Phosphorylated Cellulose-Based Porous Monoliths for Efficient and Eco-Friendly Heavy Metal Ion Adsorption
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
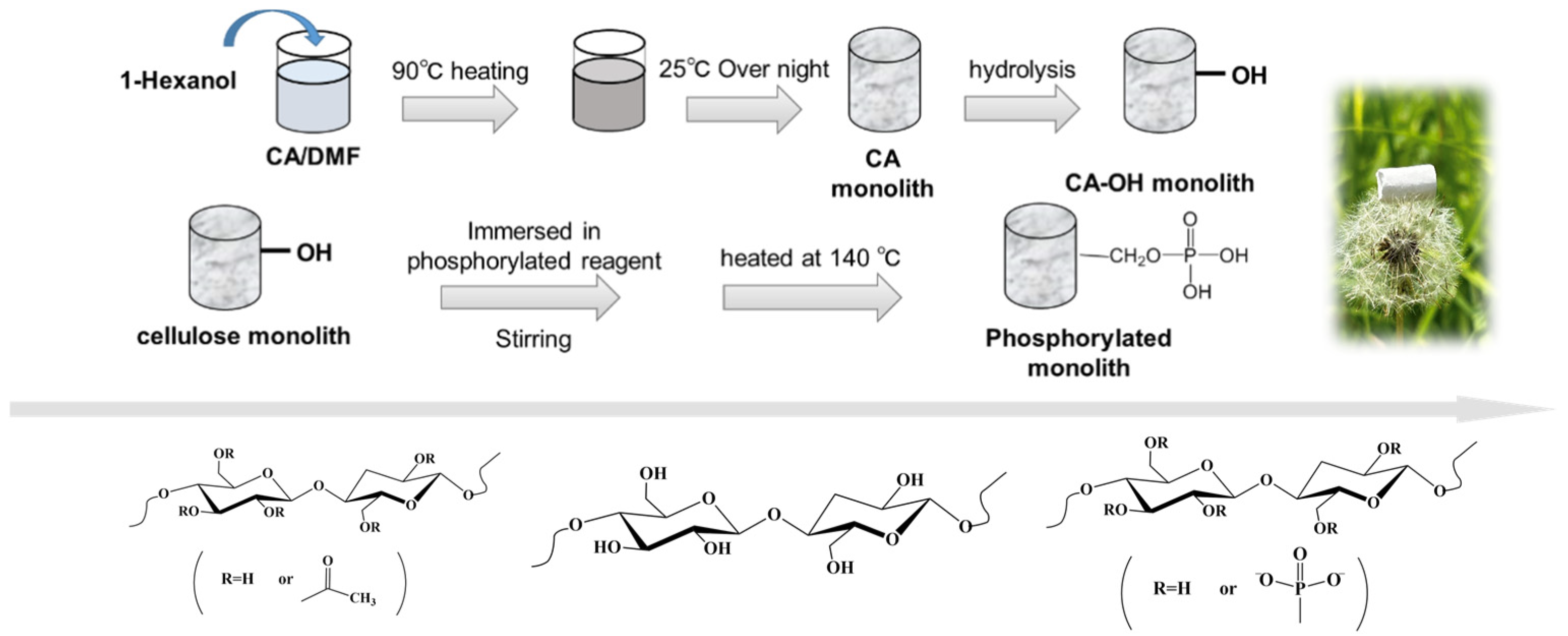
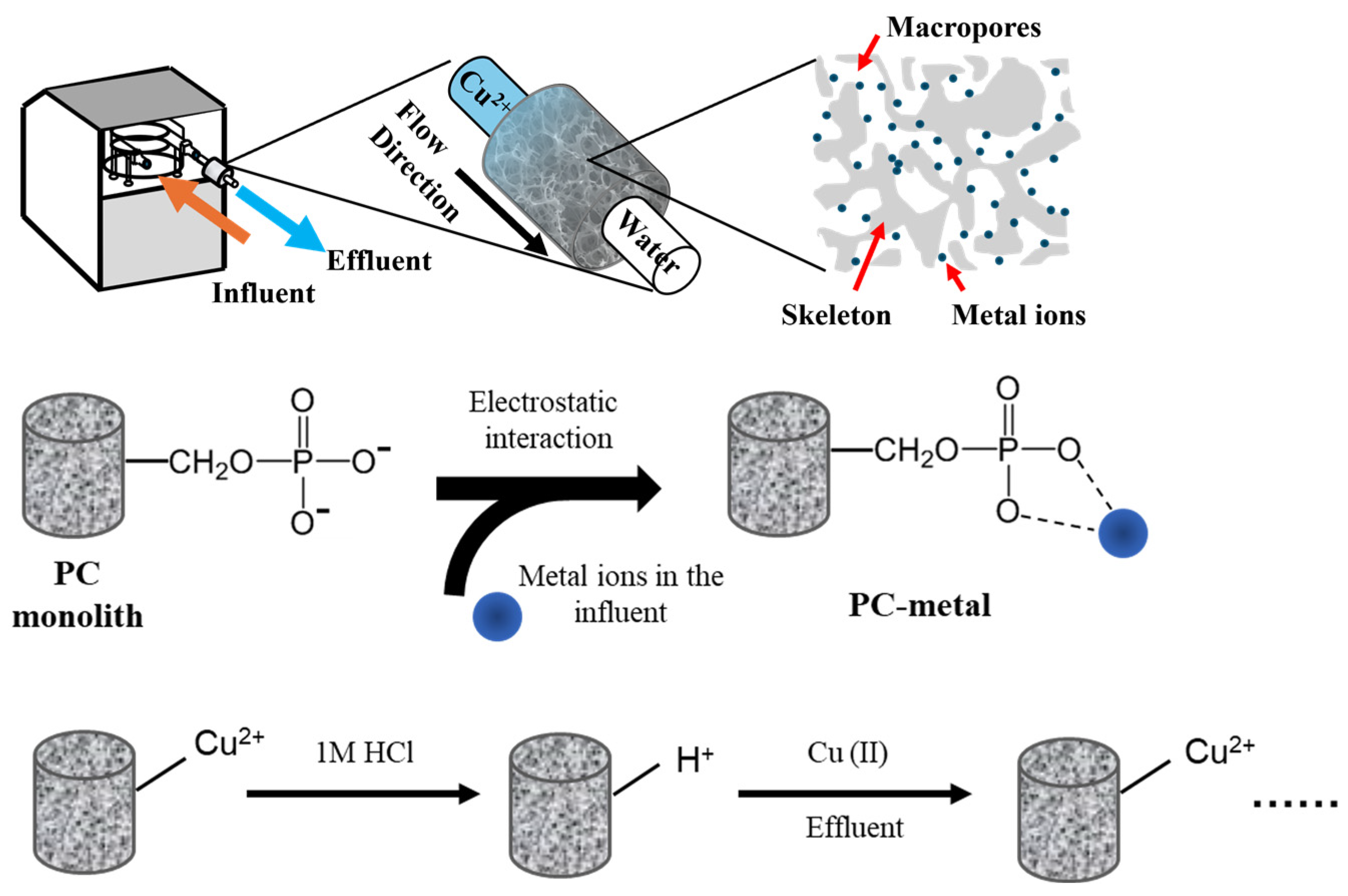
2.2. Preparation of Monoliths
2.2.1. Preparation of Cellulose Monolith
2.2.2. Preparation of Phosphorylated Cellulose Monoliths
2.3. Characterization
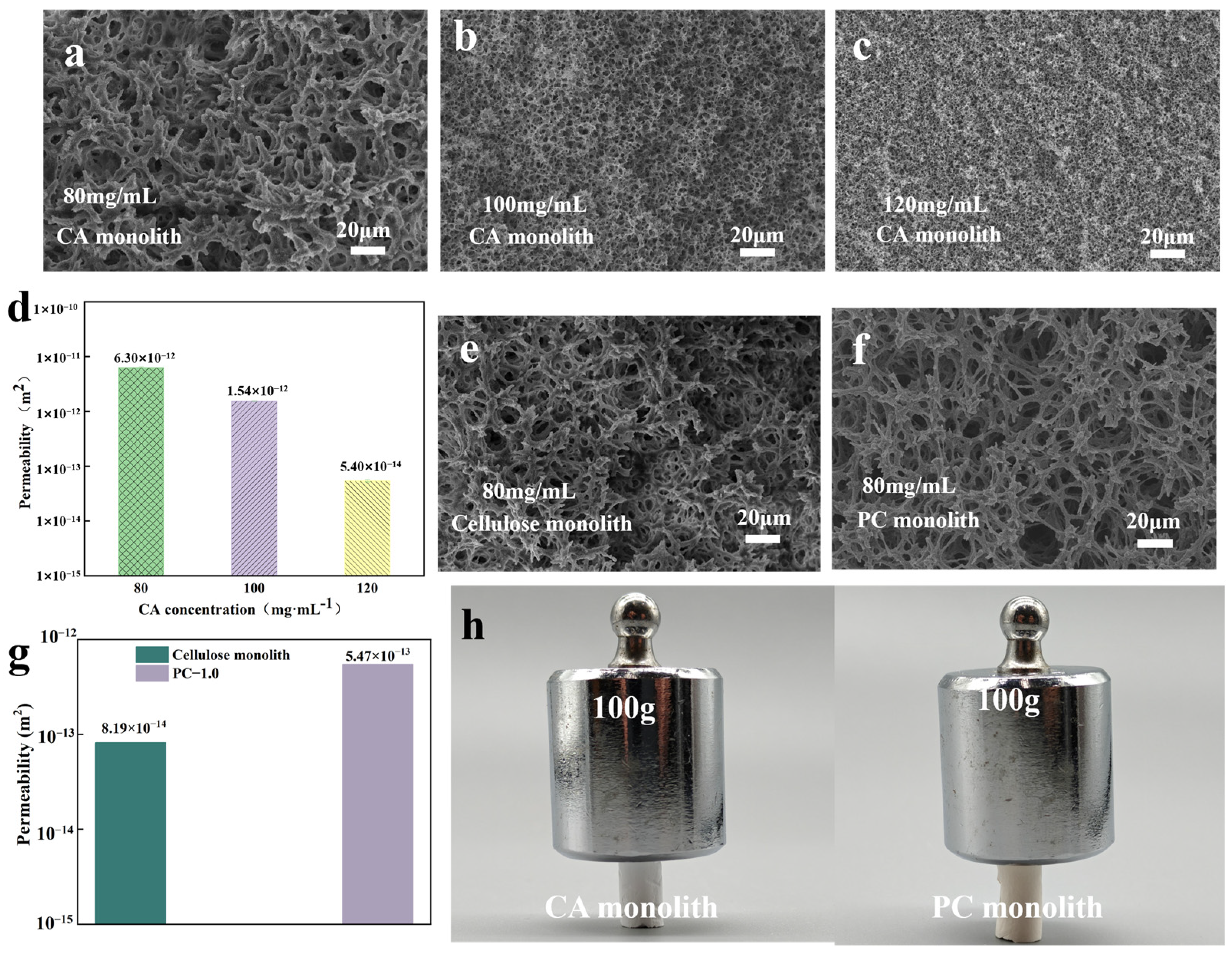
2.4. Permeability Testing
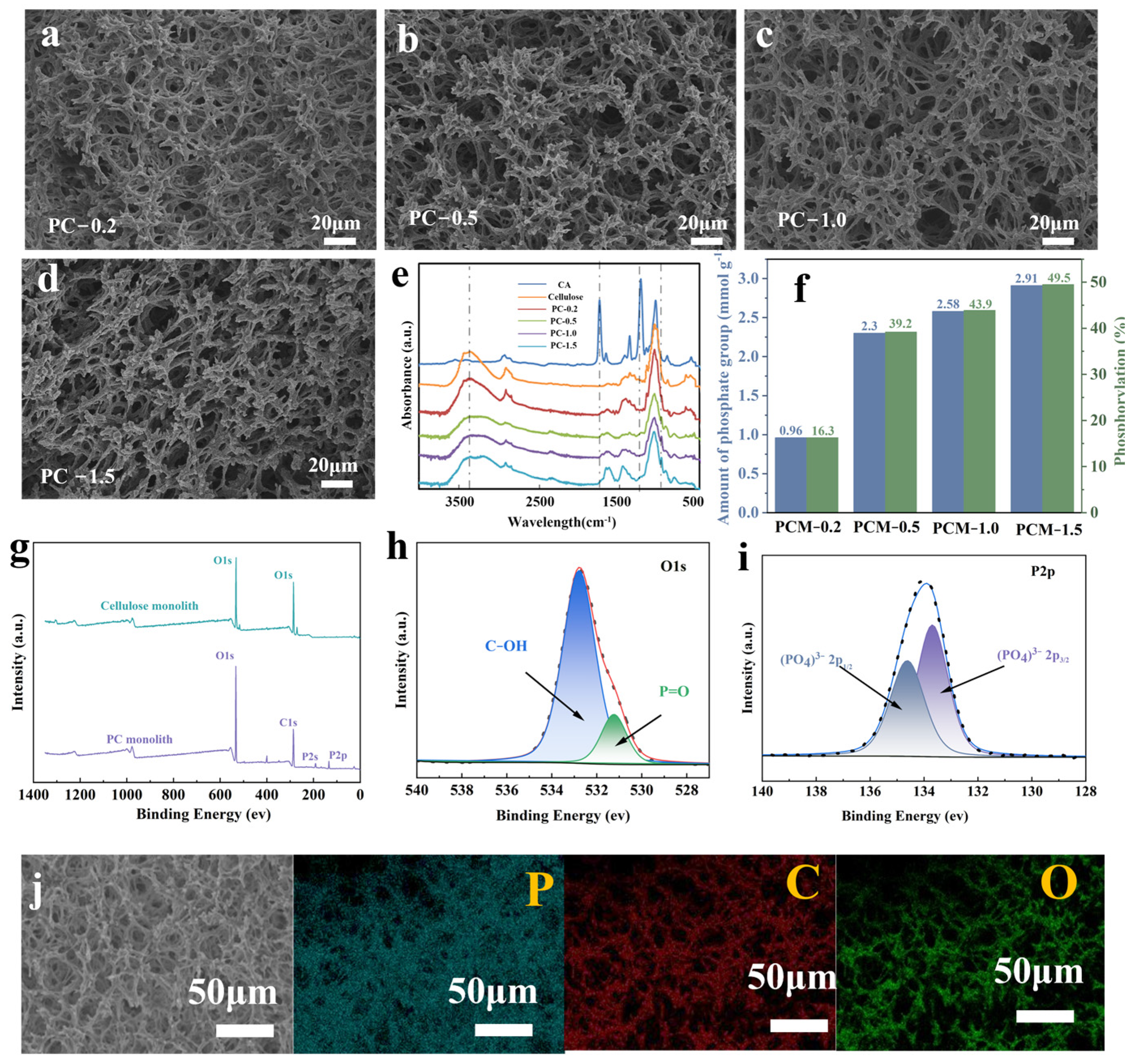
2.5. Determination of the Degree of Phosphorylation
2.6. Dynamic Adsorption Experiments and Recyclability
3. Results and Discussion
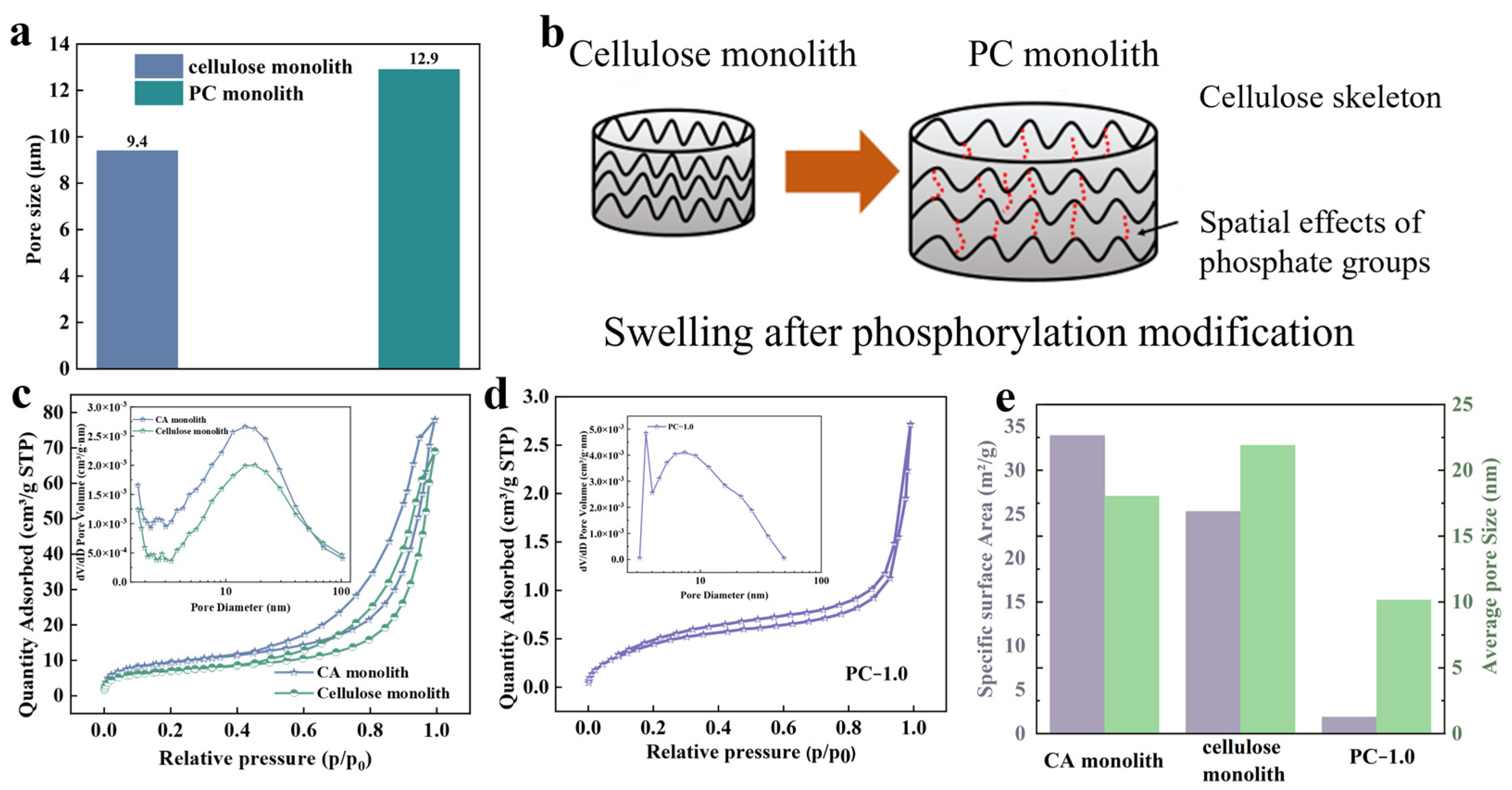
3.1. Morphological and Chemical Characterization of Monolithic Structures
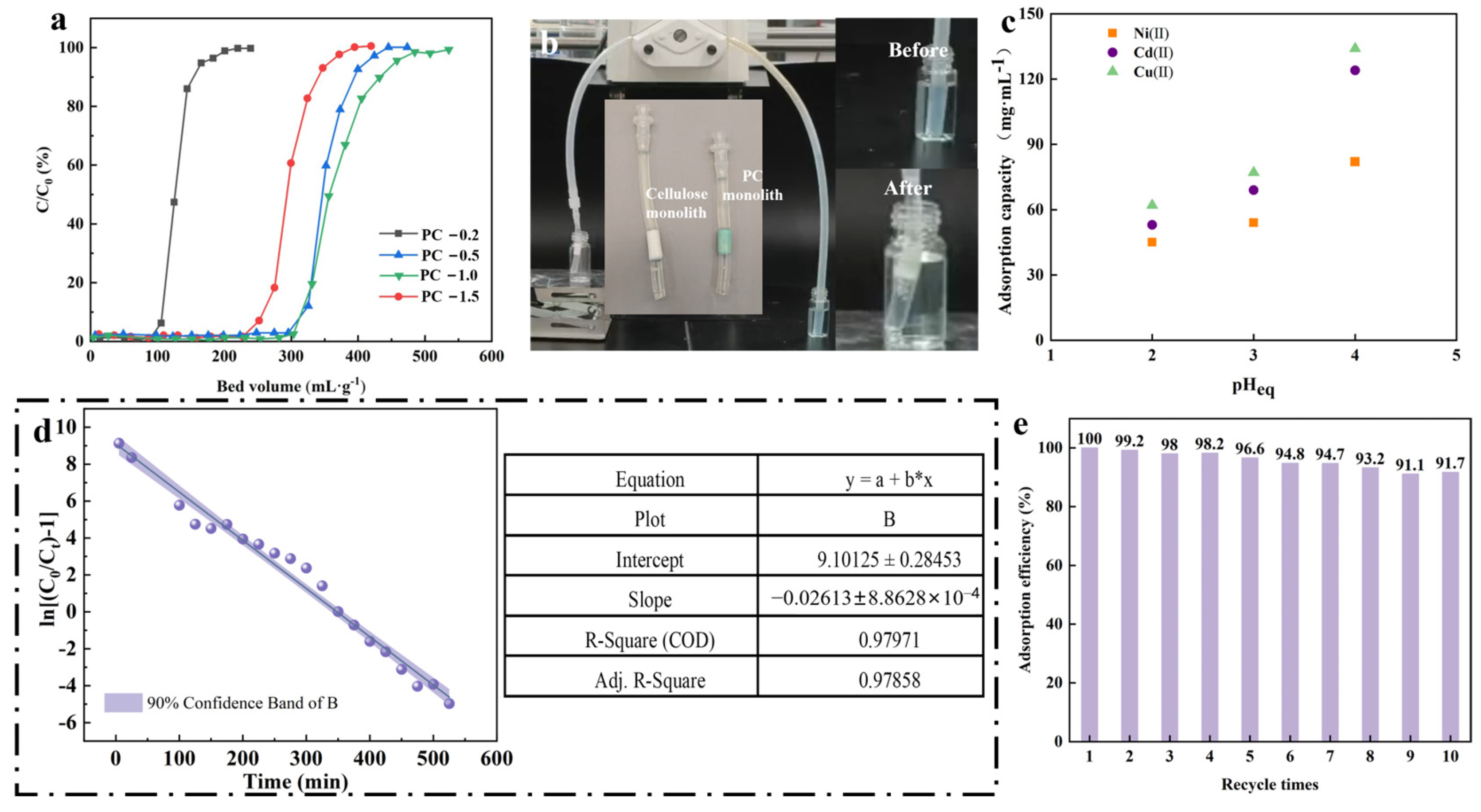
3.2. Continuous Flow Adsorption and Regeneration Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clemens, S.; Ma, J.F. Toxic Heavy Metal and Metalloid Accumulation in Crop Plants and Foods. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2016, 67, 489–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Chen, C.T. Heavy metal pollution status in surface sediments of the coastal Bohai Bay. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1901–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ablouh, E.H.; Kassab, Z.; Semlali Aouragh Hassani, F.Z.; El Achaby, M.; Sehaqui, H. Phosphorylated cellulose paper as highly efficient adsorbent for cadmium heavy metal ion removal in aqueous solutions. RSC Adv. 2021, 12, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Chan, G.Y.S.; Lo, W.-H.; Babel, S. Physico–chemical treatment techniques for wastewater laden with heavy metals. