Improved Tribological Properties of Blanking Punches for Copper Alloys Utilizing Deterministic Surface Texturing by Machine Hammer Peening
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Objective
3. Materials and Methods
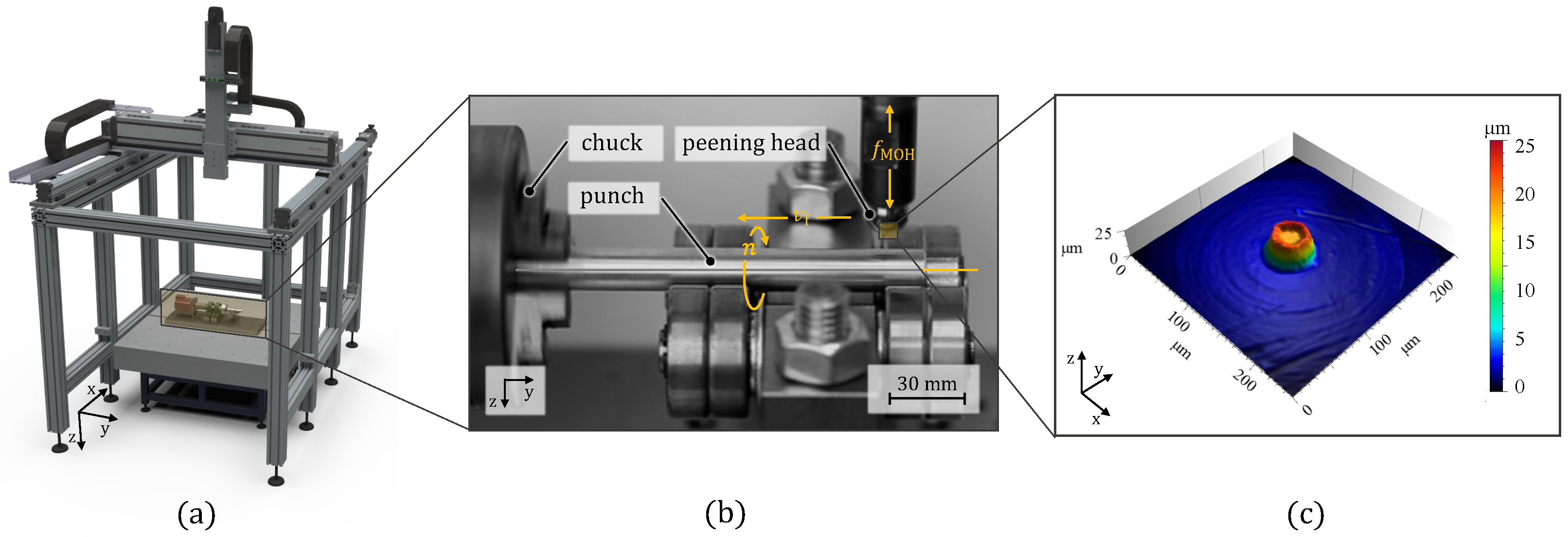
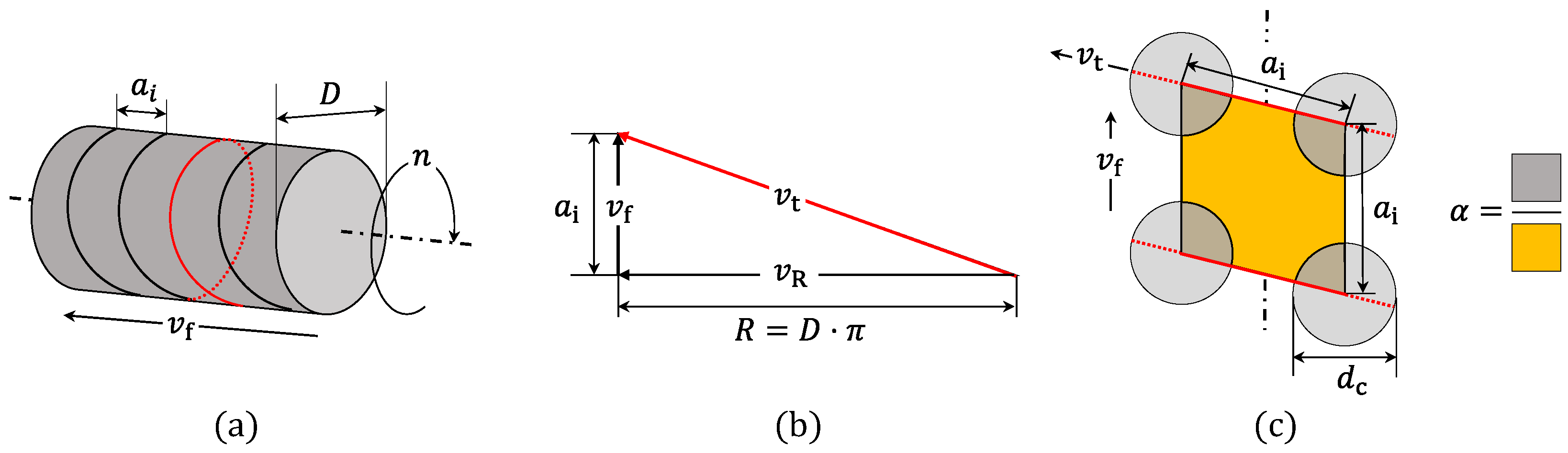
3.1. Microtexturing Cell
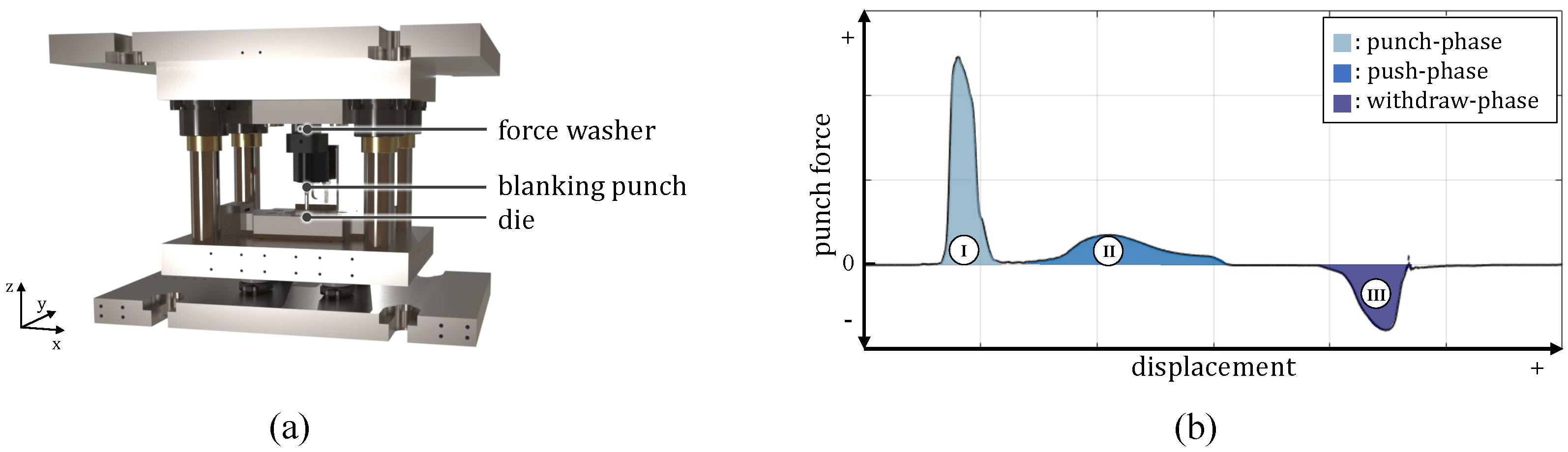
