Scratch Resistance and Damage Mechanisms Arising in Titanium Carbide–Nickel Aluminide-Based Laser DED Clads on D2 Tool Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Materials
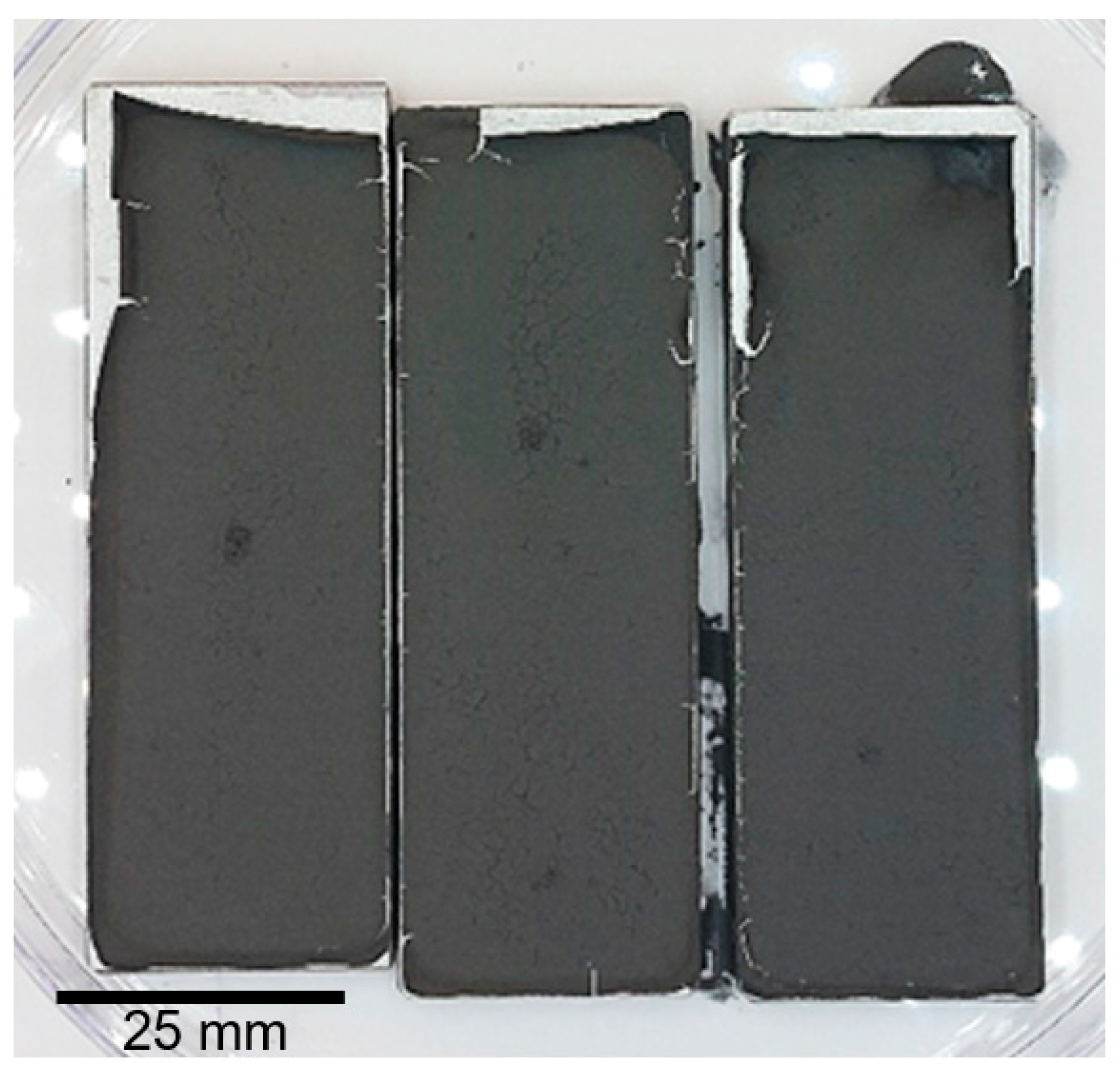
2.2. Laser Cladding
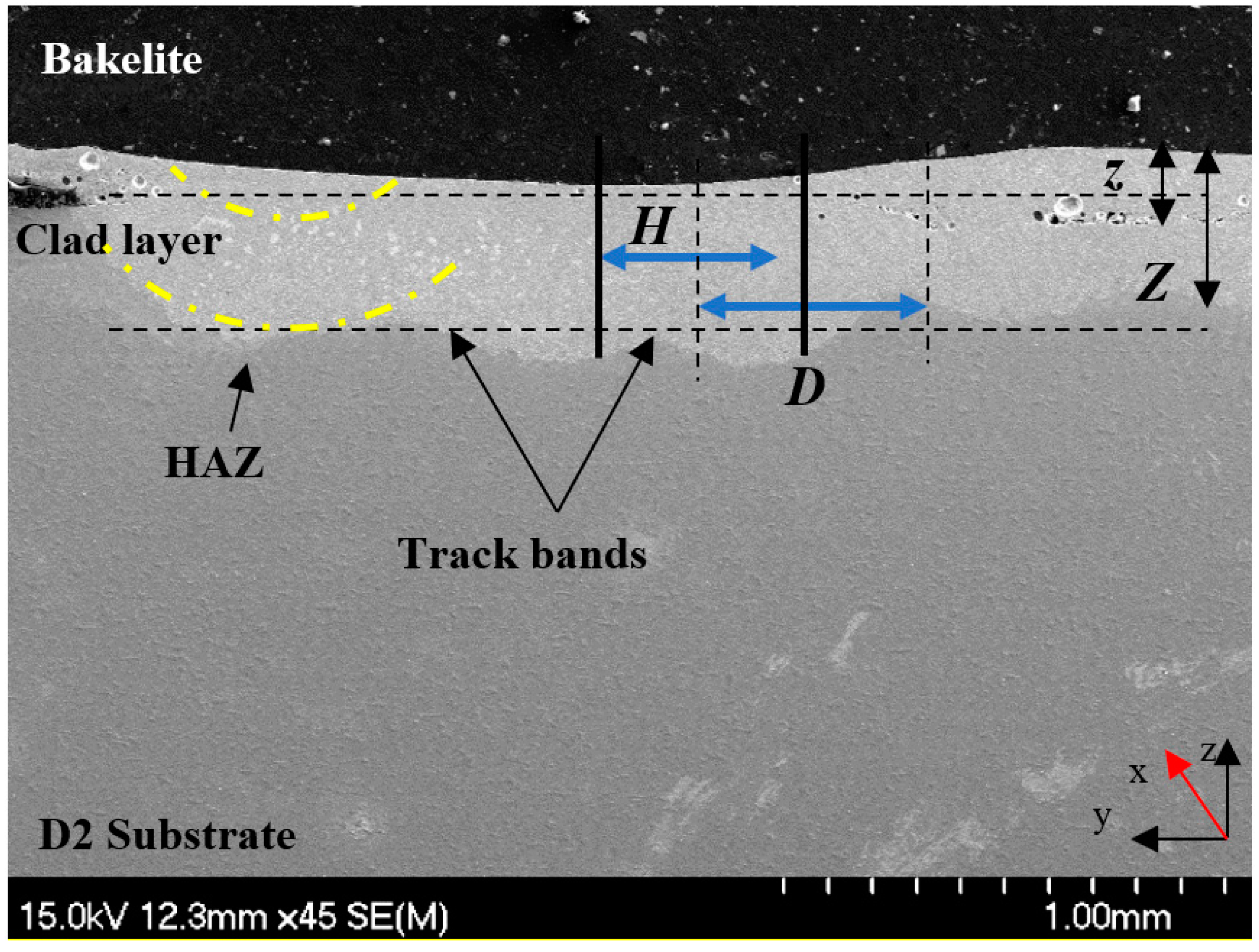
2.3. Microstructural Characterisation
2.4. Mechanical Testing
2.4.1. Micro-Vickers Indentation
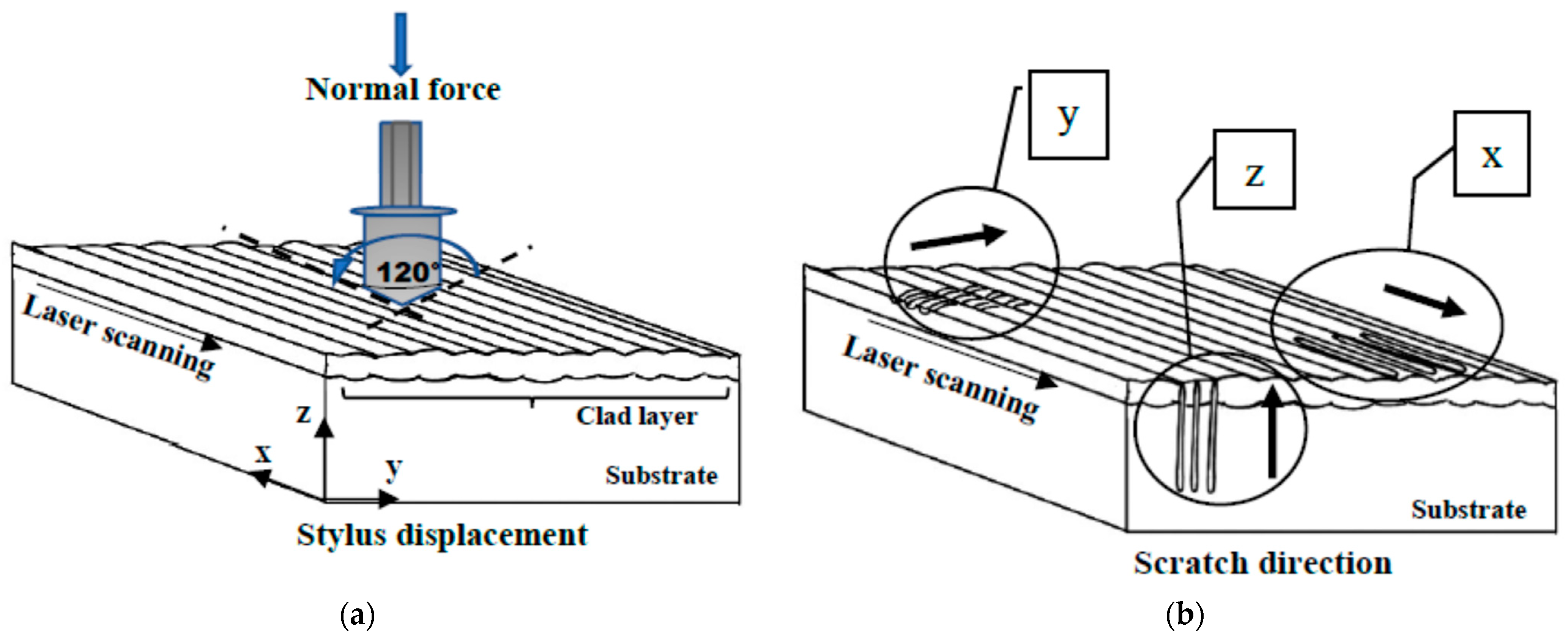
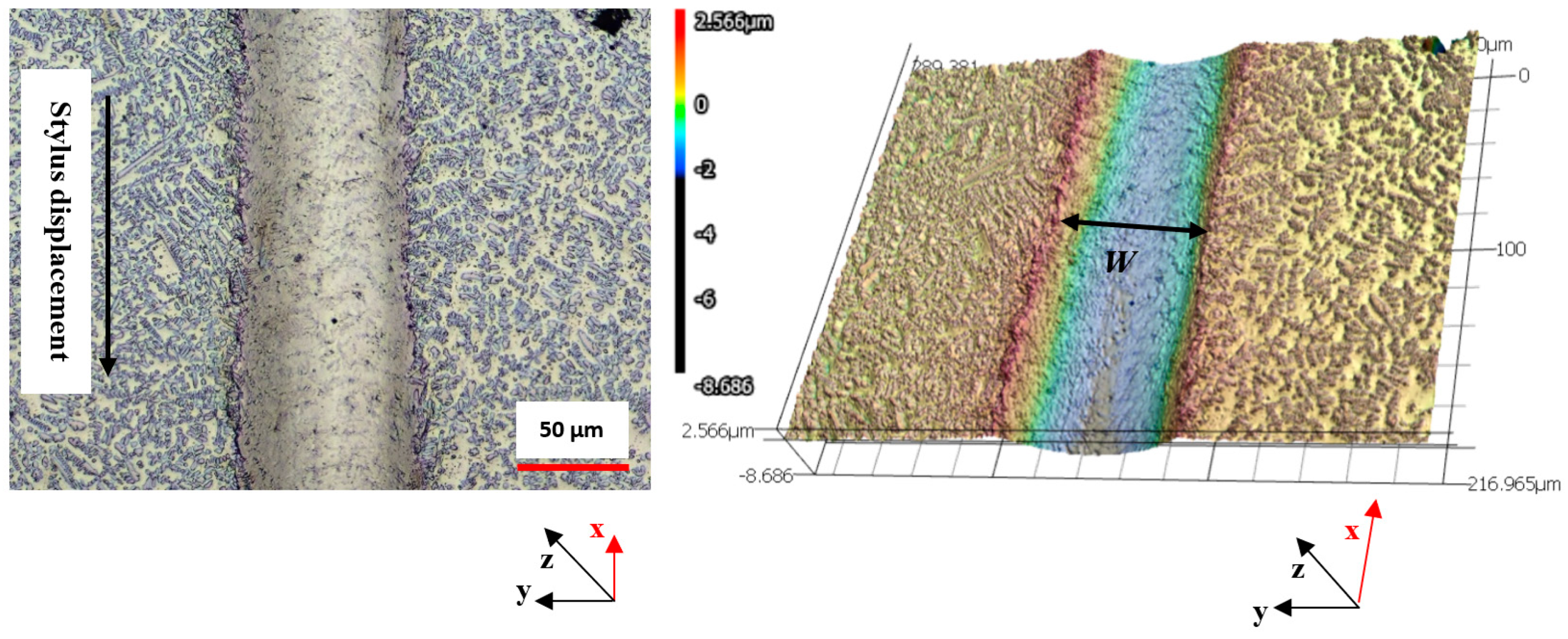
2.4.2. Scratch Test Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
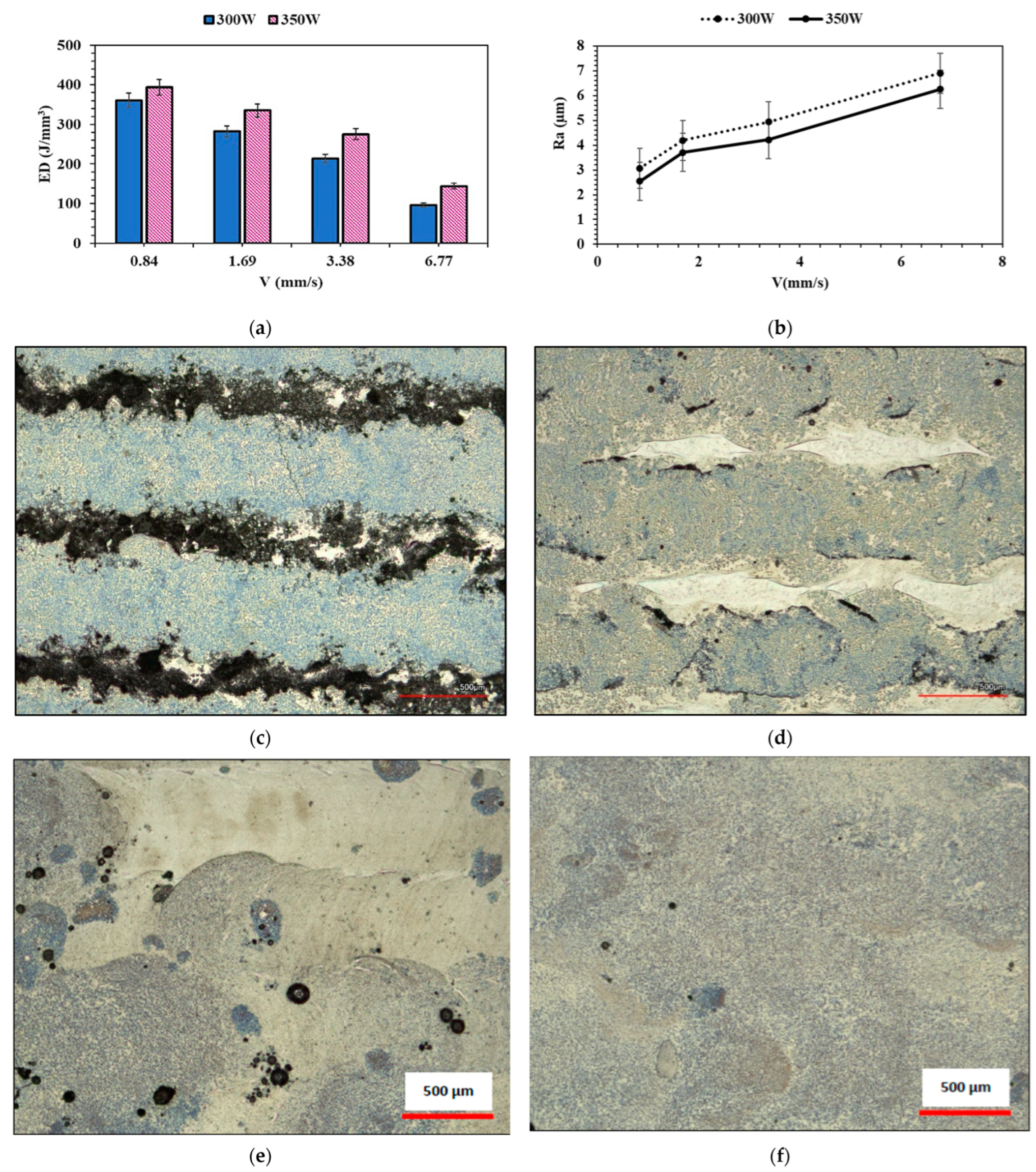
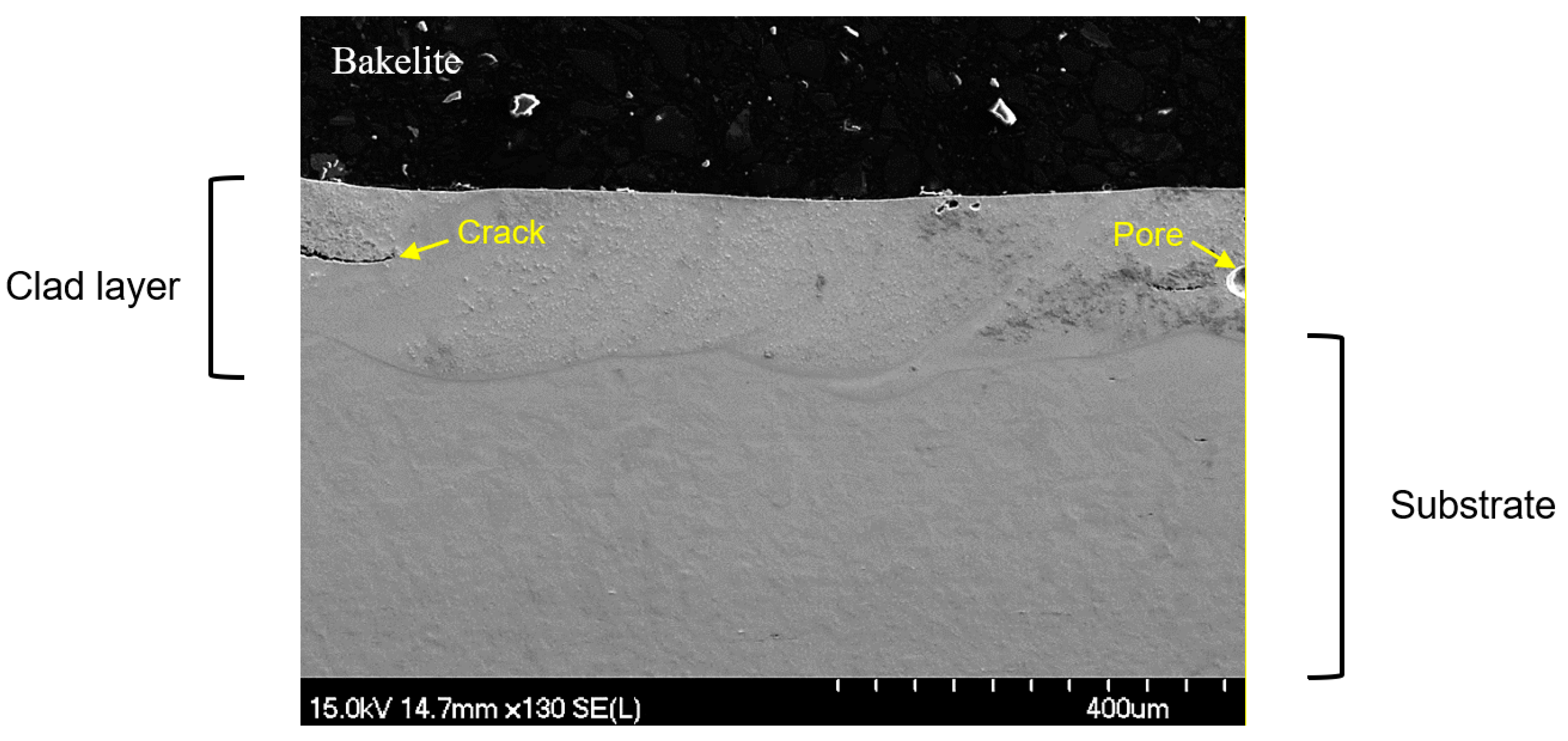
3.1. Directed Energy Deposition Laser Cladding
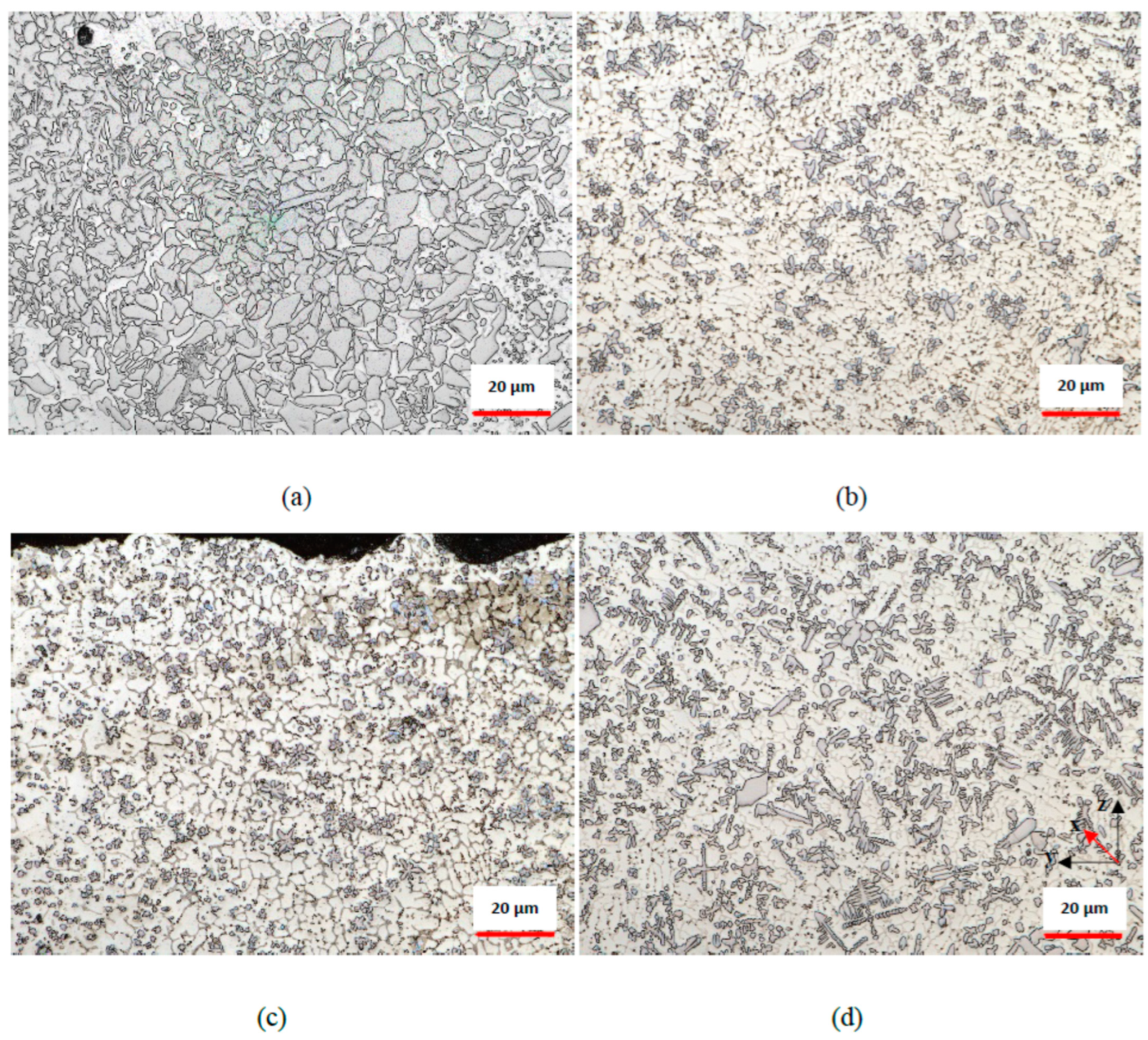
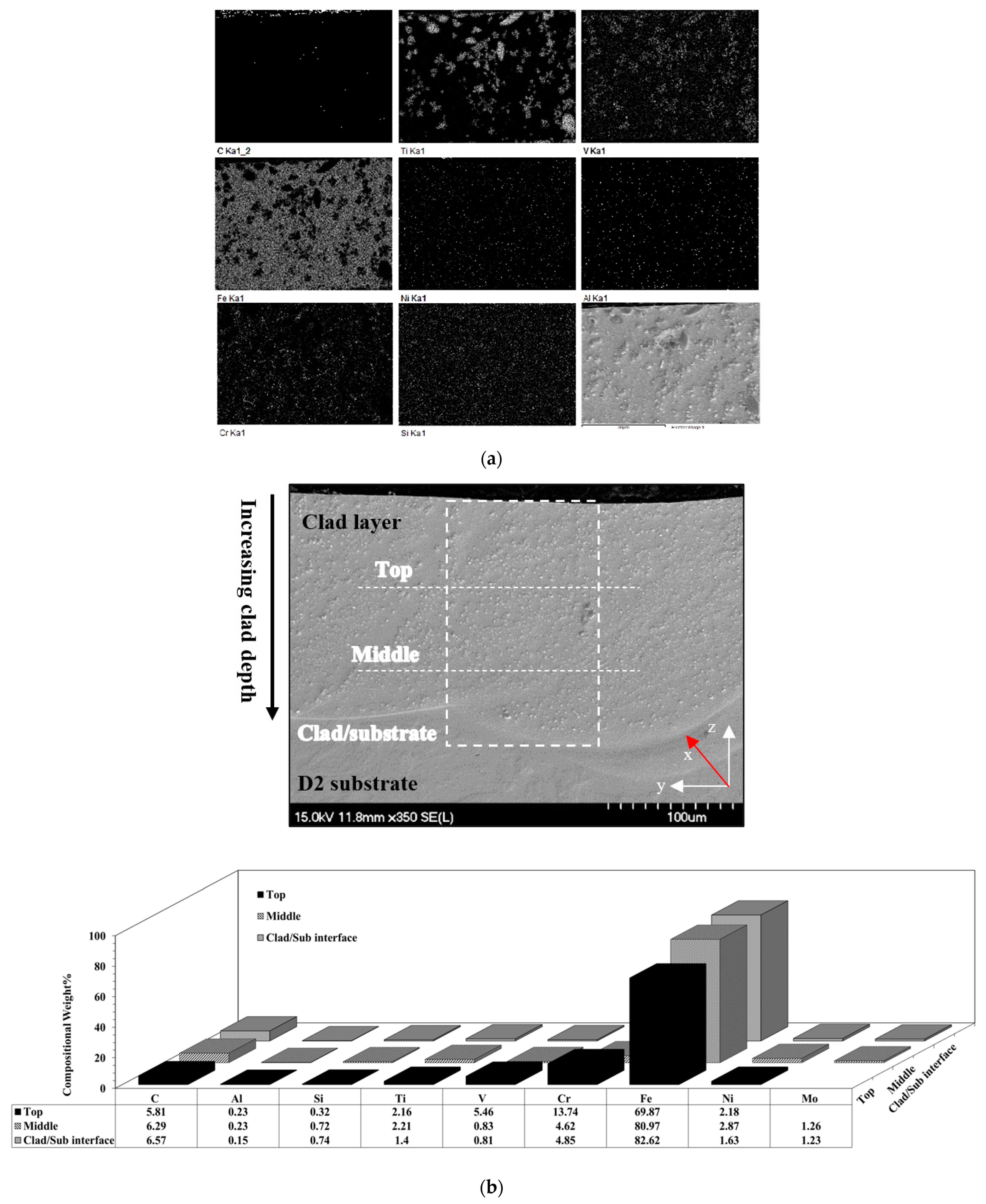
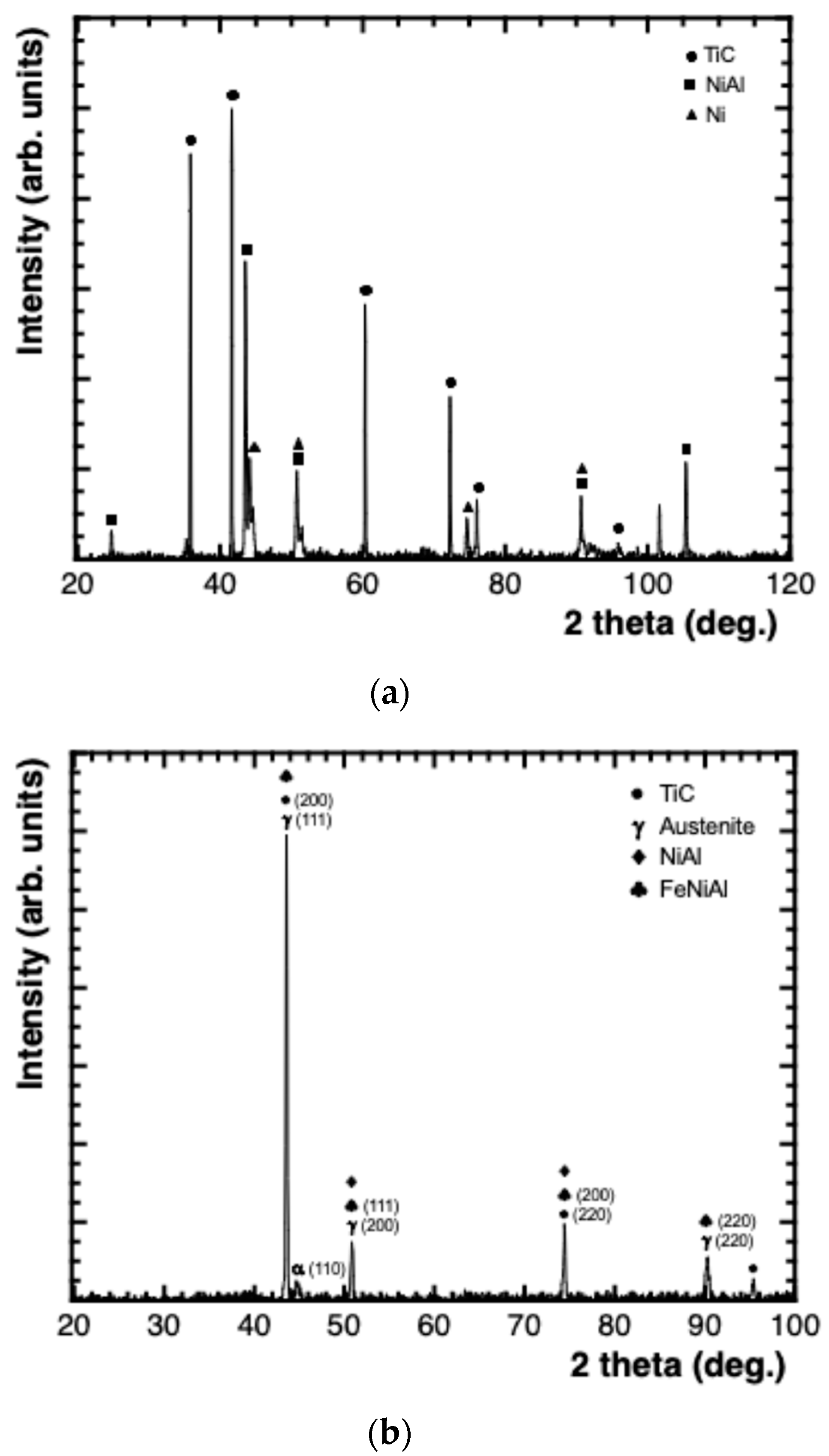
3.2. Microstructural and Phase Analysis
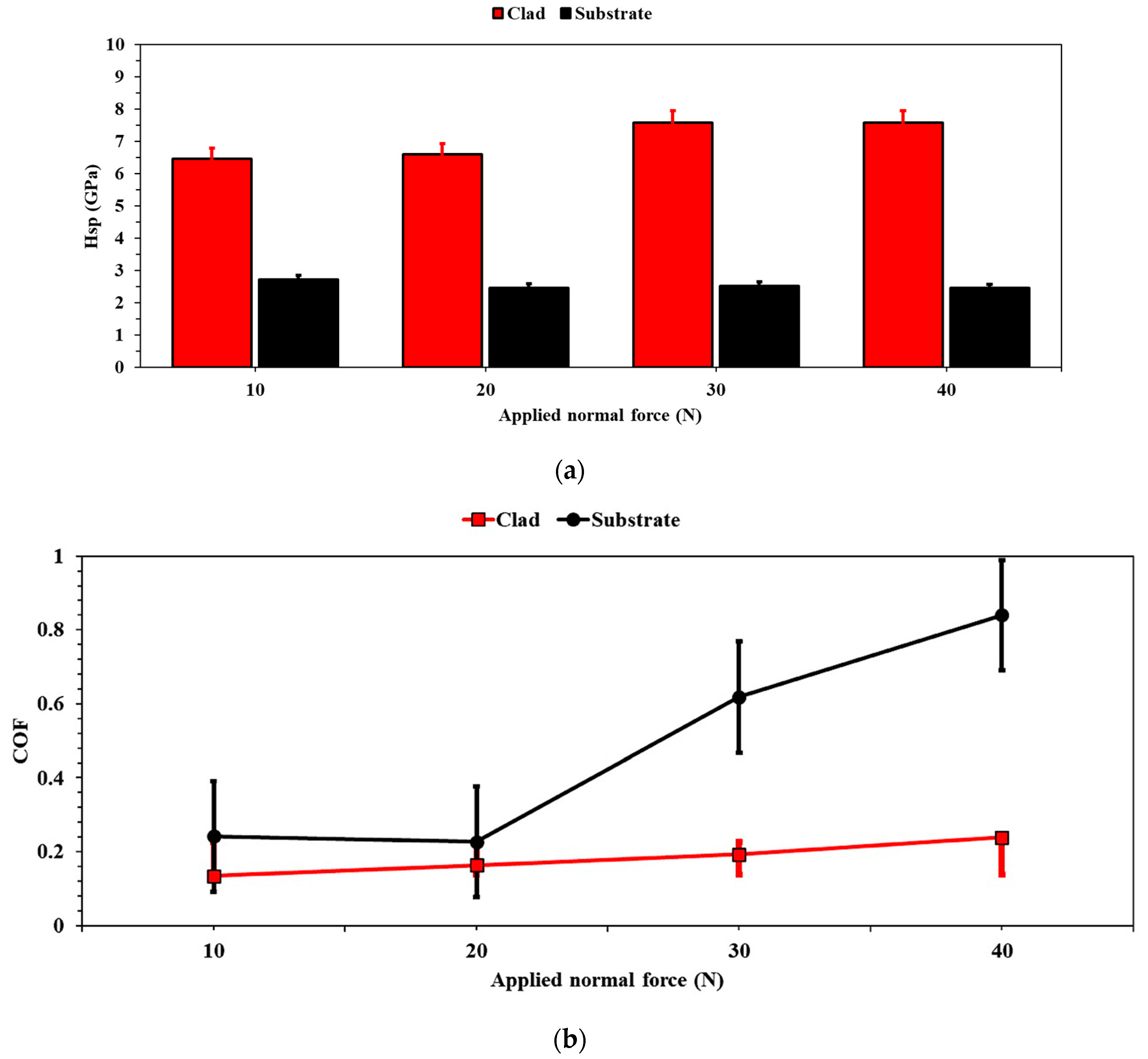
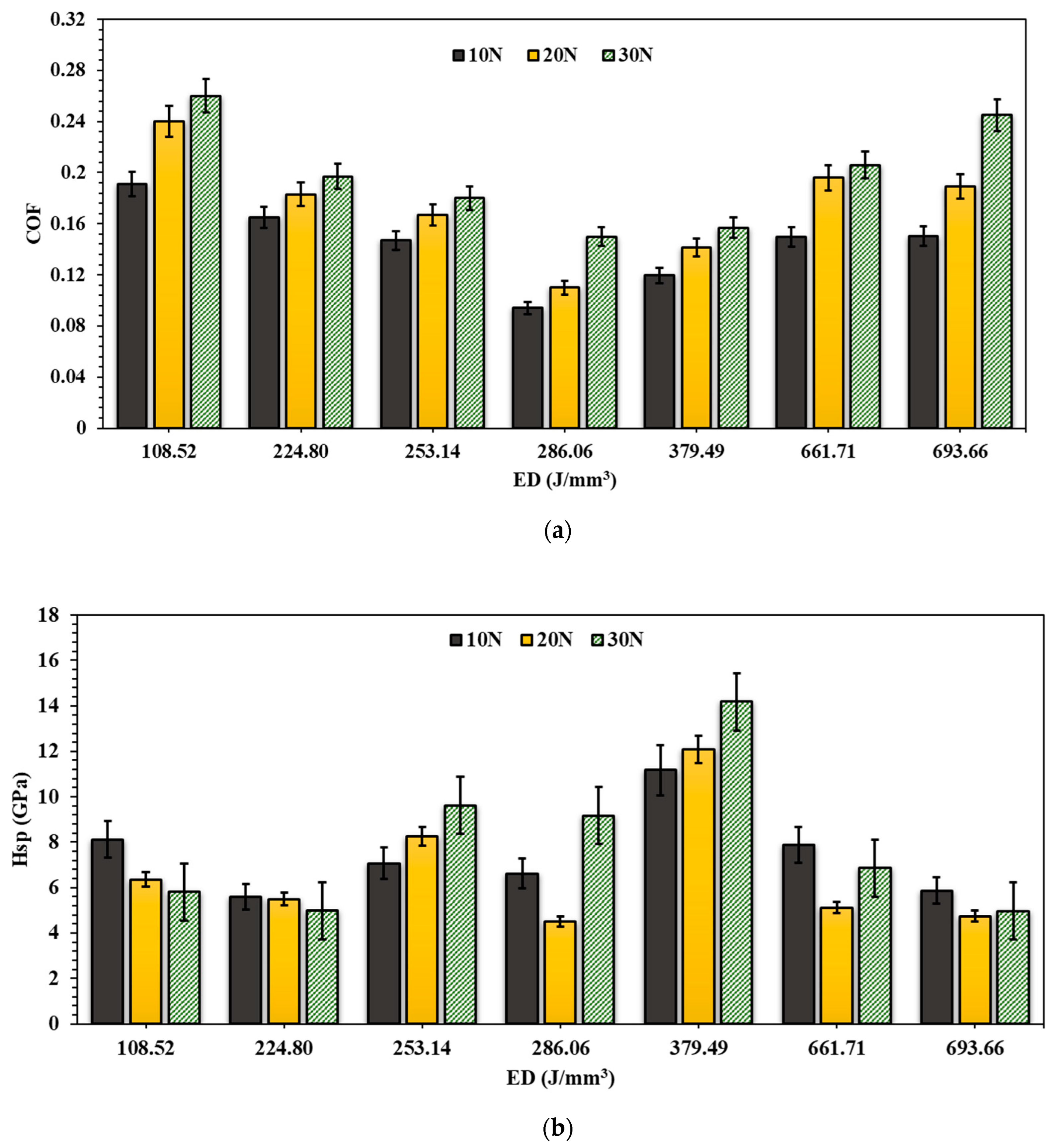
3.3. Microhardness Evaluation
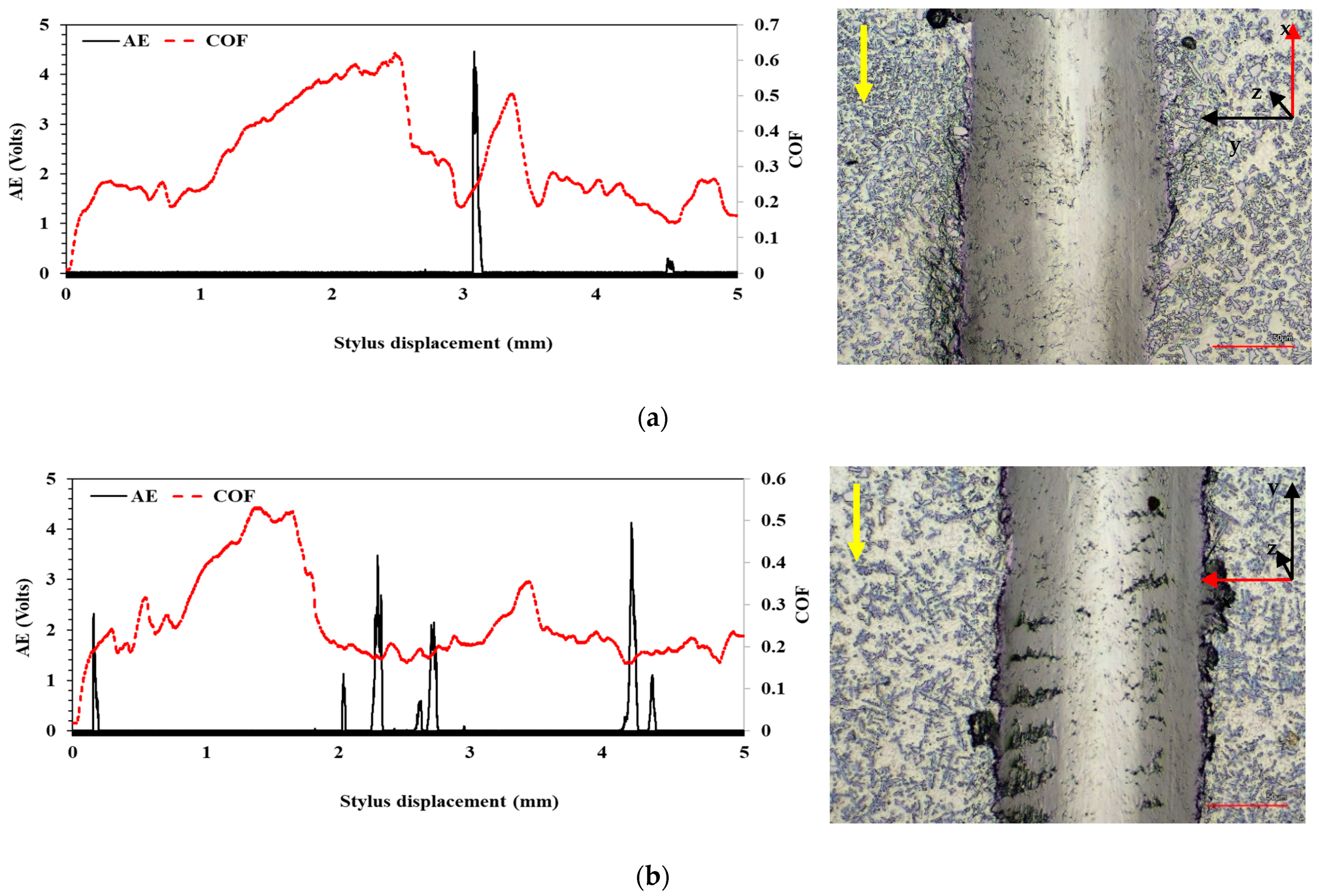
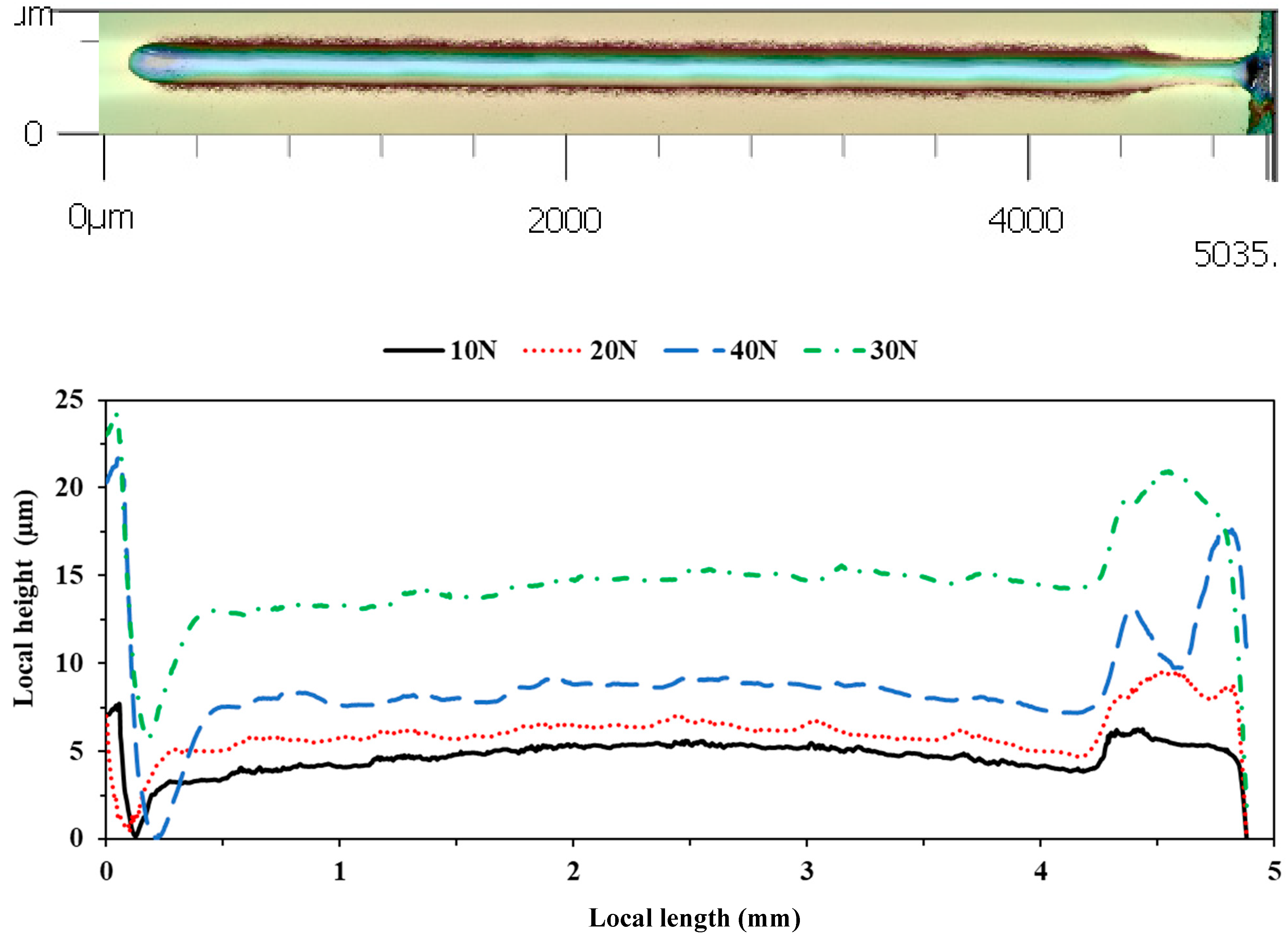
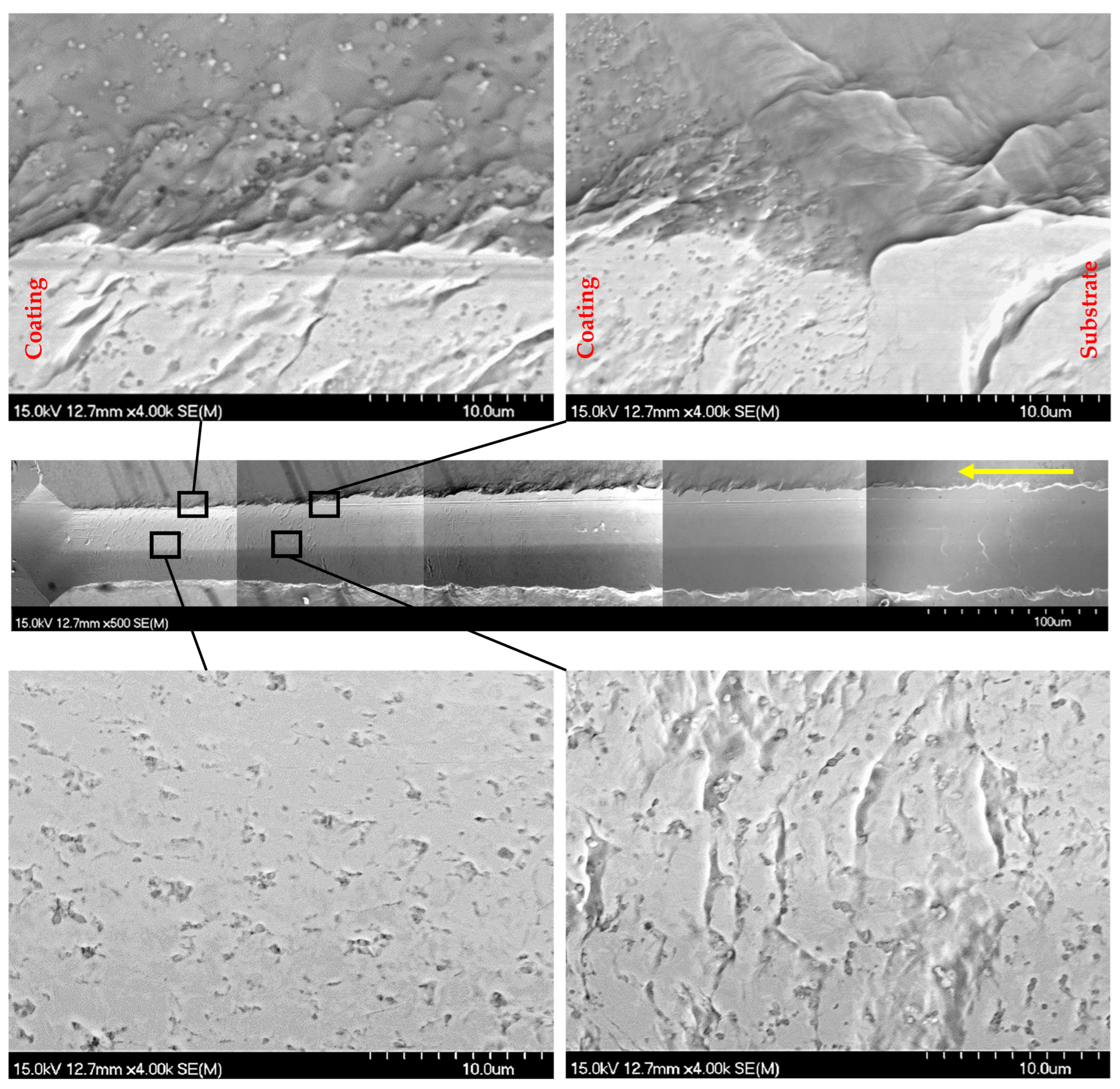
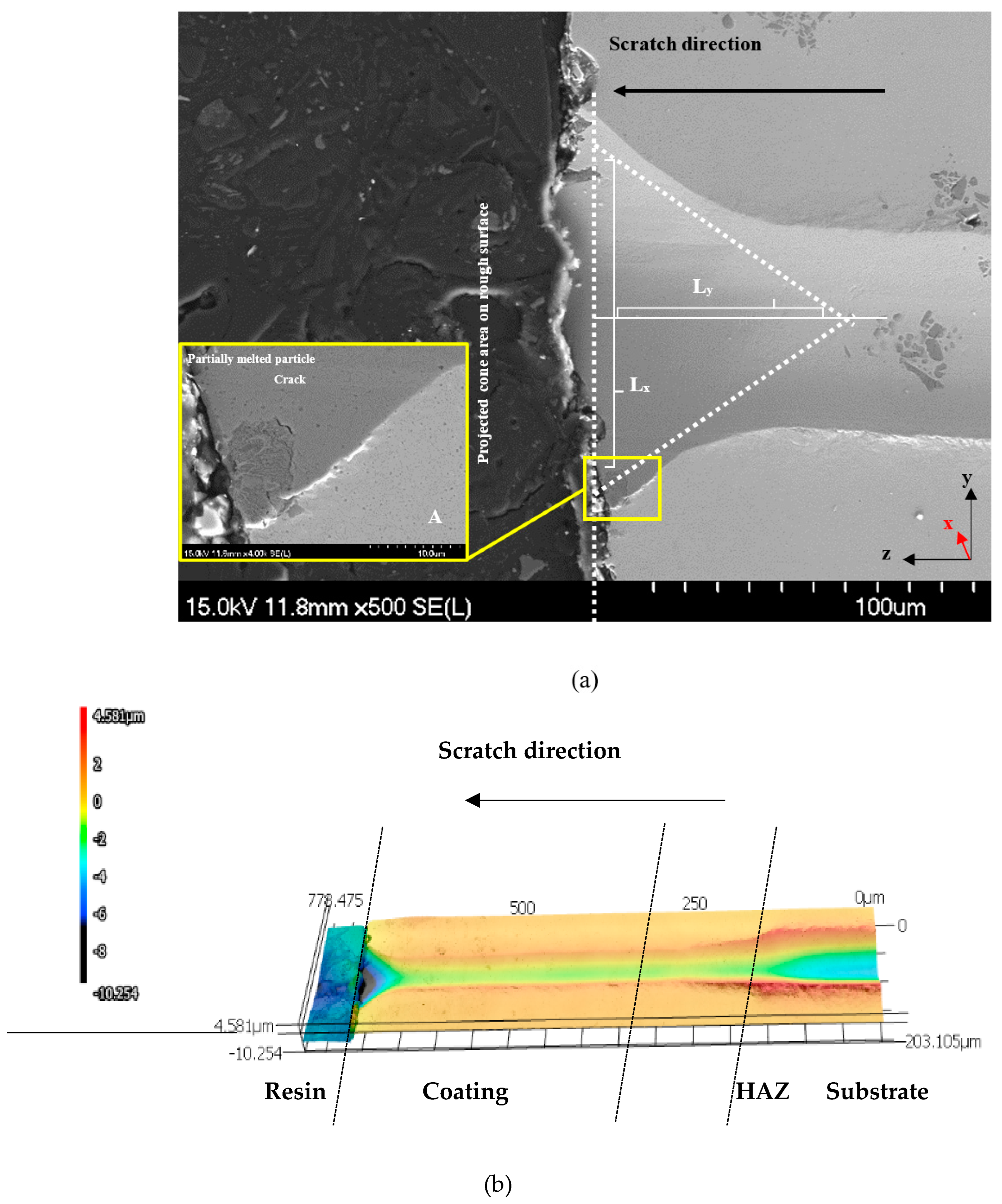
3.4. Scratch Testing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palin-Luc, T.; Jeddi, D. The gigacycle fatigue strength of steels: A review of structural and operating factors. Procedia Struct. Integ. 2018, 13, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olorundaisi, E.; Jamiru, T.; Adegbola, A.T. Mitigating the effect of corrosion and wear in the application of high strength low alloy steels (HSLA) in the petrochemical transportation industry—A review. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 6, 1265k9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamurthy, S.; Atrens, A. Stress corrosion cracking of high-strength steels. Corros. Rev. 2013, 31, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedani, M. Microstructural evolution of tool steels after Nd-YAG laser repair welding. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattire, P.; Paul, S.; Singh, R.; Yan, W. Experimental characterization of laser cladding of CPM 9V on H13 tool steel for die repair applications. J. Manuf. Process. 2015, 20, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leunda, J.; Soriano, C.; Sanz, C.; Navas, V.G. Laser cladding of vanadium-carbide tool steels for die repair. Phys. Procedia 2011, 12, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabeza, M.; Castro, G.; Merino, P.; Penaa, G.; Roman, M. A study of laser melt injection of TiN particles to repair maraging tool steels. Surf. Interface Anal. 2014, 46, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Zou, Z.; Wang, X.; Qu, S. Laser cladding of in situ TiB2/Fe composite coating on steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 6489–6494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, W.; Zhong, N.; Gang, W.; Haishan, W. Microstructure and wear behavior of laser cladding VC-Cr7C3 ceramic coating on steel substrate. Mater. Des. 2013, 49, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Yao, Z.; Tang, H. Microstructure and corrosion resistance of ceramic coating on carbon steel prepared by plasma electrolytic oxidation. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2010, 204, 1685–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, Z.; Gaier, M.; Froning, M.J.; Plucknett, K.P. The aqueous corrosion and wear responses of HVOF-deposited TiC-Ni3Al cermet coatings on AISI 4130 steel substrates. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2023, 473, 130018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, J.; Sasaki, Y.; Fukuhara, S.; Abe, N.; Tukamoto, M. Surface modification of Cr3C2-NiCr cermet coatings by direct diode laser. Vacuum 2006, 80, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zou, B.; Zhao, S.; Hui, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Cai, X.; Cao, X. Fabrication and properties of ZrC-ZrB2/Ni cermet coatings on a magnesium alloy by atmospheric plasma spraying of SHS powders. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 15537–15544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arata, Y.; Kobayashi, A.; Habara, Y. Ceramic coatings produced by means of a gas tunnel-type plasma jet. J. Appl. Phys. 1987, 62, 4884–4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Wu, Y.; Hong, S.; Long, W.; Cheng, J. Wet abrasive wear behavior of WC-based cermet coatings prepared by HVOF spraying. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 1829–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, A.; Hahn, H. Synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline Ni/ZrO2 composite coatings. Nanostruct. Mater. 1999, 12, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouilland-Paille, L.; Ettaqi, S.; Benayoun, S.; Hantzpergue, J.J.J. Structural and mechanical characterization of Ti/TiC cermet coatings synthesized by laser melting. Surf. Coat. Tech. 1997, 88, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Liu, W.; Xiong, H.; Qin, R.; Huang, S.; Zhang, G.; Gao, C. In-situ reaction of Ti-Si-C composite powder and formation mechanism of laser deposited Ti6Al4V/ (TiC+Ti3SiC2) system functionally graded material. Mater. Des. 2019, 183, 108155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Ye, Z.; Ye, G.; He, R.; Wang, H.; Cong, W. The reinforcement mechanisms of graphene oxide in laser-directed energy deposition fabricated metal and ceramic matrix composites: A comparison study. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 119, 1975–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, R.; Meng, C.; Swift, G.A. Sintering properties of submicron TiC powders from carbon coated titania precursor. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 3131–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, T.L.; Plucknett, K.P. The sliding wear of TiC- and Ti(C,N) cermets prepared with a stoichiometric Ni3Al binder. Wear 2014, 318, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantelis, D.I.; Bouyiouri, E.; Kouloumbi, N.; Vassiliou, P.; Koutsomichalis, A. Wear and corrosion resistance of laser surface hardened structural steel. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2002, 161, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, E.; Byrne, G.; Collins, D.N. A review of the use of high power diode lasers in surface hardening. J. Mater. Proc. Tech. 2004, 155–156, 1855–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clare, A.; Oyelola, O.; Folkes, J.; Farayibi, P. Laser