Study on the Influence of Airfoil and Angle of Attack on Ice Distribution and Aerodynamic Performance of Blade Surface
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Icing Wind Tunnel Experimental Research Method
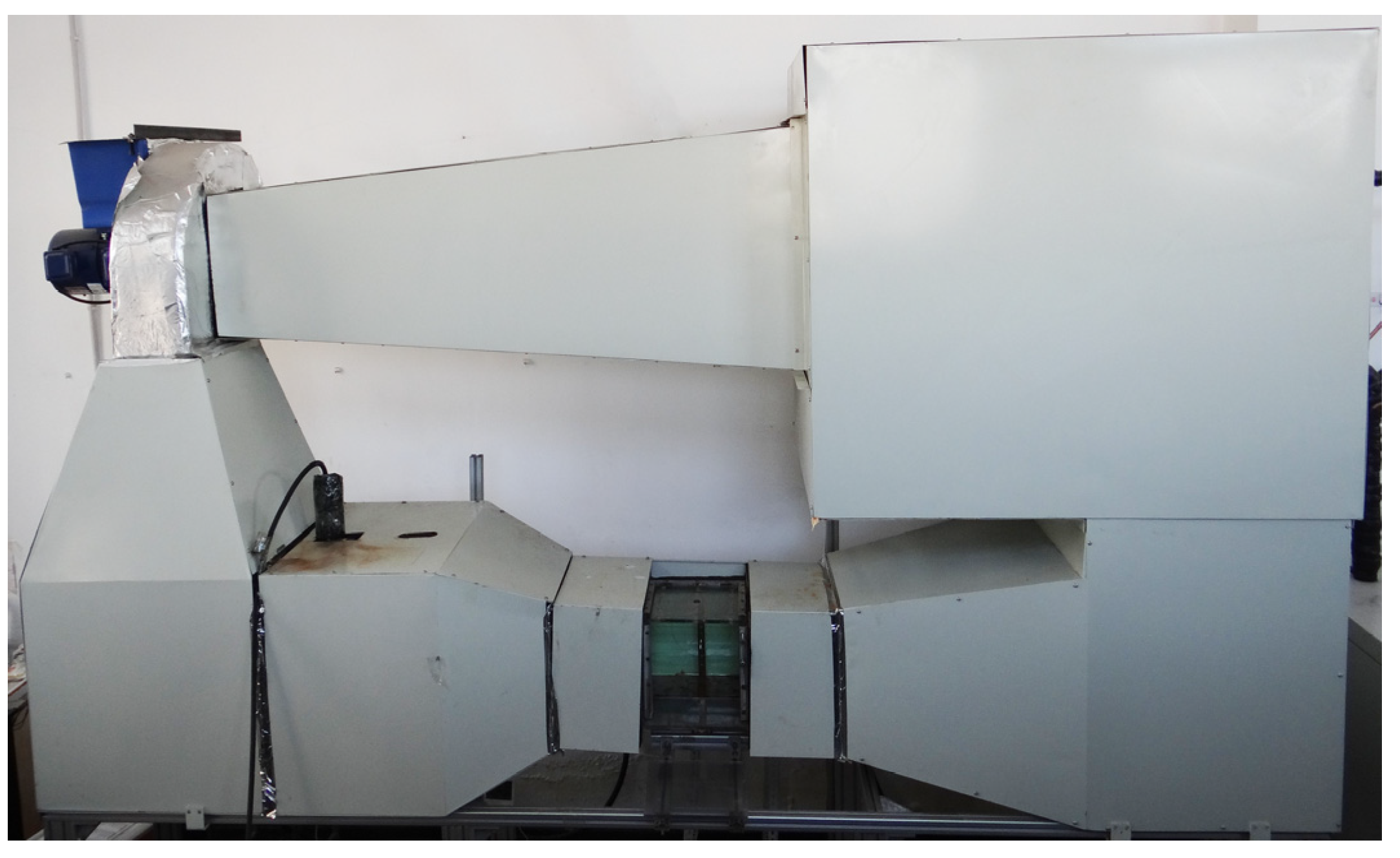
2.1.1. Blade Airfoil Section Icing Wind Tunnel Experimental System
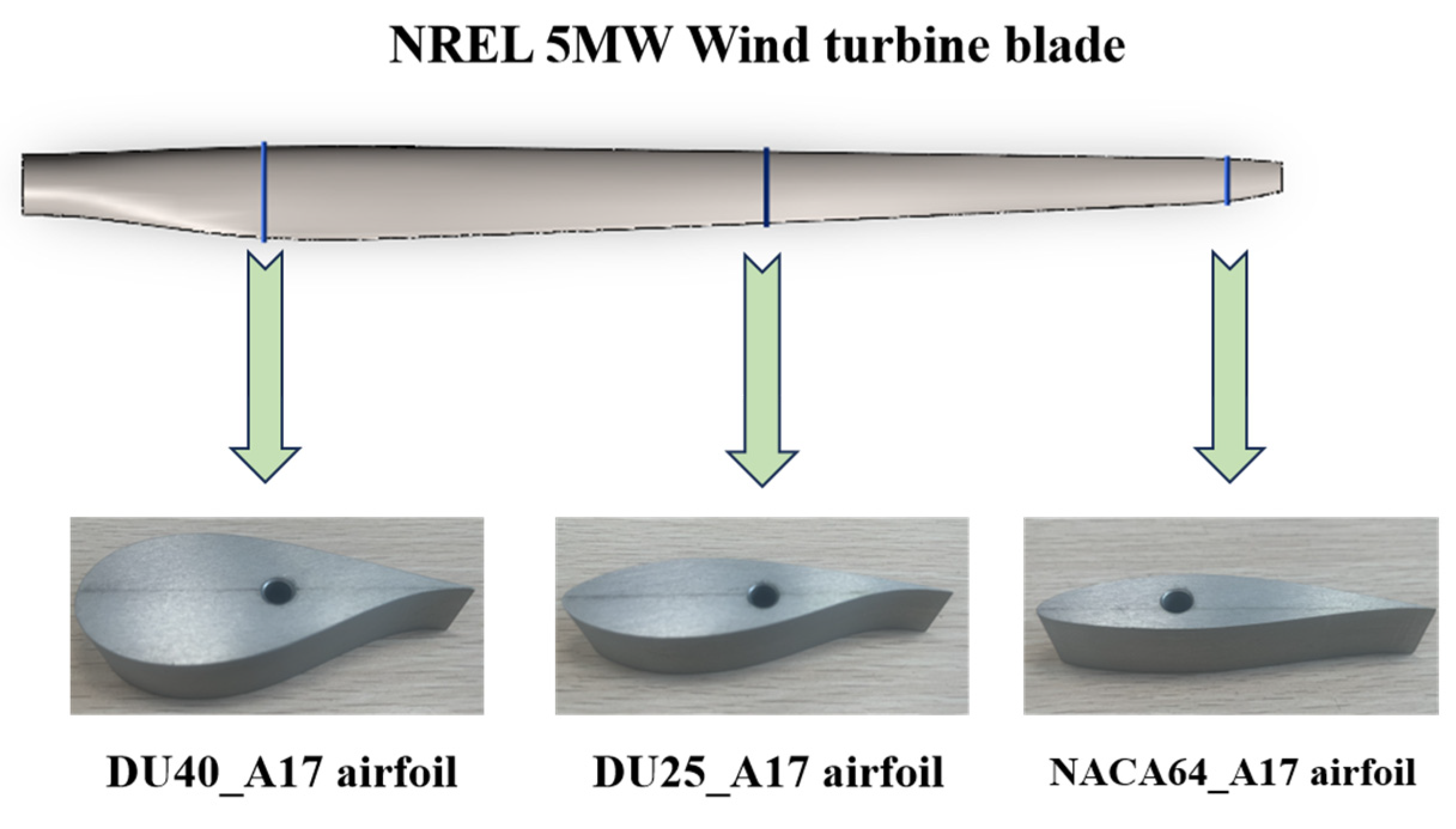
2.1.2. Experimental Model
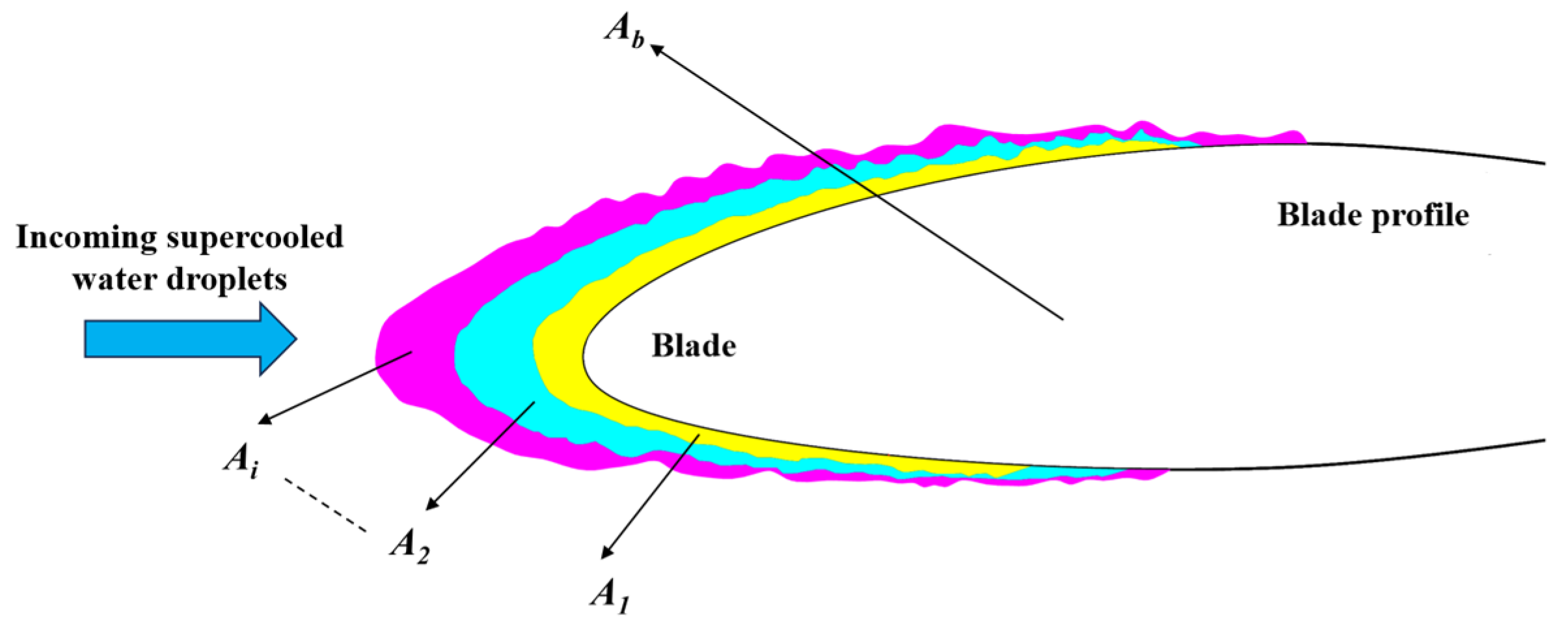
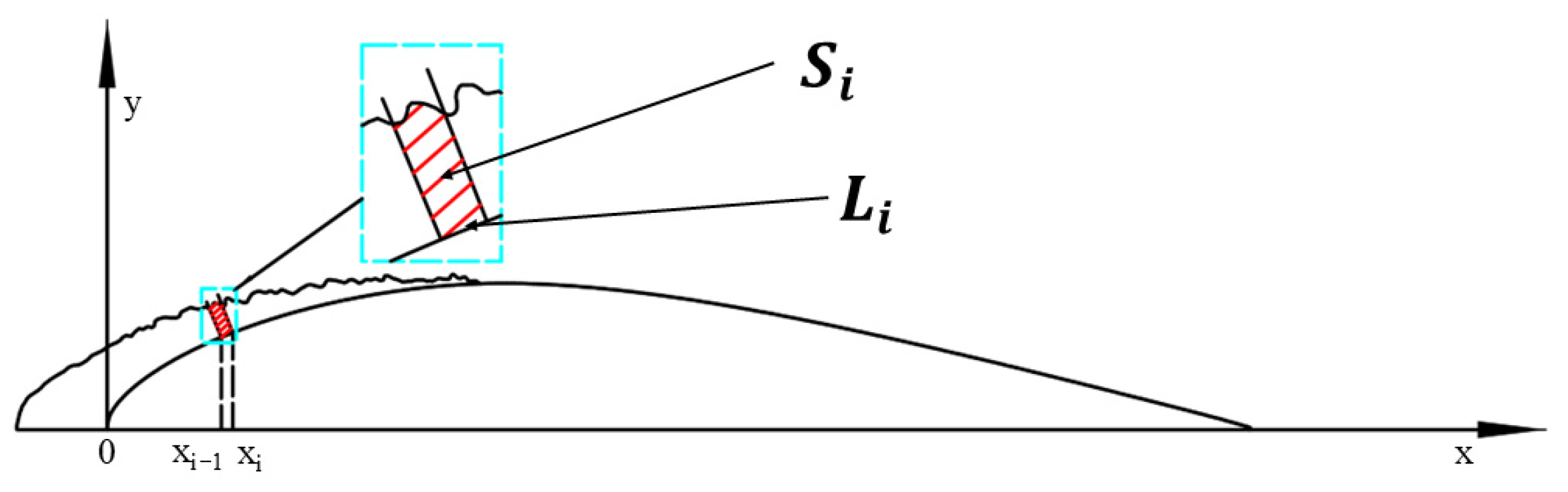
2.1.3. Evaluating Indicator
- (1)
- Blade material
- (2)
- Blade Airfoils
- (3)
- Angle of attack
2.2. Numerical Simulation Method of Aerodynamic Performance
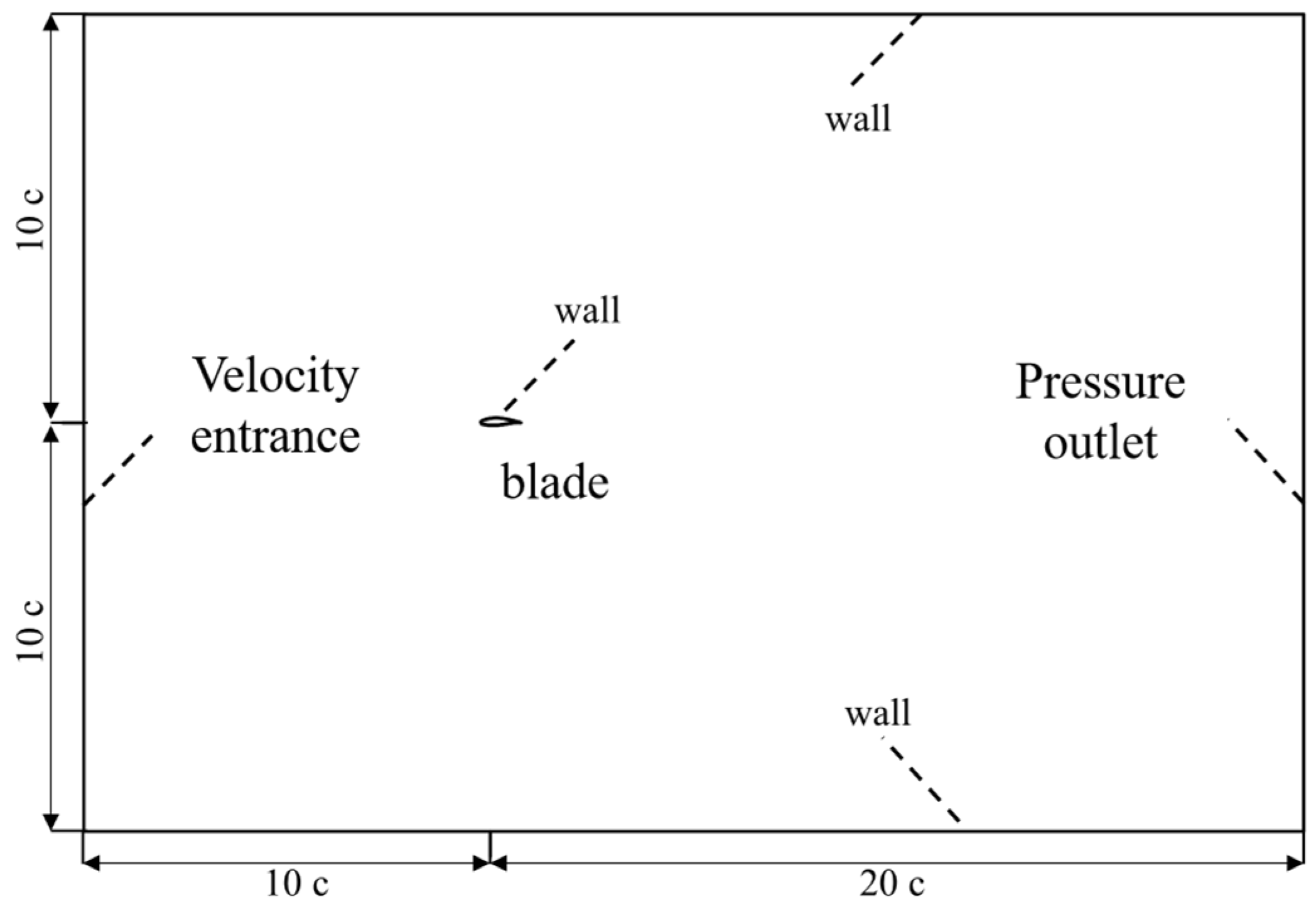
2.2.1. Geometric Model and Boundary Conditions
Computational Domain
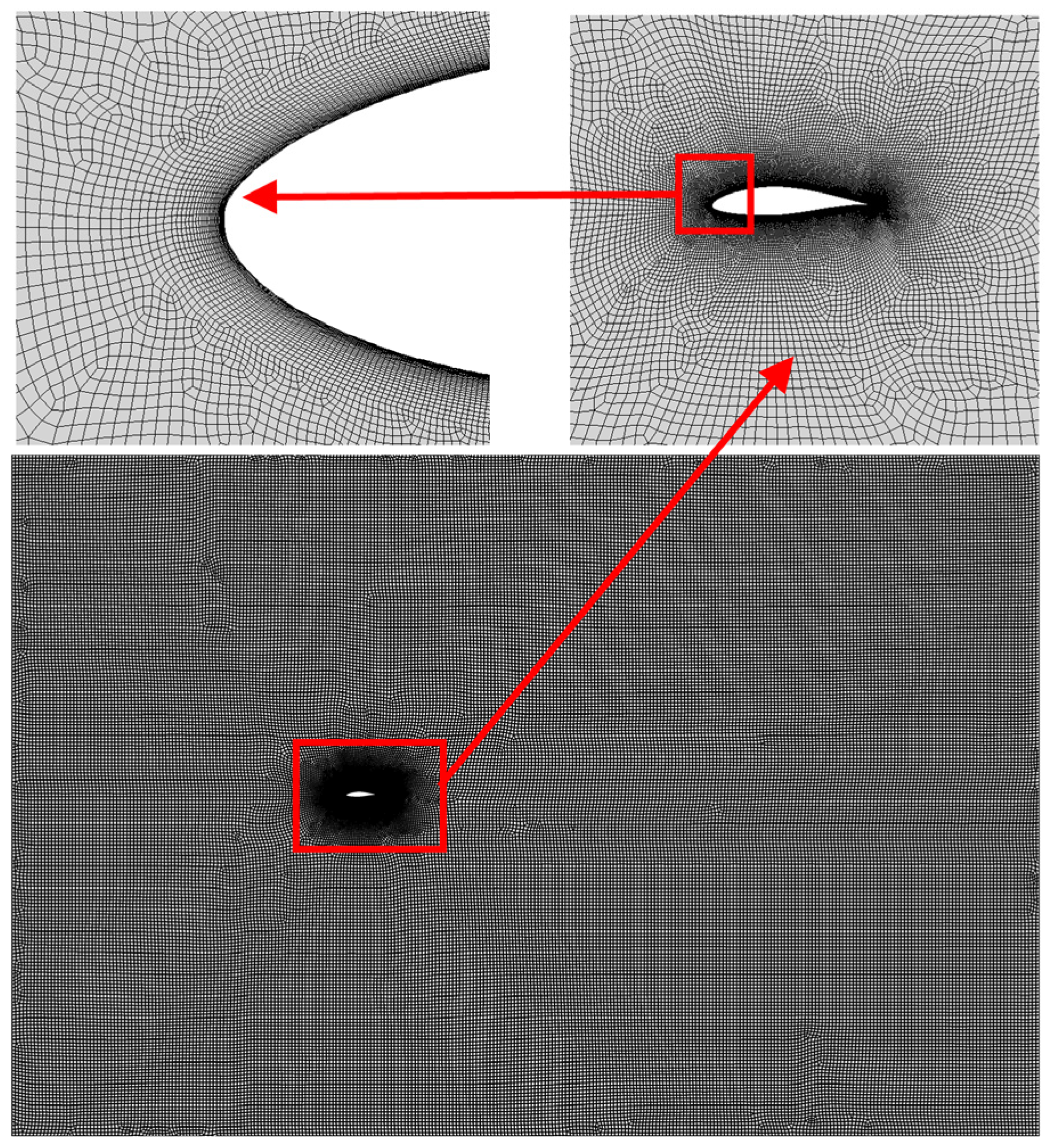
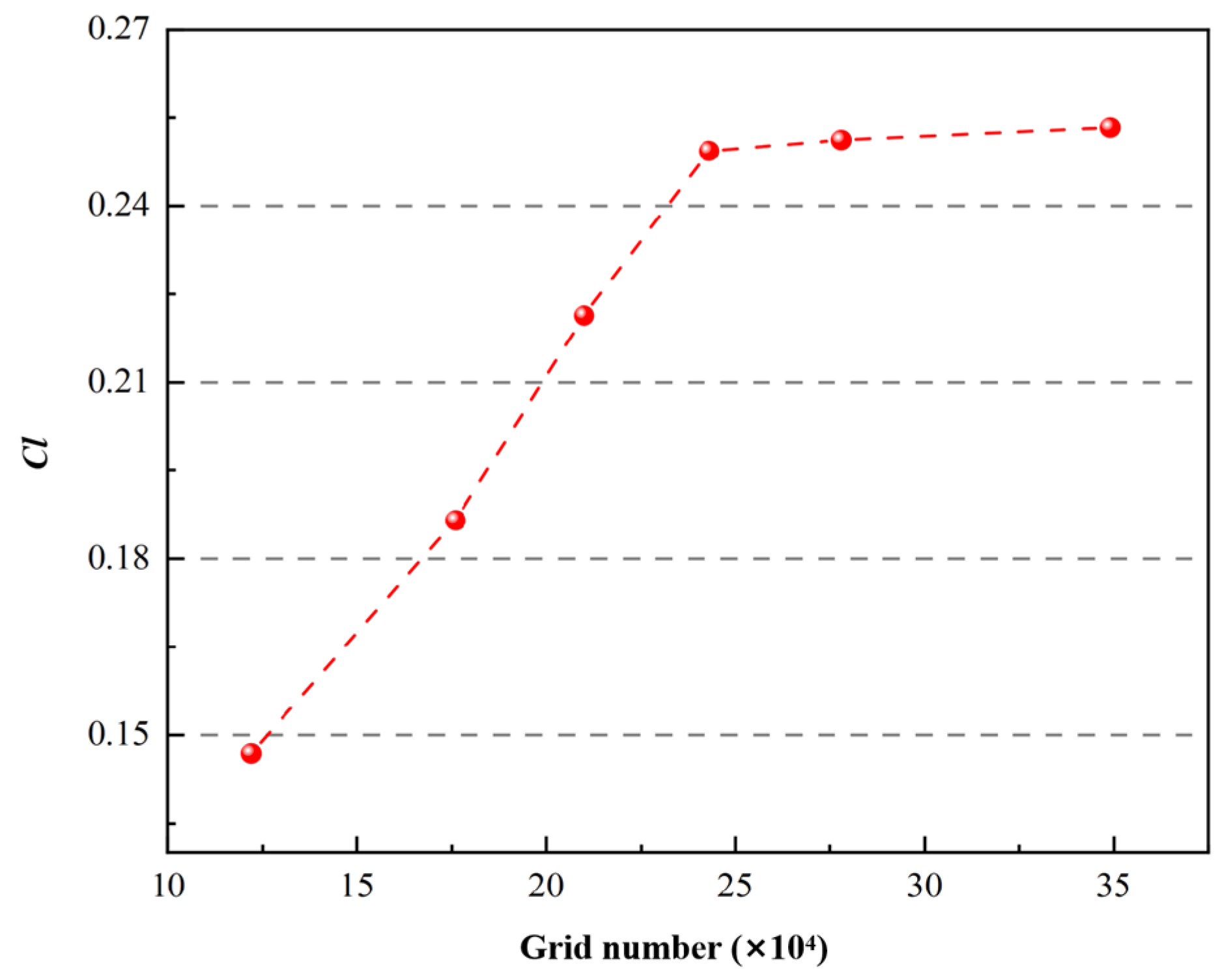
2.2.2. Grid Division and Independence Verification
Mesh Generation and Independence Verification
3. Results and Discussion
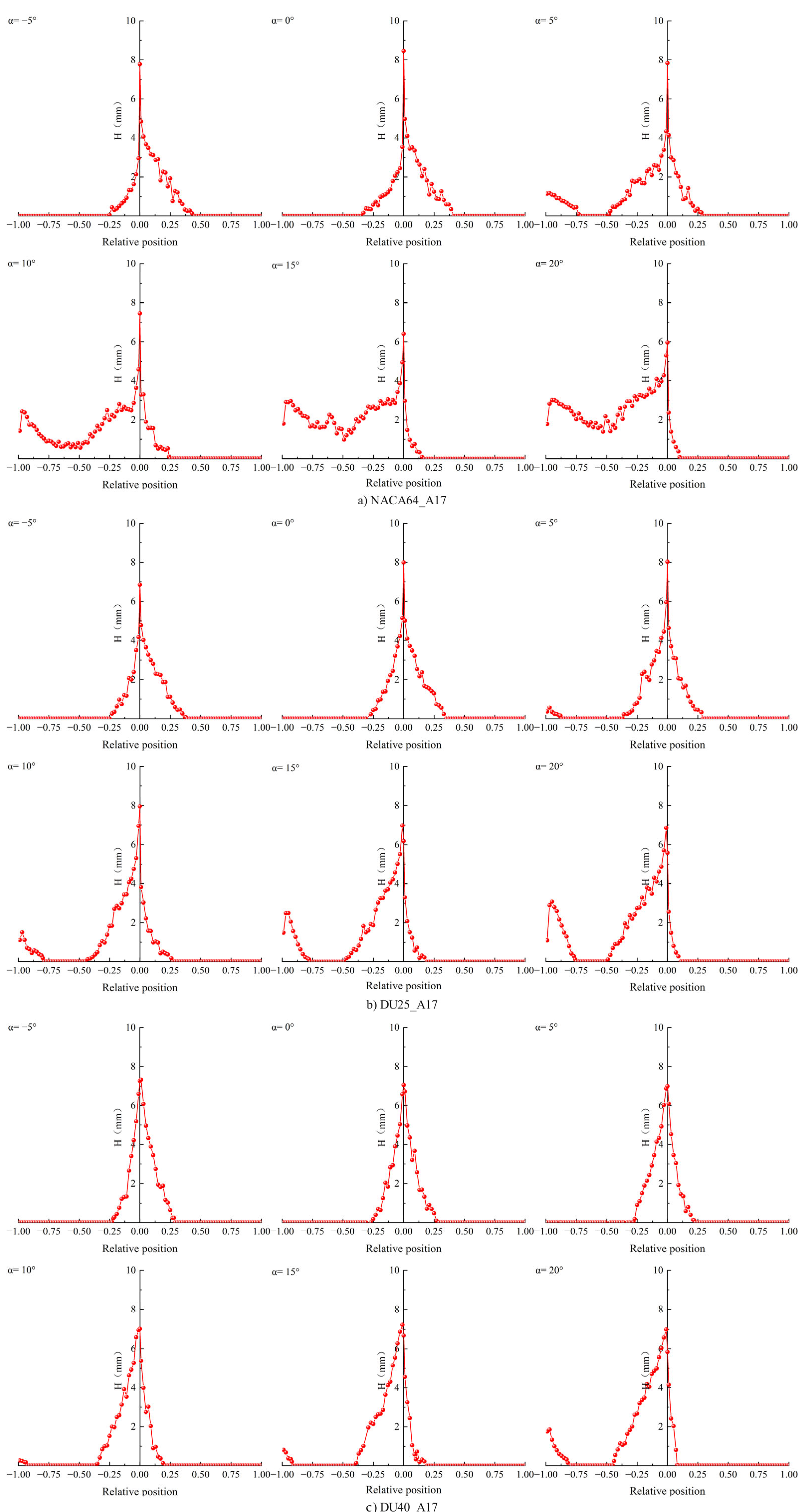
3.1. Surface Icing Distribution of Blade Airfoil Sections
3.1.1. Influence of Blade Material
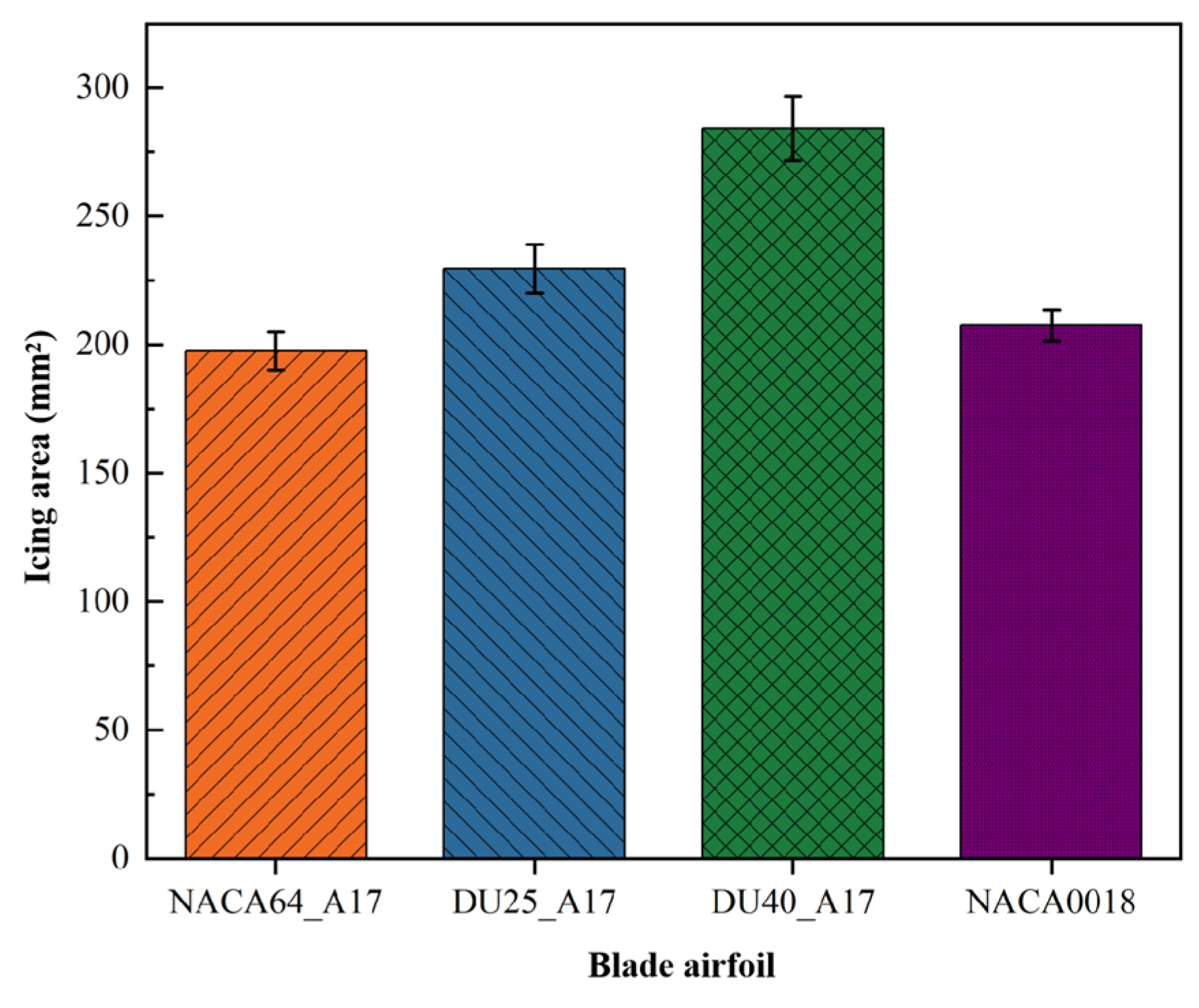
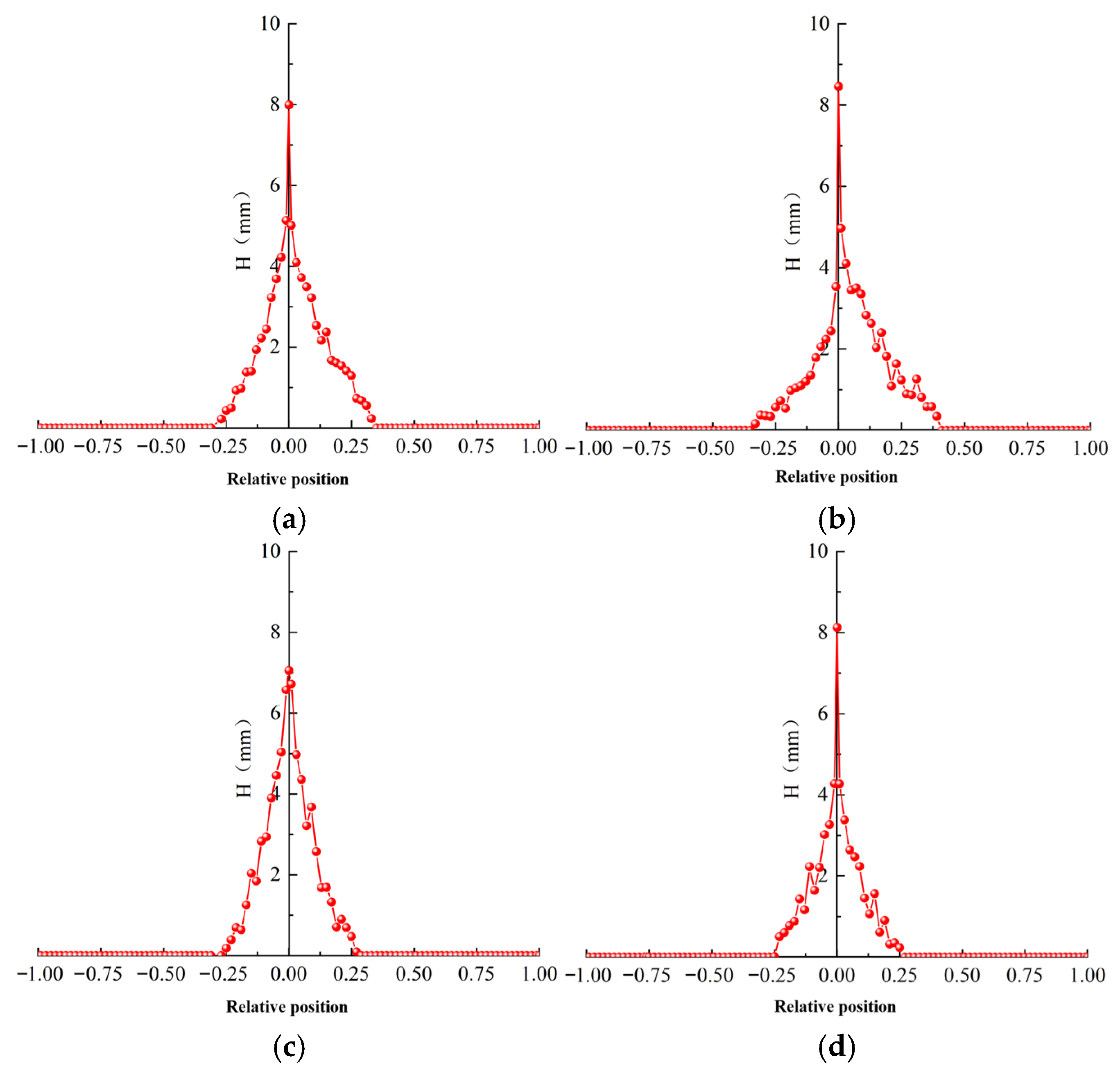
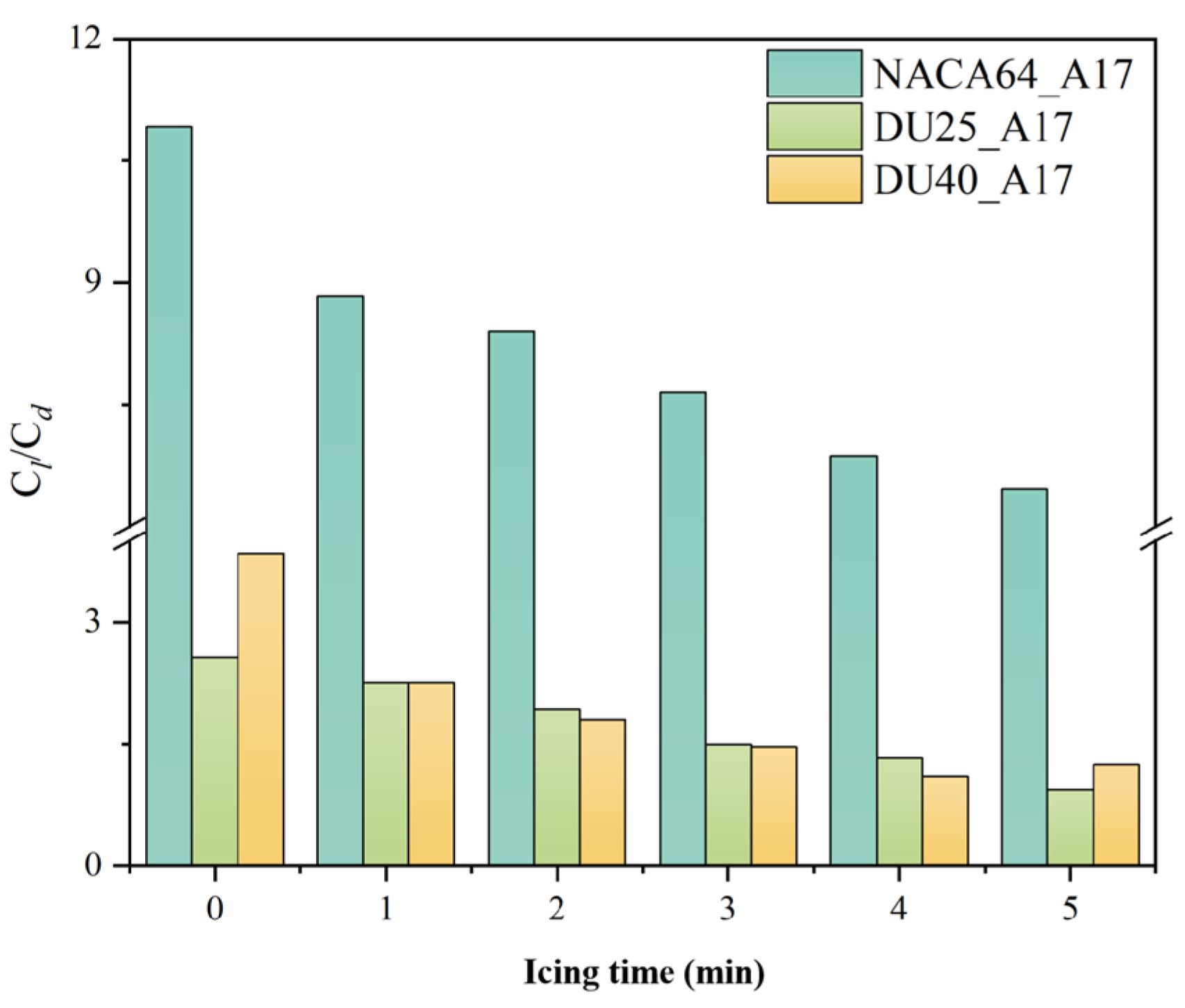
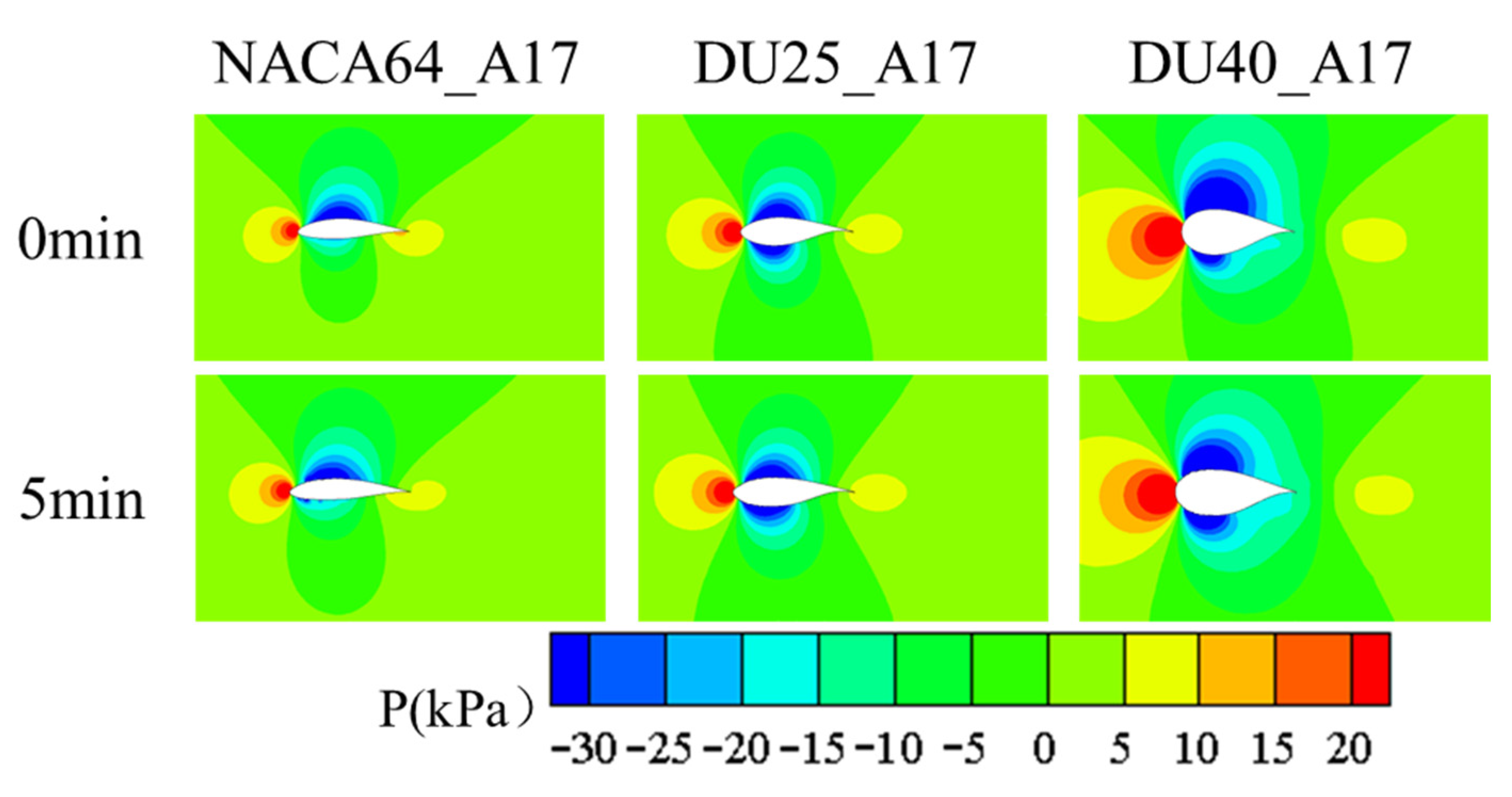
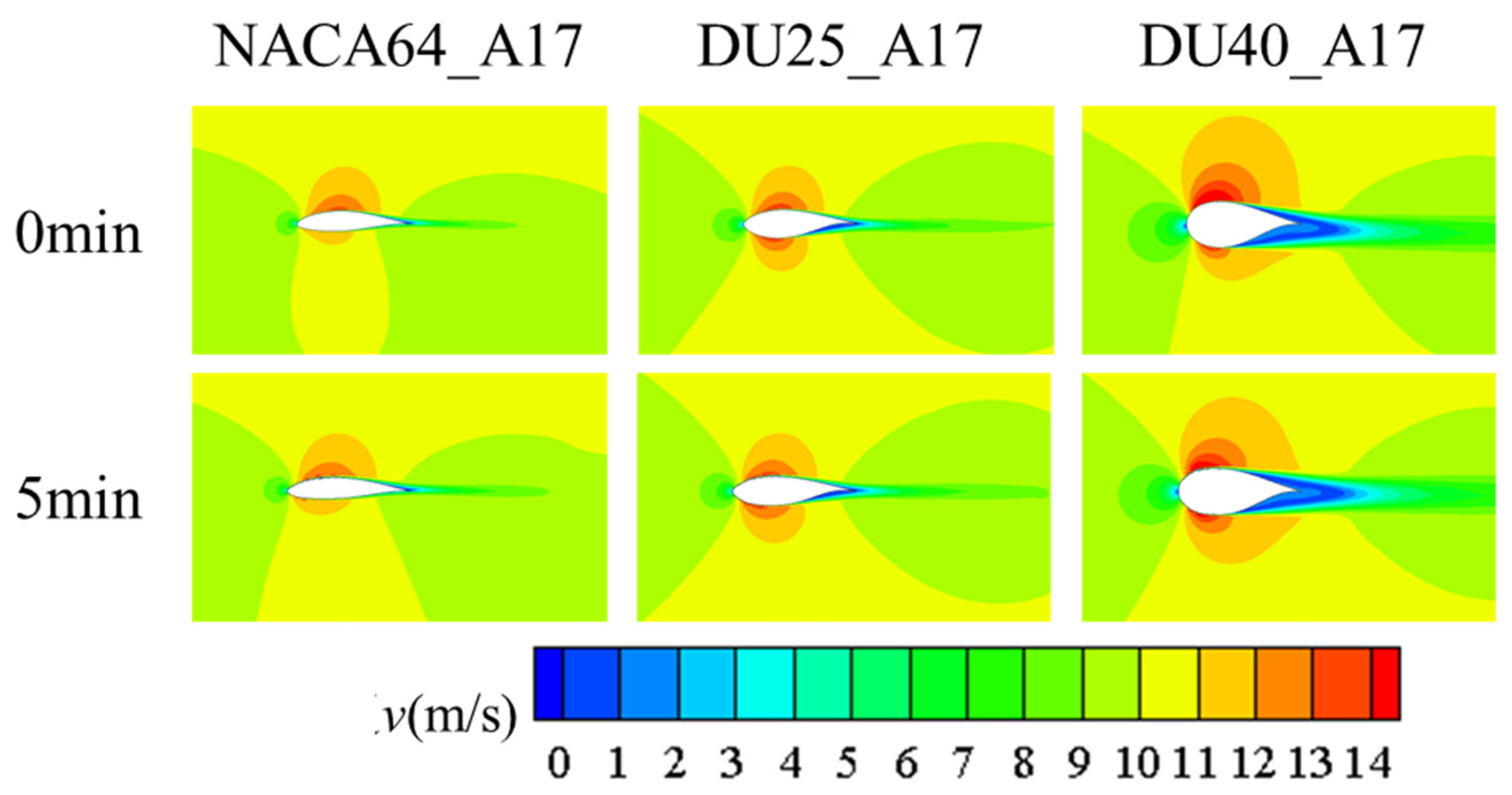
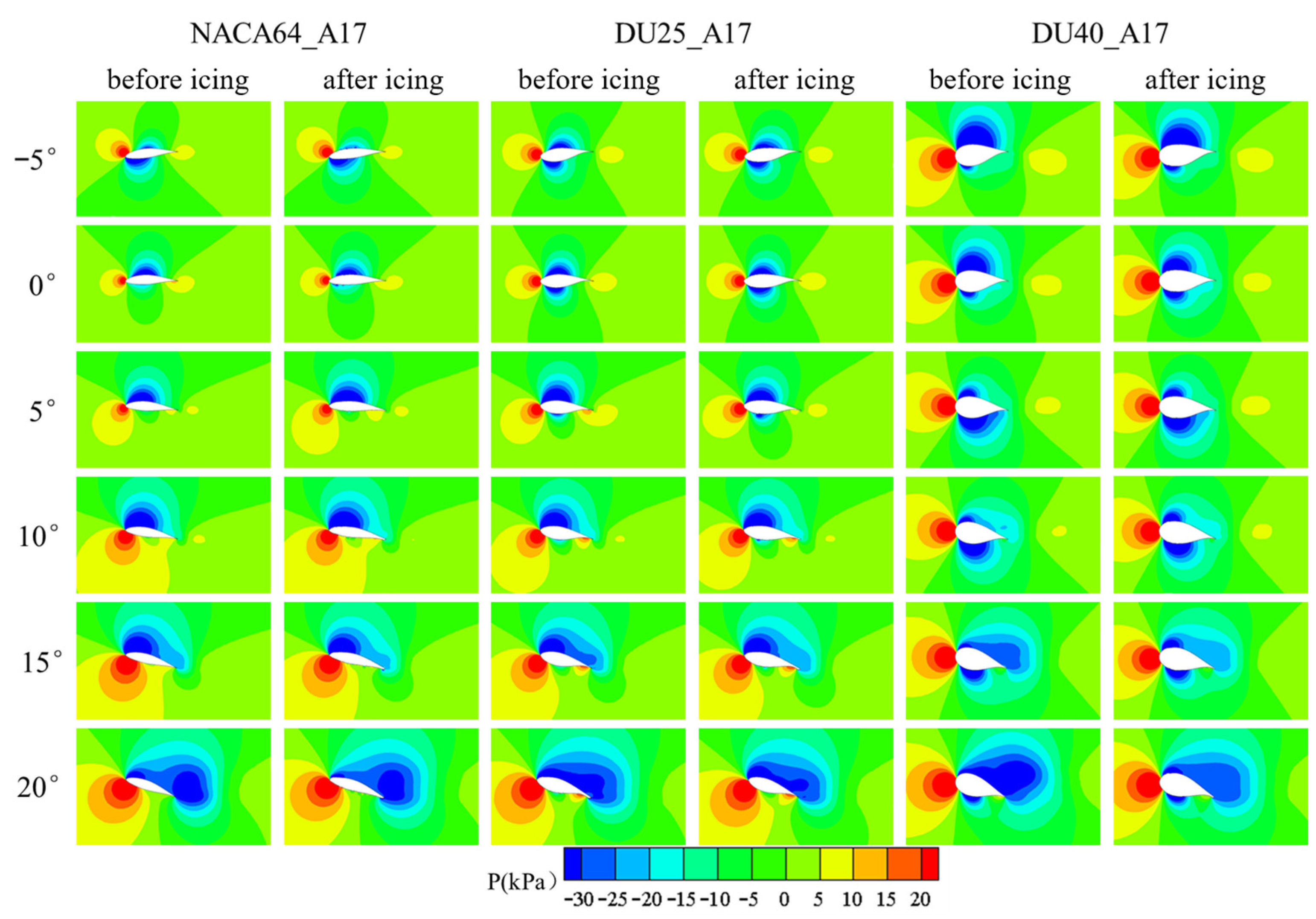
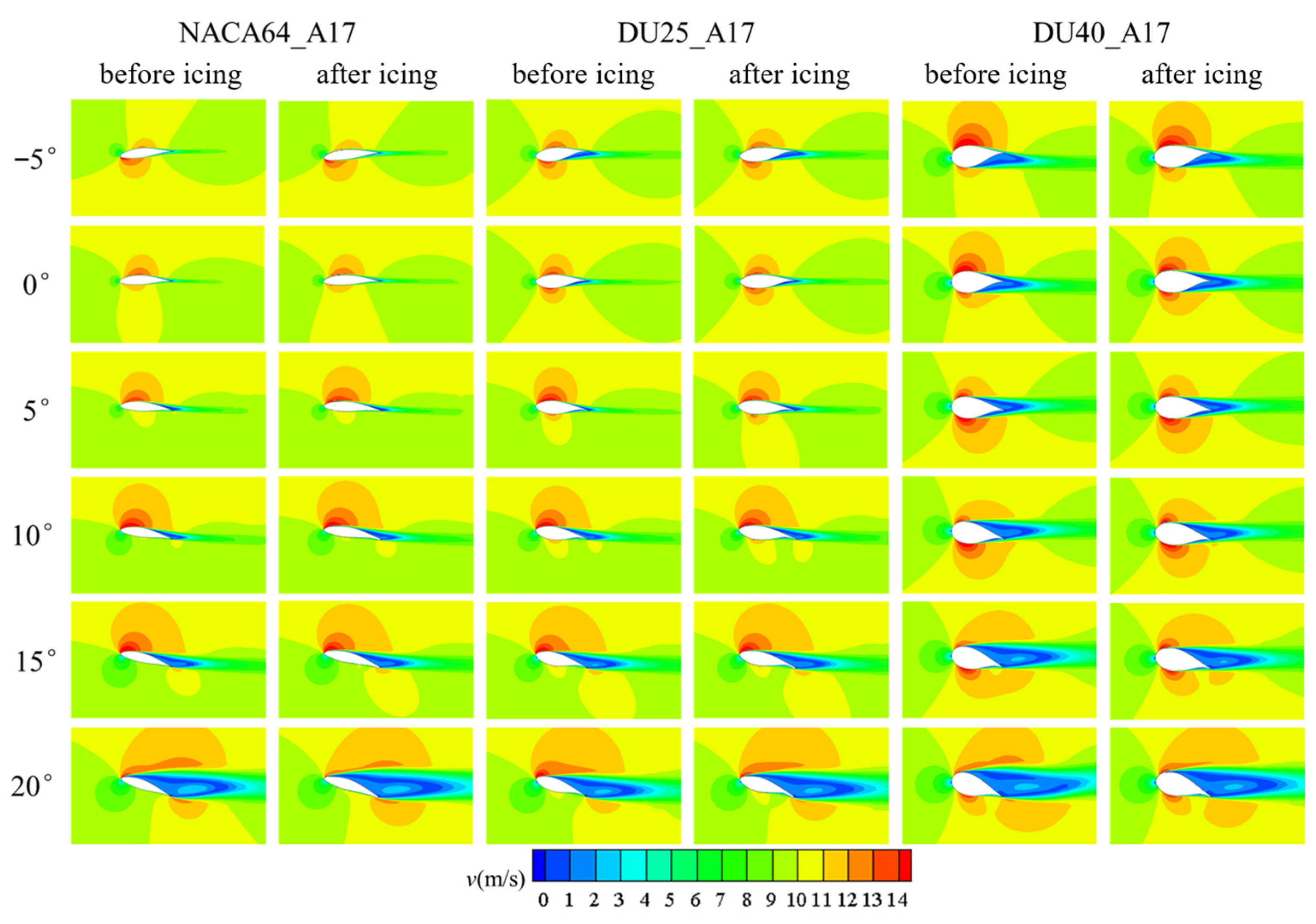
3.1.2. Influence of Blade Airfoil
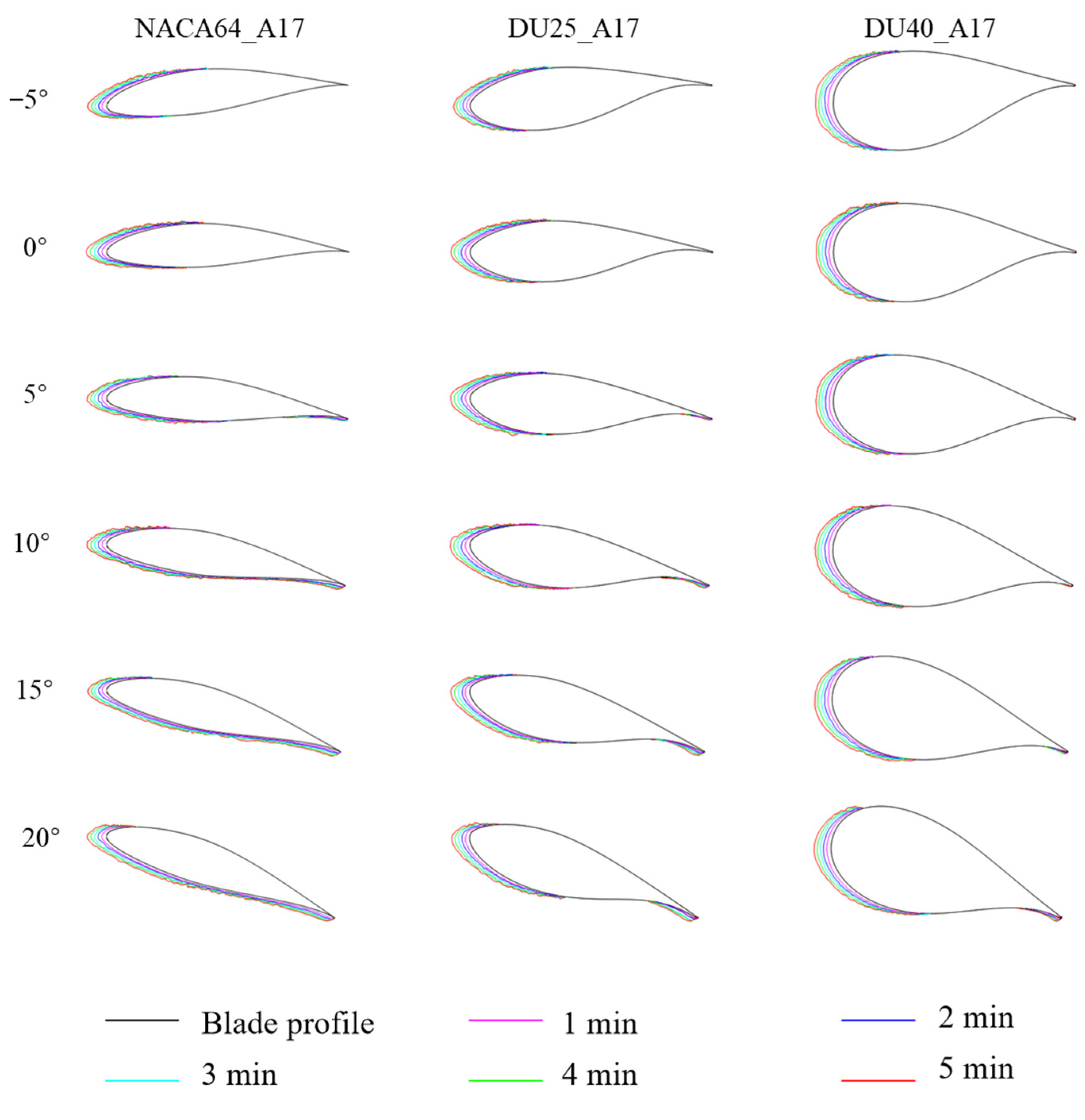
