Research on Pavement Performance of Steel Slag Asphalt Mastic and Mixtures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Asphalt Binder and Aggregates
2.1.2. Filler
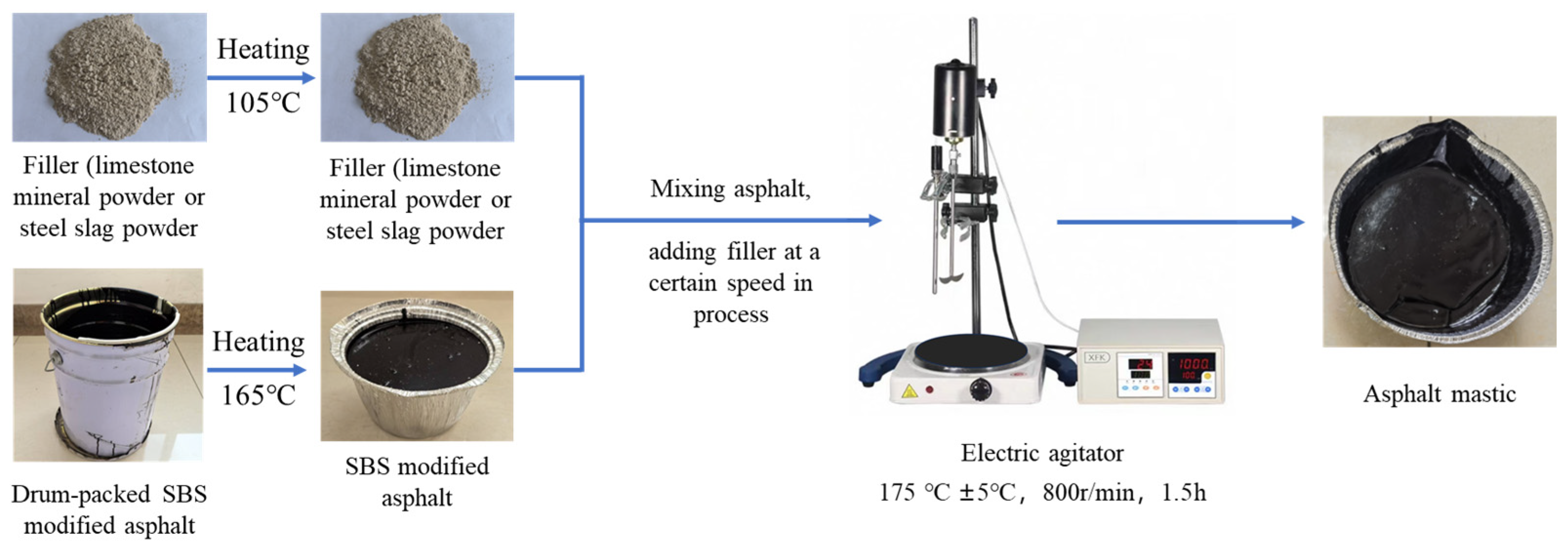
2.1.3. The Preparation of Asphalt Mastic
- Binder Preparation: SBS-modified asphalt was homogenized in a 165 °C oven until achieving fluid state, then poured into a stainless steel mixing tank (volume 500 ± 5 mL) with a certain mass (800 g per piece) and cooled to ambient temperature.
- Filler Treatment: Both the experimental limestone mineral filler and steel slag powder were dried in an oven at 105 °C to constant mass and cooled to room temperature prior to mixing. The two kinds of materials after drying and cooling were individually weighed according to the replacement mass ratio of the test design.
- Mastic Fabrication:
- ○
- The SBS-modified asphalt sample prepared in the first step was reheated to the flowing state in the oven at 165 °C.
- ○
- Then, it was placed in the heating sleeve of the base of the asphalt high-speed mixer (the temperature of the base heating sleeve was set to 175 ± 5 °C).
- ○
- The high-speed mixer (equipped with 20 mm four-blade inclined rotor) was initiated and allowed to stir for a certain time until the temperature of the SBS-modified asphalt in the stainless steel mixing tank was stable.
- ○
- Then, the limestone mineral filler (MF) was added at three times, and the four-blade inclined rotor remained stirring during the addition process.
- ○
- When adding steel slag powder as replacement for mineral filler, the steel slag powder should be added according to the adding process of the limestone mineral filler after it is stirred until no limestone ore powder float is visible to the eye in the asphalt.
- ○
