cleaning technology in removing metal layers from ceramic surfaces.
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials and Equipment
In the experiment, a self-made ceramic substrate covering an Al metal layer was used as the experimental material. The ceramic substrate comprised Al2O3 and B4C in a mass ratio of 8:2. The thickness of the Al metal layer was 50 μm, while that of the ceramic substrate is 2 mm. The material was cut into samples with a radius of 30 mm, as shown in Figure 1a.

Figure 1.
Experimental sample and laser cleaning system: (a) experimental sample 40 W; (b) laser cleaning system.
The laser cleaning system used in the experiment is composed of a nanosecond fiber, a computer control system, and a dust collection system to collect the peeled-off coating during the cleaning, as shown in Figure 1b. The laser has a wavelength of 1064 nm, a rated power of 200 W, a laser pulse frequency of 20–500 kHz, a cleaning speed of up to 10,000 mm/s, a laser pulse width of 50–650 ns, and a spot diameter of approximately 0.2 mm. The ambient conditions during the laser cleaning process were recorded, with an air temperature of 23.3 °C and a humidity level of 43%.
2.2. Experimental Methods
The efficacy of laser cleaning is predominantly determined by process parameters, notably laser power, laser pulse width, and laser frequency. To explore the impact of these parameters on the laser cleaning of Al metal layers, three distinct experimental sets were designed, each varying a different parameter while keeping all others constant.
Following the cleaning experiments, images of the surface microstructure and morphology were captured using a PXS5-B microscope (Xi’an Ceiwei Optoelectronic Technology Co., Ltd., Xi’an, China), and a VEGA3 TESCAN scanning electron microscope (SEM) (TESCAN Brno, s.r.o., Brno, Czechia). Additionally, the surface roughness was quantitatively measured using a TR200 surface roughness tester (Jinan Youbide Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd., Jinan, China).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Impact of Laser Power on Removal Efficiency of Al Metal Layer
This study examines the impact of varying laser powers on the efficiency of Al metal layer removal. Specifically, lasers with power settings of 40 W, 80 W, 120 W, 160 W, and 200 W were employed for removing the Al metal layer. In order to ensure the accuracy of the results, all other parameters, including laser pulse width (200 ns), laser frequency (240 kHz), speed (6000 mm/s), and cleaning pass (1), were kept constant throughout the experiments.
A PXS5-B microscope was employed to analyze the microstructure images of the surface, post-laser cleaning across varying laser powers. The findings are depicted in Figure 2. It is evident that the thickness of the residual Al metal layer diminishes as the laser power escalates. At 120 W, the Al metal layer on the sample surface is effectively eradicated, with negligible to no residual metal layer observed.

Figure 2.
Microstructure images of test material after laser cleaning using different laser powers (50×).
After laser cleaning with different laser powers, the surface morphology images of the substrate surface were measured near the center of the substrate surface by SEM. In the SEM study, a carbon coater was employed to treat the surface of the sample. The SEM images are shown in Figure 3. From the figure, it can be observed that at a 40 W laser power, there is a significant amount of residual Al metal layer remaining on the substrate surface. As the laser power increases, the residual Al metal layer decreases. When the laser power reaches 120 W, the Al metal layer is removed. However, at a laser power of 160 W, signs of surface burning and cracking begin to appear, indicating significant thermal damage to the substrate, as shown in Figure 3l,o. Therefore, a laser power of 120 W demonstrates a more effective removal of the Al metal layer without damaging the ceramic substrate.
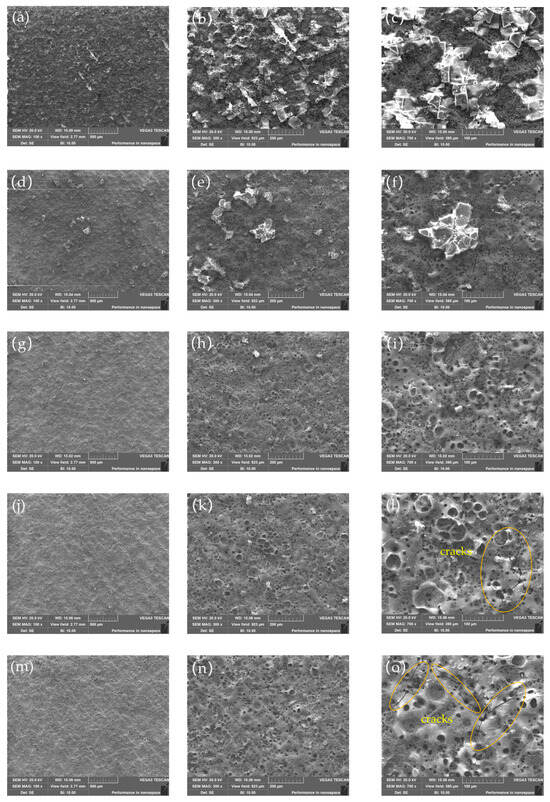
Figure 3.
