CO2 Adsorption of Aminopropyltrimethoxysilane-and-Tetraethylenepentamine-Co-Modified Mesoporous Silica Gel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sorbent Preparation
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Adsorption and Regeneration
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
3.2. CO2 Adsorption Performance
3.2.1. Effect of the Amine Loading
3.2.2. Effect of the Adsorption Temperature
3.2.3. Effect of Influent Flow Rate
3.3. Regeneration
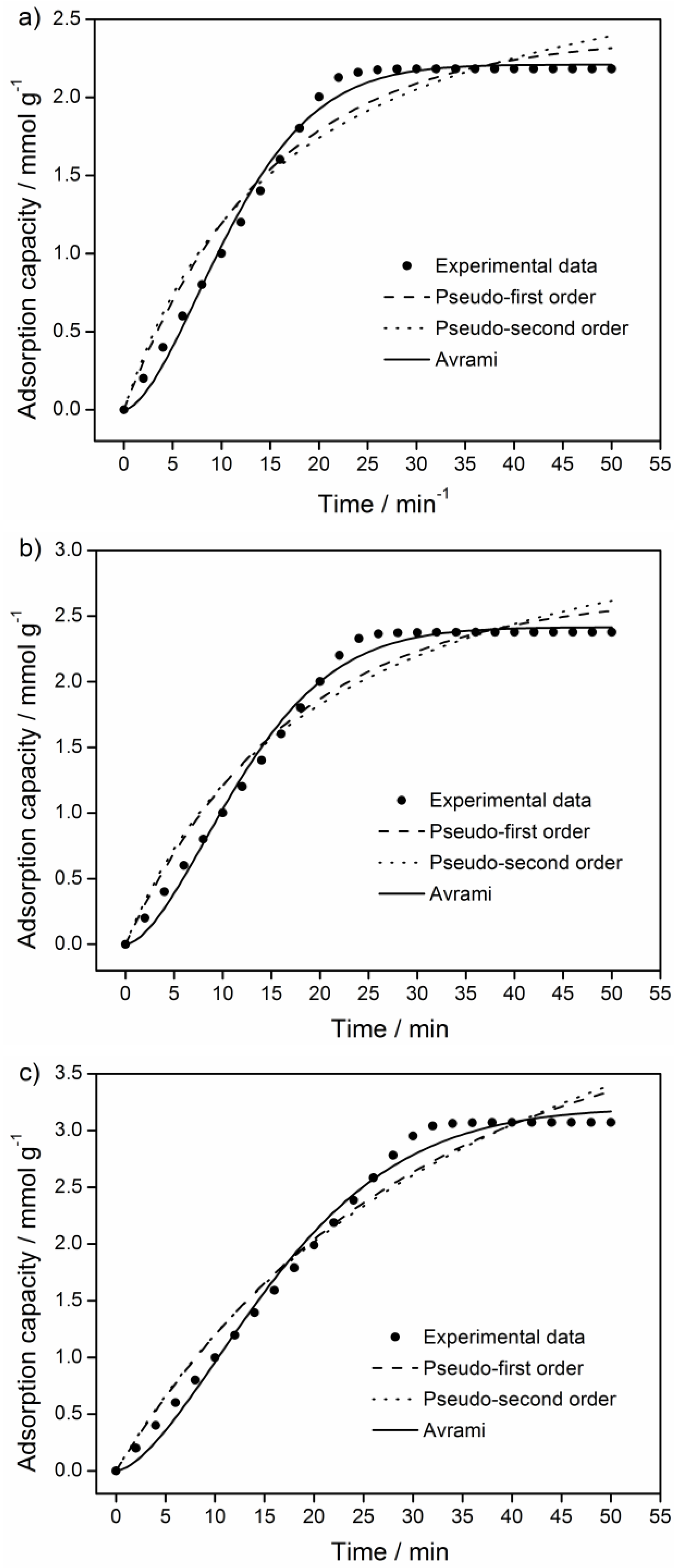
3.4. CO2 Adsorption Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, L.; Zhao, N.; Wei, W.; Sun, Y. A review of research progress on CO2 capture, storage, and utilization in Chinese Academy of Sciences. Fuel 2013, 108, 112–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xu, Z.; Fan, M.; Gupta, R.; Slimane, R.B.; Bland, A.E.; Wright, I. Progress in carbon dioxide separation and capture: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notz, R.; Tönnies, I.; McCann, N.; Scheffknecht, G.; Hasse, H. CO2 Capture for Fossil Fuel-Fired Power Plants. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2011, 34, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinrad, R. Greenhouse Gas Bulletin; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA): Columbia, WA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, K.