- After the steel slag powder was added, it was stirred for 90 min at the stirring rate of 800 r/min to ensure that the fillers were evenly distributed in the SBS-modified asphalt.
2.1.4. Mix Design of AC-13
2.2. Test Methods
2.2.1. Asphalt Mastic Performance Test Methods
Penetration, Softening Point, Ductility and Viscosity Index
Pull-Off Test
Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR)
Bending Beam Rheometer (BBR)
2.2.2. Asphalt Mixture Performance Test Methods
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Performance of Asphalt Mastic with Steel Slag Powder
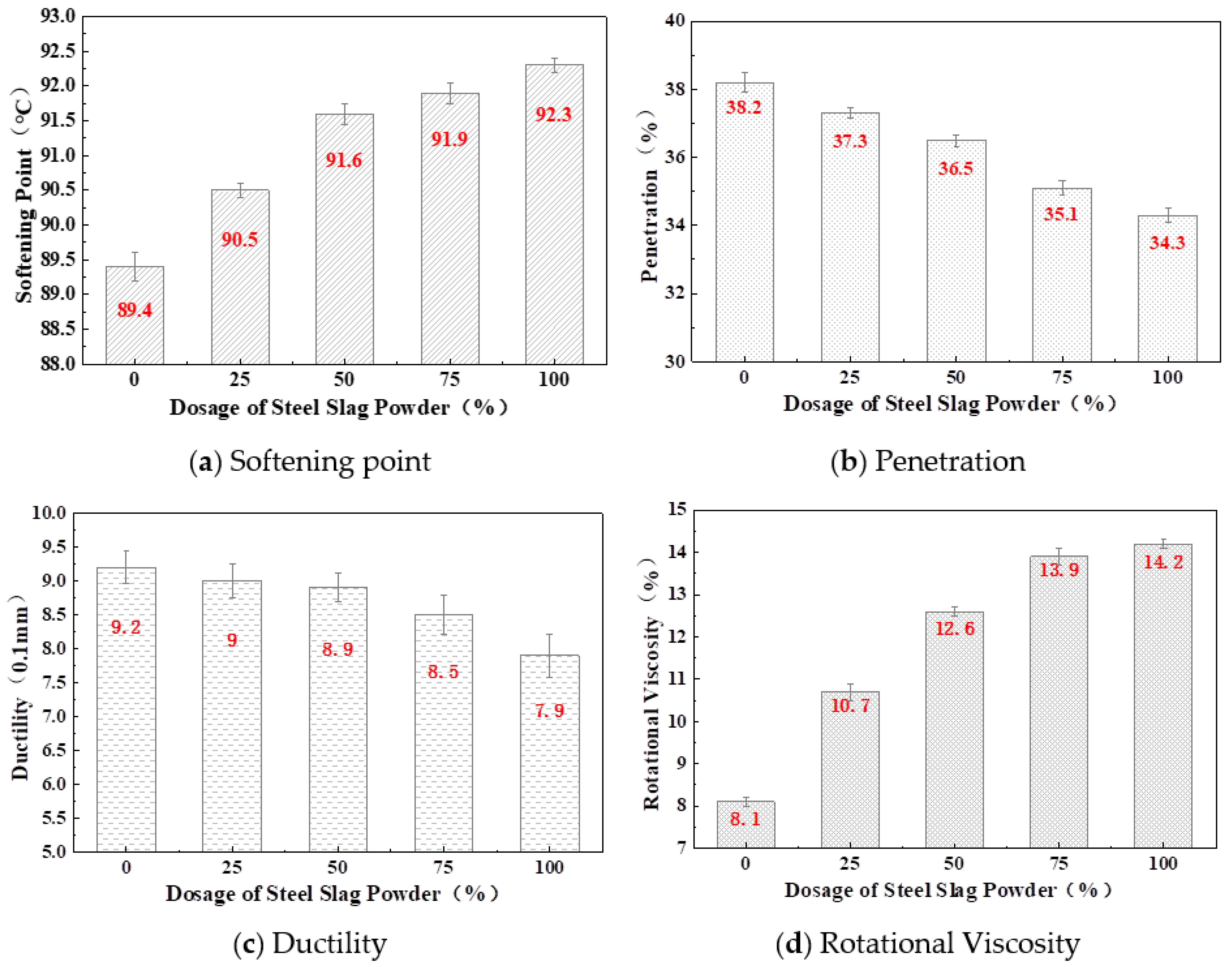
3.1.1. Penetration, Softening Point, Ductility, Viscosity, and Bonding Strength
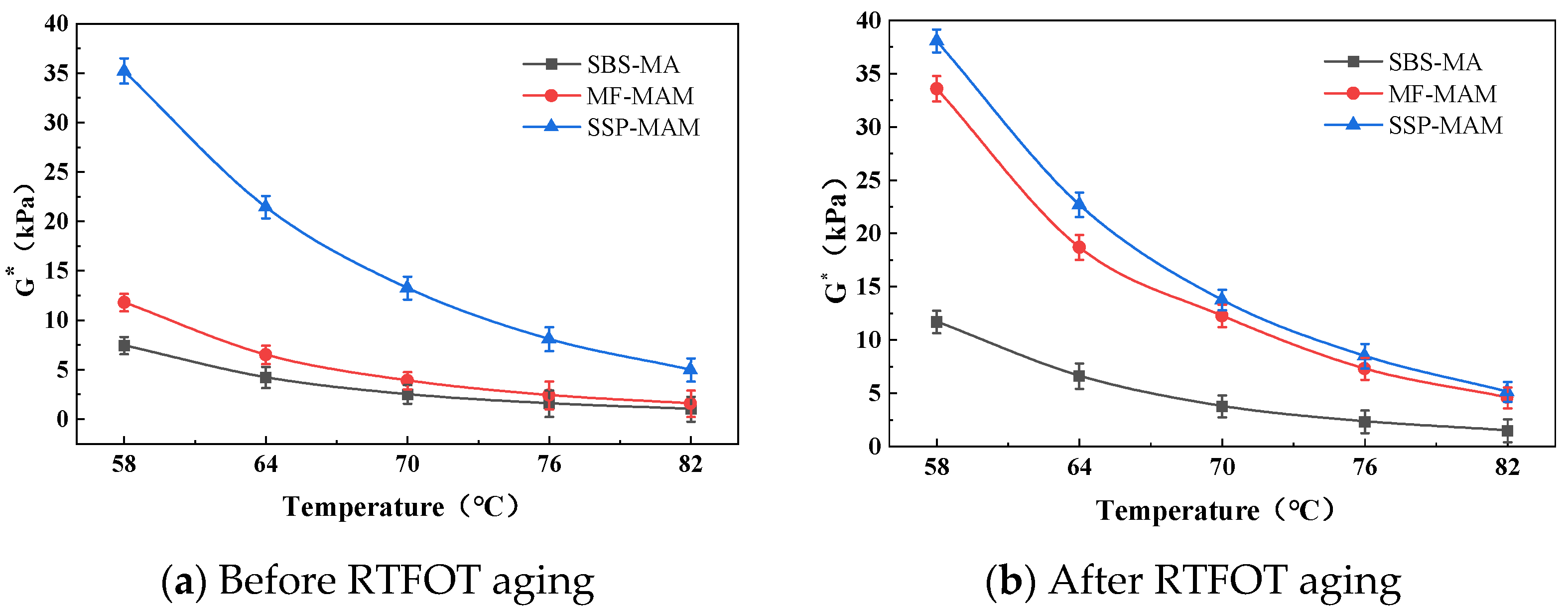
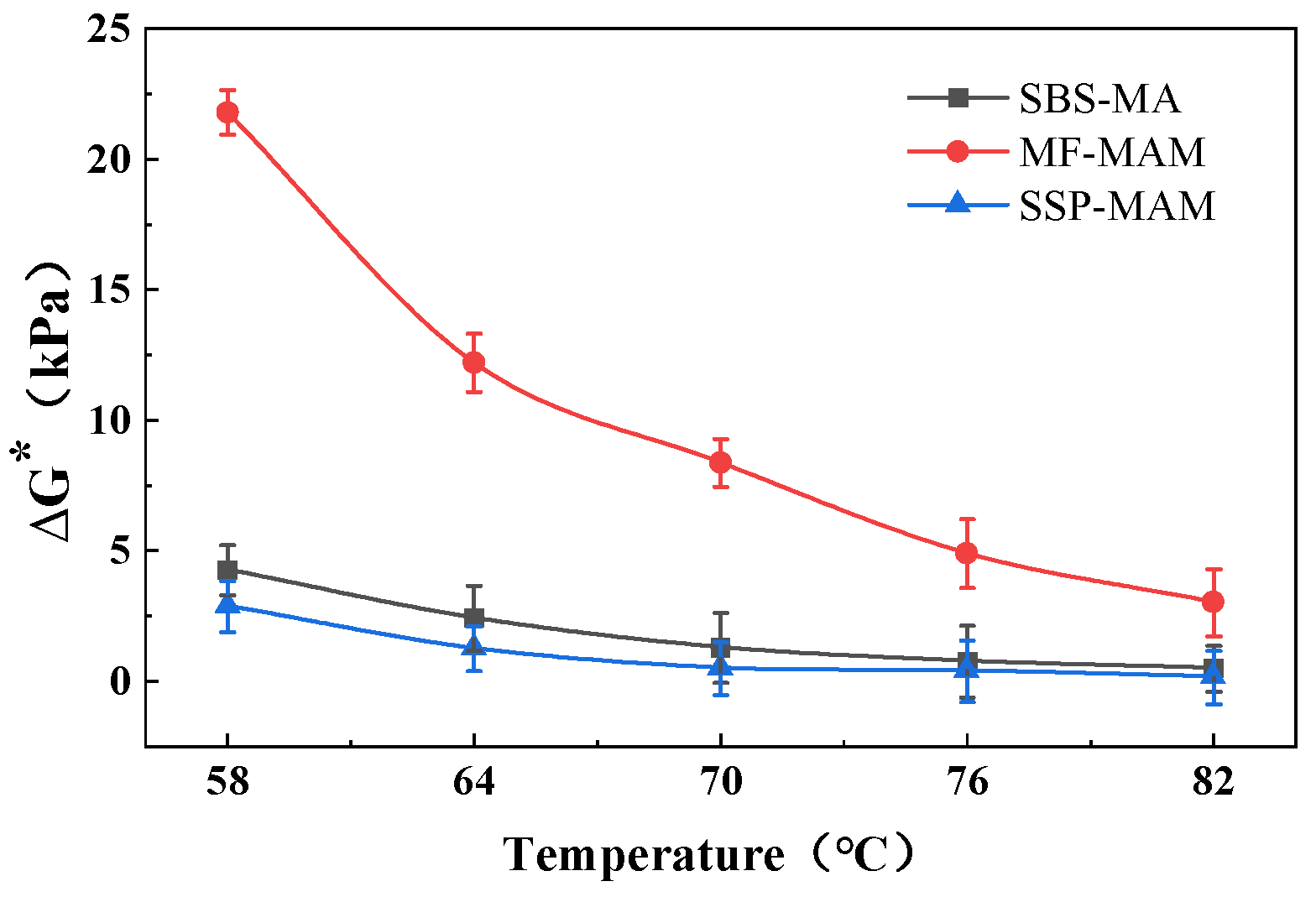
3.1.2. High-Temperature Rheological Property
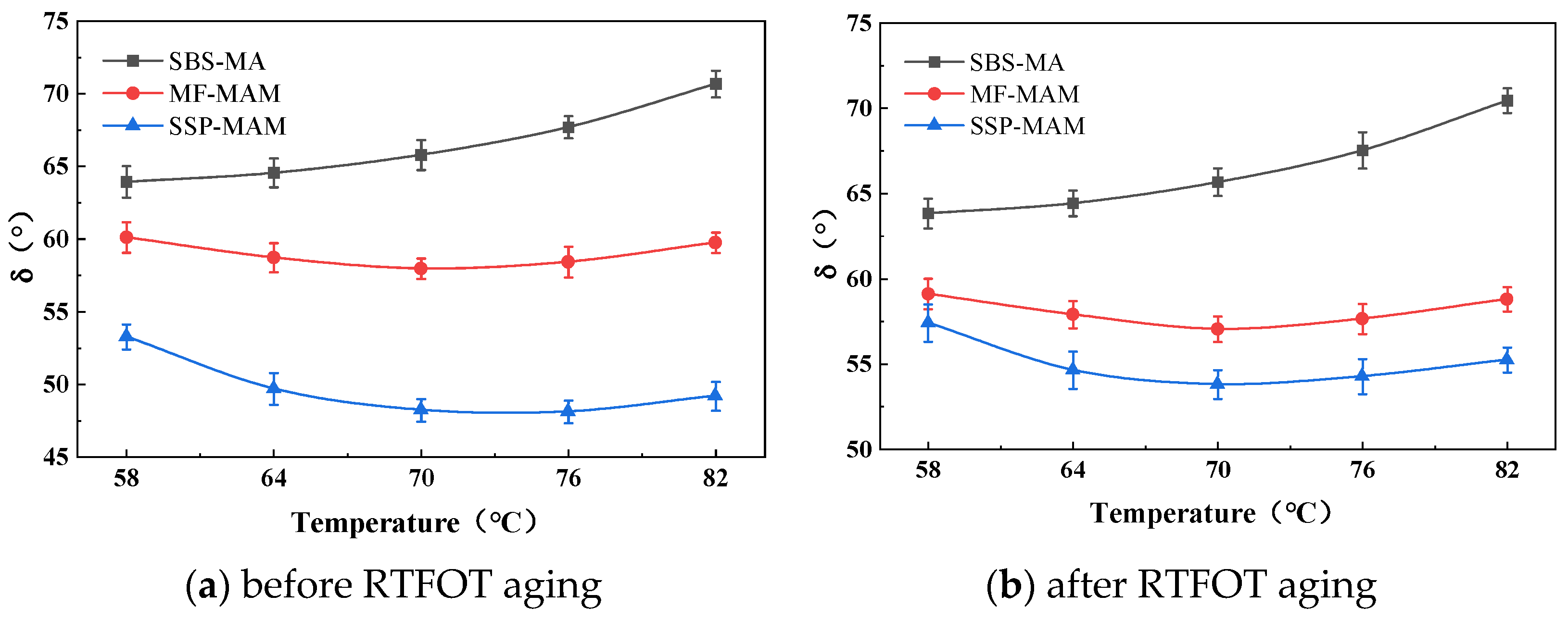
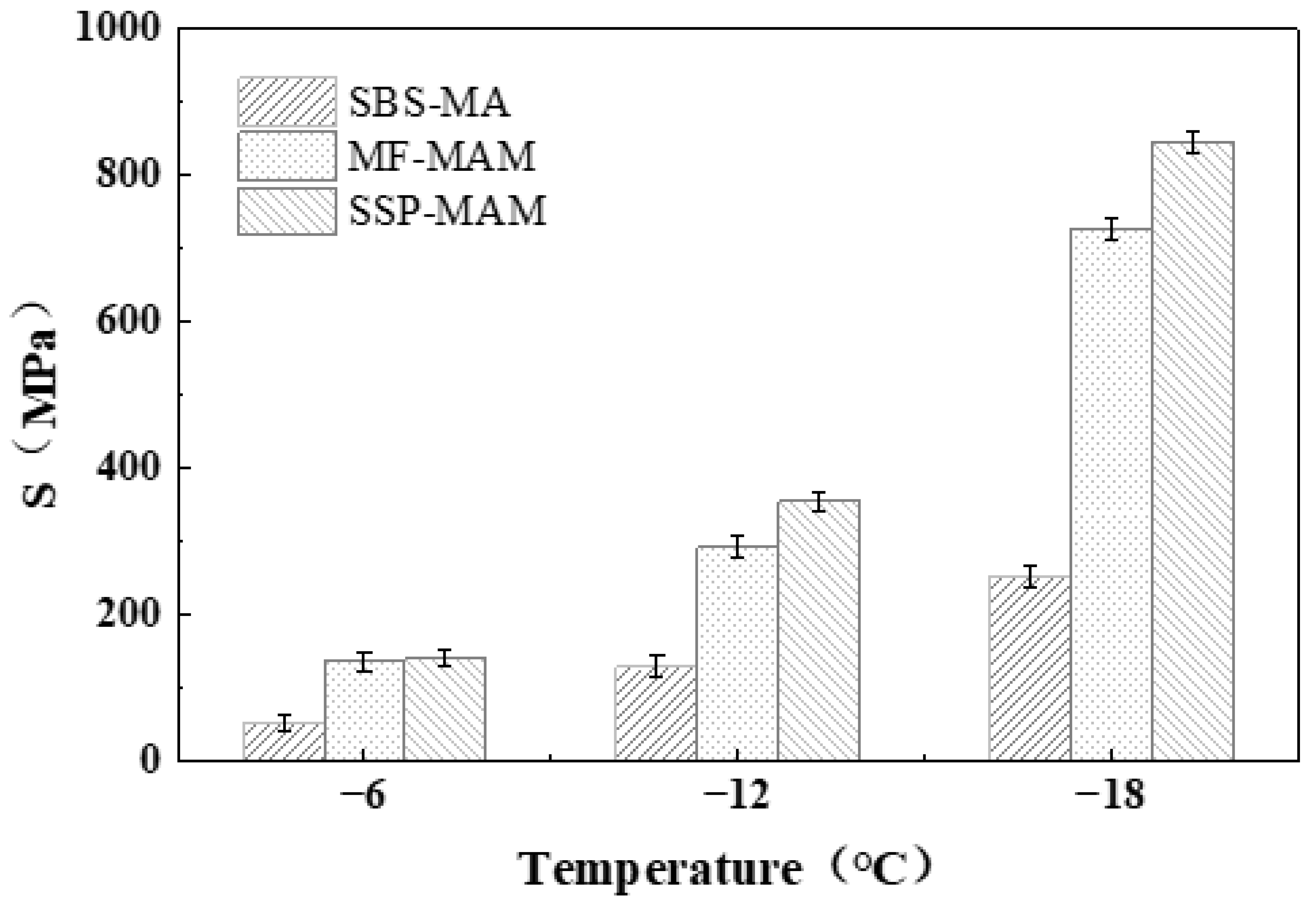
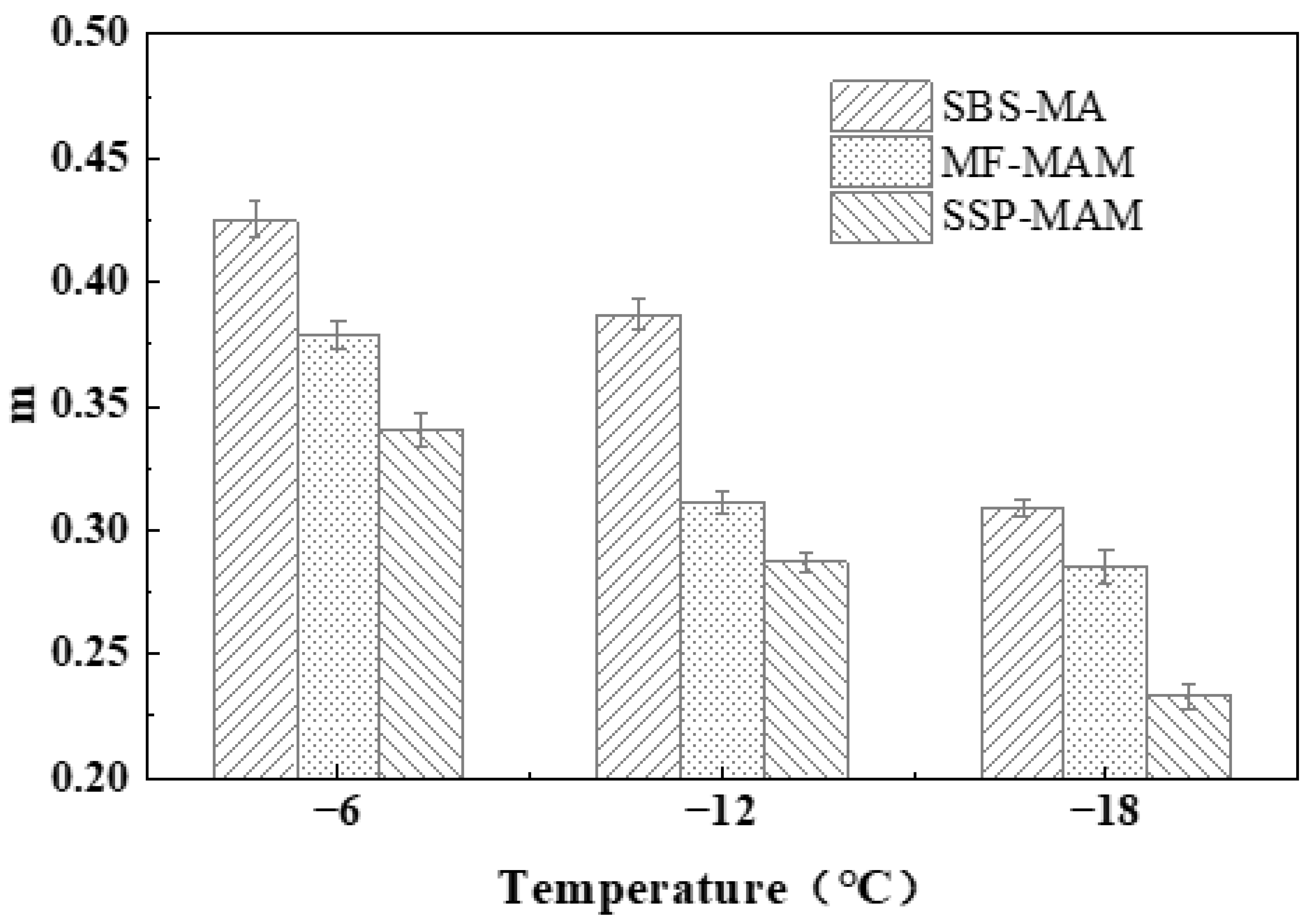
3.1.3. Low-Temperature Rheological Property
3.2. Performance Evaluation of Steel Slag Powder Asphalt Mixture
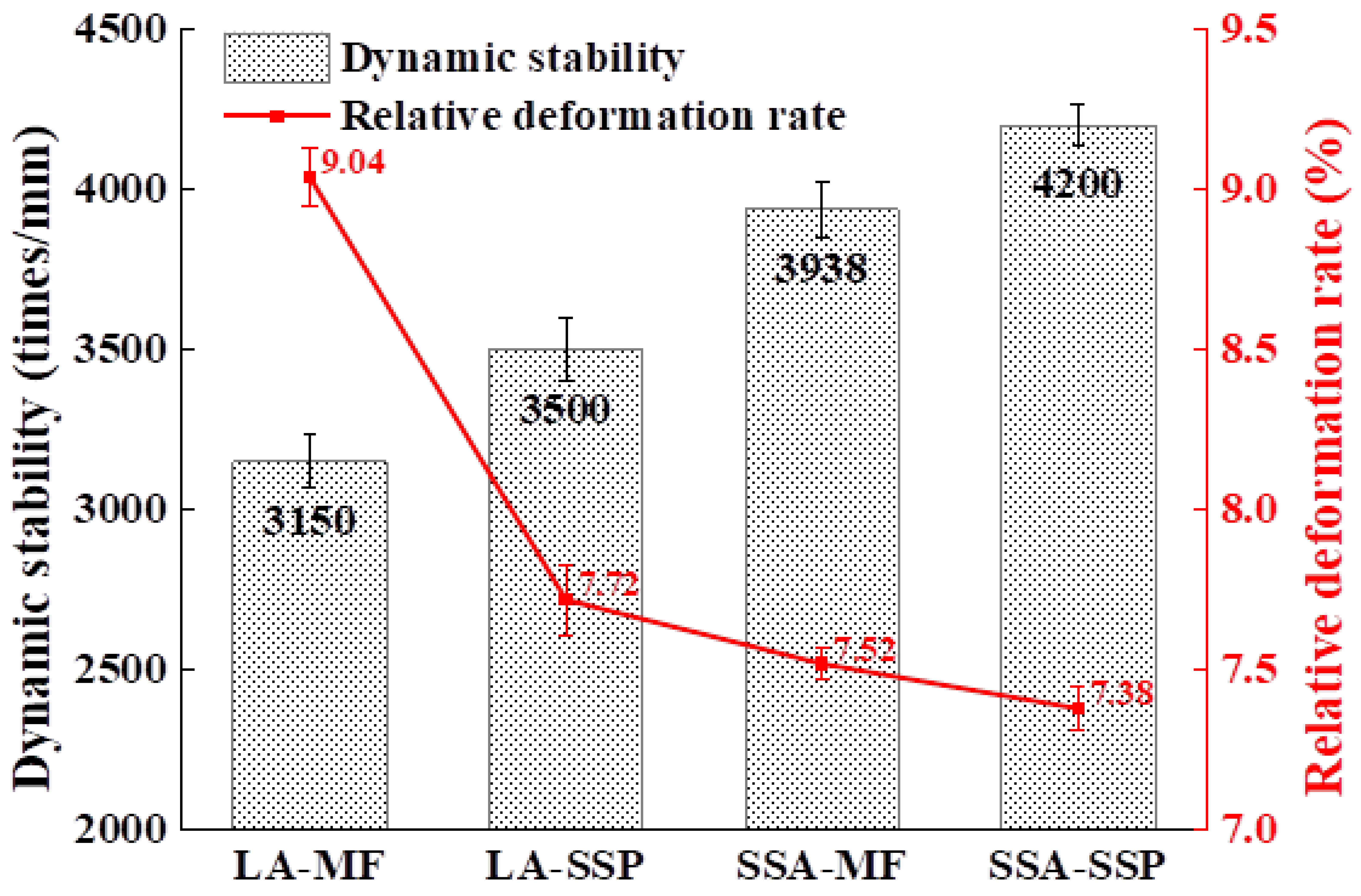
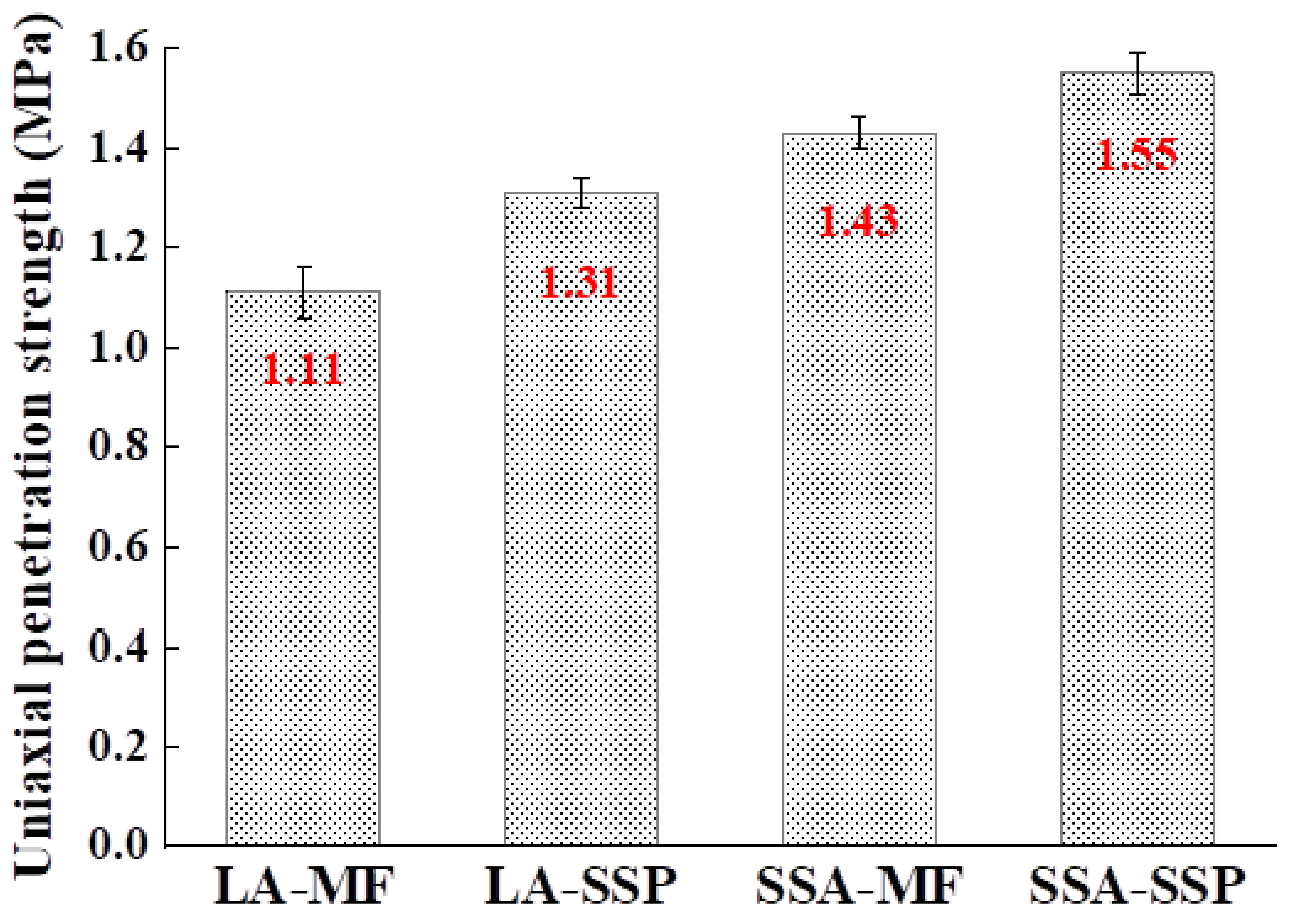
3.2.1. High-Temperature Performance
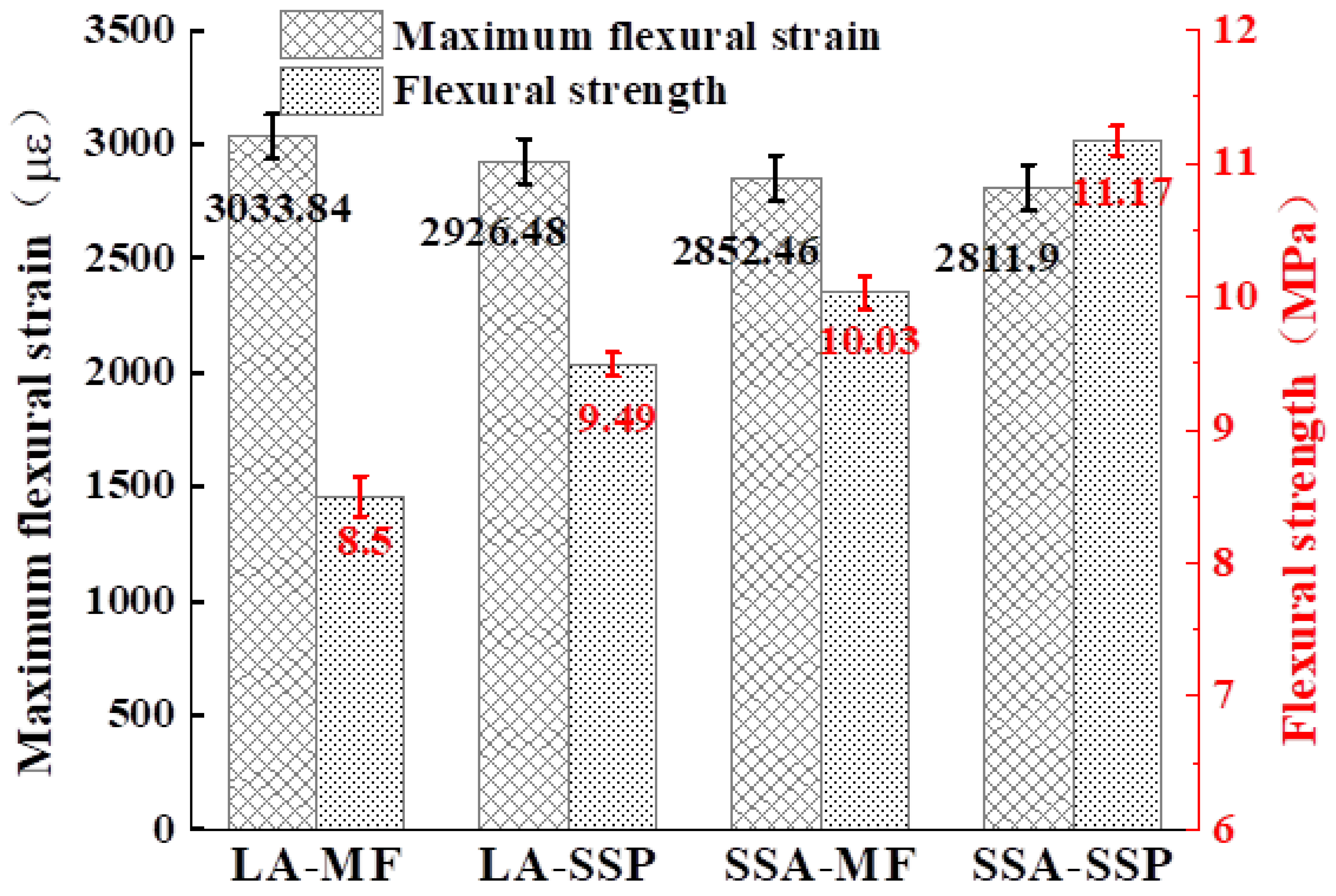
3.2.2. Low-Temperature Performance
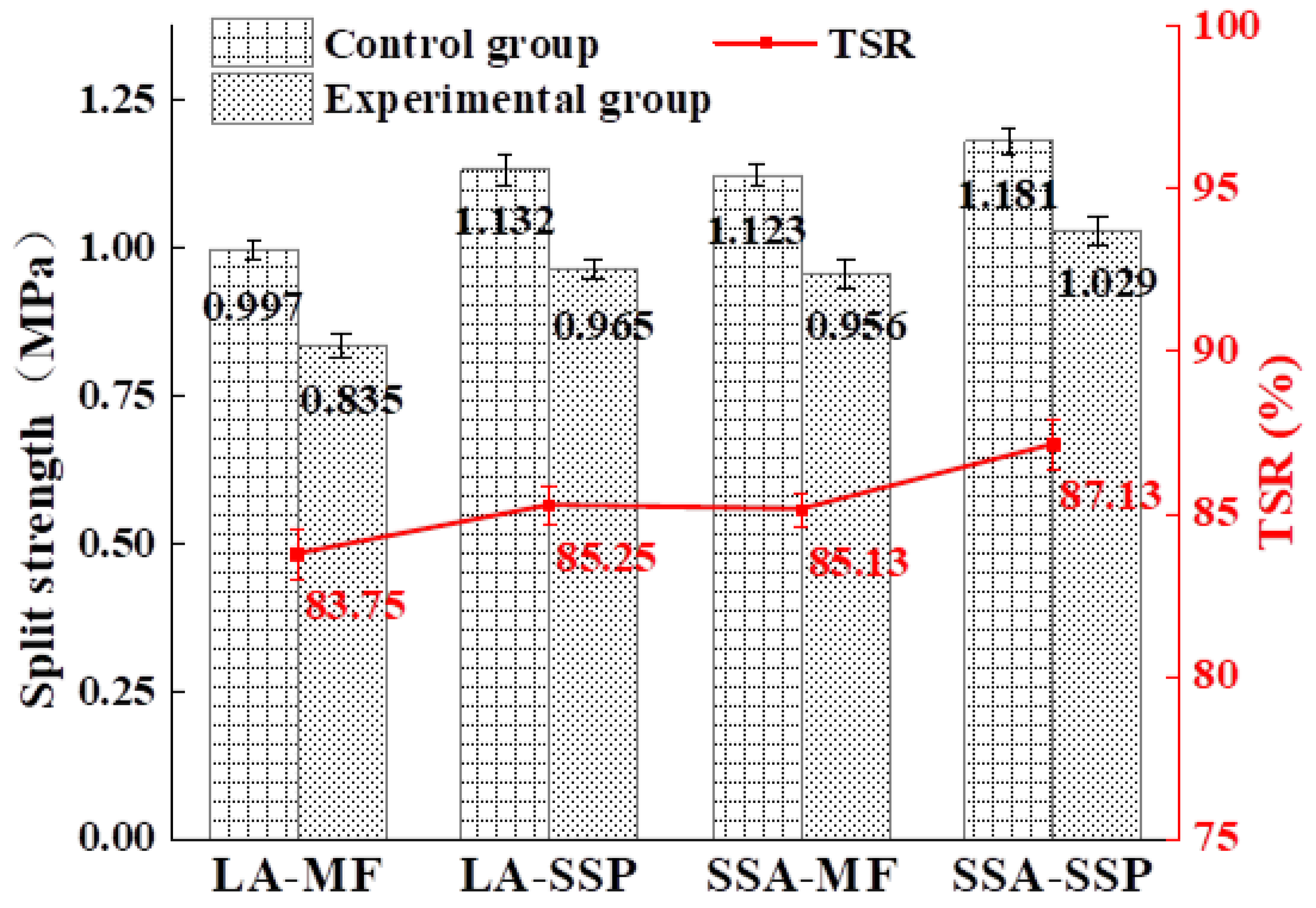
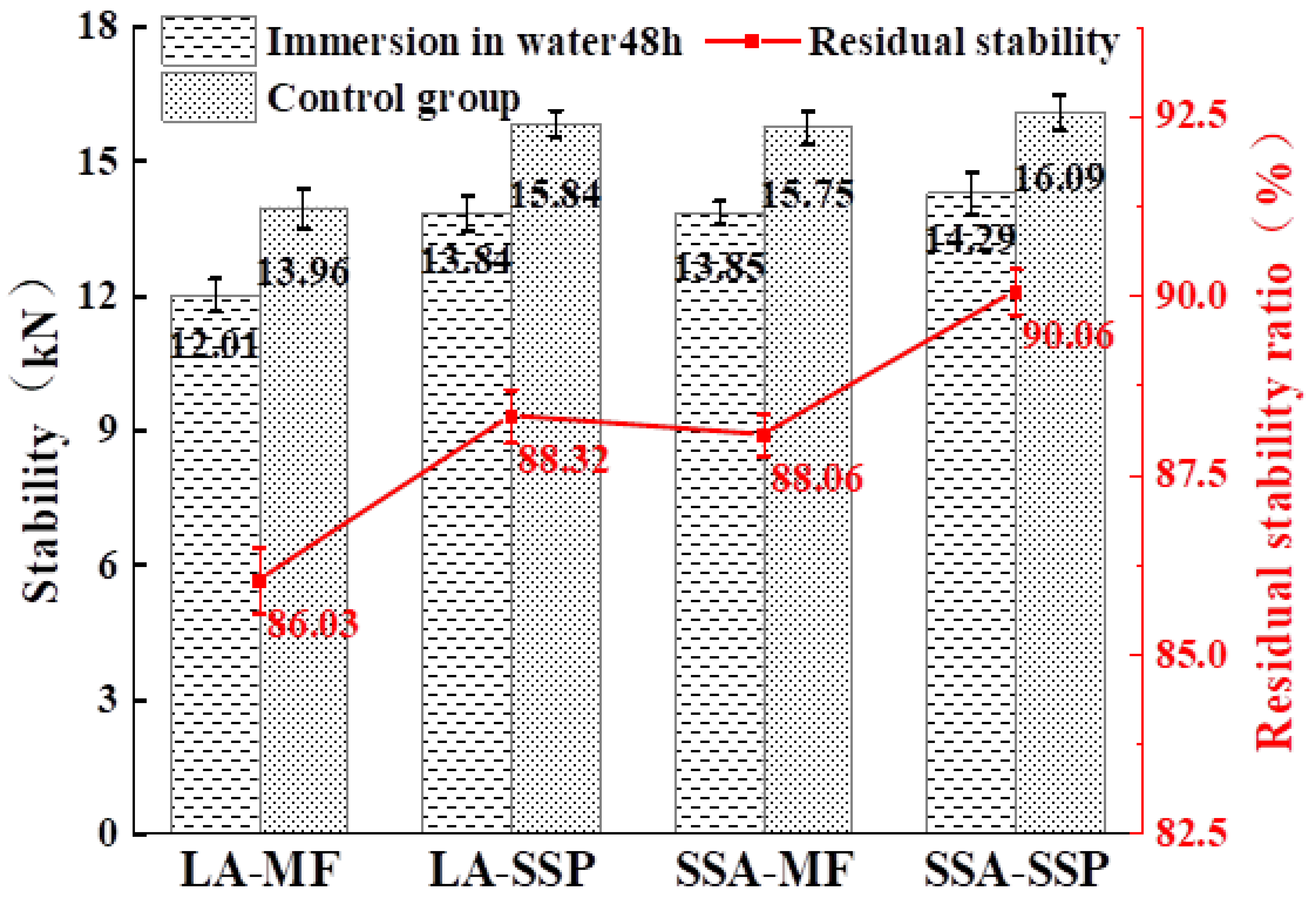
3.2.3. Water Stability
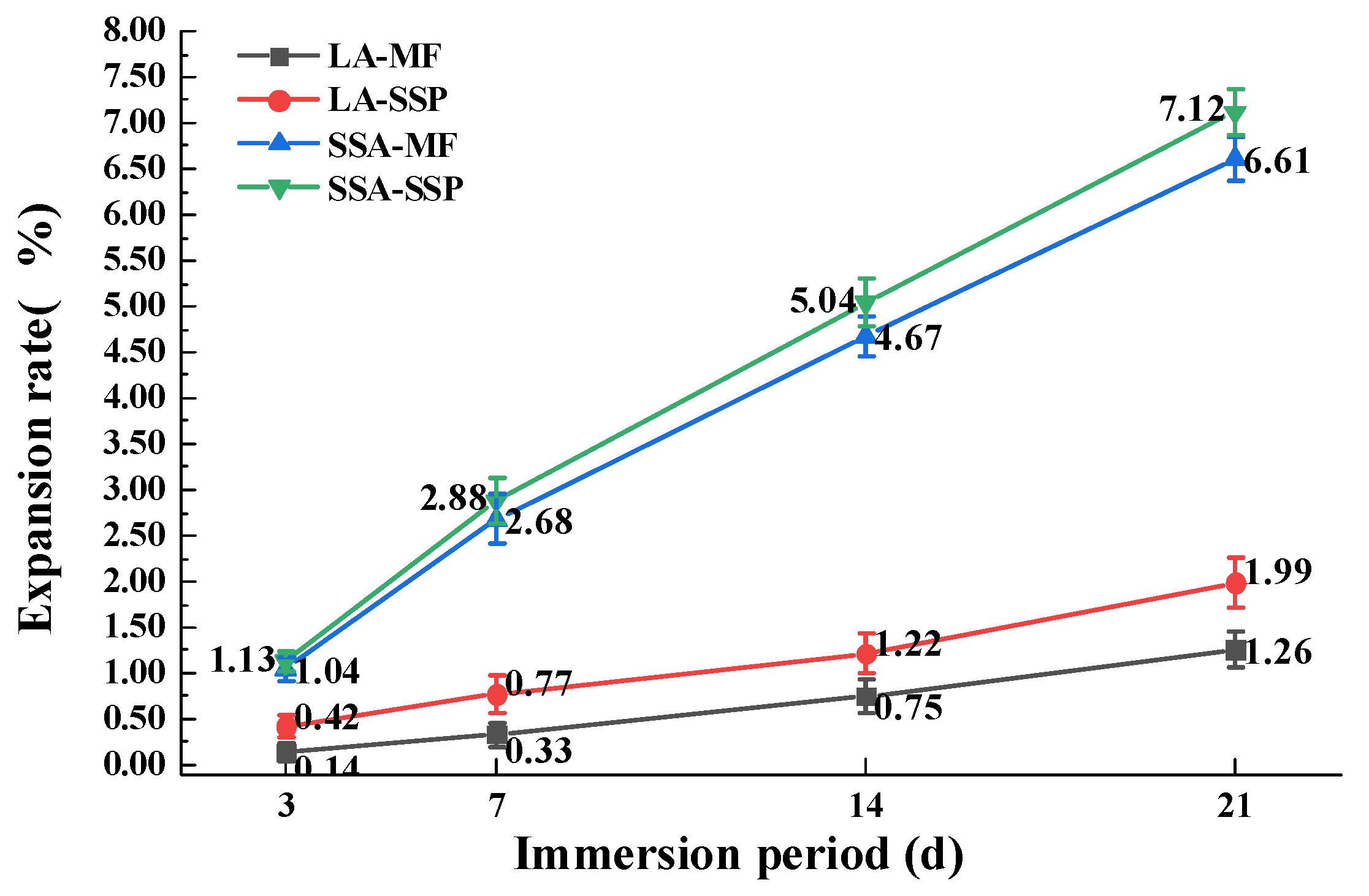
3.2.4. Volume Stability
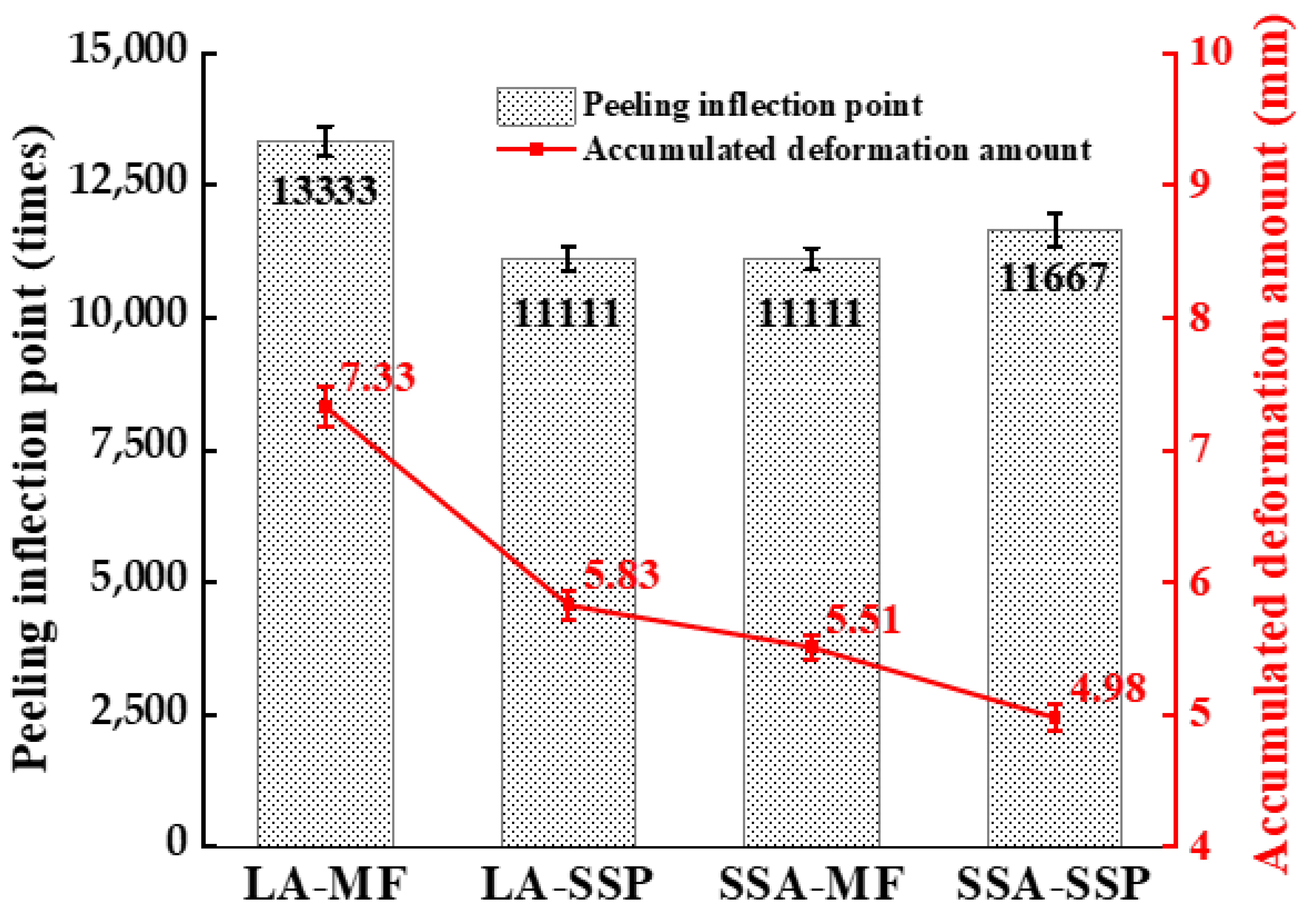
3.2.5. Fatigue Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, D.; Chou, L.; Wang, Y.; Luo, H.-L. Performance evaluation of asphalt concrete test road partially paved with industrial waste basic oxygen furnace slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 78, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessa, L.S. Evaluation of polishing and degradation resistance of natural aggregates and steel slag using the aggregate image measurement system. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 75, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yan, F.; Zhou, B. Testing and evaluation for anti-skid performance of steel slag asphalt pavement based on texture features. Mater. Rep. 2024, 38 (Suppl. S1), 315–321. [Google Scholar]
- E, G.; Cao, W.; Chen, L. Rules of voids in coarse aggregate formed by the packing of steel slag coarse aggregates and its application. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2024, 24, 8290–8296. [Google Scholar]
- Asi, I.M.; Qasrawi, H.Y.; Shalabi, F.I. Use of steel slag aggregate in asphalt concrete mixes. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2007, 34, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goli, H.; Hesami, S.; Ameri, M. Laboratory Evaluation of Damage Behavior of Warm Mix Asphalt Containing Steel Slag Aggregates. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2017, 29, 04017009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wen, W.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, X.; Ning, Y.; Liang, Z.; Ma, Z. Research on the Interaction Capability and Microscopic Interfacial Mechanism between Asphalt-Binder and Steel Slag Aggregate-Filler. Coatings 2022, 12, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhu, X.; Lin, Z.; Tan, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y. Study on the Improvement and Mechanism of Anti-sliding Functional Characteristics of Steel Slag SMA-13 Asphalt Mixture. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. (Transp. Sci. Eng.) 2024, 48, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Fu, G.; Zhang, M.; Gao, H. Effect of coarse and fine steel slag aggregates on the performance of AC-13 asphalt mixture. Shandong Jiaotong Keji 2024, 03, 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, A.; Liu, B.; Guo, Y.; Yu, P.; Yu, M. Skid resistance attenuation of steel slag asphalt mixtures on tunnel pavement. J. Build. Mater. 