Thermodynamic Analysis of Wetting Transitions on Micro/Nanopillared Superhydrophobic Surfaces
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
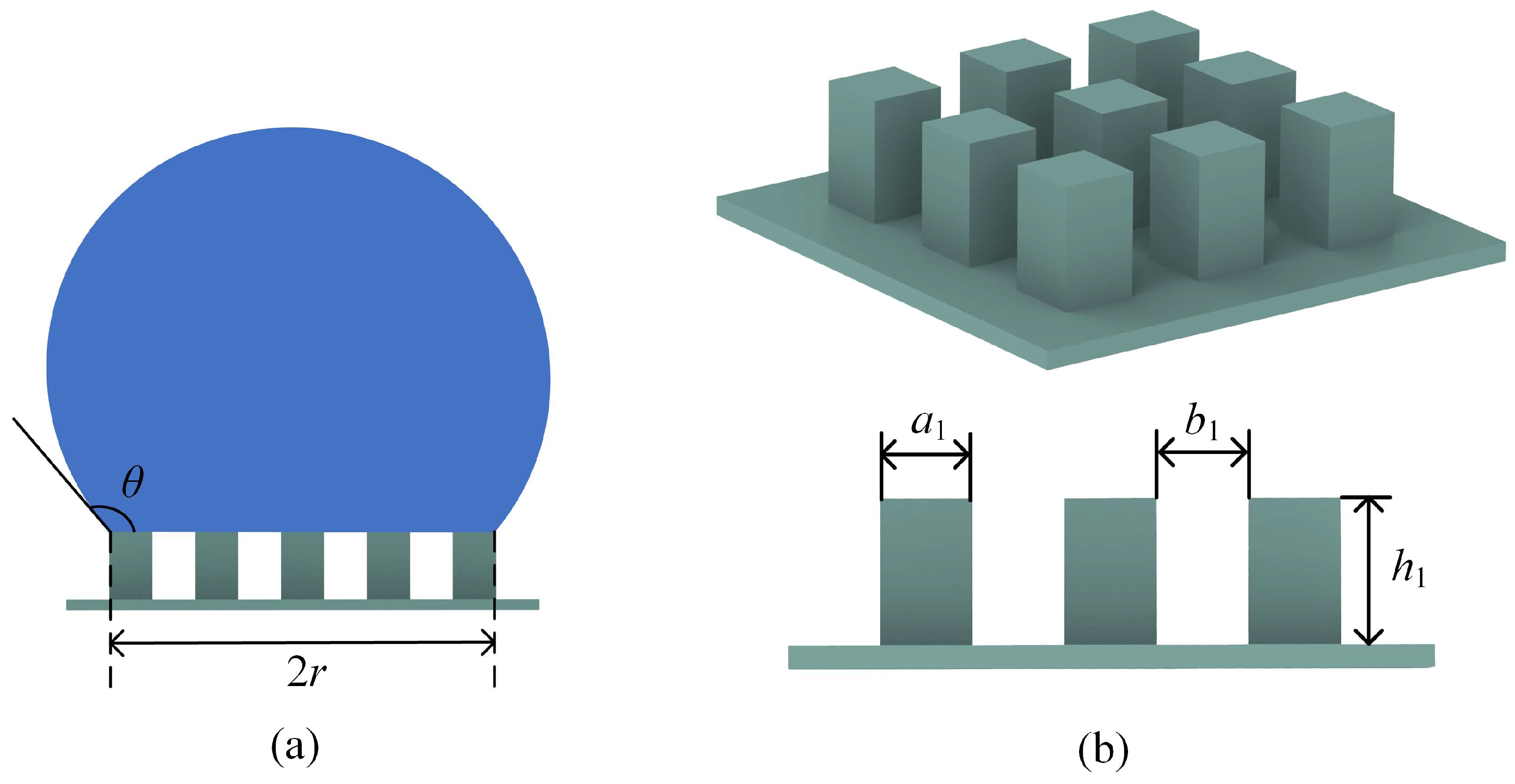
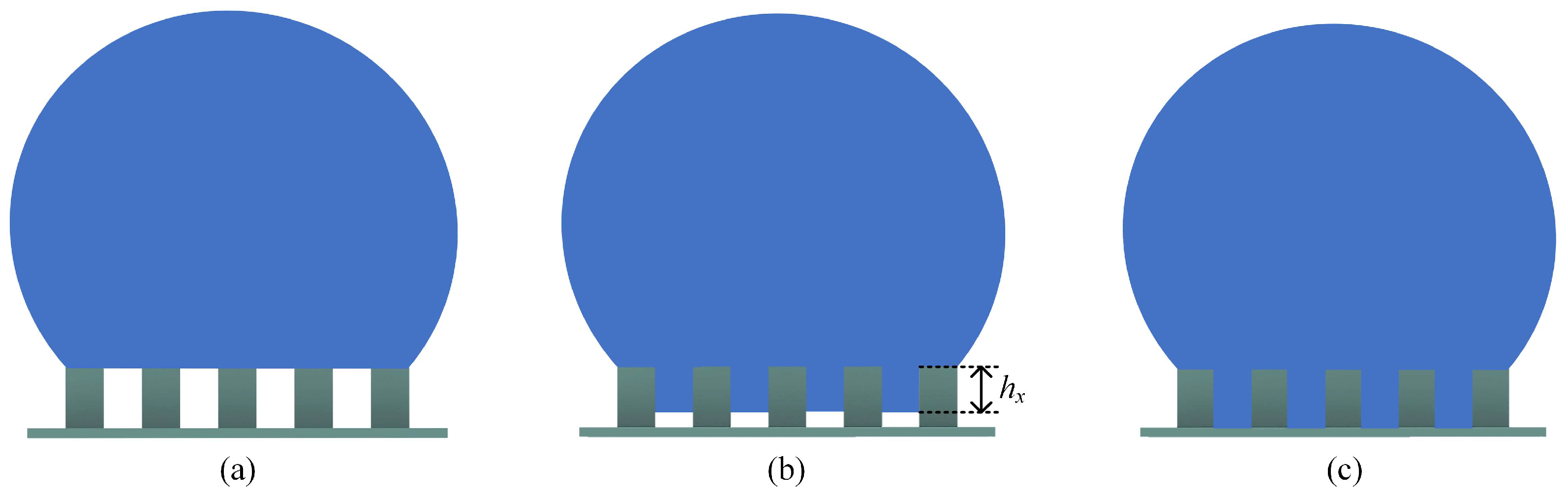
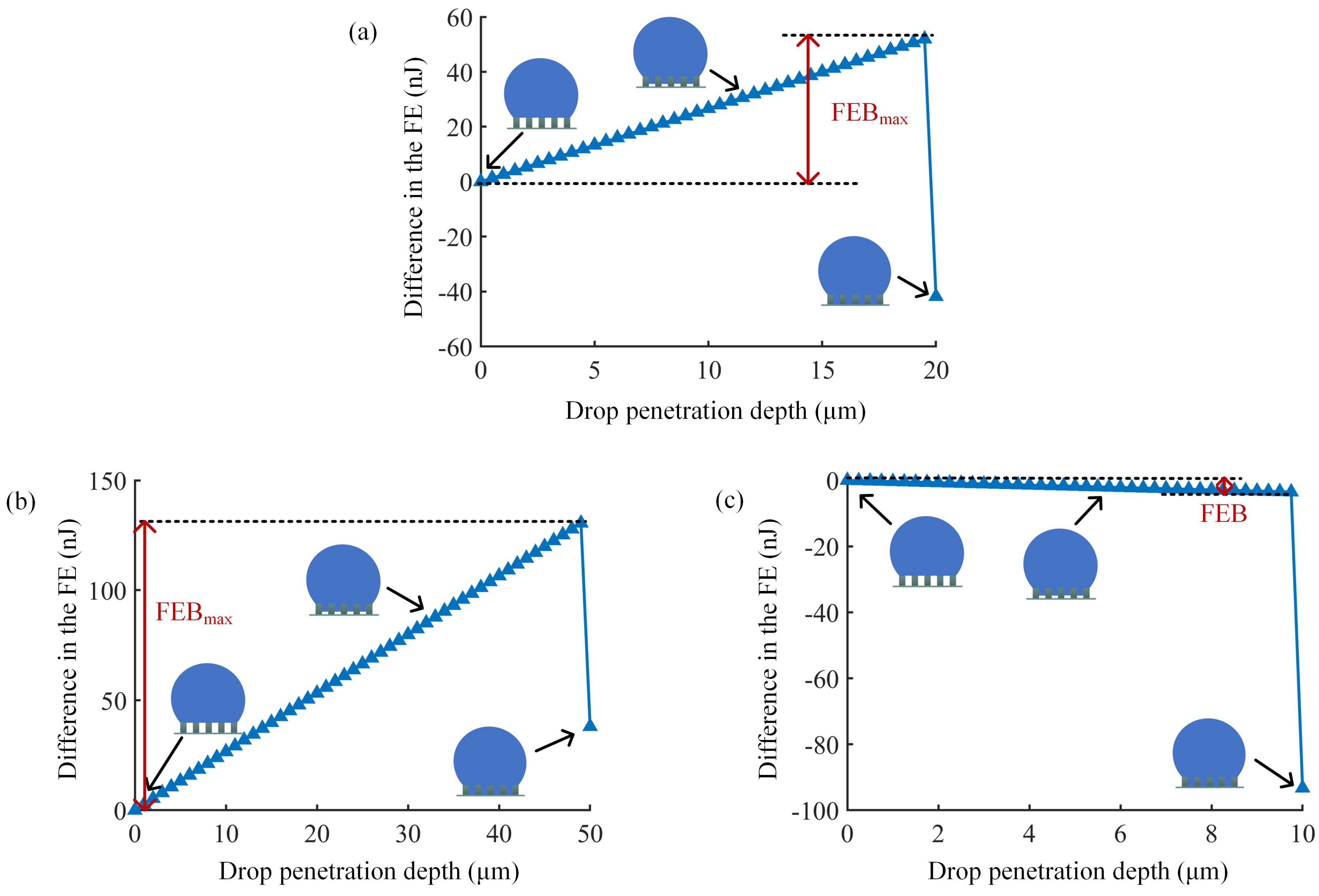
3.1. Three Typical Cases of Wetting Transition
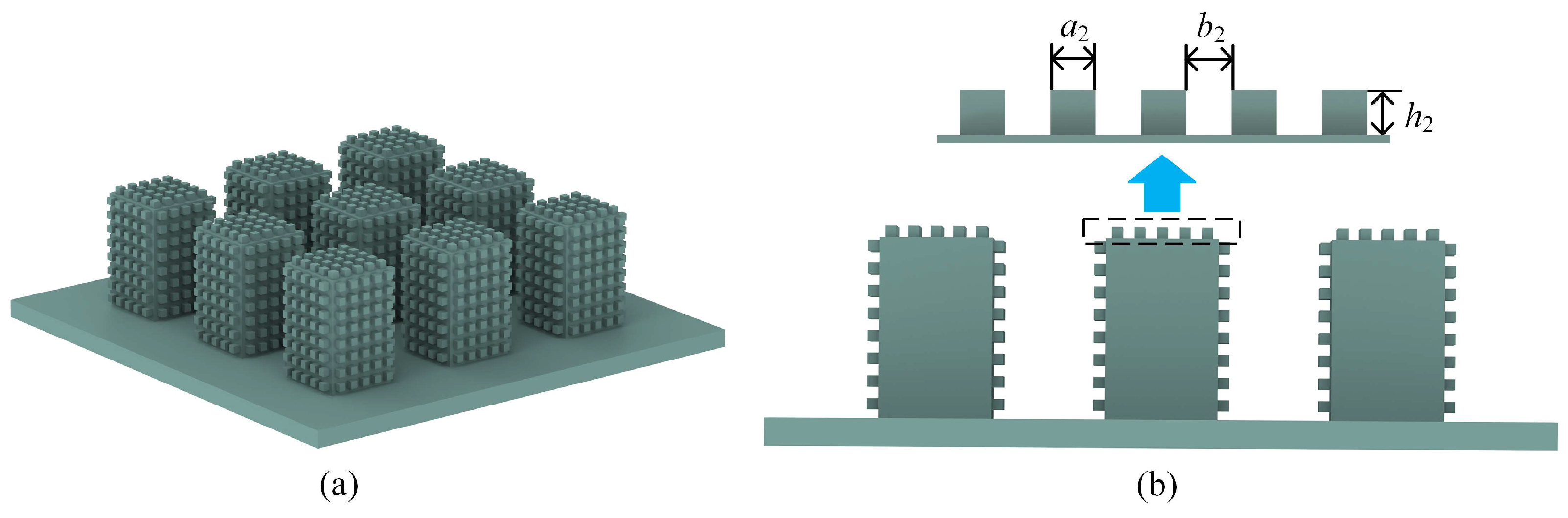
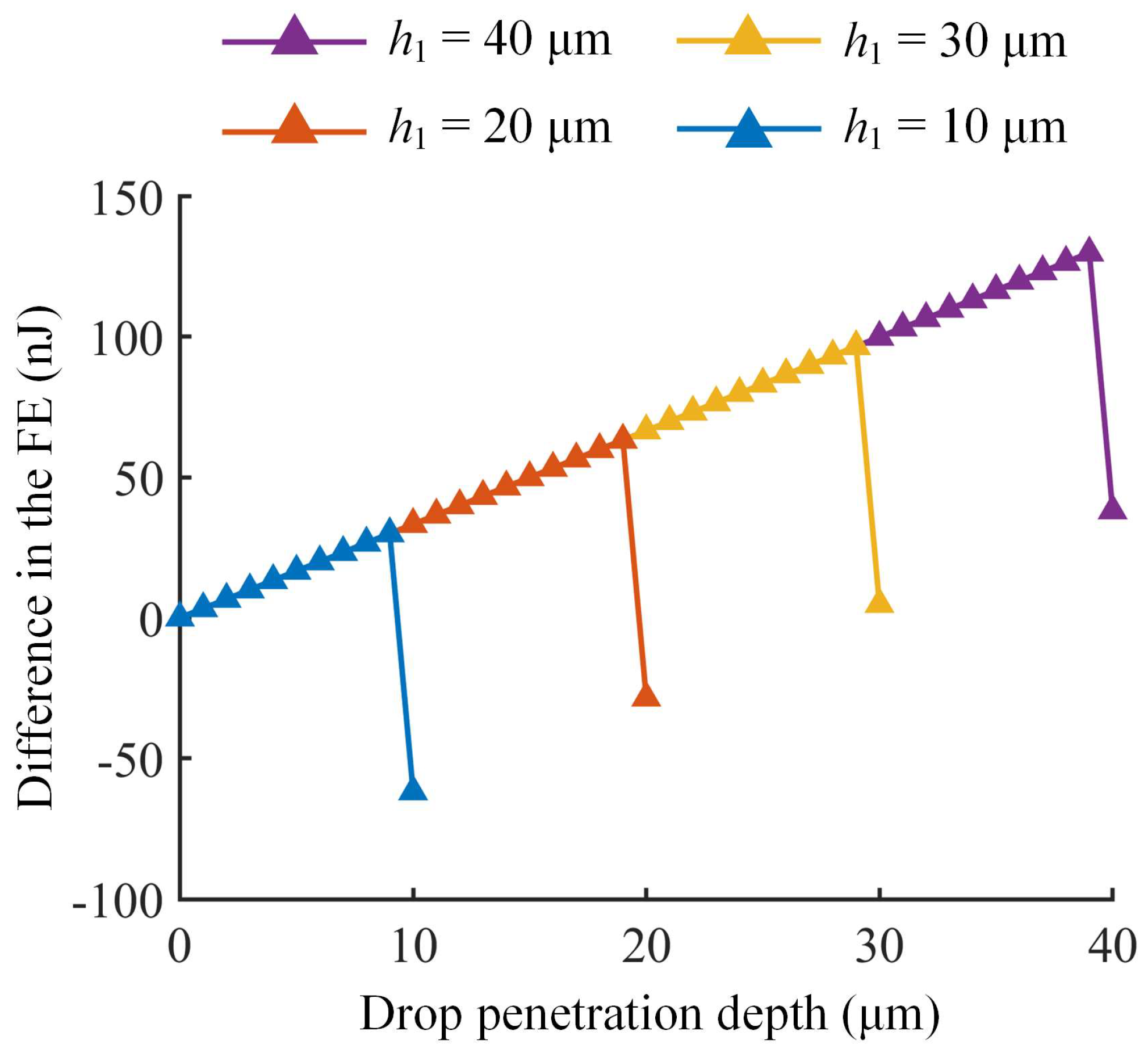
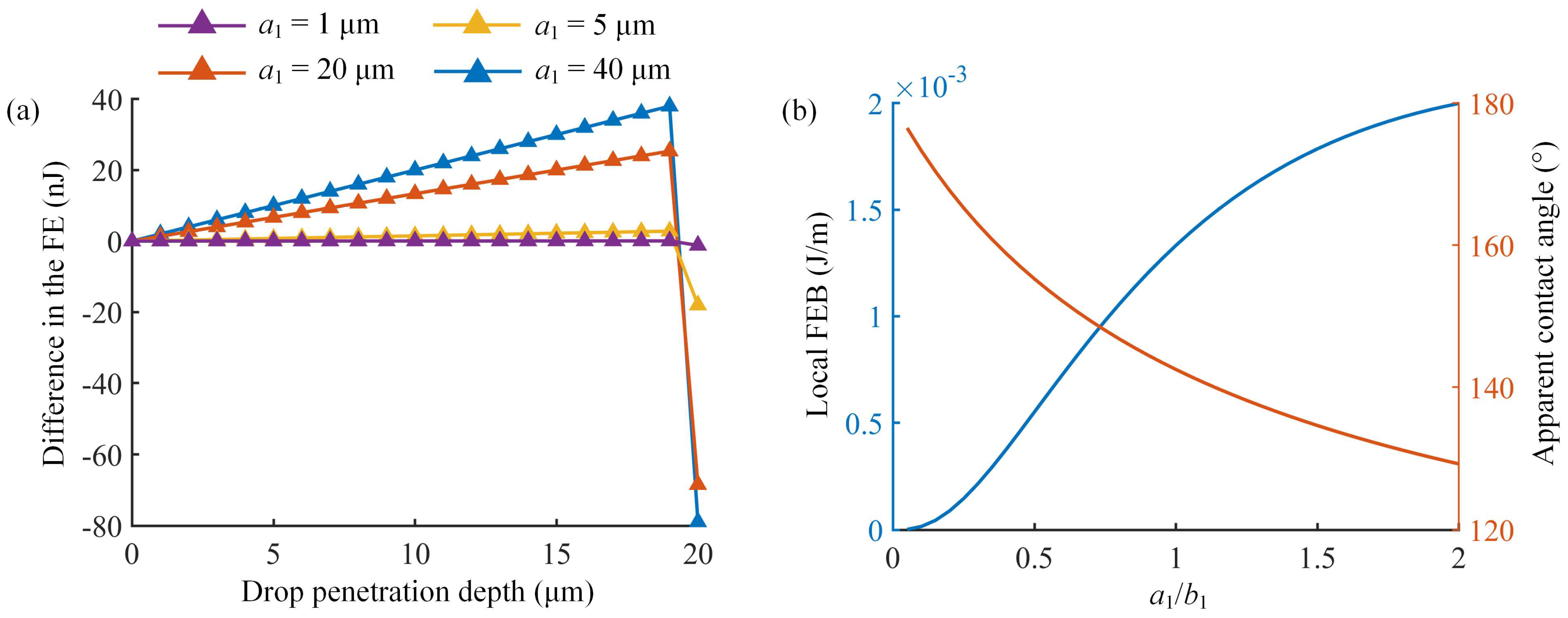
3.2. Influence of Micropillar Structural Parameters on C–W Transitions
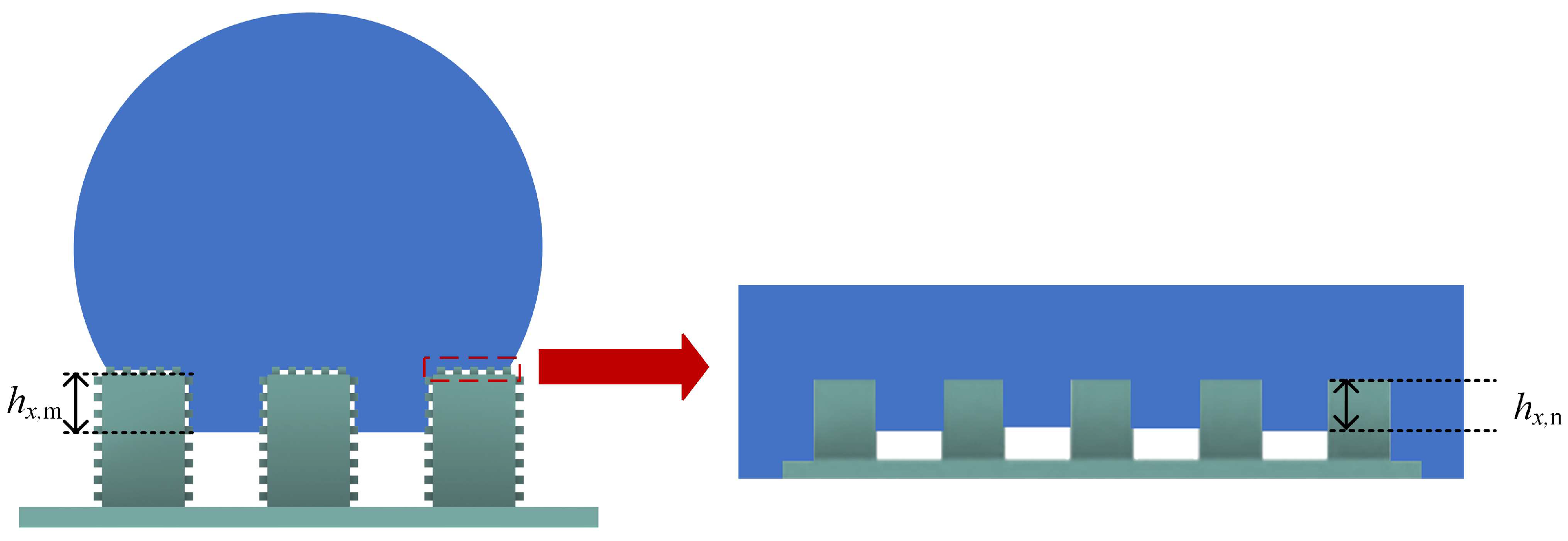
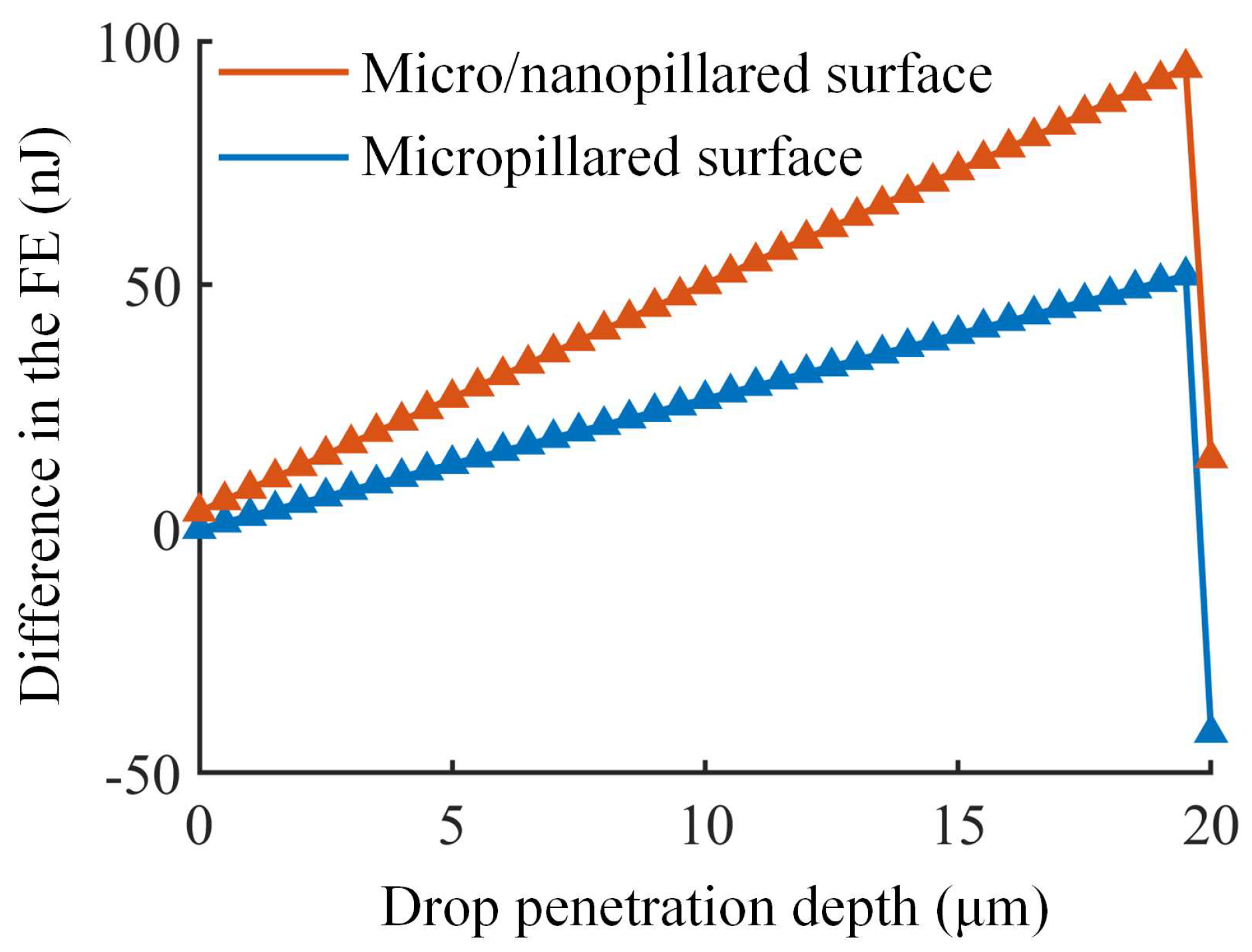
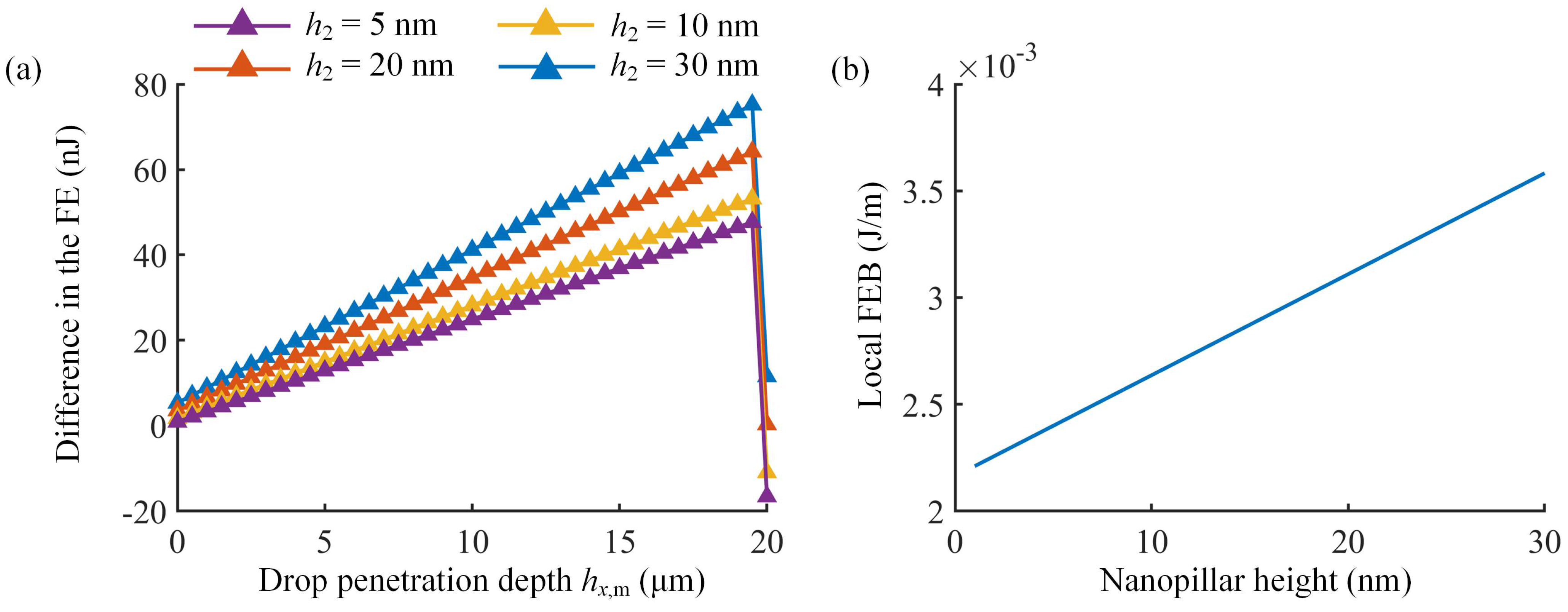
3.3. Analysis of FEB on Micro/Nanopillared Superhydrophobic Surfaces
3.4. Experimental Validation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Guo, Z. Recent advances in self-healing superhydrophobic coatings. Nano Today 2023, 51, 101933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; An, K. Recent advances and strategies in mechanical stability of superhydrophobic surfaces. Prog. Org. Coat. 2024, 194, 108595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Guo, S.; Liu, X.; Guo, Z.; Yu, C.; Ning, Y.; Liu, K.; Jiang, L. Directional liquid dynamics on superwetting interfaces. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2024, 11, 021316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Guo, Z. Recent advances in biomimetic superhydrophobic surfaces: Focusing on abrasion resistance, self-healing and anti-icing. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 16404–16419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, K.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, S.; Du, J.; Li, C.; Meng, S. Recent Advances on the Abrasion Resistance Enhancements and Applications of Superhydrophobic Materials. Chem. Rec. 2023, 23, e202200298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Duan, C.; Fu, M.; Zhang, J.; Huang, H.; Hu, Y.; Shi, J.; Ye, D. Scalable Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Coating with Rough Coral Reef-Like Structures for Efficient Self-Cleaning and Oil-Water Separation: An Experimental and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. Small 2023, 19, 2207118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Ma, K.; Yin, H.; Zhou, C.; He, W.; Yu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, Y. Superhydrophobic Coating Based on Nano-Silica Modification for Antifog Application of Partition Glass. Coatings 2024, 14, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgaonkar, A.; McNamara, G. Environmental Impact and Life Cycle Cost Analysis of Superhydrophobic Coatings for Anti-Icing Applications. Coatings 2024, 14, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Liu, Y.; Ye, S.; Sheng, L.; Wu, B.; Huang, L. Preparation of Robust Superhydrophobic Coatings Using Hydrophobic and Tough Micro/Nano Particles. Coatings 2024, 14, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Hu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; An, Y. A Rapidly Self-Healing Superhydrophobic Coating Made of Polydimethylsiloxane and N-nonadecane: Stability and Self-Healing Capabilities. Coatings 2024, 14, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Li, C.; Hu, J.; Zhang, C.; Dong, Z. Bioinspired Superwetting Open Microfluidics: From Concepts, Phenomena to Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2301017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amit, K.; Assam, A.; Raj, A. Pressure-flow characteristics of a microchannel combining super-hydrophobicity and wall compliance. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2023, 27, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jin, H.; Nie, S.; Zhang, P.; Gao, N. Dynamic behavior of water droplets and flashover characteristics on a superhydrophobic silicone rubber surface. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 201602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, S.; Liu, S.; Zuo, Z.; Gao, Y.; Wu, C.; Liang, X. Super-hydrophobic silicone rubber for outdoor electrical insulation. Nano Today 2024, 58, 102406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of Solid Surfaces to Wetting by Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Gou, X.; Zhang, J.; Liang, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Hou, X.; Chen, F. A Review of Smart Superwetting Surfaces Based on Shape-Memory Micro/Nanostructures. Small 2023, 19, 2206463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. An analytical approach for determining contact angle hysteresis on smooth, micropillared, and micropored homogeneous surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 679, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko, E. Progress in understanding wetting transitions on rough surfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.Q.; Li, Y.J.; Li, X.Q.; Sun, W. Theoretical analysis of droplet transition from Cassie to Wenzel state. Chin. Phys. B 2015, 24, 116801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. An analytical model for the receding contact angle on smooth homogeneous surfaces. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 708, 135954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, L.; Guo, Z.; Liang, Y.; Liu, W. Water super-repellent behavior of semicircular micro/nanostructured surfaces. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 3725–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, W.; Liu, T. Mechanism study on shape evolution and wetting transition of droplets during evaporation on superhydrophobic surfaces. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 518, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Tam, J.; Erb, U.; Liang, W. Thermodynamic analysis on wetting state transitions of rough surfaces with 3D irregular microstructure. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 34, 102378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Nai, X.; Liu, X.; Dong, Y.; Li, W. Analytical modeling of superhydrophobic surfaces with the microstructures composed of fibers and hemispheres. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 682, 132891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Tan, Z. Free energy barrier in wetting parallel-structured surfaces. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 655, 130214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Amirfazli, A. Microtextured superhydrophobic surfaces: A thermodynamic analysis. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 132, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, J.; Fang, G.; Li, W.; Amirfazli, A. Wetting Transition on Textured Surfaces: A Thermodynamic Approach. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 23976–23986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.S.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, Z.H. Effects of Hydraulic Pressure on the Stability and Transition of Wetting Modes of Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Langmuir 2005, 21, 12207–12212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, L.; Wagner, E.; Hoffmann, P. Water Wetting Transition Parameters of Perfluorinated Substrates with Periodically Distributed Flat-Top Microscale Obstacles. Langmuir 2007, 23, 1723–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Theoretical analysis of contact angle hysteresis of suspended drops on micropillared superhydrophobic surfaces. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 666, 131244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Dong, J.; Du, Y.; Han, J.; Niu, Y. Theoretical Analysis of Contact Angle and Contact Angle Hysteresis of Wenzel Drops on Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, T., III. An essay on the cohesion of fluids. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1805, 95, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Levkin, P.A. 3D Microprinting of Super-Repellent Microstructures: Recent Developments, Challenges, and Opportunities. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2213916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Ma, B.; Xu, C.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Wang, X. Research progress on superhydrophobic surface corrosion prevention of magnesium alloys: A review. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 110962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Peng, Y.; You, H.; Guan, X.; Lv, J.; Yang, C. Recent Developments in the Fabrication and Application of Superhydrophobic Suraces. Chem. Rec. 2024, 24, e202400065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akuoko, S.Y.; Kwon, K.-S. Fabrication and Applications of Nature-Inspired Surfaces with Selective Wettability. Langmuir 2024, 40, 15969–15995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drelich, J.W.; Boinovich, L.; Chibowski, E.; Della Volpe, C.; Hołysz, L.; Marmur, A.; Siboni, S. Contact angles: History of over 200 years of open questions. Surf. Innov. 2020, 8, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Xie, S.; Guo, Z. The Challenge of Superhydrophobicity: Environmentally Facilitated Cassie–Wenzel Transitions and Structural Design. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2305961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broom, M.; Willmott, G.R. Water drop impacts on regular micropillar arrays: The impact region. Phys. Fluids 2022, 34, 017115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.-X.; Cai, Z.-H.; Ding, Q.; Zhu, K.-Q.; Yang, Y.-R.; Wang, X.-D. Bouncing dynamics of nanodroplets impacting superhydrophobic surfaces: The coupling influence of wetting transitions and scale effects. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 657, 130579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinchasik, B.-E.; Wang, H.; Möhwald, H.; Asanuma, H. Fully Reversible Transition between Cassie and Wenzel States via Acoustic Waves. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 3, 1600722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmeneva, M.; Nikityuk, P.; Hans, M.; Surmenev, R. Deposition of Ultrathin Nano-Hydroxyapatite Films on Laser Micro-Textured Titanium Surfaces to Prepare a Multiscale Surface Topography for Improved Surface Wettability/Energy. Materials 2016, 9, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, K.-Y.; Cho, K.-H.; Chen, L.-J. Preparation of Superhydrophobic Surfaces of Hierarchical Structure of Hybrid from Nanoparticles and Regular Pillar-Like Pattern. Langmuir 2009, 25, 14187–14194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Different Cases | Micropillar Spacing (μm) | Micropillar Height (μm) | Micropillar Width (μm) | Observed Wetting State | Theoretical Results | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local FEB (J/m) | FE Difference Between the Wenzel and Cassie States (nJ) | Calculated Wetting State | |||||