3.2. Blanking
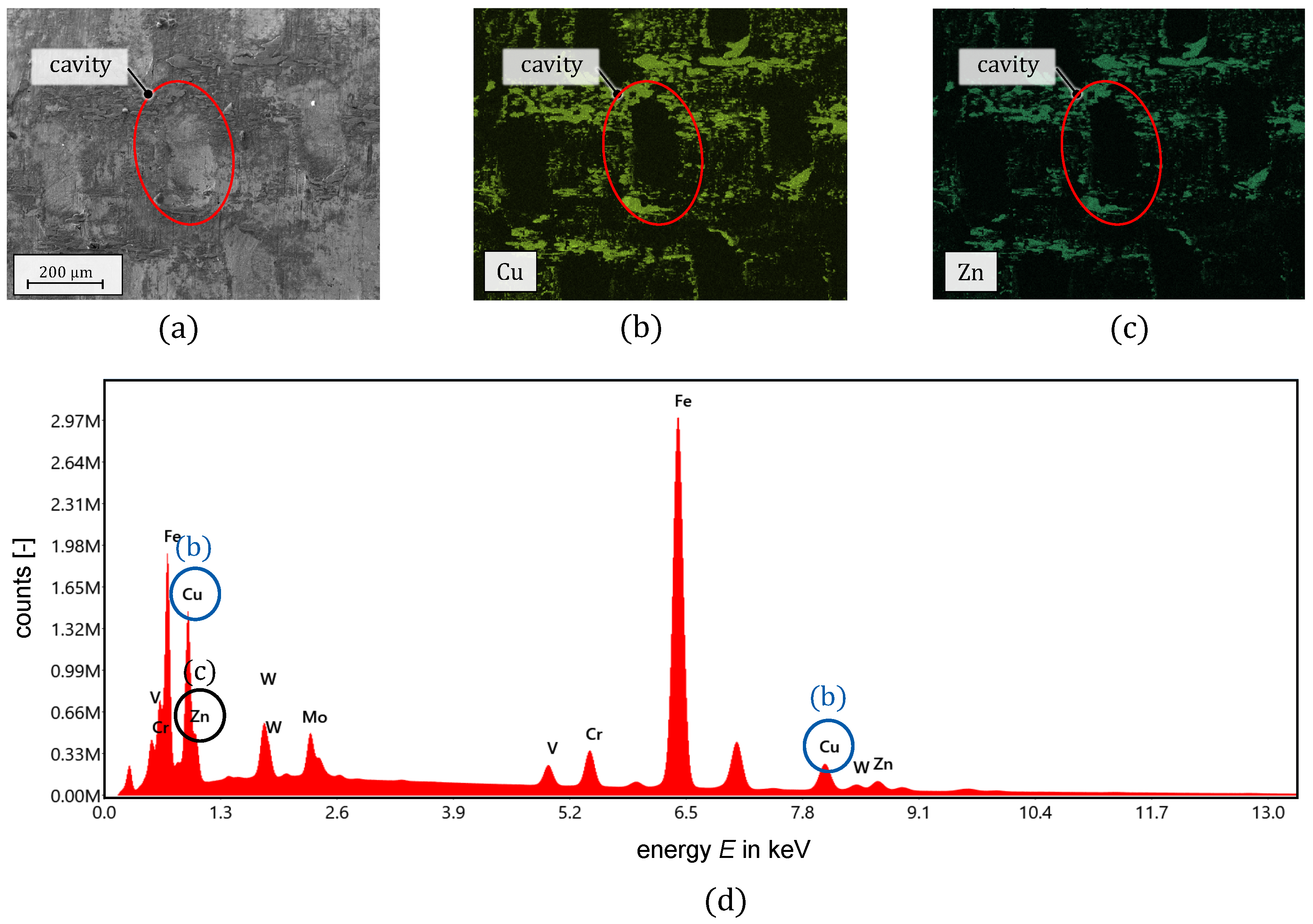
3.3. Microscopic Surface and EDX Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
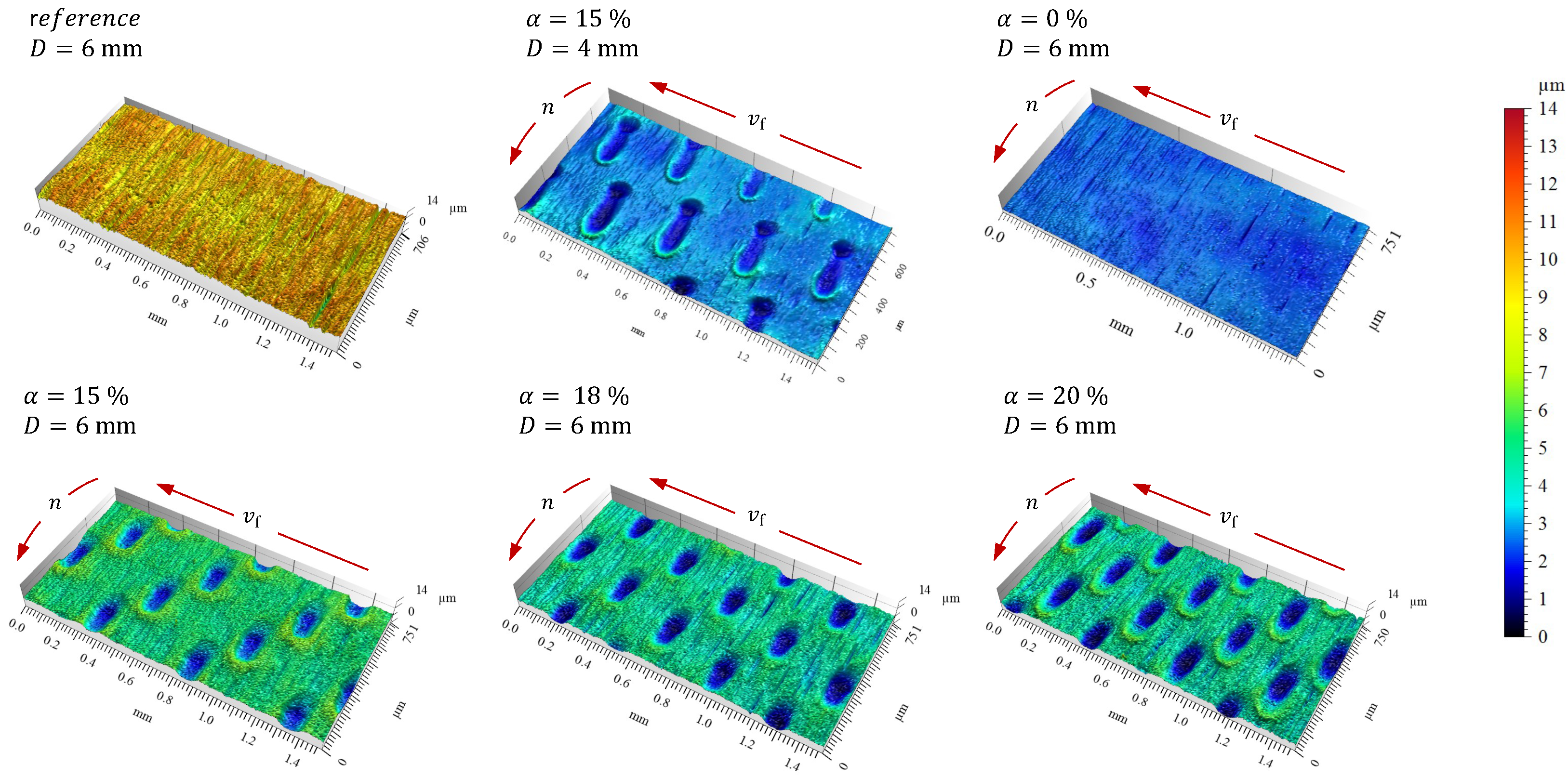
