Physical Properties and Rheological Characteristics of Cigarette Butt-Modified Asphalt Binders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Asphalt
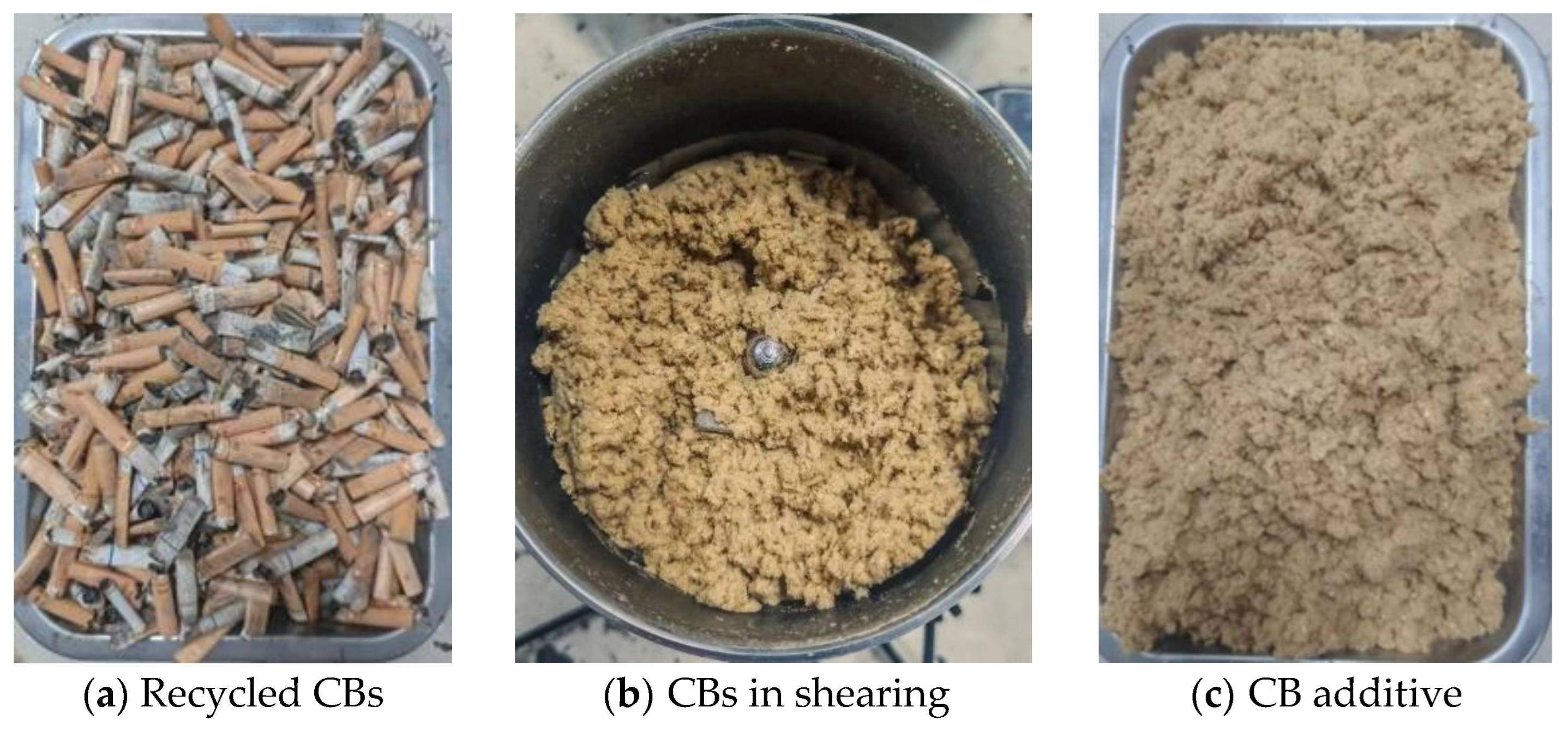
2.1.2. Preparation of CB Modifier
2.1.3. Preparation of CB-Modified Asphalt Binder
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Physical Property Tests
2.2.2. Viscosity Test
2.2.3. Storage Stability Test
