Surface Modification of Screen-Printed Carbon Electrodes
Abstract
1. Introduction
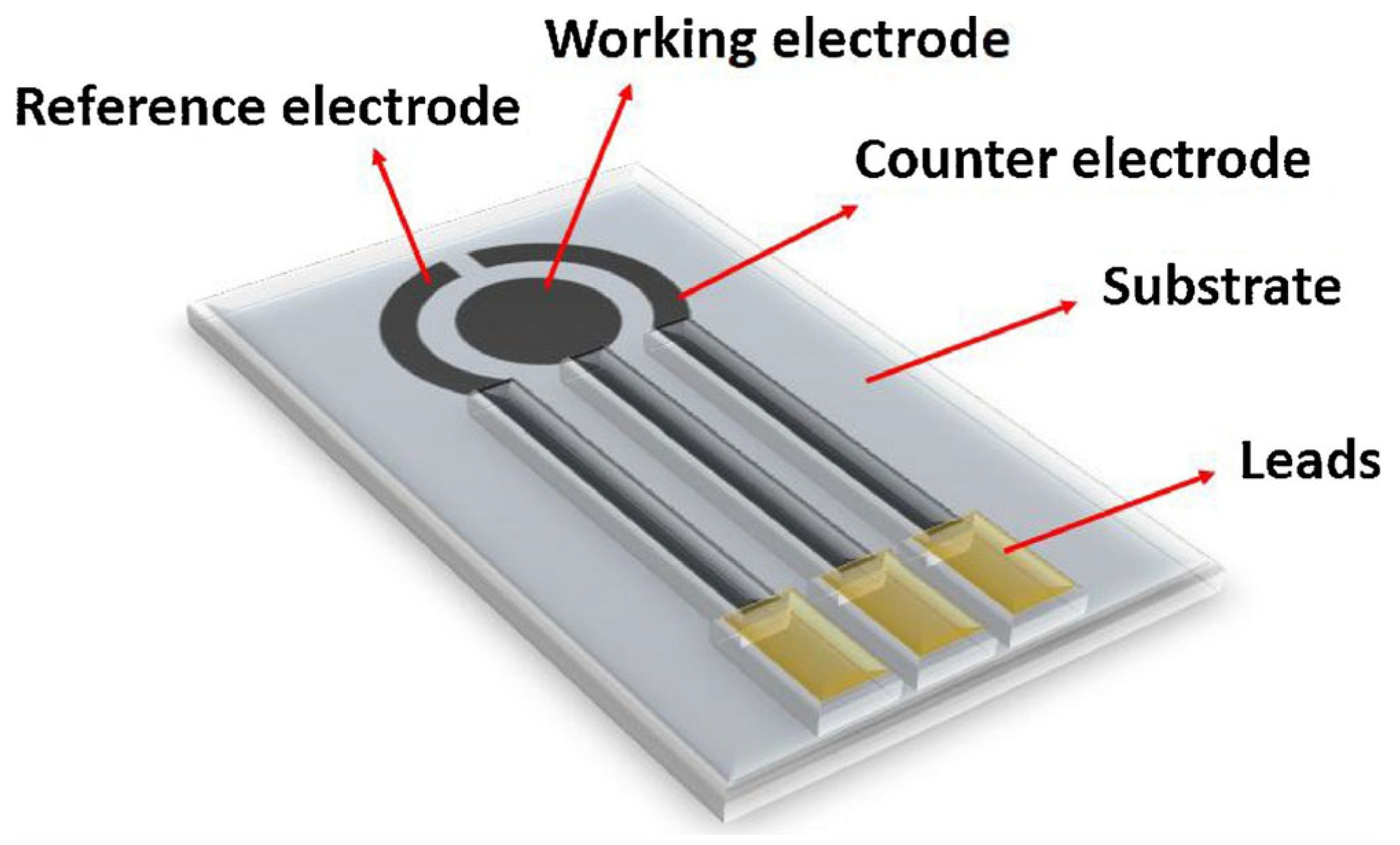
2. Structural Features of SPCE
- (1)
- Choosing the mesh or screen design to determine the SPE size and shape is important.
- (2)
- Obtaining the correct conductive inks and materials for the substrate.
- (3)
- A thin film was made by layer-by-layer (LBL) deposition to choose the inks for the substrate.
- (4)
- The film was dried using hot air and IR radiation and cured to set the ink. Analytical tests can be performed after placing an insulating material over the electrical circuits. This is achieved by placing a single drop of the sample (analyte) solution on the SPE surface [22].
Commercial Platforms for Working with SPCEs
3. Electrochemical Methods Used for SPCE Characterization and Application
3.1. Cyclic Voltammetry (CV)
3.2. Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV)
3.3. Square Wave Voltammetry (SWV)
3.4. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS)
3.5. Linear Sweep Voltammetry
3.6. Chronoamperometry
4. Use of SPCEs in Flow Injection Systems
5. Electrochemical Sensors Based on Unmodified SPCE
6. Surface Modification of SPCE for Use in Electrochemical Sensors
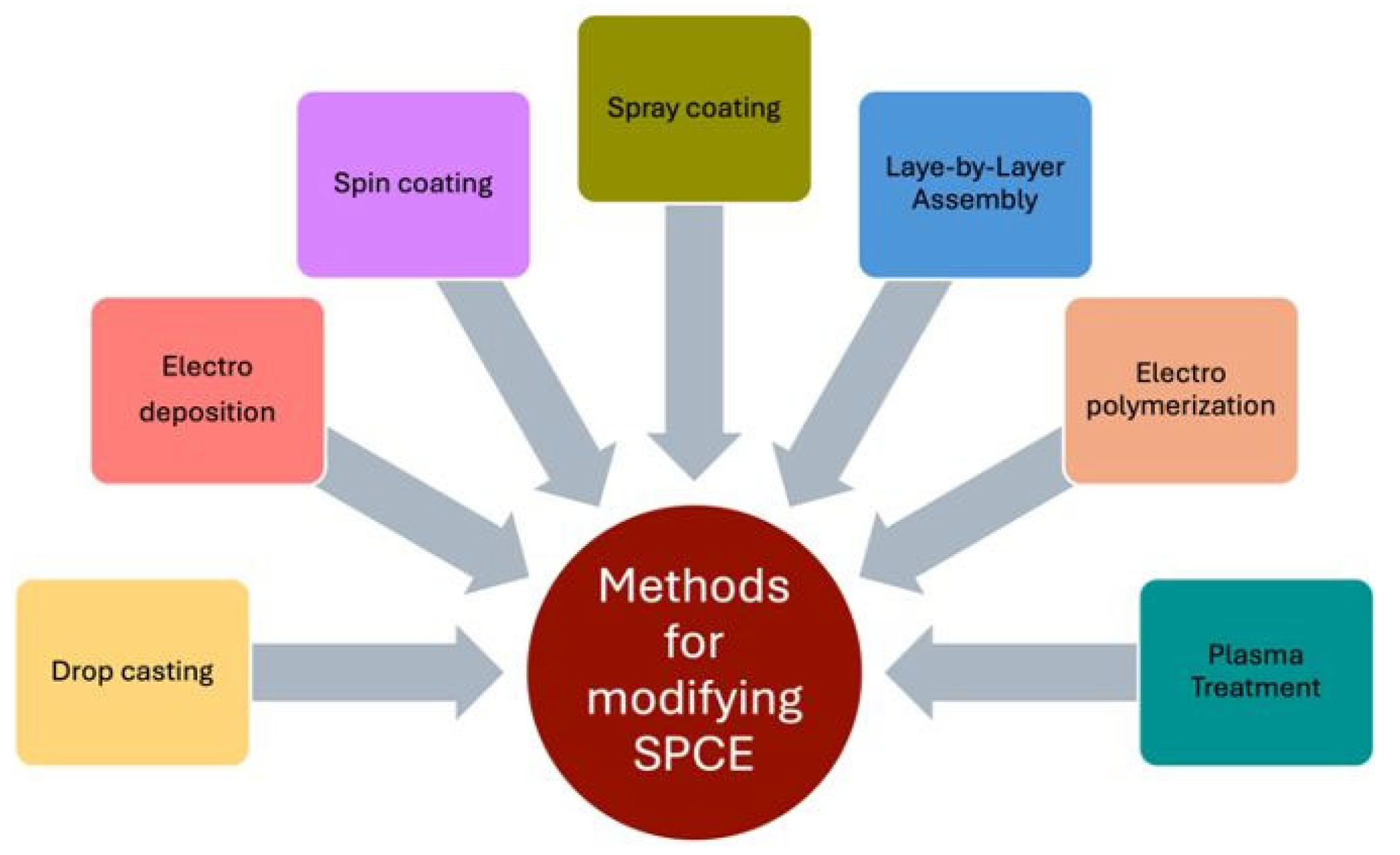
6.1. Modification Methods for SPCE
6.2. Types of Modifications
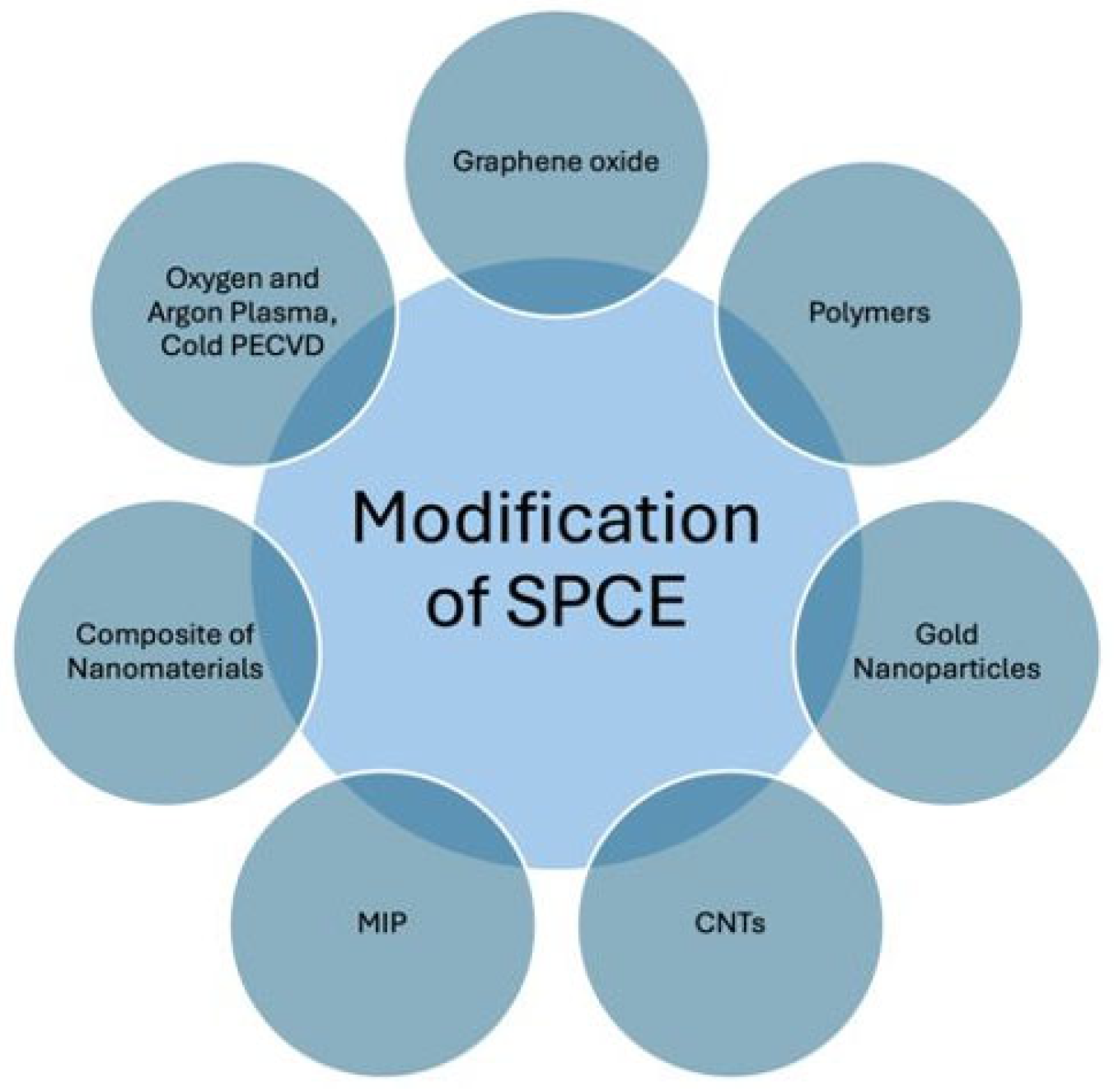
6.2.1. Plasma Modification
Cold Atmospheric Plasma Modification
Oxygen Plasma Modification
Cold Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
Argon Plasma Treatment
6.2.2. Modification by Gold Nanoparticles
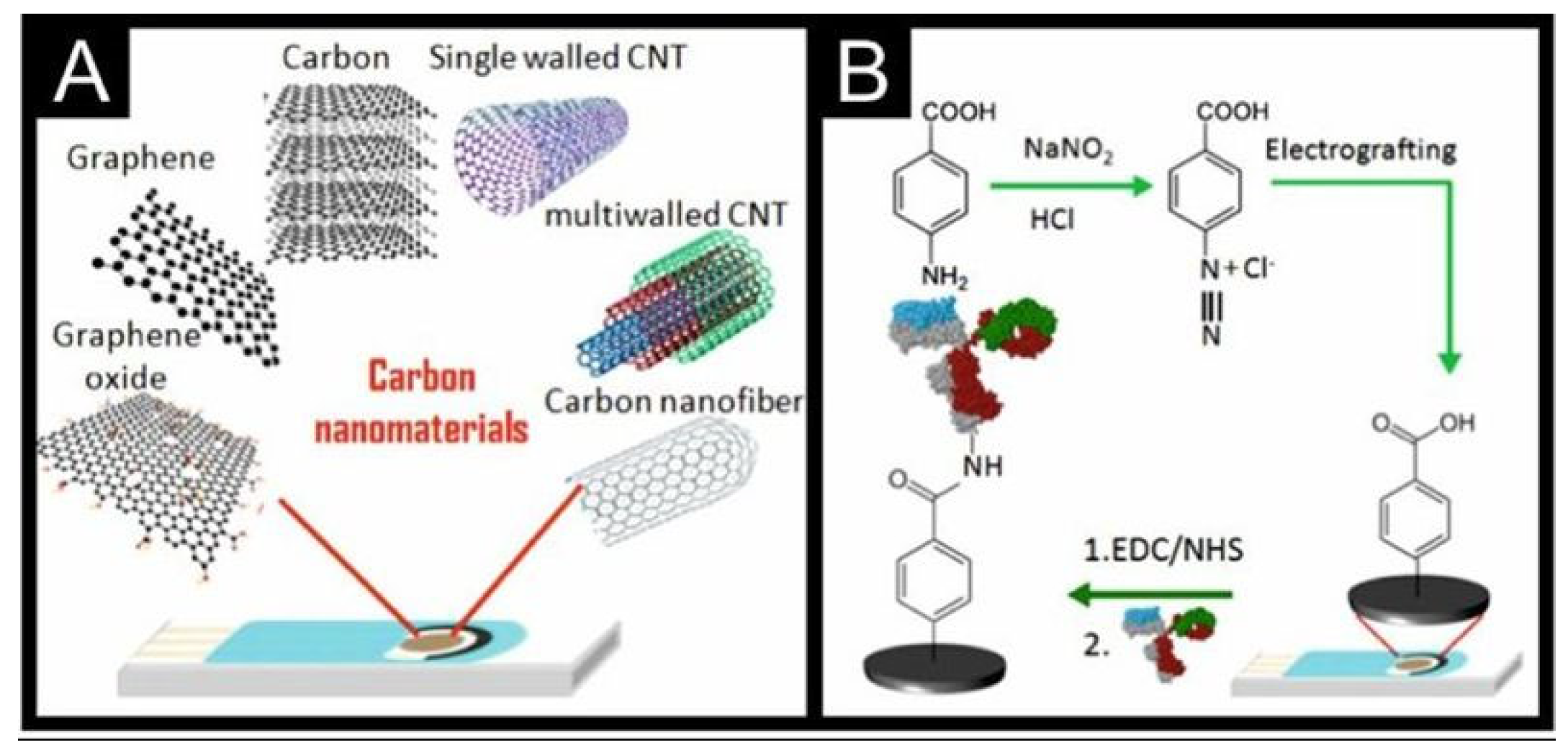
6.2.3. Modification by Carbon-Based Nanomaterials
Graphene Oxide
Carbon Nanotubes
6.2.4. Modification by Polymers
6.2.5. Modification Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIP)

6.2.6. Modification by Composite Nanostructures
7. Comparative Analysis of Using Unmodified SPCE vs. Modified SPCE
8. Use of Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes for Multi-Analyte Detection
9. Greener and More Sustainable Methods for Producing SPCEs
10. Advances in Integrating Modified SPCEs for Wearable Sensors
11. Conclusions and Future Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baranwal, J.; Barse, B.; Gatto, G.; Broncova, G.; Kumar, A. Electrochemical sensors and their applications: A review. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, A.C.; Gorey, B.; Chandra, S.; Chapman, J. Carbon nanomaterials and their application to electrochemical sensors: A review. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2018, 7, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, F.; Sala, A.; Fahs, A.; Morrin, A.; Nanteuil, C.; Laffite, G.; Nicholls, I.A.; Regan, F.; Brisset, H.; Branger, C. Investigation of the modification of gold electrodes by electrochemical molecularly imprinted polymers as a selective layer for the trace level electroanalysis of PAH. Electrochem. Commun. 2024, 169, 107837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, M.S.; Kadu, A.K. Thiol-based chemically modified carbon screen-printed electrode for simultaneous quantification of trace level Pb (II) and Cd (II). Anal. Sci. 2024, 40, 1449–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reanpang, P.; Themsirimongkon, S.; Saipanya, S.; Chailapakul, O.; Jakmunee, J. Cost-effective flow injection amperometric system with metal nanoparticle loaded carbon nanotube modified screen printed carbon electrode for sensitive determination of hydrogen peroxide. Talanta 2015, 144, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, M.O.; Srikanth, B.; Zhu, P.-Y.; Chuang, C.-H. Impedimetric immunosensor utilizing polyaniline/gold nanocomposite-modified screen-printed electrodes for early detection of chronic kidney disease. Sensors 2019, 19, 3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, D.W.; LeBlanc, G.; Meschievitz, M.E.; Cliffel, D.E. Electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 685–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, Z.; Roushani, M.; Hosseini, H.; Choobin, H. An electrochemical immunosensor using SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-nickel hydroxide nanoparticles bio-conjugate modified SPCE for ultrasensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. Microchem. J. 2021, 170, 106718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argoubi, W.; Saadaoui, M.; Aoun, S.B.; Raouafi, N. Optimized design of a nanostructured SPCE-based multipurpose biosensing platform formed by ferrocene-tethered electrochemically-deposited cauliflower-shaped gold nanoparticles. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1840–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedaghat, S.; Kasi, V.; Nejati, S.; Krishnakumar, A.; Rahimi, R. Improved performance of printed electrochemical sensors via cold atmospheric plasma surface modification. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 10562–10573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crapnell, R.D.; Ferrari, A.G.-M.; Dempsey, N.C.; Banks, C.E. Electroanalytical overview: Screen-printed electrochemical sensing platforms for the detection of vital cardiac, cancer and inflammatory biomarkers. Sens. Diagn. 2022, 1, 405–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, R.R.; Lakshmanakumar, M.; Arockia Jayalatha, J.; Rajan, K.; Sethuraman, S.; Krishnan, U.M.; Rayappan, J.B.B. Fabrication of screen-printed electrodes: Opportunities and challenges. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 8951–9006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahdost-Fard, F.; Roushani, M. Designing of an ultrasensitive BCM-7 aptasensor based on an SPCE modified with AuNR for promising distinguishing of autism disorder. Talanta 2020, 209, 120506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyuni, W.T.; Putra, B.R.; Fauzi, A.; Ramadhanti, D.; Rohaeti, E.; Heryanto, R. A brief review on fabrication of screen-printed carbon electrode: Materials and techniques. Indones. J. Chem. Res. 2021, 8, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, S. Screen-printed carbon electrodes. In Electrochemistry of Carbon Electrodes; Alkire, R.C., Bartlett, P.N., Lipkowski, J., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2015; pp. 425–444. [Google Scholar]
- Reanpang, P.; Chailapakul, O.; Jakmunee, J. Fabrication of a home-made SPCE modified with thionine for determination of hydrogen peroxide. Chiang Mai J. Sci 2018, 45, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Zuo, J.; Qiu, S.; Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. Reduced graphene oxide-modified screen-printed carbon (rGO-SPCE)-based disposable electrochemical sensor for sensitive and selective determination of ethyl carbamate. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 3329–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroon, N.; Stine, K.J. Electrochemical detection of hormones using nanostructured electrodes. Coatings 2023, 13, 2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyuni, W.T.; Putra, B.R.; Heryanto, R.; Rohaeti, E.; Yanto, D.H.Y.; Fauzi, A. A simple approach to fabricate a screen-printed electrode and its application for uric acid detection. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2021, 16, 210221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sánchez, M.I.; Gómez-Monedero, B.; Agrisuelas, J.; Iniesta, J.; Valero, E. Highly activated screen-printed carbon electrodes by electrochemical treatment with hydrogen peroxide. Electrochem. Commun. 