The Effect of CeO2 Content on the Microstructure and Properties of TiC/WC/Co Composite Cladding Layers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
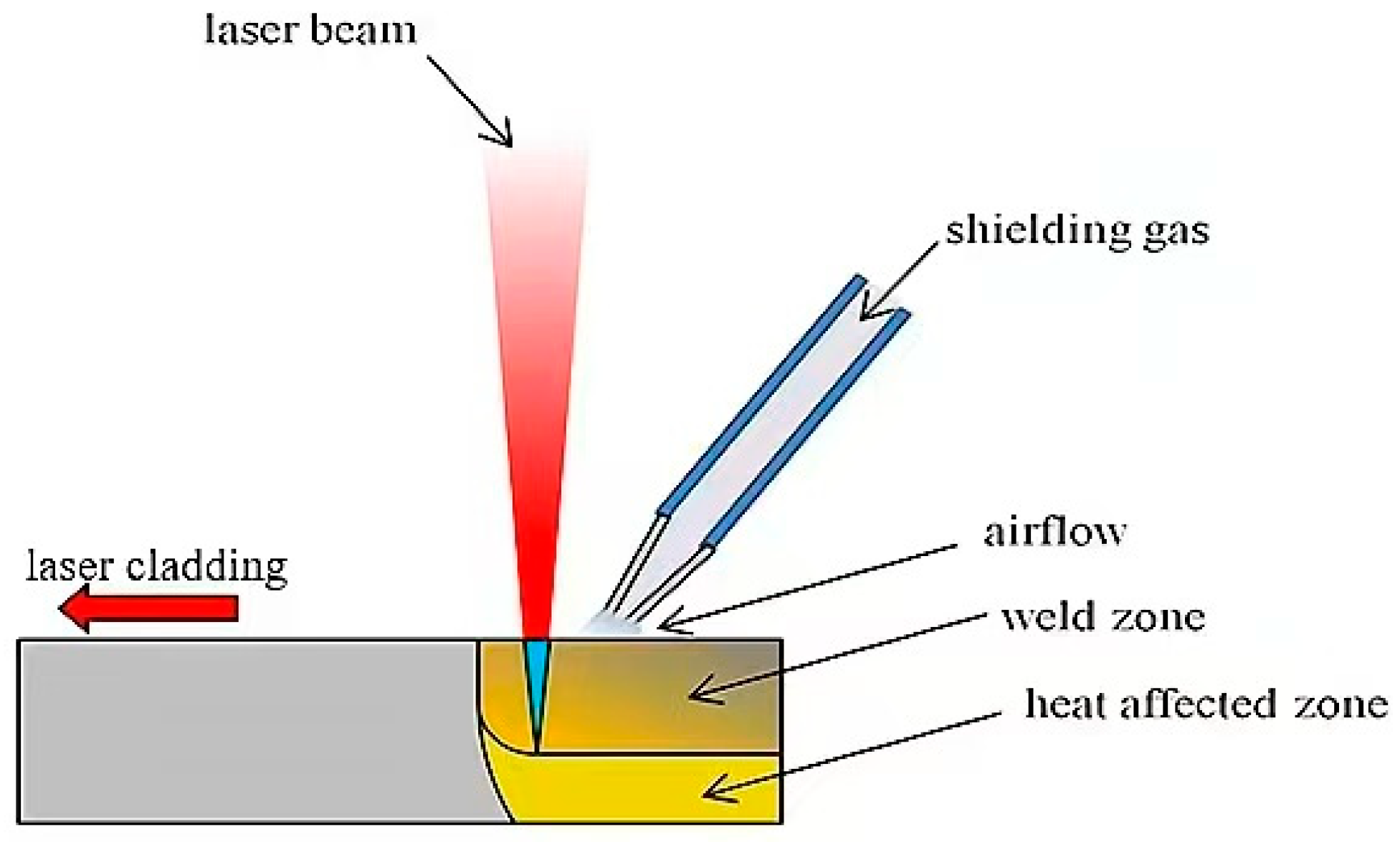
2.2. Methods
2.3. Hardness Measurement
3. Results
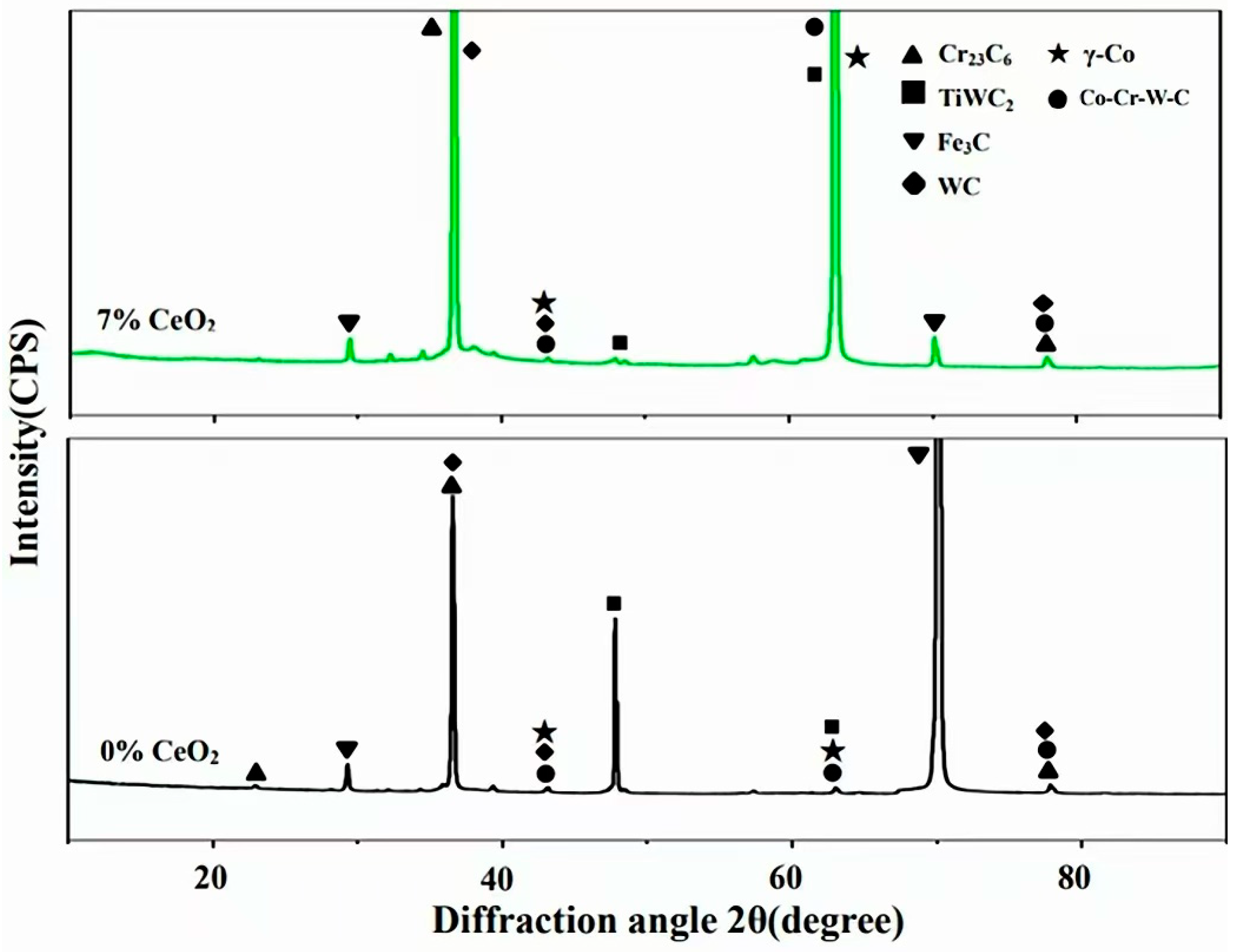
3.1. XRD Analysis of Co-Based Composite Cladding Layers
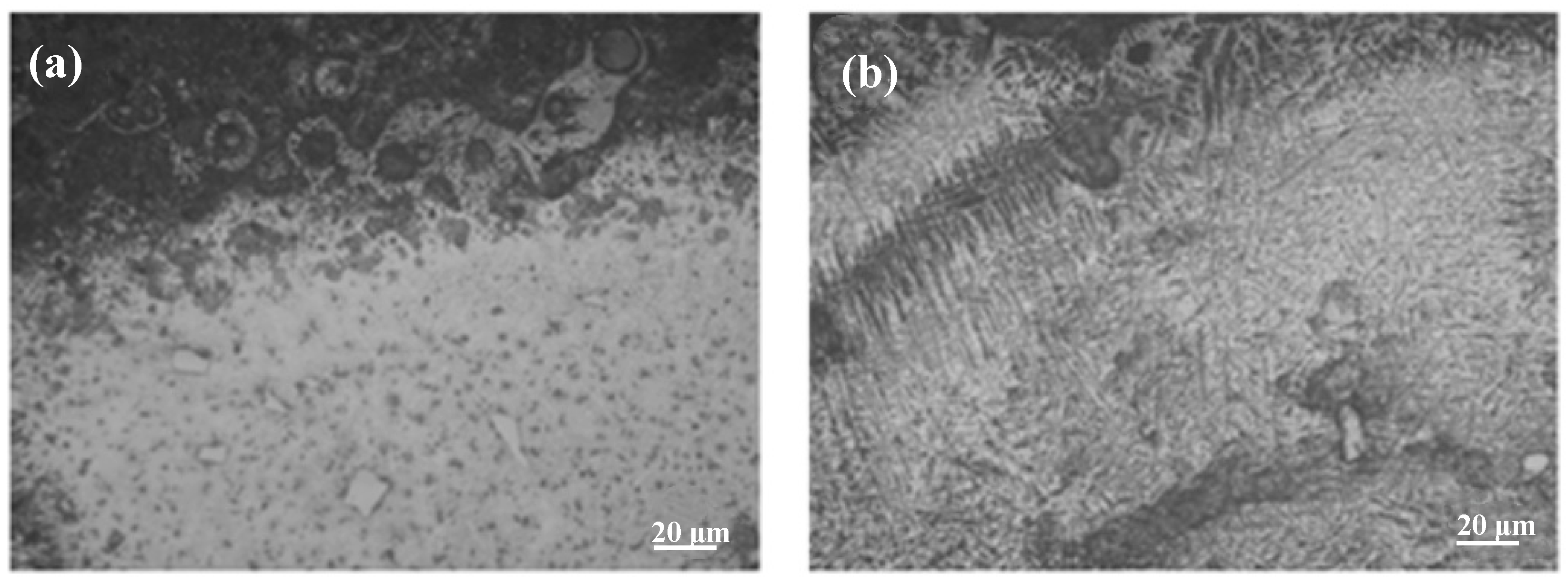
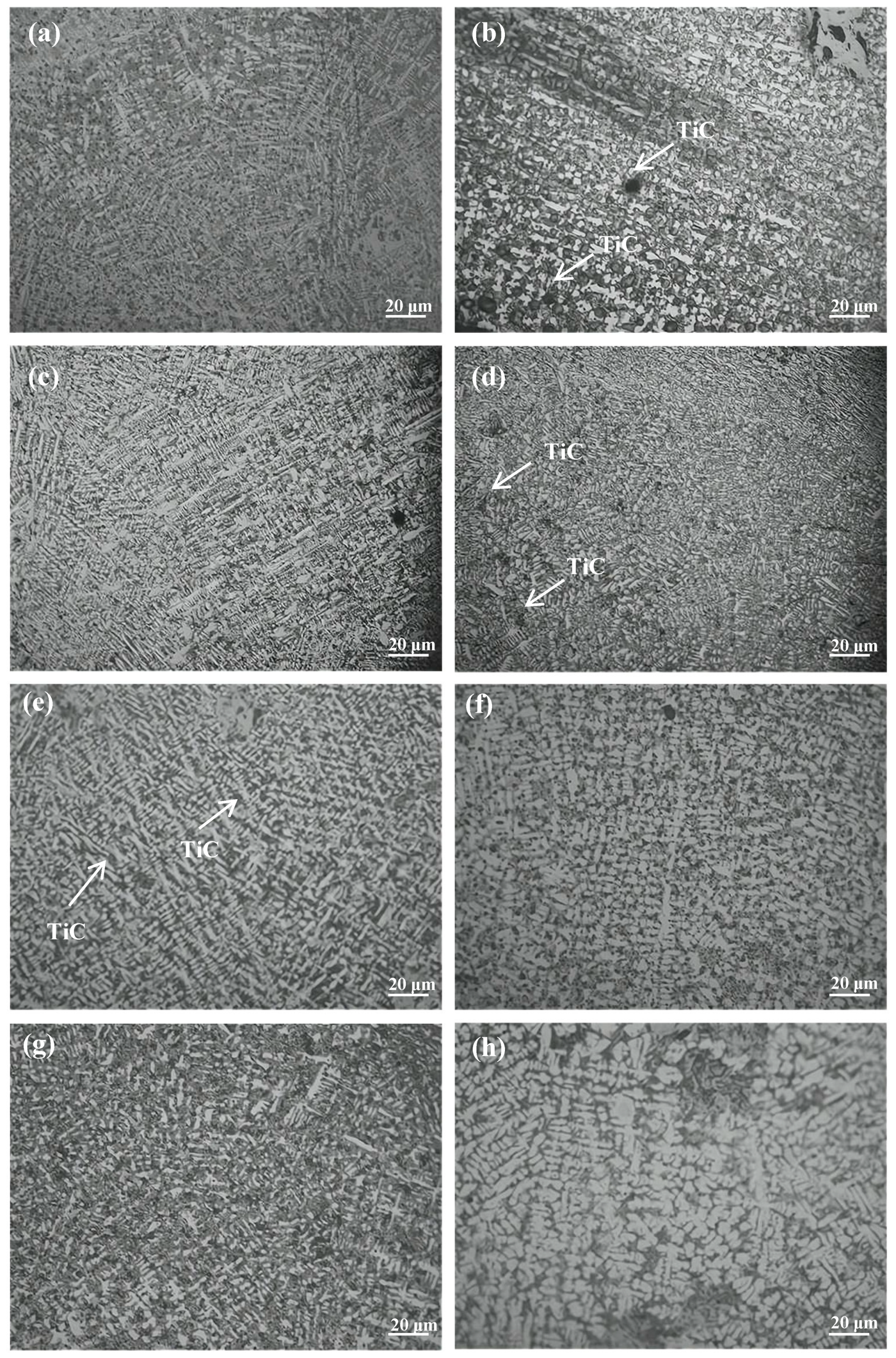
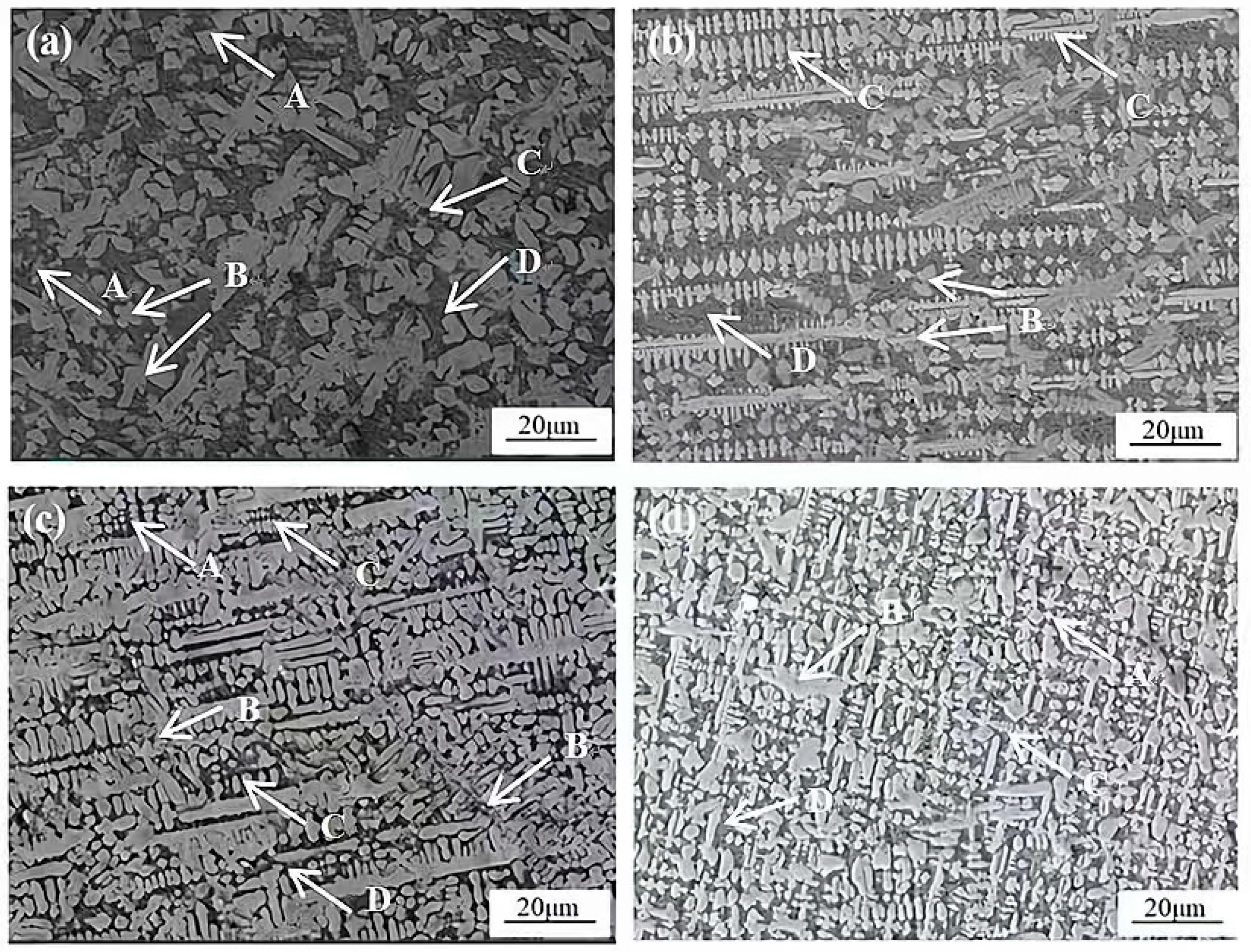
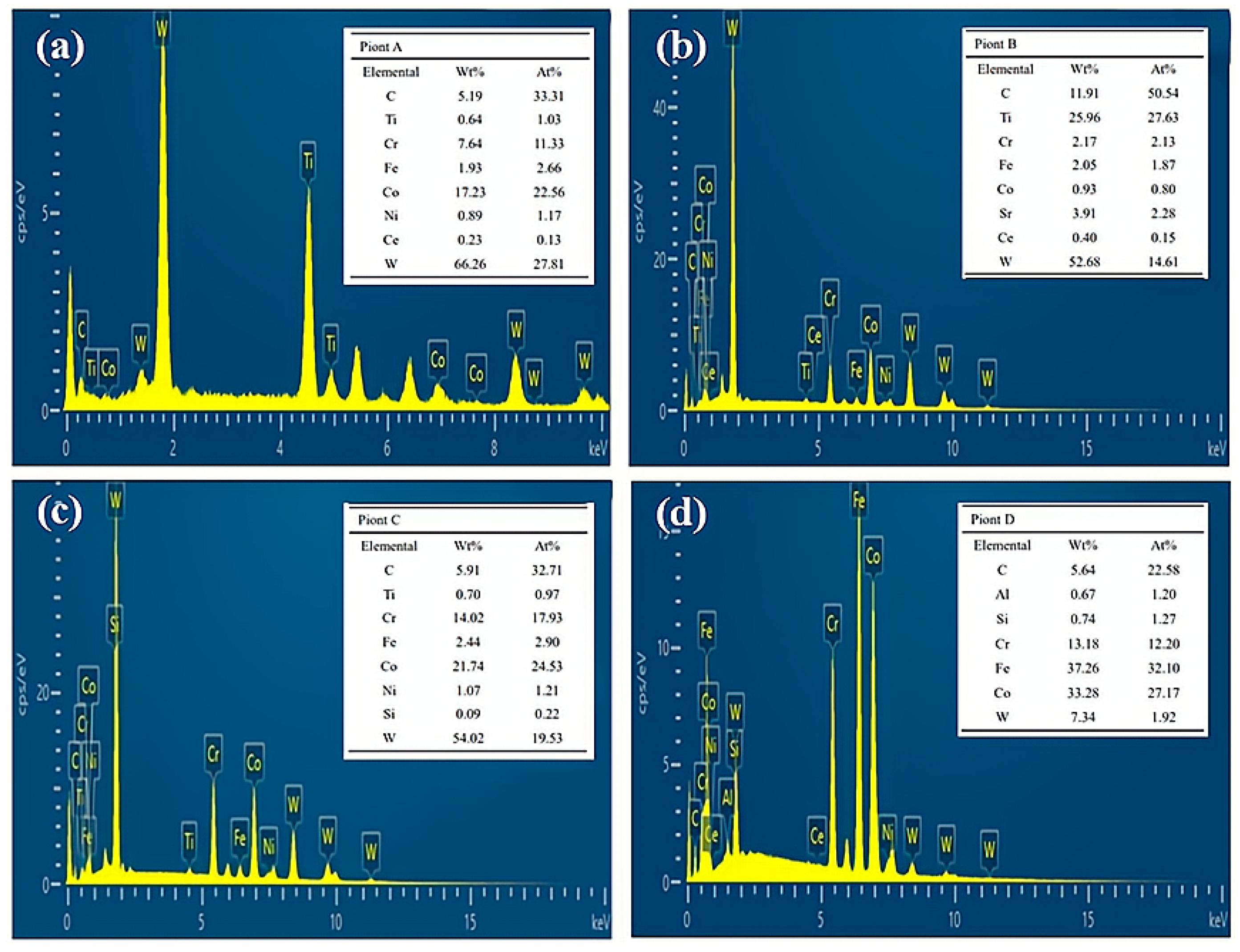
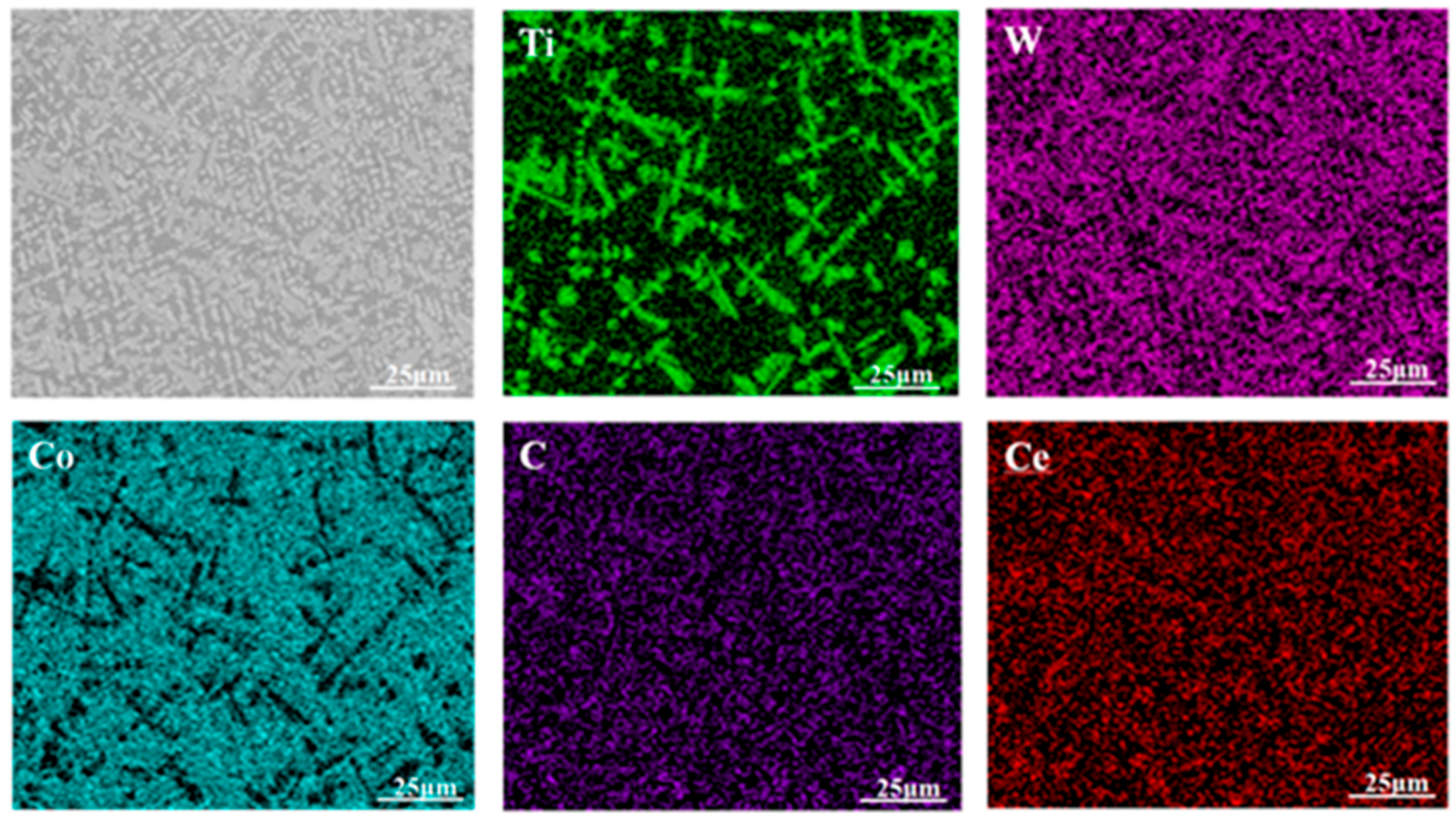
3.2. Microstructural Characteristics of Composite Cladding Layers
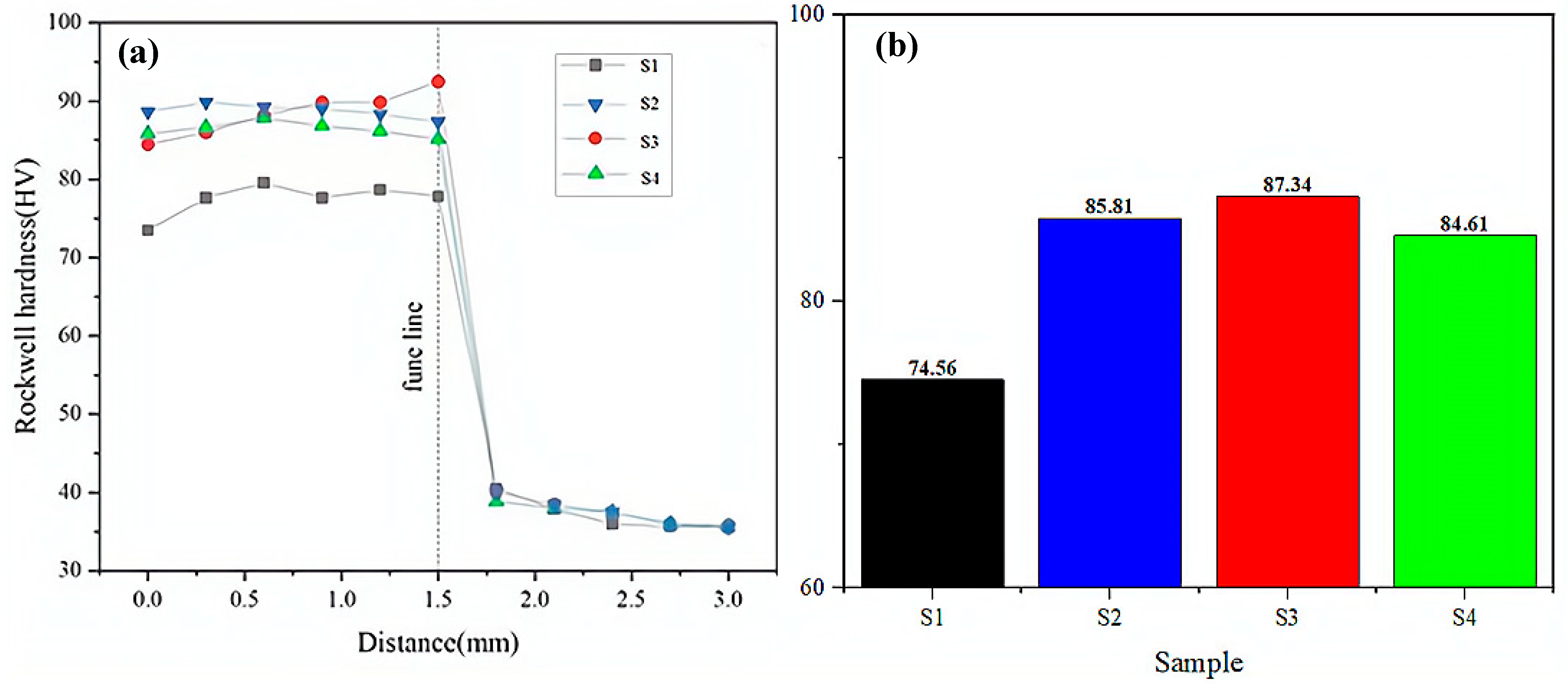
3.3. Hardness and Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- While the addition of CeO2 preserved the original phase constituents (γ-Co, TiWC2, WC, Cr23C6, Fe3C, and Co-Cr-W-C) in the composite coating, it induced notable modifications in their morphological features, particularly in terms of grain refinement and spatial distribution;
- The secondary dendrite arm spacing (SDAS) of the γ-Co phase, the sizes of TiWC2 dendrites and WC dendrites, as well as the fraction of iron-containing compounds all exhibit a non-monotonic trend, initially decreasing and then increasing with raising CeO2 content. Notably, the morphology of TiWC2 evolves from a cruciform shape to a granular shape, and finally to a dendritic shape. At 2 wt.% CeO2, WC dendrites are entirely suppressed, and the SDAS of γ-Co reaches the minimum value. However, when the CeO2 content increases to 4 wt.%, localized dendrite coarsening occurs, accompanied by a significant increase in dendrite packing density and a marked reduction in the eutectic fraction;