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 118, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Hu, R.; Zhao, X.; Liu, T.; Bai, Z. A novel chitosan/cellulose phosphonate composite hydrogel for ultrafast and efficient removal of Pb(II) and Cu(II) from wastewater. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 336, 122104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, M.; Asiri, A.M.; Azum, N.; Monti, S.; Karim, Z. Chemo-enzymatic functionalized sustainable cellulosic membranes: Impact of regional selectivity on ions capture and antifouling behavior. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 278, 118937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Heavy metal adsorption onto agro-based waste materials: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 157, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, M.A. New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2011, 4, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matlock, M.M.; Howerton, B.S.; Atwood, D.A. Chemical precipitation of heavy metals from acid mine drainage. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4757–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, N.A.A.; Mohammed, R.H.; Lawal, D.U. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A comprehensive and critical review. npj Clean. Water 2021, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan Ngah, W.S.; Hanafiah, M.A. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater by chemically modified plant wastes as adsorbents: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3935–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Gendy, A.A.; Mohamed, S.H.; Abd-Elkader, A.H. Ion exchanger from chemically modified banana leaves. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 96, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelatontsev, D. Production of versatile biosorbent via eco-friendly utilization of non-wood biomass. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Huang, J.; Dufresne, A. Preparation, properties and applications of polysaccharide nanocrystals in advanced functional nanomaterials: A review. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 3274–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Kimura, S.; Nishiyama, Y.; Isogai, A. Cellulose nanofibers prepared by TEMPO-mediated oxidation of native cellulose. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2485–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, B.; Raj, M.C.; Joy, J.; Moores, A.; Drisko, G.L.; Sanchez, C. Nanocellulose, a Versatile Green Platform: From Biosources to Materials and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 11575–11625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yingkong, P.; Tanskul, S. Adsorption of Iron(III) and Copper(II) by Bacterial Cellulose from Rhodococcus sp. MI 2. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 1948–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recepoğlu, Y.K.; Yüksel, A. Synthesis, characterization and adsorption studies of phosphorylated cellulose for the recovery of lithium from aqueous solutions. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2021, 55, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.D.; Kirti, N.; Katiyar, P.; Singh, H. A critical review on three-dimensional cellulose-based aerogels: Synthesis, physico-chemical characterizations and applications as adsorbents for heavy metals removal from water. Cellulose 2023, 30, 3397–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhu, Y.J.; Wu, J.; Zheng, J.Q.; Zhao, X.Y.; Lu, B.Q.; Chen, F. Chitosan-coated mesoporous microspheres of calcium silicate hydrate: Environmentally friendly synthesis and application as a highly efficient adsorbent for heavy metal ions. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2014, 418, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, A.G.; Paul, S.A.; Latha, M.S. Remediation of heavy metals and dyes from wastewater using cellulose-based adsorbents. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 17, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ke, Y.; Shang, Q.; Yang, X.; Wang, D.; Liao, G. Fabrication of multifunctional biomass-based aerogel with 3D hierarchical porous structure from waste reed for the synergetic adsorption of dyes and heavy metal ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, S.; Singhal, R.S. The potential of supercritical drying as a “green” method for the production of food-grade bioaerogels: A comprehensive critical review. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 141, 108738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Luo, Q.; Xu, J.; Li, K.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, H. A Novel Freeze-Drying-Free Strategy to Fabricate a Biobased Tough Aerogel for Separation of Oil/Water Mixtures. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 3779–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Xue, T.; Yang, F.; Fan, W.; Liu, T. Bidirectional anisotropic polyimide/bacterial cellulose aerogels by freeze-drying for super-thermal insulation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Phule, A.D.; Elkaee, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Zaman, M.W.U.; Yang, J.H.; Jeon, S.-C. Conversion of PET bottles into carbonaceous adsorbents for Pb(II) removal from aqueous solutions via KOH activation. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 66, 106092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, A.; Karczewski, J.; Eder, P.; Kolanowski, T.; Szalata, M.; Wielgus, K.; Szalata, M.; Kim, D.; Shin, S.R.; Slomski, R.; et al. Scaffolds for drug delivery and tissue engineering: The role of genetics. J. Control Release 2023, 359, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhou, Z.; Ismail, N.; Tocci, E.; Figoli, A.; Khayet, M.; Matsuura, T.; Cui, Z.; Tavajohi, N. Membrane formation by thermally induced phase separation: Materials, involved parameters, modeling, current efforts and future directions. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 669, 121303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Ma, W.; Wang, X. A review on microporous polyvinylidene fluoride membranes fabricated via thermally induced phase separation for MF/UF application. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 639, 119759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, Z. Advances in hierarchically porous materials: Fundamentals, preparation and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 202, 114641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, P.V.; Rego, R.M.; Yap, P.L.; Losic, D.; Kurkuri, M.D. Unveiling cutting-edge advances in high surface area porous materials for the efficient removal of toxic metal ions from water. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2024, 146, 101314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Almatrafi, E.; Tang, L.; Song, B.; Zhou, C.; Zeng, Y.; Zeng, G.; Liu, Z. Processable Conjugated Microporous Polymer Gels and Monoliths: Fundamentals and Versatile Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 39701–39726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Asoh, T.