Superhydrophilic Surface Creation and Its Temporal Transition to Hydrophobicity on Copper via Femtosecond Laser Texturing
Abstract
1. Introduction
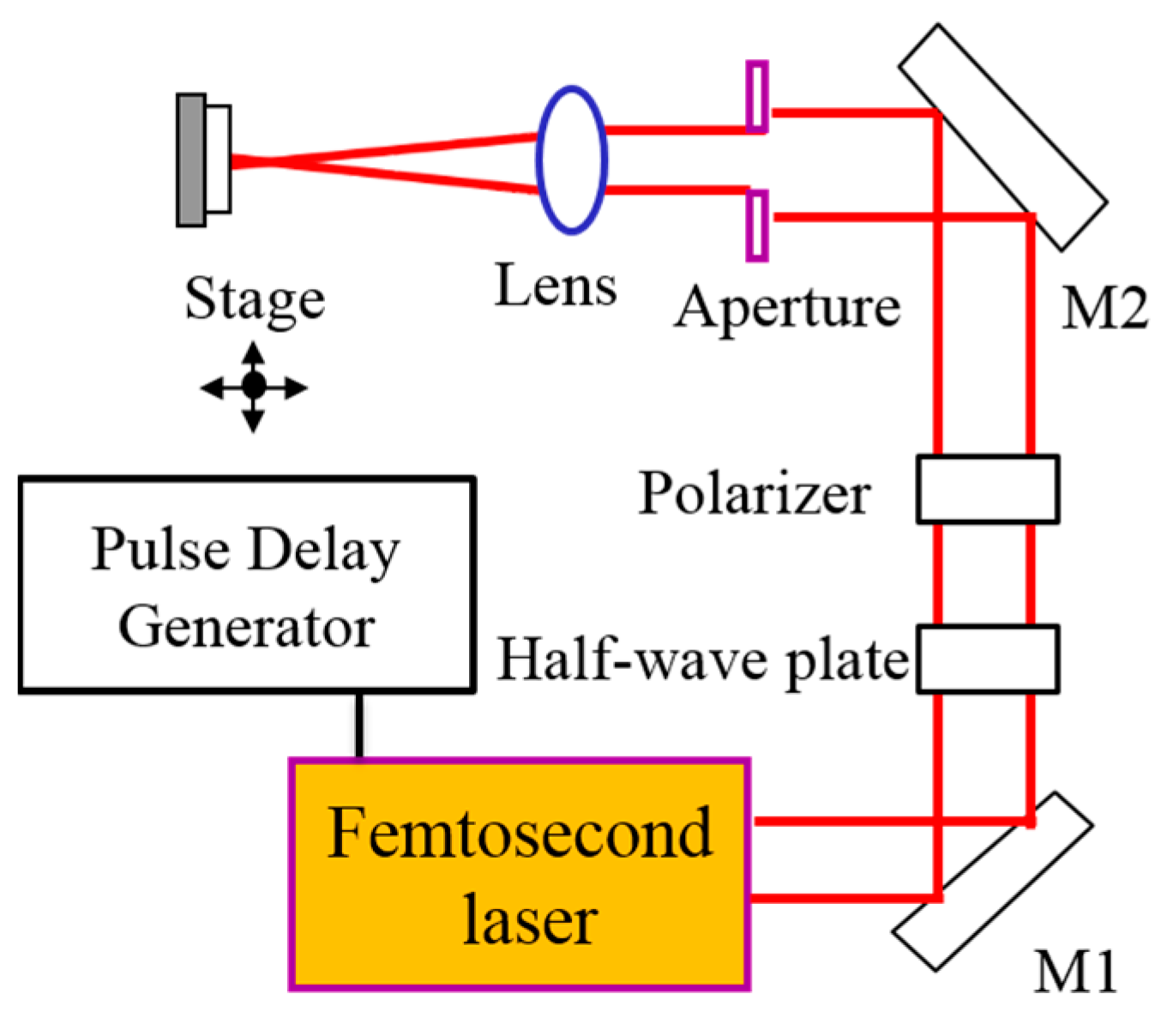
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
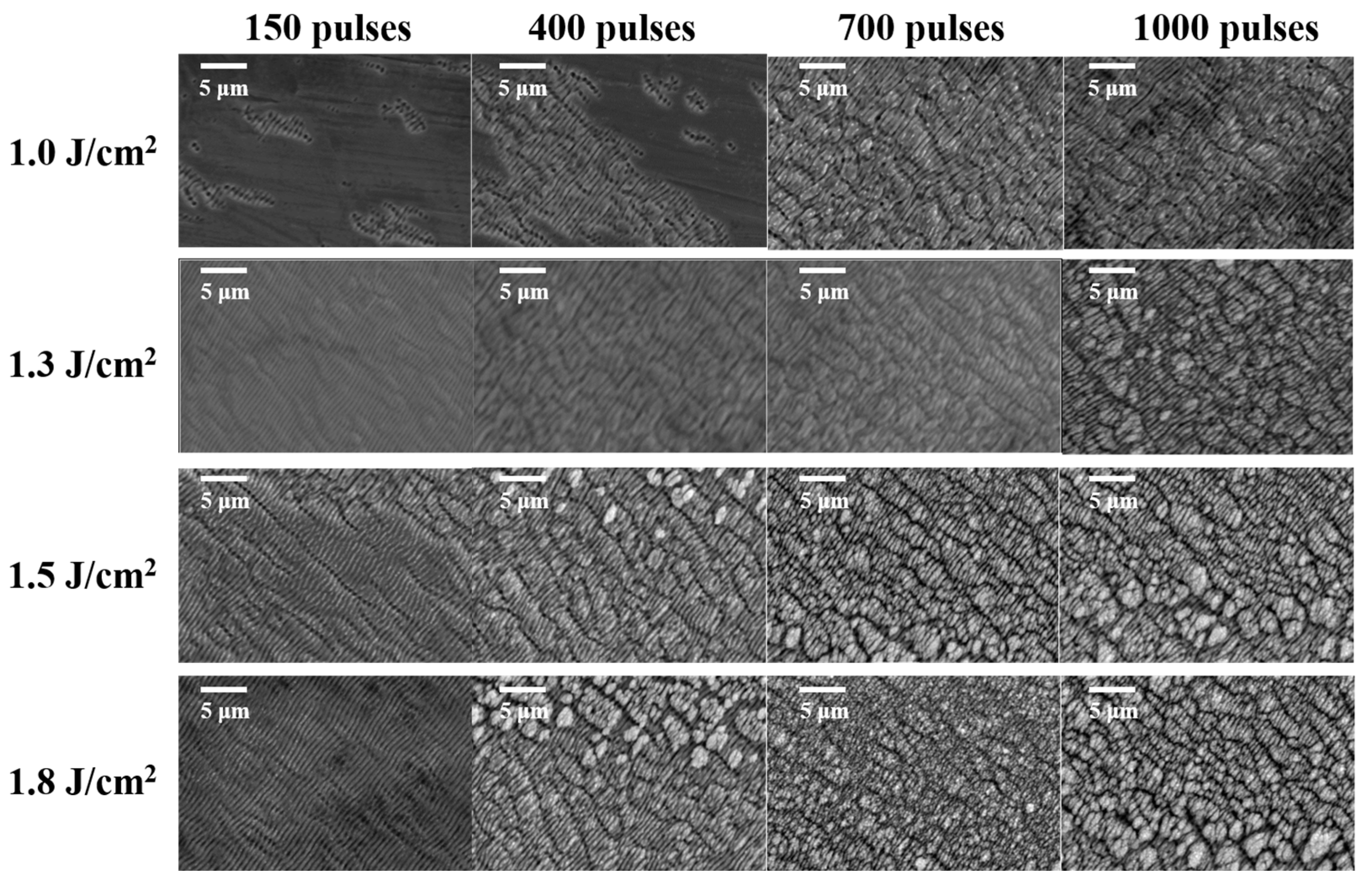
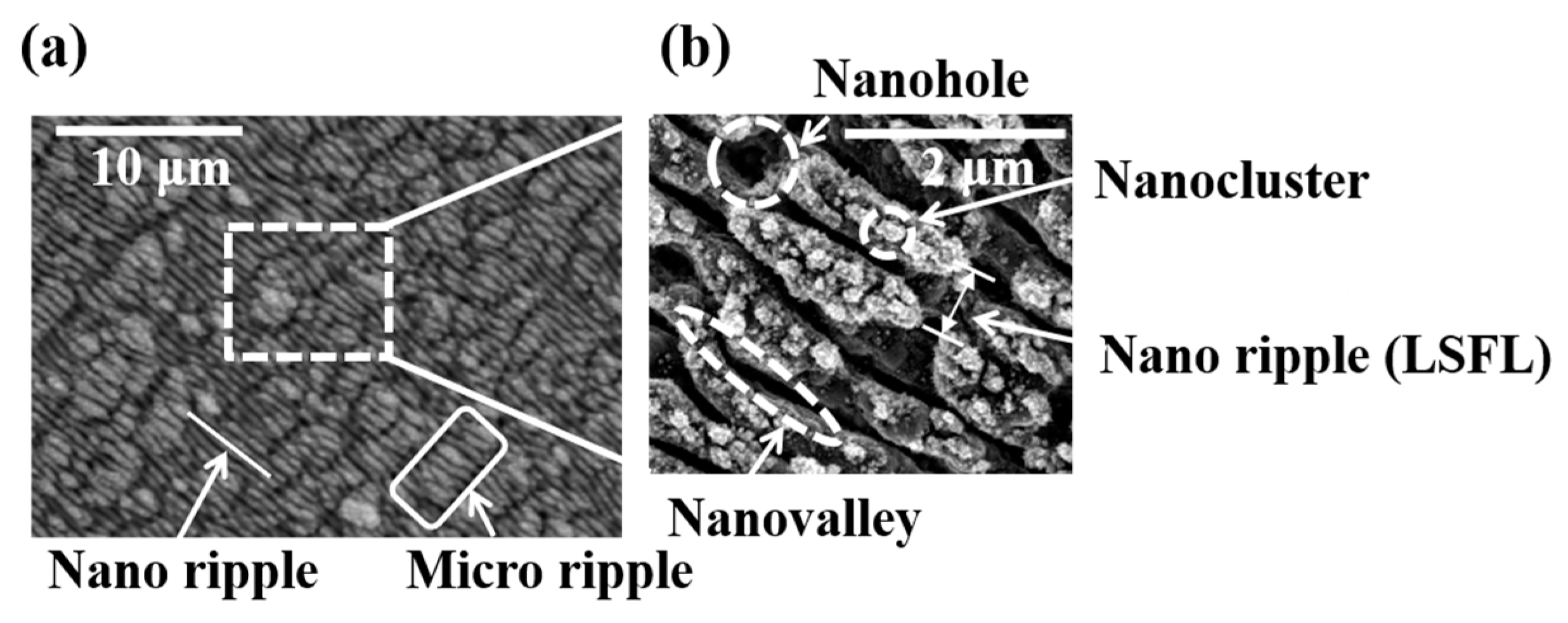
3.1. LIPSS Varying with Laser Parameters
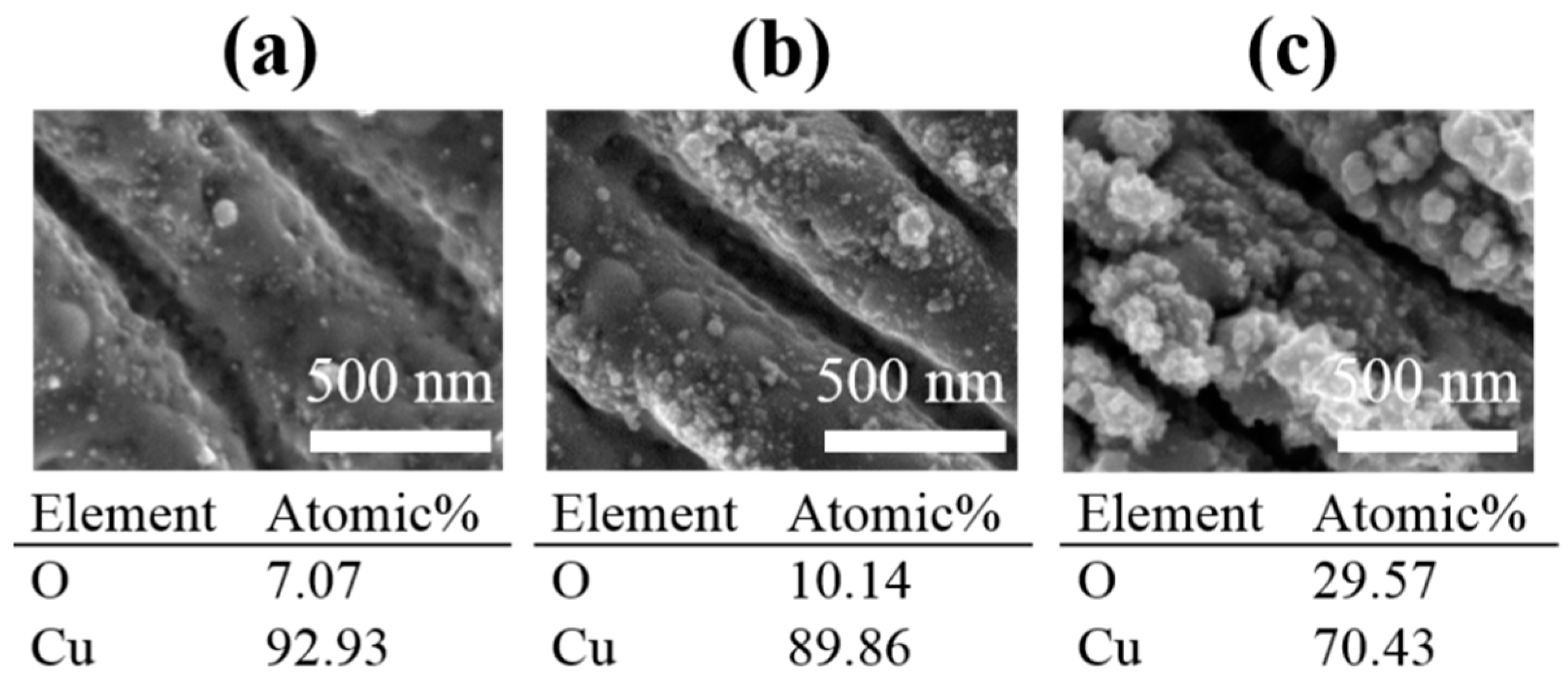
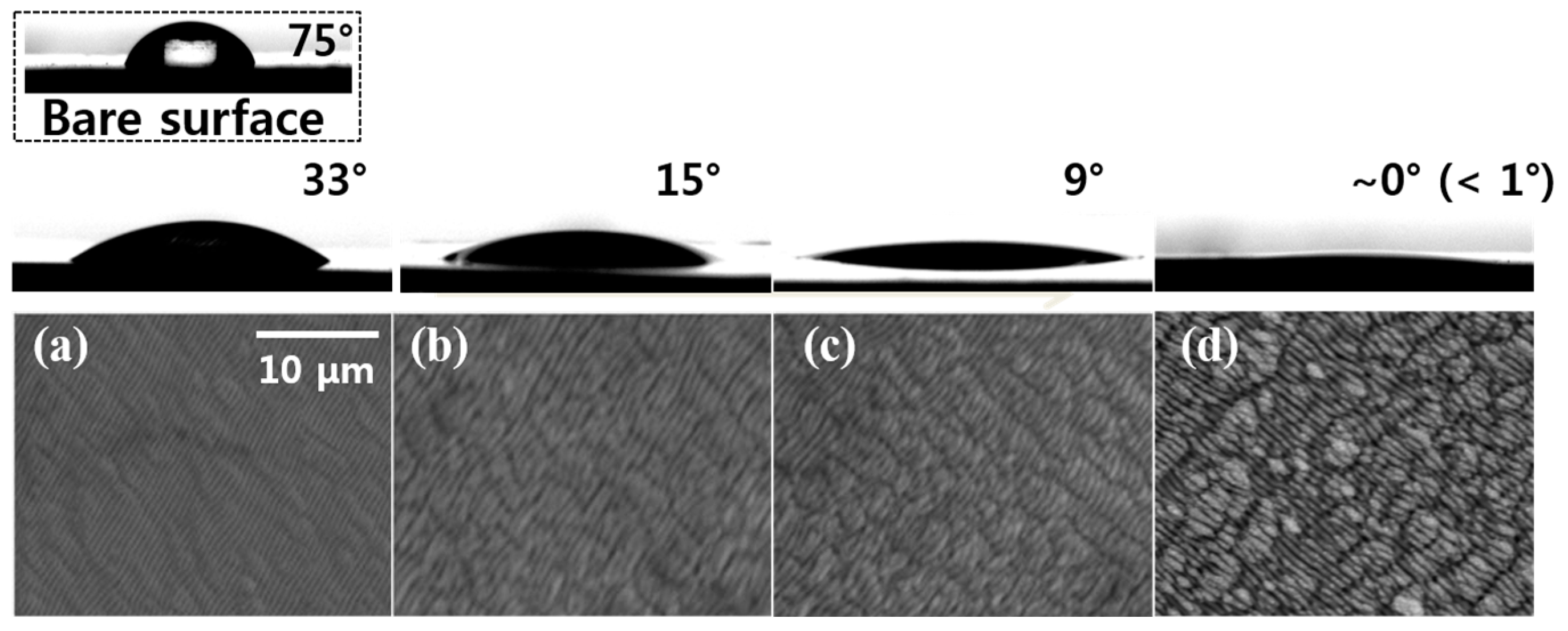
3.2. Wettability of the Laser-Modified Surfaces
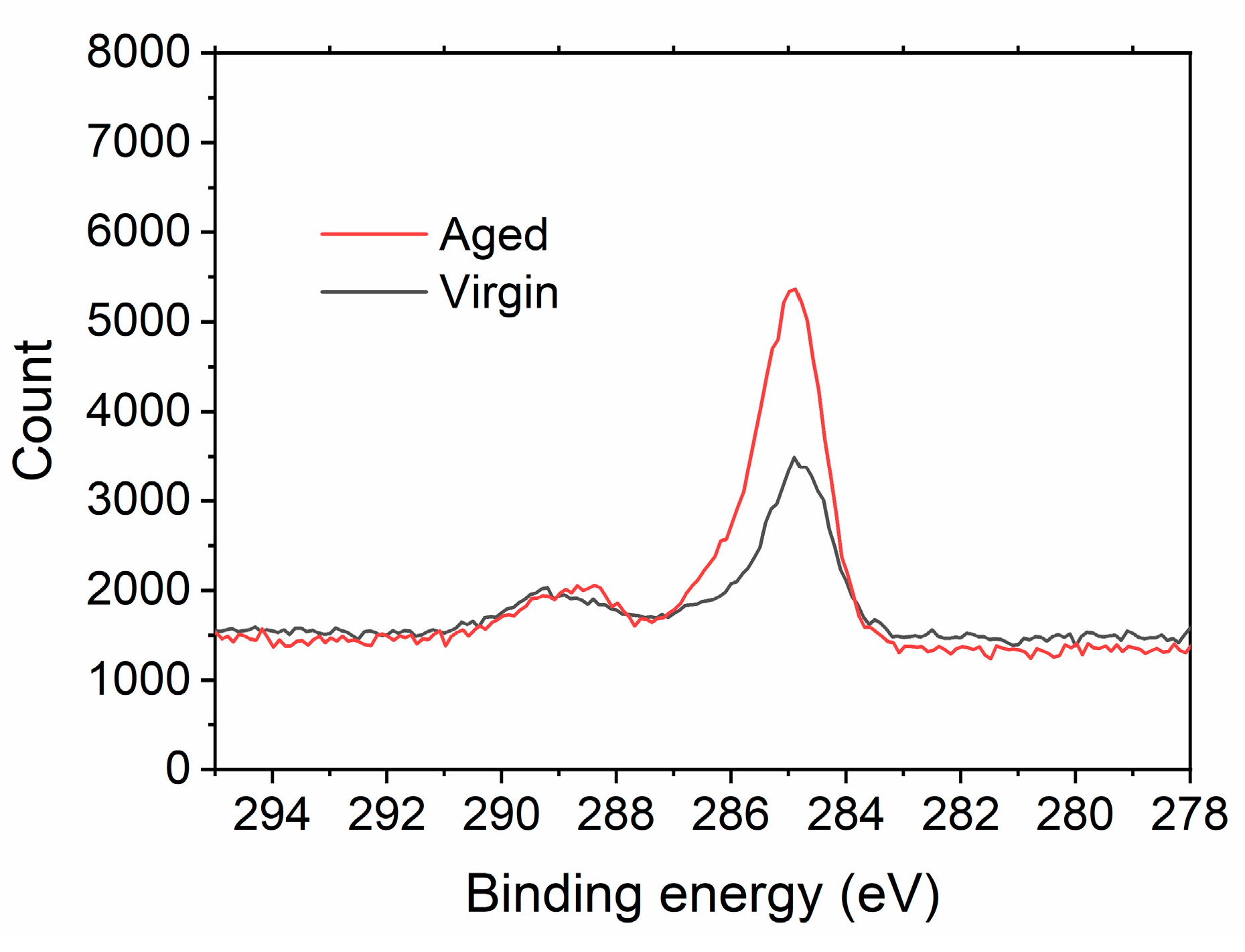
3.3. Aging Effect: Transition from Superhydrophilic to Hydrophobic Surface
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, X.J.; Jiang, L. Design and Creation of Superwetting/Antiwetting Surfaces. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 3063–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Zhou, W.; Nai, S.M.L. Effect of Interface Wettability on Additively Manufactured Metal Matrix Composites: A Case Study of 316L-Y2O3 Oxide Dispersion-Strengthened Steel. Metals 2024, 14, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.; Zaplotnik, R.; Primc, G.; Vesel, A.; Mozetič, M. Evolution of the Surface Wettability of Vertically Oriented Multilayer Graphene Sheets Deposited by Plasma Technology. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, J.; Shen, D.; Lu, Y.; Dong, L.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Fan, X. Wettability conversion on ZnO nanowire arrays surface modified by oxygen plasma treatment and annealing. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2005, 413, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, J. Wettability of dual-scaled surfaces fabricated by the combination of a conventional silicon wet-etching and a ZnO solution method. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2009, 19, 095002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, B.T.; Cui, T. Superhydrophilic surface modification of copper surfaces by layer-by-layer self-assembly and liquid phase deposition of TiO2 thin film. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 354, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, C.-V.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, J.; Guo, C. Scalable Wettability Modification of Aluminum Surface through Single-Shot Nanosecond Laser Processing. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wróblewski, P. The theory of the surface wettability angle in the formation of an oil film in internal combustion piston engines. Materials 2023, 16, 4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, E.L.; Barberoglou, M.; Zorba, V.; Manousaki, A.; Pagkozidis, A.; Stratakis, E.; Fotakis, C. Reversible photoinduced wettability transition of hierarchical ZnO structures. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 2891–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiamchai, P.; Chindaudom, P.; Horprathum, M.; Patthanasettakul, V.; Limsuwan, P. Design and investigation of photo-induced super-hydrophilic materials for car mirrors. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 3428–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.J.; Yang, E.L. Non-UV driven self-cleaning and anti-fogging glasses prepared by ultrasonic nebulization of TiO2 hydrosol. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 549, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, A.R.; Jenkins, J.; Attinger, D. Boiling heat transfer on superhydrophilic, superhydrophobic, and superbiphilic surfaces. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 57, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H.D.; Kim, H.; Ahn, H.S.; Jo, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, M.H. Effects of nano-fluid and surfaces with nano structure on the increase of CHF. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2010, 34, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.S.; Lee, C.; Kim, H.; Jo, H.; Kang, S.; Kim, J.; Shin, J.; Kim, M.H. Pool boiling CHF enhancement by micro/nanoscale modification of zircaloy-4 surface. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2010, 240, 3350–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Yin, Q.; Zhou, Y. Superhydrophilicity of anodic aluminum oxide films: From “honeycomb” to “bird’s nest”. Thin Solid Film. 2009, 517, 6012–6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.; Li, L. Wettability characteristics of a modified mild steel with CO2, Nd: YAG, excimer and high power diode lasers. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1999, 32, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tseng, S.-F.; Hsiao, W.-T.; Chen, M.-F.; Huang, K.-C.; Hsiao, S.-Y.; Lin, Y.-S.; Chou, C.-P. Surface wettability of silicon substrates enhanced by laser ablation. Appl. Phys. A 2010, 101, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.-L.; Tsai, T.-K.; Yang, H.-P.; Huang, J.-Z. Effect of ultra-fast laser texturing on surface wettability of microfluidic channels. Microelectron. Eng. 2012, 98, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, D.; Bhattacharya, S.; Mazumder, J. Control of the wetting properties of an AISI 316L stainless steel surface by femtosecond laser-induced surface modification. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2012, 22, 105019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kietzig, A.-M.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G.; Englezos, P. Patterned superhydrophobic metallic surfaces. Langmuir 2009, 25, 4821–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caputo, G.; Nobile, C.; Kipp, T.; Blasi, L.; Grillo, V.; Carlino, E.; Manna, L.; Cingolani, R.; Cozzoli, P.D.; Athanassiou, A. Reversible wettability changes in colloidal TiO2 nanorod thin-film coatings under selective UV laser irradiation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shoji, M. Nucleation site interaction in pool boiling on the artificial surface. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2003, 46, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatpun, S.; Watanabe, M.; Shoji, M. Experimental study on characteristics of nucleate pool boiling by the effects of cavity arrangement. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2004, 29, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowiec, A.; Haugen, H. Subwavelength ripple formation on the surfaces of compound semiconductors irradiated with femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 4462–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, C. Ultrafast dynamics of femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface pattern formation on metals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R.; Gottmann, J.; Horn, A.; Kreutz, E.W. Subwavelength ripple formation induced by tightly focused femtosecond laser radiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 8576–8579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.; Makin, V.; Guo, C. Periodic ordering of random surface nanostructures induced by femtosecond laser pulses on metals. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Dasari, K.; Rosenfeld, A.; Grunwald, R. Extended-area nanostructuring of TiO2 with femtosecond laser pulses at 400 nm using a line focus. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 155302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kietzig, A.-M.; Negar Mirvakili, M.; Kamal, S.; Englezos, P.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G. Laser-patterned super-hydrophobic pure metallic substrates: Cassie to Wenzel wetting transitions. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2011, 25, 2789–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahyari, E.; Nivas, J.J.; Oscurato, S.L.; Salvatore, M.; Ausanio, G.; Vecchione, A.; Fittipaldi, R.; Maddalena, P.; Bruzzese, R.; Amoruso, S. Laser surface texturing of copper and variation of the wetting response with the laser pulse fluence. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 470, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.; Xu, C.; Ren, L. Superhydrophobic copper surface textured by laser for delayed icing phenomenon. Langmuir 2020, 36, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Može, M.; Zupančič, M.; Steinbücher, M.; Golobič, I.; Gjerkeš, H. Nanosecond laser-textured copper surfaces hydrophobized with self-assembled monolayers for enhanced pool boiling heat transfer. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, W.; Xiong, D. Direct laser texturing technique for metal surfaces to achieve superhydrophobicity. Mater. Today Phys. 2022, 23, 100651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, D.V.; Dunn, A.; Wasley, T.J.; Kay, R.W.; Stringer, J.; Smith, P.J.; Connaughton, C.; Shephard, J.D. Nanosecond laser textured superhydrophobic metallic surfaces and their chemical sensing applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; He, Z.; Zhou, C.; Xie, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhou, P.; Zhu, Y.; Hong, W.; Zhou, Z. Hierarchical micro-and nanostructures induced by nanosecond laser on copper for superhydrophobicity, ultralow water adhesion and frost resistance. Mater. Des. 2018, 155, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J. On the role of surface plasmon polaritons in the formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures upon irradiation of silicon by femtosecond-laser pulses. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, Q.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhang, J.; Yao, J.; Xu, J. Formation mechanism of high spatial frequency laser-induced periodic surface structures and experimental support. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 580, 152107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Krüger, J.; Höhm, S.; Rosenfeld, A. Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures. J. Laser Appl. 2012, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Krüger, J. Pulse number dependence of laser-induced periodic surface structures for femtosecond laser irradiation of silicon. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, N.; Xu, Z. Origin of laser-induced near-subwavelength ripples: Interference between surface plasmons and incident laser. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 4062–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razi, S.; Asghari, M.; Mollabashi, M. Angle-and polarization-dependent reflection and backscattering from FS-LIPSS covered stainless steel surfaces: Experimental study. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2020, 135, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Shi, P.; Yan, W.; Chen, L.; Qian, L.; Kim, S.H. Thickness and structure of adsorbed water layer and effects on adhesion and friction at nanoasperity contact. Colloids Interfaces 2019, 3, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B.; Jung, Y.C.; Koch, K. Micro-, nano-and hierarchical structures for superhydrophobicity, self-cleaning and low adhesion. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2009, 367, 1631–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Ji, B.; Zhang, K.; Gao, H.; Huang, Y.; Hwang, K. Nano to micro structural hierarchy is crucial for stable superhydrophobic and water-repellent surfaces. Langmuir 2010, 26, 4984–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, N. Capillary bridges on hydrophobic surfaces: Analytical contact angle determination. Langmuir 2022, 38, 6201–6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakabe, S.; Hashida, M.; Tokita, S.; Namba, S.; Okamuro, K. Mechanism for self-formation of periodic grating structures on a metal surface by a femtosecond laser pulse. Phys. Rev. B—Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2009, 79, 033409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipe, J.; Young, J.F.; Preston, J.; Van