- During laser cladding, the introduced CeO2 underwent thermal decomposition at elevated temperature, releasing Ce atoms that preferentially segregated around TiWC2 phases and associated dendrites. These Ce atoms exerted a coordinated regulatory effect on multiple phases through two primary mechanisms: (1) grain refinement via heterogeneous nucleation and (2) the modification of molten pool surface tension characteristics. The Ce-mediated regulation simultaneously influenced the γ-Co matrix, TiWC2 precipitates, and WC reinforcing phases, and even unmolten TiC particles dispersed in the coating;
- The coating hardness exhibited a distinct non-monotonic dependence on CeO2 content, demonstrating an initial increase followed by subsequent decrease. The coating exhibited peak hardness performance at the optimal CeO2 addition of 4 wt.%, with the hardness value reaching 91.37 HRC—representing a 1.57-fold enhancement relative to the substrate material.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Oliveira Fernandes, D.; Anflor, C.T.M.; Goulart, J.N.V.; Baranoğlu, B. Nodular Cast Iron GGG40, 60, 70 Mechanical Characterization from Bars and Blocks Obtained from Brazilian Foundry. Metals 2022, 12, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghareb Parast, M.S.; Jamal Khani, M.; Azadi, M.; Azadi, M. Effect of plasma nitriding on high-cycle fatigue properties and fracture behaviors of GJS700 nodular cast iron under cyclic bending loading. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2021, 44, 2077–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakova, A.; Razavi, J.; Cabeza, S.; Gadalinska, E.; Reid, M.; Paradowska, A.; Ganguly, S.; Berto, F.; Mehmanparast, A. The Effect of Surface Treatment and Orientation on Fatigue Crack Growth Rate and Residual Stress Distribution of Wire Arc Additively Manufactured Low—Carbon Steel Components. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 2988–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Pan, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.; Lian, G.F.; Cao, Q.; Que, L.Z. Microstructure, toughness, and tribological properties of laser cladded Mo2FeB2-based composite coating with in situ synthesized WC and La2O3 addition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 449, 128947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.Y.; Wen, C.; Ang, H.Q. Influence of laser parameters on the microstructures and surface properties in laser surface modification of biomedical magnesium alloys. J. Magnes. Alloys 2024, 12, 72–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Su, H.; Yu, M.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Jiang, H.; Yang, P.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Large-size Complex-structure Ternary Eutectic Ceramic Fabricated Using Laser Powder Bed Fusion Assisted with Finite Element Analysis. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 72, 103627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Xiang, D.; Ju, J. Research and Progress of Laser Cladding: Process, Materials and Applications. Coatings 2022, 12, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhan, H.; Wan, Q.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W. Multi-Objective Optimization of Process Parameters for Rectangular Laser Cladding of Fe-Based Alloy Wear-Resistant Coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2025, 503, 131990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.L.; Ren, Z.C.; Hu, J.L.; Hou, Y.Y.; Zheng, H.Y. Laser cladding-spraying fabrication of Al/Ni/WC@SMP-MoS2 composite coating with enhanced anti-corrosion and self-lubricating property. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2025, 503, 132017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.R.; Zou, M.; Lu, S.; Li, L.F.; Zhuang, X.L.; Feng, Q. A novel high-Cr CoNi-based superalloy with superior high-temperature microstructural stability, oxidation resistance and mechanical properties. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2024, 31, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Fu, H.G.; Ma, T.T.; Guo, X.Y.; Lin, J. Microstructure and wear resistance of AlCoCrFeNi-WC/TiC composite coating by laser cladding. Mater. Charact. 2022, 194, 112479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.B.; Wang, Q.T.; Chen, C.R.; Lian, G.F.; Huang, X. Effects of WC addition on the morphology, microstructure and mechanical properties of Fe50/TiC/WC laser claddings on AISI 1045 steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 427, 127781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.K.; Shi, W.Q.; Huang, J. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TiC/WC-Reinforced AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloys Prepared by Laser Cladding. Crystals 2024, 14, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Li, G.H.; Du, F.M.; Yu, M. Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Ni–WC–TiC Alloy Coating Fabricated by Laser. Lubricants 2023, 11, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Gao, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Zhan, X. Morphological Characteristics of Precipitated Phases in Laser Cladding (Nano WC + Micron TiC)/Ti6Al4V Coatings with Different Composite Ceramic Contents. Met. Mater. Int. 2024, 30, 2581–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Hu, S.S. Effect of nano-CeO2 on microstructure and wear resistance of Co-based coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 276, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.N.; Chen, C.Z.; Zhang, C.F. Effect of nano-CeO2 on microstructure properties of TiC/TiN+TiCN-reinforced composite coating. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2013, 36, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.M.; Weng, Y.T.; Zhang, L.; Lu, J.; Huang, X.B.; Long, F.Q.; Zhang, W.P. Uncovering the Effect of CeO2 on the Microstructure and Properties of TiAl/WC Coatings on Titanium Alloy. Coatings 2024, 14, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.X.; Sang, S.B.; Zhu, T.B.; Li, Y.W.; Wang, H. Enhancing Hardness and Wear Resistance of MgAl2O4/Fe-Based Laser Cladding Coatings by the Addition of CeO2. Coatings 2024, 14, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Q.; Zhang, J.W.; Chen, D.L.; Huang, J.; Shi, W.Q.; An, F.J.; Wu, X.L. Study on the Effect of CeO2 on the Performance of WC + Ni60 Laser Cladding Coating. Lubricants 2025, 13, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Yang, Q.; Yang, F.; Zhang, H.W.; Zhang, T.G.; Wang, H.; Ma, Q. Comparative Investigation on Wear Properties of Composite Coatings with Varying CeO2 Contents. Coatings 2022, 12, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.J.; Fan, G.R.; Dong, D.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Z.L.; Zhao, D.; Guo, Y.N.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, M. In-situ synthesis and characterization of calcium phosphate coatings on rapidly solidified zirconia toughened alumina eutectic bioceramics by laser cladding. Mater. Des. 2023, 232, 112173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.C.; Wang, G.; Ren, K.; Di, Y.L.; Wang, L.P.; Rong, Y.M.; Wang, H.D. Marangoni flow patterns of molten pools in multi-pass laser cladding with added nano-CeO2. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 59 Pt A, 103156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.J.; Wang, C.L.; Zhang, K.X.; Liang, M.L.; Xie, Y.G.; Liu, W.J.; Yang, J.J.; Zhou, S.F. Nucleation and strengthening mechanism of laser cladding aluminum alloy by Ni-Cr-B-Si alloy powder based on rare earth control. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2021, 294, 117145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.F.; Ma, M.X.; Liu, W.J.; Zhong, M.L.; Zhang, H.J.; Zhang, W.M. Laser cladding in-situ carbide particle reinforced Fe-based composite coatings with rare earth oxide addition. J. Rare Earths 2009, 27, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Yang, F.; Zhang, H.W.; Zhang, T.G.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.T.; Ma, Q. Influence of CeO2 addition on forming quality and microstructure of TiCx-reinforced CrTi4-based laser cladding composite coating. Mater. Charact. 2021, 171, 110732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.G.; Li, Q.S.; Sun, B.; Zhao, Q.H.; Wang, Z.J.; Niu, W.F.; Wang, X.; Dang, L.H.; Ma, Q.J. Effects of CeO2 on Microstructural Evolution, Corrosion and Tribology Behavior of Laser Cladded TiC Reinforced Co-based Coatings. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2021, 16, 210511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.W.; Shen, Y.F. Surface morphologies, tribological properties, and formation mechanism of the Ni–CeO2 nanocrystalline coatings on the modified surface of TA2 substrate. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 249, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Zuo, D.W.; Li, X.F.; Chen, K.M.; Huang, M.M. Effects of CeO2 nanoparticles on microstructure and properties of laser cladded NiCoCrAlY coatings. J. Rare Earths 2010, 28, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Z.; Huang, K.P.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zheng, C.J.; Li, M.K.; Wang, L.L.; Wu, K.K.; Tan, H.; Yi, X.M. Wear mechanisms and micro-evaluation of WC + TiC particle-reinforced Ni-based composite coatings fabricated by laser cladding. Mater. Charact. 2023, 197, 112699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terent’ev, A.V.; Blagoveshchenskij, Y.V.; Isaeva, N.V.; Lancev, E.A.; Smetanina, K.E.; Murashov, A.A.; Nokhrin, A.V.; Boldin, M.S.; Chuvil’deev, V.N.; Shcherbak, G.V. Study of the Phase Composition and Microstructure of Complex Carbide (Ti, W)C Obtained by Spark Plasma Sintering of WC and TiC Powders. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 2024, 15, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Ren, W.; Zuo, W.; Wang, Y. Comparative Study on the Reinforcement Effects of WC and TiC in the Laser Cladding Layer of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. J. Manuf. Process. 2025, 134, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Jin, C.; Sun, Y.; Song, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Huo, J.; Gao, M. Accelerated Crystallization Kinetics and Grain Refinement in Mg-Ni-Y Metallic Glass via Multiple Rare Earth Elements Doping. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 999, 175080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Dong, Z.; Jiang, B.; Lei, B.; Yang, H.; He, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, C.; Yuan, M.; Yang, H.; et al. Influence of Alloying Element Segregation at Grain Boundary on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Mg-Zn Alloy. Mater. Des. 2022, 224, 111322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