| Case 1 | 3 | 1 | 6 | Wenzel | 0.0243 | −21.3 | Wenzel |
| 3 | 1.41 | 6 | Cassie | 0.0243 | −11.3 | Wenzel | |
| 3 | 3.05 | 6 | Cassie | 0.0243 | 28.6 | Cassie | |
| Case 2 | 6 | 1.5 | 6 | Wenzel | 0.008 | −24.0 | Wenzel |
| 6 | 2.76 | 6 | Cassie | 0.008 | −13.9 | Wenzel | |
| 6 | 5.02 | 6 | Cassie | 0.008 | 4.2 | Cassie | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Dong, J.; Liu, J.; Han, S. Thermodynamic Analysis of Wetting Transitions on Micro/Nanopillared Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Coatings 2025, 15, 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15020140
Li Y, Dong J, Liu J, Han S. Thermodynamic Analysis of Wetting Transitions on Micro/Nanopillared Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Coatings. 2025; 15(2):140. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15020140
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yufeng, Jialong Dong, Junyan Liu, and Sheng Han. 2025. "Thermodynamic Analysis of Wetting Transitions on Micro/Nanopillared Superhydrophobic Surfaces" Coatings 15, no. 2: 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15020140
APA StyleLi, Y., Dong, J., Liu, J., & Han, S. (2025). Thermodynamic Analysis of Wetting Transitions on Micro/Nanopillared Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Coatings, 15(2), 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15020140