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, W. Integrated CO2 absorption-mineralization process by the MEA+MDEA system coupled with Ba(OH)2: Absorption kinetics and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 502, 158102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Suo, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Enhancing CO2 adsorption performance of porous nitrogen-doped carbon materials derived from ZIFs: Insights into pore structure and surface chemistry. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 335, 126117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, T.; Hu, X.; Hao, J.; Guo, Q. Mechanism and kinetics of CO2 adsorption for TEPA-impregnated hierarchical mesoporous carbon in the presence of water vapor. Powder Technol. 2020, 368, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; He, X.; Luo, J. Random and block copolymer membranes based on flexible etheric-aliphatic soft segments designed for CO2/CH4 separation. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2018, 54, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.Y.; Yang, R.T.; Chinn, D.; Munson, C.L. Amine-Grafted MCM-48 and Silica Xerogel as Superior Sorbents for Acidic Gas Removal from Natural Gas. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 2427–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zeng, W.; Song, M.; Wang, F.; Hu, X.; Guo, Q.; Liu, Y. Polyetheramine improves the CO2 adsorption behavior of tetraethylenepentamine-functionalized sorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 364, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Guo, Q. Development of hybrid amine-functionalized MCM-41 sorbents for CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, R.; Calleja, G.; Arencibia, A.; Sanz-Pérez, E.S. Development