Surface morphology image of the surface after removing Al metal layers at different laser powers: (a–c) 40 W; (d–f) 80 W; (g–i) 120 W; (j–l) 160 W; (m–o) 200 W; (a,d,g,j,m) 100×; (b,e,h,k,n) 300×; (c,f,i,l,o) 700×.
Subsequently, a TR200 Surface Roughness Tester was employed to measure the surface roughness of the substrate surface after laser cleaning at different laser powers. In the experiment, surface roughness tests were conducted at three randomly selected locations near the center of the material’s surface. A single sampling length of 2.5 mm was used for each measurement, and the arithmetic mean of the absolute deviations of each point from the mean line within the sampling length was recorded as the surface roughness result Ra. The repeatability error across the three measurements was within 0.5 μm. The arithmetic mean deviation of the roughness profile Ra and root mean square deviation of the roughness profile Rq after laser cleaning at different laser powers are presented in Table 1. In addition, the surface roughness Ra and Rq, prior to laser cleaning—specifically, the surface roughness of the Al metal layer—is also detailed in Table 1. The test results indicate that an increase in laser power from 40 W to 200 W results in a corresponding rise in Ra from 9.426 µm to 13.846 µm and in Rq from 11.254 µm to 17.176 µm. The minimal discrepancy between Ra and Rq suggests that the micro-profile shape of the surface post-laser cleaning is notably uniform and regular. Both Ra and Rq exhibit an upward trend that gradually slows and eventually stabilizes. This is because as the laser power increases, the temperature generated becomes higher, which enhances the removal effect on the Al metal layer and consequently increases the surface roughness of the substrate. At a laser power of 120 W, the Al metal layer on the substrate surface can be completely removed, resulting in a stabilized change in roughness. However, there is a risk of surface burning and damage beyond this power level of 120 W. Therefore, to achieve both the effective removal of the Al metal layer and minimal damage to the substrate surface, the optimal laser cleaning power is determined to be 120 W.

Table 1.
Average surface roughness after removing Al metal layers at different laser powers.
3.2. Impact of Laser Pulse Width on Removal Efficiency of Al Metal Layer
In examining the impact of varying laser pulse widths on the removal efficiency of Al metal layers, lasers with pulse widths of 50 ns, 200 ns, 350 ns, 500 ns, and 650 ns were employed for cleaning and removal tasks. Based on the findings presented in Section 3.1, a laser power of 120 W was selected to investigate the relationship between laser pulse width and the removal efficiency of the Al metal layer. Throughout the experiment, all other parameters remained consistent: the laser frequency was set at 240 kHz, the speed was maintained at 6000 mm/s, and the number of cleaning passes was fixed at one.
Figure 4 depicts surface microstructure images post-laser cleaning at varying laser pulse widths. It is evident from the figure that a substantial amount of the Al metal layer remains on the substrate surface when the laser pulse width is 50 ns. However, as the laser pulse width escalates, the efficiency of the Al metal layer’s removal improves significantly, leaving virtually no residue at 200 ns.
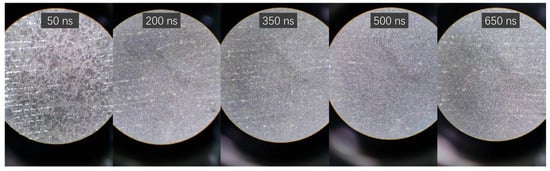
Figure 4.
Surface microstructure image of the surface after removing Al metal layers with different laser pulse widths (50×).
After laser cleaning with different laser powers, surface morphology images of the substrate surface are measured near the center of the substrate surface by SEM, as shown in Figure 5. It can be observed that when the laser pulse width is 50 ns, a significant amount of the Al metal layer remains on the substrate surface. As the laser pulse width increases, the removal effect of the Al metal layer improves, with almost no residue on the substrate surface at a pulse width of 200 ns. When the laser pulse width is further increased, since the Al metal layer has been completely removed, the laser begins to cause ablation damage to the substrate surface, resulting in a large number of holes and cracks.