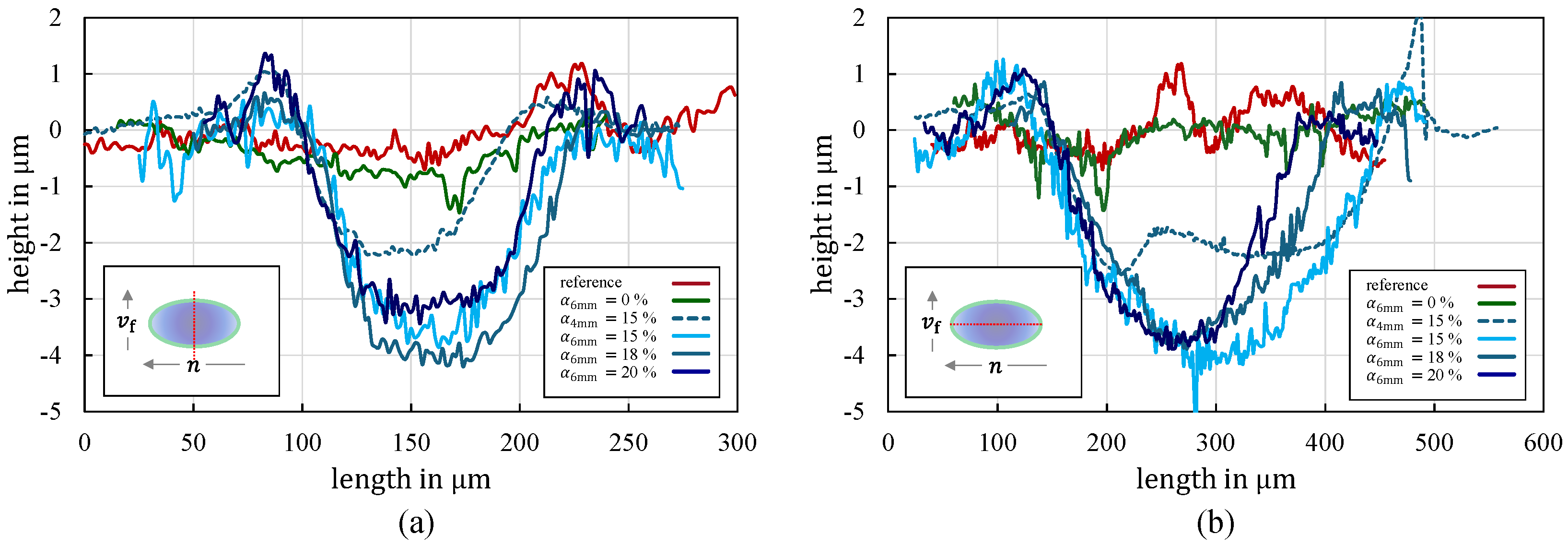
4.1. Textured Punch Surfaces
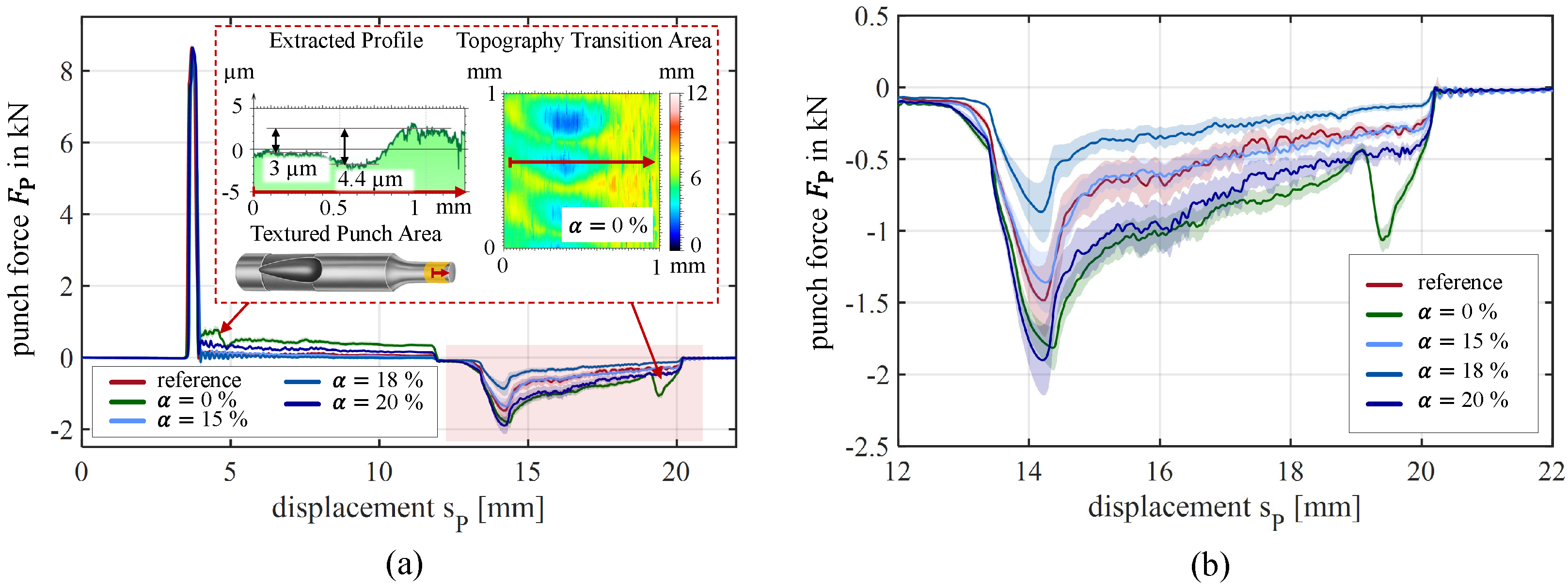
4.2. Process Performance
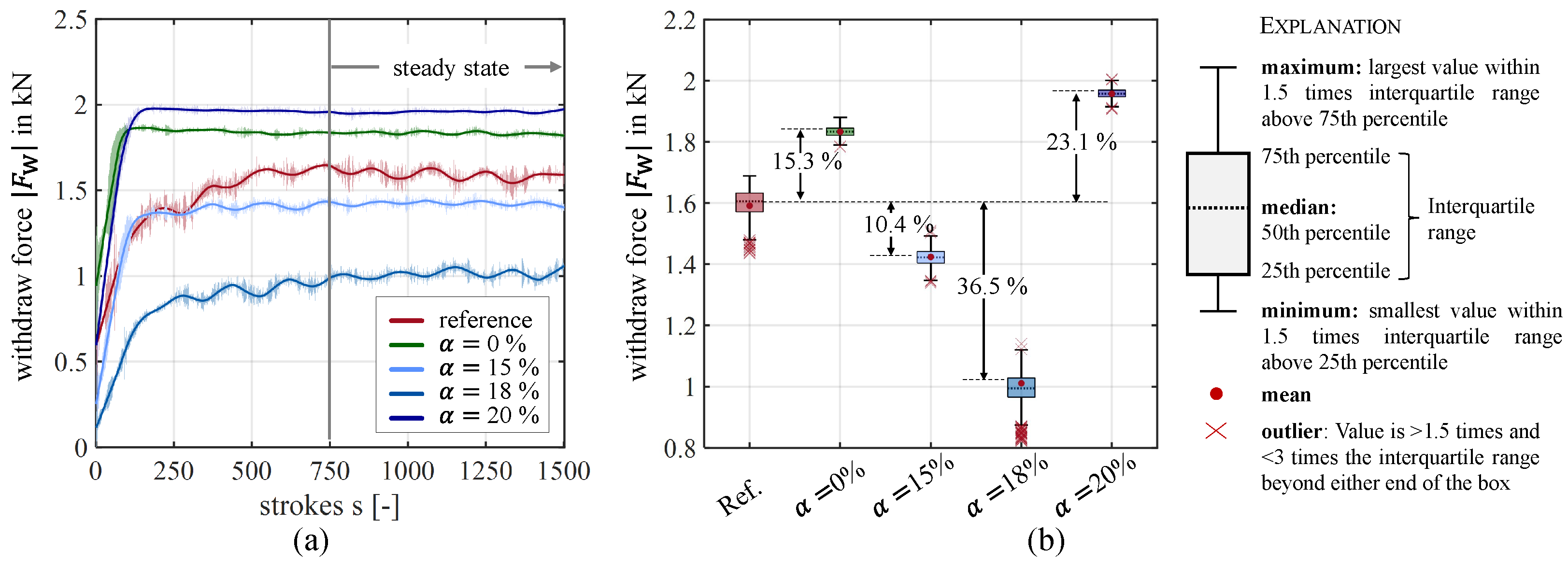