2019, 22, 284–291. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Hu, L.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, P. Volume expansibility of asphalt mixture mixed with steel slag. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2024, 24, 6901–6906. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Song, X. Study on road performance of steel slag fine aggregate asphalt mixture. Sichuan Build. Mater. 2023, 49, 163–166. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, R. Research on Performance and Fatigue Damage of Steel Slag Fine Aggregates in Asphalt Mixture. Master’s Thesis, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, D.; Wu, S.; Chen, M.; Zhao, M.; Shu, B. Characteristics of different types of basic oxygen furnace slag filler and its influence on properties of asphalt mastic. Materials 2019, 12, 4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J. Study on the Influence of Steel Slag Powder on the Water Stability Performance of Asphalt Concrete. Highw. Transp. Technol. (Appl. Technol. Ed.) 2020, 16, 93–95. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, H.; Yao, L.; Ma, X.; Lv, D.; Ou, Y. Performance of asphalt mastic with steel slag filler. J. Henan Univ. Urban Constr. 2020, 29, 54–59+86. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H. Performance evaluation and improving mechanisms of steel slag power based asphalt mixture. J. Shandong Univ. (Eng. Sci.) 2023, 53, 32–38+48. [Google Scholar]
- Xao, Z.; Chen, M.; Wu, S.; Xie, J.; Kong, D.; Qiao, Z.; Niu, C. Moisture susceptibility evaluation of asphalt mixtures containing steel slag powder as filler. Materials 2019, 12, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Study on surface physical properties of steel slag powder and rheological properties of asphalt mortar at high temperature. Fujian Archit. Constr. 2021, 10, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, B.; Xie, J.; Xiao, Y. Effects of steel slag fillers on the rheological properties of asphalt mastic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 145, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Jiang, H. Research on characteristics of steel slag powder and its application in asphalt mixture. J. Chongqing Jiaotong Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2008, 04, 576–579. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S. Research on the Preparation of Permeable Steel Slag Asphalt Mixture and Interface Mechanism. Master’s thesis, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi’an, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Meng, Q. Water Stability of Steel Slag Aggregate asphalt Interface. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 42, 99–107+152. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zhang, C.; Ding, W.; Wang, B.; Li, T. Research on adhesion characteristics of steel slag-asphalt interface. J. Dalian Univ. Technol. 2022, 62, 254–262. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, P.; An, W.; Chen, X. Evaluation of steel slag-asphalt adhesion based on surface energy theory. Mod. Transp. Metall. Mater. 2025, 5, 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, P.; An, W.; Wang, L.; Chen, X. Study on the adhesion between multi-scale steel slag aggregate and asphalt interface. In Proceedings of the World Transport Conference (WTC2024) (Highway Engineering), Qingdao, China, 26 June 2024; pp. 