Driel, H. Laser-induced periodic surface structure. I. Theory. Phys. Rev. B 1983, 27, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizi-Bandoki, P.; Valette, S.; Audouard, E.; Benayoun, S. Effect of stationary femtosecond laser irradiation on substructures’ formation on a mold stainless steel surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 270, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Sohn, I.-B.; Jeong, S. Parallel ripple formation during femtosecond laser grooving of ceramic. Appl. Phys. A 2011, 103, 1053–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.-M.; Cheng, S.-L.; Hong, S.-J.; Sheng, Y.-J.; Tsao, H.-K. Superhydrophilicity to superhydrophobicity transition of CuO nanowire films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, M.-D.; Wang, B.; Li, E.; Zhang, X.-h.; Song, X.-m.; Yan, H. The fabrication of superhydrophobic copper films by a low-pressure-oxidation method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 5824–5827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Yung, K.C.; Xie, C. UV Nd: YAG laser ablation of copper: Chemical states in both crater and halo studied by XPS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2003, 217, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudennec, Y.; Lecerf, A. The transformation of Cu (OH) 2 into CuO, revisited. Solid State Sci. 2003, 5, 1471–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, T.-Y. Oxygen adsorption induced superhydrophilic-to-superhydrophobic transition on hierarchical nanostructured CuO surface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 377, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platzman, I.; Brener, R.; Haick, H.; Tannenbaum, R. Oxidation of polycrystalline copper thin films at ambient conditions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazy, M.R.; Blais, S.; Fréchette, L.G. Mechanism of wettability transition in copper metal foams: From superhydrophilic to hydrophobic. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 6416–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conradi, M.; Sever, T.; Gregorčič, P.; Kocijan, A. Short-and long-term wettability evolution and corrosion resistance of uncoated and polymer-coated laser-textured steel surface. Coatings 2019, 9, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


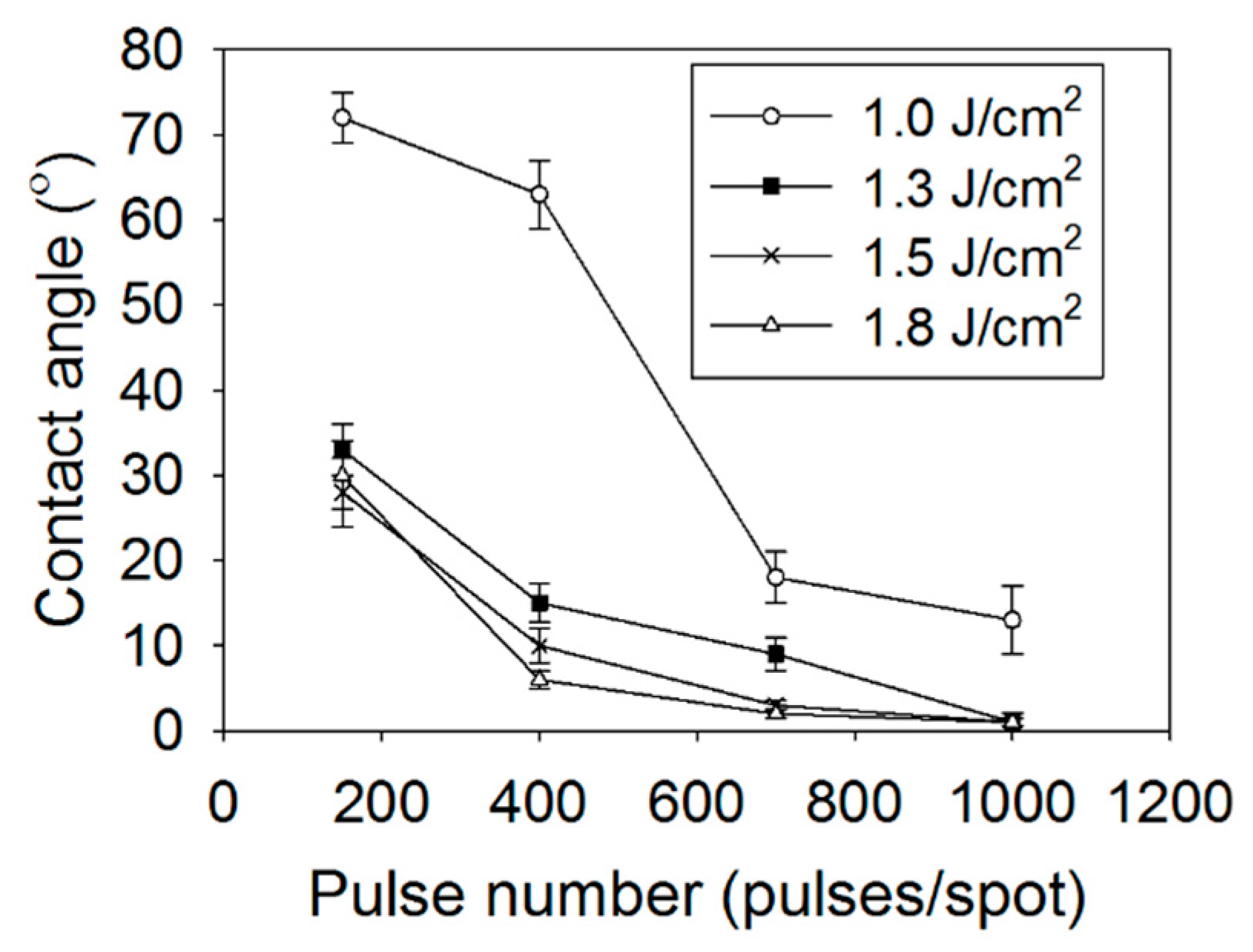
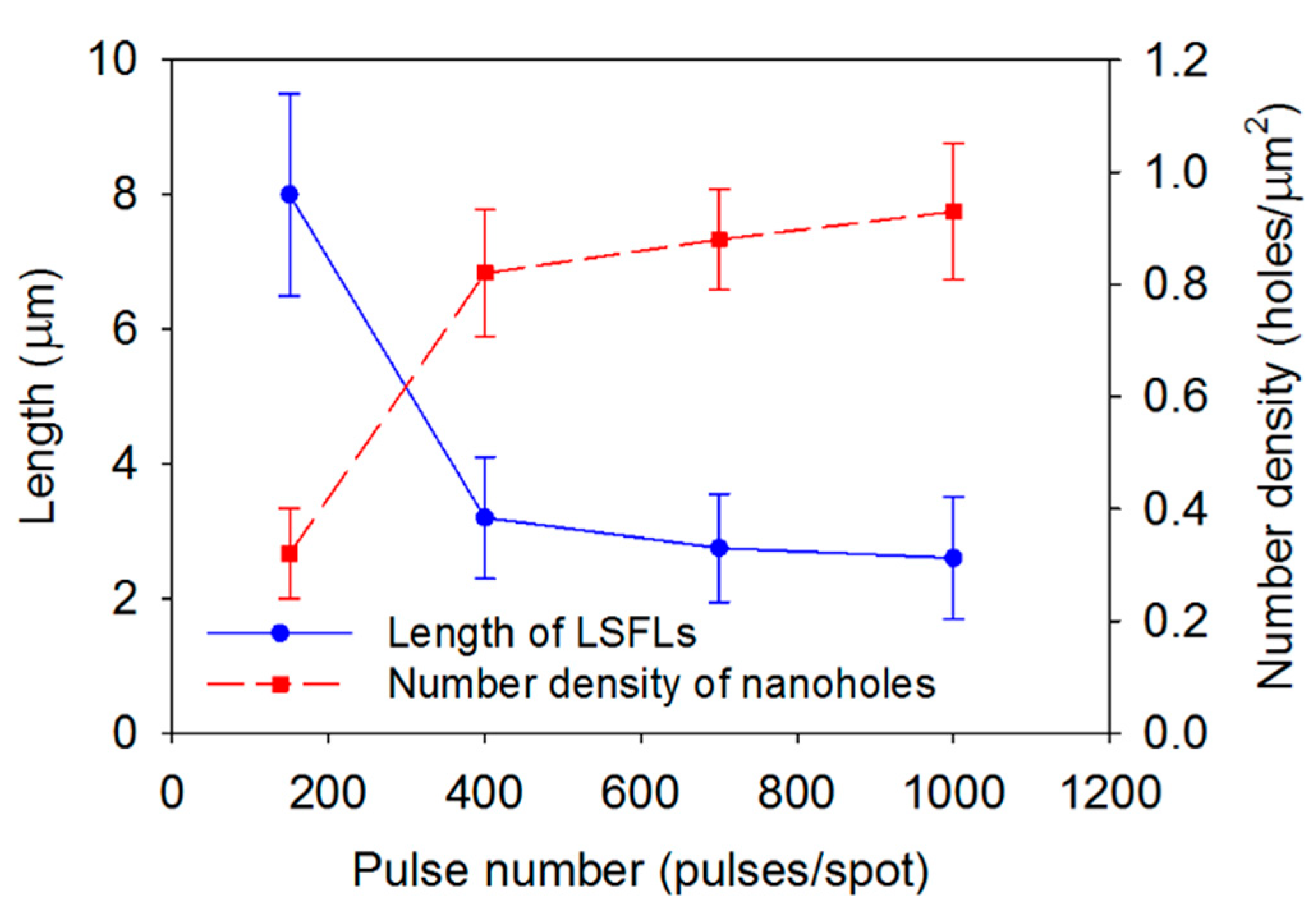

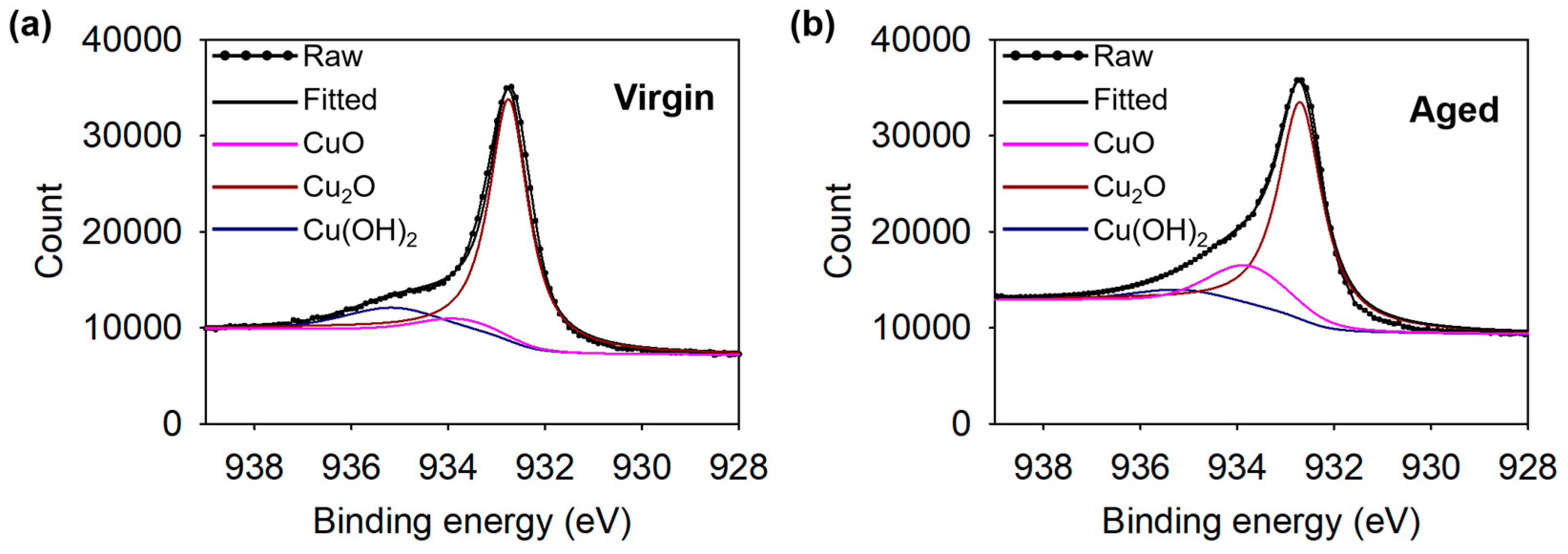

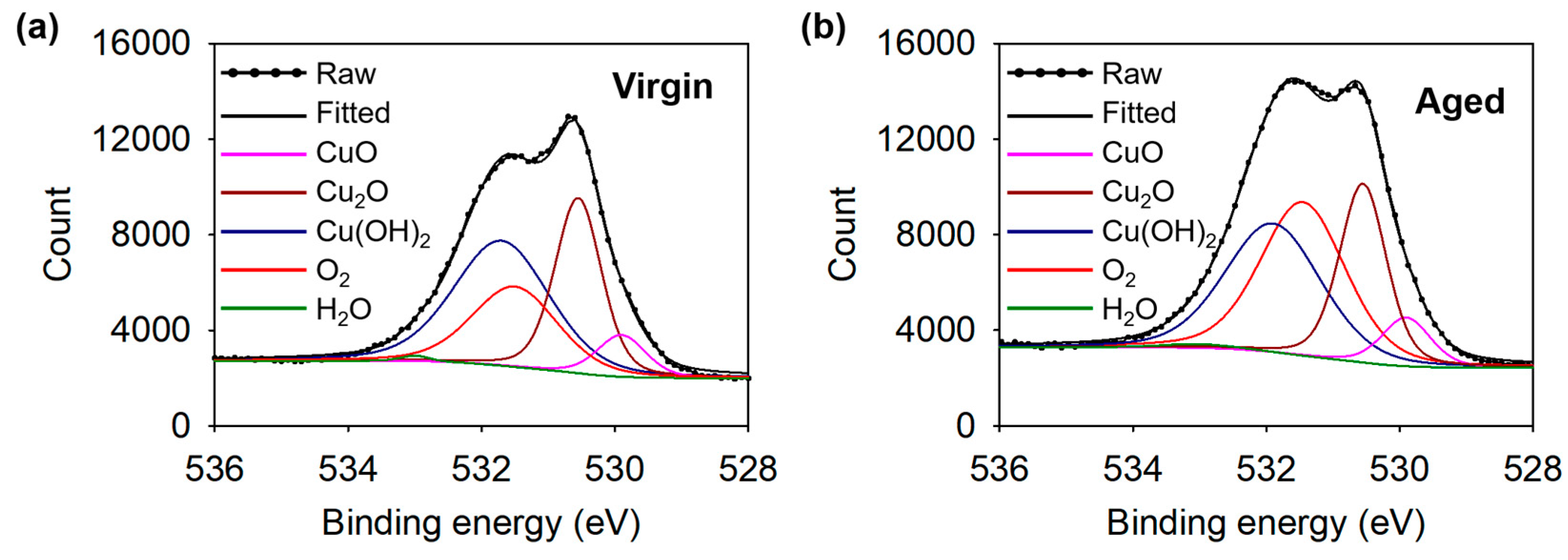
| Scanning Speed [μm/s] | Overlapped Pulse Number [Pulses/Spot] |
|---|---|
| 500 | 150 |
| 187.5 | 400 |
| 107.1 | 700 |
| 75 | 1000 |
| Cu/Cu2O | CuO | Cu(OH)2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak (eV) | Area (%) | FWHM (eV) | Peak (eV) | Area (%) | FWHM (eV) | Peak (eV) | Area (%) | FWHM (eV) | |
| Virgin | 932.7 | 76.76 | 0.97 | 933.8 | 8.31 | 2.00 | 935.1 | 14.93 | 2.40 |
| Aged | 932.7 | 72.52 | 1.10 | 933.8 | 19.85 | 2.00 | 935.1 | 7.63 | 2.40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ha, J. Superhydrophilic Surface Creation and Its Temporal Transition to Hydrophobicity on Copper via Femtosecond Laser Texturing. Coatings 2024, 14, 1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14091107
Ha J. Superhydrophilic Surface Creation and Its Temporal Transition to Hydrophobicity on Copper via Femtosecond Laser Texturing. Coatings. 2024; 14(9):1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14091107
Chicago/Turabian StyleHa, Jeonghong. 2024. "Superhydrophilic Surface Creation and Its Temporal Transition to Hydrophobicity on Copper via Femtosecond Laser Texturing" Coatings 14, no. 9: 1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14091107
APA StyleHa, J. (2024). Superhydrophilic Surface Creation and Its Temporal Transition to Hydrophobicity on Copper via Femtosecond Laser Texturing. Coatings, 14(9), 1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14091107