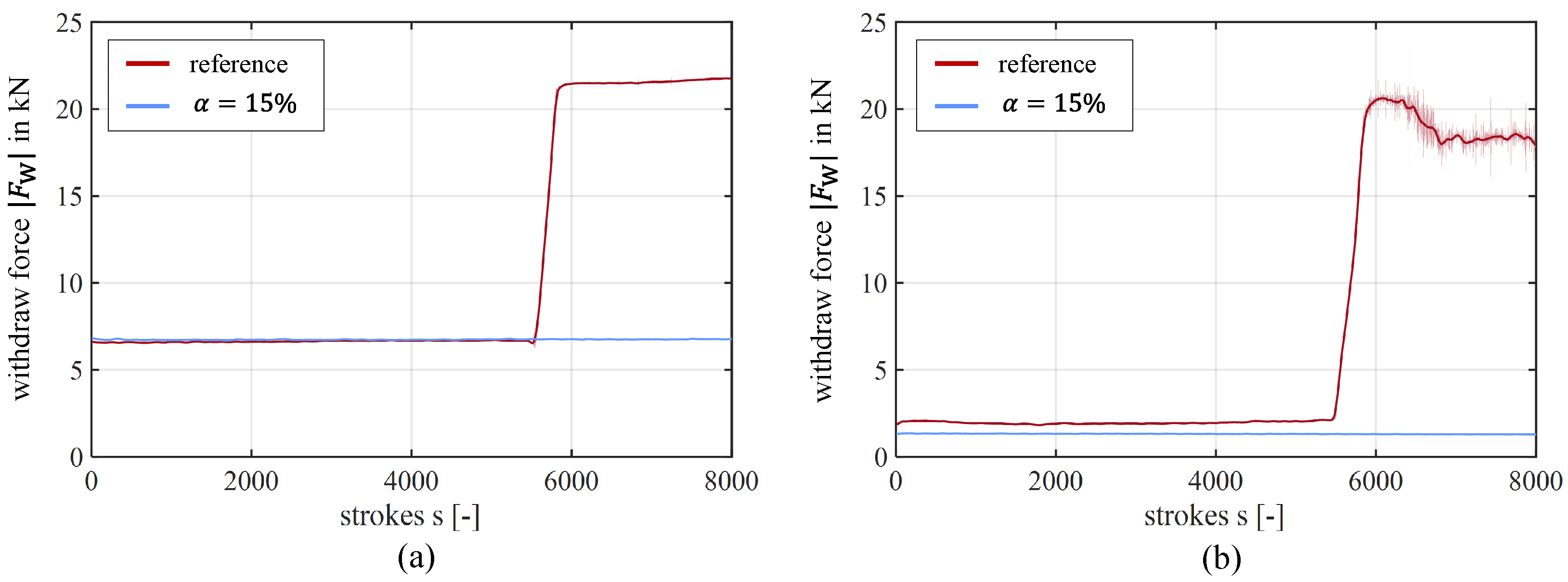
4.3. Wear Sensitive Blanking
5. Conclusions
- The lowest possible speeds should be set to reduce material accumulation and the formation of elongated cavities.