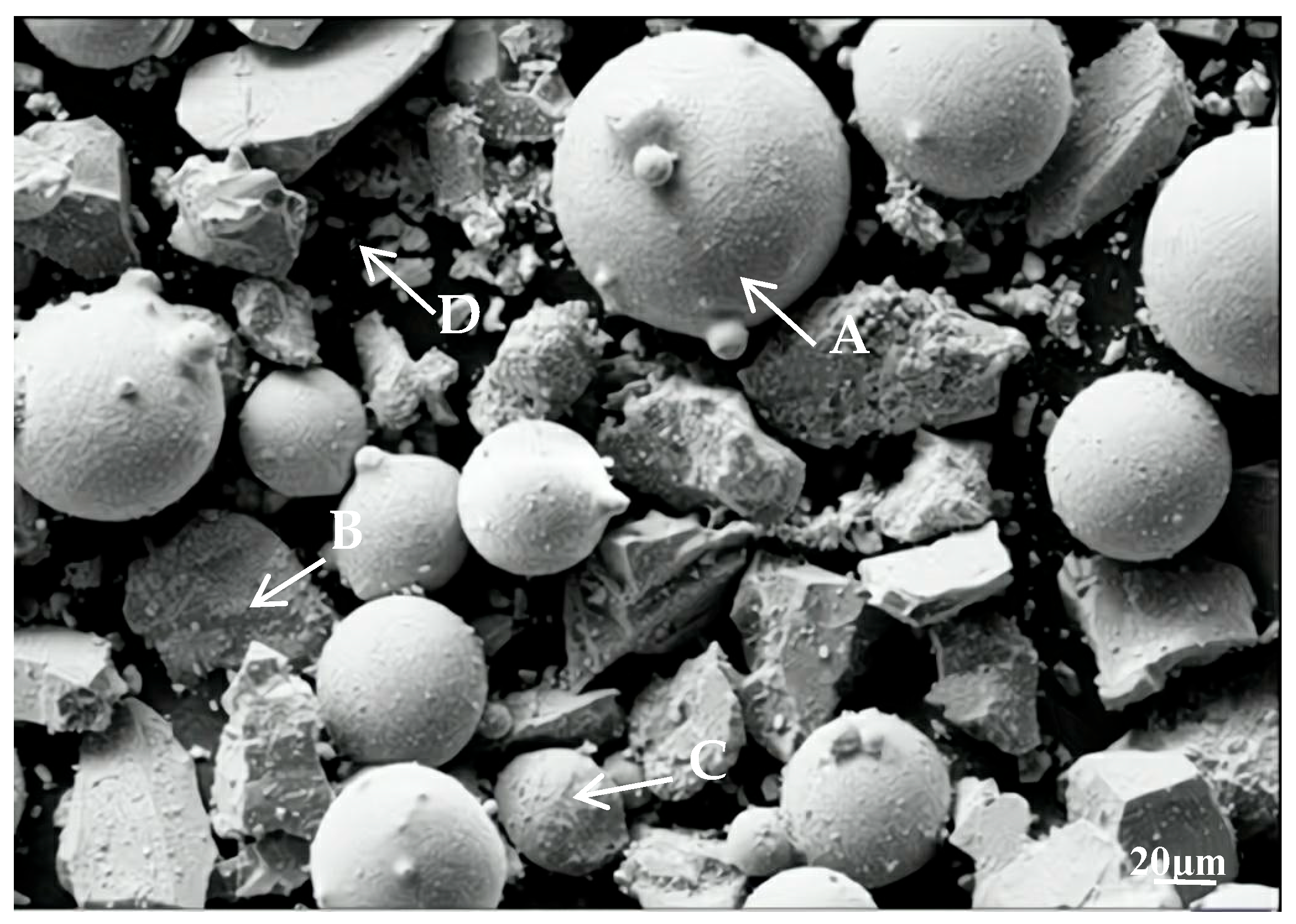

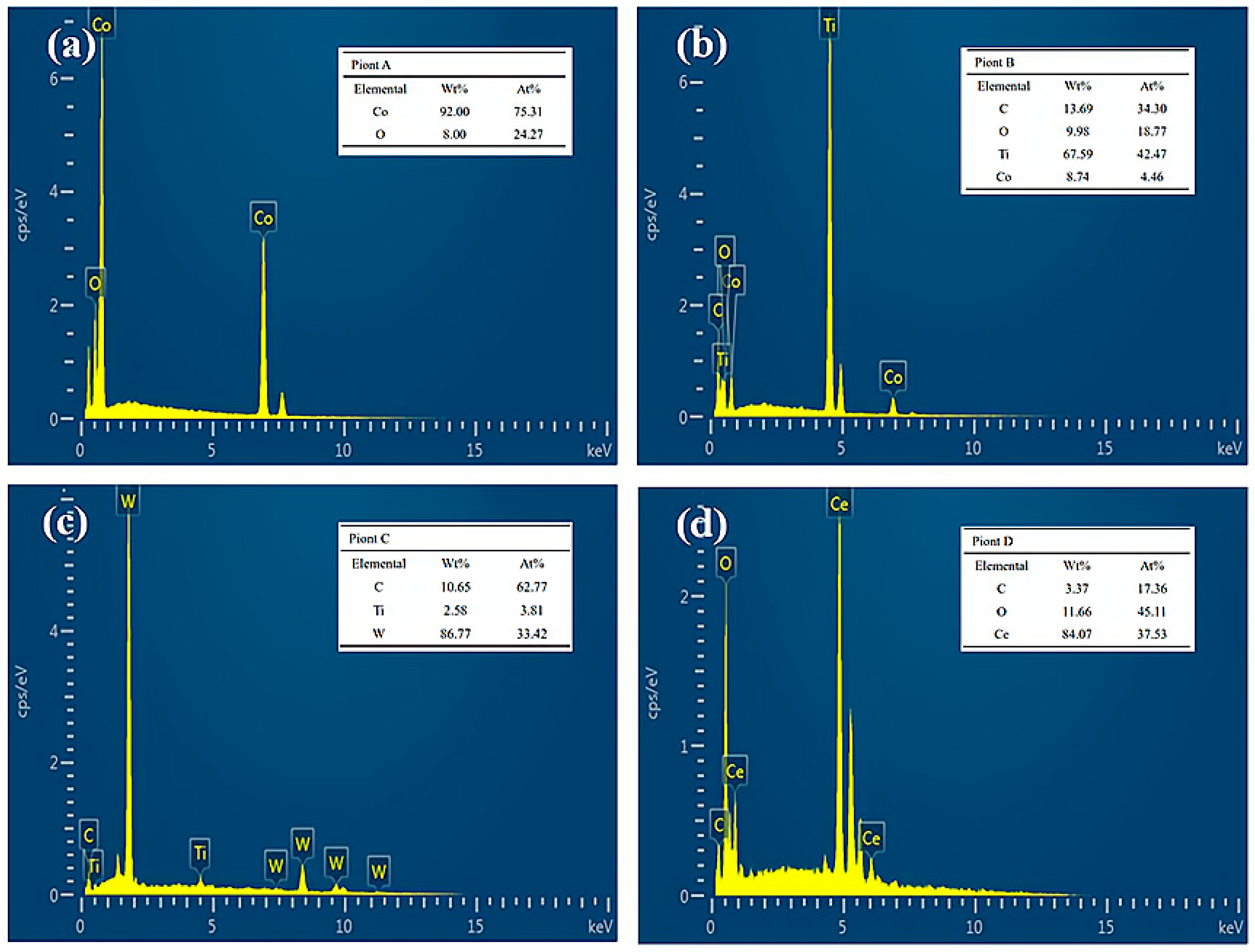

| Element | C | Cu | Si | Ni | Mn | S | P | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | 3.33 | 0.32 | 2.71 | - | 0.42 | 0.012 | 0.036 | Bal. |
| Element | C | Cr | Si | W | Fe | Mo | Ni | Mn | B | Co |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | 1.21 | 29.56 | 1.26 | 5.09 | 2.62 | 0.38 | 2.59 | 0.22 | - | Bal. |
| Sample No. | CeO2 | Co6+TiC+WC (7:3:3) |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0 | 100 |
| S2 | 2 | 98 |
| S3 | 4 | 96 |
| S4 | 7 | 93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tong, W.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Qi, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, J. The Effect of CeO2 Content on the Microstructure and Properties of TiC/WC/Co Composite Cladding Layers. Coatings 2025, 15, 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050530
Tong W, Xu Q, Liu Y, Qi Z, Wang J, Liu J. The Effect of CeO2 Content on the Microstructure and Properties of TiC/WC/Co Composite Cladding Layers. Coatings. 2025; 15(5):530. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050530
Chicago/Turabian StyleTong, Wenhui, Qingqi Xu, Yunyi Liu, Zi’ao Qi, Jie Wang, and Jiadong Liu. 2025. "The Effect of CeO2 Content on the Microstructure and Properties of TiC/WC/Co Composite Cladding Layers" Coatings 15, no. 5: 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050530
APA StyleTong, W., Xu, Q., Liu, Y., Qi, Z., Wang, J., & Liu, J. (2025). The Effect of CeO2 Content on the Microstructure and Properties of TiC/WC/Co Composite Cladding Layers. Coatings, 15(5), 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050530