cladding for railway repair and preventative maintenance. J. Laser Appl. 2012, 24, 032004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memarrashidi, Z.; Plucknett, K.P. Factors influencing the aqueous corrosion of high performance ceramic-metal composites. J. Mater. Res. 2017, 32, 3333–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plucknett, K.P.; Becher, P.F.; Waters, S.B. Flexure strength of melt-infiltration processed TiC/Ni3Al composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1998, 81, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, Z.; Sparling, W.A.; Stewart, T.L.; Gray, P.; Gaier, M.; Froning, M.J.; Mazzanti, G.; Plucknett, K.P. Gelation-based feed-stock technologies for HVOF thermal spray development: Micro-composite powder preparation and HVOF coating microstructure. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2023, 452, 129089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.R.; Li, X.X.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Cao, Y. Microstructure and characterizations of one-step forming TiC/Ni3Al–Ni3Al multicoating on 316L stainless steel. Powder Metall. 2016, 59, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Pai, N.; Rosenkran, A.; Shirvan, K.; Marian, M. Review: Tribological behavior of additively manufactured metal components. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2022, 6, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, R.B.; Plucknett, K.P. A comparison of anionic and cationic polyelectrolytes for the aqueous colloidal processing of titanium carbide ceramics. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2011, 29, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyserkani, E.; Khajepour, A.; Corbin, S.F. Laser Cladding; CRC Press LLC.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sreekanth, S.; Ghassemali, E.; Hurtig, K.; Joshi, S.; Andersson, J. Effect of direct energy deposition process parameters on single-track deposits of alloy 718. Metals 2020, 10, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.D.; Peng, Y. Melt pool shape and dilution of laser cladding with wire feeding. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2000, 104, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Shen, Y. Effects of processing parameters on consolidation and microstructure of W-Cu components by DMLS. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 473, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E2546-15; Standard Practice for Instrumented Indentation Testing. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- ASTM G171-03; Standard Test Method for Scratch Hardness of Materials Using a Diamond Stylus. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009.
- ASTM C1624-05; Standard Test Method for Adhesion Strength and Mechanical Failure Modes of Ceramic Coatings by Quantitative Single Point Scratch Testing. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- ISO 27307-15; Thermal Spraying, Evaluation of Adhesion/Cohesion of Thermal Sprayed Ceramic Coatings by Transverse Scratch Testing. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/51692.html (accessed on 7 March 2025).