- The texturing of the lateral surface with a coverage ratio of 18% contributed to a reduction in the required withdrawal force of 36.6%.
- This allows the amount of lubricant required to be reduced while maintaining the tribological system, offering the potential for minimum quantity lubrication.
- It has been shown that microtexturing using MHP can also inhibit progressive adhesive wear.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AR | Aspect Ratio |
| COF | Coefficient of Friction |
| CNS | Contact Normal Stress |
| CVD | Chemical Vapor Desposition |
| EDX | Energy-dispersive X-Ray Spectrometer |
| MHP | Machine Hammer Peening |
| MPHDL | MicroPlastic Hydro Dynamic Lubrication |
| PVD | Physical Vapor Desposition |
| REACH | Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals |
References
- Schmidt, R.; Zimmermann, A.; Möhring, M.; Nurcan, S.; Keller, B.; Bär, F. Digitization-perspectives for conceptualization. In Advances in Service-Oriented and Cloud Computing, Proceedings of the Workshops of ESOCC 2015, Taormina, Italy, 15–17 September 2015; Revised Selected Papers 4; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 263–275. [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg, J.; Holmström, J.; Lyytinen, K. Digitization and phase transitions in platform organizing logics: Evidence from the process automation industry. Manag. Inf. Syst. Q. 2020, 44, 129–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, B.; Magne, P.; Malysz, P.; Yang, Y.; Pantelic, V.; Preindl, M.; Korobkine, A.; Jiang, W.; Lawford, M.; Emadi, A. Making the case for electrified transportation. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2015, 1, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Romero, J.; Osterman, M.; Das, D.; Pecht, M. Life cycle trends of electronic materials, processes and components. Microelectron. Reliab. 2019, 99, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzepieciński, T. Recent developments and trends in sheet metal forming. Metals 2020, 10, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, S.; Pauliuk, S. Sector-level estimates for global future copper demand and the potential for resource efficiency. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 193, 106941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Amouzegar, Z.; Khalili, S.; Asadi, S.; Aghajani, S.; Aryanrad, P.; Afkhami, A.; Madrakian, T.; Thomas, S.; Nguyen, T. Miniaturization—An introduction to miniaturized analytical devices. In Micro-and Nanotechnology Enabled Applications for Portable Miniaturized Analytical Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Arinbjarnar, Ú.; Schumann, P.; Moske, J.; Breunig, A.; Groche, P.; Nielsen, C. A review of methods and effects for improving production robustness in industrial micro-deep drawing. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2024, 17, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramonian, S.; Altan, T.; Campbell, C.; Ciocirlan, B. Determination of forces in high speed blanking using FEM and experiments. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2013, 213, 2184–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconnet, E.; Chambert, J.; Makich, H.; Monteil, G. Prediction of abrasive punch wear in copper alloy thin sheet blanking. Wear 2015, 338, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigvant, M.; Pilthammar, J.; Hol, J.; Wiebenga, J.; Chezan, T.; Carleer, B.; Boogaard, T. Friction in sheet metal forming: Influence of surface roughness and strain rate on sheet metal forming simulation results. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 29, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, N.; Ceron, E. Off-line testing of tribo-systems for sheet metal forming production. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 966, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colglazier, W. Sustainable development agenda: 2030. Science 2015, 349, 1048–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, D.D.; Bay, N.; Andreasen, J. Lubricant test for punching and blanking. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on the Technology of Plasticity, Yokohama, Japan, 27 October–1 November 2002; Volume 1, pp. 757–762. [Google Scholar]
- Arinbjarnar, Ú.; Moghadam, M.; Nielsen, C. Performance of inert particles as lubricant additives compared to fully formulated industrial forming oils in sheet metal forming. Discov. Mech. Eng. 2024, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Sulaiman, M. Assessment of lubricant performance enhanced with nanoadditive in punching and blanking of aluminium. J. Tribol. 2024, 43, 169–184. [Google Scholar]
- Bowman, D.; Van Calster, G. Reflecting on REACH: Global implications of the European Union’s chemicals regulation. Nanotech. L. Bus. 2007, 4, 375. [Google Scholar]
- Totre, A.; Nishad, R.; Bodke, S. An overview of factors affecting in blanking processes. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. (IJETAE) 2013, 3, 390–395. [Google Scholar]