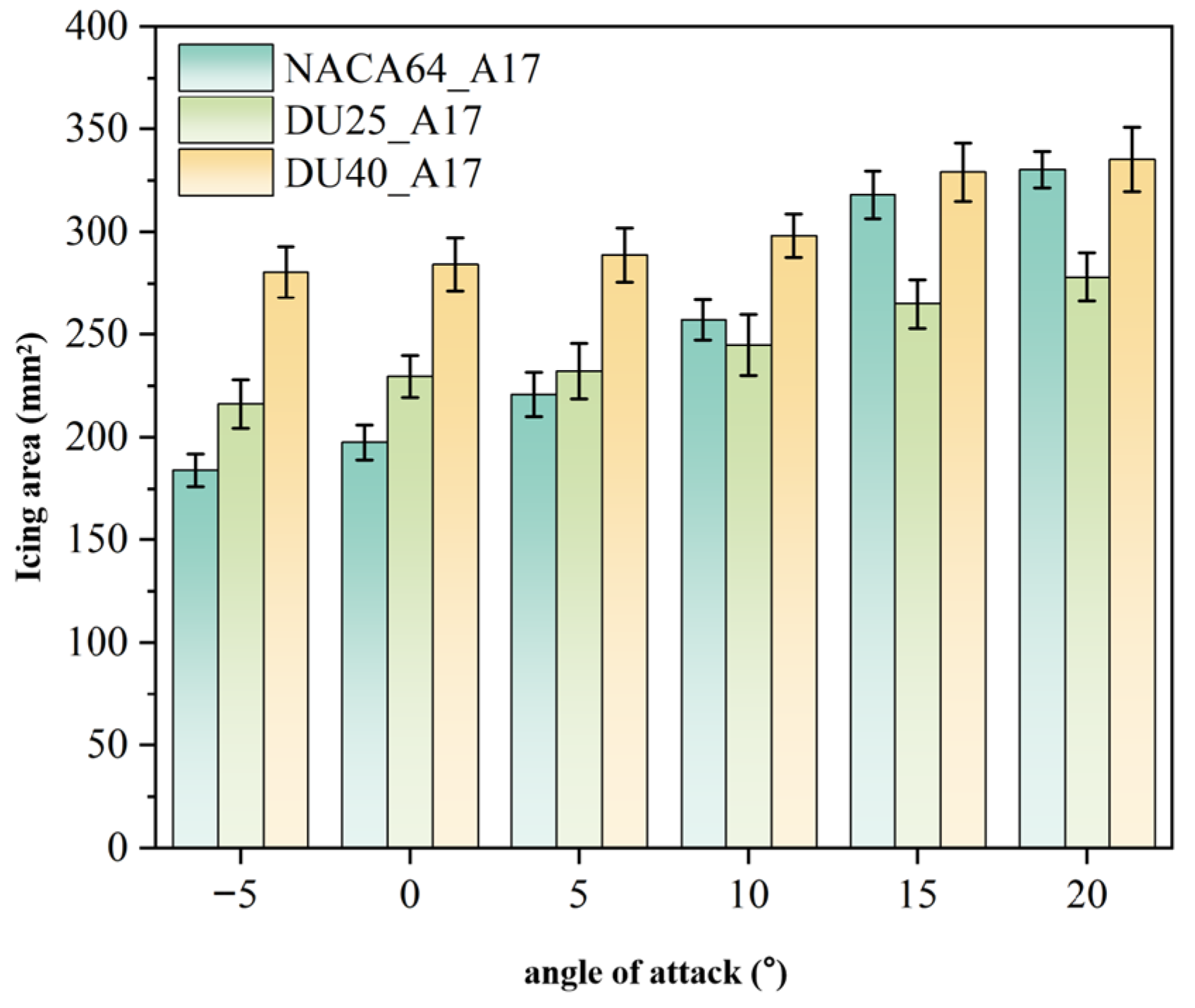
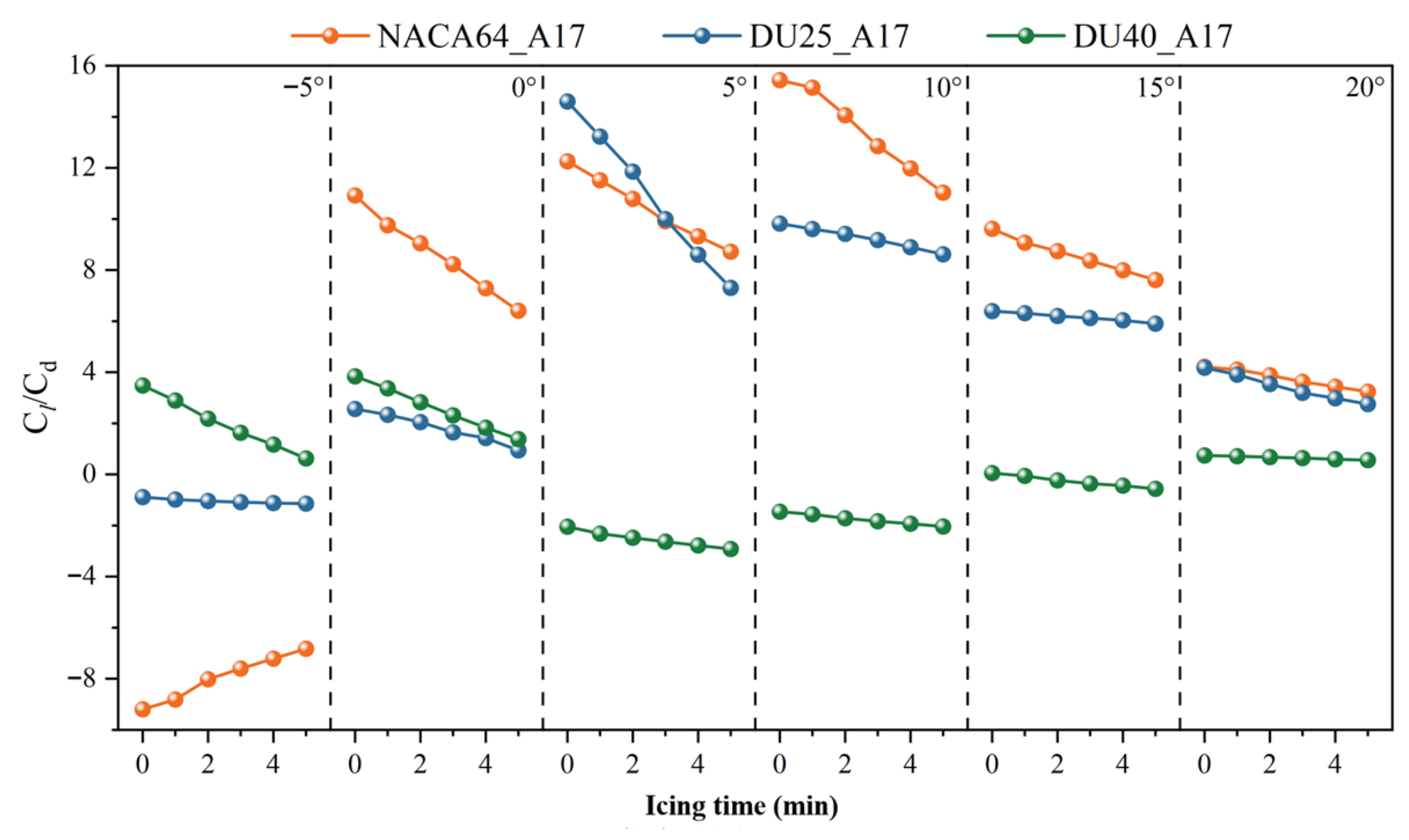
3.1.3. Influence of Angle of Attack
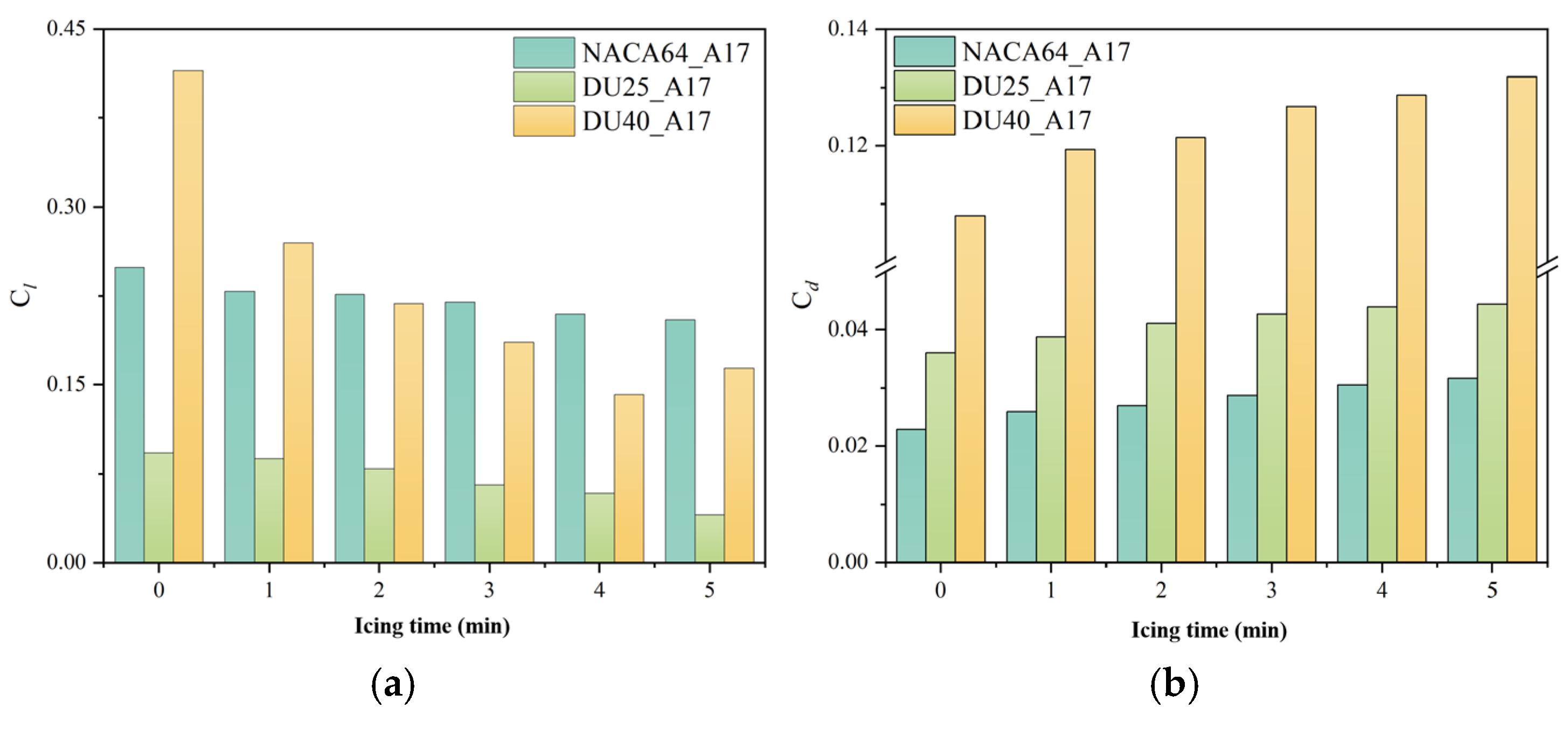
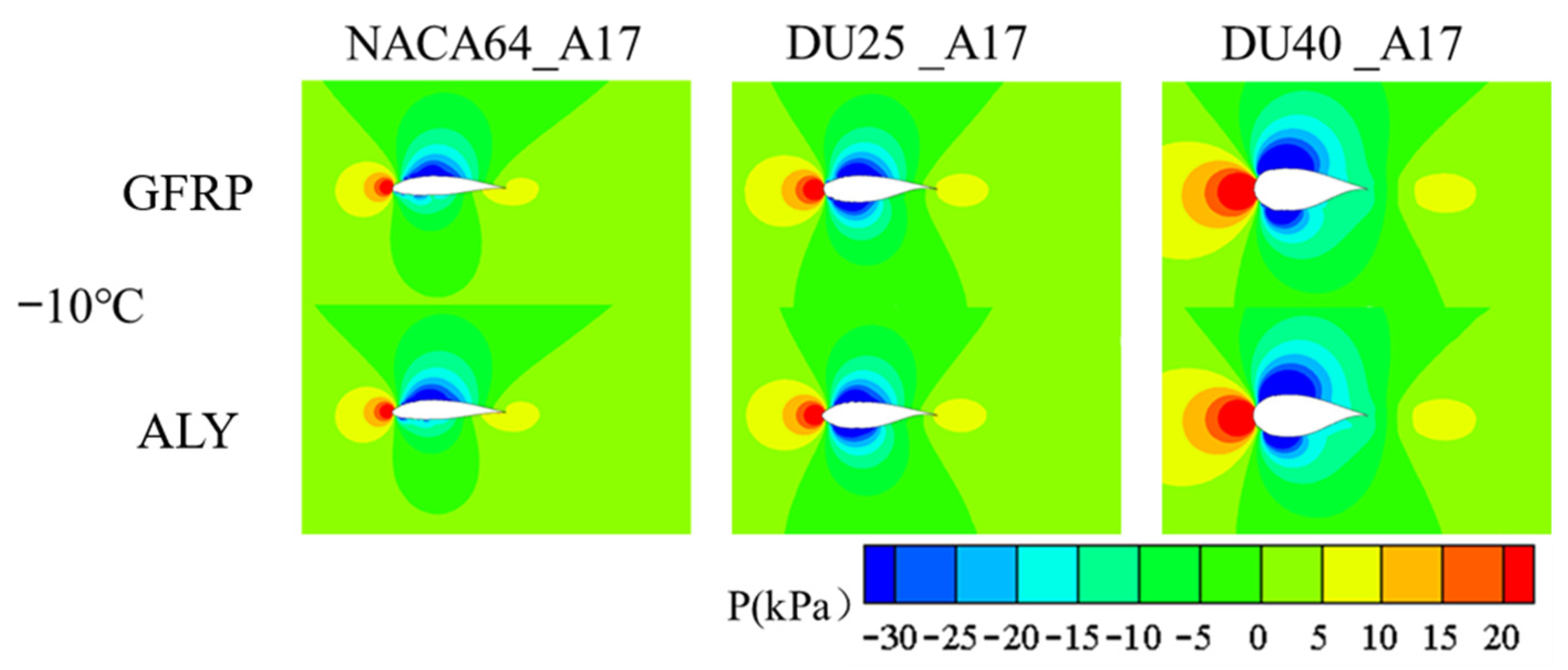
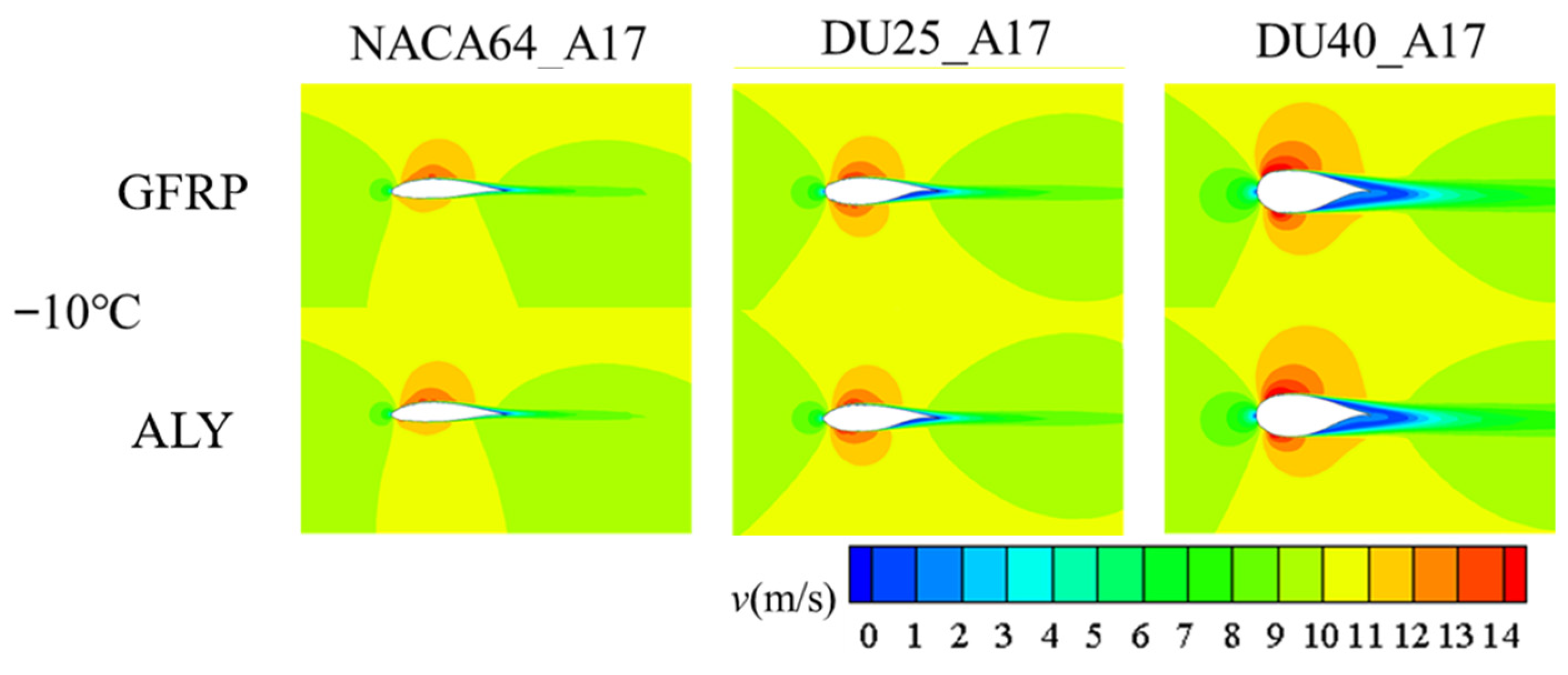
3.2. The Impact of Icing on the Aerodynamic Performance of Wind Turbine Blades
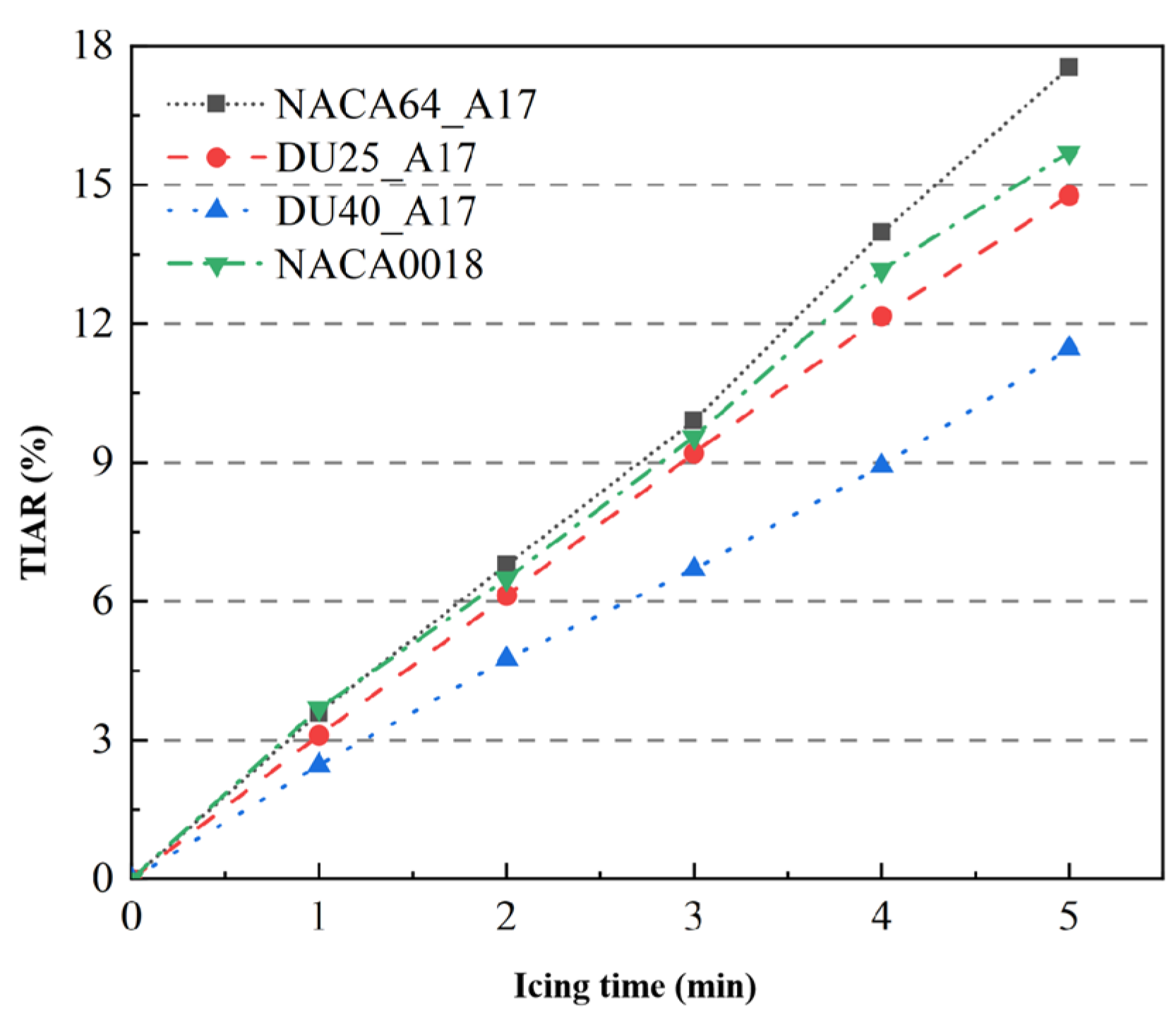
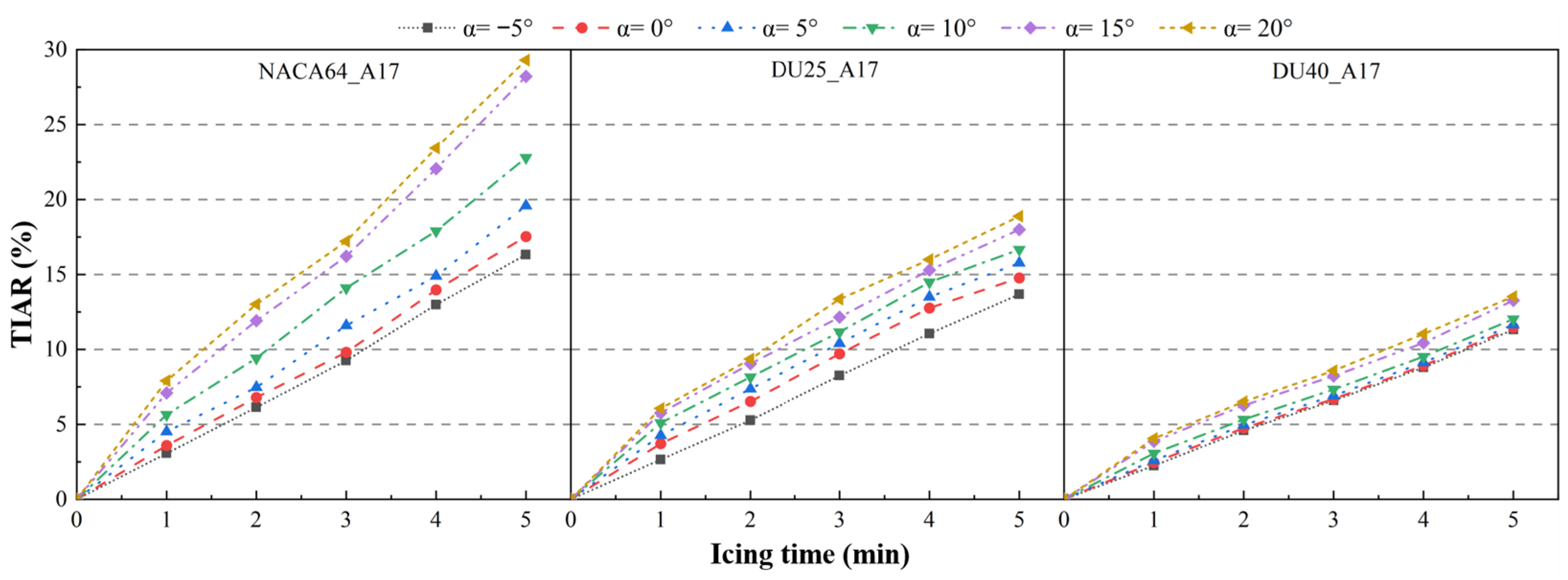
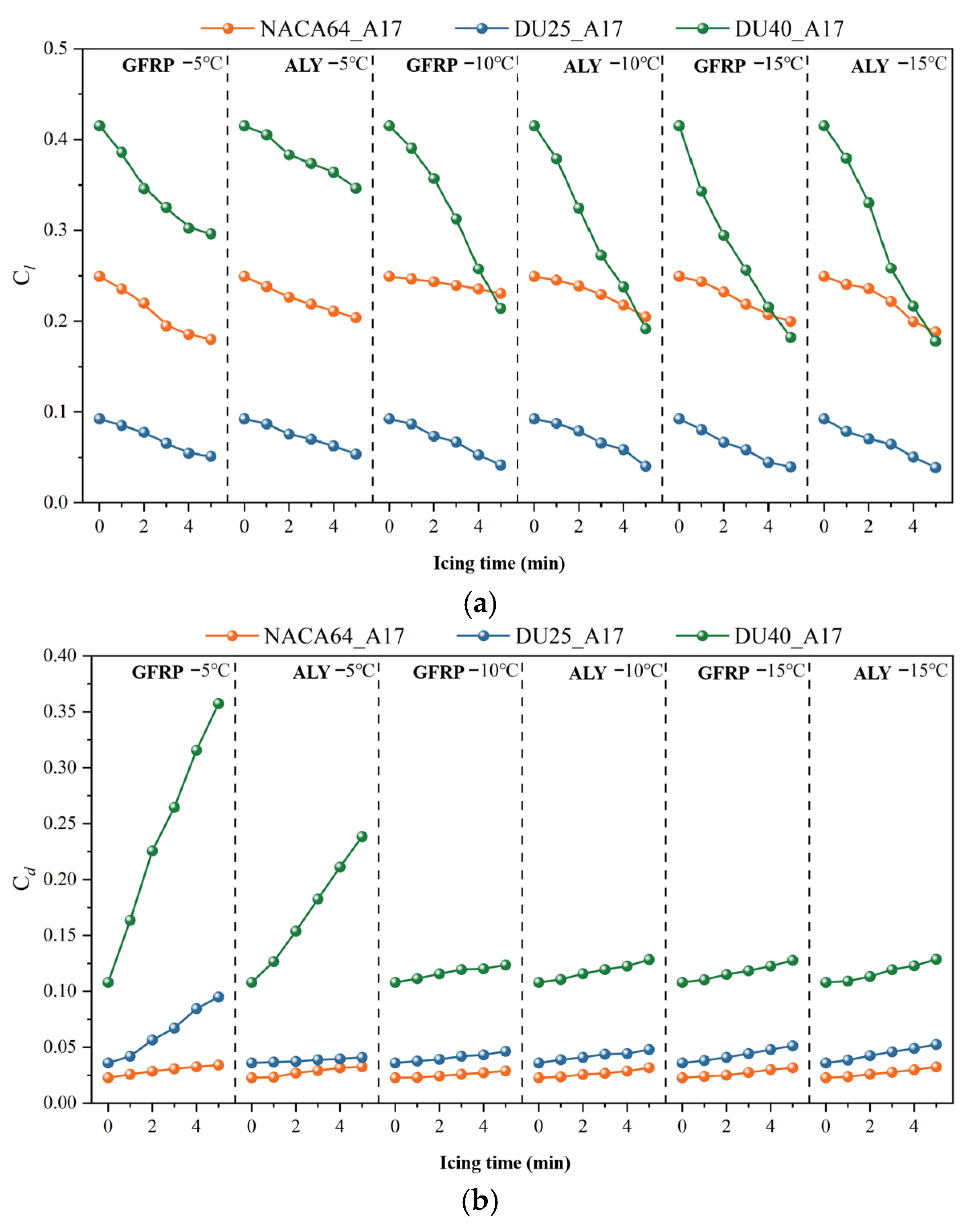
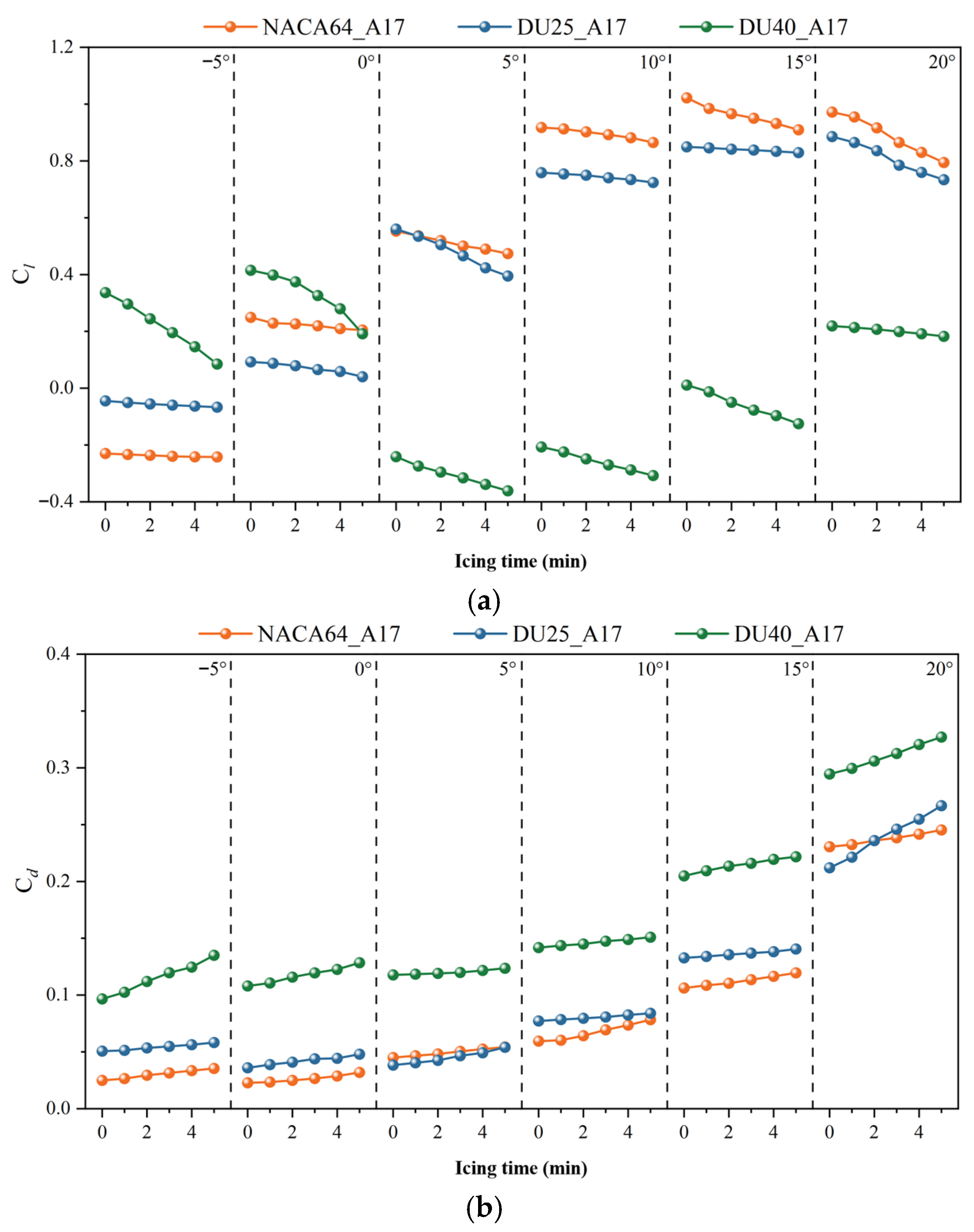
3.2.1. Effect of Icing Time
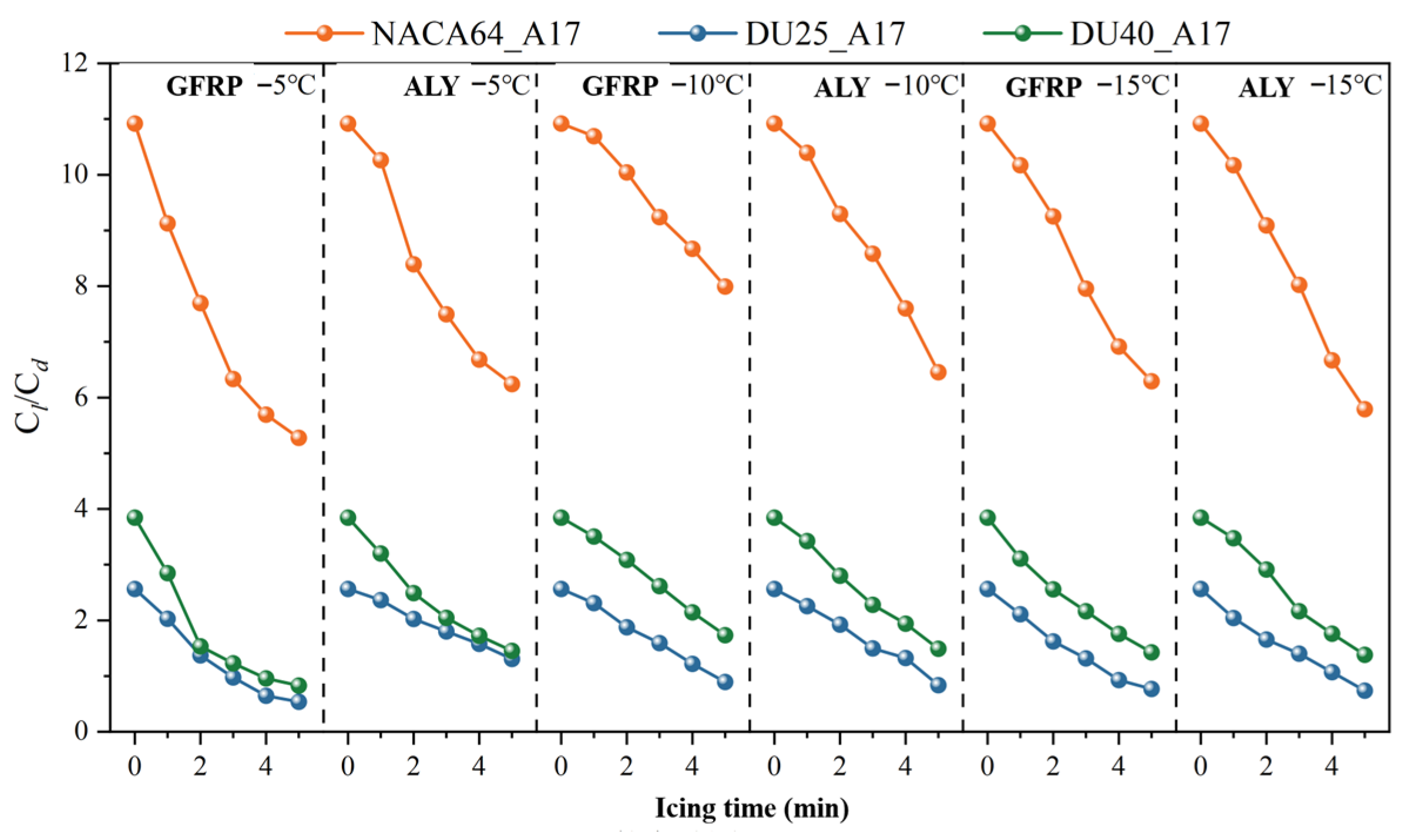
3.2.2. Influence of Blade Material
3.2.3. Influence of Blade Angle of Attack
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jung, C.; Schindler, D. Efficiency and effectiveness of global onshore wind energy utilization. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 280, 116788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukenmez, N.; Yuksel, Y.E.; Ozturk, M. Design and thermodynamic analysis of a solar-wind energy-based combined system for cleaner production of hydrogen with power, heating, hot water and clean water. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 94, 256–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitassa, B.; Yenlide, T. Does homeownership promote households’ consumption of clean energy in Togo? Energy Build. 2025, 346, 116240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadorsky, P. Wind energy for sustainable development: Driving factors and future outlook. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 289, 125779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.; Schindler, D. Global future onshore wind energy droughts intensify under climate change. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 523, 146391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desalegn, B.; Gebeyehu, D.; Tamrat, B.; Tadiwose, T.; Lata, A. Onshore versus offshore wind power trends and recent study practices in modeling of wind turbines’ life-cycle impact assessments. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2023, 17, 100691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Caglar, A.E.; Pinzon, S. Pathways to decarbonization: Assessing the influence of government effectiveness, economic dynamics, and wind and solar energy adoption on CO2 emissions. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 394, 127413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Luo, Y.; Li, P.; Chang, R.; Liao, Z.; Huang, L. Systematic evaluation of transformer-based time series forecasting models for post-processing WRF-simulated wind speed and predicting short-term power output. Appl. Energy 2026, 403, 127070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Li, C.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, M. A novel framework for temporal super-resolution of wind in urban energy applications. Renew. Energy 2026, 256, 124336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Guo, S.; Chen, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H. Icing diagnosis method of wind turbine blade based on mechanism and data driving. Renew. Energy 2025, 255, 123820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Q.; Jiang, X.L. A Review of Wind Turbine Icing and Anti/De-Icing Technologies. Energies 2024, 17, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yao, F.; Tu, H.; Peng, S.; Huang, M.; Liu, M.; Mei, J.; Wang, J. One-piece insulating superhydrophobic photothermal coating for suppression of icing and thermal aging of wind turbine blades. Prog. Org. Coat. 2025, 209, 109630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quayson-Sackey, E.; Nyantekyi-Kwakye, B.; Ayetor, G.K. Technological advancements for anti-icing and de-icing offshore wind turbine blades. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2025, 231, 104400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, M.C.; Ahsbahs, T.; Langreder, W.; Thøgersen, M.L. On the modelling chain for production loss assessment for wind turbines in cold climates. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2023, 216, 103989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Song, X.