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Sun, S.; Zheng, B.; Guo, C.; He, L. Analysis of Adhesion Test of Steel Slag based on Microscopic Characteristics. Transp. Energy Conserv. Environ. Prot. 2024, 20, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Miao, Y.; Mo, L. Effects of surface morphology of steel slag aggregates on asphalt absorption and adhesion performance. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2023, 23, 14406–14419. [Google Scholar]
- Albayati, A.H.; Oukaili, N.K.; Mustafa, M.; Allawi, A.A.; Said, A.I.; Ibrahim, T.H. Experimental Study to Investigate the Performance-Related Properties of Modified Asphalt Concrete Using Nanomaterials Al2O3, SiO2, and TiO2. Materials 2024, 17, 4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Ma, H.; Zhang, H.; Kong, C.; Jiao, X.; Song, X. Cracking mechanism of steel slag aggregate during asphalt mixture production. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2024, 24, 14846–14853. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Guo, P.; Chen, X.; Yao, B. Study on Re-cracking Behavior of Steel Slag Asphalt Mixture at Different Healing Efficiencies. Highw. Eng. 2024, 49, 167–174+188. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y. Mix proportion design and performance verification of recycled asphalt mixture with steel slag. Highw. Transp. Inn. Mong. 2024, 06, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wei, S. Engineering properties and performance of asphalt mixtures incorporating steel slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 128, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Yang, C.; Huang, Y.; Liu, L. Effect of Steel Slag Content on Performance of Rubber Mixture ARAC-13. Mater. Rep. 2023, 37, 66–72. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Wu, S.; Xie, J.; Liu, T.; Wang, J. Research on Composition Design and Performance of Ultrathin Wear Layer of Asphalt Pavement. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. (Transp. Sci. Eng.) 2024, 48, 964–968. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, W.; Huang, W.; Wang, X.; Sun, J.; Luo, S. Performance of mixtures of epoxy asphalt and steel slag and its composition optimization. Thermosetting Resin 2024, 39, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Zhou, S.; Zheng, H.; Han, F.; Wang, H. Research on road performance of porous steel slag asphalt mixture. New Build. Mater. 2024, 51, 144–148. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C. Experimental Study on the Influence of Steel Slag on the Properties of Ultra-Thin Wear Layer. Master’s thesis, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, H.; Wu, S.; Yang, C.; Xie, J. Investigation on the Composition Design and Performance of OGFC5 Steel Slag Asphalt Mixture. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. (Transp. Sci. Eng.) 2024, 48, 959–963+968. [Google Scholar]
- JTG F40-2004; Technical Specification for Highway Asphalt Pavement Construction. People’s Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2004.
- GBT 25824-2010; Steel Slag for Road. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2010.
- JTG 3432-2024; Test Methods of Aggregates for Highway Engineering. People’s Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2024.
- JTG E20-2011; Highway Engineering Asphalt and Asphalt Mixture Test Regulations. People’s Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2011.
- ASTM D4541-22; Standard Test Method for Pull-Off Strength of Coatings Using Portable Adhesion Testers. American National Standards Institute: New York, NY, USA, 2022.
- AASHTO T324-2014; Hamburg Wheel-Track Testing of Compacted Hot-Mix Asphalt (HMA). Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- CSN EN 12697-24; Bituminous Mixtures-Test Methods for Hot Mix Asphalt Part 24: Resistance to Fatigue. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2018.
- Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Xu, G.; Shi, C. Physical, rheological and chemical characterization of aging behaviors of thermochromic asphalt binder. Fuel 2018, 211, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wan, G.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, Y. Study on the recovery law of rheological properties of aged asphalt with bio-oil-based recycling agents. Mater. Rep. 2025, 39, 24110036. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.Y. Study on Asphalt-Filler Interaction and Prediction of Asphalt Mastic Performance. Ph.D. Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2019. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, H.; Shen, Z.; Zhi, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, Y. Investigating Mechanisms of Porous Structure of Steel Slag Affecting Low-temperature Crack Resistance of Asphalt Mixture. J. Beijing Univ. Technol. 2024, 50, 82–93. [Google Scholar]





| Test Project | Test Values | Threshold Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (100 g, 5 s, 25 °C)/0.1 mm | 53 | 40~60 | ||
| Softening point (5 °C)/°C | 83.5 | ≥60 | ||
| Ductility (5 cm/min, 5 °C) | 32 | ≥20 | ||
| Rotational viscosity at 135 °C (Pa·s) | 1.8 | ≤3 | ||
| Flash point (°C) | 326 | ≥230 | ||
| Solubility in trichloroethylene (%) | 99.92 | ≥99 | ||
| Elastic recovery at 25 °C (%) | 93 | ≥75 | ||
| Storage stability (phase separation assessed by 48-h softening point difference) (°C) | 0.3 | ≤2.5 | ||
| Residue after thin film oven test (TFOT, 163 ± 1 °C, 5.5 ± 1 r/min, 5 h) | Mass loss (%) | 0.009 | ±1.0 | |
| Penetration ratio at 25 °C (%) | 75 | ≥65 | ||
| Ductility at 5 °C (cm) | 19 | ≥15 | ||
| Original SBS-modified asphalt | Rutting factor G*/sinδ (kPa) | 76 °C | 1.995 | ≥1.0 |
| 70 °C | 3.326 | |||
| Residue after rolling thin film oven test (RTFOT, 163 ± 0.5 °C, 15 ± 0.2 r/min, 85 min) | Mass loss (%) | −0.049 | ±1.0 | |
| Rutting factor G*/sinδ (kPa) | 2.789 | 2.789 | ≥2.2 | |
| 4.553 | 4.553 | |||
| Residue after pressure-aging vessel (PAV, 90~110 °C, 2.1 MPa, 20 h) | Aging temperature (°C) | 100 °C | ||
| Fatigue factor G*/sinδ (kPa) | 31 °C | 643.2 | ≤5000 | |
| 28 °C | 990.7 | |||
| Bending creep stiffness modulus S (MPa) | −6 °C | 85.6 | ≤300 | |
| −12 °C | 132 | |||
| Creep rate m-value | −6 °C | 0.432 | ≥0.30 | |
| −12 °C | 0.369 | |||
| Test Project | The Size of Steel Slag Aggregate/mm | The Size of Limestone Aggregate/mm | Threshold Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10~15 | 5~10 | 10~15 | 5~10 | ||
| Apparent specific gravity | 3.33 | 3.34 | / | / | ≥2.9 |
| / | / | 2.742 | 2.732 | ≥2.6 | |
| Water absorption (%) | 2.25 | 2.32 | / | / | ≤3.0 |
| / | / | 0.69 | 0.54 | ≤2.0 | |
| Aggregate crushing value (%) | 10.1 | / | 20.3 | / | ≤26 |
| Soundness (%) | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ≤12 |
| Los Angeles abrasion loss (%) | 9.5 | 10.4 | / | / | ≤26 |
| / | / | 20.2 | 22.3 | ≤28 | |
| Polished stone value (PSV) | 66 | / | 44 | / | ≥42 |
| Flakiness and elongation index (≥9.5 mm particles) (%) | 4.5 | 9.9 | ≤12 | ||
| Material finer than 0.075 mm by washing (%) | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.6 | ≤1 |
| Soft particles content (%) | 0.3 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 1.9 | ≤3 |
| Adhesion to asphalt (level) | 5 | 5 | ≥4 | ||
| Free calcium oxide (f-CaO) content (%) | 2.14 | 1.48 | / | / | ≤3 |
| Expansion rate (%) | 0.82 | / | / | ≤1.8 | |
| Test Project | Steel Slag | Limestone | Threshold Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apparent specific gravity | 3.314 | / | ≥2.9 |
| / | 2.728 | ≥2.5 | |
| Water absorption (%) | 2.38 | 1.07 | / |
| Free calcium oxide (f-CaO) content (%) | 1.14 | / | / |
| Test Project | Limestone Mineral Powder | Steel Slag Power | Threshold Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apparent specific gravity | 2.705 | 3.301 | ≥2.5 | |
| Water content (%) | 0.42 | 0.63 | ≤1 | |
| Size range | <0.6 mm (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| <0.15 mm (%) | 97.3 | 98.2 | 90~100 | |
| <0.075 mm (%) | 87.8 | 91.8 | 75~100 | |
| Appearance | No agglomeration | No agglomeration | No agglomeration | |
| Hydrophilic coefficient (%) | 0.53 | 0.58 | <1 | |
| Specific surface area (m2/g) | 0.78 | 1.80 | - | |
| Chemical Composition Content (%) | CaO | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | MgO | MnO | P2O5 | Al2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel slag power | 47.61 | 16.74 | 20.67 | 6.25 | 5.14 | 1.85 | 1.74 |
| Limestone mineral powder | 73.65 | 16.14 | 0.55 | 2.64 | 0.49 | 3.98 | 2.55 |
| Gradation Type | Sieve Size (mm) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 13.2 | 9.5 | 4.75 | 2.36 | 1.18 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.075 | |
| LA-MF | 100.0 | 96.6 | 74.7 | 44.1 | 31.4 | 23.8 | 15.8 | 10.1 | 7.4 | 5.8 |
| LA-SSP | 100.0 | 96.6 | 74.7 | 44.1 | 31.4 | 23.8 | 15.8 | 10.1 | 7.2 | 5.5 |
| SSA-MF | 100 | 96.7 | 74.3 | 43.6 | 30.2 | 23.2 | 15.6 | 10.3 | 7.6 | 5.3 |
| SSA-SSP | 100 | 96.7 | 74.3 | 43.6 | 30.2 | 23.2 | 15.6 | 10.2 | 7.2 | 5.4 |
| Gradation Type | Optimum Asphalt Content (%) | Percent Air Void VV (%) | Percent Voids in Mineral Aggregate VMA (%) | Percent Voids Filled with Asphalt VFA (%) | Marshall Stability (kN) | Flow Value (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LA-MF | 4.8 | 2.400 | 4.3 | 14.9 | 71.1 | 14.2 | 2.2 |
| LA-SSP | 4.8 | 2.416 | 4.2 | 14.4 | 70.8 | 15.94 | 3.1 |
| SSA-MF | 4.6 | 2.762 | 4.4 | 14.0 | 68.6 | 16.12 | 2.9 |
| SSA-SSP | 4.5 | 2.782 | 4.5 | 14.0 | 67.9 | 16.3 | 2.6 |
| Threshold values | / | / | 4~6 | 14~16 | 65~75 | ≥8 | 1.5~4 |
| Performance Parameter | Test Methods | Test Condition | Specification |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-temperature performance | Wheel-tracking test | 60 °C, 1600 times of rolling | JTG E20-2011 [43] |
| uniaxial penetration strength test | 60 °C | JTG E20-2011 [43] | |
| Hamburg wheel-tracking test | 50 °C, 20,000 times of rolling | AASHTO T324-2014 [45] | |
| Low-temperature performance | Three-point bending test | −10 °C | JTG E20-2011 [43] |
| Moisture stability | freeze–thaw splitting test | −18 °C, freeze–thaw treatment for 16 h | JTG E20-2011 [43] |
| immersed Marshall stability test | 60 °C, 48 h immersion treatment | JTG E20-2011 [43] | |
| Volumetric stability | Water immersion expansion test | 60 °C, 72 h immersion treatment | JTG E20-2011 [43] |
| Fatigue resistance | Two-point bending trapezoidal beam fatigue test | 10 °C, 25 Hz, 130 με | CSN EN 12697-24 [46] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, J.; Wei, J.; Xu, F.; Xu, Q.; Kang, L.; Wu, W.; Shi, W.; Yan, X. Research on Pavement Performance of Steel Slag Asphalt Mastic and Mixtures. Coatings 2025, 15, 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050525
Guo J, Wei J, Xu F, Xu Q, Kang L, Wu W, Shi W, Yan X. Research on Pavement Performance of Steel Slag Asphalt Mastic and Mixtures. Coatings. 2025; 15(5):525. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050525
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Jianmin, Jincheng Wei, Feiping Xu, Qinsheng Xu, Liang Kang, Wenjuan Wu, Wencheng Shi, and Xiangpeng Yan. 2025. "Research on Pavement Performance of Steel Slag Asphalt Mastic and Mixtures" Coatings 15, no. 5: 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050525
APA StyleGuo, J., Wei, J., Xu, F., Xu, Q., Kang, L., Wu, W., Shi, W., & Yan, X. (2025). Research on Pavement Performance of Steel Slag Asphalt Mastic and Mixtures. Coatings, 15(5), 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050525