2018, 91, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadav, J.K.; Umrania, V.V.; Rathod, K.J.; Golakiya, B.A. Development of silver/carbon screen-printed electrode for rapid determination of vitamin C from fruit juices. LWT 2018, 88, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paimard, G.; Ghasali, E.; Baeza, M. Screen-printed electrodes: Fabrication, modification, and biosensing applications. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesakumar, N.; Berchmans, S.; Alwarappan, S. Chemically modified carbon based electrodes for the detection of reduced glutathione. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 264, 448–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbelkar, A.; Ahlmark, R.; Zhou, X.; Austin, K.; Fan, G.; Yang, V.Y.; Furst, A. Carbon electrode-based biosensing enabled by biocompatible surface modification with DNA and proteins. Bioconjugate Chem. 2023, 34, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iula, G.; Miglione, A.; Kalligosfyri, P.M.; Spinelli, M.; Amoresano, A.; Di Natale, C.; Darwish, I.A.; Cinti, S. On-body electrochemical measurement of sweat lactate with the use of paper-based fluidics and 3D-printed flexible wearable biosensor. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2025, 417, 3825–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okpara, E.C.; Fayemi, O.E.; Sherif, E.-S.M.; Ganesh, P.S.; Swamy, B.K.; Ebenso, E.E. Electrochemical evaluation of Cd2+ and Hg2+ ions in water using ZnO/Cu2ONPs/PANI modified SPCE electrode. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2022, 35, 100476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Yoshii, K.; Asahi, M.; Chiku, M.; Kitazumi, Y. Cyclic voltammetry part 1: Fundamentals. Electrochemistry 2022, 90, 102005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.G.; Sombers, L.A. Fast scan cyclic voltammetry: Chemical sensing in the brain and beyond. Anal. Chem. 2017, 90, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, M.; Abrams, D.J.; Cardinale, L.; Goss, Z.; Romero-Arenas, A.; Stahl, S.S. Cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry: Mechanistic tools for organic electrosynthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 566–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Yoshii, K.; Asahi, M.; Chiku, M.; Kitazumi, Y. Cyclic voltammetry part 2: Surface adsorption, electric double layer, and diffusion layer. Electrochemistry 2022, 90, 102006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Chen, C.; Lu, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, Q. Smartphone-based cyclic voltammetry system with graphene modified screen printed electrodes for glucose detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, Y.; Morali, U.; Erol, S.; Avci, H. Investigation of electrochemical behavior of potassium ferricyanide/ferrocyanide redox probes on screen printed carbon electrode through cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Turk. J. Chem. 2021, 45, 1895–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselló, A.; Serrano, N.; Díaz-Cruz, J.M.; Ariño, C. Discrimination of beers by cyclic voltammetry using a single carbon screen-printed electrode. Electroanalysis 2021, 33, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbei, E.E.; Alexandru, P.; Busila, M. Cyclic voltammetry of screen-printed carbon electrode coated with Ag-ZnO nanoparticles in chitosan matrix. Materials 2023, 16, 3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashat, Z.B.A.; Abdullah, F.; Wahab, A.A.; Shakhih, M.F.M.; Roslan, A.S. Development of non-enzymatic screen-printed carbon electrode sensor for glucose using cyclic voltammetry. Environ. Toxicol. Manag. 2022, 2, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venton, J.; DiScenza, D.J. Voltammetry in Electrochemistry for Bioanalysis; Patel, B., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 27–50. [Google Scholar]
- Jazi, H.K.; Sarafbidabad, M.; Henda, M.B.; Ahmadipour, M. The effect of laser surface texturing on ZnO/MWCNT nanocomposite modified screen-printed carbon electrode for non-enzymatic glucose biosensor. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2025, 151, 111845. [Google Scholar]
- Crespi, F. Differential pulse voltammetry: Evolution of an in vivo methodology and new chemical entries, a short review. J. New Dev. Chem. 2020, 2, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyszczuk-Rotko, K.; Kozak, J.; Węzińska, A. Electrochemically activated screen-printed carbon electrode for determination of ibuprofen. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberto, E.; Bastos-Arrieta, J.; Pérez-Ràfols, C.; Serrano, N.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Díaz-Cruz, J.M. Voltammetric determination of sulfamethoxazole using commercial screen-printed carbon electrodes. Microchem. J. 2023, 193, 109125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirasirichote, A.; Punrat, E.; Suea-Ngam, A.; Chailapakul, O.; Chuanuwatanakul, S. Voltammetric detection of carbofuran determination using screen-printed carbon electrodes modified with gold nanoparticles and graphene oxide. Talanta 2017, 175, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaraj, S.; Sakthivel, M.; Chen, S.-M.; Elshikh, M.S.; Chen, T.-W.; Yu, M.-C.; Ho, K.-C. Electrochemical sensing of anti-inflammatory agent in paramedical sample based on FeMoSe2 modified SPCE: Comparison of various preparation methods and morphological effects. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1083, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirceski, V.; Skrzypek, S.; Stojanov, L. Square-wave voltammetry. ChemTexts 2018, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirceski, V.; Guziejewski, D.; Stojanov, L.; Gulaboski, R. Differential square-wave voltammetry. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 14904–14910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirceski, V.; Gulaboski, R.; Lovric, M.; Bogeski, I.; Kappl, R.; Hoth, M. Square-wave voltammetry: A review on the recent progress. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 2411–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Shah, B. Electrochemical sensing and biosensing based on square wave voltammetry. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 2158–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirceski, V.; Gulaboski, R. Recent achievements in square-wave voltammetry (a review). Maced. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2014, 33, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Dogan-Topal, B.; Ozkan, S.A.; Uslu, B. The analytical applications of square wave voltammetry on pharmaceutical analysis. Open Chem. Biomed. Methods J. 2010, 3, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulaboski, R.; Mirceski, V. Calculating of square-wave voltammograms—A practical on-line simulation platform. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2024, 28, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Shi, Z.; Liu, Z.; Low, S.S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, T.; Chen, Z.; Yu, X.; Lu, Y.; Lu, D. Smartphone-based square wave voltammetry system with screen-printed graphene electrodes for norepinephrine detection. Smart Mater. Med. 2020, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newair, E.F.; Kilmartin, P.A.; Garcia, F. Square wave voltammetric analysis of polyphenol content and antioxidant capacity of red wines using glassy carbon and disposable carbon nanotubes modified screen-printed electrodes. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 1225–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, C.E.; Cunha-Silva, H.; Kuberski, S.L.; Cox, J.A.; Arcos-Martínez, M.J.; Arroyo-Mora, L.E. Electrochemical detection of fentanyl with screen-printed carbon electrodes using square-wave adsorptive stripping voltammetry for forensic applications. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 873, 114425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Novais, A.; Arantes, L.C.; Almeida, E.S.; Rocha, R.G.; Lima, C.D.; de Almeida Melo, L.M.; Richter, E.M.; Munoz, R.A.A.; dos Santos, W.T.P.; da Silva, R.A.B. Fast on-site screening of 3, 4-methylenedioxyethylamphetamine (MDEA) in forensic samples using carbon screen-printed electrode and square wave voltammetry. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 403, 139599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsukov, Y.; Macdonald, J.R. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Charact. Mater. 2012, 2, 898–913. [Google Scholar]
- Pajkossy, T.; Jurczakowski, R. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in interfacial studies. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2017, 1, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazanas, A.C.; Prodromidis, M.I. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy─ a tutorial. ACS Meas. Sci. Au 2023, 3, 162–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagles, E.; García-Beltrán, O.; Calderón, J.A. Evaluation of the usefulness of a novel electrochemical sensor in detecting uric acid and dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid using a screen-printed carbon electrode modified with single walled carbon nanotubes and ionic liquids. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 258, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, S.F.; Lim, L.S.; Pang, S.C.; Sum, M.S.H.; Perera, D. Carbon nanoparticle modified screen printed carbon electrode as a disposable electrochemical immunosensor strip for the detection of Japanese encephalitis virus. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Ono, K. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. In Microscopy and Microanalysis for Lithium-Ion Batteries; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; pp. 301–350. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, A.; Hannah, A.; Kendrick, S.; Tucker, N.; MacGregor, G.; Connolly, P. Identification and characterisation of Staphylococcus aureus on low cost screen printed carbon electrodes using impedance spectroscopy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 110, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.Y.; Yang, J.C.; Hong, S.W.; Park, J. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical impedimetric sensors on screen-printed carbon electrodes for the detection of trace cytokine IL-1β. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 204, 114073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randviir, E.P. A cross examination of electron transfer rate constants for carbon screen-printed electrodes using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy and cyclic voltammetry. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 286, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendrachari, S. Investigation of Electrochemical Pitting Corrosion by Linear Sweep Voltammetry: A Fast and Robust Approach. In Voltammetry; Maxato, N.W., Gwebu, S.S., Hhlongo, G.H., Eds.; Intechopen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Xu, X.; Cole, R.B. On-line linear sweep voltammetry− electrospray mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 2478–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houam, S.; Affoune, A.M.; Atek, I.; Kesri, F.; Guermeche, R.S.; Chelaghmia, M.L.; Nacef, M.; Khelifi, O.; Banks, C.E. Determination of the standard rate constant for soluble-soluble quasi-reversible electrochemical systems by linear sweep voltammetry: Application to the electrochemical oxidation on screen-printed graphite electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 449, 142200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthi, F.A.; Hasan, I. Screen-printed carbon electrode modified by δ-MnO2/S@ g-C3N4 nanocomposite for dopamine sensing using linear sweep voltammetry. J. Electron. Mater. 2024, 53, 2115–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Henawee, M.; Saleh, H.; Attia, A.K.; Hussien, E.M.; Derar, A.R. Carbon nanotubes bulk modified printed electrochemical sensor for green determination of vortioxetine hydrobromide by linear sweep voltammetry. Measurement 2021, 177, 109239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoub, S.A.B.; Yusof, N.A.; Hajian, R. Gold Nanoparticles/Ionophore-Modified Screen-Printed Electrode for Detection of Pb (II) in River Water Using Linear Sweep Anodic Stripping Voltammetry. Sens. Mater. 2017, 29, 555–565. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, V. Electrodeposition of pyrogallol versus pyrocatechol using cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 909, 116142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, P.; Pittson, R.; Hart, J.P. Development of a simple, low cost chronoamperometric assay for fructose based on a commercial graphite-nanoparticle modified screen-printed carbon electrode. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phasuksom, K.; Sirivat, A. Chronoampermetric detection of enzymatic glucose sensor based on doped polyindole/MWCNT composites modified onto screen-printed carbon electrode as portable sensing device for diabetes. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 28505–28518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.; Her, J.; Lee, H.; Shim, Y.-B.; Ban, C. Highly sensitive amperometric detection of cardiac troponin I using sandwich aptamers and screen-printed carbon electrodes. Talanta 2017, 165, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros Azeredo, N.F.; Ferreira Santos, M.S.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Wang, J.; Angnes, L. Screen-printed technologies combined with flow analysis techniques: Moving from benchtop to everywhere. Anal. Chem. 2021, 94, 250–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squissato, A.L.; Munoz, R.A.; Banks, C.E.; Richter, E.M. An overview of recent electroanalytical applications utilizing screen-printed electrodes within flow systems. ChemElectroChem 2020, 7, 2211–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, S.A.; Alyammahi, A.R.; Fanjul-Bolado, P. Development and characterization of novel flow injection, thin-layer, and batch cells for electroanalytical applications using screen-printed electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 16690–16699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upan, J.; Reanpang, P.; Chailapakul, O.; Jakmunee, J. Flow injection amperometric sensor with a carbon nanotube modified screen printed electrode for determination of hydroquinone. Talanta 2016, 146, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, Y.; Zen, J.-M.; Kumar, A.S.; Chen, P.-Y. Flow injection analysis of zinc pyrithione in hair care products on a cobalt phthalocyanine modified screen-printed carbon electrode. Talanta 2004, 62, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, Y.; Gao, Q.; Qi, B.; Yang, X. Electropolymerization of Azure B on a screen-printed carbon electrode and its application to the determination of NADH in a flow injection analysis system. Microchim. Acta 2004, 148, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, M.; Thirumalraj, B.; Chen, S.