Fog-Proof and Anti-Reflection Nano-Coating Prepared by Atmosphere Plasma Spraying
Abstract
1. Introduction
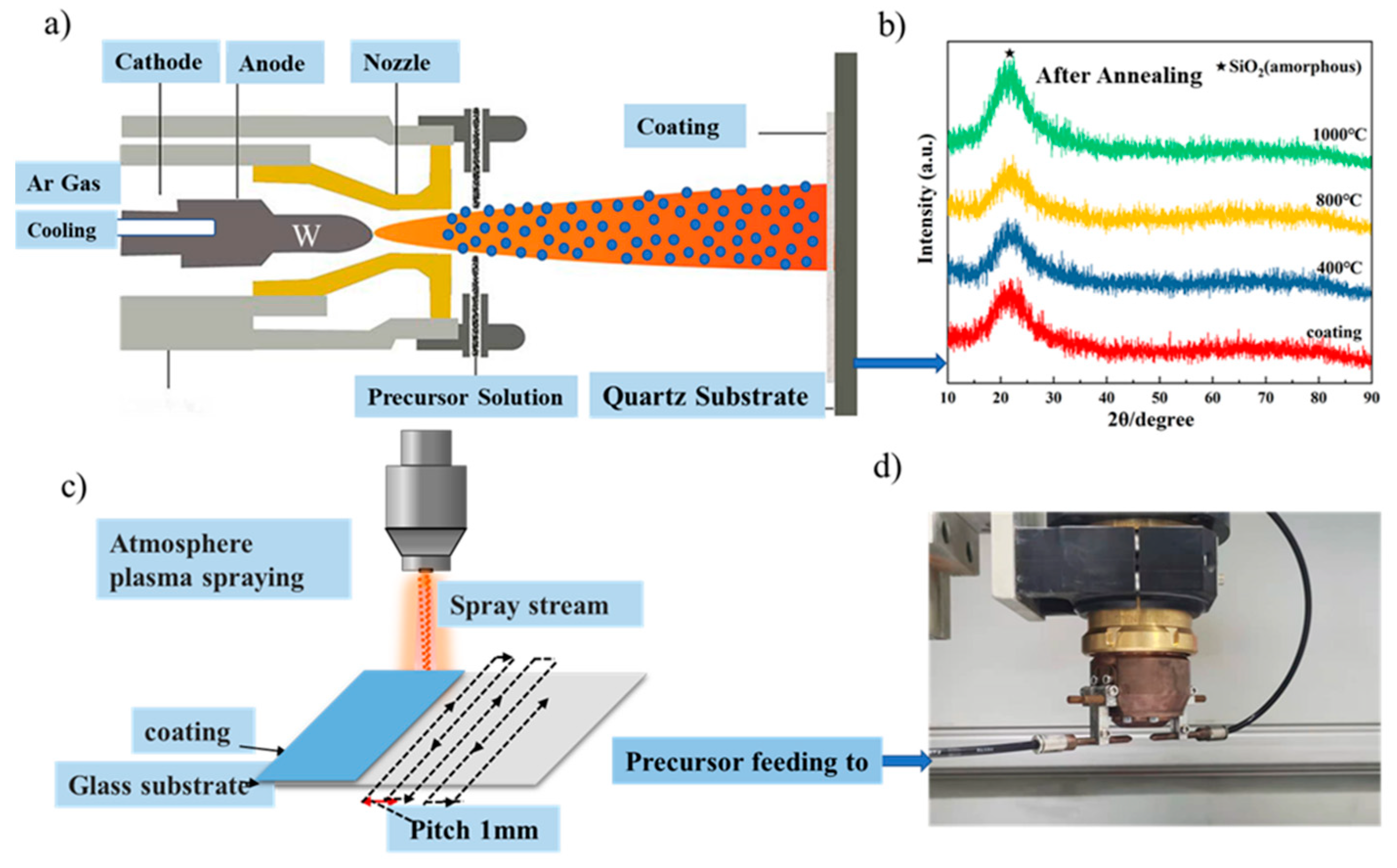
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Preparation of Nano-Coatings
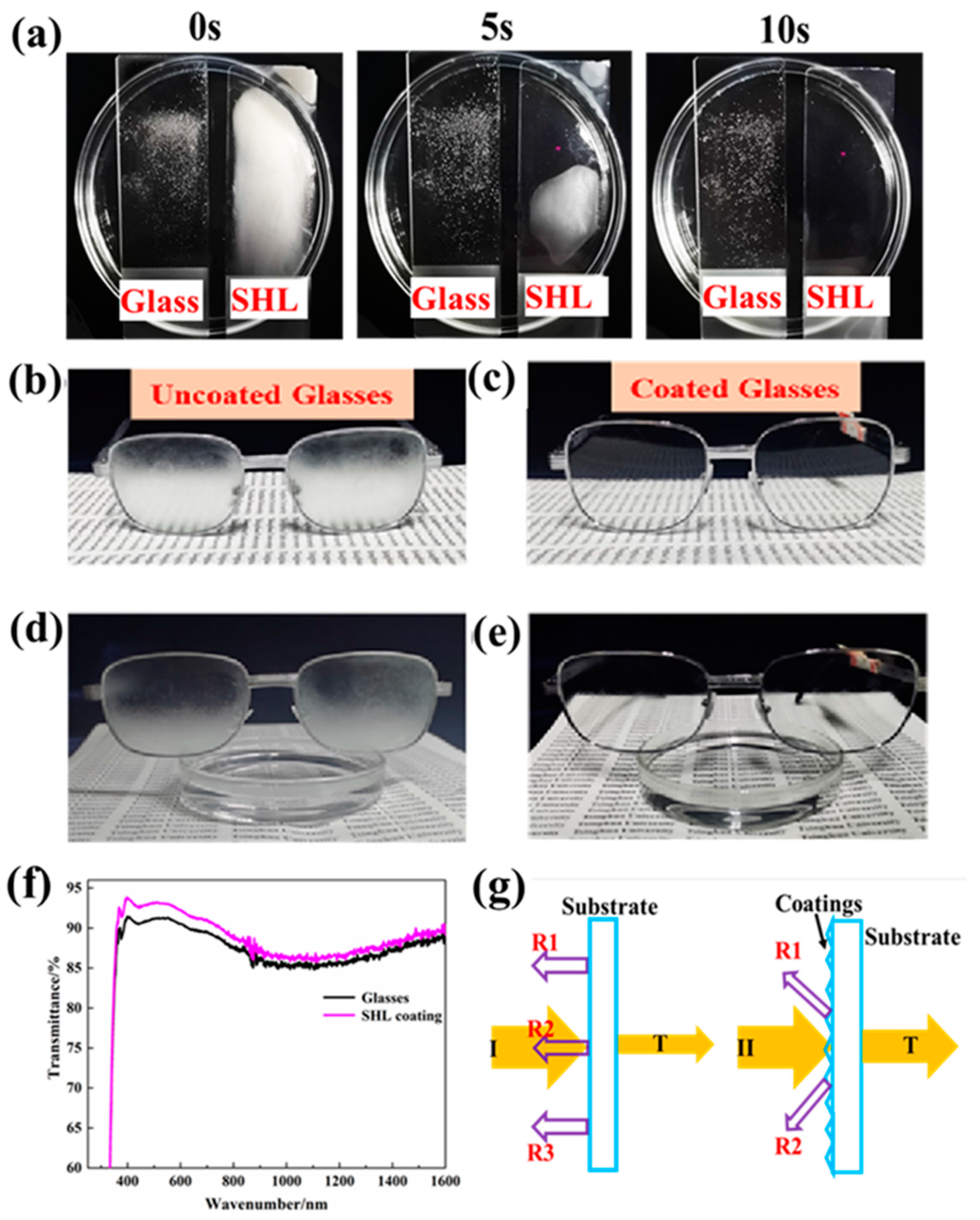
2.2. Fog-Proof Testing
2.3. Characterization
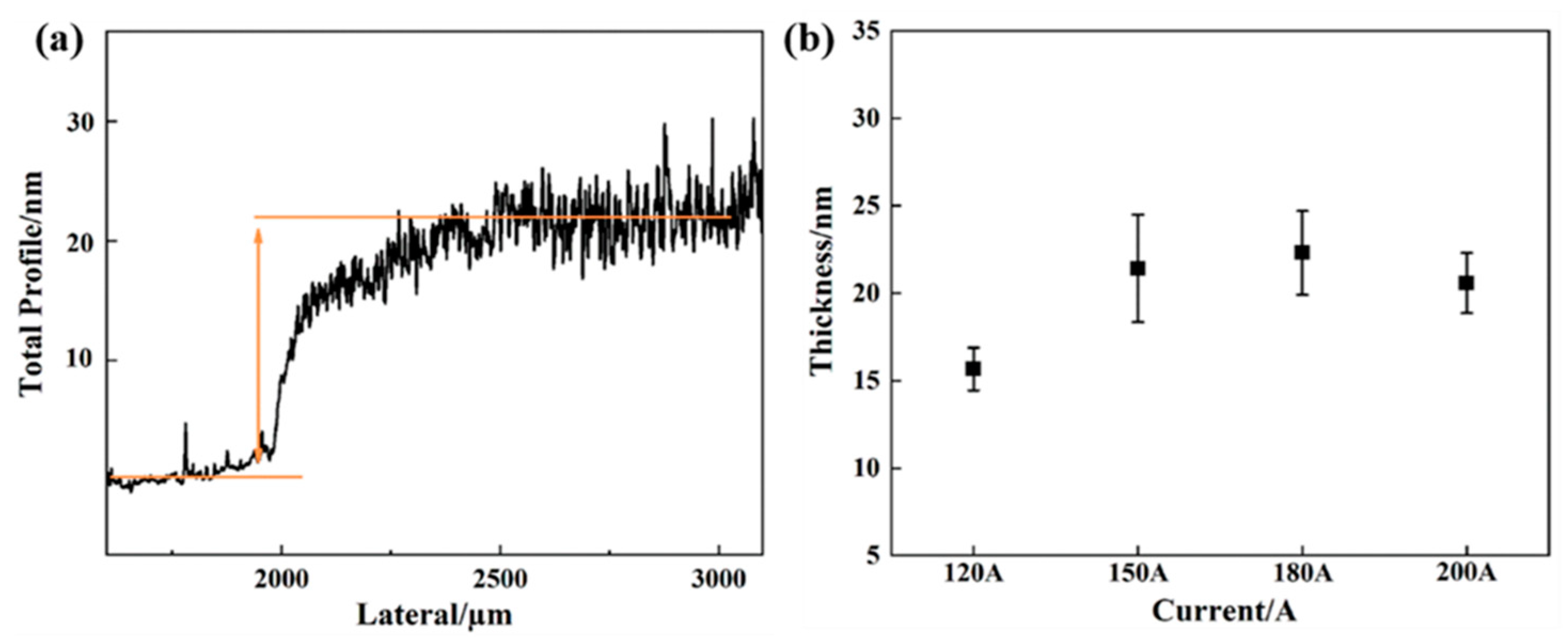
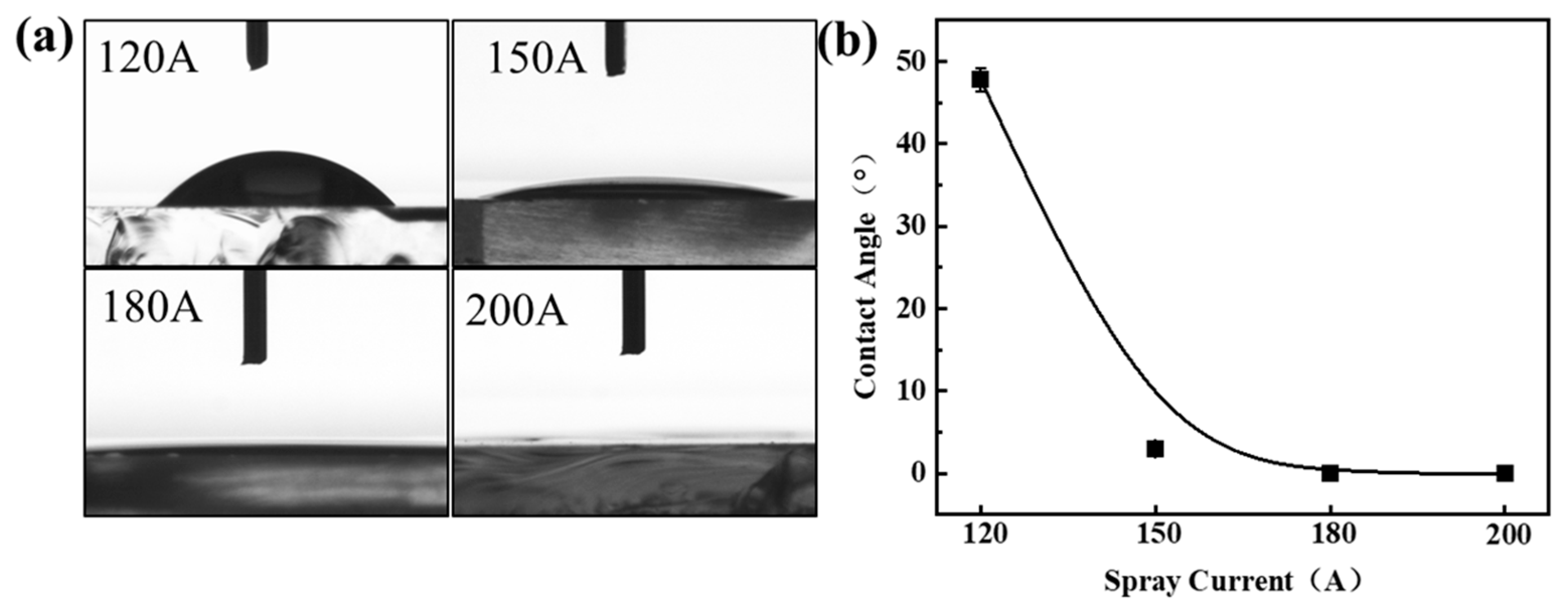
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, L.; He, J. Antifogging and antireflection coatings fabricated by integrating solid and mesoporous silica nanoparticles without any post-treatments. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 3293–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Tang, Y.; Gong, J.; Gong, D.; Chi, L.; Lin, C.; Chen, Z. Transparent superhydrophobic/superhydrophilic TiO2-based coatings for self-cleaning and anti-fogging. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 7420–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, K.; Yao, X.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Surfaces with Superwettability: New Insight on Theory, Design, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 8230–8293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, H.A.; Macleod, H.A. Thin-Film Optical Filters, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; He, J. Recent progress in antireflection and self-cleaning technology—From surface engineering to functional surfaces. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 61, 94–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Dou, Y.; Wei, M.; Evans, D.G.; Duan, X. Antireflection/antifogging coatings based on nanoporous films derived from layered double hydroxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 169, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, W.A.; Xin, J.H.; Tao, X. Superhydrophobic silica nanocomposite coating by a low-temperature process. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 87, 1782–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zheng, S.; Liu, H.; Tang, J.; Miao, W.; Wang, H.; Tian, Y.; Yang, H.; Jiang, L. A Magnetic Gated Nanofluidic Based on the Integration of a Superhydrophilic Nanochannels and a Reconfigurable Ferrofluid. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1805953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Xiangde, L.; Park, J.; Choi, D.; Heo, J.; Chang, M.; Lee, C.; Hong, J. Superhydrophilic coatings with intricate nanostructure based on biotic materials for antifogging and antibiofouling applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 309, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zheng, S.; Peng, S.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, Y. Superlyophilic Interfaces and Their Applications. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Dong, Z.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Designs of Superhydrophobic and Superhydrophilic Materials. ACS Cent. Sci. 2018, 4, 1102–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Su, B.; Jiang, L. Interfacial material system exhibiting superwettability. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6872–6897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, B.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Interfaces with Superwettability: From Materials to Chemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 1727–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- England, M.W.; Urata, C.; Dunderdale, G.J.; Hozumi, A. Anti-Fogging/Self-Healing Properties of Clay-Containing Transparent Nanocomposite Thin Films. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2016, 8, 4318–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Ren, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, D.; Xu, W.; Qin, Y. Superhydrophilic and Underwater Superoleophobic Poly(propylene) Nonwoven Coated with TiO2 by Atomic Layer Deposition. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 8, 2001485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-Y.; Park, J.-J.; Lee, J.-G.; Lee, M.-W.; Kim, H.-Y.; Oh, J.-H.; Seong, T.