-A.; Uyama, H. Cationic functionalization of cellulose monoliths using a urea-choline based deep eutectic solvent and their applications. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 160, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuura, K.; Mizuno, H. Flameproofing of cotton fabrics with urea and phosphoric acid in organic solvent. Sen’i Gakkaishi 1966, 22, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, K.; Cao, X.; Sun, R. Cellulose acetate fibers prepared from different raw materials with rapid synthesis method. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.M.; Ali, A.A.; Hazarika, M.P. Synthesis and characterization of cellulose acetate from rice husk: Eco-friendly condition. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 112, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, S.M.; Dos Santos, D.C.; Motta, J.F.G.; Santos, R.R.D.; Chavez, D.W.H.; Melo, N.R. Structure and functional properties of cellulose acetate films incorporated with glycerol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 209, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, R.J.; Lawrie, G.; Lambert, L.K.; Whittaker, M.; Jack, K.S.; Grondahl, L. Phosphorylation of alginate: Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of in vitro mineralization capacity. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahsis, L.; Ablouh, E.H.; Hanani, Z.; Sehaqui, H.; El Achaby, M.; Julve, M.; Stiriba, S.E. Copper phosphorylated cellulose nanofibers mediated azide-alkyne cycloaddition click reaction in water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 324, 121501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Rashid, S.A.; Abdullah, L.C.; Rahman, N.A. Preparation of electrospun cellulose acetate/chitosan membranes for efficient sorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 699, 134698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, J.; Tian, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, S.; Qing, Y.; Jiang, Z. Cellulose Nanofibrils Aerogel Cross-Linked by Poly(vinyl alcohol) and Acrylic Acid for Efficient and Recycled Adsorption with Heavy Metal Ions. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 4167–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, B.; Xu, Z.; Liang, P.; Zhang, J.; Christie, P.; Liu, H.; Wu, S.; Liu, X. Three-dimensional macroscopic aminosilylated nanocellulose aerogels as sustainable bio-adsorbents for the effective removal of heavy metal ions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 190, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, W.; Yin, L.; Lin, X.; Yu, Y.; Lian, D.; Shi, Z.; Chen, P.; Tang, M.; Yang, C. Simultaneous Adsorption of Cu2+ and Cd2+ by a Simple Synthesis of Environmentally Friendly Bamboo Pulp Aerogels: Adsorption Properties and Mechanisms. Polymers 2022, 14, 4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Wang, M.; Wu, T.; Guo, L.; Han, W. Covalent Crosslinking Cellulose/Graphene Aerogels with High Elasticity and Adsorbability for Heavy Metal Ions Adsorption. Polymers 2023, 15, 2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Monoliths | Urea (g) | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|
| Cellulose acetate monolith | / | CA monolith |
| Cellulose monolith | / | / |
| Phosphorylated cellulose monolith | 0.2 | PC-0.2 |
| Phosphorylated cellulose monolith | 0.5 | PC-0.5 |
| Phosphorylated cellulose monolith | 1.0 | PC-1.0 |