-M.; Al-Hemaid, F.M.; Ali, M.A.; Elshikh, M.S. Development of electrochemical sensor for the determination of palladium ions (Pd2+) using flexible screen printed un-modified carbon electrode. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 485, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, F.D.; Rodrigues, J.A.; Ramos, R.M. Electrochemical Sensing of Vitamin D3: A Comparative Use of Glassy Carbon and Unmodified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrodes. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.A.H.; Majdinasab, M.; Latif, U.; Nasir, M.; Gokce, G.; Anwar, M.W.; Hayat, A. Development of a disposable electrochemical sensor for detection of cholesterol using differential pulse voltammetry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 159, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Sangaranarayanan, M. Electroanalytical Sensor Based on Unmodified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode for the Determination of Levo-Thyroxine. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mincu, N.-B.; Lazar, V.; Stan, D.; Mihailescu, C.M.; Iosub, R.; Mateescu, A.L. Screen-Printed Electrodes (SPE) for in vitro diagnostic purpose. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Arduini, F.; Carbone, M.; Sansone, L.; Cacciotti, I.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G. Screen-printed electrodes modified with carbon nanomaterials: A comparison among carbon black, carbon nanotubes and graphene. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 2230–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosrokhavar, R.; Motaharian, A.; Hosseini, M.R.M.; Mohammadsadegh, S. Screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE) modified by molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) nanoparticles and graphene nanosheets for determination of sertraline antidepressant drug. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, R.A.; Quinaz, M.B. Development of a Nafion/MWCNT-SPCE-based portable sensor for the voltammetric analysis of the anti-tuberculosis drug ethambutol. Sensors 2016, 16, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala-Benuzzi, M.L.; Raba, J.; Soler-Illia, G.J.; Schneider, R.J.; Messina, G.A. Novel electrochemical paper-based immunocapture assay for the quantitative determination of ethinylestradiol in water samples. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 4104–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madej, M.; Trzcińska, A.; Lipińska, J.; Kapica, R.; Fronczak, M.; Porada, R.; Kochana, J.; Baś, B.; Tyczkowski, J. Electrochemical sensing platform based on screen-printed carbon electrode modified with plasma polymerized acrylonitrile nanofilms for determination of bupropion. Microchim. Acta 2023, 190, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhaimi, N.F.; Baharin, S.N.A.; Jamion, N.A.; Zain, Z.M.; Sambasevam, K.P. Polyaniline-chitosan modified on screen-printed carbon electrode for the electrochemical detection of perfluorooctanoic acid. Microchem. J. 2023, 188, 108502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, M.; Kumar, M.D.; Kaniraja, G.; Ananthappan, P.; Vasantha, V.S.; Karunakaran, C. Gold nanoparticles enhanced molecularly imprinted poly (3-aminophenylboronic acid) sensor for myo-inositol detection. Microchem. J. 2023, 189, 108536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thunkhamrak, C.; Chuntib, P.; Ounnunkad, K.; Banet, P.; Aubert, P.-H.; Saianand, G.; Gopalan, A.-I.; Jakmunee, J. Highly sensitive voltammetric immunosensor for the detection of prostate specific antigen based on silver nanoprobe assisted graphene oxide modified screen printed carbon electrode. Talanta 2020, 208, 120389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Lin, Y.-J.; Huang, Y.-C.; Liao, Y.-T.; Lin, S.-P. Detection of lactate in human sweat via surface-modified, screen-printed carbon electrodes. Talanta 2023, 265, 124888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.-D.; Hossain, M.M.; Gurudatt, N.; Choi, C.S.; Shiddiky, M.J.; Park, D.-S.; Shim, Y.-B. Microfluidic neurotransmitters sensor in blood plasma with mediator-immobilized conducting polymer/N, S-doped porous carbon composite. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 313, 128017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, W.-T.; Wang, M.-J.; Howlader, M.M. Interleukin-6 electrochemical sensor using poly (o-phenylenediamine)-based molecularly imprinted polymer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 404, 135282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongpakdee, T.; Crenshaw, K.; Wong, H.M.F.; de Oliveira, M.F.; Nacapricha, D.; McCord, B.R. The development of screen-printed electrodes modified with gold and copper nanostructures for analysis of gunshot residue and low explosives. Forensic Sci. Int. 2024, 364, 112243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddaoui, M.; Raouafi, N. Chlortoluron-induced enzymatic activity inhibition in tyrosinase/ZnO NPs/SPCE biosensor for the detection of ppb levels of herbicide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 219, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saengsookwaow, C.; Rangkupan, R.; Chailapakul, O.; Rodthongkum, N. Nitrogen-doped graphene–polyvinylpyrrolidone/gold nanoparticles modified electrode as a novel hydrazine sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 227, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durai, L.; Badhulika, S. Ultra-selective, trace level detection of As3+ ions in blood samples using PANI coated BiVO4 modified SPCE via differential pulse anode stripping voltammetry. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 111, 110806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhen, Q.; He, Y.; Chen, X.; Lyu, W.; Han, R.; Ding, M. An electrochemical sensor for indole in plasma based on MWCNTs-chitosan modified screen-printed carbon electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L. Molecularly imprinted sensor based on Ag-Au NPs/SPCE for lactate determination in sweat for healthcare and sport monitoring. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2021, 16, 211043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuliska, S.; Zakiyyah, S.N.; Hartati, Y.W.; Einaga, Y.; Maksum, I.P. Electrochemical aptasensor for ultrasensitive detection of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) using gold-modified SPCE. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2025, 47, 100765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangphatthanarungruang, J.; Pasakon, P.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Tuantranont, A.; Intasanta, V.; Karuwan, C. Facile surface modification of the poly (l-cysteine) on 2D-printed reduced graphene oxide electrode to fabricate a highly sensitive electrochemical sensor for determining the antipsychotic drug olanzapine. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 46, 104145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, A.; Haider, W.; Rolland, M.; Marty, J.-L. Electrochemical grafting of long spacer arms of hexamethyldiamine on a screen printed carbon electrode surface: Application in target induced ochratoxin A electrochemical aptasensor. Analyst 2013, 138, 2951–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hue, N.T.; Pham, T.N.; Dinh, N.X.; Van Tuan, H.; Thuy, N.T.T.; Nam, M.H.; Lam, V.D.; Le, A.