DC Sputtered Ultra-Thin Au Films and the Effect of Their Morphologies on Au-Catalyzed CIGS Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
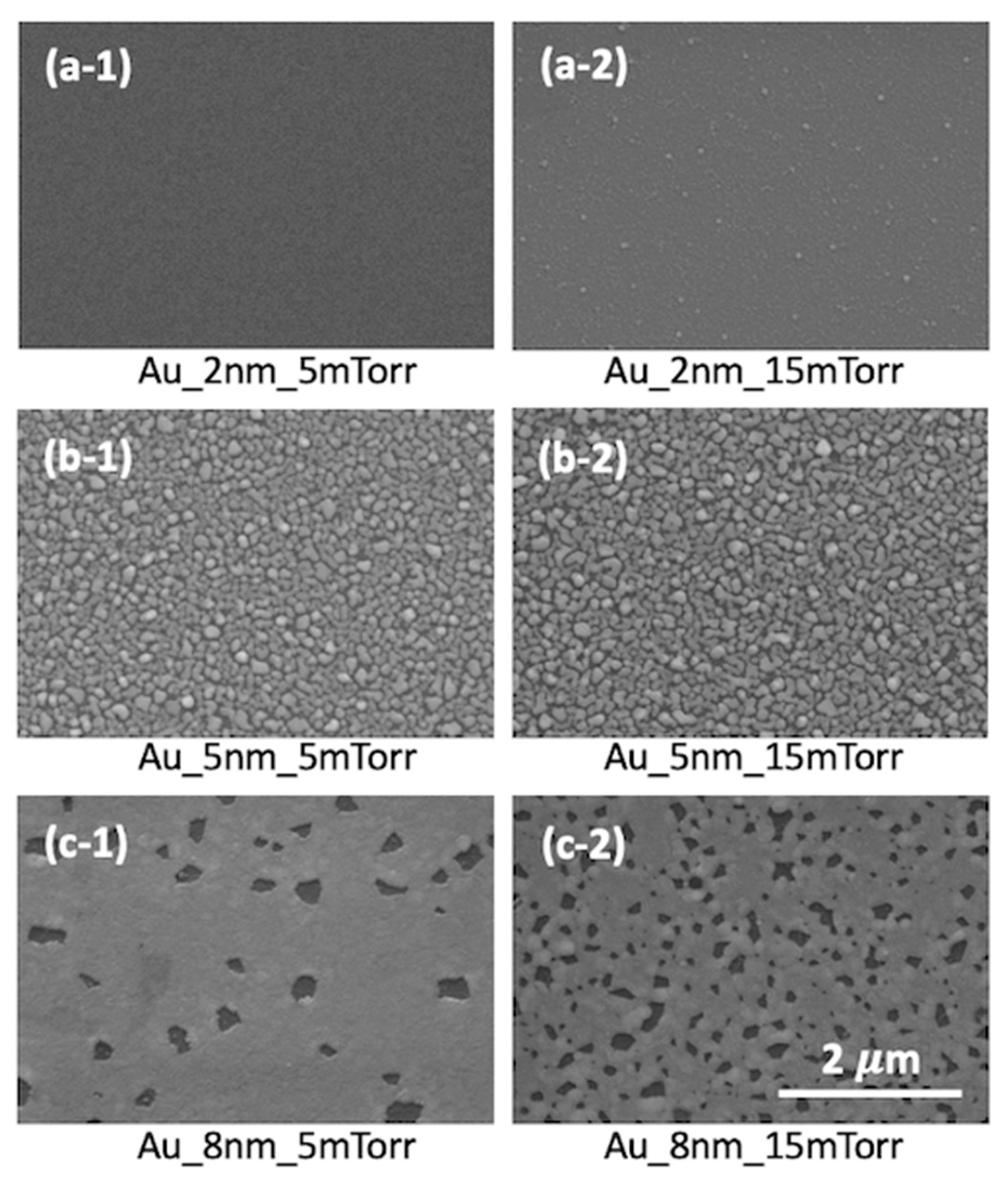
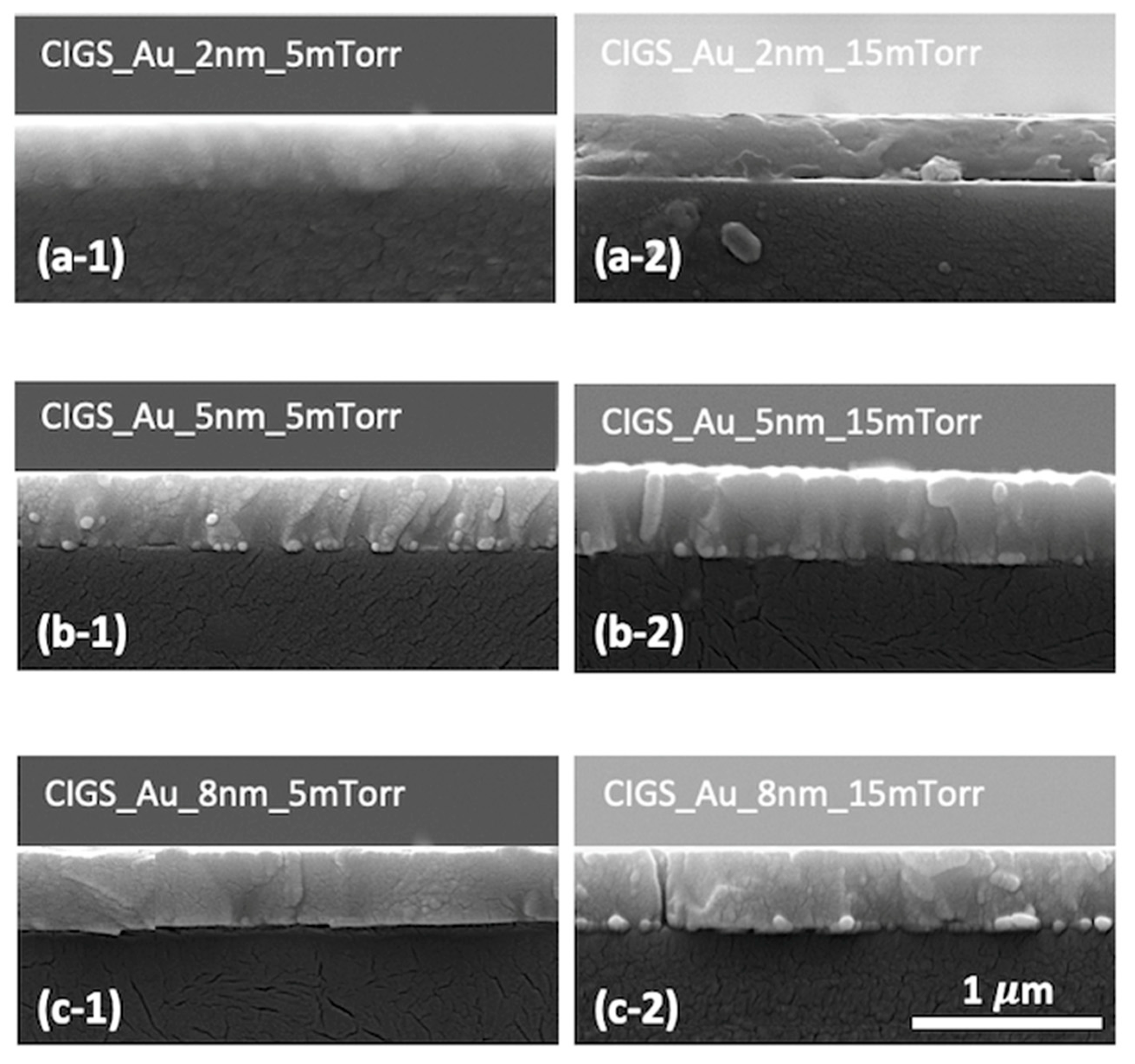
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pillai, S.; Green, M.A. Plasmonics for photovoltaic applications. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2010, 94, 1481–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kac, H.; Baltakesmez, A.; Çaldıran, Z.; Aydogan, S.; Yılmaz, M.; Sevim, M. Optical and electrical characterization of organic solar cells obtained using gold and silver metal nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 6986–6990. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Kim, T.G.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, W.; Bang, A.; Moon, S.W.; Song, J.; Shin, J.-H.; Yu, J.S.; Choi, S. Label-free surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy biosensor for on-site breast cancer detection using human tears. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 7897–7904. [Google Scholar]
- Siampour, H.; Abbasian, S.; Moshaii, A.; Amirsoleimani, A.R. Stable, reproducible, and binder-free gold/copper core–shell nanostructures for high-sensitive non-enzymatic glucose detection. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18945. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zou, K.; Xing, W.; Hou, X.; Zeng, Y.; Cai, Y.; Xu, R.; Zhang, H.; Cai, W. Au ordered array substrate for rapid detection and precise identification of etomidate in E-liquid through surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Kamakshi, K.; Silva, J.P.B.; Sekhar, K.C.; Marslin, G.; Moreira, J.A.; Conde, O.; Almeida, A.; Pereira, M.; Gomes, M.J.M. Influence of substrate temperature on the properties of pulsed laser deposited silver nanoparticle thin films and their application in SERS detection of bovine serum albumin. Appl. Phys. B 2016, 122, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, J. Ultrathin Metal films for Transparent Electrodes of Flexible Optoelectronic Devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1606641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Schmidt, V.; Senz, S.; Gosele, U. Epitaxial growth of silicon nanowires using an aluminium catalyst. Nat. Nanotech 2016, 1, 186–189. [Google Scholar]