| Phosphorylated cellulose monolith | 1.5 | PC-1.5 |
| Phosphorylated cellulose monolith | 1.5 | PC-1.5 |
| Adsorbent | Adsorption Property (mg/g) | Efficiency (%) and Cycle Times (x) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| cellulose acetate/chitosan membranes | 46.7 | 91.5% (6) | [40] |
| Cellulose nanofibril-PVA-AA aerogel | 30.0 | 89% (5) | [41] |
| Aminosilylated nanocellulose aerogels | 99.0 | / | [42] |
| Bamboo Pulp Aerogels | 72.73 | <80% (3) | [43] |
| Covalent Crosslinking Cellulose/G Aerogels | 80.12 | 90.5% (5) | [44] |
| PC-1.0 | 172 | 91.7% (10) | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Liao, Z.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ren, Y.; Yang, Z. Phosphorylated Cellulose-Based Porous Monoliths for Efficient and Eco-Friendly Heavy Metal Ion Adsorption. Coatings 2025, 15, 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050557
Shu Y, Zhang G, Liao Z, Liang Y, Wang Q, Ren Y, Yang Z. Phosphorylated Cellulose-Based Porous Monoliths for Efficient and Eco-Friendly Heavy Metal Ion Adsorption. Coatings. 2025; 15(5):557. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050557
Chicago/Turabian StyleShu, Yuhang, Guangyu Zhang, Zhipeng Liao, Yao Liang, Qidong Wang, Yu Ren, and Zhaohang Yang. 2025. "Phosphorylated Cellulose-Based Porous Monoliths for Efficient and Eco-Friendly Heavy Metal Ion Adsorption" Coatings 15, no. 5: 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050557
APA StyleShu, Y., Zhang, G., Liao, Z., Liang, Y., Wang, Q., Ren, Y., & Yang, Z. (2025). Phosphorylated Cellulose-Based Porous Monoliths for Efficient and Eco-Friendly Heavy Metal Ion Adsorption. Coatings, 15(5), 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050557