- Bull, S.J.; Berasetegui, E.G. An overview of the potential of quantitative coating adhesion measurement by scratch testing. Tribol. Int. 2006, 39, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, L.; Fortunato, A.; Ceschini, L. CoCr alloy processed by selective laser melting (SLM): Effect of laser energy density on microstructure, surface morphology, and hardness. J. Manuf. Proc. 2020, 52, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, K.; Zhang, D.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Liu, W.; Shen, Z. Textures formed in a CoCrMo alloy by selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 631, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadolkar, P.; Dahotre, N.B. Variation of structure with input energy during laser surface engineering of ceramic coatings on aluminum alloys. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 199, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chande, T.; Mazumder, J. Estimating effects of processing conditions and variable properties upon pool shape, cooling rates, and absorption coefficient in laser welding. J. Appl. Phys. 1984, 56, 1981–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.S.; Chen, C.Z.; Chen, L.B.; Chen, L.X. Study on the microstructure and wear resistance of the composite coatings fabricated on Ti-6Al-4V under different processing conditions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 253, 1494–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaier, M.; Todorova, T.Z.; Russell, Z.; Farhat, Z.N.; Zwanziger, J.W.; Plucknett, K.P. The influence of intermetallic ordering on wear and indentation properties of TiC-Ni3Al cermets. Wear 2019, 426–427, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Qiu, F.; Jin, S.; Jiang, Q. High room-temperature plastic and work-hardening effect of the NiAl-matrix composites reinforced by particulates. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weertman, J.R.; Farkas, D.; Hemker, K.; Kung, H.; Mayo, M.; Mitra, R.; Van Swygenhoven, H. Structure and mechanical behavior of bulk nanocrystalline materials. MRS Bull. 1999, 24, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzakis, K.D.; Asimakopoulos, A.; Michailidis, N.; Kompogiannis, S.; Maliaris, G.; Giannopoulos, G.; Pavlidou, E.; Erkens, G. The inclined impact test, an efficient method to characterize coatings’ cohesion and adhesion properties. Thin Solid Films 2004, 469–470, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacombe, R. Adhesion Measurement Methods; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vencl, A.; Arostegui, S.; Favaro, G.; Zivic, F.; Mrdak, M.; Mitrović, S.; Popovic, V. Evaluation of adhesion/cohesion bond strength of the thick plasma spray coatings by scratch testing on coatings cross-sections. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


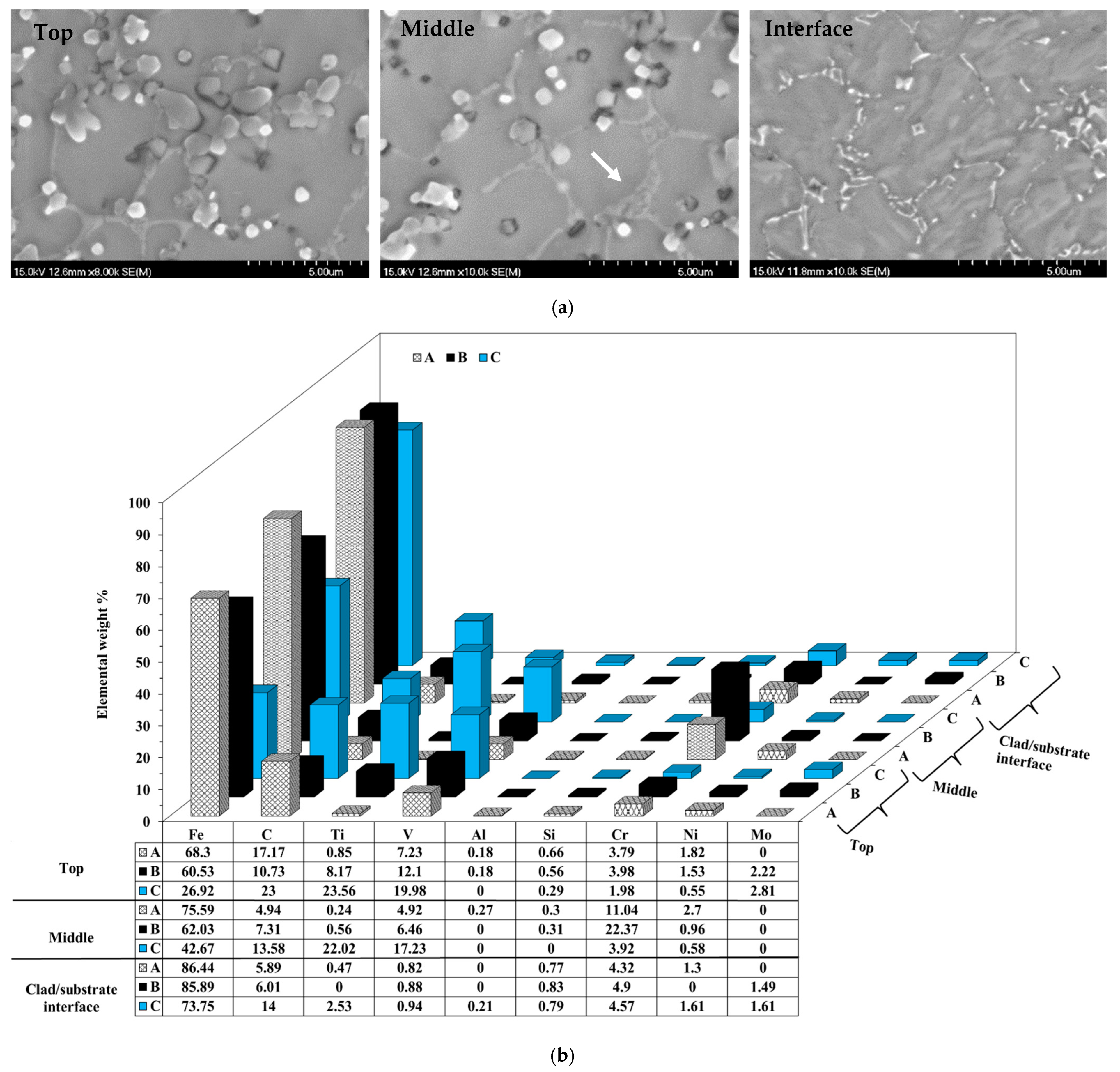
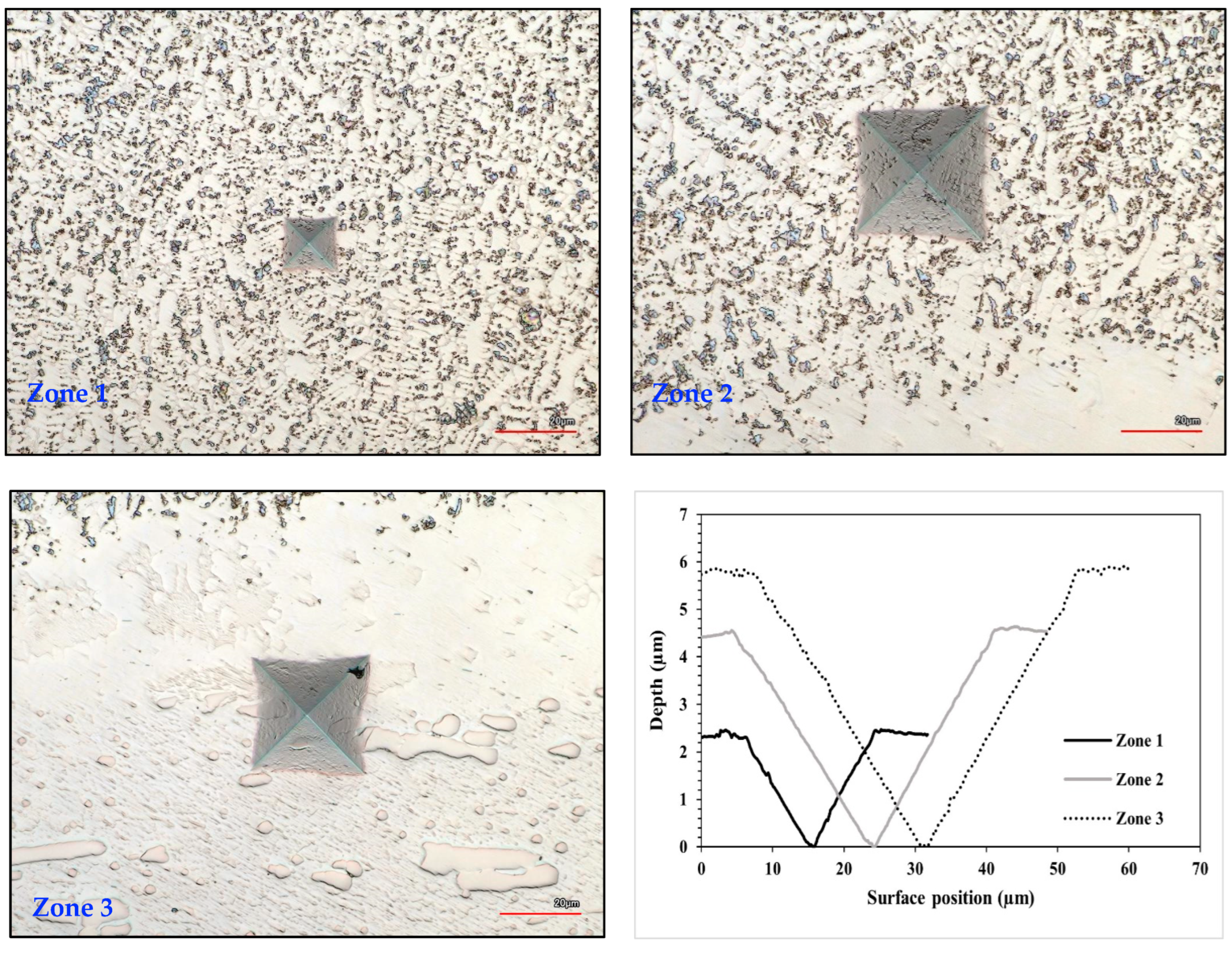