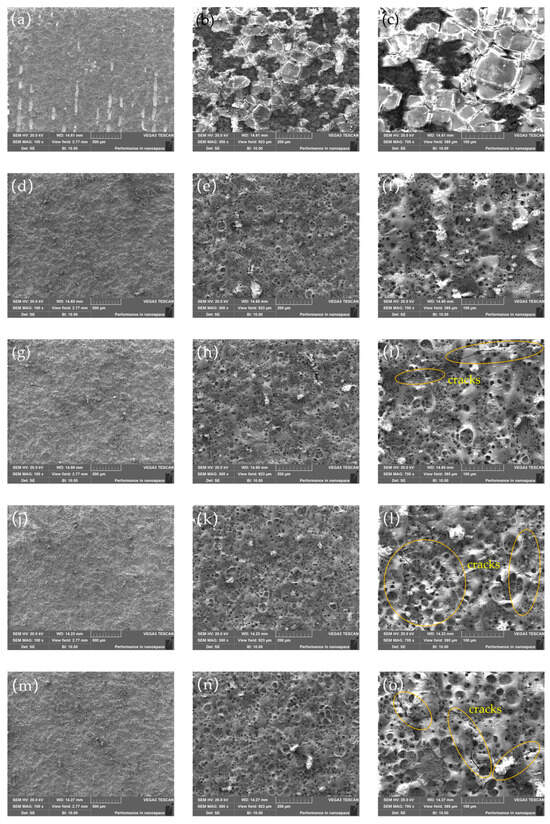
Figure 5.
Surface morphology image of the surface after removing Al metal layers with different laser pulse widths: (a–c) 50 ns; (d–f) 200 ns; (g–i) 350 ns; (j–l) 500 ns; (m–o) 650 ns; (a,d,g,j,m) 100×; (b,e,h,k,n) 300×; (c,f,i,l,o):700×.
Subsequently, the surface roughness of the substrate surface after laser cleaning at different laser widths was measured. The measurement method was the same as Section 3.1. The arithmetic mean deviation of the roughness profile Ra and root mean square deviation of the roughness profile Rq after laser cleaning at different laser widths are presented in Table 2. Based on these test results, it can be seen that as the laser pulse width increases, Ra increases from 9.02 µm at a laser pulse width of 50 ns to 14.727 µm at a laser pulse width of 350 ns, while Rq increases from 10.554 µm to 18.053 µm. After that, with a further increase in laser pulse width, the surface average roughness remains stable. The minimal discrepancy between Ra and Rq suggests that the micro-profile shape of the surface post-laser cleaning is notably uniform and regular. Overall, the average surface roughness shows a trend of first increasing and then stabilizing. This is because when the laser pulse width is short, the laser power is at its peak for a shorter time, resulting in a poor removal of the Al metal layer. As the laser pulse width increases, the laser power stays at its peak for a longer time, leading to a better removal of the Al metal layer, resulting in a stabilized change in roughness. However, there is a risk of surface burning and damage beyond a laser width of 200 ns. Therefore, to achieve a good removal effect for the Al metal layer while minimizing damage to the substrate surface, the optimal laser pulse width for laser cleaning is 200 ns.

Table 2.
Average surface roughness after removing Al metal layers with different laser pulse widths.
3.3. Impact of Laser Frequency on Removal Efficiency of Al Metal Layer
In examining the impact of varying laser frequencies on the removal efficiency of Al metal layers, lasers with frequency settings of 50 kHz, 240 kHz, and 450 kHz were employed for cleaning and removal tasks. Based on the findings presented in Section 3.1, a laser with a power of 120 W and width of 200 ns was selected to investigate the relationship between laser frequencies and the removal efficiency of the Al metal layer. Throughout the experiment, all other parameters remained consistent: the speed was maintained at 6000 mm/s, and the number of cleaning passes was fixed at one.
Figure 6 depicts the surface microstructure images post-laser cleaning at varying laser frequencies. It is evident from the figure that a substantial amount of the Al metal layer remains on the substrate surface when the laser frequency is 50 kHz. However, as the laser pulse width escalates, the efficiency of Al metal layer removal improves significantly, leaving virtually no residue at 240 kHz.