-T.; Huy, T.Q. AuNPs-modified screen-printed electrodes (SPCE and SPPtE) for enhanced direct detection of chloramphenicol. J. Electron. Mater. 2022, 51, 1669–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Han, G.H.; Hong, S.; Park, J.; Bang, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Ahn, S.H. Electrodeposition: An efficient method to fabricate self-supported electrodes for electrochemical energy conversion systems. Exploration 2022, 2, 20210077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zangari, G. Electrodeposition of alloys and compounds in the era of microelectronics and energy conversion technology. Coatings 2015, 5, 195–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, J.; Mano, J.F. Molecular interactions driving the layer-by-layer assembly of multilayers. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 8883–8942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, J.J.; Cui, J.; Bjornmalm, M.; Braunger, J.A.; Ejima, H.; Caruso, F. Innovation in layer-by-layer assembly. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 14828–14867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F.-X.; Pagliaro, M.; Xu, Y.-J.; Liu, B. Layer-by-layer assembly of versatile nanoarchitectures with diverse dimensionality: A new perspective for rational construction of multilayer assemblies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3088–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pundir, C.S.; Devi, R. Biosensing methods for xanthine determination: A review. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2014, 57, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandoj, F.; Nardis, S.; Di Natale, C.; Paolesse, R. Porphyrinoid thin films for chemical sensing. In Encyclopedia of Interfacial Chemistry: Surface Science and Electrochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 422–443. [Google Scholar]
- Friebe, C.; Hager, M.D.; Winter, A.; Schubert, U.S. Metal-containing polymers via electropolymerization. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Reis, R.; Chen, Z.; Milne, N.; Winther-Jensen, B.; Kong, L.; Dumée, L.F. Plasma modification and synthesis of membrane materials—A mechanistic review. Membranes 2018, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Zhao, L.; Nikiforov, A.; Giraudon, J.-M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Tu, X. A review of the advances in catalyst modification using nonthermal plasma: Process, Mechanism and Applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 308, 102755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyona, M. A theoritical study on spin coating technique. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 2, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, H.A.M.; Jameel, D.A. Modeling and the main stages of spin coating process: A review. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. Trends 2021, 2, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, F.; Ismail, A.F. Spray coating methods for polymer solar cells fabrication: A review. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 39, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederichi, D.; Scaliante, M.H.N.O.; Bergamasco, R. Structured photocatalytic systems: Photocatalytic coatings on low-cost structures for treatment of water contaminated with micropollutants—A short review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 23610–23633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.K.S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Compton, R.G. A mini-review: How reliable is the drop casting technique? Electrochem. Commun. 2020, 121, 106867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Xing, L.; Xiang, J.; Cui, L.; Jiao, J.; Sai, H.; Li, Z.; Li, F. Formation of uniform reduced graphene oxide films on modified PET substrates using drop-casting method. Particuology 2014, 17, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamian, M.; Soltani-Kordshuli, F. Development of multiple-droplet drop-casting method for the fabrication of coatings and thin solid films. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2018, 15, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kava, A.A.; Henry, C.S. Exploring carbon particle type and plasma treatment to improve electrochemical properties of stencil-printed carbon electrodes. Talanta 2021, 221, 121553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, I.G.; Gallina, F.C.; da Silva, A.P.; da Silva, A.C.; Júnior, F.E.B.; de Carvalho, A.E.; Lanza, M.R.; Martelli, S.M.; Barros, W.R. Disposable and flexible screen-printed-carbon electrode modified with Au/poly-beta-cyclodextrin as electrochemical platform for estriol detection. Microchem. J. 2024, 206, 111521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaki, S.; Saito, M.; Nagai, H.; Tamiya, E. Surface Modification of Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode through Oxygen Plasma to Enhance Biosensor Sensitivity. Biosensors 2024, 14, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, R.R.; Adhikari, K.R.; Gardner, S.; Sunilkumar, S.; Sanas, S.; Mohammad, H.; Thomas, V. Inkjet-printed plasma-functionalized polymer-based capacitive sensor for PAHs. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 105659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.F.; Rocha, R.G.; Castro, S.V.; Joao, A.F.; Borges, P.H.; Rocha, D.P.; de Siervo, A.; Richter, E.M.; Nossol, E.; Gelamo, R.V. Reactive oxygen plasma treatment of 3D-printed carbon electrodes towards high-performance electrochemical sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 347, 130651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-H.; Hsu, C.-L.; Yuan, C.-J.; Tang, S.-F.; Chiang, H.-J.; Jang, H.-D.; Chang, K.-S. Improvement of the inter-electrode reproducibility of screen-printed carbon electrodes by oxygen plasma etching and an image color level method for quality control. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.S.; Muthuraman, G.; Zen, J.-M. The role of oxygen functionalities and edge plane sites on screen-printed carbon electrodes for simultaneous determination of dopamine, uric acid and ascorbic acid. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 10, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamouss, F.; Tessier, P.-Y.; Djouadi, M.; Besland, M.-P.; Boujtita, M. Examination of the electrochemical reactivity of screen printed carbon electrode treated by radio-frequency argon plasma. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 1798–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanyong, P.; Rawlinson, S.; Davis, J. Gold nanoparticle modified screen-printed carbon arrays for the simultaneous electrochemical analysis of lead and copper in tap water. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 2361–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syafira, R.S.; Devi, M.J.; Gaffar, S.; Irkham; Kurnia, I.; Arnafia, W.; Einaga, Y.; Syakir, N.; Noviyanti, A.R.; Hartati, Y.W. Hydroxyapatite-gold modified screen-printed carbon electrode for selective SARS-CoV-2 antibody immunosensor. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 950–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakiyyah, S.N.; Satriana, N.P.; Fransisca, N.; Gaffar, S.; Syakir, N.; Irkham, I.; Hartati, Y.W. Gold nanoparticle-modified screen-printed carbon electrodes for label-free detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA using drop casting and spray coating methods. ADMET DMPK 2025, 13, 2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yi, Z.; Liang, Q.; Zhen, J.; Wang, R.; Li, M.; Zeng, L.; Li, Y. In situ deposition of gold nanoparticles and L-Cysteine on screen-printed carbon electrode for rapid electrochemical determination of As (III) in water and tea. Biosensors 2023, 13, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eissa, S.; Alshehri, N.; Rahman, A.M.A.; Dasouki, M.; Abu-Salah, K.M.; Zourob, M. Electrochemical immunosensors for the detection of survival motor neuron (SMN) protein using different carbon nanomaterials-modified electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 101, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magar, H.S.; Hassan, R.Y.; Abbas, M.N. Non-enzymatic disposable electrochemical sensors based on CuO/Co3O4@ MWCNTs nanocomposite modified screen-printed electrode for the direct determination of urea. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-L.; Chang, K.-H.; Hu, C.-C.; Cheng, W.-L.; Zen, J.-M. Improved voltammetric peak separation and sensitivity of uric acid and ascorbic acid at nanoplatelets of graphitic oxide. Electrochem. Commun. 2010, 12, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, K.; Kim, H. Fabrication of nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide modified screen printed carbon electrode (N-rGO/SPCE) as hydrogen peroxide sensor. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Guo, P.; Liu, H.; Lu, J.; Xie, Q. Graphene oxide modified screen-printed electrode for highly sensitive and selective electrochemical detection of ciprofloxacin residues in milk. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viet, N.X.; Hoan, N.X.; Takamura, Y. Development of highly sensitive electrochemical immunosensor based on single-walled carbon nanotube modified screen-printed carbon electrode. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 227, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuntib, P.; Themsirimongkon, S.; Saipanya, S.; Jakmunee, J. Sequential injection differential pulse voltammetric method based on screen printed carbon electrode modified with carbon nanotube/Nafion for sensitive determination of paraquat. Talanta 2017, 170, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.; Garmroodi, A. Sensitive detection of sulfasalazine at screen printed carbon electrode modified with functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 727, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, L.; Yang, W.; Han, J.; Li, C.; Liu, Q.; Xiang, Z.; Wu, J. The Construction and Mechanism of SPCE/Cu2O@ MWCNTs Electrochemical Sensor for Menthone Detection for Epileptic Seizures Prediction. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, 2500764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, D.A.; Camargo, J.R.; Pradela-Filho, L.A.; Lima, A.P.; Munoz, R.A.; Takeuchi, R.M.; Janegitz, B.C.; Santos, A.L. A lab-made screen-printed electrode as a platform to study the effect of the size and functionalization of carbon nanotubes on the voltammetric determination of caffeic acid. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, J.R. Polymer Science and Technology; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Awuzie, C.I. Conducting polymers. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 5721–5726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.K.; Prusty, S. Review on conducting polymers and their applications. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2012, 51, 1487–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šišoláková, I.; Gorejová, R.; Chovancová, F.; Shepa, J.; Ngwabebhoh, F.A.; Fedorková, A.S.; Sáha, P.; Oriňaková, R. Polymer-based electrochemical sensor: Fast, accurate, and simple insulin diagnostics tool. Electrocatalysis 2023, 14, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, M.; Gupta, P.; Goyal, R.N.; Shim, Y.-B. Graphene/conducting polymer nano-composite loaded screen printed carbon sensor for simultaneous determination of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filik, H.; Avan, A.A. Conducting polymer modified screen-printed carbon electrode coupled with magnetic solid phase microextraction for determination of caffeine. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BelBruno, J.J. Molecularly imprinted polymers. Chem. Rev. 2018, 119, 94–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, H.; Ding, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, L.; Kong, Y.; Zheng, G. An electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted poly (o-phenylenediamine) for the detection of thymol. Anal. Biochem. 2024, 691, 115551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Yin, M.; Rui, B.; Liu, T.; Song, W.; Sun, L.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Han, M.; Gou, G. A novel molecularly imprinted polymer sensor for sweat cortisol with embedded probe based on the co-deposition of Prussian Blue and Polypyrrole. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2024, 8, 100217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, B.E.; Gavrila, A.-M.; Sarbu, A.; Iovu, H.; Brisset, H.; Miron, A.; Iordache, T.-V. Uncovering the behavior of screen-printed carbon electrodes modified with polymers molecularly imprinted with lipopolysaccharide. Electrochem. Commun. 2021, 124, 106965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsenzadeh, E.; Ratautaite, V.; Brazys, E.; Ramanavicius, S.; Zukauskas, S.; Plausinaitis, D.; Ramanavicius, A. Design of molecularly imprinted polymers (MIP) using computational methods: A review of strategies and approaches. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2024, 14, e1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, F. Nanocomposites: New Trends and Developments; BoD–Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bogue, R. Nanocomposites: A review of technology and applications. Assem. Autom. 2011, 31, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omanović-Mikličanin, E.; Badnjević, A.; Kazlagić, A.; Hajlovac, M. Nanocomposites: A brief review. Health Technol. 2020, 10, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okpala, C.C. Nanocomposites–an overview. Int. J. Eng. Res. Dev 2013, 8, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Okpala, C.C. The benefits and applications of nanocomposites. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Tech 2014, 12, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Ibáñez-Redín, G.; Wilson, D.; Gonçalves, D.; Oliveira, O., Jr. Low-cost screen-printed electrodes based on electrochemically reduced graphene oxide-carbon black nanocomposites for dopamine, epinephrine and paracetamol detection. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 515, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Su, L.; Wu, X. Electrodeposited rGO/AuNP/MnO2 Nanocomposite-Modified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode for Sensitive Electrochemical Sensing of Arsenic (III) in Water. Biosensors 2023, 13, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, A.S.; Botas, C.; Martin-Yerga, D.; Alvarez, P.; Menéndez, R.; Costa-Garcia, A. Comparative study of screen-printed electrodes modified with graphene oxides reduced by a constant current. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, B282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adarakatti, P.S.; Foster, C.W.; Banks, C.E.; Kumar, A.N.S.; Malingappa, P. Calixarene bulk modified screen-printed electrodes (SPCCEs) as a one-shot disposable sensor for the simultaneous detection of lead(II), copper(II), and mercury(II) ions: Application to environmental samples. Sens. Act. A 2017, 267, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, C.; Bayraktepe, D.E.; Yazan, Z. Highly sensitive direct simultaneous determination of zinc(II), cadmium(II), lead(II), and copper(II) based on in-situ-bismuth and merucry thin-film plated screen-printed carbon electrode. Monatshefte Fur Chem.-Chem. Mon. 2021, 152, 1527–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunpatee, K.; Kaewdorn, K.; Duangtong, J.; Chaiyo, S.; Chailapakul, O.; Kalcher, K.; Kerr, M.; Samphao, A. A new disposable electrochemical sensor for the individual and simultaneous determination of carbamate pesticides using a nanocomposite modified screen-printed electrode. Microchem. J. 2022, 177, 107318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgobbi, L.F.; Razzino, C.A.; Machado, S.A.S. A disposable electrochemical sensor for simultaneous detection of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim antibiotics in urine based on multiwalled nanotubes decorated with Prussian blue nanocubes modified screen-printed electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 191, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al borhani, W.; Rhouati, A.; Cialla-May, D.; Popp, J.; Zourob, M. Multiplex electrochemical aptasensor for the simultaeous detection of linomycin and newmycin antibiotics. Talanta 2025, 282, 126922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yan, F.; Tang, J.; Zhai, C.; Ju, H. A disposable multianalyte electrochemical immunosensor array for automated simultaneous determination of tumor markers. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, G.; Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Ju, H.; Yan, F. Electrochemical stripping analysis of nanogold label-induced silver deposition for ultrasensitive multiplexed detection of tumor markers. Anal. Chem. Acta. 2012, 721, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, M.A.; Shamsipur, M.; Saber, R.; Sarkar, S. Simultaneous determination of CYC and VEGF165 tumor markers based on immobilization of flavin adenine dinucleotide and thionine as probes on reduced graphene oxide-poly(amidoamine)/gold nanocomposite modified dual working screen-printed electrode. Sens. Actuat. B 2017, 240, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakchin, P.S.; Nakhjavani, S.A.; Saber, R.; Ghanbari, H.; Omidi, Y. Recent advances in simultaneous electrochemical multi-analyte sensing platforms. Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 92, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, R.C.B.; Costa-Rama, E.; Viswanathan, S.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Costa-García, A.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Gonzalez-García, M.B. Voltammetric immunosensor for the simultaneous analysis of the breast cancer biomarkers CA 15-3 and HER2-ECD. Sens. Actuat. B 2018, 255, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, A.; Serafin, V.; Garoz, J.; Montero-Calle, A.; Gonzáles-Cortés, A.; Arenas, C.; Camps, J.; Barderas, R.; Yañez-Sedeño, P.; Campuzano, S.; et al. Electrochemical immunoplatform to improve the reliability of breast cancer diagnosis through the simultaneous determination of RANKL and TNF in serum. Sens. Actuat. B 2020, 314, 128096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrente-Rodriguez, R.M.; Campuzano, S.; Montiel, R.-V.; Gamella, M.; Pingarron, J.M. Electrochemical bioplatforms for the simultaneous determination of interleukin(IL)-8 and mRA and IL-8 protein oral cancer biomarkers in raw saliva. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovarova, A.; Kastrati, G.; Pekarkova, J.; Metelka, R.; Drbohlavova, J.; Bilkova, Z.; Selesovska, R.; Korecka, L. Biosensor with electrochemically active nanocomposites for signal amplification and simultaneous detection of three ovarian cancer biomarkers. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 469, 143213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.; Dubey, N.; Yadav, A.K.; Saraya, A.; Sharma, R.; Solanki, P.R. Disposable paper-based screen-printed electrochemical immunoplatform for dual detection of esophageal cancer biomarkers in patients’ serum samples. Mater. Adv. 2024, 5, 2153–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Ha, S.M.; Gurudat, N.G.; Heo, W.; Hyun, K.A.; Kim, J.; Jung, H. Machine learning-powered electrochemical aptasensor for simultaneous monitoring of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and bisphenol A in variable pH environments. J. Hazard Mater. 2024, 462, 132775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Araujo Andreotti, I.A.; Orzari, L.O.; Camargo, J.R.; Faria, R.C.; Marcolino-Junior, L.H.; Bergamini, M.F.; Gatti, A.; Janegitz, B.C. Disposable and flexible electrochemical sensor made by recyclable material and low cost conductive ink. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 840, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhimaraya, K.; Manjunatha, J.G.; Moulya, K.P.; Tighezza, A.M.; Albaqami, M.D.; Sillanpää, M. Detection of levofloxacin using a simple and green electrochemically polymerized glycine layered carbon paste electrode. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, N.O.; Paschoalin, R.T.; Bilatto, S.; Sorigotti, A.R.; Farinas, C.S.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Machado, S.A.; Oliveira, O.N., Jr.; Raymundo-Pereira, P.A. Flexible, bifunctional sensing platform made with biodegradable mats for detecting glucose in urine. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 2209–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, N.O.; Teixeira, S.C.; Calegaro, M.L.; Machado, S.A.S.; Ferreira Soares, N.F.; de Oliveira, T.V.; Raymundo-Pereira, P.A. Flexible and sustainable printed sensor strips for on-site, fast decentralized self-testing of urinary biomarkers integrated with a portable wireless analyzer. Chem. Engineer. J. 2023, 472, 14477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janus, K.A.; Zach, M.; Achtsnicht, S.; Drinic, A.; Kopp, A.; Keusgen, M.; Schöning, M.J. Modification of a bioabsorbable carbon electrode on silk-fibroin carriers: Setting the composition and adjustment of the working potential. Sens. Diagn. 2025, 4, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szałapak, J.; Zdanikowski, B.; Kądziela, A.; Lepak-Kuc, S.; Dybowska-Sarapuk, Ł.; Janczak, D.; Raczyński, T.; Jakubowska, M. Carbon-based composites with biodegradable matrix for flexible paper electronics. Polymers 2024, 16, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Maiti, P. Paper-based sustainable biosensors. Mater. Adv. 2024, 5, 3563–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, C.S.K.; Tan, S.N.; Floresca, C.Z. A “green” cellulose paper based glucose amperometric biosensor. Sens. Actuat. B 2014, 193, 536–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos Oliveira, R.; Burger Veríssimo de Oliveira, W.; Cunha de Souza, C.; Mendes Fernandes, B.L.; Costa Matos, M.A.; Pedrosa Lisboa, T.; Camargo Matos, R. Composite Material from Waste ABS 3D Filaments and Graphite: A Cost-Effective and Sustainable Alternative for Electrochemical Sensor Manufacturing and Voltammetric Analysis of Acebutolol. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202402782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Sahoo, J.; Gandhi, S. Sustainable and Eco-Friendly 3D-Printed Electrochemical Sensors. In Additively Manufactured Electrochemical Sensors; Manjunatha, J.G., Hussain, C.M., Eds.; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 369–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Nie, J.; Cao, Y.; Gao, C.; Wang, M.; Lu, X.; Ma, X.; Zhang, P. A review of how to improve Ti3C2Tx MXene stability. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 154097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Yang, M.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, G.; et al. Constructing an electrochemical sensor with screen-printed electrodes incorporating Ti3C2Tx-PDA-AgNPs for lactate detection in sweat. Talanta 2025, 285, 127423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parilla, M.; Detamornat, U.; Dominguez-Robles, J.; Donnelly, R.F.; De Wael, K. Wearable hollow microneedle sensing patches for the transdermal electrochemical monitoring of glucose. Talanta 2022, 249, 123695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravi, S.; Soltanian, S.; Servati, A.; Khademhosseini, A.; Zu, Y.; Servati, P. Screen-printed textile-based electrochemical biosensor for noninvasive monioring of glucose in sweat. Biosensors 2023, 13, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Electrode Structure | Real World Sample Studied | Analyte | Detection Method | Limit of Detection | Linear Range | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIP/Graphene/SPCE | Human serum and tablet | STR | DPV | 1.99 × 10−9 M | 5.0 × 10−9 to 7.5 × 10−7 M | [85] |
| Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 spike protein antigen/Ni(OH)2 NPs/SPCE | Human serum | SARS-CoV-2-specific viral antibodies. | DPV | 0.3 fg mL− 1 | 1 fg mL−1 to 1 μg mL−1 | [8] |
| Ab-HSA/AuNCs/Polyaniline/SPCE | - | HSA | EIS | 3 μg mL−1 | 3–300 μg mL−1 | [6] |
| Nafion/MWCNT-SPCEs | Human urine and serum | ETB | SWV | 8.4 ×10 −4 mgμL−1 | [86] | |
| Anti-EE2/Paper microzones + SNs/r-GO/SPCE | River water | EE2 | SWV | 0.1 ng L−1 | 0.5−120 ng L−1 | [87] |
| Cyst/4-CP/SPCE | Water samples | Cd (II)and Pb(II) | SWASV | 0.882 nM Cd (II) and 0.65 nM Pb (II) | 0.01 μM to 0.7 μM | [4] |
| pp-AN/SPCE sensor | River, ground, and wastewater, synthetic urine, and human serum | Bupropion | SCV | 0.21 μmol L−1 | 0.63–10.0 and 10.0–50.0 μmol L−1 | [88] |
| PANI-CHT/SPCE | Industrial, rural, and residential water samples | PFOA | DPV | 1.08 ppb | 5–150 ppb | [89] |
| PAPBA/AuNPs/SPCE | Plasma sample | MI | CV | 1.0 nM | 500 nM to 60 μM | [90] |
| H-FeMoSe2/SPCE | Paramedical tablet | MES | DPV | 0.8 nM | 0.004–57, 63.57–145.59 mM | [42] |
| Pd-CNT/SPCE | Disinfectant, hair colorant, and milk samples | H2O2 | FI-Amp | 20 uM | 0.1–1.0 mM | [5] |
| AgNPs-GO/SPCE | Human serum | PSA | DPV | 0.27 ng mL−1 | 0.75–100.0 ng mL−1 | [91] |
| Apt/AuNR/SPCE | Human urine and plasma | BCM-7 | DPV | 334 amol L−1 | 1 fmol L−1 to 25 nmol L−1 | [13] |
| LDH/SPCE | Human sweat | Lactate | EIS | 0.1 mM | 0.1–100 mM | [92] |
| ß-CD/MWCNTs/SPCE | Human serum | Cholesterol | DPV | 0.5 nM | 1 nM to 3 M | [81] |
| EB-p-TBA/HPC/SPCE | Human blood plasma | NTs | CA | 0.034 nM | 0.05–130 nM | [93] |
| MIP-P-o-PD/APTES/Au/O2/SPCE | Human serum | IL-6 | DPV | 1.74 pg mL−1 | 2 to 400 pg mL−1 | [94] |
| Au-SPCE Cu/Au-SPCE | Cartridge, shooting, and explosive samples | Pb, Sb, and Zn Nitrate, Nitrite | ASV LSV | 51, 29, 67 mM 130, 120 mM | 100–700 μg L−1 0–0.6 mM | [95] |
| Tyr/GA/ZnO NPs/SPCE | River, well, and tap water | Chlortoluron | CA | 0.02 uM | 1–100 nM | [96] |
| NG/PVP/AuNPs/SPCE | Fruit and vegetable samples | Hydrazine | SWV | 0.07 uM | 2–300 uM | [97] |
| ZnO NPs/MWCNTs/LSPCE | Glucose | CV | 0.43 mM | 1–100 mM | [36] | |
| PANI@BiVO4 nanoflakes/SPCE | Human serum | As3+ ions | DPASV | 0.0072 ppb | 0.01 to 300 ppb | [98] |
| MWCNTs-CS/SPCE | Plasma | Indole | DPV | 0.5 μg L−1 | 5- 100 μg L−1 | [99] |
| MIP/Ag-Au NPs/SPCE | Sweat | Lactate | Amperometry | 0.003 μM | 1–220 μM | [100] |
| LE/ZnO NPs/Cu2O NPs/PANI/SPCE OE/ZnO NPs/Cu2O NPs/PANI/SPCE | - | Cd2+ and Hg2+ ions | SWV | 3.04,1.08 ppb 5.08, 2.72 ppb | 2.2–12 mM, and 0.17–1.5 mM for Cd2+ 2.95–11.8 mM and 0.12–1.2 mM for Hg2+ | [26] |
| AuNPs/SPCE | Whole blood | HbA1c | DPV | 8.34 pg mL−1 | 1 to 104 pg mL−1 | [101] |
| poly(L-Cys)@SPrGOE | Human serum | Olanzapine | SWV | 0.91 nM | 10–1000 and 1500–5000 nM | [102] |
| Apt/HMA/SPCE | Beer samples | OTA | DPV | 0.1 mg L−1 | 0.12–8.5 mg L−1 | [103] |
| cfAuNPs/SPCE | Human serum and honey | hIgG H2O2 | DPV CA | 0.11 ng mL−1 0.66 ng mL−1 | 0.11–50 ng mL−1 0.7–70 ng mL−1 | [9] |
| Au/SPCEs Au/SPPtEs | - | CAP | CV DPV | 0.2 mM | 0.25–50 mM | [104] |
| Modification Method | Performance | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Drop-casting | Used manually for small areas; produces a non-uniform layer and is hard to reproduce. It is quite easy to modify any electrode with it, and it produces transparent, flexible, and conductive films. | [119,120,121] |
| Electrodeposition | Performed in aqueous solutions under mild conditions for modification of metals, alloys, and self-controlled and high-performance electrodes. | [105,106] |
| Electro polymerization | Uses conducting monomers to coat electrodes, controls the polymer thickness, and prevents electrode fouling. | [110,111,112] |
| Spin Coating | Used in microfabrication to form a desired uniform film/layer on a flat surface by using a spin coater. | [115,116] |
| Spray coating | Used to coat on a large scale with high-speed application to produce a non-uniform film through the nozzle of a sprayer. | [117,118] |
| Layer-by-layer assembly | Simple, robust, cost-effective, and versatile method to coat and deposit controlled uniform layers on substrates by using an oppositely charged material layer-wise. | [107,108,109] |
| Plasma Treatment | Uses ionization processes to modify and catalytically modify the surface without damaging it. | [113,114] |
| Modification Type | Selectivity | Sensitivity | Fabrication Complexity | Scalability | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gold-based nanomaterials | Extremely High | Very High | Low to High | Moderate | High |
| Carbon-based nanomaterials | Low | Very High | Moderate | Very High | Good |
| Polymers | Low, but can be engineered | High | Low to Moderate | Low to High | High |
| MIP | High | High | Extremely complex | Very Low | Moderate to High |
| Plasma treatment | Low | High | Low | High | High |
| Biological recognition elements (aptamers, antibodies, enzymes) | High | High | High | High | Low |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haroon, N.; Stine, K.J. Surface Modification of Screen-Printed Carbon Electrodes. Coatings 2025, 15, 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15101182
Haroon N, Stine KJ. Surface Modification of Screen-Printed Carbon Electrodes. Coatings. 2025; 15(10):1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15101182
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaroon, Naila, and Keith J. Stine. 2025. "Surface Modification of Screen-Printed Carbon Electrodes" Coatings 15, no. 10: 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15101182
APA StyleHaroon, N., & Stine, K. J. (2025). Surface Modification of Screen-Printed Carbon Electrodes. Coatings, 15(10), 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15101182