of high efficiency adsorbents for CO2 capture based on a double-functionalization method of grafting and impregnation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 1956–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zeng, W.; Hu, P.; Liu, S.; Lin, Y.; He, Z.; Xin, C.; Kong, X.; Xu, J. Effect of Additives on CO2 Adsorption of Polyethylene Polyamine-Loaded MCM-41. Molecules 2024, 29, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Guo, T.; Tian, W.; Hao, J.; Guo, Q. The competitive adsorption mechanism of CO2, H2O and O2 on a solid amine adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 416, 129007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyeok, J.J.; Dong, K.Y.; Sung, H.J. Metal-organic framework (MOF-808) functionalized with ethyleneamines: Selective adsorbent to capture CO2 under low pressure. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 58, 101932. [Google Scholar]
- Hang, Z.; Goeppert, A.; Prakash, G.K.S.; Olah, G. Applicability of linear polyethylenimine supported on nano-silica for the adsorption of CO2 from various sources including dry air. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 52550–52562. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zeng, W.; Xin, C.; Kong, X.; Hu, X.; Guo, Q. The development of activated carbon from corncob for CO2 capture. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 33069–33078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kong, F.; Zeng, W.; Zhang, H.; Xin, C.; Kong, X. The Resource Utilization of Poplar Leaves for CO2 Adsorption. Molecules 2024, 29, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ke, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, Z.; Komarneni, S. Clover leaf-shaped Al2O3 extrudate as a support for high-capacity and cost-effective CO2 sorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 1505–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, X.; Fang, Y.; Ding, J. Preparation and performance of form-stable polyethylene glycol/silicon dioxide composites as solid-liquid phase change materials. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, L.D.; Tripp, C.P. Reaction of (3-Aminopropyl)dimethylethoxysilane with Amine Catalysts on Silica Surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 232, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Shang, H.; Li, L.; Yan, X.; Yan, Z.; Liu, C.; Zha, Q. Efficient CO2 capture on low-cost silica gel modified by polyethyleneimine. J. Nat. Gas. Chem. 2012, 21, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keramati, M.; Ghoreyshi, A.A. Improving CO2 adsorption onto activated carbon through functionalization by chitosan and triethylenetetramine. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2014, 57, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyapal, S.; Filburn, T.; Trela, J. Performance and Properties of a Solid Amine Sorbent for Carbon Dioxide Removal in Space Life Support Applications. Energy Fuels 2001, 15, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didas, S.A.; Kulkarni, A.R.; Sholl, D.S.; Jones, C.W. Role of Amine Structure on Carbon Dioxide Adsorption from Ultradilute Gas Streams such as Ambient Air. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 2058–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xiao, J.; Wei, X.; Ding, J.; Wang, X.; Song, C. Development of a new clay supported polyethylenimine composite for CO2 capture. Appl. Energy 2014, 113, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, J.; Jie, C.; Ye, Q.; Hua, P.; Shao, Z.; Shi, Y. Dynamic performance of CO2 adsorption with tetraethylenepentamine-loaded KIT-6. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2010, 134, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauth, D.J.; Gray, M.L.; Pennline, H.W.; Krutka, H.M.; Ault, A.M. Investigation of Porous Silica Supported Mixed-Amine Sorbents for Post-Combustion CO2 Capture. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 2483–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.; Son, W.J.; You, K.S.; Ahn, J.W.; Ahn, W.S. Carbon dioxide capture using amine-impregnated HMS having textural mesoporosity. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 161, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Khatri, R.A.; Chuang, S.S.C.; Soong, Y.; Gray, M.M. Thermal and Chemical Stability of Regenerable Solid Amine Sorbent for CO2 Capture. Energy Fuels 2006, 20, 1514–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, M.; Darbis, N.D.A.; Din, A.T.M.; Hameed, B.H. Fixed-bed column adsorption of carbon dioxide by sodium hydroxide modified activated alumina. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 233, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Yang, S.; Choi, D.K.; Row, K.H. Adsorption of carbon dioxide using polyethyleneimine modified silica gel. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 27, 1910–1915. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, B.S. Carbon dioxide adsorption on polyacrylamide-impregnated silica gel and breakthrough modeling. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 261, 708–716. [Google Scholar]
- Wurzbacher, J.A.; Gebald, C.; Steinfeld, A. Separation of CO2 from air by temperature-vacuum swing adsorption using diamine-functionalized silica gel. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 3584–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Hong, S.-H.; Kim, K.-M.; Lee, C.-H. Adsorption equilibria and kinetics of silica gel for N2O, O2, N2, and CO2. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 251, 117326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zeng, W.; Liu, W.; Cao, X.; Hou, C.; Ding, Q.; Lü, Y. CO2 adsorption of lignite chars after one-step KOH activation. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 13755–13763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zeng, W.; Kong, X.; Xin, C.; Dong, Y.; Hu, X.; Guo, Q. Development of Low-Cost Porous Carbons through Alkali Activation of Crop Waste for CO2 Capture. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 46992–47001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

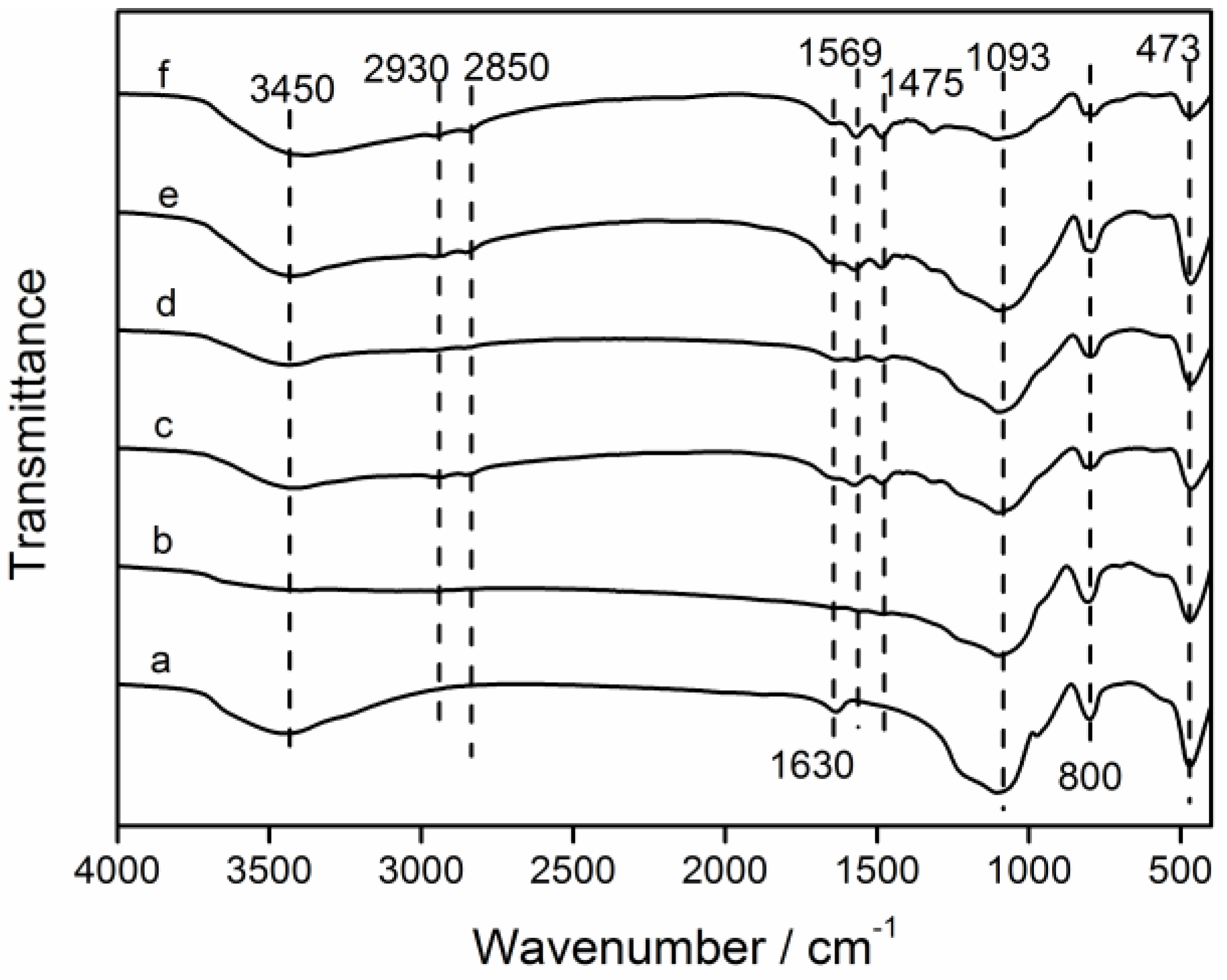
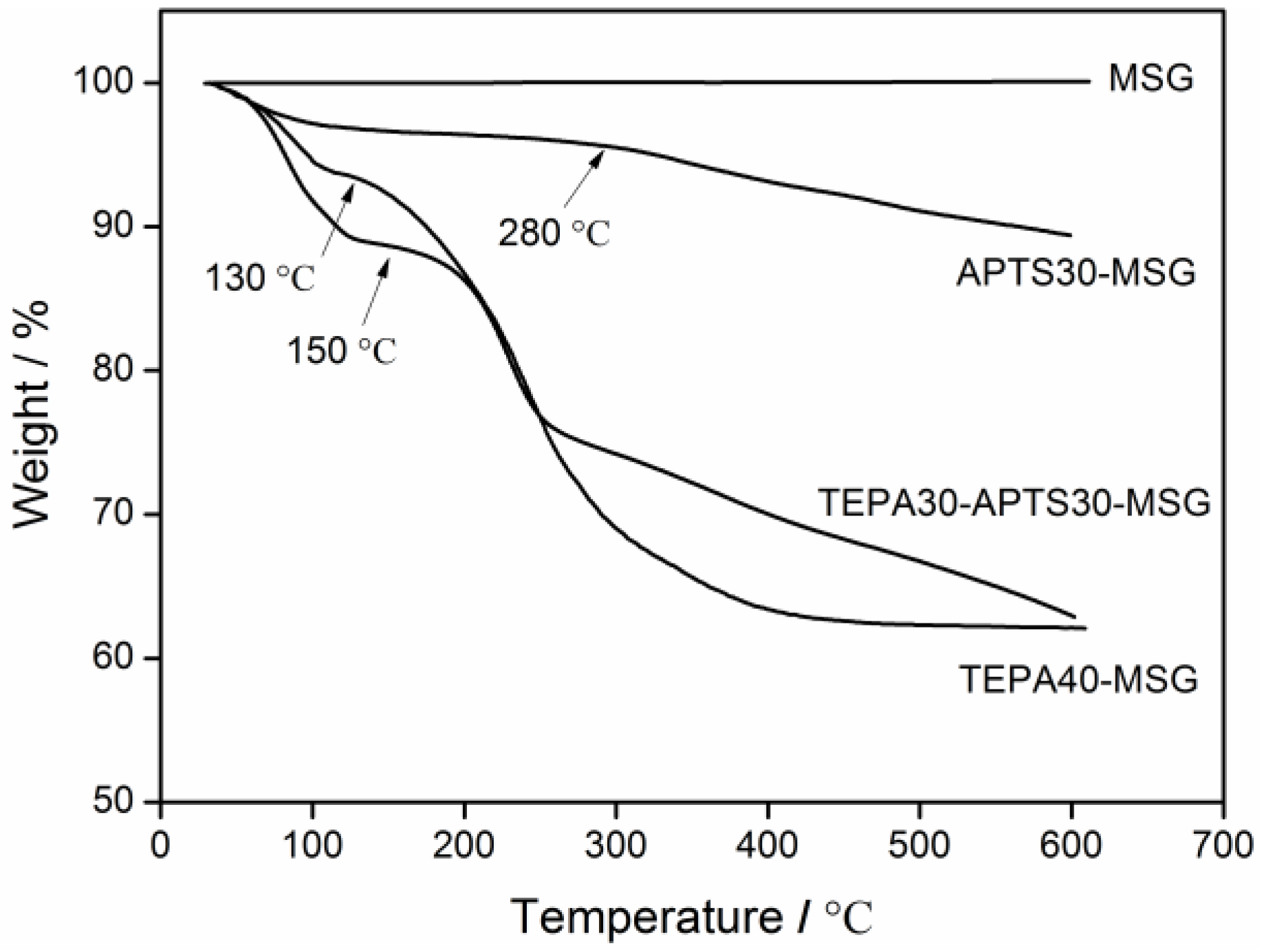
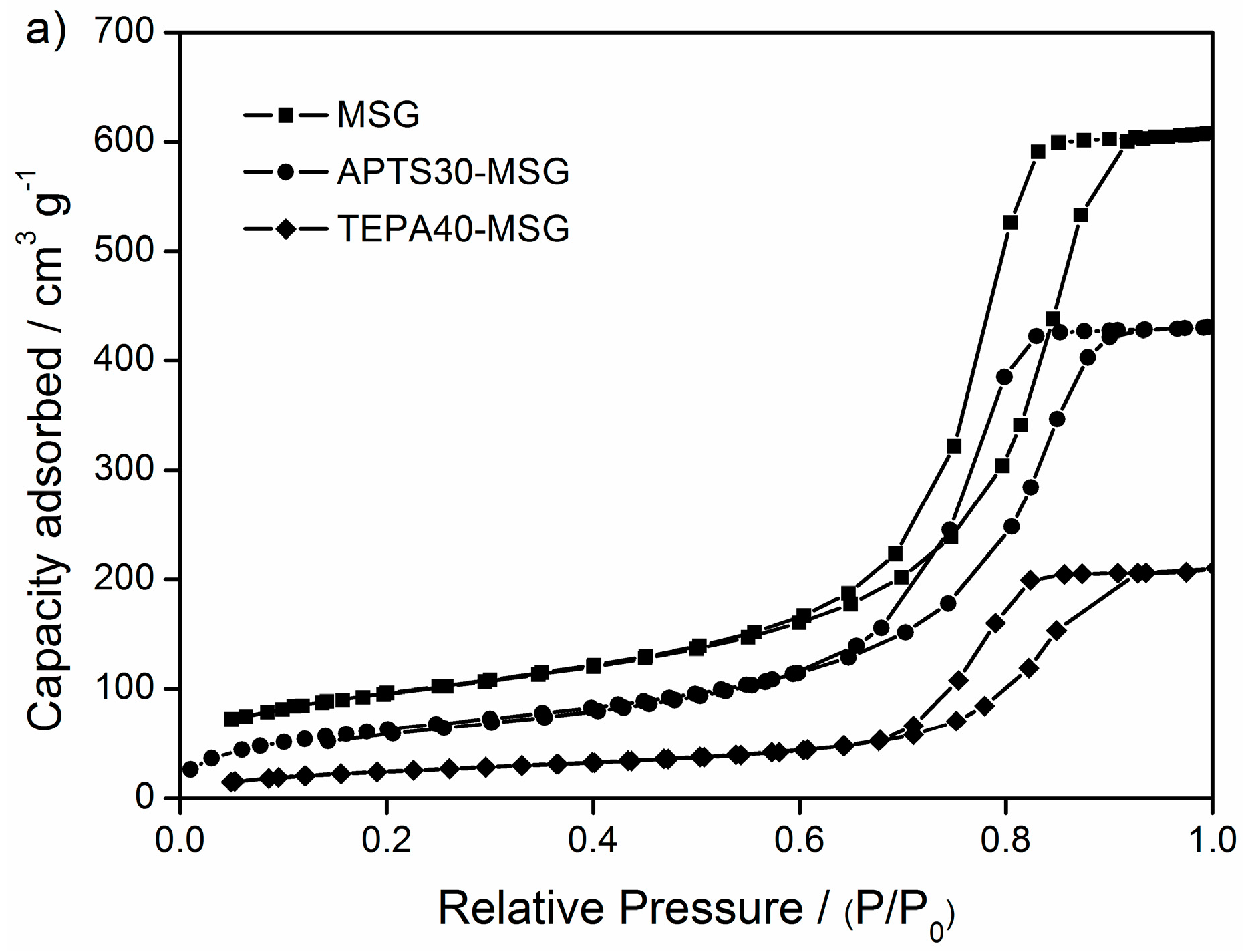
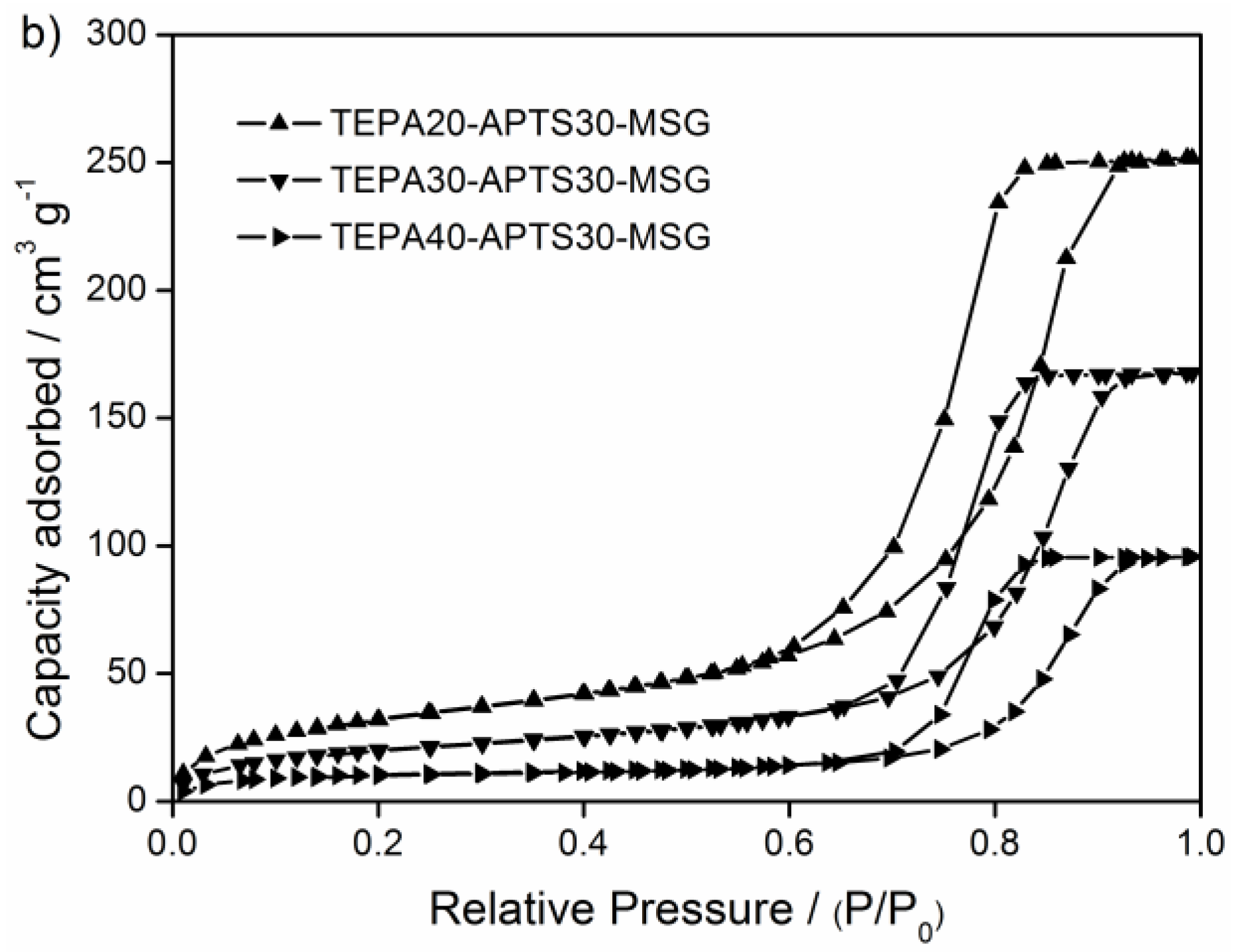