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Jia, Y.; Cai, C.; Li, Q.A. Fault diagnosis of wind turbine blade icing based on feature engineering and the PSO-ConvLSTM-transformer. Ocean Eng. 2024, 302, 117726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamraoui, F.; Fortin, G.; Benoit, R.; Perron, J.; Masson, C. Atmospheric icing impact on wind turbine production. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2014, 100, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, H. Multifunctional wearable protective fabrics for wind turbine blades: Triple-functional co-design of electrothermal de-icing/anti-icing, pressure sensing, and environmental protection. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 520, 165690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Yao, F.; Huang, H.; Tang, Q.; Tu, H.; Wang, J. Low-light/low-power de-icing composite coatings with thermal insulation and tunable optical radiation absorption for all-weather anti-icing of wind turbine blades. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 512, 162061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xiao, F.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, J. An expert features enhanced temporal and contextual contrasting learning model for detecting wind turbine blade icing. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 160, 111745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhang, S.P.; Shen, G.Q.; Zhou, L. Acoustic emission-based wind turbine blade icing monitoring using deep learning technology. Renew. Energy 2025, 247, 122980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germeshausen, R.; Heim, S.; Wagner, U.J. Support for renewable energy: The case of wind power. J. Public Econ. 2025, 250, 105468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; Guo, W.; Feng, F. An experimental study on icing distribution and adhesion characteristics of wind turbine blades in saltwater Condition. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2026, 170, 111575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resor, B.R. Definition of a 5Mw/61.5M Wind Turbine Blade Reference Model; U.S. Department of EnergyOffice of Scientific and Technical Information: Washington, DC, USA, 2013.
- Xu, Z.; Na, P.Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.X. Ice Distribution Characteristics on the DU25 and NACA63-215 Airfoil Surfaces of Wind Turbines as Affected by Ambient Temperature and Angle of Attack. Coatings 2024, 14, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revstedt, J.; Szasz, R.; Ivanell, S. LES and DES of flow and ice accretion on wind turbine blades. In Proceedings of the Conference on Modelling Fluid Flow (CMFF’25), the 19th International Conference on Fluid Flow Technologies, Budapest, Hungary, 26–29 August 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Maleksabet, Z.; Kozinski, J.; Tarokh, A. Impact of ice accretion on the aerodynamic characteristics of Wind turbine airfoil at low Reynolds numbers. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2025, 239, 104618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Chen, J.Z.; Lo, Y.L.; Fu, C.L. Numerical and Experimental Studies on the Aerodynamics of NACA64 and DU40 Airfoils at Low Reynolds Numbers. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Yang, K.; Zhang, L.; Bai, J.Y. Experimental study of Reynolds number effects on performance of thick CAS wind turbine airfoils. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2017, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Hu, H. An experimental study on the aerodynamic performance degradation of a wind turbine blade model induced by ice accretion process. Renew. Energy 2019, 133, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

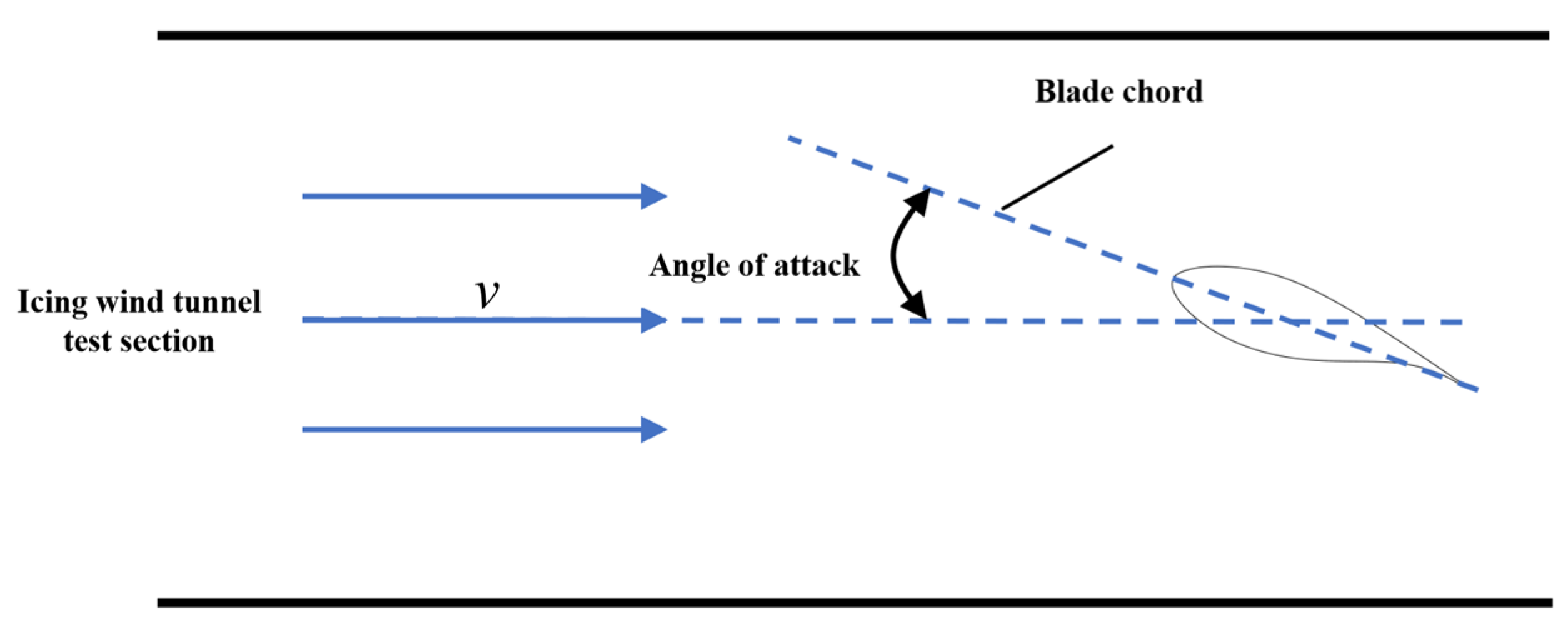
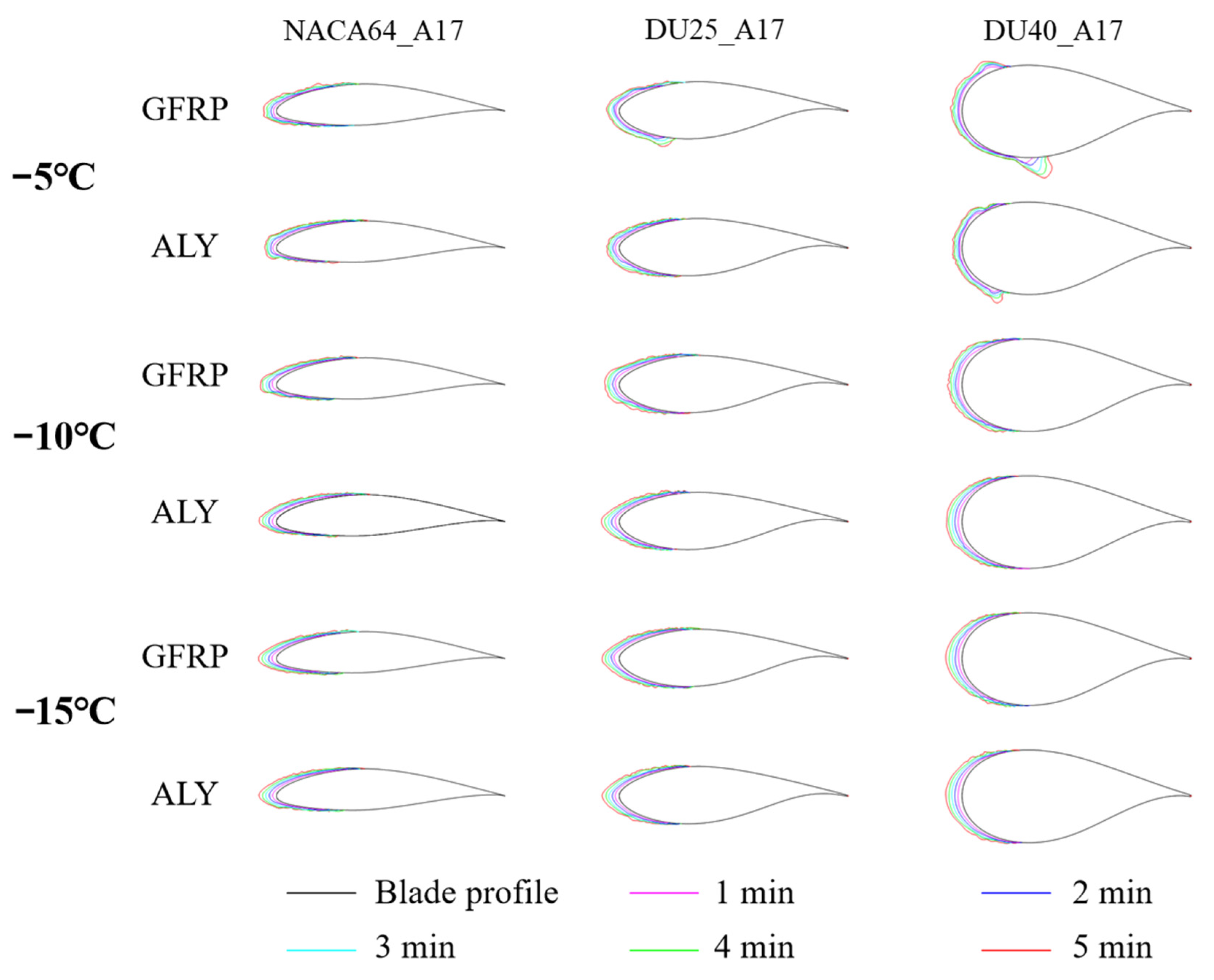
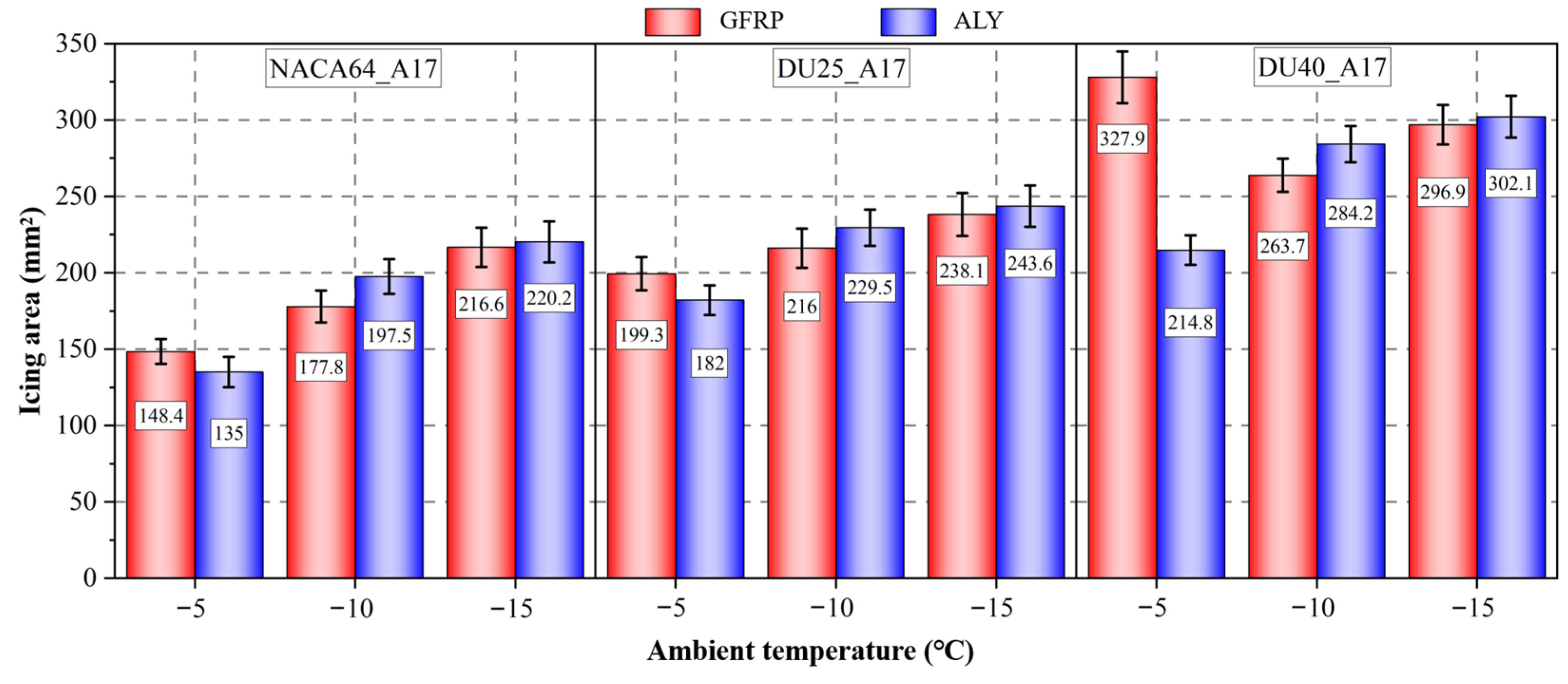
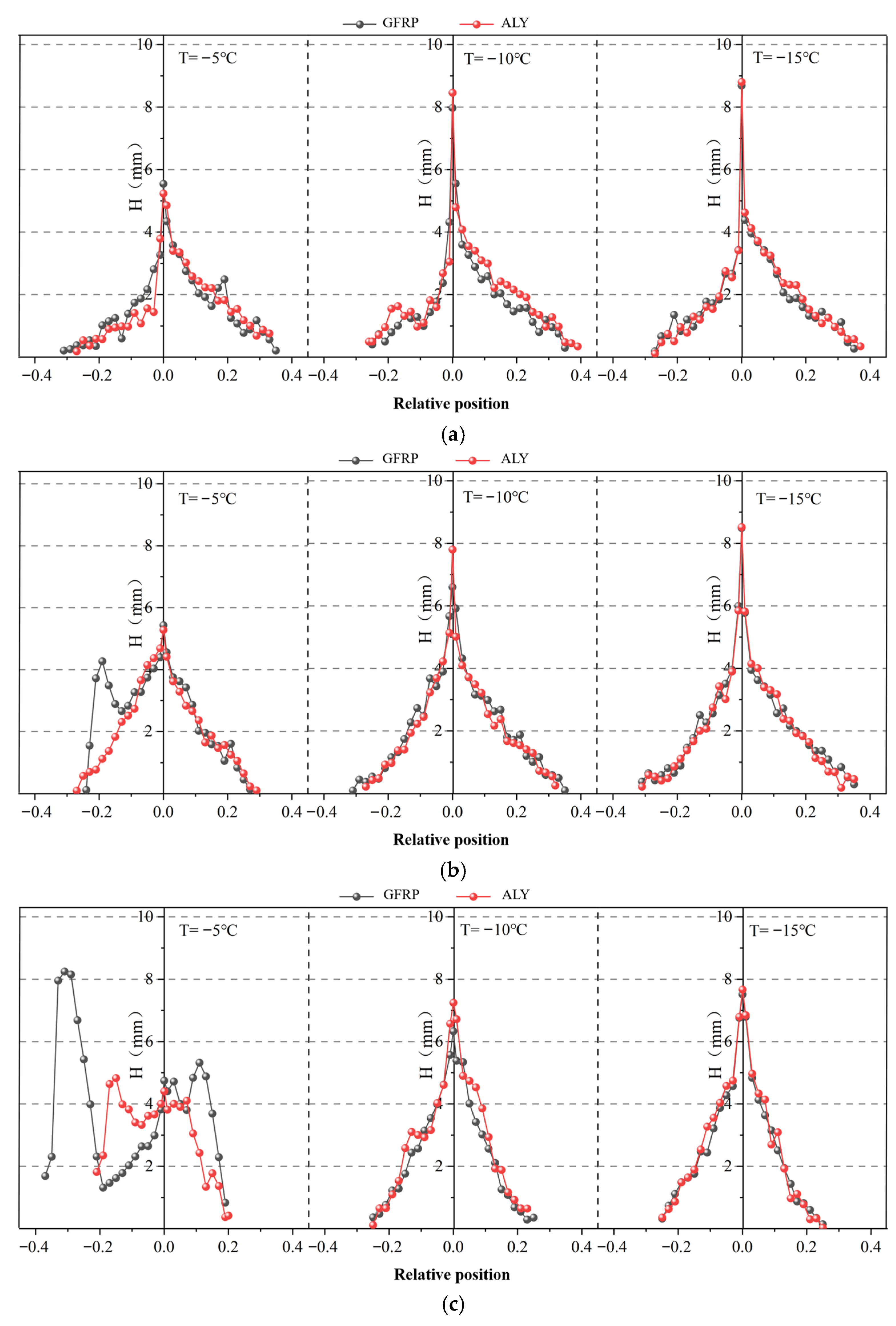

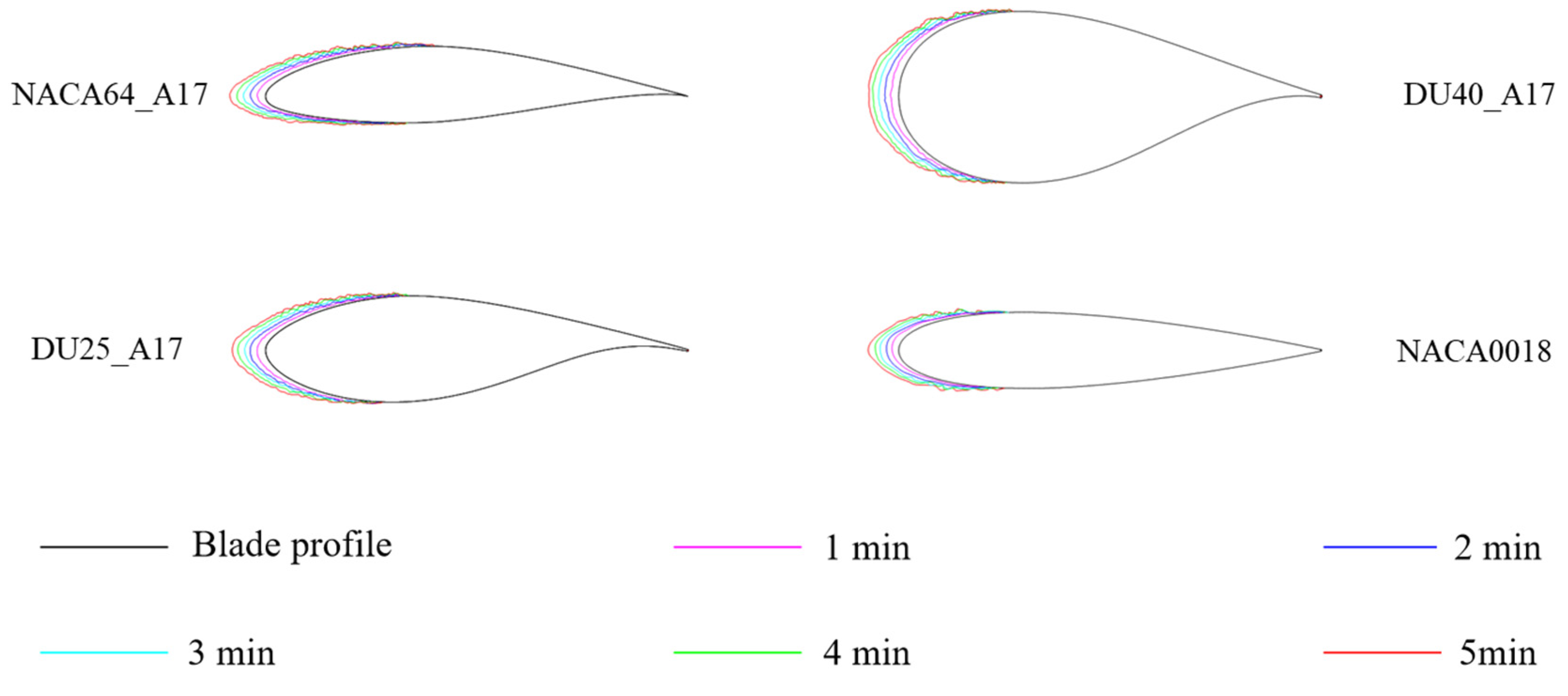
| Blade Material | Test Temperature (°C) | Test Wind Speed (m/s) | Angle of Attack (°) | Chord Length (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GFRP | −5, −10, −15 | 10 | 0 | 100 |
| ALY |
| Blade Airfoils | Test Temperature (°C) | Test Wind Speed (m/s) | Angle of Attack (°) | Chord Length (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NACA64_A17 | −10 | 10 | 0 | 100 |
| DU25_A17 | ||||
| DU40_A17 | ||||
| NACA0018 |