-Y.; Kim, D.; James, S.C.; van Hest, M.F.A.M.; et al. Tuning Hydrophobicity with Honeycomb Surface Structure and Hydrophilicity with CF4 Plasma Etching for Aerosol-Deposited Titania Films. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 95, 3955–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, J.G.; Kim, D.; Oh, J.H.; Seong, T.Y.; Van Hest, M.F.A.M.; Yoon, S.S. Superhydrophilic transparent Titania films by supersonic aerosol deposition. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 96, 1596–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrakellis, P.; Gogolides, E. Hydrophobic and superhydrophobic surfaces fabricated using atmospheric pressure cold plasma technology: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 254, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, N.; Pugh, M.; Moreau, C.; Dolatabadi, A. Developing hydrophobic and superhydrophobic TiO2 coatings by plasma spraying. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 289, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugica-Vidal, R.; Alba-Elias, F.; Sainz-Garcia, E.; Pantoja-Ruiz, M. Hydrophobicity attainment and wear resistance enhancement on glass substrates by atmospheric plasma-polymerization of mixtures of an aminosilane and a fluorocarbon. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 347, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhen, Y.; Xu, F.; Ma, Z.; Gao, L. Oxygen vacancy induced superhydrophobicity of air plasma spraying deposited Y2O3 coatings. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2025, 45, 116871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovish, M.Q.; Hilt, F.; Rolston, N.; Xiao, Q.; Dauskardt, R.H. Open Air Plasma Deposition of Superhydrophilic Titania Coatings. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1806421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhao, J.; Wu, C.; Li, B.; Sun, C.; Huang, S.; Tian, X. Highly durable antifogging coatings resistant to long-term airborne pollution and intensive UV irradiation. Mater. Des. 2020, 194, 108956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomga, J.; Varshney, P.; Nanda, D.; Satapathy, M.; Mohapatra, S.S.; Kumar, A. Fabrication of durable and regenerable superhydrophobic coatings with excellent self-cleaning and anti-fogging properties for aluminium surfaces. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 702, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, B.; Wang, F.W.; Tobelmann, B.; Wang, J.; Landini, J.; Gunaratne, N.; Kovac, J.; Miller, T.; Mosurkal, R.; Tuteja, A. Design of Abrasion-Resistant, Long-Lasting Antifog Coatings. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 13018–13028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momoli, R.; Giacomazzo, S.; Gandin, A.; Brusatin, G. Anti-fog nanocomposite coatings of enhanced durability. J. Sol-Gel. Sci. Technol. 2022, 101, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Liang, R.; Liu, G.; Pan, W. Zinc coating on steel by atmosphere plasma spray and their anti-corrosion behavior. Mater. Lett. 2022, 314, 131825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, O.S.A.; Mukherjee, B.; Islam, A.; Keshri, A.K. Instant Tuning of Superhydrophilic to Robust Superhydrophobic and Self-Cleaning Metallic Coating: Simple, Direct, One-Step, and Scalable Technique. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 4616–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Bai, Y. Review of suspension and solution precursor plasma sprayed thermal barrier coatings. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 14299–14312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, I.M. High laser damage threshold porous silica antireflective coating. Appl. Opt. 1986, 25, 1481–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nostell, P.; Roos, A.; Karlsson, B. Optical and mechanical properties of sol-gel antireflective films for solar energy applications. Thin. Solid Films 1999, 351, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaei, R.; Eshaghi, A. Optical and superhydrophilic properties of nanoporous silica-silica nanocomposite thin film. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 699, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budunoglu, H.; Yildirim, A.; Bayindir, M. Flexible and mechanically stable antireflective coatings from nanoporous organically modified silica colloids. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 9671–9677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Spraying Currents (A) | 120; 150; 180; 200 |
|---|---|
| Spraying times | 1 |
| Precursor velocity (mL/min) | 25 |
| Mixture velocity (mL/min) | 470 |
| Scanning speed (mm/s) | 100 |
| Scanning pitch (mm) | 1 |
| Distance from nozzle to substrate (mm) | 60 mm |
| Element and Functional Group Content in the Surface (at%) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Sprayed Under 120 A | Sprayed Under 180 A | |
| Si | 31.8 | 30.2 |
| C | 5.8 | 3.8 |
| O | 62.2 | 65.5 |
| -Si-CH3 | 1.9 | 1.4 |
| -Si-CHx(x<3) | 17.9 | 16.9 |
| SiOx | 10.0 | 11.9 |
| -Si-CH3 | 2.0 | 1.4 |
| -Si-CHx(x<3) | 3.8 | 2.4 |
| -O-Si-C | 35.5 | 19.3 |
| SiOx | 26.9 | 46.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, X.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, G.; Wang, D.; Xing, Y.; Pan, W. Fog-Proof and Anti-Reflection Nano-Coating Prepared by Atmosphere Plasma Spraying. Coatings 2025, 15, 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15030331
Zhong X, Zhou Z, Liu G, Wang D, Xing Y, Pan W. Fog-Proof and Anti-Reflection Nano-Coating Prepared by Atmosphere Plasma Spraying. Coatings. 2025; 15(3):331. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15030331
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Xiqiang, Zimo Zhou, Guanghua Liu, Dan Wang, Yan Xing, and Wei Pan. 2025. "Fog-Proof and Anti-Reflection Nano-Coating Prepared by Atmosphere Plasma Spraying" Coatings 15, no. 3: 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15030331
APA StyleZhong, X., Zhou, Z., Liu, G., Wang, D., Xing, Y., & Pan, W. (2025). Fog-Proof and Anti-Reflection Nano-Coating Prepared by Atmosphere Plasma Spraying. Coatings, 15(3), 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15030331