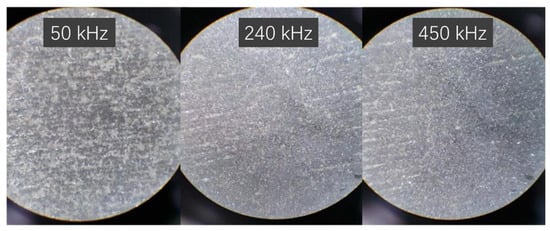
Figure 6.
Microstructure images of test material after laser cleaning using different laser frequencies (50×).
After laser cleaning with different laser powers, surface morphology images of the substrate surface were measured near the center of the substrate surface by SEM, as shown in Figure 7. It can be observed that when the laser frequency is 50 kHz, a significant amount of the Al metal layer remains on the substrate surface. As the laser frequency increases, the removal effect of the Al metal layer improves, with almost no residue on the substrate surface at a pulse frequency of 240 kHz. When the laser frequency is further increased, since the Al metal layer has been completely removed, the laser begins to cause ablation damage to the substrate surface, resulting in a large number of holes and cracks.
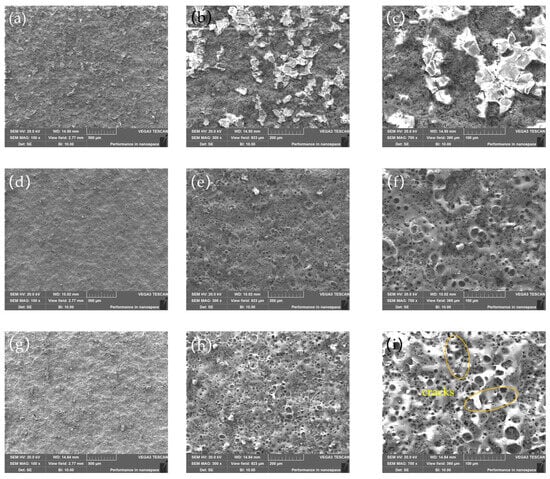
Figure 7.
Surface morphology image of the surface after removing Al metal layers at different laser frequencies: (a–c) 50 kHz; (d–f) 240 kHz; (g–i) 450 kHz; (a,d,g) 100×; (b,e,h) 300×; (c,f,i): 700×.
The surface roughness of the substrate surface after laser cleaning at different laser frequencies was measured. The Ra and Rq after laser cleaning at different laser widths are presented in Table 3. Based on these test results, it can be seen that as the laser pulse frequency increases, Ra increases from 10.326 µm at a laser frequency of 50 kHz to 13.129 µm at a laser frequency of 240 kHz, while Rq increases from 12.249 µm to 15.772 µm. After that, with a further increase in laser pulse width, the surface average roughness remains stable. The minimal discrepancy between Ra and Rq suggests that the micro-profile shape of the surface post-laser cleaning is notably uniform and regular. Overall, the average surface roughness shows a trend of first increasing and then stabilizing, which is consistent with the influence of the laser power and pulse width. This is because when the cleaning speed is constant, a lower frequency results in a smaller number of laser pulses acting on the coating surface, leading to an insufficient cleaning ability. As the laser frequency increases, the number of laser pulses acting on the coating surface increases, leading to better removal of the Al metal layer, resulting in a stabilized change in roughness. However, there is a risk of surface burning and damage when further increasing the frequency.

Table 3.
Average surface roughness after removing Al metal layers at different laser frequencies.
3.4. Discussions
Figure 8 illustrates the mechanism of the laser-induced cleaning of an Al metal layer from a ceramic substrate. When the laser beam interacts with the Al metal layer, it absorbs the beam’s energy, generating a local high-temperature area almost instantly. Given aluminum’s low melting point of approximately 660 °C, it is prone to rapid surface melting or even vaporization under high temperatures. Concurrently, heat continues to transfer inward. Aluminum’s high thermal conductivity enables it to absorb the majority of the heat, while the ceramic substrate—with its lower thermal conductivity—creates a thermal gradient between the Al metal layer and itself. Moreover, the disparity in thermal expansion coefficients, where aluminum has a higher coefficient than ceramics, leads to differential expansion. This generates interfacial stresses that cause the aluminum coating to expand and ultimately delaminate from the ceramic substrate. In conclusion, the process of the laser cleaning of metal layers primarily involves two steps:
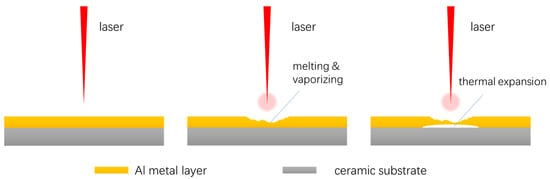
Figure 8.