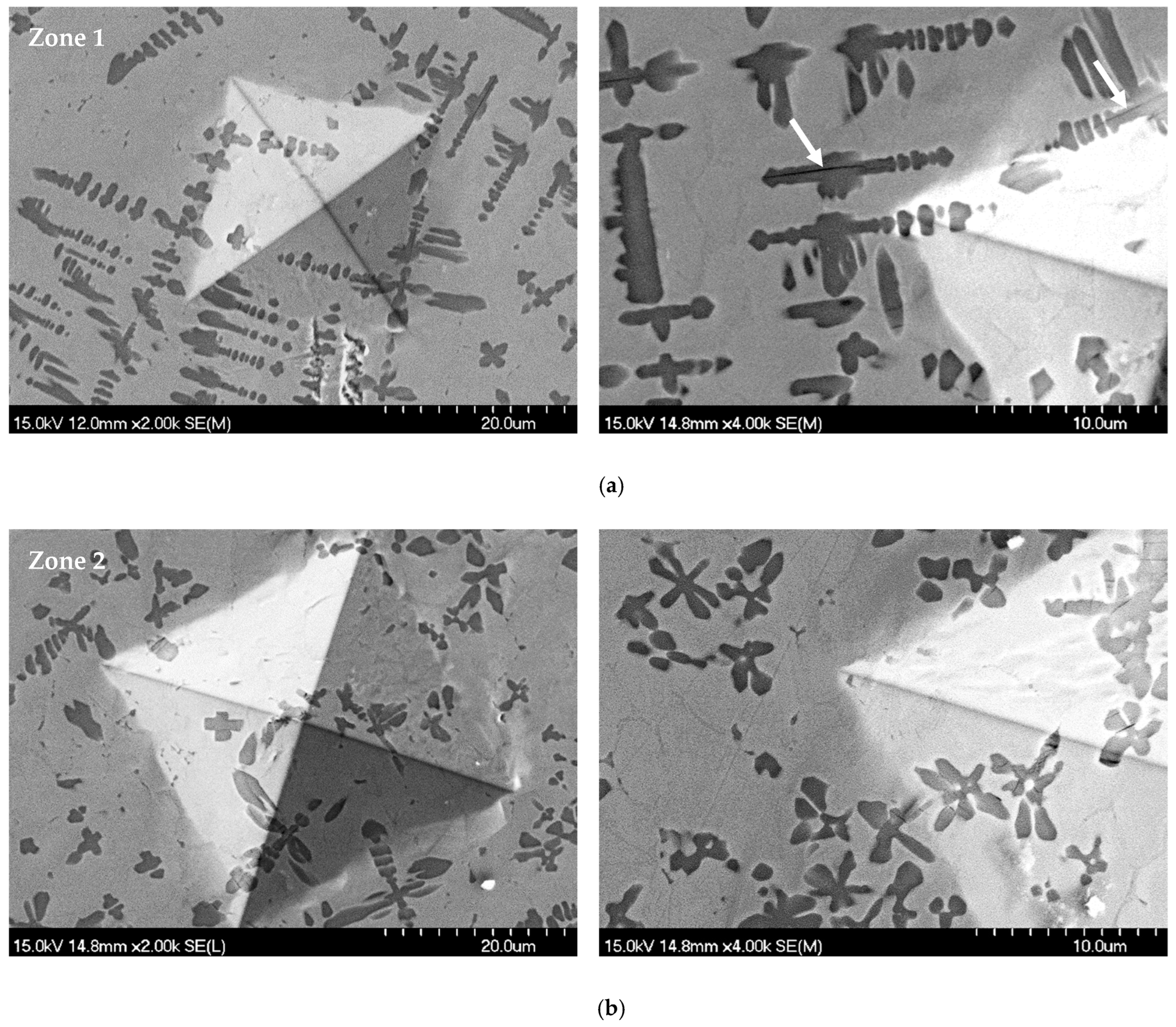
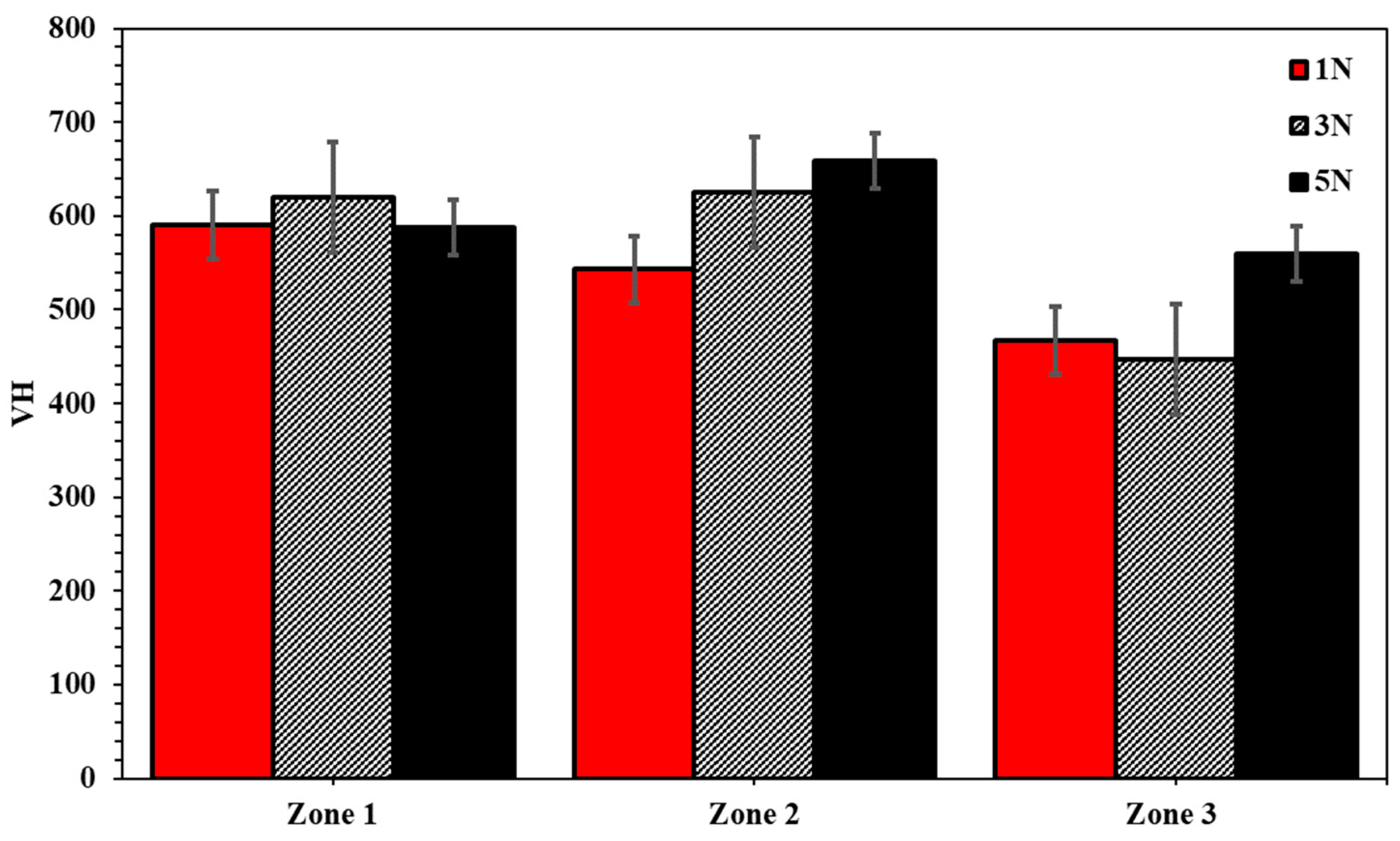


| Composition | Processing Technique | Hardness | Thickness (µm) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr3C2/25% Ni–Cr | High-velocity oxyfuel (HVOF), direct diode laser | HV 1032 | [12] | |
| ZrB2–ZrC/Ni | Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS), atmospheric plasma spraying (APS) | HV0.1 525.02 (±96.08) | ~200 to 300 | [13] |
| Al2O3 | Gas tunnel-type plasma jet | HV 1200 | ~100 to 150 | [14] |
| WC–Cr3C2/Ni and WC/Ni | HVOF | HV0.3 1188 and 1105 | 320 to 370 | [15] |
| Ni/ZrO2 | Electroplating | HV25 260 to 600 | Not given | [16] |
| Ti/TiC | Laser melting (LM) | HV 700 | 100 to 250 before HAZ | [17] |
| Ti/SiC | Laser deposition (LD) | HV 647.5 | ~150 hard layer (HAZ to 400) | [18] |
| Graphene oxide/TiC | Powder-fed laser deposition (PFLD) | HV0.1 250–350 | 432 per layer (10 layers) | [19] |
| TiC/20 wt.% Ni (bulk) | Sintering | HV 219 to 1295 | Not applicable | [20] |
| TiC/20 vol.% Ni3Al (bulk) | Vacuum sintering | HV5 1260 | Not applicable | [21] |
| Clad Component Compositions | Compositional wt.% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| TiC | NiAl | Ni | |
| TiC-30 vol.% Ni3Al | 60.23 | 5.26 | 14.53 |
| TiC-40 vol.% Ni3Al | 51.62 | 13.91 | 38.44 |
| TiC-50 vol.% Ni3Al | 43.02 | 17.39 | 48.05 |
| C | Cr | Mo | V | Mn | Si | Fe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AISI D2 Tool Steel | 1.55 | 12 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.35 | 0.25 | Balance |
| Indenter Poisson ratio | 0.7 | ||
| Indenter elastic modulus (GPa) | 1140 | ||
| Sample Poisson ratio | 0.238 | ||
| Applied force | 1 N | 3 N | 5 N |
| Loading/unloading rate (µm/s) | 15 | 30 | 70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Russell, Z.; Amegadzie, M.Y.; David, A.M.S.; Plucknett, K.P. Scratch Resistance and Damage Mechanisms Arising in Titanium Carbide–Nickel Aluminide-Based Laser DED Clads on D2 Tool Steel. Coatings 2025, 15, 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15030330
Russell Z, Amegadzie MY, David AMS, Plucknett KP. Scratch Resistance and Damage Mechanisms Arising in Titanium Carbide–Nickel Aluminide-Based Laser DED Clads on D2 Tool Steel. Coatings. 2025; 15(3):330. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15030330
Chicago/Turabian StyleRussell, Zhila, Mark Yao Amegadzie, Achilles Marian Sonica David, and Kevin Paul Plucknett. 2025. "Scratch Resistance and Damage Mechanisms Arising in Titanium Carbide–Nickel Aluminide-Based Laser DED Clads on D2 Tool Steel" Coatings 15, no. 3: 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15030330
APA StyleRussell, Z., Amegadzie, M. Y., David, A. M. S., & Plucknett, K. P. (2025). Scratch Resistance and Damage Mechanisms Arising in Titanium Carbide–Nickel Aluminide-Based Laser DED Clads on D2 Tool Steel. Coatings, 15(3), 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15030330