| Sorbent | SBET [m2 g−1] | Pore Volume [cm3 g−1] | Pore Diameter [nm] |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSG | 334.12 | 0.93 | 8.07 |
| APTS30-MSG | 237.26 | 0.67 | 7.51 |
| TEPA20-APTS30-MSG | 123.33 | 0.41 | 7.88 |
| TEPA30-APTS30-MSG | 75.21 | 0.28 | 8.77 |
| TEPA40-APTS30-MSG | 38.08 | 0.18 | 9.84 |
| TEPA40-MSG | 93.41 | 0.32 | 8.25 |
| Sample | Breakthrough Time [min] | Breakthrough Adsorption Capacity [mmol g−1] | Saturated Adsorption Capacity [mmol g−1] |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSG | 2 | 0.20 | 0.35 |
| TEPA10-MSG | 6 | 0.60 | 0.76 |
| TEPA20-MSG | 10 | 1.01 | 1.22 |
| TEPA30-MSG | 16 | 1.61 | 1.83 |
| TEPA40-MSG | 18 | 1.81 | 2.21 |
| TEPA50-MSG | 14 | 1.41 | 1.96 |
| APTS20-MSG | 8 | 0.80 | 1.09 |
| TEPA20-APTS20-MSG | 12 | 1.21 | 1.68 |
| TEPA30-APTS20-MSG | 22 | 2.21 | 2.38 |
| TEPA40-APTS20-MSG | 26 | 2.61 | 2.83 |
| TEPA50-APTS20-MSG | 16 | 1.61 | 1.93 |
| APTS30-MSG | 10 | 1.01 | 1.11 |
| TEPA10-APTS30-MSG | 14 | 1.41 | 1.73 |
| TEPA20-APTS30-MSG | 20 | 2.01 | 2.19 |
| TEPA30-APTS30-MSG | 28 | 2.81 | 3.04 |
| TEPA40-APTS30-MSG | 22 | 2.21 | 2.40 |
| Support | Amine | Loading [%] | Temperature [°C] | CO2 Partial Pressure [kPa] | Adsorption Capacity [mmol g−1] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSG | PEI | 33 | 25 | — | 1.07 | [32] |
| MSG | PEI | 30 | 75 | 15 | 2.12 | [22] |
| MSG | Poly- AAM | 39 | 60 | 17 | 0.64 | [33] |
| MSG | AEATPMS | 28 | 70 | 60 | 0.58 | [34] |
| MSG | TEPA | 40 | 70 | 15 | 2.21 | Present work |
| MSG | TEPA/ APTS | 30/30 | 70 | 15 | 3.04 | Present work |