- Podgornik, B.; Zajec, B.; Bay, N.; Vižintin, J. Application of hard coatings for blanking and piercing tools. Wear 2011, 270, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, U.; Chakkingal, U.; Venugopal, P. A review of fine blanking: Influence of die design and process parameters on edge quality. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzakis, K.; Michailidis, N.; Skordaris, G.; Kombogiannis, S.; Hadjiyiannis, S.; Efstathiou, K.; Erkens, G.; Rambadt, S.; Wirth, I. Effect of the cutting edge radius and its manufacturing procedure, on the milling performance of PVD coated cemented carbide inserts. CIRP Ann. 2002, 51, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Jain, V.; Ramkumar, J. Micro texturing on metallic surfaces: State of the art. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2018, 232, 941–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez-Corral, E.; Jerez-Mesa, R.; Llumà, J.; Wagner, V.; Dessein, G.; Travieso-Rodriguez, J. Wear resistance enhancement of AISI 1045 steel by vibration assisted ball burnishing process. Procedia CIRP 2016, 108, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidi, F.; Parlinska-Wojtan, M.; Hoffmann, P.; Wasmer, K. Effects of laser surface texturing on the wear and failure mechanism of grey cast iron reciprocating against steel under starved lubrication conditions. Wear 2017, 386, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Vorholt, J.; Yang, M. Lubrication analysis of micro-dimple textured die surface by direct observation of contact interface in sheet metal forming. Metals 2019, 9, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, K.; Makino, T.; Nawa, M.; Miyata, S. Tribological effects of punch with micro-dimples in blanking under high hydrostatic pressure. CIRP Ann. 2016, 65, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, C.; Bleicher, F.; Habersohn, C.; Bauer, C.; Goessinger, S. The use of machine hammer peening technology for smoothening and structuring of surfaces. In Proceedings of the Annals of DAAAM for 2012 & Proceeding of the 23rd International DAAAM Symposium, Zadar, Croatia,, 24–27 October 2012; Volume 23, pp. 331–337. [Google Scholar]
- Hönnige, J.; Colegrove, P.; Williams, S. Improvement of microstructure and mechanical properties in wire+ arc additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V with machine hammer peening. Procedia Eng. 2017, 216, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjassoho, B.; Kozeschnik, E.; Lechner, C.; Bleicher, F.; Goessinger, S.; Bauer, C. Induction of residual stresses and increase of surface hardness by machine hammer peening technology. Ann. DAAAM 2012, 23, 697–702. [Google Scholar]
- Steitz, M.; Stein, P.; Groche, P. Influence of hammer-peened surface textures on friction behavior. Tribol. Lett. 2015, 58, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sticht, P.; Hohmann, J.; Groche, P. Effects of machine hammer peened surface textures on the tribological behavior of stamping tools. In Advanced Surface Enhancement, Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Advanced Surface Enhancement (INCASE 2019)—Research Towards Industrialisation; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 108–120. [Google Scholar]
- Schumann, P. Improved Process Efficiency with Microtextured Blanking Punches Using MHP. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Tribology in Manufacturing Processes, Alcoy, Spain, 26–28 June 2024; Volume 3, p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Schumann, P.; Groche, P.; Lindner, R. Influence of different deterministic surface texturing processes on friction and tool life for load collectives in sheet metal forming. In Proceedings of the Tribology International Conference, Lisbon, Portugal, 26–28 April 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Uehara, Y.; Wakuda, M.; Yamauchi, Y.; Kanzaki, S.; Sakaguchi, S. Tribological properties of dimpled silicon nitride under oil lubrication. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 24, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, P.; Martin, D.; Kubik, C.; Schneider, T.; Groche, P. Analysis and evaluation of the clamping force on the tool surface during the blanking process. In NUMISHEET 2022, Proceedings of the 12th International Conference and Workshop on Numerical Simulation of 3D Sheet Metal Forming Processes, Toronto, ON, USA, 10–14 July 2022; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 655–670. [Google Scholar]