- Ly, L.Q.; Bonvicini, S.N.; Shi, Y. Platinum nanoparticle formation by pulsed laser-induced dewetting and its application as catalyst in silicon nanowire growth. J. Phys. Chem. C 2025, 129, 4553–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Jin, F.; Su, Z.; Zhao, H.; Luo, Y.; Chu, B.; Li, W. All thermal-evaporated surface plasmon enhanced organic solar cells by Au nanoparticles. Org. Electron. 2016, 39, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-C.; Chen, Y.-J.; Chen, W.T.; Yen, Y.-T.; Kao, T.S.; Chuang, T.-Y.; Liao, Y.-K.; Wu, K.-H.; Yabushita, A.; Hsieh, T.-P.; et al. Toward omnidirectional light absorption by plasmonic effect for high-efficiency flexible nonvacuum Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin film solar cells. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 9341–9348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lie, S.; Brun, A.; Wong, L.H.; Etgar, L. Semitransparent perovskite solar cells with >13% efficiency and 27% transperancy using plasmonic Au nanorods. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 11339–11349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsey, G.; Moore, A.; Heffner, C.; Ueda, A.; Mu, R.; Collins, W.E. The growth and characterization of Au-catalyzed gallium oxide nanowires. MRS Adv. 2024, 9, 1318–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, S.; Jin, Y.; Liu, J.G.; Gong, M.; Sun, X. Growth of GaN nanorods via Au catalyst-assisted CVD. Chem. Vap. Depos. 2005, 11, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Y.-C.; Wen, C.-Y.; Reuter, M.C.; Su, D.; Stach, E.A.; Ross, F.M. Controlling the growth of Si/Ge nanowires and heterojunctions using silver-gold alloy catalysts. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6407–6415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givargizov, E.I. Fundamental aspects of VLS growth. J. Cryst. Growth 1975, 31, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, V.; Sengar, B.S.; Awasthi, V.; Aaryashree; Sharma, P.; Mukherjee, C.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, S. Localized surface plasmon resonance on Au nanoparticles: Tuning and exploitation for performance enhancement in ultrathin photovoltaics. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 26216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.T.; Nguyen, T.M.A.; Sai, C.D.; Le, T.H.Y.; Tran, T.N.A.; Bach, T.C.; Le, V.V.; Pham, N.H.; Ngac, A.B.; Nguyen, V.T.; et al. Efficient surface enhanced Raman scattering substrates based on complex gold nanostructures formed by annealing sputtered gold thin films. Opt. Mater. 2021, 121, 111488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedl, E.; Bregović, V.B.; Rakić, I.