Laser cleaning mechanism of Al metal layer from ceramic substrate.
Phase 1: Upon irradiation of the metal layer’s surface by the laser beam, local temperatures are generated at an exceedingly high level, leading to immediate melting or even vaporization and resulting in the removal of the metal layer in the affected area.
Phase 2: As the metal layer thins to only a few or tens of atomic layers, a stark difference in thermal expansion coefficients between the metal and ceramic substrate leads to the expansion of the metal layer under laser heat. At such a reduced thickness, delamination and warping occur between the metal and ceramic layers, resulting in the metal layer breaking into small fragments that detach from the substrate surface.
During the laser cleaning process, the energy exerted on the cleaning position is the primary cause of the temperature elevation, deformation, melting, and even vaporization of the aluminum coating. This energy is collectively influenced by factors such as cleaning speed, laser power, pulse width, frequency, spot size, and spot overlap rate. Given the constraints of the experimental conditions in this study, it was not feasible to fully discern the influence laws of all these parameters. In future research, efforts will be directed towards two main objectives: firstly, to enhance the understanding of the influence laws of the aforementioned factors in order to derive normalized parameters that impact the cleaning effect; and secondly, to improve the testing conditions. Tools such as energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) and thermal imaging will be employed to further elucidate the mechanism of the laser cleaning of metal coatings on ceramic substrates.
4. Conclusions
This study introduces an innovative approach for the removal of Al metal coatings using nanosecond pulsed lasers to clean Al metal layers from ceramic substrate surfaces. It investigates the influence of laser power and pulse width on the efficiency of Al metal layer removal from a ceramic substrate. The findings of this research contribute to advancing laser cleaning technology as an eco-friendly method for removing Al metal layers from ceramic substrates. The primary conclusions of this study are as follows:
- (1)
- The efficiency of Al metal layer removal is significantly influenced by both laser power and pulse width. When the laser power is too low, the Al metal layer may not be fully removed due to insufficient energy. Conversely, if the laser power is too high, it can potentially cause substantial damage to the ceramic substrate.
- (2)
- For the ceramic substrate coated with an Al metal layer (50 μm) in this study, considering both the effectiveness of removal and the potential damage to the ceramic substrate, the optimal laser cleaning procedure determined from our research comprises a laser power of 120 W, a pulse width of 200 ns, a frequency of 240 kHz, a cleaning speed of 6000 mm/s, and a singular cleaning cycle.
- (3)
- The localized high temperatures induced by laser irradiation, coupled with the differential thermal expansion coefficients between the metal layer and the ceramic substrate, collectively facilitate the removal of the Al metal layer during the laser cleaning process.
Notwithstanding its findings, this study acknowledges certain limitations. The impact of the laser spot size and the rate of spot overlap remain unexplored. Future investigations will concentrate on determining the normalized parameters that influence the cleaning effect and delve into the underlying mechanism, utilizing tools such as EDS and thermal imaging.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.L. and W.H.; Methodology, Y.L., H.W. (Hangchao Wang), and Y.Q.; Formal analysis, Y.L., H.W. (Hangchao Wang), and W.H.; Investigation, H.W. (Hang Wang) and Y.Q.; Resources, Y.Q.; Data curation, H.W. (Hang Wang); Writing—original draft, H.W. (Hangchao Wang) and H.W. (Hang Wang); Writing—review and editing, Y.L., W.H., H.W. (Hang Wang), and Y.Q.; Supervision, Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Science and Technology Major Project of China, grant number 2019-VI-0015-0130.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bocchese, F.; Delvaux, X.; Colaux, J.L.; Houssiau, L.; Lucas, S. Neutral salt spray aging effect on low emissivity coating. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 40, 103055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Weng, X.L.; Xie, J.L.; Deng, L.J. Effects of shape, size and solid content of Al pigments on the low-infrared emissivity coating. Mater. Res. Innov. 2015, 19, S325–S330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Duan, Y.; Pan, X. Research on Laser Cleaning Technology for Aircraft Skin Surface Paint Layer. Materials 2024, 17, 2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Tang, H.; Guo, P.; Ren, R. Study on mechanism of chip formation of grinding plasma-sprayed alumina ceramic coating. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 5951–5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, B.; Deng, Z. Grinding of nanostructured ceramic coatings: Surface observations and material removal mechanisms. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2002, 42, 1665–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacchi, D.; Rizzi, G.; Bardi, U.; Scrivani, A. Chemical stripping of ceramic films of titanium aluminum nitride from hard metal substrates. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 165, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozo-Antonio, J.S.; Rivas, T.; Fiorucci, M.P.; López, A.J.; Ramil, A. Effectiveness and harmfulness evaluation of graffiti cleaning by mechanical, chemical and laser procedures on granite. Microchem. J. 2016, 125, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Mativenga, P.; Goffin, N.; Liu, W.; Liu, Z.; Mirhosseini, N.; Jones, L.; Woolley, E.; Li, L. Energy consumption and performance optimisation of laser cleaning for coating removal. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2022, 37, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, M.; Wang, Z.; Shen, L.; Qiu, M.; Tian, Z.; Ahsan, M.N.; Wang, C. Properties of jet-plated Ni coating on Ti alloy (Ti6Al4V) with laser cleaning pretreatment. Metals 2019, 9, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheer Ud Din, S.; Shi, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, W. Evaluation of the Laser Cleaning Efficacy of Q235 Steel Using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. Metals 2022, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tian, J.; Ma, Z.; Zhou, W.; Qin, Y. Numerical analysis and experimental study of the laser cleaning of ceramic insulator contamination. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 49285–49296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Yuan, S.; Yang, S.; Gao, M.; Fu, Y.; Hu, T.; Li, X.; Fan, X.; Zhang, W. Waterjet-guided laser processing of SiC/SiC ceramic matrix composites to obtain high cleanliness and low oxidation damage characteristics surfaces. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 484, 130791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Yin, F. Research Progress in Application of Laser Cleaning Technology. Mater. Prot. 2020, 53, 142–146. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Guan, Y. Real-time monitoring of laser cleaning for hot-rolled stainless steel by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Metals 2021, 11, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Nam, H.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, S.-W. Lift-Off Ablation of Metal Thin Films for Micropatterning Using Ultrashort Laser Pulses. Metals 2021, 11, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, E.; Baker, H.J.; Nowak, K.M.; Villarreal, F.J.; Hall, D.R. Highly localized CO2 laser cleaning and damage repair of silica optical surfaces. In Laser-Induced Damage in Optical Materials: 2004, Proceedings of the Boulder Damage Symposium XXXVI, 2004, Boulder, CO, USA, 20–22 September 2004; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; Volume 5647, pp. 165–176. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, L.; Yin, F.; Wang, S.; Sun, J.; Yin, H. A review of thermal effects and substrate damage control in laser cleaning. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2024, 174, 110613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Xu, Z.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, L.; Xu, J.; Shan, D.; Chen, Y.; Guo, B. Mechanism and application of laser cleaning: A review. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2022, 157, 107130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairand, B.P.; Clauer, A.H. Effect of water and paint coatings on the magnitude of laser-generated shocks. Opt. Commun. 1976, 18, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Sun, W.; Wu, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S. The fundamental mechanisms of laser cleaning technology and its typical applications in industry. Processes 2023, 11, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Song, M.K.; Han, M.S.; Kim, J.-D. A study on the application of laser cleaning process in shipbuilding industries using 100 W fiber laser. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2021, 35, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balling, P.; Schou, J. Femtosecond-laser ablation dynamics of dielectrics: Basics and applications for thin films. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2013, 76, 036502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundar, M.; Hüsein, K.S.; Alhaji, M.K. Developments in Surface Contamination and Cleaning: Applications of Cleaning Techniques; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 251–288. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Shan, D.; Guo, B. Removal mechanism of laser cleaning for inorganic thermal control coatings on aluminum alloys. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 633, 157578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmdahl, R.; Brune, J.; Pätzel, R. Ultraviolet Laser Cleaning of Carbon Fiber Composites. Powder Met. Met. Ceram. 2016, 55, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Yu, L.; Zhuo, J.; Chen, Z.; Yao, J.; Wang, L. Study on removal mechanism of TC4 oxide film by nanosecond pulsed laser cleaning in air environment. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 181, 111856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wang, M.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y. An environmentally friendly laser cleaning method to remove oceanic micro-biofoulings from AH36 steel substrate and corrosion protection. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 127961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).