| Kinetic Model | Parameter | 40 °C | 55 °C | 70 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order model | qe,cal (qe,exp) | 2.39 (2.18) | 2.67 (2.37) | 4.04 (3.04) |
| kf | 0.0351 | 0.0602 | 0.0689 | |
| R2 | 0.9606 | 0.9615 | 0.9714 | |
| Pseudo-second-order model | qe,cal (qe,exp) | 3.19 (2.18) | 3.68 (2.37) | 6.26 (3.04) |
| ks | 0.0038 | 0.0134 | 0.0188 | |
| R2 | 0.9401 | 0.9450 | 0.9656 | |
| Avrami | qe,cal (qe,exp) | 2.21 (2.18) | 2.41 (2.37) | 3.20 (3.04) |
| ka | 0.0523 | 0.0703 | 0.0768 | |
| na | 1.6706 | 1.6645 | 1.5888 | |
| R2 | 0.9926 | 0.9920 | 0.9912 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Zeng, W.; Kong, X. CO2 Adsorption of Aminopropyltrimethoxysilane-and-Tetraethylenepentamine-Co-Modified Mesoporous Silica Gel. Coatings 2025, 15, 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050554
Wang X, Chen L, Zeng W, Kong X. CO2 Adsorption of Aminopropyltrimethoxysilane-and-Tetraethylenepentamine-Co-Modified Mesoporous Silica Gel. Coatings. 2025; 15(5):554. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050554
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xia, Linlin Chen, Wulan Zeng, and Xiangjun Kong. 2025. "CO2 Adsorption of Aminopropyltrimethoxysilane-and-Tetraethylenepentamine-Co-Modified Mesoporous Silica Gel" Coatings 15, no. 5: 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050554
APA StyleWang, X., Chen, L., Zeng, W., & Kong, X. (2025). CO2 Adsorption of Aminopropyltrimethoxysilane-and-Tetraethylenepentamine-Co-Modified Mesoporous Silica Gel. Coatings, 15(5), 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050554