| Angle of Attack (°) | Test Temperature (°C) | Test Wind Speed (m/s) | Chord Length (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| −5 | −10 | 10 | 100 |
| 0 | |||
| 5 | |||
| 10 | |||
| 15 | |||
| 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Jiao, C.; Wu, T.; Zheng, R.; Liang, D.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y. Study on the Influence of Airfoil and Angle of Attack on Ice Distribution and Aerodynamic Performance of Blade Surface. Coatings 2025, 15, 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15121416
Wang C, Jiao C, Wu T, Zheng R, Liang D, Liu Z, Li Y. Study on the Influence of Airfoil and Angle of Attack on Ice Distribution and Aerodynamic Performance of Blade Surface. Coatings. 2025; 15(12):1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15121416
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chuanxi, Chong Jiao, Tong Wu, Ruxin Zheng, Dong Liang, Zhiyuan Liu, and Yan Li. 2025. "Study on the Influence of Airfoil and Angle of Attack on Ice Distribution and Aerodynamic Performance of Blade Surface" Coatings 15, no. 12: 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15121416
APA StyleWang, C., Jiao, C., Wu, T., Zheng, R., Liang, D., Liu, Z., & Li, Y. (2025). Study on the Influence of Airfoil and Angle of Attack on Ice Distribution and Aerodynamic Performance of Blade Surface. Coatings, 15(12), 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15121416