Š.; Mandić, Š.; Samec, Ž.; Bergmann, A.; Sancho-Parramon, J. Optical properties of annealed nearly percolated Au thin films. Opt. Mater. 2023, 135, 113237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Wang, R.; Zhu, P.; Wang, F.; Dong, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Fabrication of gold nanoparticle decorated surfaces for controlled nucleation of plasmonic microbubbles. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 36, 102591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, G.; Shymkiv, D.; Krokhin, A.; Littler, C.; Syllaios, A.J.; Philipose, U. Plasmonic properties of gold nanoparticle arrays fabricated using a sequential dewetting process. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2025, 126, 081103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.-C.; Chien, T.-Y.; Cheng, Y.-W.; Hsieh, C.-K.; Syu, W.-L.; Wang, K.-S.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, J.-S.; Chen, C.-C.; Liu, T.-Y. Reproducible SERS substrates manipulated by interparticle spacing and particle diameter of gold nano-island array using in-situ thermal evaporation. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 303, 123190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, D.; Pimentel, A.C.; Mateus, T.; Leita, J.P.; Soares, J.; Falca, B.P.; Arau, A.; Vicente, A.; Filonovich, S.A.; Águas, H.; et al. Influence of the layer thickness in plasmonic gold nanoparticles produced by thermal evaporation. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffino, F.; Grimaldi, M.G. Atomic force microscopy study of the growth mechanisms of nanostructured sputtered Au film on Si(111): Evolution with film thickness and annealing time. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 104321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, Y.K.; Mohapatra, S.; Kabiraj, D.; Tripathi, A.; Pivin, J.C.; Avasthi, D.K. Growth of Au nanostructures by annealing electron beam evaporated thin films. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2007, 9, S410–S414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-Y.; Sui, M.; Pandey, P.; Zhang, Q.; Kim, E.-S.; Lee, J. Systematic control of self-assembled Au nanoparticles and nanostructures through the variation of deposition amount, annealing duration, and temperature on Si (111). Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Yu, M.; Wang, G.; Sun, X.; Lian, J. Temperature-dependent morphology evolution and surface plasmon absorption of ultrathin gold island films. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 9000–9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinský, P.; Slepička, P.; Hnatowicz, V.; Švorčík, V. Early stages of growth of gold layers sputter deposited on glass and silicon substrates. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keles, F.; Atasoy, Y.; Seyhan, A. Sputtered Mo-bilayer thin films with reduced thickness and improved electrical resistivity. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 126455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keles, F.; Badradeen, E.; Karabacak, T. Self-anti-reflective density-modulated thin films by HIPS technique. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 335703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keles, F.; Cansizoglu, H.; Badraddin, E.O.; Brozak, M.P.; Watanabe, F.; Karabacak, T. HIPS-GLAD core shell nanorod array photodetectors with enhanced photocurrent and reduced dark current. Mater. Res. Express 2016, 3, 105028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-Y.; Sui, M.; Pandey, P.; Zhang, Q.-Z.; Kunwar, S.; Salamo, G.J.; Lee, J. Precise control of configuration, size and density of self-assembled Au nanostructures on 4H-SiC (0001) by systematic variation of deposition amount, annealing temperature and duration. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2016, 18, 3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Tang, L.; Liu, G. Annealed gold nanoshells with highly-dense hotspots for large-area efficient Raman scattering substrates. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 262, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Shi, L.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X. A novel SERS substrate platform: Spatially stacking plasmonic hotspots films. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Keleş, F. DC Sputtered Ultra-Thin Au Films and the Effect of Their Morphologies on Au-Catalyzed CIGS Films. Coatings 2025, 15, 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15111274
Keleş F. DC Sputtered Ultra-Thin Au Films and the Effect of Their Morphologies on Au-Catalyzed CIGS Films. Coatings. 2025; 15(11):1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15111274
Chicago/Turabian StyleKeleş, Filiz. 2025. "DC Sputtered Ultra-Thin Au Films and the Effect of Their Morphologies on Au-Catalyzed CIGS Films" Coatings 15, no. 11: 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15111274
APA StyleKeleş, F. (2025). DC Sputtered Ultra-Thin Au Films and the Effect of Their Morphologies on Au-Catalyzed CIGS Films. Coatings, 15(11), 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15111274