- Moghadam, M.; Villa, M.; Moreau, P.; Dubois, A.; Dubar, L.; Nielsen, C.; Bay, N. Analysis of lubricant performance in punching and blanking. Tribol. Int. 2020, 141, 105949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, D.; Bay, N.; Andreasen, J. Analysis of pick-up development in punching. CIRP Ann. 2002, 51, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubik, C.; Groche, P. Force-based inline detection of wear evolution during blanking of cold rolled steels. Prod. Eng. 2024, 18, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambli, R. Blanking tool wear modeling using the finite element method. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2001, 41, 1815–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Zhuang, X.; Zhao, Z. State-of-the-art and future challenge in fine-blanking technology. Prod. Eng. 2019, 13, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconnet, E.; Makich, H.; Chambert, J.; Monteil, G.; Picart, P. Numerical and experimental analyses of punch wear in the blanking of copper alloy thin sheet. Wear 2012, 296, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welm, M.; Tröber, P.; Weiss, H.; Demmel, P.; Golle, R.; Volk, W. Thermoelectrically based approaches to reduce adhesive wear during blanking. JOM 2020, 72, 2525–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, D.; Johnson, R. The influence of crystal structure and some properties of hexagonal metals on friction and adhesion. Wear 1968, 11, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, F.; Rowe, G. The adhesion of clean metals. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1956, 233, 429–442. [Google Scholar]
- Tabor, D. Interaction between surfaces: Adhesion and friction. Surf. Phys. Mater. 1974, 11, 475–529. [Google Scholar]
- Bay, N. Mechanisms producing metallic bonds in cold welding. Weld. J. 1983, 62, 137. [Google Scholar]
- Lind, L.; Peetsalu, P.; Põdra, P.; Adoberg, E.; Veinthal, R.; Kulu, P. Description of punch wear mechanism during fine blanking process. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference DAAAM Baltic Industrial Engineering, Tallinn, Estonia, 22–24 April 2010; pp. 504–509. [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno, T.; Okamoto, M. Effects of lubricant viscosity at pressure and sliding velocity on lubricating conditions in the compression-friction test on sheet metals. J. Lubr. Technol. 1982, 104, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, I.; Martins, P.; Bay, N.; Andreasen, J.; Bech, J. Influences of lubricant pocket geometry and working conditions upon micro-lubrication mechanisms in upsetting and strip drawing. Int. J. Surf. Sci. Eng. 2010, 4, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bech, J.; Bay, N.; Eriksen, M. A study of mechanisms of liquid lubrication in metal forming. CIRP Ann. 1998, 47, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K. Micro-mechanisms of wear—Wear modes. Wear 1992, 153, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayaba, T.; Kato, K. The adhesive transfer of the slip-tongue and the wedge. Asle Trans. 1981, 24, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trezona, R.; Allsopp, D.; Hutchings, I. Transitions between two-body and three-body abrasive wear: Influence of test conditions in the microscale abrasive wear test. Wear 1999, 225, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groche, P.; Resch, F. Dry forming of aluminum alloys–Wear mechanisms and influencing factors. Mater. Werkst. 2015, 46, 813–828. [Google Scholar]

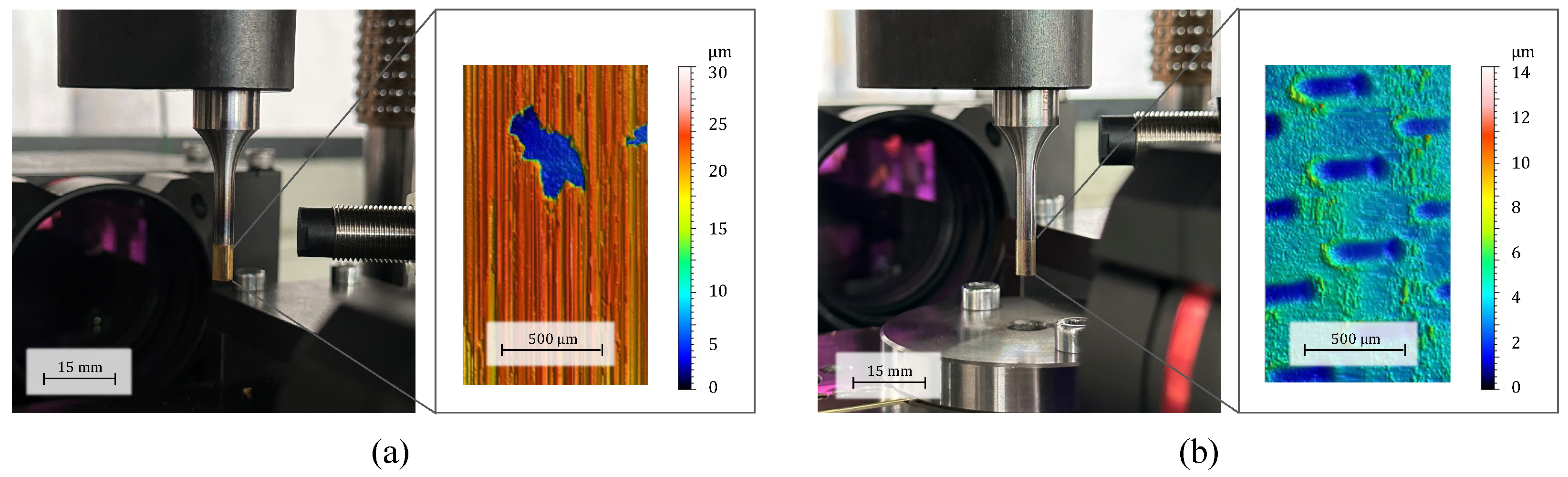
| D | n | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in% | in mm | in mm | in mm/min | in 1/min | in% | in Hz |
| 0 | 0.356 | 6 | 20.16 | 56.64 | 40 | 50 |
| 15 | 0.356 | 4 | 30.23 | 84.94 | ||
| 15 | 0.356 | 6 | 20.16 | 56.64 | ||
| 18 | 0.330 | 6 | 17.30 | 52.44 | ||
| 20 | 0.308 | 6 | 15.12 | 49.05 |
| Material | s | D | N (strokes) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in MPa | in mm | in mm | in 1/min | in mm | ||
| CuZn30 | 0.4 | 6 | 300 | 7.4 | 1500 | |
| 4 | 600 | 9 | until failure |
| in% | in% | in µm | in µm | in µm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 154mm | 18.2 | 1.76 | 14.7 | 0.68 |
| 156mm | 16.1 | 1.75 | 12.9 | 0.78 |
| 186mm | 18.4 | 1.89 | 23.0 | 0.85 |
| 206mm | 22.3 | 2.06 | 25.4 | 0.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schumann, P.; Arne, V.; Groche, P. Improved Tribological Properties of Blanking Punches for Copper Alloys Utilizing Deterministic Surface Texturing by Machine Hammer Peening. Coatings 2025, 15, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15020136
Schumann P, Arne V, Groche P. Improved Tribological Properties of Blanking Punches for Copper Alloys Utilizing Deterministic Surface Texturing by Machine Hammer Peening. Coatings. 2025; 15(2):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15020136
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchumann, Philipp, Viktor Arne, and Peter Groche. 2025. "Improved Tribological Properties of Blanking Punches for Copper Alloys Utilizing Deterministic Surface Texturing by Machine Hammer Peening" Coatings 15, no. 2: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15020136
APA StyleSchumann, P., Arne, V., & Groche, P. (2025). Improved Tribological Properties of Blanking Punches for Copper Alloys Utilizing Deterministic Surface Texturing by Machine Hammer Peening. Coatings, 15(2), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15020136