2.2.4. Temperature Sweep Test
2.2.5. Frequency Sweep Test
3. Results and Discussion
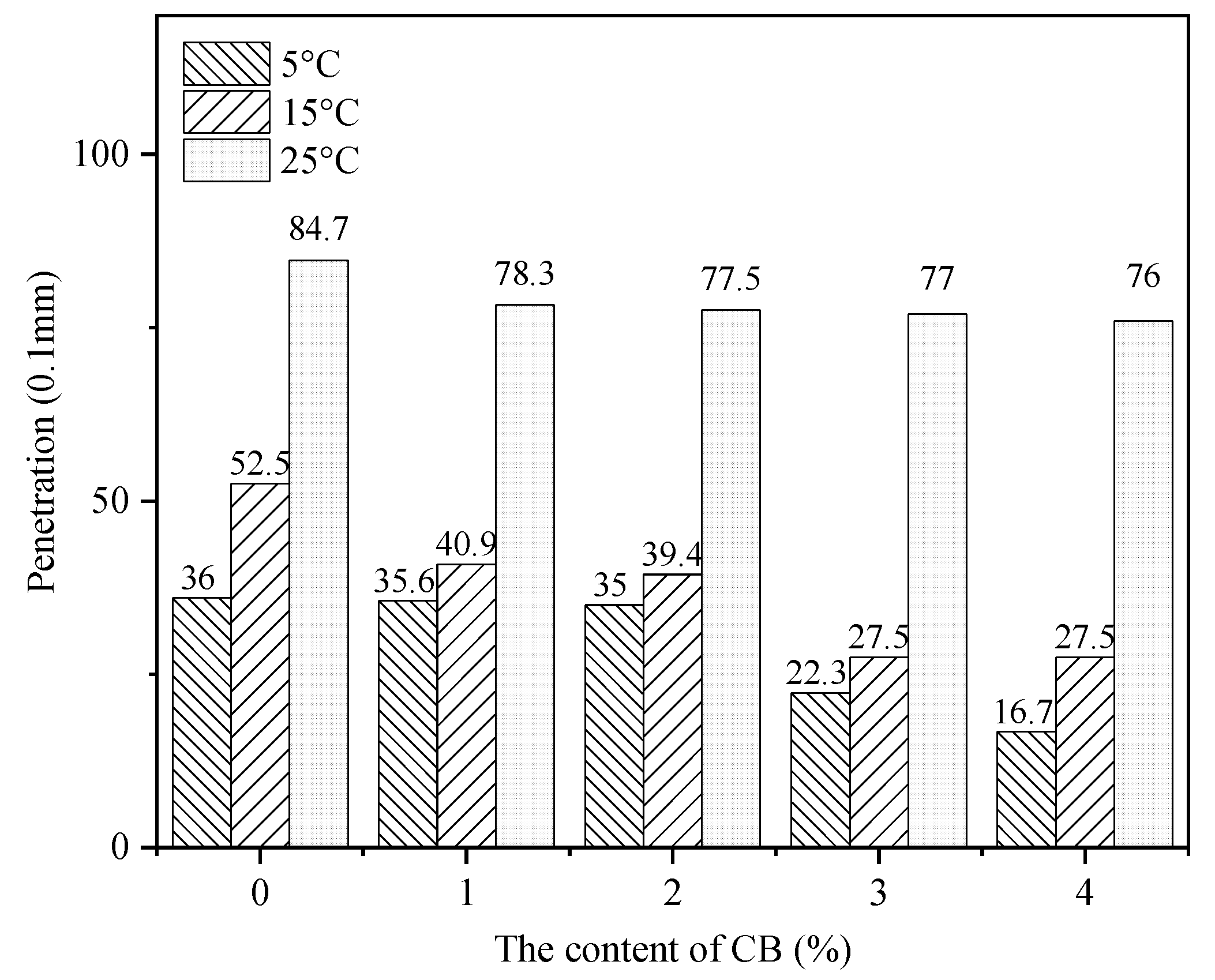
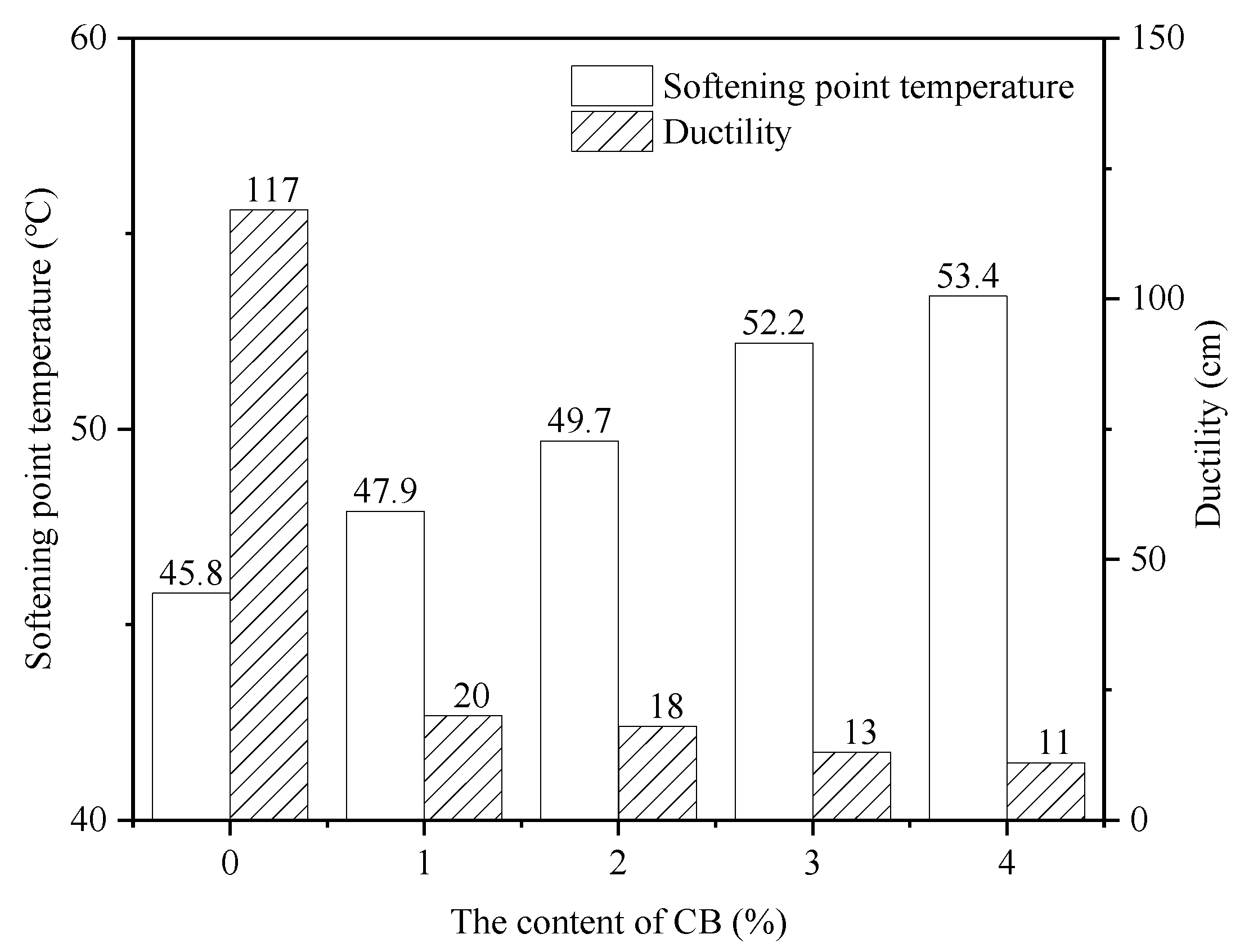
3.1. Physical Properties
3.2. Brinell Viscosity
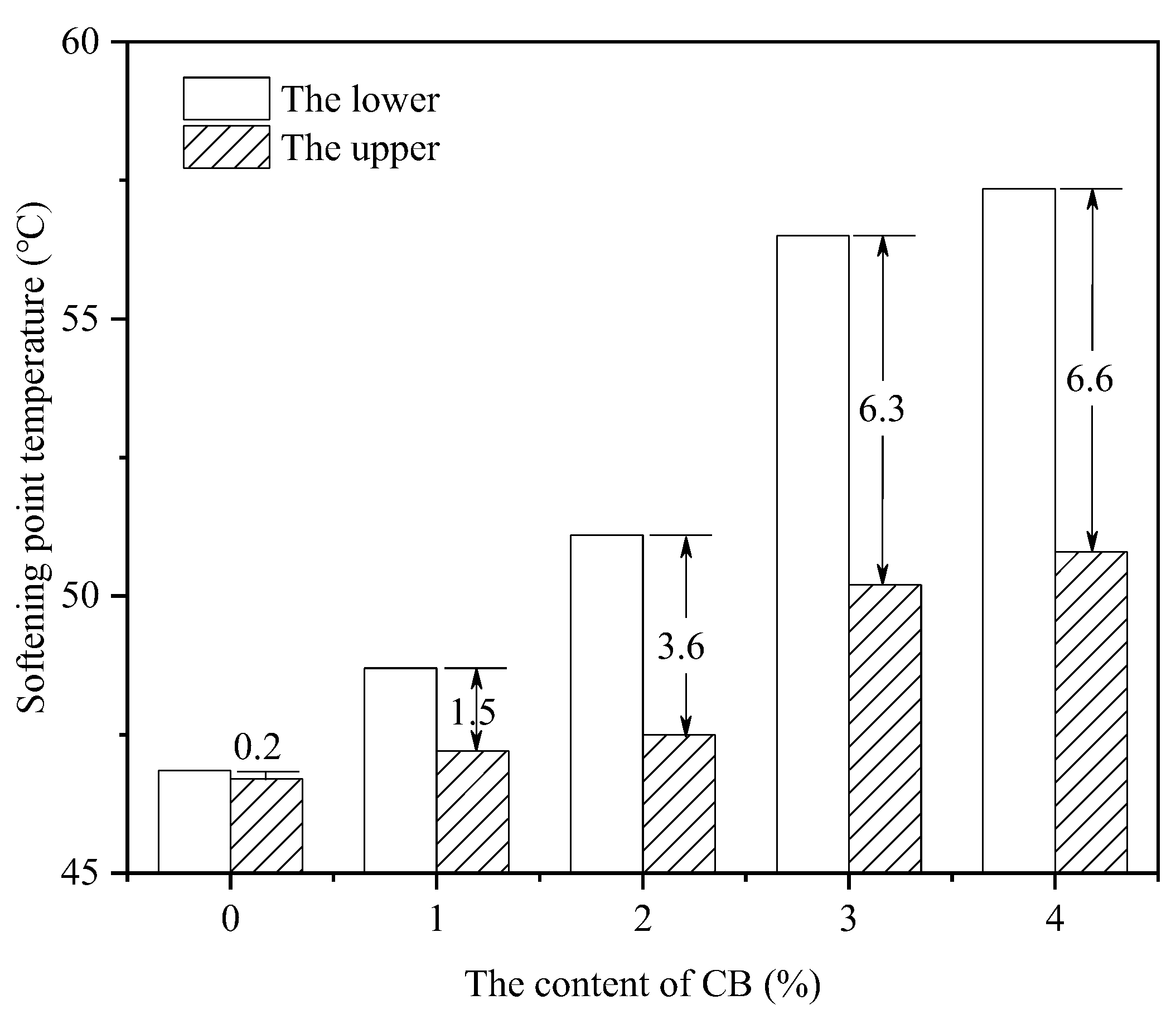
3.3. Storage Stability
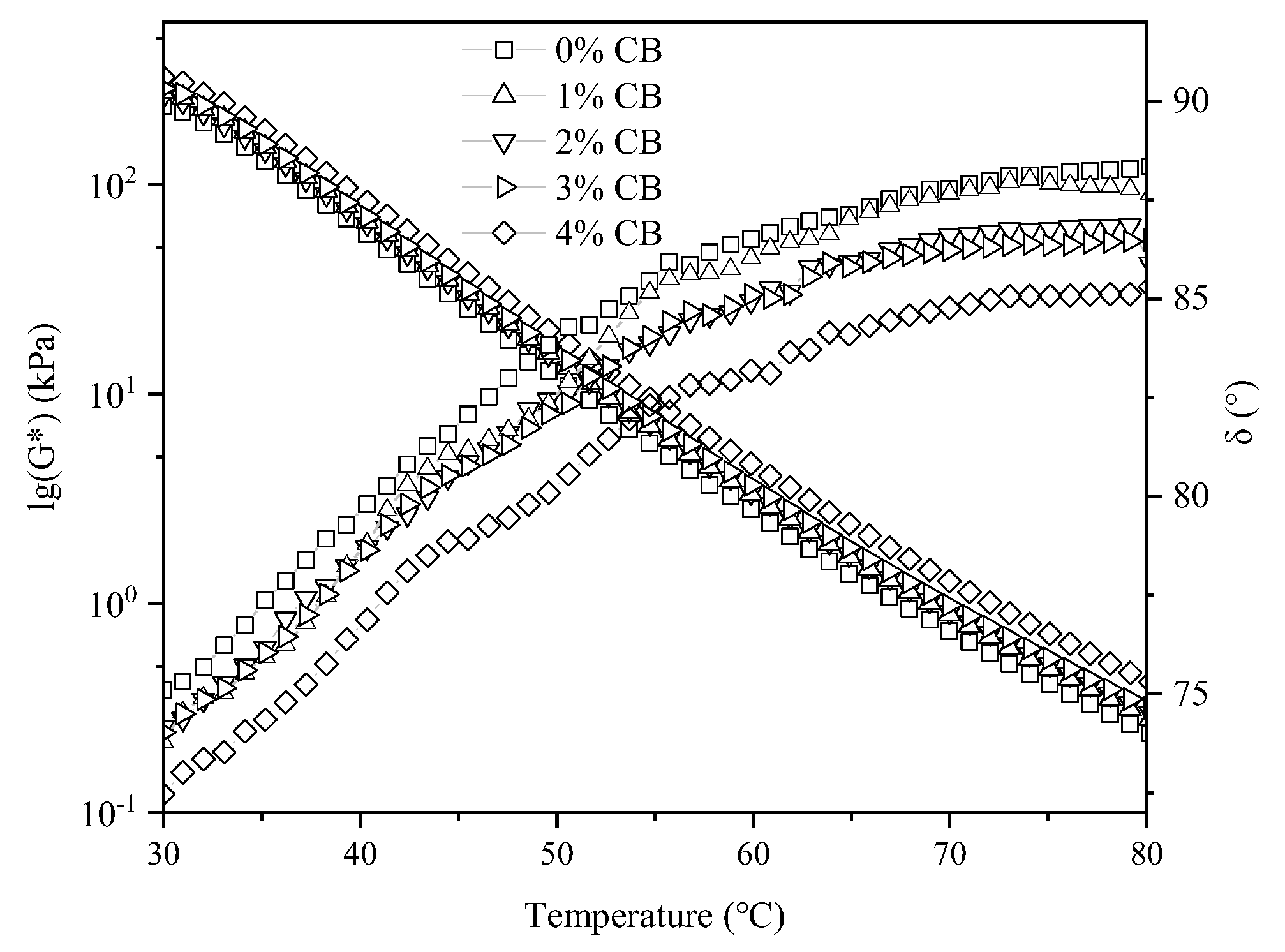
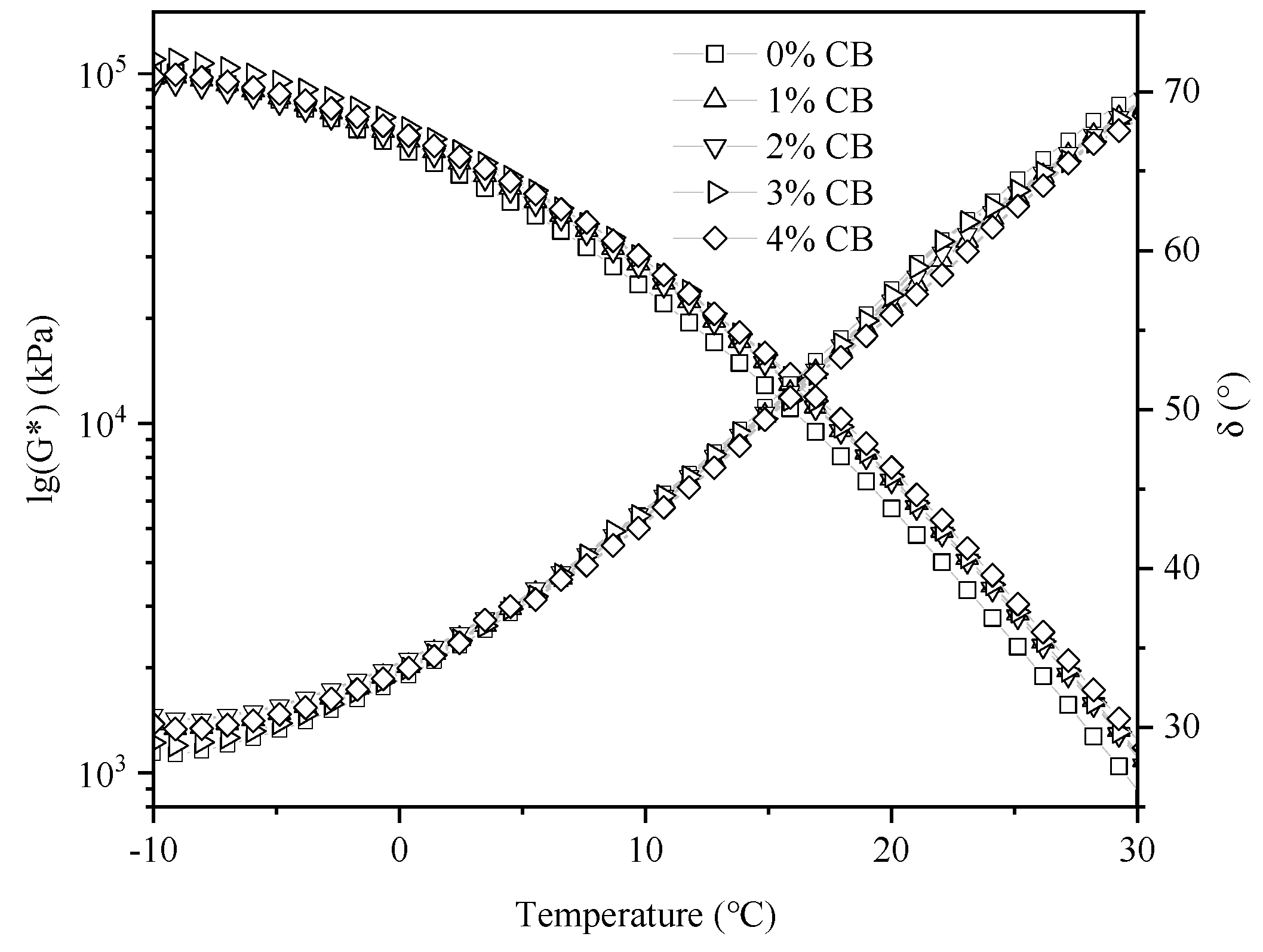
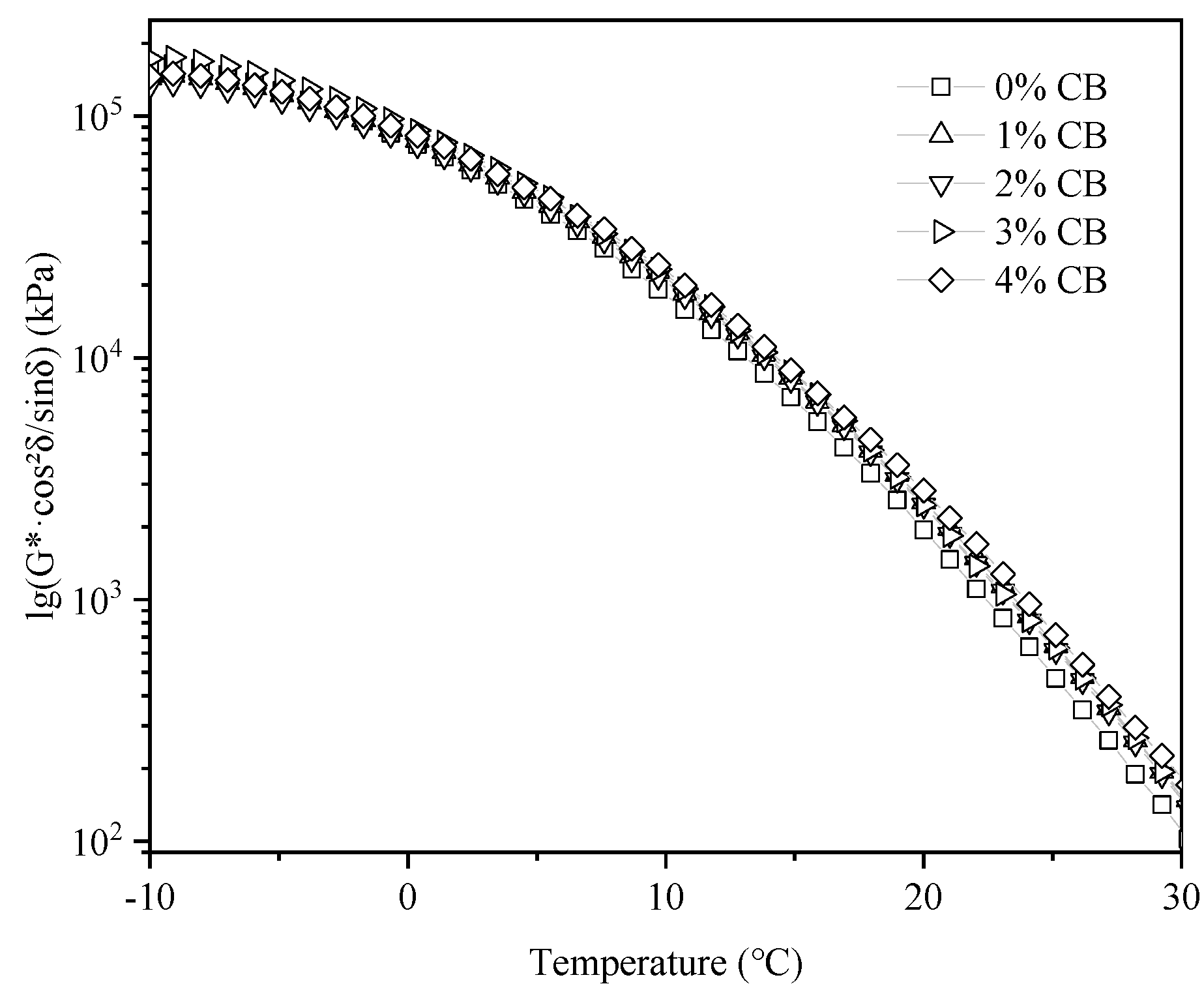
3.4. Temperature Sweep Tests
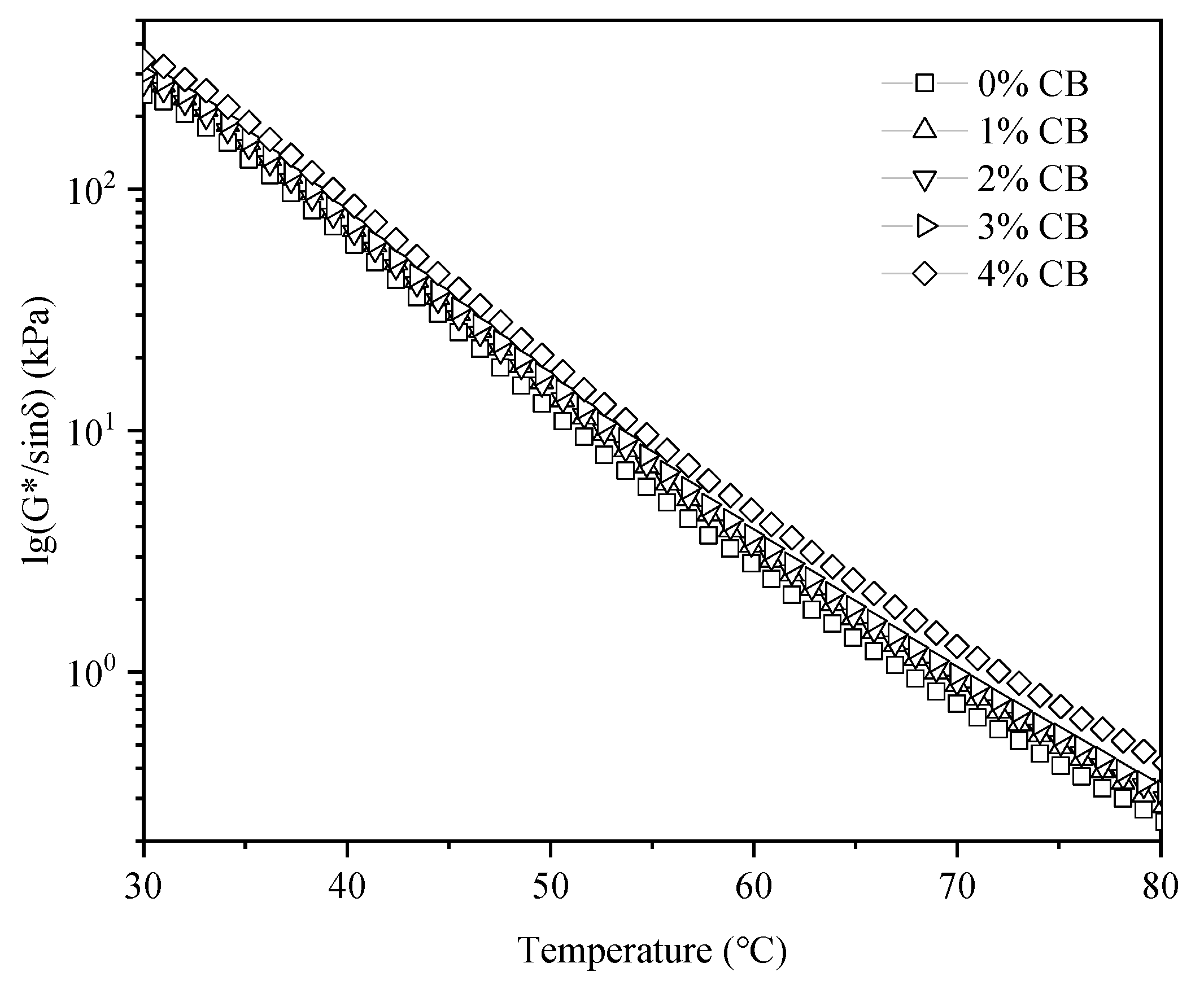
3.5. Frequency Sweep Test
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The cellulose acetate fibers in CBs can add consistency and hardness to asphalt. With the increase in the CB content in the asphalt mixtures, the penetration value of the CB-modified asphalt adhesive decreased, the softening point increased, the ductility dropped significantly, and the viscosity increased, leading to poorer storage stability. CBs enhanced the shear resistance and high-temperature stability of the asphalt binder but reduced its low-temperature crack resistance and storage stability.
- (2)
- CBs can enhance the high-temperature stability of asphalt binders but reduce their low-temperature stability. At the same temperature, as the CB content increased, the G* of the modified asphalt binder gradually increased, indicating a higher proportion of elastic components in the modified asphalt and an improved resistance to deformation. The G* of the modified asphalt also showed an upward trend with the increasing loading frequency, suggesting that the asphalt’s resistance to deformation improved with the increase in the loading frequency.
- (3)
- This study provides a reference for applying CB-modified asphalt. Recycling CBs contributes to environmental protection and promotes recycling efforts. However, when the content of CBs reaches 2%, the storage stability of the modified asphalt fails to meet the requirements of the Chinese standard JTG F40-2004 for SBS-modified asphalt. Further research is needed to improve the storage stability and low-temperature stability of CB-modified asphalt mixtures.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Q&A: World No Tobacco Day 2022: Q&A. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/q-a-world-no-tobacco-day-2022 (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment, PRC. Bulletin on the State of China’s Marine Ecological Environment; Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2023.
- Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Xue, Y. Reutilization of recycled cellulose diacetate from discarded cigarette filters in production of stone mastic asphalt mixtures. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 770150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, F.X.; Coulis, M. Comparison of cellulose vs. plastic cigarette filter decomposition under distinct disposal environments. Waste Manag. 2018, 72, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleimani, F.; Dobaradaran, S.; De-la-Torre, G.E.; Schmidt, T.C.; Saeedi, R. Content of toxic components of cigarette, cigarette smoke vs. cigarette butts: A comprehensive systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 152667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroz, I.; Scapolio, L.G.B.; Cesarino, I.; Leão, A.L.; Bonanomi, G. Toxicity of cigarette butts and possible recycling solutions—A literature review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 10450–10473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaughter, E.; Gersberg, R.M.; Watanabe, K.; Rudolph, J.; Stransky, C.; Novotny, T.E. Toxicity of cigarette butts, and their chemical components, to marine and freshwater fish. Tob. Control 2011, 20 (Suppl. 1), i25–i29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobaradaran, S.; Soleimani, F.; Akhbarizadeh, R.; Schmidt, T.C.; Marzban, M.; BasirianJahromi, R. Environmental fate of cigarette butts and their toxicity in aquatic organisms: A comprehensive systematic review. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, M.B.D.H.; Duarte, M.A.B.; Garcez, L.R.; Rubim, J.C.; Gatti, T.H.; Suarez, P.A.Z. Prcess development for cigarette butts recycling into cellulose pulp. Waste Manag. 2017, 60, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamzah, Y.; Umar, L. Preparation of creating active carbon from cigarette filter waste using microwave-induced KOH activation. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 853, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maderuelo-Sanz, R.; Escobar, V.G.; Meneses-Rodríguez, J.M. Potential use of cigarette filters as sound porous absorber. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 129, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajerani, A.; Kadir, A.A.; Larobina, L. A practical proposal for solving the world’s cigarette butt problem: Recycling in fired clay bricks. Waste Manag. 2016, 52, 228–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, D.; Djordjevic, M.V.; Brunnemann, K.D. Changes in cigarette design and composition over time and how they influence the yields of smoke constituents. J. Smok. Relat. Disord. 1995, 6, 9–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, D.; Hoffman, I.; El-Bayoumy, K. The less harmful cigarette: A controversial issue. A tribute to Ernst L. Wynder. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2001, 14, 767–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, D.H.I. The changing cigarette, 1950–1995. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 1997, 50, 307–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novotny, T.E.; Hardin, S.N.; Hovda, L.R.; Novotny, D.J.; McLean, M.K.; Khan, S. Tobacco and cigarette butt consumption in humans and animals. Tob. Control 2011, 20 (Suppl. 1), i17–i20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, R.L. Regulating the disposal of cigarette butts as toxic hazardous waste. Tob. Control. 2011, 20 (Suppl. 1), i45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimei, J.; Wu, Z.; Song, J.; Liu, X. Research on the road performance of cigarette butts modified asphalt mixture. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1168, 022053. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.T.; Mohajerani, A. Thermal conductivity and environmental aspects of cigarette butt modified asphalt. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajerani, A.; Tanriverdi, Y.; Nguyen, B.T.; Wong, K.K.; Dissanayake, H.N.; Johnson, L.; Whitfield, D.; Thomson, G.; Alqattan, E.; Rezaei, A. Physico-mechanical properties of asphalt concrete incorporated with encapsulated cigarette butts. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 153, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tareq Rahman, M.; Mohajerani, A. Recycling waste cigarette butts in dense graded asphalt. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2021, 33, 04021313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tataranni, P.; Sangiorgi, C. A preliminary laboratory evaluation on the use of shredded cigarette filters as stabilizing fibers for stone mastic asphalts. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlawat, Y.; Bhardawaj, A.; Bhardwaj, R. An experimental study on the stability and flow characteristics of mastic asphalt mix using cigarette butt additive. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 65, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG E20-2011; Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering. China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Rahman, M.T.; Mohajerani, A.; Giustozzi, F. Possible use of cigarette butt fiber modified bitumen in stone mastic asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 263, 120134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T.; Mohajerani, A.; Giustozzi, F. Possible recycling of cigarette butts as fiber modifier in bitumen for asphalt concrete. Materials 2020, 13, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Ddong, Z.; Tan, Y.; Liu, Z.Y. Investigating the interactions of the saturate, aromatic, resin, and asphaltene four fractions in asphalt binders by molecular simulations. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG F40-2004; Technical Specifications for Construction of Highway Asphalt Pavements. China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2004.




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, X.; Chen, X.; Yu, J.; Cheng, G.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, L. Physical Properties and Rheological Characteristics of Cigarette Butt-Modified Asphalt Binders. Coatings 2025, 15, 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15020170
Hu X, Chen X, Yu J, Cheng G, Yuan Y, Zhang L. Physical Properties and Rheological Characteristics of Cigarette Butt-Modified Asphalt Binders. Coatings. 2025; 15(2):170. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15020170
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Xinhe, Xianglong Chen, Jie Yu, Gang Cheng, Yunxiao Yuan, and Lizhou Zhang. 2025. "Physical Properties and Rheological Characteristics of Cigarette Butt-Modified Asphalt Binders" Coatings 15, no. 2: 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15020170
APA StyleHu, X., Chen, X., Yu, J., Cheng, G., Yuan, Y., & Zhang, L. (2025). Physical Properties and Rheological Characteristics of Cigarette Butt-Modified Asphalt Binders. Coatings, 15(2), 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15020170




